General
Mak 70th Grad PhD Citations Session 2
Published
6 years agoon
College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS)
MANIRAGABA Fred
Determinants of quality of life of older persons in rural Uganda
Mr. Fred Maniragaba investigated the determinants of quality of life of older persons in rural Uganda. In this study, quality of life focused on physical health, intimacy, and social participation dimensions. The findings show that more than 3 in 10 older persons had low scores on social participation, intimacy and physical health. Overall, 4 in every 10 older persons had poor quality of life. The distribution of poor quality of life varied by sex, wealth status, region of residence, education, engagement in physical activity and HIV sero-status. The study recommended that older persons should be economically empowered, included in HIV prevention interventions such as safe sex education, embrace active ageing; and educated ones should be encouraged to participate in community social engagements. This study was funded by Makerere University and Consortium for Advanced Research and Training in Africa (CARTA). It was supervised by Dr. Betty Kwagala and Professor James Ntozi.
TURYAREEBA Dickson
The Augmented Solow Growth Model, Total Factor Productivity Growth and the Cross-Country Income Growth Disparities in Africa
Mr. Turyareeba Dickson’s study was purposely to make a scholarly contribution to the growth accounting debate on the relative importance of factor accumulation and total factor productivity growth in explaining cross-country differences in income growth in Africa. His study found that differences in both factor accumulation and total factor productivity growth can explain the cross-country differences in income growth in Africa. His study results however showed that differences in factor accumulation played a more important role than differences total factor productivity growth in explaining growth disparities in Africa and in the clusters. Mr. Turyareeba Dickson’s study revealed that to spur more economic growth in Africa, there is the need for governments to design policies that boost gross capital formation; earmark extra resources for human capital development and for increased investment in ICT infrastructure; create incentives for credit expansion to the private sector and devise stronger policies against inflation. To foster economic growth in Sub-Saharan Africa, results showed that governments need to increase investments in ICT infrastructure, implement outward-looking development strategies, expand credit to the private sector and implement population growth control measures. The study was self-funded and supervised by Associate Professors: Eseza Kateregga and Elia Hisali.
College of Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS)
ADUWO Jennifer Rose (Ms)
A Machine Learning Model for Automatic Field Based Classification of Cassava Mosaic Disease and its Severity
Ms. ADUWO Jennifer Rose investigated how machine learning can be used for detection of cassava mosaic disease (CMD) and its severity using field based cassava leaf images. The study employed an experimental design. A total of 340 healthy and 313 CMD infected cassava leaf images were collected from National Crops Resources Research Institute (NaCRRI), Uganda for the experiments. The developed machine learning Artificial Neural Network model provided accuracy rate of 97.2% for CMD classification and 88% for CMD severity grading. Within the model, CMD classification including its severity could be implemented on a mobile phone. In terms of policy, NaCRRI could spearhead the development of a policy on integration of machine learning in CMD management and engagement of Agricultural Extension Workers to detect CMD and its severity using the developed model. This study was self-funded and supervised by Dr. Joyce Nakatumba Nabende and Dr. Ernest Mwebaze.
KABURU Dennis Mugambi
An adjustable usable security approach for a continuous user authentication scheme
Mr. KABURU Dennis research developed an adjustable usable security approach that enhances the alignment of security and usability attributes to achieve a better interaction in continuous user authentication schemes. He established that software developers have neglected the effect of the authentication approaches on the cognitive processes of a user, resulting into not user-friendly systems. Through experiments, the resultant approach showed a threshold that adjusts user interactions at different times and a technique that quantitatively recommends combinations that minimize the cognitive load and usability deficiency. Software developers can use this approach as a platform that enables their reasoning of how their use of authentication mechanisms affects end user efficiency and make refined decisions that improve usability of user interactions in a continuous authentication scheme. This study was funded by METEGA, and was supervised by Dr. Julianne Sansa–Otim and Dr. Tony Bulega.
MASABO Emmanuel
Integrated feature engineering approach for classification and detection of polymorphic malware using machine learning
Mr. MASABO Emmanuel’s research focused on the security of computer systems, by investigating the challenges related to the eradication of malware. The study showed that poor detection of current malware by existing technologies is due to polymorphism in today’s malware, which enables them to disguise themselves by creating infinite number of new variants of themselves in order to evade detection systems. This study developed a new machine learning approach to effectively address the aforementioned problem. The findings showed improved performance both in terms of classification and detection of polymorphic malware. This study was funded by Metega, and was supervised by Dr. Kyanda Swaib Kaawaase and Dr. Julianne Sansa Otim.
NAKIBUULE Rose (Ms)
Traffic flow speed and congestion monitoring in resource-constrained crowded cities
Ms. NAKIBUULE Rose's study was to develop a low cost collection tool and computer vision based computation models for monitoring traffic flow speed and congestion levels of unstructured traffic flow found in resource-constrained crowded cities. Current computer vision methods tailored for traffic flow speed and congestion monitoring are costly and computationally expensive. The study revealed that by assembling a set of off-the-shelf hardware components and programming smartphone cameras as automatic image sensors reduce data acquisition costs by 80% as compared to conventional closed circuit televisions (CCTVs). The study developed a tool for real-time traffic flow monitoring and data acquisition. This study was funded by NUFFIC, DAAD, and College of Computing and Information Sciences, and was supervised by Dr. John Alexander Quinn, Dr. Ernest Mwebaze and Dr. Joyce Nakatumba-Nabende
NINA Olivia (Ms)
Indigenous knowledge utilization strategies for HIV prevention in Uganda: a study of secondary school adolescents, Kampala District
Ms. NINA Olivia investigated approaches for enhancing use of Indigenous Knowledge (IK) in the context of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) prevention among adolescents. Prevention programs that blended biomedical and IK were known to be more successful than those that did not. With increasing HIV infections among adolescents, promoting combination of approaches was critical to increasing access to accurate comprehensive information. However, existing national guidelines on use of IK were limited, fragmented and their implementation was not yet clear. The study revealed that the IK information being used contained misinformation. Ties between IK sources and adolescents were too weak to support IK use. The study recommended development of a specific national IK school health policy. Synergies between indigenous information sources and adolescents needed to be strengthened and documented IK integrated into existing HIV prevention information. This study was self-sponsored, and was supervised by Assoc. Prof. Ruth Nalumaga and Prof. Robert Ikoja-Odongo.
OMODA-ONYAIT Godfrey
A model for personalizing learning in an E-learning System
Mr. OMODA-ONYAIT Godfrey’s research investigated the requirements for personalizing learning in an e-learning system to address the issue of learner diversity and changing learner needs. A survey was conducted to gather requirements for the model using questionnaires and interviews. The findings were used to develop the model. Model evaluation was done using experts, and prototyping; and the model was found suitable. The following factors were established for determining personalized learning: learner commitment; learner motivation; learner engagement; and learner experience. From a practical point of view, the results provided a generic model that can help practitioners and policy makers in personalizing and implementing learning in an e-learning system, hence addressing learner diversity and their changing needs. This study was self-funded, and was supervised by Prof. Jude T. Lubega and Assoc. Prof. Gilbert Mayiga.
College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Bio-security (CoVAB)
YAJJ Nuol Aywel Madut
Brucellosis at human-domestic animal interface in Greater Bahr el Ghazal States, South Sudan
Mr. YAJJ Nuol Aywel Madut assessed the prevalence of brucellosis among humans and domestic animals in pastoral settings in post-conflict Greater Bahr el Ghazal States, South Sudan. Brucellosis prevalence was high both in human and animals due to the lack of control measures and awareness and the disease was common among febrile patients attending outpatient department (OPD) in Wau Hospital. The consumption of infected animal products played a major role in transmission of brucellosis. Age, herd size, lactation, health status, hygroma and history of abortion were factors associated with the infection. There is need for mandatory routine testing for brucellosis among herders and other high-risk groups, and control should be accomplished at the animal level since people have a social and cultural tendency to consume raw animal products. This study was funded by NORHED and was supervised by Assoc. Prof. George William Nasinyama and Assoc. Prof. Clovice Kankya.
Please click the links below to navigate to the PhD Citations for the respective Sessions.
< Director’s Message | Session 1: Part1: Part2 : Part3 | Session 2 | Session 3 | Session 4 >
#Mak70thGrad
You may like
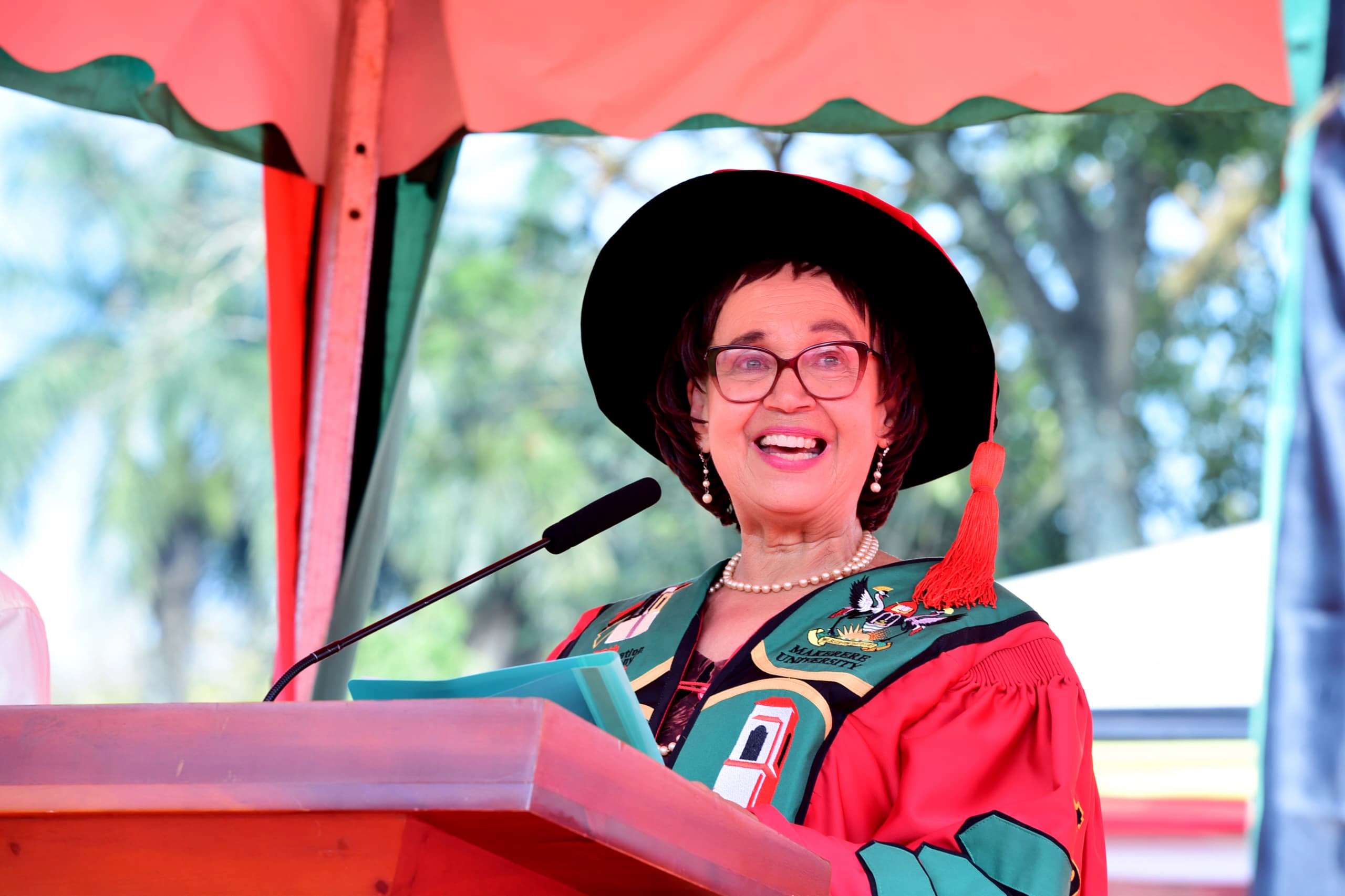

The Board Chairperson of the Makerere University Endowment Fund (MakEF), Dr. Margaret Blick Kigozi, has urged graduands in Health and Life Sciences to uphold professional ethics and serve humanity with diligence and compassion.
Her appeal came during the passing out of graduates from the College of Natural Sciences (CoNAS), the College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Bio-Security (CoVAB), the College of Health Sciences (CHS) and the School of Public Health (SPH) on Day Two of the 76th Graduation Ceremony of Makerere University.
“Class of 2026, you are now part of the Makerere legacy. Wherever you go clinics, laboratories, farms, boardrooms, or classrooms, you carry this institution with you. Serve your patients with skill and compassion. Care for animals and communities responsibly. Question boldly and keep learning,” Dr Kigozi, said.
Delivering the commencement address, Dr. Kigozi lauded the graduates for their dedication to careers that directly impact lives and communities. She encouraged them to use their knowledge generously and exercise their power gently.
“Your education has trained you to ask better questions. Your humanity must guide the answers. Never forget that behind every chart, every case, every animal, every experiment, there is life. And life deserves care, patience, and dignity. Give every person you come in contact with care, patience and dignity,” Dr Kigozi, noted.
As the graduates embark on their professional journeys, Dr. Kigozi emphasized the importance of cultivating basic business acumen and financial literacy to ensure sustainability in their work.

“You do not need to become accountants but you must be able to read the essentials: understand simple financial statements, budgets and key metrics so you can judge whether a clinic, lab, or program is sustainable. You are encouraged to start your business. There are numerous investment opportunities in your areas of training. You can provide services to our people and create jobs,” Dr Kigozi, said.
She shared candidly how, when she first stepped into leadership, she realised she did not understand balance sheets or budgets well enough. So, she returned to Makerere for short courses to strengthen herself.
“A well-run Hospital, clinic or lab delivers better outcomes, attracts staff, and secures funding. Business savvy is not only about profit, it’s about sustainability and the freedom to serve ethically and effectively. Carry clinical skill with business sense so your work endures and grows,” Dr. Kigozi, noted.
Quoting renowned writer and producer Shonda Rhimes, creator of Grey’s Anatomy, who once reflected that succeeding in one area of life can sometimes mean falling short in another, Dr. Kigozi encouraged women graduates to intentionally balance professional ambition with family responsibilities.
“When one area thrives, another is often under strain. When Navio was graduating from school I had to manage the Presidential Investor Round Table on the same day as Executive Director Uganda Investment Authority. I chose my job and delegated his siblings to attend Navios graduation. I learnt from this. I choose family always after that thing you achieve once and keep forever,” Dr Kigozi, said.
In his speech, the Prof Barnabas Nawangwe, the Vice Chancellor, informed the congregation that Makerere’s ranking on all university ranking platforms has remained stable, placing Makerere among the top 10 African universities and within the top 4.5% globally.
“In the Times Higher Education global ranking, Makerere University made a formidable jump from the 1200-1500 bracket to the 800-1000 bracket. This was no mean achievement and I congratulate all members of the Makerere Community on this stellar performance,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
General
Graduation marks the next phase of accountability, graduates told
Published
2 days agoon
February 25, 2026
“A degree is not a finish line. Graduation is not the end of learning, It is the beginning of accountability,” Prof. Nicholas Ozor, the Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network Nairobi, Kenya (ATPS), said.
Delivering a keynote address under the theme ‘Knowledge with purpose’, during Makerere University’s 76th graduation ceremony on Tuesday 24th February, Prof Ozor, challenged graduates to see their degrees not as status symbols, but as instruments of responsibility.
In his speech, he painted a candid picture of the world the graduates are stepping into, one marked by climate change, technological disruption, inequality, food insecurity and the rapid spread of misinformation. Yet rather than framing these challenges as obstacles, he described them as opportunities for purposeful leadership.
“Into this world, you step, armed with knowledge, credentials, and potential. Your degrees do not make you better than others. They make you responsible for others,” Prof Ozor, said.
Addressing graduands from College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES)
College of Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS), College of Education and External Studies (CEES) and School of Law (SoL), Prof. Ozor tailored his message to each field of study.
To graduates of the School of Law, he described the legal profession as a moral calling, urging them to use the law to protect the vulnerable and uphold justice with courage.
“Uganda, Africa, and the world do not need lawyers who only know how to argue. They need lawyers who know why they argue. Use the law to protect the weak, not intimidate them. Use your knowledge to defend justice, not delay it. Let integrity define your reputation not merely your résumé,” Prof Ozor, said.
For graduands who might feel that shortcuts will be tempting and silence will feel safer than truth, Prof. Ozor reminded them that justice does not need clever people, but courageous ones.
To the College of Education and External Studies, he underscored the transformative power of teachers, reminding them that classrooms shape nations long before policies do.
“Every nation rises and falls on the quality of its teachers. Never underestimate the power of a classroom. Teach not only for examinations, but for understanding. Teach not only content, but character. Teach learners how to think not what to think. Education is quiet work but its impact echoes across generations,” Prof Ozor, noted.
He called upon graduands from the College of Computing and Information Sciences, to use technology to solve African problems, not merely to imitate foreign solutions.
“Technology is powerful, but it is not neutral. Every line of code carries values. Every system you design affects real lives. Build for inclusion. Build for accessibility. Build for truth. Do not let innovation outrun ethics. The future will not belong to those who know the most technology, but to those who use it wisely,” He noted.
During the ceremony, Prof Ozor announced that the African Technology Policy Studies Network is offering PhD scholarships and postdoctoral fellowships in Artificial Intelligence, inviting deeper collaboration with Makerere.
For graduates of the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, he highlighted their critical role at the intersection of sustainability and survival, calling on them to blend indigenous knowledge with scientific innovation to secure Africa’s food systems and protect its ecosystems.
In closing, he reminded graduands that their integrity will open doors their degrees cannot, their humility will teach them lessons success never will, and their resilience will matter more than their grades.
Five principles to be remembered:
- Embrace lifelong learning. The world changes too fast for static knowledge.
- Choose purpose over comfort. Impact matters more than income.
- Build character before career. Skills get you hired; character sustains you.
- Serve something larger than yourself. Give back to your communities and your country.
- Believe in Africa, and act. Do not wait for solutions from elsewhere. Be the solution.
General
Over 9,200 to graduate at Makerere University’s 76th Graduation
Published
3 days agoon
February 24, 2026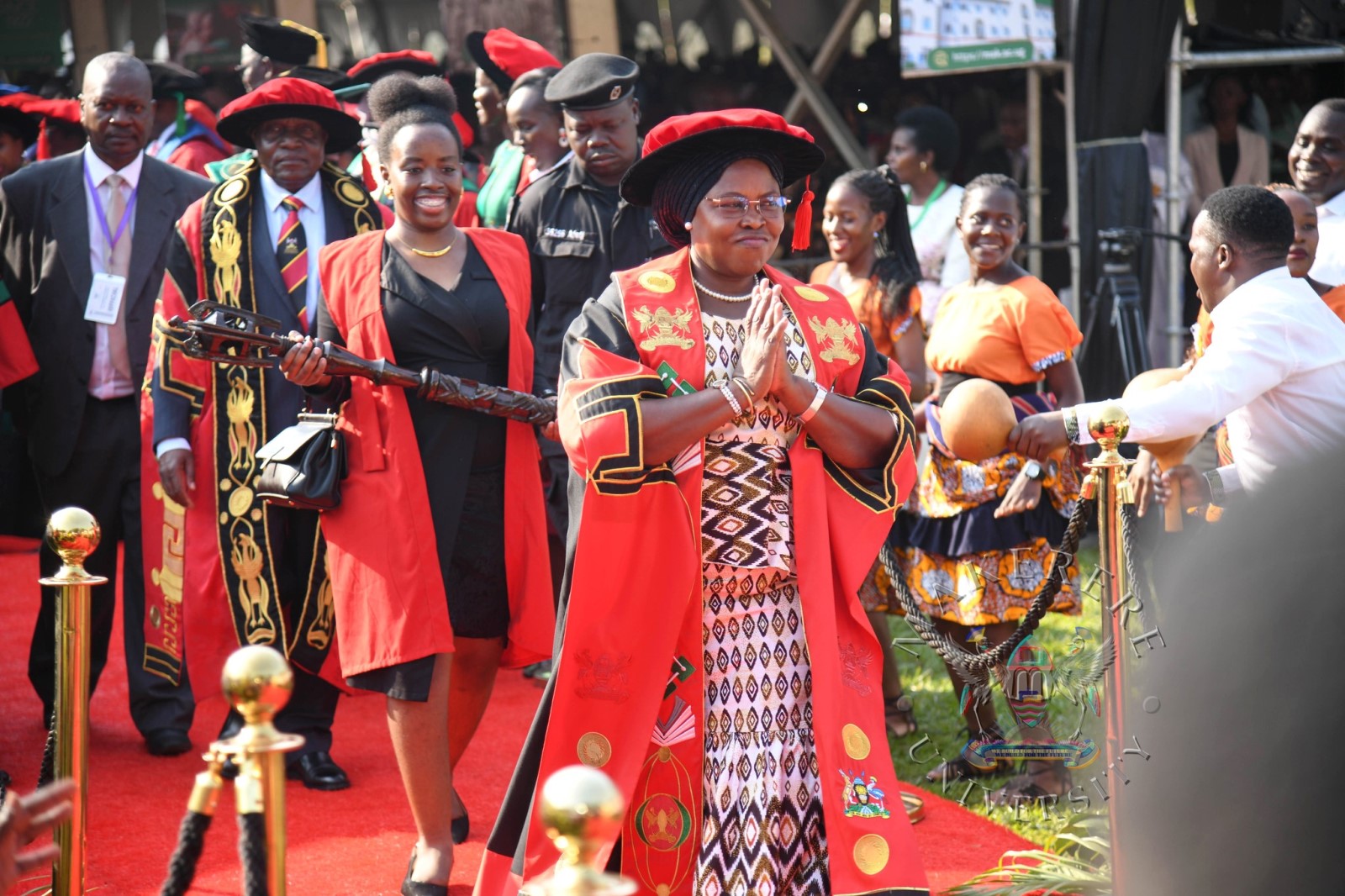
Pomp and colour defined the opening day of the Makerere University’s 76th Graduation Ceremony as thousands gathered to celebrate academic excellence and new beginnings.
The historic ceremony has brought together scholars, families, friends and industry partners in a vibrant celebration of achievement and possibility. Throughout the four-day event, the University will confer degrees and award diplomas to 9,295 graduands in recognition of their dedication and hard work.
Among the graduates, 213 will receive Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degrees, 2,503 will graduate with Master’s degrees, and 6,343 will earn Bachelor’s degrees. In addition, 206 students will graduate with postgraduate diplomas, while 30 will be awarded undergraduate diplomas.
Of the total number of graduands, 4,262 are female and 5,033 are male. According to Vice Chancellor, this marks the first time in 15 years that male graduands have outnumbered their female counterparts.
The best overall graduand in the Sciences, Esther Ziribaggwa, graduated on the opening day with the Bachelor of Agricultural and Rural Innovation and an impressive Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) of 4.77.
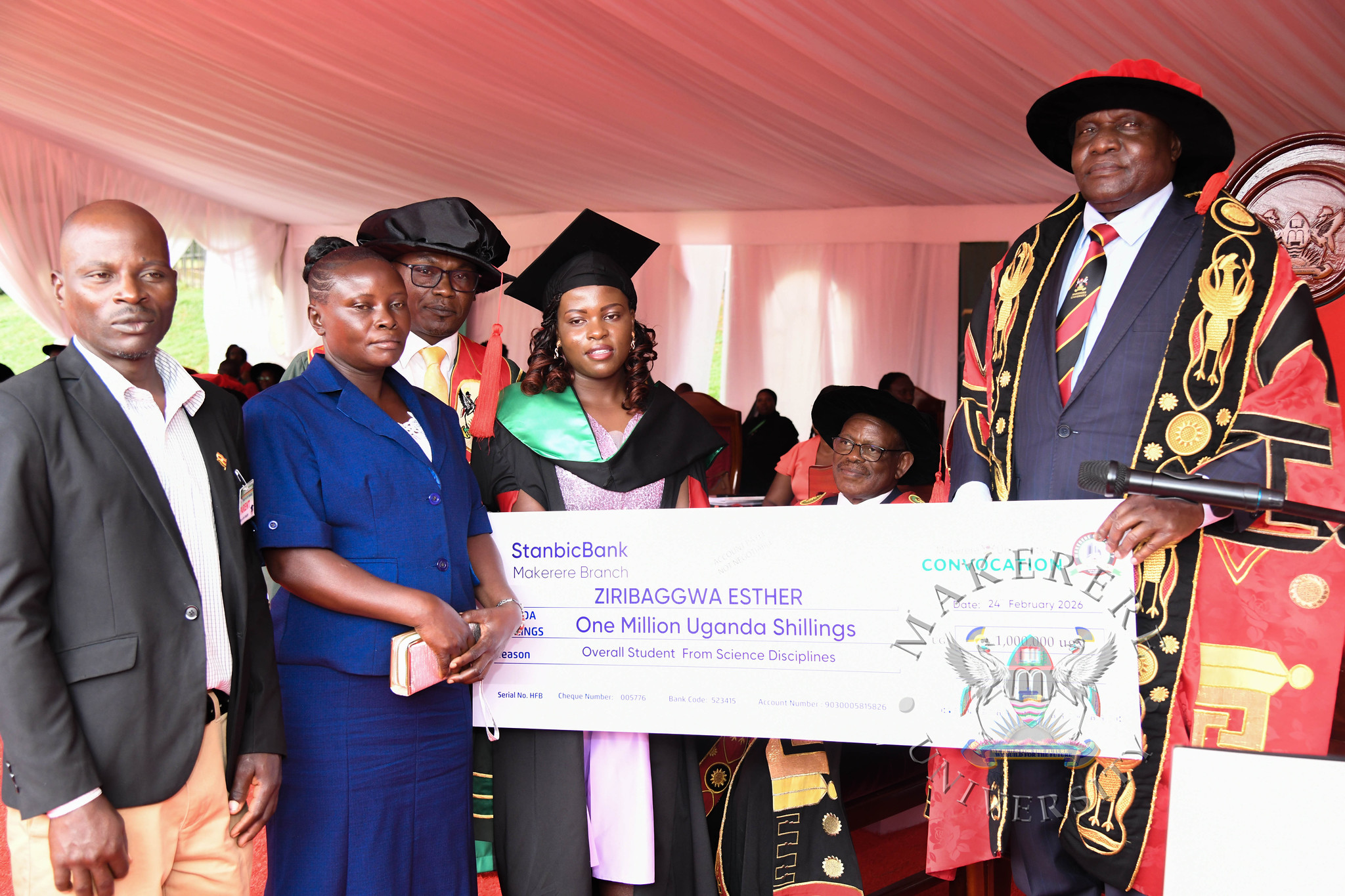
The ceremony marks a proud moment for Makerere University as it continues to nurture top-tier professionals across diverse fields.
While presiding over the graduation, the State Minister for Primary Education, Hon. Dr. Joyce Moriku Kaducu, on behalf of the First Lady and Minister of Education and Sports, Hon. Janet Kataaha Museveni, pointed out that Makerere University is a model institution, where leaders are nurtured, scholars are sharpened, and where dreams have been given direction.
In her address, Hon. Museveni, highlighted Government’s deliberate investment in research, innovation, and infrastructure to strengthen higher education in Uganda.
“The establishment of the Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund (RIF), supports high-impact research and innovation that directly contributes to national priorities and development. Through this initiative, thousands of researchers and innovators have pursued practical, scalable solutions that are transforming communities and key sectors across Uganda,” Mrs Museveni, said.
The Minister also noted that Parliament’s approved a USD 162 million concessional loan to upgrade science, technology, and innovation infrastructure at Makerere University. The funding will facilitate the construction of modern laboratories, smart classrooms, and state-of-the-art facilities for Engineering and Health Sciences, investments expected to position the University firmly within the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
“Government has embarked on the construction of a National Stadium at Makerere University and other institutions of higher learning across the country. This will promote physical education, strengthen talent identification, and boost investment in the sports sector,”
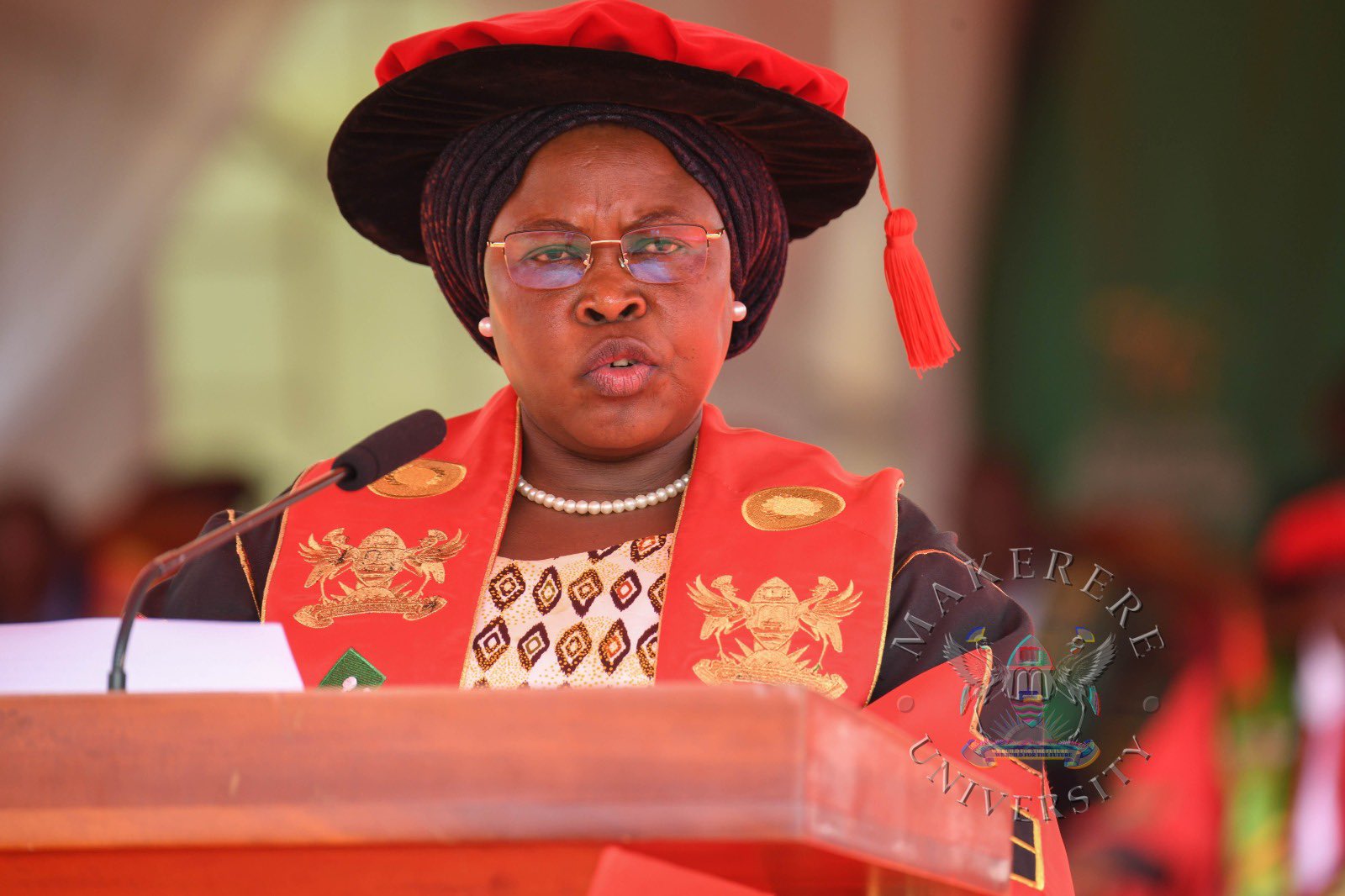

Turning to the graduands, the Minister encouraged them to see themselves not merely as job seekers, but as job creators and solution-makers.
Uganda and Africa need innovators who will modernize agriculture; engineers who will build quality infrastructure; healthcare professionals who will strengthen health systems; and educators who will inspire the next generation,” the Honourable Minister said.
She reminded graduates that they are entering a rapidly changing world shaped by Artificial Intelligence, climate change, and shifting global markets. To thrive, she advised them to remain adaptable, creative, and committed to lifelong learning.
She also encouraged graduates interested in entrepreneurship to tap into the Government’s Parish Development Model, which provides community-based financing and production support.
Quoting Proverbs 3:5–6, the Minister urged the graduates to trust in God as they embark on their next chapter.
She extended special appreciation to the Mastercard Foundation for its 13-year partnership with Makerere University in expanding access to education and empowering young people in Uganda and beyond.
In his speech, the Chancellor of Makerere University, Dr Crispus Kiyonga, urged graduands to harness research, innovation and technology to drive Uganda’s transformation.
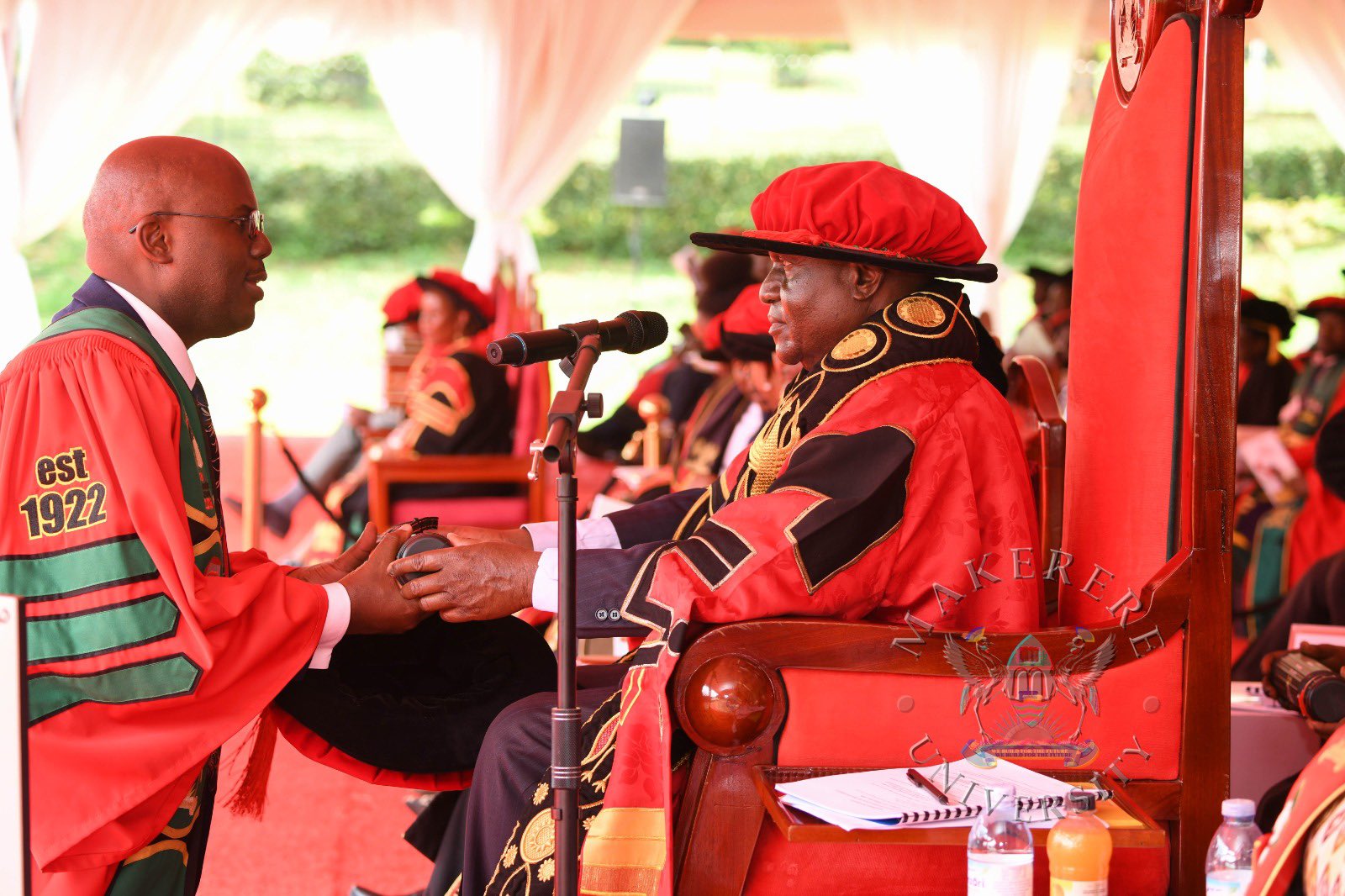

“This is a milestone in your lives. You have invested time, discipline and hard work to attain these qualifications. It is important that you derive value from this achievement, not only for yourselves, but for your families and for society.” Dr Kiyonga, said.
Dr. Kiyonga expressed gratitude to the Government of Uganda for its continued financial support to the University, particularly the funding allocated under MakRIF, which he described as critical in strengthening the institution’s research capacity.
“Research plays a very vital role in the development of any community. Makerere as the oldest University in the country is doing a significant amount of research, However, more work is required to mobilize additional resources to further strengthen research at the University.” Dr Kiyonga, noted.
Acknowledging the challenges of a competitive job market, Dr. Kiyonga encouraged graduates to think beyond traditional employment pathways.
“It is true that the job market may not absorb all of you immediately. But the knowledge you have acquired is empowering. You can create work for yourselves, individually or in teams.” Dr Kiyonga, said.
He advised the graduands to embrace discipline, integrity and adaptability in the workplace, and to take advantage of technology and digital platforms to innovate and respond to societal challenges.
“Every development challenge presents an opportunity. Believe that you can apply your knowledge to create solutions with impact.” He said.
Addressing the congregation, the Vice Chancellor, Prof Barnabas Nawangwe, congratulated the graduands, particularly staff and societal leaders on their respective achievements.
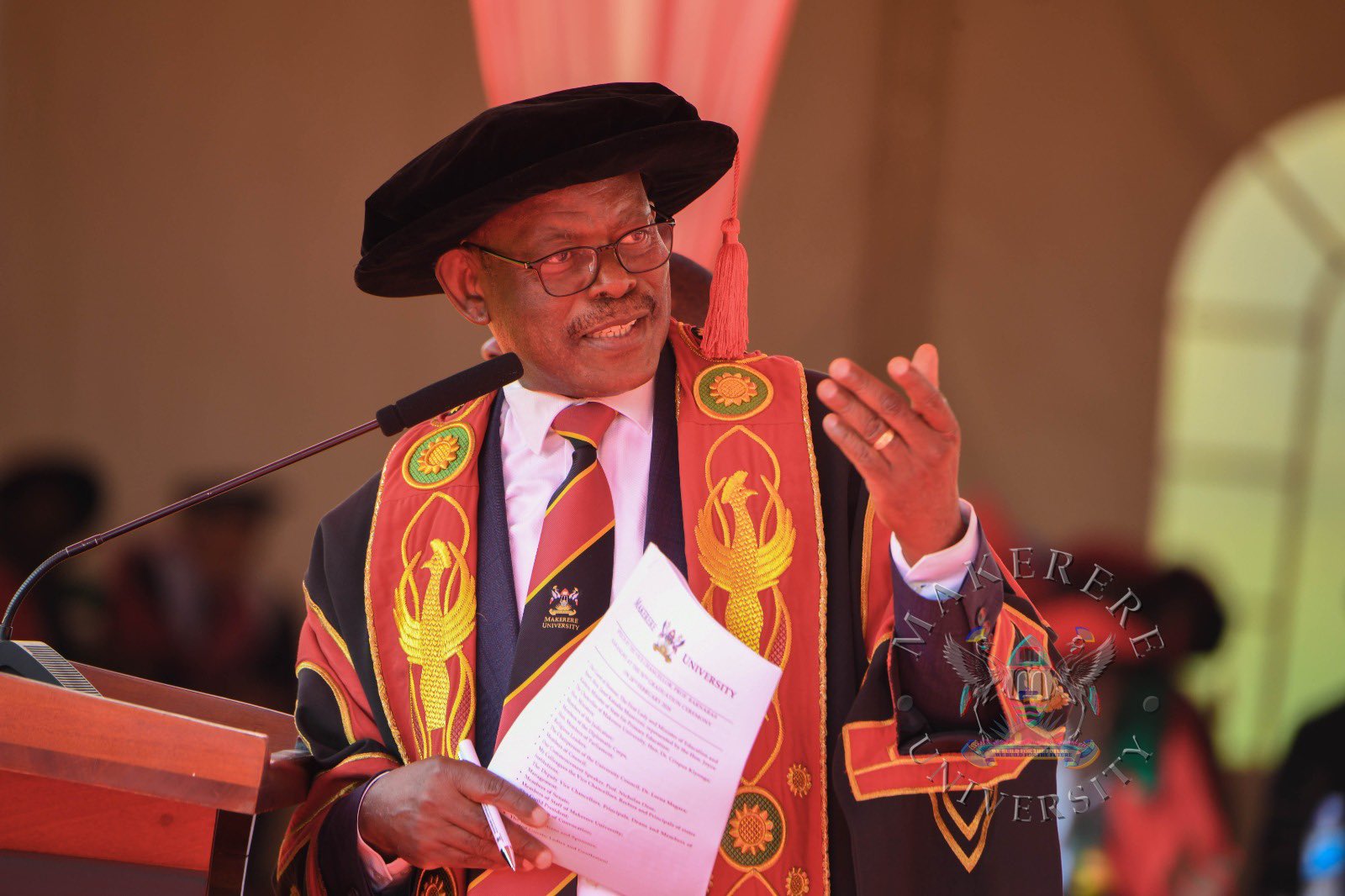

“I congratulate all our graduands upon reaching this milestone. In a special way I congratulate the members of staff, Ministers, and Members of Parliament that are graduating today as well as children and spouses of members of staff,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
In his speech, Prof Nawangwe, recognized outstanding PhD students, particularly members of staff. who completed their PhDs in record time without even taking leave from their duties.
He called upon graduates not to despise humble beginnings but rather reflect on the immense opportunities around them and rise to the occasion as entrepreneurs.
“You are all graduating with disciplines that are needed by society. We have equipped you with the knowledge and skills that will make you employable or create your own businesses and employ others. Do not despair if you cannot find employment. Instead, reflect on the immense opportunities around you and rise to the occasion as an entrepreneur,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
Prof Nawangwe called upon the graduands of PhDs to use their degrees to transform the African continent.
“As you leave the gates of Makerere I urge you to put to good use the knowledge you have received from one of the best universities in the World to improve yourselves, your families, your communities, your Country and humanity. Let people see you and know that you are a Makerere alumnus because of the way you carry yourself in society with dignity and integrity. Put your trust in God and honour your parents and opportunities will be opened for you,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
Delivering a key note address, Prof. Nicholas Ozor, the Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network Nairobi, Kenya ((ATPS). Reminded the graduates that a degree is not a finish line but the beginning of accountability. “The world is a complex, fast changing and deeply unequal. Degrees make you responsible for others not better than them,” Prof Ozor, said.
Trending
-

 Humanities & Social Sciences4 days ago
Humanities & Social Sciences4 days agoMeet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 Agriculture & Environment1 week ago
Agriculture & Environment1 week agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-

 General3 days ago
General3 days ago76th Graduation Highlights
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
