Natural Sciences
72nd Graduation: Doctoral Citations – CoNAS
Published
4 years agoon


ADAKU Christopher
Chemical Structure and Properties of Anthocyanins from Selected Plant Species from Uganda.
Mr. ADAKU Christopher investigated a class of bioactive phytochemicals known as anthocyanins from selected indigenous plants, with the purpose of identifying ingredients for the development of nutraceuticals and for application as natural food colourants. This follows the increasing availability of natural health products with unsubstantiated health claims and the health concern associated with the use of synthetic food colourants. During the study, eleven new and seven known compounds were isolated and their properties deciphered. The compounds exhibited colour and stability required for food colourant application and showed remarkable antioxidant activity which is indicative of their potential beneficial health effects. These findings will lead to the development of nutraceuticals and other natural health products with guaranteed safety and efficacy. The isolated compounds can also be used as natural functional food colurants, especially for colouring refrigerated foods such as yoghurt, ice cream and beverages. This study was funded by SIDA through DRGT and MUTHI and supervised by Prof. Byamukama Robert and Prof. Kiremire Bernard (RIP).

ANYWAR Godwin
Ethnopharmacology, cytotoxicity, antiviral and immunomodulatory profiles of medicinal plant species used by herbalists in treating people living with HIV/AIDS in Uganda
Mr. ANYWAR Godwin investigated the cytotoxicity, antiviral activity and immunomodulatory potential of medicinal plant species used by herbalists to treat people living with HIV/AIDS (PLHIV) in Uganda. The study was motivated by the fact that PLHIV widely use untested herbal medicines even when already on antiretroviral treatment. The results from this study showed several plant species are mainly used to treat opportunistic infections among PLHIV. Two of the most widely used plant species, Albizia coriaria and Warburgia ugandensis were highly toxic to the human glioblastoma cell line used (U87.CD4.CXCR4). Regression analysis also showed that the plant extracts had varying selective anti-HIV-1 activities in vitro. The plant extracts also elicited different immune responses by stimulating different cytokines from Peripheral Mononuclear Blood Cells (PMBCs). Godwin recommend testing of crude plant extract mixtures used by the herbalists, and isolating and testing pure compounds from the most promising plant species. The study was funded by the Consortium for Advanced Research Training in Africa (CARTA), and DAAD and supervised by Prof. Esezah Kakudidi, Dr. Andreas Shubert, Prof. Robert Byamukama and Prof. Christian Jassoy.

ENEKU John Paul
Optimization of the electrical resistivity of magnetron sputtered aluminium and boron co-doped zinc oxide thin films for solar cells.
Mr. ENEKU John Paul investigated co-doping of zinc oxide thin films with both aluminium and boron elements to develop a transparent thin film material of very low electrical resistivity for application as a transparent front electrode in thin film solar cells. This offers a low cost and eco-friendly alternative to the costly and toxic Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) electrode which currently dominates the solar cell market. The thin film based solar cells have the potential to significantly lower the price of photovoltaics based electricity. The investigation established that the co-doped zinc oxide thin film material can be used effectively as a transparent electrode in thin-film solar cells and can replace the costly standard Indium Tin Oxide (ITO). This study was funded by Makerere Universsity and International Science Program (ISP, Sweden) and supervised by Prof. Tom Otiti and Prof. Julius Mwabora.

BUTTIBWA Mary
Utilizing heated pollen and androgenesis pathways for the production of haploids in cassava
Ms. BUTTIBWA Mary investigated how heat-treatment of pollen facilitates production of haploids in cassava. Pollen, a fine powdery substance that comes from the male part of flowers and an equivalent of sperms animals, can be heat-inactivated and used hasten cassava embryo development. Because cassava’s reproduction cycle is too long it is difficult to quickly develop new varieties. The haploid technology can shorten this by 50%. Using heated pollen in pollination fostered the development of cassava embryos that further grew into haploid plants in a short time. The heated pollen germinated on the stigma but no fertilization was achieved; however, embryo development was stimulated. Early embryo rescue techniques rescued immature embryos on an artificial growth medium and re-generated into plants. This work contributes to the genetic improvement of cassava. The study was funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation through The International Centre for Tropical Agriculture and was supervised by Prof. Arthur Tugume and Dr. Robert Kawuki.

INUWA Badamasi
Effect of xenoestrogenic substances on fish health and reproductive potential of Nile tilapia, Nile perch and lungfish from two-distinctly polluted sites of Lake Victoria: the “more polluted”
Mr. INUWA Badamasi studied the effect of xenoestrogenic substances on fish health and reproductive potential of Nile tilapia, Nile perch and lungfish from two-distinctly polluted sites of Lake Victoria: the “more polluted” (Kasenyi, Ggaba, Port bell, Jinja) and the “less polluted” (Kasensero, Bale, and Bukakata). The motivation for this research was the decline in the wild fish stocks population of Lake Victoria, attributable to several factors, including pollution. Specifically, the study examined the liver conditions and gonadal development of fishes under different levels of pollution. Severe liver alterations were higher in fishes from more polluted compared to those from less polluted areas. Indeed, the chemical contamination of Lake Victoria could have caused the liver lesions and other changes in the fishes. Overtime, such chemical contamination could lead to negative impacts on the consumption of fish and fish products if actions are not taken to mitigate the risks. This study was funded by the Nigerian Federal Ministry of Education and supervised by Assoc Prof Charles Masembe and Dr. Robinson Odong.

KITO Luliro Silas
The Numerical Range of Linear Relations and Stability Theorems.
Mr. KITO Luliro Silas studied the numerical range and stability theorems of linear maps on some mathematical spaces with the purpose of establishing the existence and uniqueness of solutions (solvability) to linear relation inclusions. In this study, he explored the effects of small alterations on certain maps between special spaces that are of mathematical interest in solving certain differential equations. The study found that within a certain degree of change, a small alteration on the map will not affect a particular set of characteristics of the map. These results are useful but not limited to; solving problems formulated when modelling airflow around an obstruction for example calculation of forces and moments on aircrafts, modelling fission weapon detonation, determination of mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns and ocean currents, solving fluid dynamics problems that require computation of fluid properties such as flow velocity, pressure, density and fluid temperature as functions of space and time. This study was funded by SIDA and was supervised by Assoc. Prof. Gerald Wanjala, Dr. Saul H. Nsubuga, Dr. Vincent. A. Ssembatya and Dr. Alex B. Tumwesigye.

KYOMUHANGI Annet
Reduced Modules Relative to Functors
Ms. KYOMUHANGI Annet’s study focused on the description of reduced modules and their dual using functors. She introduced and studied properties of a functor that measures how far a module defined over a commutative ring is from being reduced. She also found a machinery that allows one to associate a nil ideal to every ring. Since reduced modules are dualisable, Annet studied properties of their dual known as coreduced modules. She further introduced functors that describe coreduced modules and studied their properties. Moreover, she found that reduced modules simplify computations of local cohomology while coreduced modules simplify computations of local homology. The study was funded by Makerere-Sida bilateral programme (2015-2020); Project 316: Capacity building in Mathematics and its applications. Ms. Kyomuhangi was supervised by Dr. David Ssevviiri and Dr. Alex Samuel Bamunoba, both from Makerere University.

MAYANJA Edison
Mathematical Models for HIV-HCV Co-infection Dynamics under Various Control Strategies
Mr. MAYANJA Edison formulated mathematical models to study the dynamics of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV) co-infection. The HIV-HCV co- infection mathematical models which had been developed before, either ignored infection stages or considered HCV in only two stages of infection: the acute and chronic infection. However, the chronic stage of HCV is very long and consists of infected individuals that are asymptomatic yet infectious. Thus, this required deep analysis that had not been fully elucidated. In his study, he analysed the HCV chronic stage split it into: before onset of cirrhosis and its complications (Latent stage) and after onset of cirrhosis (Advanced stage). He used these mathematical models to investigate how HIV infection impacts the dynamics of HCV infection and vice versa. The study revealed that, increasing the rate of enrolment on HIV treatment reduces HCV prevalence and vice versa. Transmission probability per sexual contact and average number of sexual partners acquired per year were equally likely to result into increased HIV and HCV infections and these parameters were the most sensitive in increasing each of HIV and HCV infections. The study was funded by SIDA and was supervised by Prof. Livingstone S. Luboobi, Prof. Juma Kasozi, and Dr. Rebecca N. Nsubuga.

NABAWANDA Olivia
Flattened partitions: Pattern Avoidance and Behavior of Permutation Statistics.
Ms. NABAWANDA Olivia studied a sorting procedure (run-sort function) on permutations, where runs are rearranged in lexicographic order. The aim of the study was to investigate the behavior of the run-sort function with different permutation statistics namely runs, descents, peak-values and left-right minima. Olivia used Mathematica, a computation/mathematical software to generate the necessary data, which in turn she used in combination with bijective proofs and generating functions as the main tools. New combinatorial interpretations to several counting sequences namely A124324, Catalan, Fibonacci, Motzkin and Powers of two among others were provided as already indexed on the On-line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS) database, hence contributing to the existing body of knowledge. She also proved that the descent generating polynomials for these permutations are real rooted, and satisfy an interlacing property similar to that satisfied by the Eulerian polynomials, which are known to be real-rooted. Moreover, the run-sort function was found to possess interesting probability distribution properties. The research findings exhibited an interplay between discrete mathematics, probability theory and complex analysis. The study was funded by SIDA and supervised by Dr. Alex Samuel Bamunoba, Prof. Paul Vaderlind and Prof. Fanja Rakotondrajao of Antananarivo.

NALULE Rebecca Muhumuza
Hierarchical Models and Spatio-Temporal Processes In Data Analysis
Ms. NALULE Rebecca Muhumuza studied Hierarchical Models and Spatio-Temporal Processes in Data- Analysis with the aim of analyzing data which possesses both temporal and spatial dependence. She developed a non-linear general spatio-temporal model by extending Serfling’s model. Rebecca applied the theoretical findings to data of an outbreak of influenza in Southern Germany between 2001 and 2007. She also extended the random effect model by introducing the correlation coefficient between random effects in its definition. She again considered the problem of Bayesian estimation of heterogeneity parameter in the generalized random effects model where a comparison between the obtained results with the existing approaches was made. Rebecca used the findings for consensus building in meta-analyses of measurement results for the Newtonian constant of gravitation data and for the effectiveness of antiretroviral pre-exposure prophylaxis in preventing HIV infection. The study was funded by SIDA and was supervised by Prof Olha Bodnar, Dr. John Bosco Asiimwe and Dr. Rebecca N. Nsubuga.

NANFUKA Mary
The use of Splines for solving ill-posed problems, with application to the Cauchy problems for the Heat and Helmholtz equations
Ms. NANFUKA Mary developed a regularization procedure based on splines. The procedure was used to solve the Cauchy problems for the heat and Helmholtz equations, which are ill posed problems. The Cauchy problem for the heat equation had been previously solved by the Fourier transform method. The method, assumed that the time derivative, represented a periodic function which is not realistic. Thus, as an alternative, Mary approximated the time derivative by a cubic smoothing spline. The spline method effectively bounded the errors in the output solution according to the stability estimates. The Cauchy problem for the Helmholtz equation was regularized, by introducing a bounded approximation of the second derivative in the x-variable using cubic smoothing splines. A bound for the approximate
derivative was derived. The stability estimates, showed that the method worked pretty well and produced accurate results. The newly developed method was applied to an industrial setting for determining the surface temperature of steel and good results were achieved. The method is recommended for use for the solution to inverse problems that occur in the engineering and medical fields. The research was funded by Sida and supervised by Dr. Fredrik Berntsson, Dr.Godwin Kakuba and Assoc Prof. John Mango.

OCHEN William
Measurement and Modelling of Residual Stress in Porcelain Tiles Formulated from Different Quartz Particle Sizes in Uganda
Mr. OCHEN William studied residual stress in porcelain tiles formulated from different quartz particle sizes in Uganda. He measured residual stress using X-ray diffraction method, and modeling based on finite element method using abaqus software. His study was prompted by numerous complaints concerning the strength of the locally manufactured tiles. His study found out that residual stress decreases with an increase in quartz particle size over a range of 45-200μm. The decline in residual stress is attributed to the formation of cracks, which affects strength and hardness of the tiles. He further noted that upon sintering at 13000C, tiles with quartz particle size of 90μm exhibited properties that satisfied the ISO 13006 standard. His study therefore recommends the idea of fine quartz milling in a range of not more than 90μm. This study was funded by DAAD and supervised by Prof. Florence Mutonyi D’ujanga and Dr. Bosco Oruru.

OKELLO Omwonylee Joseph
Limiting Behaviours of the Longest Gaps Between Occurrence Epochs in Poisson Processes.
Mr. OKELLO Omwonylee Joseph investigated the asymptotic properties of longest gaps between occurrence epochs in Poisson processes using the theory of large deviations, based on the laws of large numbers. To do this, the global estimation of the distribution functions of longest gaps was derived with the help of discretization argument and the Slivnyak’s formula of Palm theory. The derived global estimation was then used to achieve Laplace transform asymptotics of the longest gaps. Through the application of Fenchel-Legendre transform, it was found out that the longest gaps satisfy two large deviation principles with exponential and power rate functions. Since this study was about the probabilistic analysis of rare events, the results not only fill the literature gaps but also provide a very useful planning tool to insurance companies, risk analyst, department of disaster preparedness, operation managers and others. The study was funded by SIDA and was supervised by Dr. Xiangfeng Yang; Dr. Richard Awichi Opaka and Dr. Fred Mayabala.

SSENYUNZI Richard Cliffe
Modelling Precipitable Water Vapour Using Global Navigation Satellite System Data over the East African Tropical Region.
Mr. SSENYUNZI Richard investigated the temporal and spatial variability of the zenith total delay and precipitable water vapour (PWV) data over the East African tropical region. The PWV data was collected from 13 geodetic permanent GNSS stations for the years 2013 to 2016. Lack of key variables such as the atmospheric water vapour, has been affecting the accuracy of weather predictions over the East African tropical region. The lack of this important parameter has been partly due to insufficient data and very scarce and unreliable tropospheric water vapour monitoring instruments in the region. In this study, the PWV, pressure and the weighted mean temperature linear models have been developed. The site-specific models developed can be utilized to supplement the GNSS and the weather stations data over the thirteen stations since they can provide estimates of nearly a similar degree of precision compared to the measured values. The study was funded by the African Development Bank and supervised by Prof. Florence Mutonyi D’ujanga and Dr. Bosco Oruru.

WAMONO Felix
Contributions to reduced rank regression modelling with applications to small area estimation.
Mr. WAMONO Felix studied the problem of decomposing residuals in the GMANOVA-MANOVA model with rank restrictions on parameters with applications in small area estimation. Firstly, Residuals in the GMANOVA-MANOVA model with rank restrictions on the mean parameters was considered. The main objective was to define residuals useful for evaluating the reduced rank restriction model. We decomposed linear spaces into four subspaces as it can be done for the Extended Growth Curve model with two “profiles”. The new residuals were defined by orthogonal projections on these subspaces. It was discussed how the new residuals could be used to test model assumptions. Secondly, Survey data from Uganda, including the 2014 Uganda Population and Housing Census data was analysed using small area estimation methodology. The GMANOVA-MANOVA model with rank restrictions on parameters was used to estimate the small area means. This study was funded by SIDA and was supervised by Prof. Dietrich von Rosen, Prof. Martin Singull, Assoc. Prof. Leonard Atuhaire and Dr. Innocent Ngaruye.
Browse Citations by College below:
< Director’s Message | CAES | CoBAMS | CoCIS | CEES | CEDAT | CHS | CHUSS | CoNAS | CoVAB | LAW | MUBS >
You may like
-


Farmers’ Preferences Drive Success in Tree-Planting, Duke Scholar Finds
-


Makerere University Unveils Pre-Award Grants Management System
-


Makerere Explores Strategic Industry Partnership with Psalms Food Industries to Strengthen Manufacturing Innovation
-


Makerere University Researchers Awarded UCIF Grant to Tackle Maize Contamination with Innovative Plant-Based Fungicide
-


Makerere Graduation Underscores Investment in Africa’s Public Health Capacity
-


Public Lecture on Research Collaboration across borders presents enormous opportunities to researchers, faculty and students
Natural Sciences
Makerere University Researchers Awarded UCIF Grant to Tackle Maize Contamination with Innovative Plant-Based Fungicide
Published
1 week agoon
March 4, 2026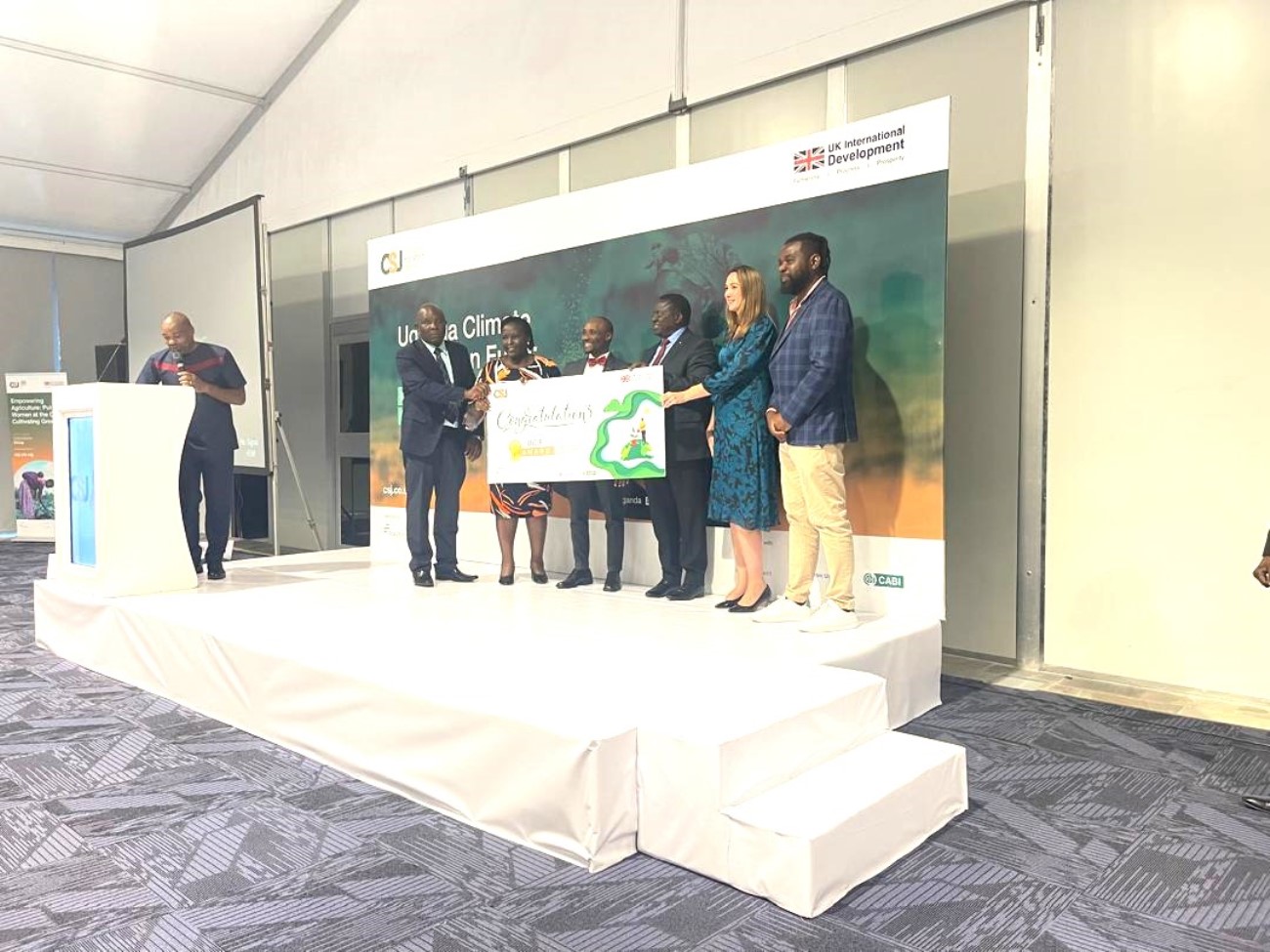
In a significant stride towards ensuring food safety and agricultural resilience, a team of researchers from Makerere University has been awarded the prestigious Uganda Climate Innovation Fund (UCIF) to support the development of a groundbreaking solution to maize contamination.
Maize, a staple food for millions of Ugandans, has long been threatened by Aspergillus fungi, which produce aflatoxins, highly toxic compounds that pose serious risks to human health, livestock, and the nation’s agricultural productivity. Recognizing the urgency of this challenge, the research team from the Department of Plant Sciences, Microbiology, and Biotechnology at the College of Natural Sciences (CoNAS), Makerere University, is pioneering the development of a plant-based organic fungicide aimed at significantly reducing Aspergillus growth and aflatoxin contamination in maize.

The initiative is spearheaded by Dr. Abubakar Sadik Mustafa (Principal Investigator), with major contributions from co-innovators Dr. Jamilu E. Ssenku, Dr. Patience Tugume, Mr. Frank Kalungi, and Mr. John Okello. The team officially received the UCIF award on 26 February 2026 at an event held at Kampala Serena Hotel.
“This recognition underscores the importance of locally-driven scientific innovation in safeguarding our food systems,” said Dr. Mustafa upon receiving the award. “Our goal is to deliver an environmentally friendly solution that not only protects maize but also contributes to public health and supports sustainable livelihoods for smallholder farmers.”

The UCIF grant, funded by the UK Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) under the Climate Smart Jobs initiative, is implemented by Palladium in collaboration with Stanbic Bank, Swissconnect, and CABI. The programme seeks to advance solutions that address the dual challenges of climate change and economic development by supporting innovations that foster sustainable agricultural practices, reduce environmental risks, and create climate-smart employment opportunities.
This breakthrough aligns closely with the global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those targeting good health and well-being (SDG 3), zero hunger (SDG 2), and climate action (SDG 13). By developing a natural, plant-based fungicide, the Makerere University team hopes to offer a scalable solution that mitigates food contamination risks while promoting environmentally sustainable farming practices across Uganda.
Natural Sciences
Mak 76th Graduation Ceremony: CoNAS Presents 16 PhDs & Best Performing Male Student in the Sciences
Published
2 weeks agoon
February 25, 2026
The College of Natural Sciences (CoNAS) presented 269 students for the award of degrees of Makerere University at the 76th graduation ceremony. Of these, 16 graduated with PhDs (4 female and 12 male), 83 with Masters (27 female and 56 male), and 170 with Bachelor’s degrees (45 female and 125 male). The College also presented the Best Performing male student in the sciences. Simon Mungudit graduated with a CGPA of 4.76 in the Bachelor of Science in Petroleum Geoscience and Production. The PhD graduates included; AfazalI Zabibu, a Lecturer at the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS); Akuyenze Paul, Kawuma Carol, Mutiso Duncan Chalo, Nabiyonga Lydia, and Osinde Cyprian (Plant Sciences, Microbiology and Biotechnology); Batte Hebert, Katende Ronald, and Namugera Frank (Mathematics), Chaciga Jimmy, Tusiime Swaleh, and Komaketch Ignatius (Physics), Kinyua Mbuci, Sekandi Peter, and Shehu Zaccheus (Chemistry), and Nakiyende Herbert (Zoology, Entomology, and Fisheries Sciences).

On the second day of the four-day graduation ceremony, which began on 24th February 2026, three colleges presented students for the award of degrees and diplomas of Makerere University. These included CoNAS, the College of Health Sciences (CHS), and the College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Biosecurity (COVAB).
Overall graduation Statistics
During the course of the 76th graduation ceremony, a total of 9,295 students will graduate with degrees and diplomas of Makerere University. Of these, 4,262 (46%) are female and 5,033 (54%) are male. A total of 213 students will graduate with PhDs, the highest number in the history of the University. 2,503 will graduate with Masters degrees; 6,343 with Bachelor’s degrees; 206 with postgraduate diplomas, and 30 with Diplomas.
Postgraduates constituted 31.4% of the total number of graduands.

Vice Chancellor’s Remarks
In his remarks, Vice Chancellor Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe commended CoNAS for its transformative research initiatives that are positively impacting communities, highlighting the NutriFishPlus Project, INNOECOFOOD Project, and a project to conserve medicinal plants in Eastern Uganda. Funded by the International Development Research Centre (IDRC) and Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR) under the Cultivate Africa’s Future Fund Phase II, the NutriFishPlus seeks to scale up fish processing technologies and empower fishing communities in Uganda.
The EU-funded INNOECOFOOD Project is transforming food production in Uganda. Through eco-innovative, climate-smart systems, the project aims to improve nutrition, protect the environment, and create jobs- especially for youth and women. Central to this effort are solar- and wind-powered ECOHUBs. These innovative centres use AI and IoT technology to support sustainable fish farming, monitor water quality, reduce losses, and increase yields.
Meanwhile, researchers from the Department of Plant Sciences, Microbiology, and Biotechnology, under the leadership of Dr. Patience Tugume, are spearheading efforts to conserve medicinal plants in Namutumba District. To date, 174 plant species have been documented, with ongoing assessments of threats from unsustainable harvesting. These plants play a vital role in treating malaria, diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers.

Efforts to Transform Makerere into a Research-led University
In his address, the Vice Chancellor reaffirmed the University Management’s commitment to transforming Makerere into a research-led institution. He expressed gratitude to the Government of Uganda for securing a USD 162 million loan from the Korea Exim Bank to support critical infrastructure development at the University. The funding will facilitate the construction of new facilities for the School of Medicine, School of Dentistry, School of Engineering, the Science and Technology Centre, and the completion of the School of Computing and Information Sciences- an unprecedented development in the University’s history.
The Vice Chancellor further highlighted the pivotal role of the Makerere University Technology and Innovations Centre (MUTIC) in advancing incubation and commercialization. “The Centre offers mentorship, business development training, intellectual property support, and industry linkages to help transform research outputs into viable enterprises.” To date, eleven spin-off companies have been established by students and staff, while the University’s Innovation Pod (UniPod) has incubated more than 100 projects in the past year. The short-term target is to establish 50 spin-off companies annually, with plans to double that number in the long term.

Prof. Nawangwe acknowledged the government’s contribution through the Makerere University Research and Innovations Fund (MakRIF). Through this initiative, the government has supported over 1,400 high-impact research and innovation projects, and facilitated the training of more than 200 PhD students.
In partnership with the Science, Technology and Innovation Secretariat in the Office of the President, the University has also introduced awards to recognize outstanding researchers and innovators. These include the Research Excellence and Innovation Commercialization Awards. “The Innovation Commercialization Award underscores the institution’s commitment to translating research into practical products, services, and technologies that address real-world challenges and support national development,” the Vice Chancellor noted.
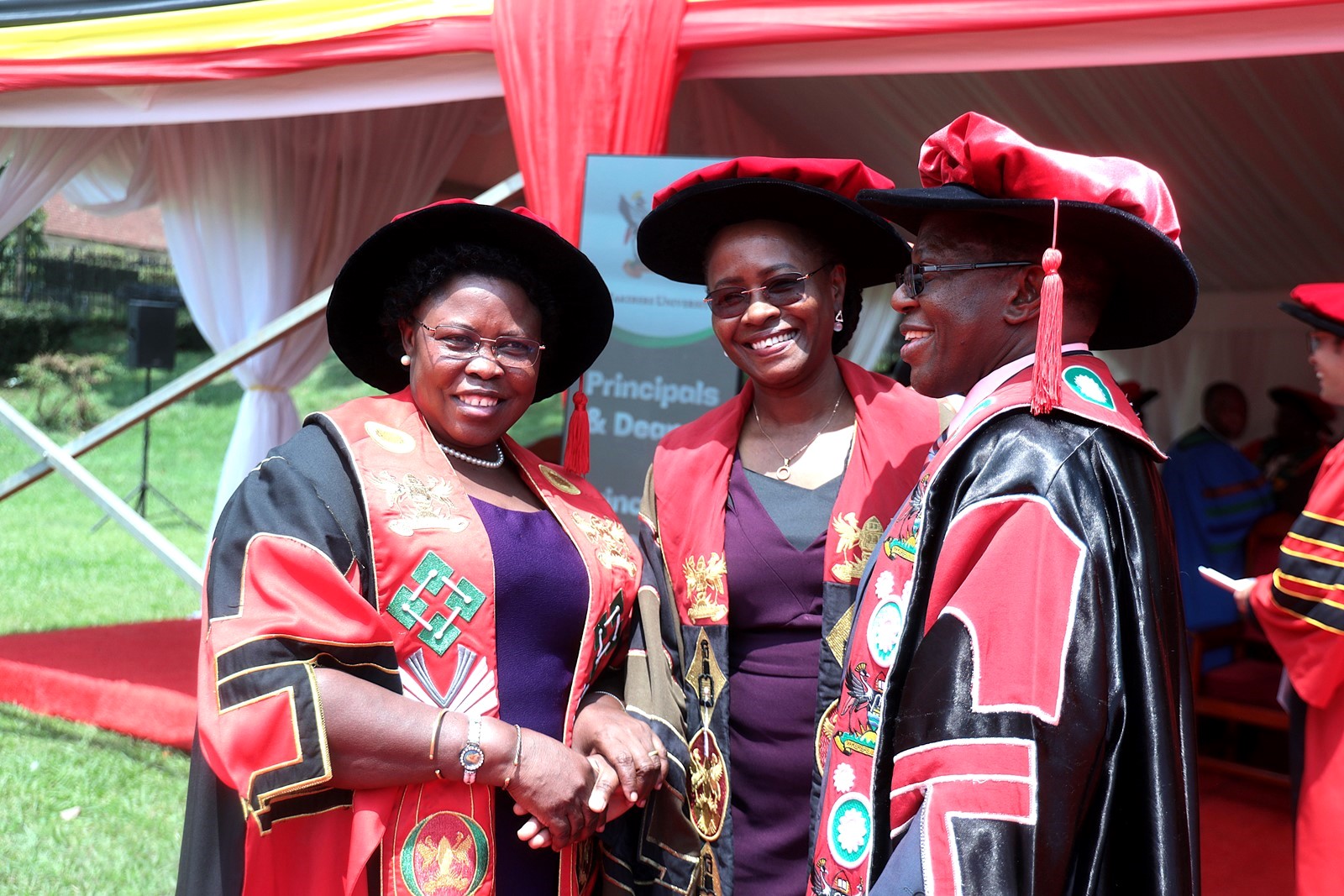

Vice Chancellor’s Message to the graduates and Appreciation to the Partners
The Vice Chancellor urged the graduates to uphold dignity, humility and diligence as they leave the gates of Makerere University, and begin the next chapter of their lives. “As you step out of the gates of Makerere, remain proud of your alma mater and serve as good ambassadors wherever you go. Use the knowledge acquired from one of the world’s leading universities to improve yourselves, your families, communities, country, and humanity at large.”
He equally appreciated the parents and guardians for supporting the students, and the development partners who have extended research funding to the university over the years. These include the Mastercard Foundation, the European Union, NORAD, Sida, IDRC, KOICA, DAAD, NIH, CDC, USAID, the Wellcome Trust, KfW, IUCEA, RUFORUM, ARUA, the PLUS Alliance, WUN, AAUN, AAP, the Madhvani Foundation, and the Government of Uganda through the Higher Education Students Financing Board. “We are equally grateful to the Embassy of China, the Chinese Chamber of Commerce, various Government Ministries, State House, private sector players, and many other partners whose generous support continues to advance our mission.”

Remarks by the Chancellor
Makerere University Chancellor, Hon. Dr. Crispus Kiyonga congratulated the graduands on their achievement and commended the staff, parents, and partners for their invaluable support. He expressed gratitude to the Government for its steadfast commitment to advancing research through the annual UGX30 billion allocation to the Makerere University Research and Innovations Fund.
He underscored the University’s contribution to Uganda’s Fourth National Development Plan (NDP IV) through advancements in science, technology, and innovation, and encouraged graduates to embrace entrepreneurship amidst an increasingly competitive job market. He further called for enhanced research funding, stronger private sector collaboration, and deeper community engagement to accelerate national development.

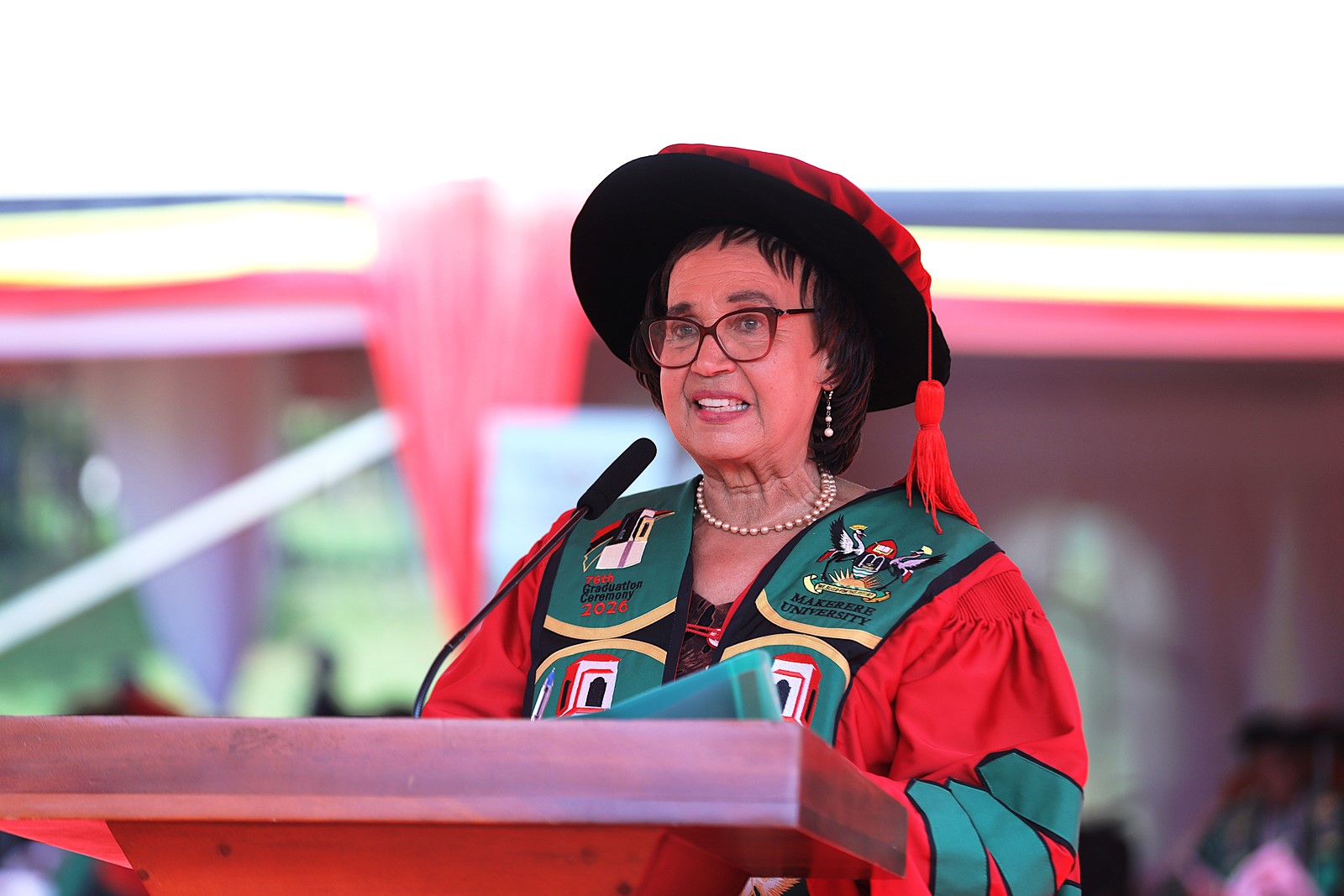
The Minister of Education and Sports
In her remarks, the Minister of Education and Sports, Hon. Janet Kataaha Museveni, represented by the Minister of State for Primary Education, Hon. Dr. Joyce Moriku Kaducu commended Makerere University for its pivotal role in driving national development. She highlighted the University’s contribution to knowledge generation and societal transformation. “The impressive number of PhD graduates this time round is testimony to the robust research output and academic excellence.” The Minister emphasized the importance of maintaining and enhancing academic standards, urging the University Administration to rigorously implement and uphold quality assurance measures that guarantee continued excellence of its programmes and global competitiveness of its graduates.
Implementing the Competence-based Education and Training
The Minister reiterated a key directive for all institutions of higher learning to prepare for the full implementation of Competence-Based Education and Training by July 2027. “This reform represents more than a policy shift. It signals a fundamental transformation in how graduates are prepared, with greater emphasis on practical skills, innovation, and problem-solving.” She urged the Vice Chancellor and his team to lead in curriculum reform, staff development, and infrastructure enhancement to ensure the successful rollout of competence-based education.
The Minister further urged the university management to ensure that all satellite campuses are fully accredited and that their programmes meet the same standards and relevance as those offered at the main campus.

Commencement Lecture by Dr. Maggie Kigozi
At the ceremony, distinguished alumnus, and Chair of the Makerere University Endowment Fund, Dr. Maggie Kigozi delivered a compelling commencement lecture, reflecting on her journey since earning her first degree in 1976. She shared three guiding messages for the new alumni as they embark on their professional paths.
Dr. Kigozi emphasized that power comes with responsibility, urging graduates entering the health and life sciences to combine their expertise with ethical leadership and financial literacy to create sustainable, compassionate practices. She highlighted the global opportunities that a Makerere degree offers, explaining how her education empowered her to make meaningful contributions across Uganda, Kenya, and Zambia.
She also encouraged the graduates to view failure as a stepping stone to excellence, noting that mistakes are not setbacks, but lessons. She underscored the importance of balance, reminding graduates to manage their personal and professional responsibilities realistically.
Research Excellence Awards
During the graduation ceremony, Makerere University recognized the top researchers and innovators from the 10 Colleges. At CoNAS, Mr. Omara Timothy from the Department of Chemistry scooped the Overall Top Research and Early Career Researcher Awards, whereas Dr Godwin Anywar from the Department of Plant Sciences, Microbiology, and Biotechnology won the Mid-Career Researcher Award.

More about Simon Mungudit, the best performing male science student – https://cns.mak.ac.ug/simon-mungudit-maks-best-male-science-student-this-year-rising-star-in-petroleum-geoscience/
Natural Sciences
BOKU University Charts New Collaboration Strategies with Mak’s Department of Zoology, Entomology & Fisheries Sciences
Published
4 weeks agoon
February 12, 2026
The Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences at Makerere University on 11th February 2026 hosted a high-level delegation from the University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna (BOKU), to discuss strategies for future collaboration in a partnership that has spanned five decades.
The meeting followed the BOKU team’s participation in the opening ceremony of the Promotion of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems towards Electricity Access in Uganda project, an initiative designed to expand access to decentralized renewable energy solutions. The project, implemented under CEDAT, is funded by the Austrian Partnership Programme in Higher Education and Research for Development (APPEAR), a programme of the Austrian Development Cooperation administered by OeAD.

Discussions at the Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences focused on deepening and broadening a historic collaboration that has shaped aquatic sciences, fisheries research, and environmental management in East Africa for half a century.
A Partnership Rooted in Limnology
The collaboration between Makerere University and BOKU traces its origins to 1975 with the establishment of the International Post-Graduate Course in Limnology (IPGL) by the late Heinz Löffler (1927-2006). The eight-month UNESCO-supported course, hosted in Lunz, Mondsee and Vienna, was designed to train scientists from developing countries in limnology – the study of inland waters.

In 1976, Dr. Gwahaba James Joshua of Makerere’s Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences became the first beneficiary from the university. Two years later, Boniface Makanga attended the UNESCO course and went on to initiate a Marine Practical Course to the Indian Ocean in 1993. That programme has since grown into over 30 years of annual field activity in Mombasa, benefiting undergraduate and master’s students and strengthening hands-on marine science training at Makerere.
Over time, IPGL evolved into a vibrant International Joint Degree Master’s Programme in Limnology and Wetland Management. The programme has built capacity for 123 aquatic professionals – 56 female and 67 male, including 20 from Makerere University. Notably, 11 dedicated limnologists are currently based within the Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences, a testament to sustained capacity development.

Expanding into Fisheries, Aquaculture and Regional Networks
The Mak-BOKU collaboration progressively expanded beyond limnology into fisheries, aquaculture, and broader freshwater ecosystem management.
Among the key initiatives was STRECAFISH (2015-2018), which focused on strengthening regional capacity in fisheries and aquaculture research and training to improve food security and livelihoods in Eastern Africa. The programme adopted a modular approach, trained 28 MSc students, supported five full PhDs and 11 MSc research projects, and facilitated 14 staff exchanges.

This momentum continued under COTRA (Collaborative Training in Fisheries and Aquaculture in East, Central and Southern Africa) from 2017 to 2023. COTRA enhanced staff and student mobility, supporting 24 master’s students (six credit-seeking and 18 degree-seeking), 12 doctoral candidates (four credit-seeking and eight degree-seeking), and 10 faculty and administrative staff. The initiative emphasized fit-for-purpose PhD training in aquaculture and fisheries to address food security challenges in Sub-Saharan Africa under the ACP-EU Cooperation Programme in Higher Education (EDULINK II), in partnership with institutions such as Lilongwe University of Agriculture and Natural Resources.

Ongoing collaborations include the Erasmus+ KA1 Learning Mobility of Individuals programme (2021-2027), which connects BOKU and Makerere with Egerton University, Kyambogo University, Addis Ababa University, Bahir Dar University and others. Additional joint initiatives include:
FreshNet: A higher education and research network for sustainable management of freshwater ecosystems in Eastern Africa, involving BOKU, Egerton University, Addis Ababa University, Bahir Dar University, EIAR and IHE Delft.

SWAQ-Uganda (2021-2026): Sustainable water quality management supporting Uganda’s development ambitions, implemented with IIASA, BOKU and Uganda’s Ministry of Water and Environment.
BIOGOLD (2024–2027): A project on biosorption for sustainable small-scale gold mining in Uganda, involving Kyambogo University, Makerere University, Gulu University, the University for Continuing Education and the University of Pretoria.

Collectively, these initiatives underscore a 50-year-old partnership that has built critical human resources at MSc and PhD levels in aquatic ecosystem management, conservation and utilization. The collaboration has also facilitated acquisition of essential research equipment, strengthened administrative capacity in project management, and nurtured a culture of knowledge sharing and innovation.

Meeting with the BOKU delegation
The BOKU delegation was led by the Rector, Prof. Eva Schulev-Steindl, a specialist in environmental law, and Vice Rector Assoc. Prof. Doris Damyanovic, an expert in landscape planning. They were accompanied by:
- Mag. Gerold Winkler, Coordinator of the Applied Limnology / Limnology and Wetland Master’s programme;
- Dr. Mathew Herrnegger, BOKU’s Africa Cooperation Country Coordinator and hydrology specialist; and
- Dr. Andreas Melcher, Africa-Uninet Coordinator from BOKU’s Institute for Development Research.
During the discussions with departmental staff, Dr. Akoll presented a detailed account of the partnership’s evolution and achievements, emphasizing its transformative impact on regional training and research capacity.

Charting the Next Chapter
As the partnership enters its sixth decade, both institutions are keen to expand into new frontiers. Key areas identified for future collaboration include:
- Enhanced staff and student exchanges;
- Joint research projects and co-publications;
- Introduction of short courses at the Makerere University Biological Field Station, Kibale beyond wildlife studies;
- Research on climate change and its effects on marine and freshwater resources;
- Advancement of basic biological research; and
- Strengthening fisheries research and innovation.

In his remarks, the Head of the Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences, Dr. Godfrey Kawooya expressed gratitude for the enduring partnership, noting that it has significantly strengthened regional training capacity and supported the education of numerous Makerere staff and students. He added that the collaboration reinforces Makerere’s standing as one of the most collaborative universities globally and aligns closely with its research agenda.
Rector Schulev-Steindl reaffirmed BOKU’s commitment to advancing the longstanding relationship, describing it as a model of North-South academic cooperation built on mutual respect, shared knowledge and tangible impact.


Event pictorial: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1HkCCZf_TCPV0V7_ZR2PSVEw1zrEGhZeJ?usp=sharing
Trending
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMakerere University commemorates 13 transformative years of partnership with Mastercard Foundation
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMakerere University and World Bank Sign Partnership to Strengthen Environmental and Social Sustainability Capacity
