Engineering, Art & Tech
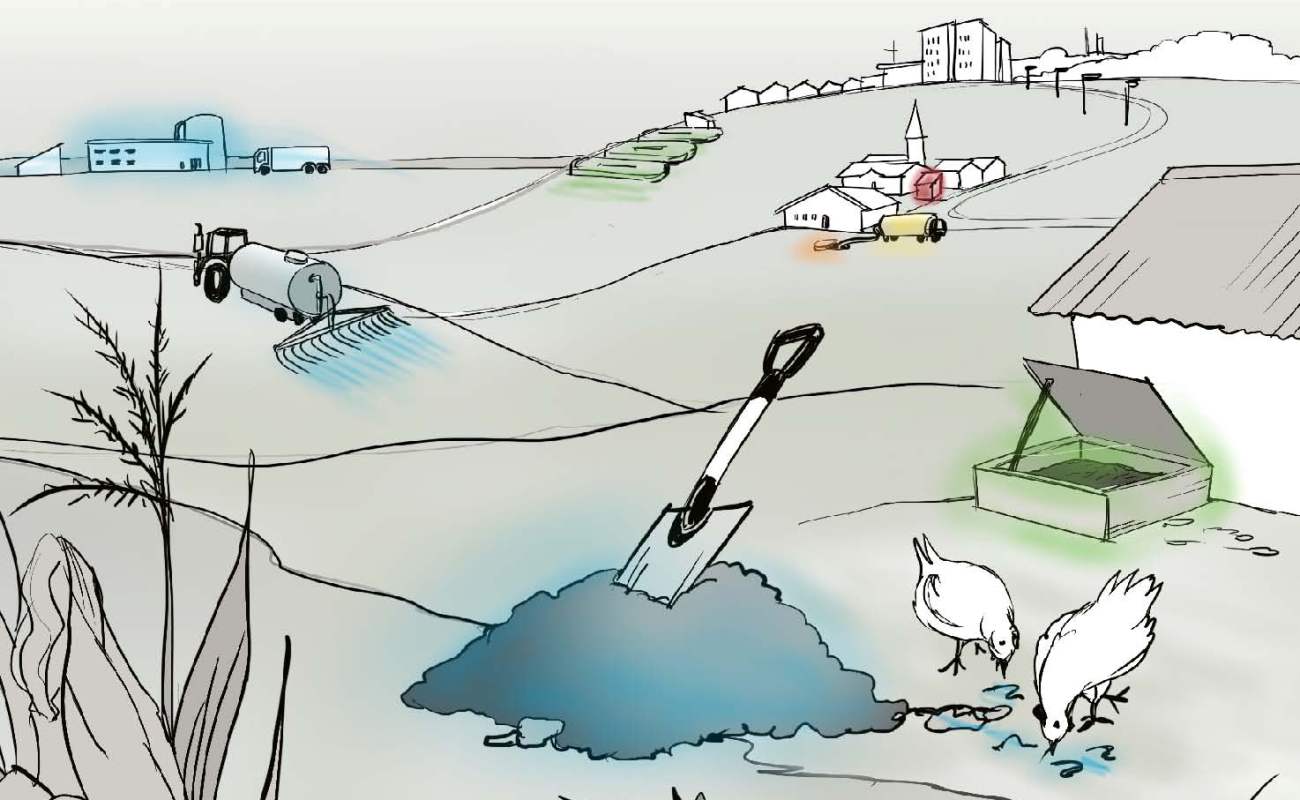
Guide to Sanitation Resource Recovery Products & Technologies
Engineering, Art & Tech
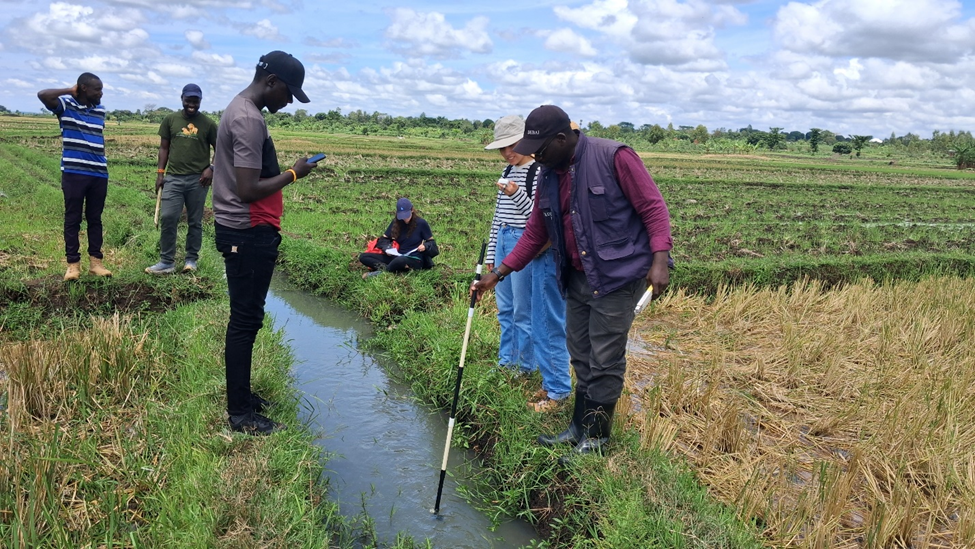
CEDAT students and staff complete intensive DIGITWATER fieldwork in Uganda
Engineering, Art & Tech
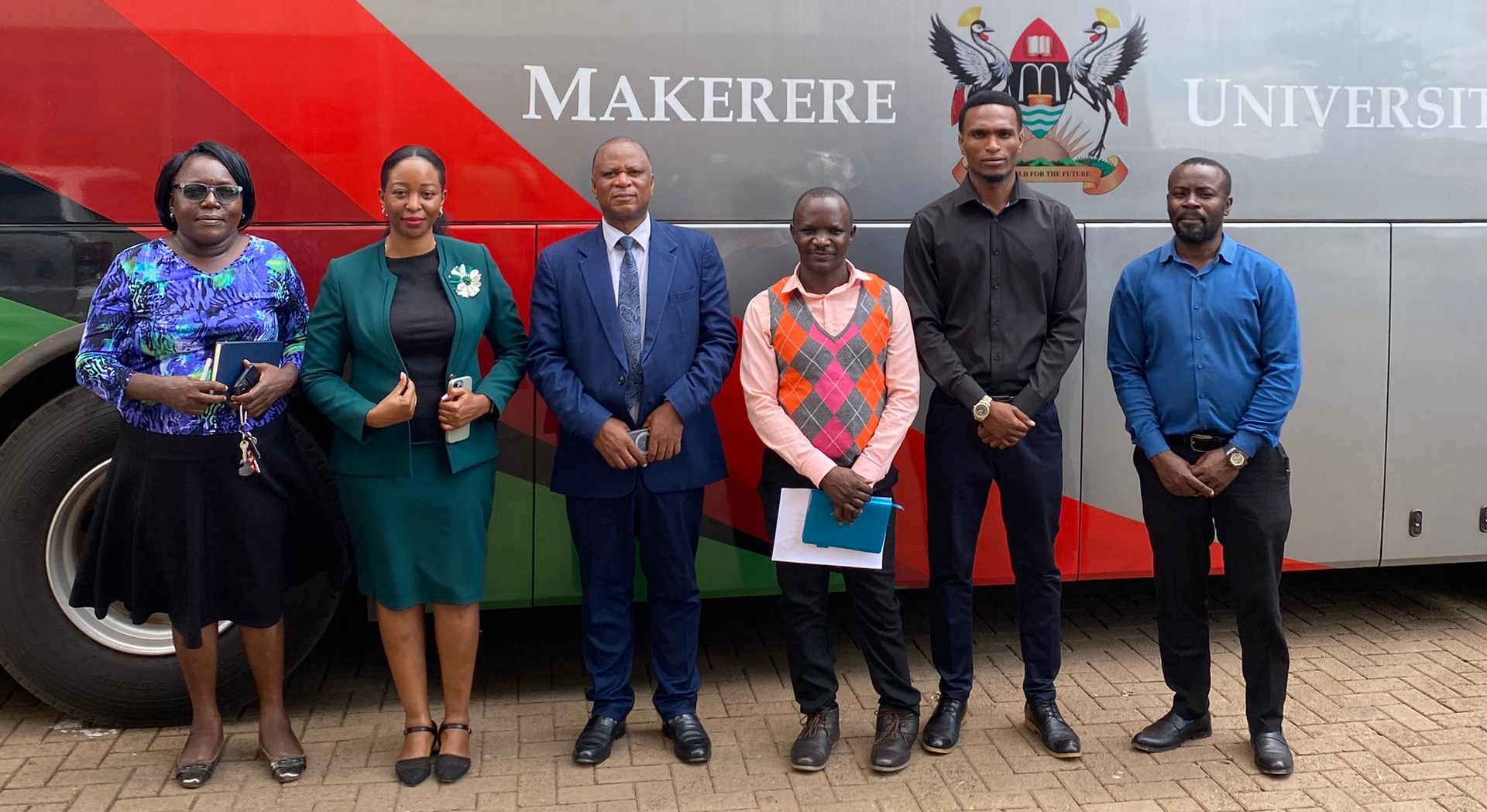
CEDAT Acquires New Executive Bus to Enhance Mobility
Engineering, Art & Tech
Makerere University Announces Call for Papers for 10th National Conference on Communication (NCC 2026)
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMakerere University commemorates 13 transformative years of partnership with Mastercard Foundation
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMakerere University and World Bank Sign Partnership to Strengthen Environmental and Social Sustainability Capacity
















