Humanities & Social Sciences
Mak Almnus Prof. Ngugi Wa Thiongo Honored, Humanities Book Launched during the Humanities Conference
Published
4 years agoon
By
Jane Anyango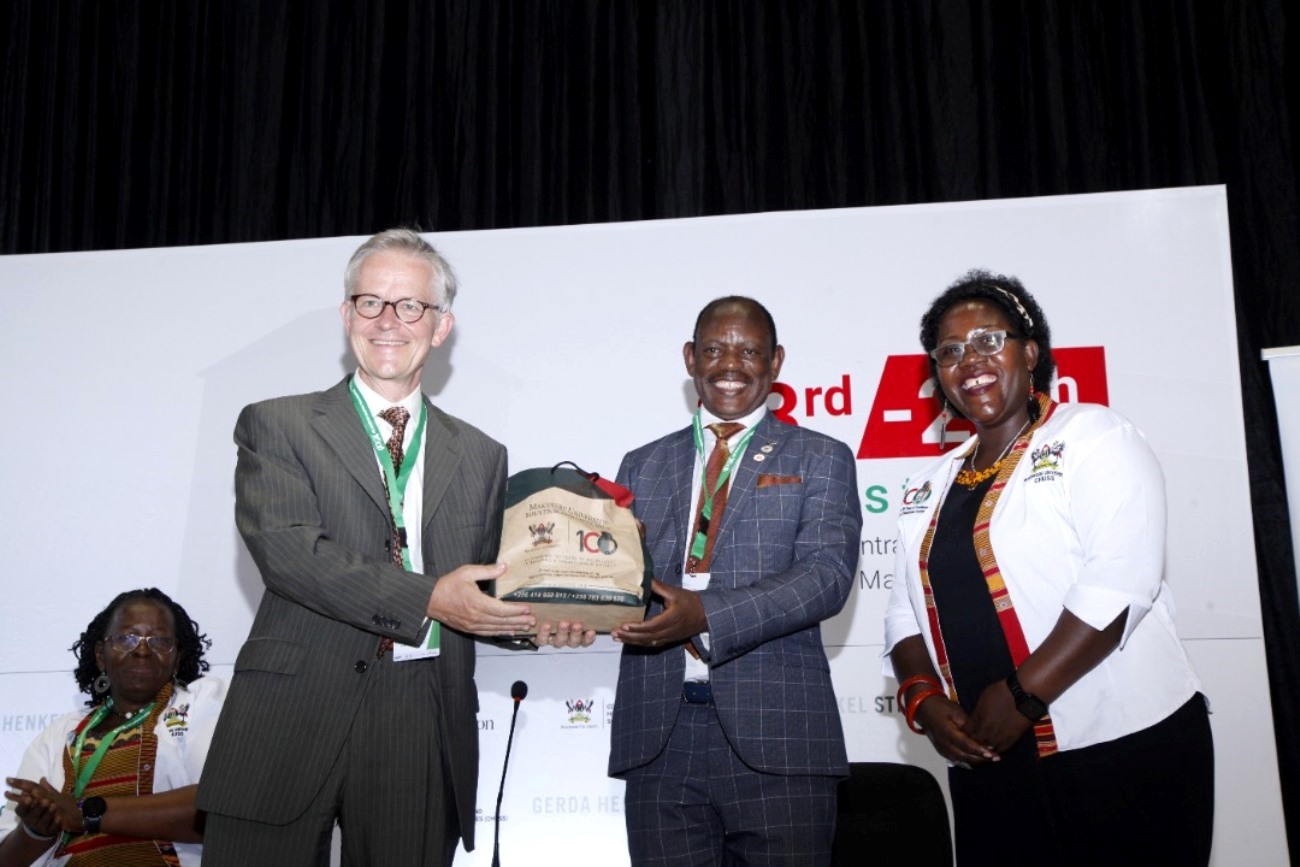
The three-day International Humanities Conference organized by the College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHUSS) was on 23rd August 2022 opened with the Graduate Mentorship session, followed by planting a tree in honor of Makerere University Alumnus Prof. Ngugi Wa Thiong’o by the Vice Chancellor Prof. Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe At the Arts Quadrangle.

Prof. Nawangwe also launched a book titled, “ Historicising Humanities at Makerere: Trends, Patterns and Prospects”. The book authored by over 20 people with 16 chapters is an outcome of a project on historicizing the humanities at Makerere supported by the Andrew Mellon Foundation of New York.
The conference convener Dr. Levis Mugumya said the key goal of the project was to rethink and reshape the role of humanities in Uganda and reexamine the basis and significance of humanities and humanistic social sciences at Makerere University from a historical perspective.
“The sixteen chapters have taken a slice of the history of some disciplines and raised questions around their basis and trajectory. It is an attempt to renew conversation and debate as well as ideational leadership of the academy “, Dr. Mugumya said
The three day Humanities conference 23rd-26th August 2022 was part of the activities to celebrate the 100 years of Makerere University service to Humanity, held at the Yusuf Lule Auditorium.
The overriding thrust of the conference was to explore how the knowledge revolutions have impacted university practices and transformed the teaching of and research in the Humanities and Social Sciences. The conference also acted as a discursive zone to interrogate innovative ways through which Humanities and Social Sciences scholarship has refocused beyond the knowledge revolutions to imagine the inevitable future economic, social, biological and political challenges to humanity.
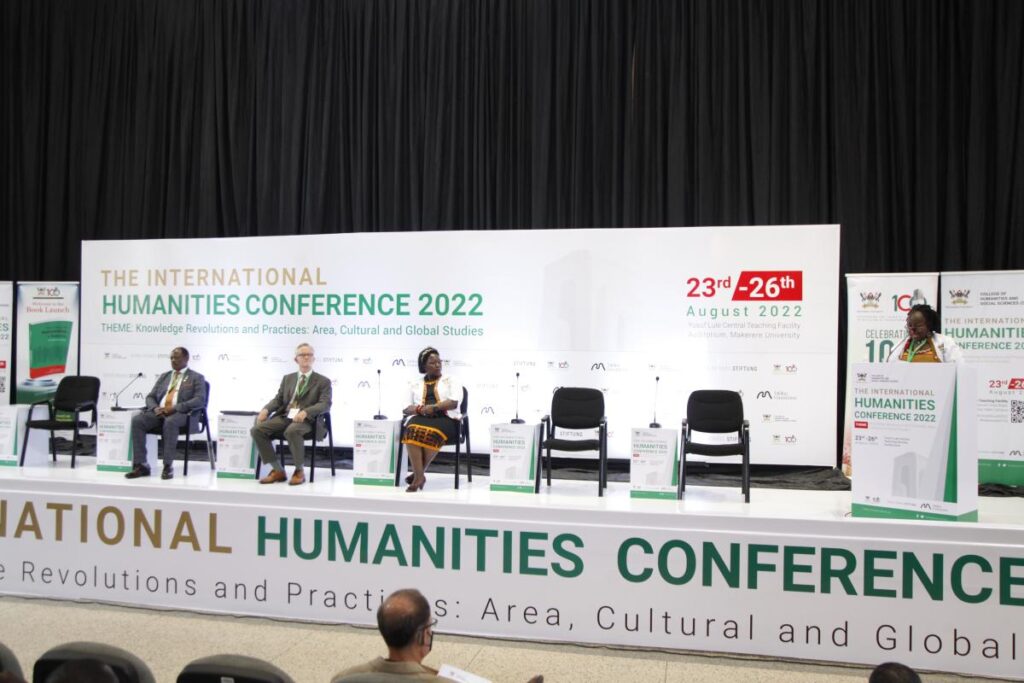
The conference was blended to enable physical and virtual engagements, presentations, and insightful and vibrant discussions. It will consist of keynote addresses, individual and panel presentations, and graduate student panel discussions.
It attracted key note speakers:- Prof. Ngungi Wa Thiong’o – a distinguished Professor of English and Comparative Literature from the University of California;Derrick Peterson – Ali Mazrui Collegiate Professor of History from the Afro-American and African Studies University of Michigan and; Nakanyike Musisi – a Professor from the African Women Education and Development, Makerere University/ University of Toronto
It would be a mistake to discredit humanities as a second class subject
The conference was officially opened by the German Ambassador to Uganda H.E Matthias Schauer. The ambassador underscored the role of humanities in society saying, it is un imaginable to create a legal regulatory system without a profound knowledge of history of society and language which is part of the humanities.
He observed that scholars in humanities and social sciences have witnessed three major knowledge revolutions since 1945 from Area studies, cultural studies and global studies. Ambassador Schauer noted that today, there are signs that scholars may be at another brink of the fourth revolution as witnessed by problems in maintaining global production process, amidst rising transport costs, political unrest and the realization that countries may not be dependent on one other.
“We have been fooling ourselves that economic interdependence would prevent out conflicts but this is not the case. We may now need a new focus on global cooperation and create new fields of research in humanities and social sciences”. He said.
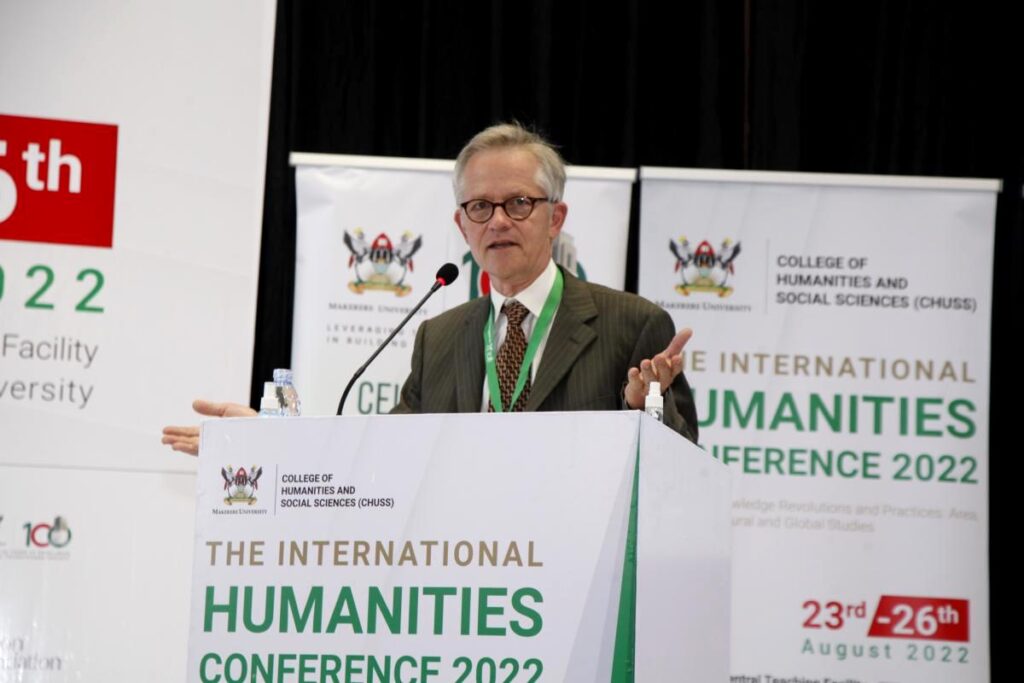

He said humanities attracts a huge number of students at universities because of the diversity of subjects and rich menu for offer. On the political debate on education, Ambassador Schauer noted that its common to hear that countries may need natural scientists, engineers and technicians to increase economic performance.
Though that may be right to some extent, Ambassador Schauer described the humanities and humanistic social sciences as vital to society saying, it would be a mistake to discredit humanities as a second class subject. He advised that young people should do what they feel passionate about.
“First of all they (Humanities) help us understand each other. Language, history and culture shapes each one of us. Without communication that works, nothing much else can work. Humanities also teach us to approach new complex issues in a systematic way to assess information and considering different facts from all sides, Humanities make us informed and critical citizens and, without humanities, democracy would not work. Humanities also foster social justice and teach us empathy and make international relations broader and stronger. Humanities encourage us to think creatively, to reflect upon ourselves and human nature and to think outside the box. Humanistic services enrich the soul and make us a cultured individual,” The ambassador asserted.
The ambassador also described as false the thinking that humanistic degrees are not marketable as degrees in STEM, business management and other natural sciences.
“At sight that might seem true, but in my experience a student who diligently study in humanistic subjects will always carry this energy and motivation successfully into his professional life and sell more as in finding a good job. Almost all employers desperately need employees who can communicate fluently, intelligently and persuasively and, employees who can organize their thoughts and synthesis their scattered information into a coherent story.
Employers need employees who are equipped with soft skills such as the ability to converse with difficult topics in a constructive manner and it is the humanities that helps them to express very well. Humanistic education will enrich you very well, emotionally, socially and intellectually and gain a wide experience while at college”, The ambassador asserted.
The Ambassador hailed the long standing relationship and collaboration that Germany enjoys with Makerere University especially with CHUSS.
He said it was now over 60 years when Germany was taught in the evening class at Makerere University as an extracurricular language program that continued till 1967 when the first bachelor of arts was established and it became the first German phonology in East Africa.
He highlighted a number of advantages of studying Germany including teacher employment opportunities in education sector, participation in internships, huge range of opportunities in tourism, training opportunities and on job trainings in companies and unique connections, interaction and demand across the world.
The ambassador encouraged the university leadership to foster the teaching of foreign languages at Makerere in prominent way at CHUSS department of European and Oriental languages and proposed the establishment of Master of Arts program in Germany as the most appealing to him.
He expressed the Germany commitment to continue funding the Ugandan students and staff in their academic and other endeavors.
CHUSS reputed for producing eminent scholars
The Vice Chancellor Makerere University Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe reported that the Humanities and Social Sciences have been at the heart of Makerere University since the introduction of History in 1946, and the East African Institute of Social Research in 1948.
He explained that the Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences is reputed for producing eminent scholars and political leaders, including Julius Nyerere, Milton Obote, Mwai Kibaki, Benjamin Mkapa, Oginga Odinga, Okot p’Bitek, Ali Mazrui, David Rubadiri, Nuruddin Farah, Ngugi wa Thiong’o, John Ruganda, V. S. Naipul and Wole Soyinka among others.
Prof. Nawangwe informed participants that CHUSS has championed the critical role of humanities and humanistic social sciences in comprehending, interpreting, and recognizing societal commonalities and differences as well as fostering critical thought, social justice, equity and democratic practice stressing that, in the 1960s and 1970s before the onslaught of neoliberalism and the emphasis on STEM, the humanities and humanistic social sciences were vibrant.
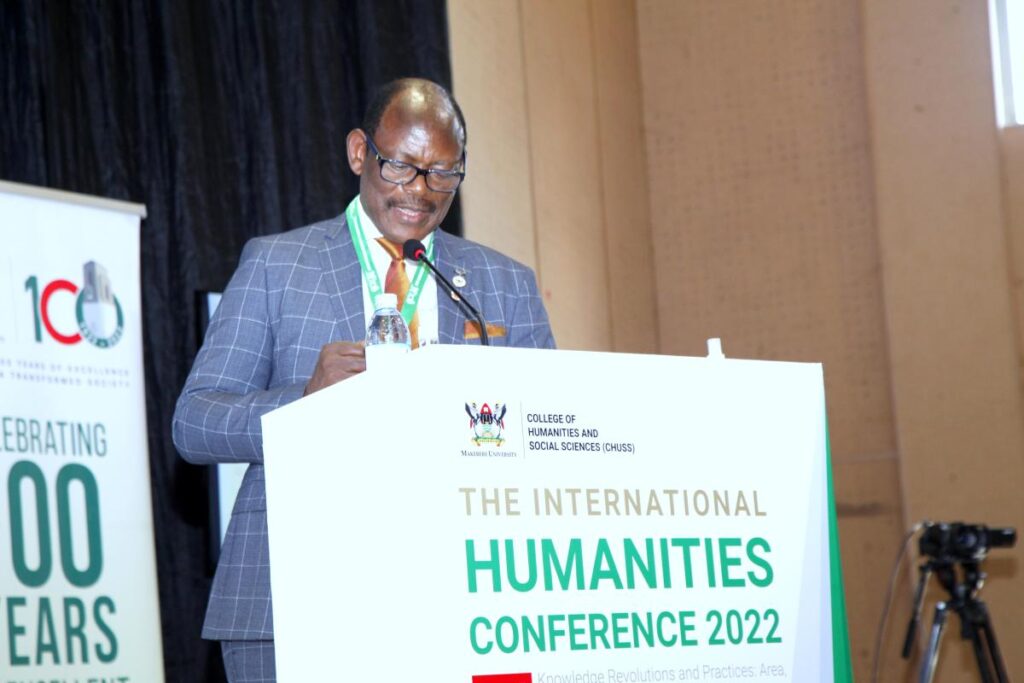

In spite of this rich history, Prof. Nawangwe pointed out that the current positionality and relevance of the disciplines of humanities and humanistic Social Sciences has come under scrutiny as compared to the natural scientific disciplines.
While the University is prized in scientific research, Nawangwe said, today’s complex global challenges such as ‘global warming, global poverty, global epidemics’ and gender inequality cannot be solely explained or resolved by natural scientific disciplines.
“It is therefore important to understand the human factor, which is central in most of the modern scientific glitches. Not only do the humanities and humanistic social sciences explicate our existence as human beings, but they also contribute to creating “tolerance and understanding between citizens”, which promote social cohesion, and challenge established positions, social norms and traditions through critical thinking, and preserve heritage, cultural memory and identity”, He said.
The Vice Chancellor was optimistic that the knowledge and strategies generated through the conference will go towards uplifting the lifestyles of the people and also aid in conducting a comprehensive review of all aspects of teaching, theorizing, research and practice in the humanities and social sciences disciplines.
Prof. Nawangwe extended appreciation to development partners for the support extended through generous acts such as sponsoring this fora, capacity building, research and developing infrastructure with particularly recognition to the Andrew Mellon Foundation and Gerda Henkel Stiftung for supporting academic activities in the College of Humanities and Social Sciences as well as the Government of Uganda for supporting research and creating an environment conducive for the same to thrive at Makerere University.
The Vice Chancellor also appreciated keynote speakers, Prof. Ngugi wa Thiong’o, Prof. Nakanyike Musisi and Prof. Derek Peterson, the participants, and all guests for honouring the invitations.
To the students (PhD and Masters), The Vice Chancellor expressed happiness that that the International Humanities Conference 2022had commenced with the Graduate Mentorship session.
“You are being nurtured and mentored to not only become the next generation of academics, but to also provide leadership and championship towards Uganda’s development and transformation of your communities.
I encourage you to actively participate in the conference so that you learn more as you pursue your PhD and Masters” Nawangwe said and applauded CHUSS management under the leadership of the Principal, Associate Professor Josephine Ahikire for hosting a number of activities in line with the centenary celebrations.
The conference looked at the world with resolve for greater humanity
The Principal CHUSS, Associate Prof. Josephine Ahikire welcomed all to the conference saying, this was the first Conference to be held after the serious lockdown for two years as the university celebrates the Humanities and Social Sciences and make a mark on the nation, continent and the world at large.
This conference themed: Knowledge revolutions and Practices: Area, Cultural and Global Studies she said , is structured as part of Makerere’s Centennial celebration aimed at exploring how the knowledge revolutions have impacted university practices, the teaching of and research in the Humanities and Social Sciences as well as human praxis.
“We use this space as a discursive zone to interrogate innovative ways through which Humanities and Social Sciences scholarship has refocused beyond the knowledge revolutions to imagine inevitable futures. We use this very space to foster critical thought about life, its afflictions, and ideals of human society – to debate and rejuvenate theory and practice”, The Principal said.

Prof. Ahikire acknowledged the friendship and partnership between Germany, Makerere and the country at large and specifically, the support by the Gerda Henkel Stiftung to the college that has soared the capacity of PhD training at CHUSS.
On behalf of CHUSS and Makerere University, the Prof Ahikire thanked the keynote speakers: Prof Ngugi who was not able to join, saying that he was and is still enthusiastic about this Conference and what happens at Makerere adding that , Prof. Ngungi has always believed/ and openly confessed that Makerere made him and Perhaps he also made Makerere.
“This symbiotic relationship is one we greatly cherish at CHUSS. Prof Nakanyike Musisi – a gem- renown historian of our time. Welcome home- proud alumnus. Prof Derek Peterson, we treasure your commitment on restoring and conserving history”, Prof. Ahikire commended.
Prof. Ahikire emphasized that the humanities have been at the heart of Makerere University since its birth and is reputed for eminent scholars, post-independence political leaders and activists. Under the ambit of the CHUSS program dubbed Humanities@ Mak 100, the Principal said, this conference was part of the efforts to galvanize humanities scholarship for even greater human utility on the African continent.
“As humanity continues to grapple with challenges such as mis -governance, conflict, climate change, and pandemics there is need for more ingenuity and inventiveness. In very specific ways, the COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated the need for a multidisciplinary approach to this unprecedented global health challenge, with the human subject at the centre.” She said adding that:“These conversations are important because our disciplines allow us to experience humanity at its best. This Conference is therefore aimed at facilitating these debates and key issues in the Humanities and Social Sciences. It is our hope that the conversations that start here do not stop here, but help us critically look at world we live in with resolve for greater humanity”.
Prof. Ahikire acknowledged the generous support of the Mellon Foundation (USA) which allowed the college to dream three years ago – when the idea of the book was proposed. The Mellon Foundation she reported has also supported various research efforts by Early Career and Senior Scholars in the college including the support for this conference that was also committed three years ago.
She thanked the University management for enabling the college to meaningfully pursue the strategic goal of a truly research led university and, the chair of the Organising Committee, the Convener of the Conference and all members of the organising committee for the job well done.
Conference planned to discuss issues important for the survival of human race
The chairperson CHUSS organizing committee Prof. Grace Bantebya said each year the college organizes a conference adding that what started as symposia has metamorphosed into great and rich academic conferences.
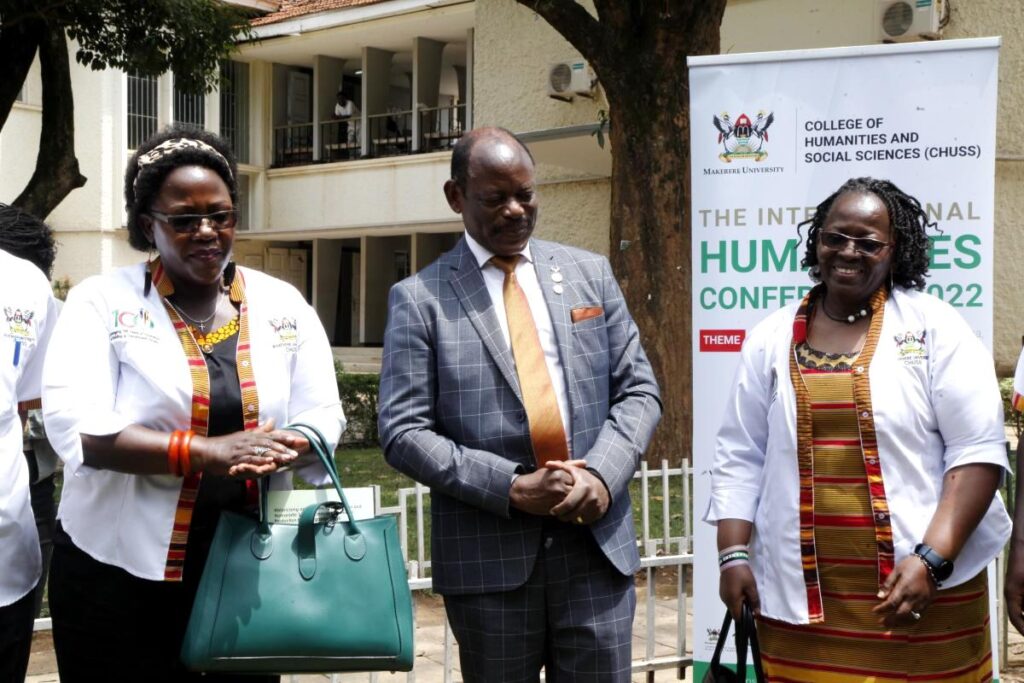

Prof. Bantebya hailed the college leadership for the support and the organizing committee for the commitment that led to the success of the conference noting that they have tirelessly worked in their different committees to see to it that it materializes.
She also thanked the Andrew Mellon Foundation and the Gerda Henkel Foundation for the support to the conference as well as the different doctoral students cohorts over the years.
“The issues this team has prepared for you to chew are those that are pertinent to our being human. It is for this reason that we are sometimes looked at as activists because issues of urgency within the global context are important for the survival of human race and this is why conferences of this nature need to keep happening”. Prof. Bantebya said.
You may like
-


Makerere Launches Scholarly Guide, Calls for Increased Research, Publication and Innovation in Africa
-


For Youth by Youth – Call for Second Cohort Applications
-


Dr. Samalie Namukose and the Quiet Work of Making Nutrition Count
-


Dr. Pamela Khanakwa Honored for Steering Record 18 PhD Candidates for the Mak 2026 Graduation
-


Call For Applications: Annual Innovation Commercialisation Award
-


Ugandan Journalists Trained on Peace and Gender-Sensitive Reporting Ahead of 2026 Elections
Humanities & Social Sciences
Dr. Pamela Khanakwa Honored for Steering Record 18 PhD Candidates for the Mak 2026 Graduation
Published
1 month agoon
January 23, 2026By
Jane Anyango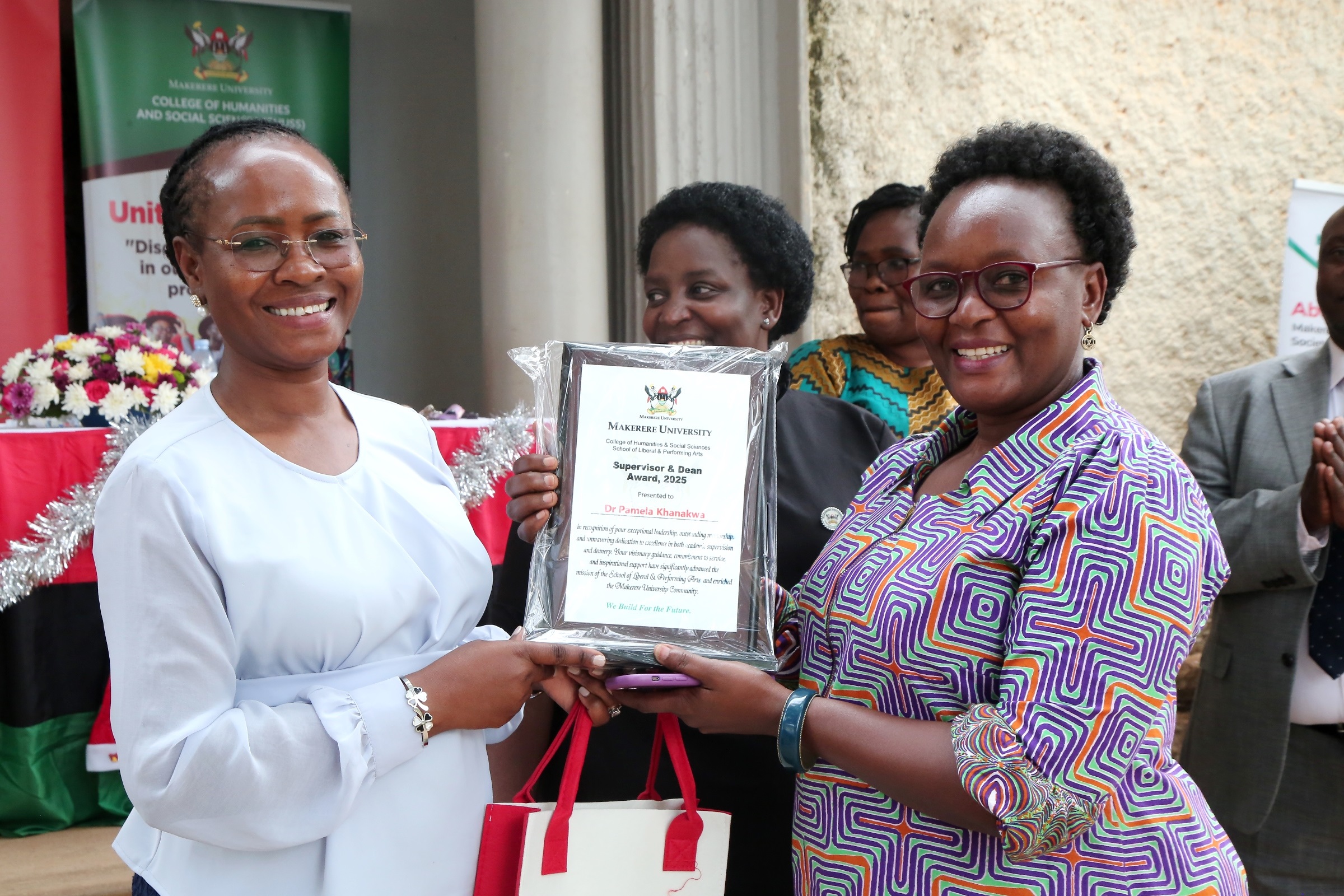
Six personally supervised, three completed in record time, as School of Liberal and Performing Arts sets a historic milestone. Dr. Pamela Khanakwa got the Award as Best PhD Supervisor and Dean
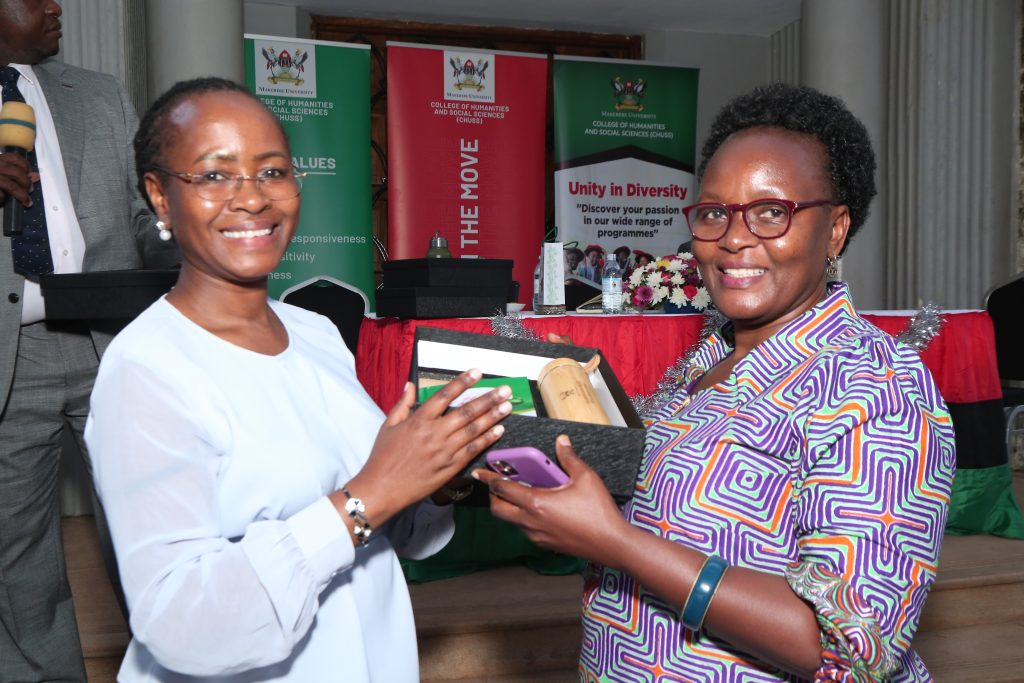

A Historic Academic Milestone for SLPA
The College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHUSS) recognised the Dean of the School of Liberal and Performing Arts (SLPA), Dr. Pamela Khanakwa, for outstanding academic leadership that has seen the School field 18 PhD candidates for the next 2026 Makerere University Graduation Ceremony scheduled for 24th-27th February. Remarkably, six of these doctoral graduates were directly supervised by Dr. Khanakwa, with three completing within the official three-year timeframe, an exceptional achievement in graduate training. The recognition was announced during the CHUSS End-of-Year Get-Together, where staff applauded Dr. Khanakwa’s dedication, humility, and relentless commitment to postgraduate supervision and timely completion.

Message to Academic Staff
Q: What message do you have for your staff following this achievement?
Dr. Khanakwa:
First, I celebrate my staff and thank them for their dedication to supervision and student support. Academic work is demanding, and material rewards are often limited, but the true satisfaction comes from seeing students succeed.
I encourage my colleagues to remain committed. Yes, the workload is heavy, but many things are possible with dedication and teamwork. Let us continue working for the good of our students, our School, and Makerere University.
Leadership Rooted in Humility
Q: Many colleagues describe you as humble, down to earth, and hardworking. What shapes this character?
Dr. Khanakwa:
I think it is largely my upbringing. My mother was a primary school teacher from the 1950s until the mid-1980s. She worked extremely hard to raise us, combining teaching with farming to ensure we had school fees and basic needs. From her, I learned humility, discipline, and the value of hard work.
I also learned that leadership positions are temporary. You occupy them today, and tomorrow you move on. So humility is essential.
My graduate training also shaped me significantly. My PhD supervisor emphasized that graduate study is a full-time job and that results matter more than noise. Let people see your work through outcomes, not announcements.
Supervision as a Two-Way Commitment
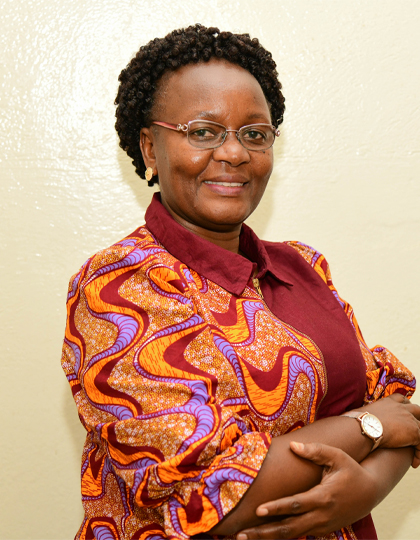

Q: How would you describe your supervision style?
Dr. Khanakwa:
I read my students’ work thoroughly, word by word. Sometimes my comments are tough, but they are honest. Supervision is a two-way commitment. I give feedback, but students must also respond and remain engaged. When that relationship works, progress happens.
Balancing Leadership, Scholarship, and Family
Q: How do you balance being a Dean, scholar, wife, mother, and daughter?
Dr. Khanakwa:
Honestly, I am not sure I balance perfectly. My mother lives far away in Bukwo, so visiting requires careful planning. My children grew up understanding the demands of academic life. I pursued my PhD in the United States and spent long periods away, but we adapted as a family.
Work has become part of my lifestyle. I use weekends to read dissertations, review manuscripts, and write. Sometimes my children ask if I ever sit without working, but this is the commitment I made. As we often say jokingly, “We humbly applied for the job, so let us do the job.”
Scholarship Beyond Supervision
Dr. Khanakwa is also an active scholar and editor. In the past year alone, she has:
- Edited scholarly volumes on archives, memory, method, and pedagogy
- Published a book with Routledge Companion
- Co-authored journal articles and book chapters with graduating students, including Priscah Asiimwe and Anatoli Lwasa Mpijja
“I feel an obligation to write with students,” she notes. “It takes time, energy, and commitment, but it is part of academic mentorship.”
Who Is Dr. Pamela Khanakwa?
Dr. Pamela Khanakwa is the Dean, School of Liberal and Performing Arts, College of Humanities and Social Sciences, Makerere University. She is a seasoned scholar, supervisor, administrator, and mentor whose leadership continues to redefine graduate training excellence. Details about Dr. Pamela Khanakwa can be accessed at: https://chuss.mak.ac.ug/en/personnel/pamela-khanakwa/
More details are available in her attached curriculum vitae.
The CHUSS End- Of-Year-Get-Together
On 12th December, 2025 the college leadership organised a get-together end of year gathering to take stock of the achievements, challenges and brainstorm together on how to move forward. The event was marked by entertainment, team building games, appreciation speeches, sharing a meal and a Christmas package for every staff
Retirees and staff recognised
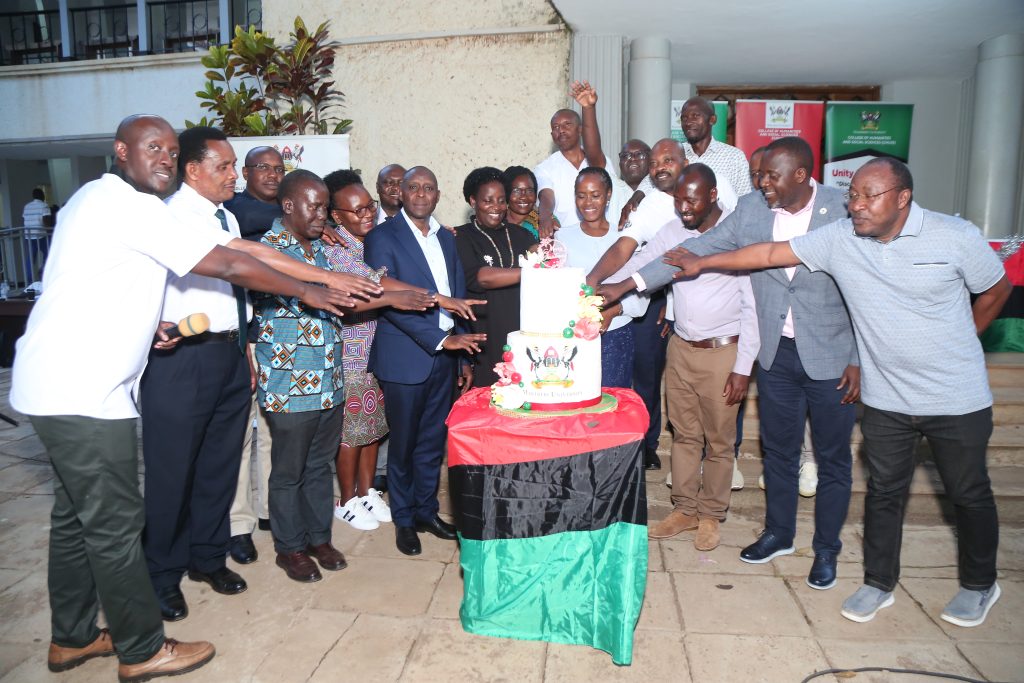

Five retired staff Dr. Micheal Wangotta Masakala, Dr. Anatole Kirigwajjo and Dr. Jackson Kizza Mukas (all from the School of Languages, Literature and Communication), Assoc. Prof. Florence Nansubuga (School of Psychology), Dr. Tusabe Gervase (School of Liberal and Perforing Arts) and Ms. Scovia Nganda Sekweyama (secretary from the School of Social Sciences) were recognised for their dedicated services to the university.
In addition to Dr. Pamela Khanakwa’s Award as Best PhD Supervisor and Dean, Ms. Birabwa Florence scooped the award of Best Registrar of the year. Birabwa is the registrar for the School of Liberal and Performing Arts.
Administrative and support staff including Ms. Mary Gyezaho and Annet Kashumbusha(both administrative secretaries in the Principals office), Farouq Lule (IT Officer), Godfrey Kakooza (cleaner), Charles Sebuguzi (driver) and Jane Anyango (Communications officer) were recognise with awards for outstanding service. Dr. Mohamed Mayanja Kajumba was from the School of Pyschology was recognised as the person with an outstanding talent in Handwriting.
The celebrations held in the Arts quadrangle were graced by the Vice Chancellor Academic Affairs Prof. Sarah Ssali and the Deputy Vice Chancellor in charge of Finance and Adminstration Prof. Ireeta Tumps.
Humanities & Social Sciences
Ugandan Journalists Trained on Peace and Gender-Sensitive Reporting Ahead of 2026 Elections
Published
1 month agoon
January 9, 2026By
Jane Anyango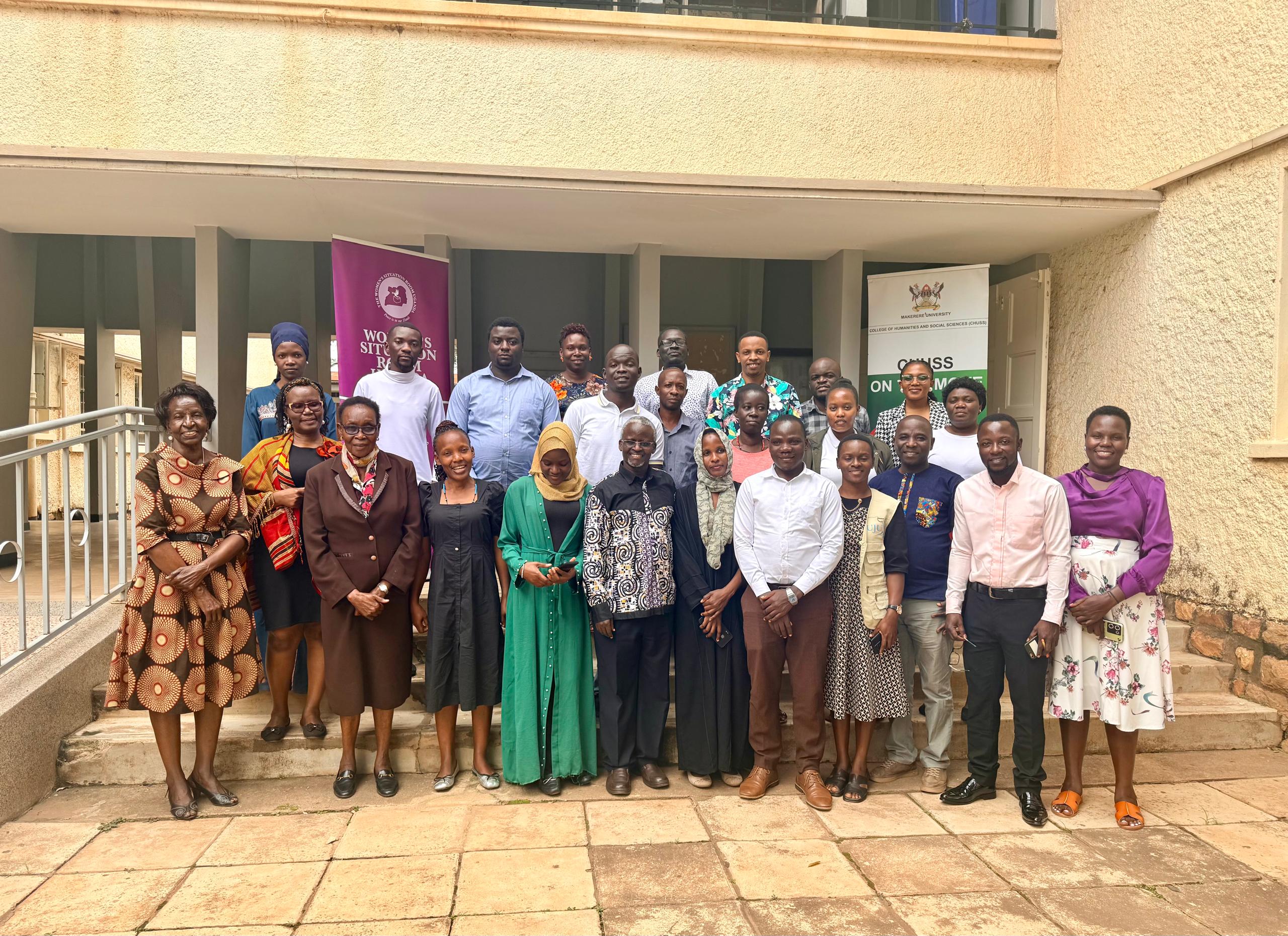
Kampala, Uganda – January 9, 2026
Ahead of the January 15 general elections, Ugandan journalists have undergone specialized training on peace and gender-sensitive reporting to ensure responsible media coverage during the election period. The two-day training, held from 8th to 9th January 2026 at Makerere University’s College of Humanities and Social Sciences Smart Room, was organized by the Women’s Situation Room (WSR) in partnership with various stakeholders and brought together journalists from across print, broadcast, and online platforms.
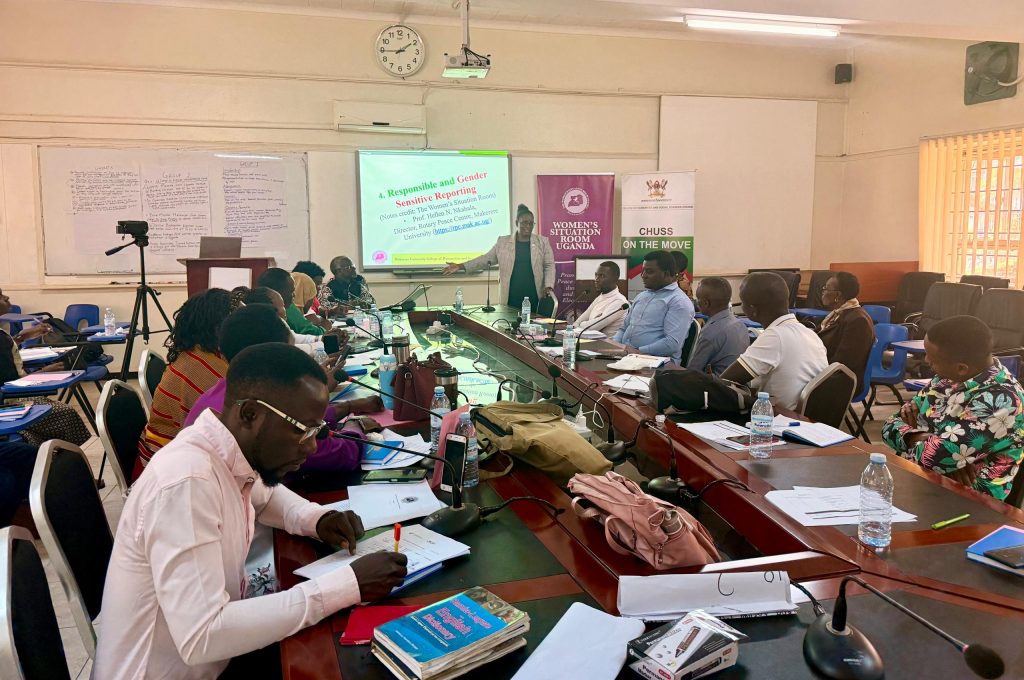

The main objective of the training was to strengthen the capacities of media in reporting and documenting electoral processes in a responsible and gender-sensitive manner. The specific objectives included: strengthening journalists’ skills to cover the 2026 elections in a fair, balanced, gender-sensitive, and non-violent partisan way; enhancing the role of media to enable citizens to be well-informed and actively participate in the election process; ensuring focused and balanced reporting on peace during and after elections; and strengthening partnerships between the WSR and media houses during the election period.
The training covered multiple critical modules. Day one focused on responsible conflict-sensitive reporting, emphasizing principles such as balance, impartiality, and accuracy. Participants explored the role of media as a relayer of the population’s voice, election monitor, catalyst for social cohesion and reconciliation, contributor to the accountability of political actors, and a platform for detecting and debunking digital media misinformation and hate speech.

Day two addressed responsible and gender-sensitive reporting. Key aspects included the definition of gender-sensitive reporting, how to become a gender-sensitive reporter, critical elements in reporting with gender awareness, packaging gender-sensitive stories, and a checklist for detecting and avoiding gender-insensitive reporting.
Her Lordship, retired Judge Justice Mary Mayitum, emphasized the importance of peace as the foundation of development and democratic engagement. “Because we value peace more than anything. Without peace, really, you can do nothing. But where there is peace, you can have time to reflect, discuss with others, and join in meaningful dialogue,” she said. She warned that the country’s past conflicts, such as those in Gulu, underscored the necessity of maintaining national harmony.
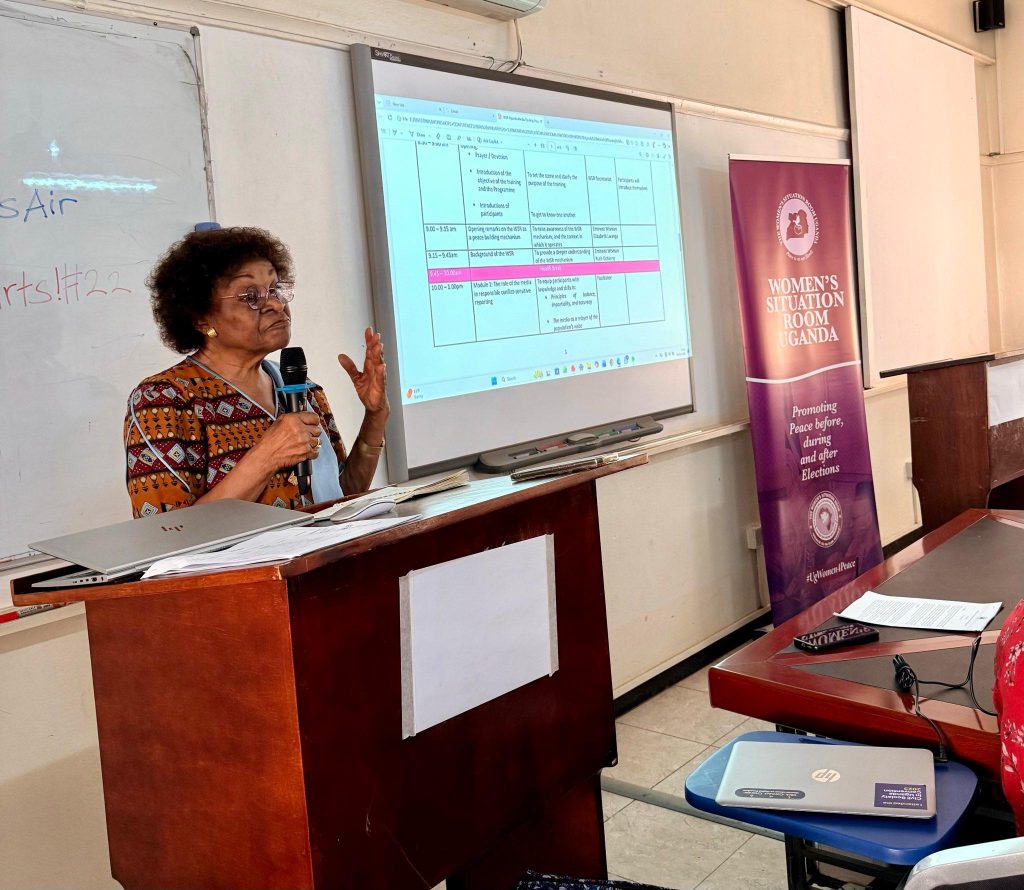

Justice Mayitum also urged other key election stakeholders to uphold peaceful conduct. “Being peaceful is the very heart of life. We have spoken to police, security personnel, political parties, and the Electoral Commission. We want politicians to have a code of conduct and to understand that it’s okay to think differently without fighting or hating one another,” she added.
Dr. William Tayebwa, lead facilitator and senior lecturer in the Department of Journalism and Communication at Makerere University, said, “This training is about conflict-sensitive reporting, peace journalism, and gender-sensitive reporting in the context of the elections. The emphasis was on giving female political candidates a voice while ensuring journalists report responsibly on election-related matters.”

Participants described the training as timely and impactful. Tony Banizengabo of CBS Wakiso District said, “We’ve benefited a lot. We’ve been trained to write stories which bring peace, not conflict. Ahead of the elections, we are very ready to be part of peacemakers.”
Dorcas Kimono of UBC TV Kampala added, “It was so timely and rich. We learned how to report without promoting or fueling violence, giving voice to victims without angering them or encouraging violators. This is very vital, especially as we approach the 2026 elections.”
The training aims to equip media personnel with the knowledge and skills to uphold professional ethics while contributing to a peaceful, inclusive, and gender-sensitive electoral process.
Humanities & Social Sciences
CHUSS Invests Over UGX 100 Million in Interactive Smart Screens, Upgrades Teaching Infrastructure
Published
1 month agoon
January 9, 2026By
Jane Anyango
The College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHUSS) has invested over UGX 100 million in the acquisition and installation of state-of-the-art interactive smart screens, marking a major step in strengthening digital teaching and learning at Makerere University.
Under the investment, 86-inch interactive 4K smart screens have been installed in major lecture rooms across the college’s schools, replacing traditional projectors and whiteboards. The upgrade is intended to modernise instructional delivery, enhance student engagement, and support blended and hybrid learning models.
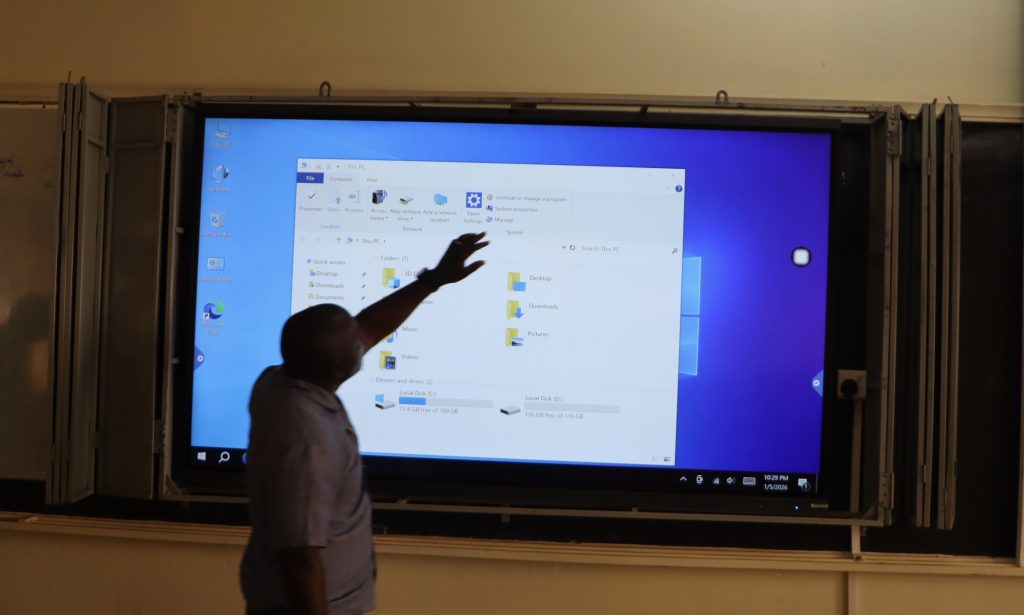
The touch-sensitive smart screens enable lecturers to write, draw, and annotate content directly on the display, while simultaneously integrating multimedia resources such as videos, presentations, and online materials. The screens support wireless screen casting from laptops, tablets, and smartphones, allowing for smooth, cable-free presentations and real-time sharing of students’ work during lectures and group discussions.
Designed to promote interactive and learner-centred pedagogy, the smart screens feature multi-touch capability that allows several users to interact with the board at the same time. This functionality supports collaborative learning, problem-solving exercises, and group presentations, making lessons more engaging and inclusive for students with diverse learning styles.

The boards are equipped with built-in cameras, microphones, and speakers, enabling seamless hybrid teaching through platforms such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet. This allows lecturers to conduct virtual and physical classes simultaneously, record full lectures, and share them with students for later review, revision, or catch-up purposes.
Running on dual Android and Windows operating systems with full internet connectivity, the smart screens provide direct access to online academic resources, digital libraries, and learning management systems. Their AI-powered features further enhance lesson organisation, content clarity, and efficient, paper-free instruction, contributing to a more sustainable learning environment.
To ensure safety and prevent misuse, the smart screens are secured in fabricated metallic safety boxes installed in the lecture rooms.
Beyond digital infrastructure, CHUSS has also undertaken additional physical improvements. The Russian Lecture Room in the School of Languages, Literature and Communication has been furnished with new chairs, tables, and a projector screen, significantly enhancing its teaching environment.
The college has further improved staff working spaces, with the School of Psychology renovating office space and classrooms in Block A, while similar renovations have been carried out in the School of Social Sciences.

The infrastructural upgrades underscore CHUSS’ commitment to improving the quality of teaching, learning, and staff working conditions in line with Makerere University’s digital transformation agenda.
Trending
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoAptitude Exam (Paper 1) Results for the Mature Age Entry Scheme 2026/2027
-

 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoHow Jimmy Osuret Turned Childhood Trauma into Evidence for Safer School Crossings
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoFor Youth by Youth – Call for Second Cohort Applications
-

 General4 days ago
General4 days agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
