Business & Management
The Women RISE Project: Building Resilience among Adolescent Girls and Young Women in Artisanal Mining Communities through Transformative Research
Published
12 months agoon

The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly affected vulnerable populations, with adolescent girls and young women in unplanned artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) settlements bearing the brunt of its impact. Already grappling with economic hardships and inadequate healthcare access, these communities faced intensified challenges during and after the crisis, further deepening the existing inequalities.
To address some of these pressing concerns, the Women RISE research Project was launched to explore the economic and health impacts of COVID-19 on adolescent girls and young women in unplanned mining communities, examining their coping mechanisms and resilience during and after the pandemic.
The Women RISE project titled, “Economic and Health Impact and the Resilience of Last Mile Populations in Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining Unplanned Settlements in Sub-Saharan Africa Before, During and After COVID-19,” focused on Ghana and Uganda as case studies.
The project team consists of the following researchers; Betty Kwagala, Makerere University (Principal Investigator), Lydia Kapiriri, McMaster University, Canada (Co-Principal Investigator), Lydia Osei, University of Ghana (Co- Investigator), Stephen Wandera, Makerere University (Co- Investigator), Fred Ngabirano, Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development, Uganda (Co- Investigator/Decision maker), Deborah Mensah, Northern Empowerment Agency- Ghana (Co- Investigator) and Miriam Mutabazi, Uganda Christian University (Co- Investigator)
The composition of the research team is testimony that the two-year collaborative project brought together leading institutions from Canada, Uganda, and Ghana to assess these challenges and develop targeted interventions to enhance future crisis preparedness, with support from the International Development Research Center (IDRC).
To share these critical findings and explore policy implications, an end of project dissemination workshop was convened on 13th March 2025 bringing on board stakeholders comprising distinguished researchers, government representatives, project participants and civil society leaders for an insightful discussion on translating research into action, ensuring that adolescent girls and young women in ASM communities are better equipped to withstand future crises. Representatives from the following Ministries actively participated in the dissemination workshop: Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development, the Ministry of Local Government, the Ministry of Health, and the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Development.
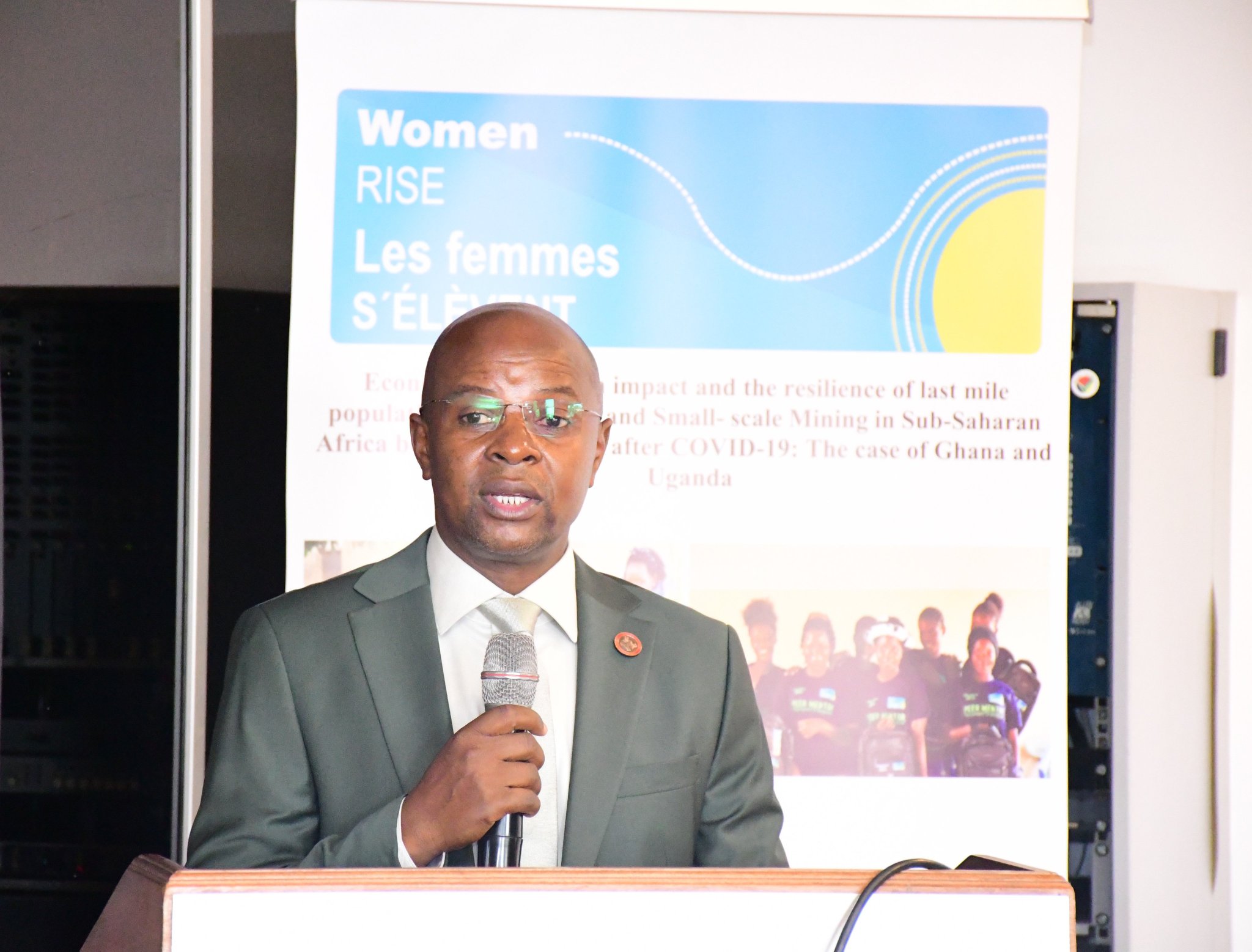

Officiating at the dissemination workshop, the Principal of the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS) at Makerere University, Prof. Edward Bbaale commended the project team for undertaking a study that highlights the pressing economic and health challenges faced by adolescent girls and young women in artisanal and small-scale mining communities in Uganda and Ghana before, during and after the CoVID-19 pandemic. He underscored the critical role of evidence-based research in shaping policies and programs that foster sustainable development.
“This collaborative project not only brings to the forefront the critical economic and health challenges faced by adolescent in the small scale mining sectors in both Uganda and Ghana, but also highlights their remarkable resilience before, during, and after COVID-19 pandemic. The work you have undertaken transcends national boundaries, reinforcing the value of international partnerships in tackling shared challenges. It is my great honor and privilege, to officially open this important workshop,” the Principal said.
Prof. Bbaale explained that research projects such as the Women Rise project, Universities play a vital role in identifying gaps and generating knowledge to guide policy and programming. He emphasized that having government, civil society, and the private sector actively engaged in research efforts significantly enhances the chances of translating findings into meaningful action. He stressed that the results of this research would be practical, policy-relevant, and instrumental in opening up more opportunities for future collaboration
“I am pleased that this project contributes meaningfully to Makerere University‘s research-led agenda, where evidence-based inquiry drives policy formulation, program design, and sustainable development. As a university, we take pride in pioneering collaborations between academia, government, and civil society, ensuring that research findings translate into actionable solutions for our communities,” he stated.
Beyond being a platform for sharing research findings, Prof. Bbaale said that the dissemination workshop serves as a critical space for dialogue among stakeholders and exploring avenues for scaling up research insights into impactful interventions. He noted that such engagements are essential in ensuring that vulnerable populations, such as adolescent girls and young women in small-scale mining communities, receive the support they need to build resilience and improve their livelihoods.
The Women RISE project created awareness of the challenges faced by adolescent girls and young women in mining areas. Some of these included: dropping out of school, early pregnancies, exposure to sexual practices and intimacy at a very early age, contracting of HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases and gender based violence.
Focusing on the health risks/challenges in artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM), Dr. Stephen Wandera, an academic member of staff at Makerere University College of Business and Management Sciences stated that the rudimentary approaches to mining without protective gear expose adolescent girls and young women to mercury and dust, while men involved in the extraction are exposed to dangerous gases and dust.
“Nearly 97% of adolescent girls and young women engage in gold ore processing using mercury without personal protective gear, which exposes them, and sometimes their children to health hazards,” he said.
Dr. Wandera shared that 28% of the women reported mercury-related health issues, including fatigue, stress, headaches, muscle and joint pain, numbness, liver problems, tremors, skin rashes, respiratory illnesses like TB and, in some cases, the birth of children with congenital defects among ASM workers, with Central Uganda being a key area of concern.
“While there are policy guidelines in place, having a policy is one thing, but following and properly implementing those guidelines is another. Unfortunately, most workers operate without personal protective equipment, exposing themselves to serious health risks. The challenge is that, as humans, we often tend to overlook the dangers if the effects are not immediately visible, assuming that everything is fine. However, this lack of protection can have long-term, detrimental health effects,” Dr. Wandera said.
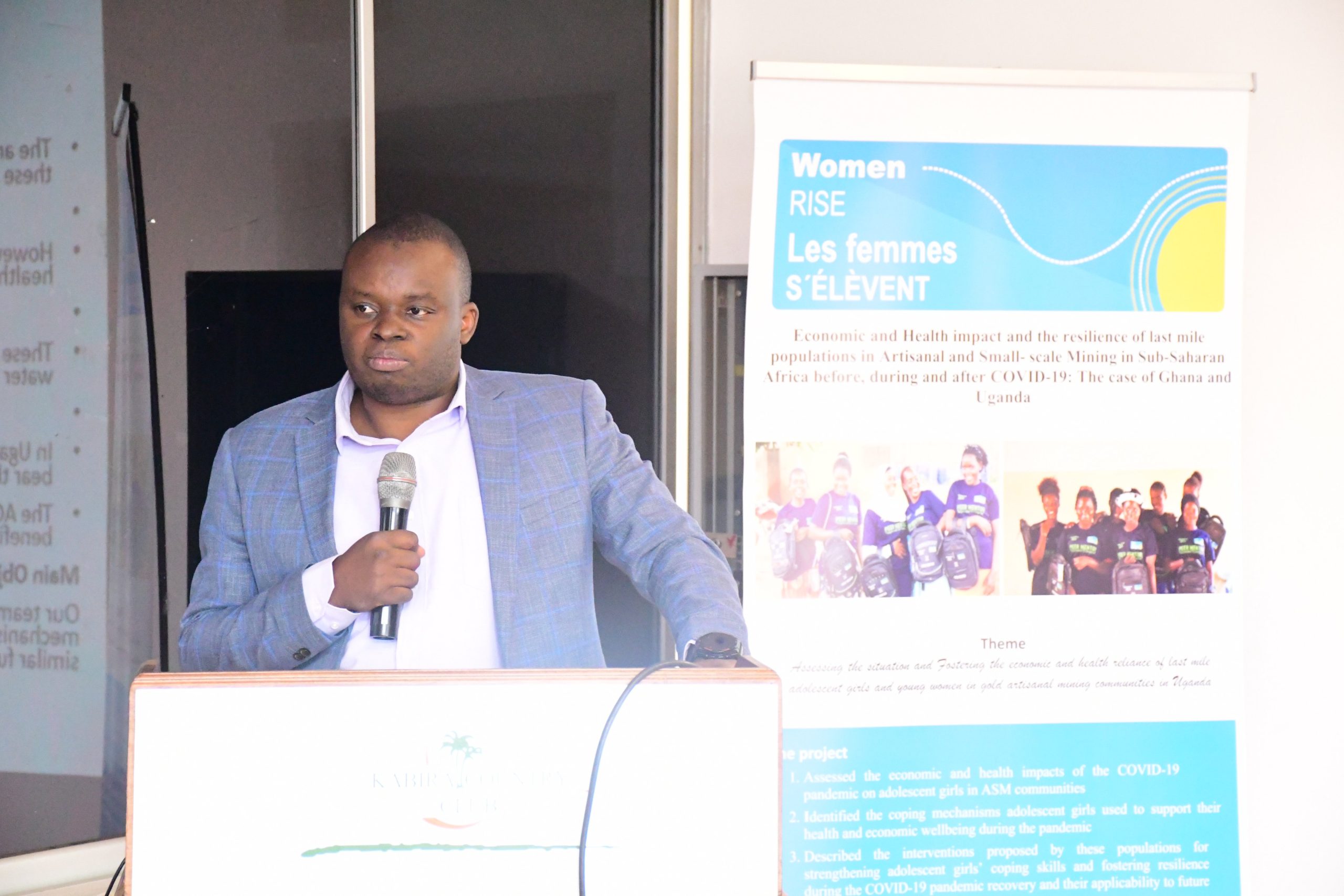

Dr. Wandera pointed out that miners in the Eastern region continue to use mercury, leading to the contamination of water sources. The health risks, he warned, extend beyond miners to entire communities, as contaminated water from mining sites drains into swamps where people cultivate rice and vegetables, posing a major public health threat.
“Mining runoff is contaminating both soils and water bodies. We visited a site where ore was being processed, and the wastewater was flowing directly into a swamp. Some of this water reached areas where people were growing rice and vegetables. As a result, these individuals will eventually consume crops contaminated by the runoff. This situation poses a significant disaster waiting to happen,” Dr. Wandera warned.
Dr. Wandera outlined key recommendations to mitigate risks in artisanal mining, including strengthening coordination with the Ministry of Health and integrating mental health support in affected areas. He stressed the importance of enforcing occupational health and safety regulations while working towards the sector’s formalization. Additionally, he advocated for establishing effective monitoring systems and conducting regular inspections to enhance mining safety. He also recommended equipping miners with resources on safer techniques and alternative technologies, implementing education and training programs on the dangers of mercury, and fostering multi-sectoral collaboration at national and local levels to address environmental, occupational, and public health concerns.
Dr. Miriam Mutabazi, Co- Investigator from Uganda Christian University presented critical findings on the health and well-being of young women in Uganda’s artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) sector. She stressed the urgent need to address sexual and reproductive health challenges in these communities, emphasizing that economic vulnerability often compels young women to engage in high-risk behaviors, exposing them to significant health risks.
She noted that the study revealed a troubling trend where adolescent girls and young women engage in risky sexual practices, often in exchange for work opportunities, cash, or gold. “We realized that transactional sex and the temporal nature of relationships lead to multiple sexual partnerships, and this is very common in the mining settings. We also found that although the reports on sexual violence were low, interaction with the different participants revealed that there was actually a lot of gender-based violence, including sexual violence,” Dr. Mutabazi explained.
The findings indicated that 28% of the young women who had ever had sex had multiple sexual partners in the past year. These behaviors, she said, compounded by widespread substance abuse, have led to alarming rates of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), with 40% of respondents reporting STI transmission.
She highlighted that the most vulnerable young women for instance those with lower wages, limited economic opportunities, and histories of sexual violence—were at the highest risk of negative reproductive health outcomes. Despite the relatively high use of modern contraceptives at 69%, adherence remained a major challenge, with inadequate access to family planning counseling and education.
In response to these findings, Dr. Mutabazi called for urgent action to protect and empower young women in the mining sector. She emphasized the need for a multi-stakeholder approach involving government, NGOs, and local leaders to strengthen health services and education in mining communities. Among the key recommendations was the prioritization of artisanal miners as a high-risk population for STIs and HIV.
Dr. Mutabazi proposed a holistic intervention strategy that includes raising awareness on behavioral change, promoting alternative income sources to reduce transactional sex, preventing sexual violence, and advocating for safer sexual practices and committed relationships. She emphasized the need to expand access to youth-friendly reproductive health services, particularly through mobile clinics that reach young women directly at their workplaces. Additionally, she called for increased investment in family planning services, enhanced health education on the dangers of mercury exposure in mining areas, and the revitalization of a multi-sectoral approach that actively involves mining host communities.
Expounding on the health hazards, Prof. Betty Kwagala, an academic member of staff at Makerere University College of Business and Management Sciences informed the participants that most women in the mining areas carry their children to work, which also exposes the children to health and occupational risks.
Prof. Kwagala who is the Principal Investigator-Women RISE project noted that although the adolescent girls and young women faced health challenges, the most driver into this unfortunate scenario, were the economic factors.
She explained that when the adolescent girls and young women were trained and financially empowered through seed funding, the majority stopped going to the mining areas. “The adolescent girls and young women formed saving groups, became entrepreneurs, some went back to school, while others created alternative sources of income,” she said. In addition, the financially empowered adolescent girls and young women were able to transform their lives and children, uplift their families, friends and communities in general.
Presenting the gender dynamics in Artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM), as well as piloted interventions and their outcomes, Prof. Kwagala revealed that artisanal mining serves as an economic lifeline for many families across Uganda. She highlighted that these communities present significant challenges, particularly for young women and adolescent girls, who face gender-based disparities and reproductive health risks.
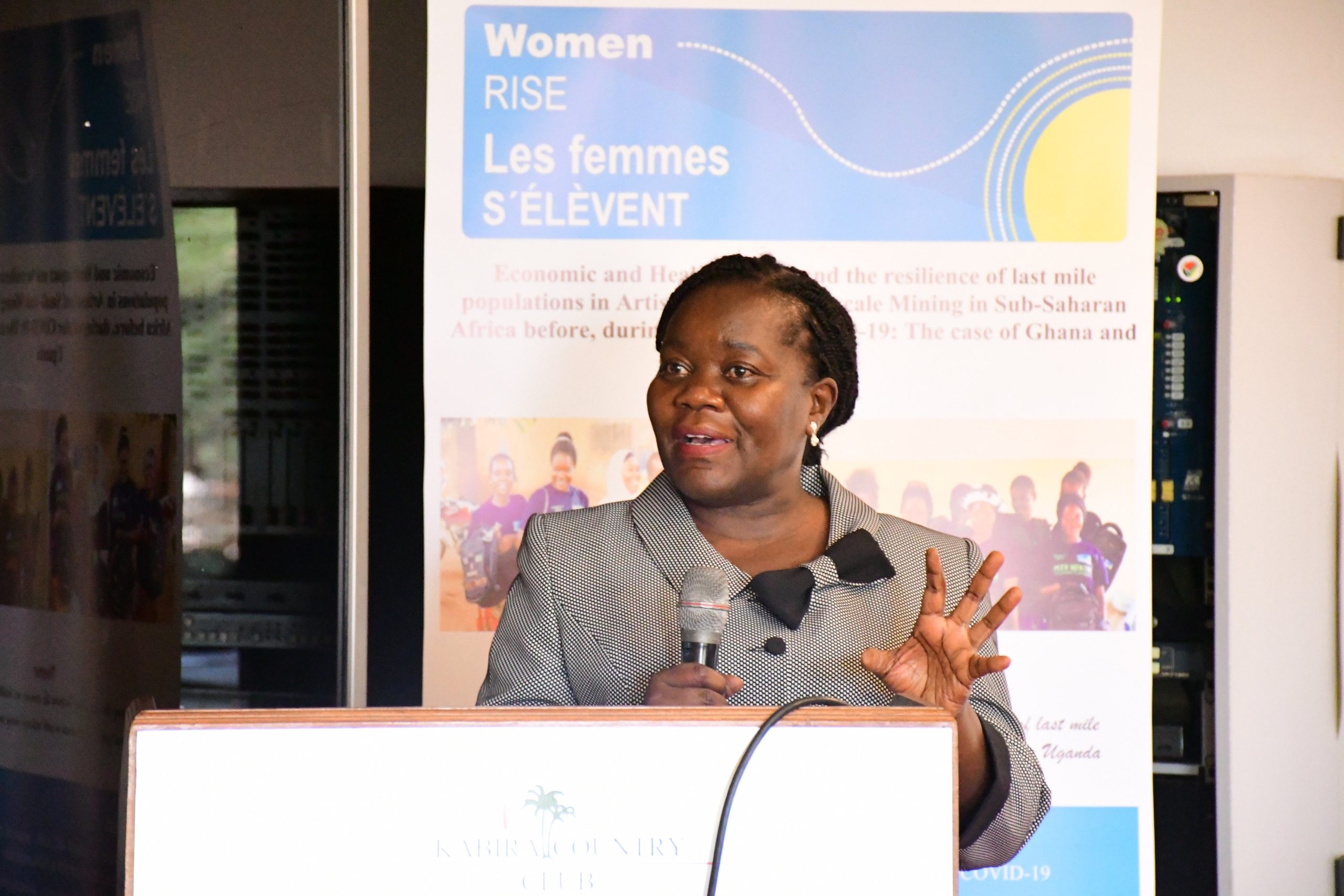
Despite their significant contributions, Prof. Kwagala said that women in artisanal mining remain marginalized. “Women are often relegated to low-paying and labour-intensive roles, such as panning and carrying ores, while men dominate the more lucrative aspects of mining. This limits women’s economic advancement and reinforces a cycle of poverty and dependence,” she said.
The findings revealed that, beyond economic marginalization, women in mining communities face an increased risk of gender-based violence. Their vulnerability is further aggravated by the absence of formal labor protections and legal recourse, highlighting the urgent need for policymakers and community leaders to take proactive measures to address these challenges.
Young women and adolescent girls in mining areas frequently encounter significant reproductive health risks. Limited access to healthcare services and inadequate sexual health education contribute to high rates of early pregnancies, unsafe abortions, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV/AIDS. Additionally, sexual exploitation is prevalent, with many women subjected to coercion and harassment in exchange for economic survival.
As a result, Prof. Kwagala emphasized the urgent need for improved healthcare infrastructure and awareness campaigns to promote safe reproductive health practices. Strengthening access to contraception, maternal healthcare, and counseling services would be a pivotal step in addressing these challenges.
Another critical issue affecting young women in mining communities is the lack of educational opportunities. Prof. Kwagala disclosed that many adolescent girls drop out of school due to financial hardships, early pregnancies, or the need to contribute to household incomes. Without proper education and vocational training, they remain trapped in exploitative labour conditions with little hope for economic mobility.
To break this cycle, Prof. Kwagala called for community-driven initiatives that provide skills training, scholarships, and mentorship programs. Equipping young women with alternative income-generating skills can empower them to seek better economic opportunities beyond the mining sector.
Prof. Kwagala called for urgent action from the government, civil society, and private stakeholders to improve conditions for young women in artisanal mining. She recommended strengthening labor laws to ensure gender equity and protect women from exploitation, establishing mobile clinics and reproductive health education programs, and creating financial literacy and entrepreneurship initiatives to help women diversify their income. Additionally, she emphasized the need for gender sensitization programs to challenge harmful cultural norms and reduce gender-based violence. She also underscored the importance of advocating for increased resource allocation to adolescent and youth programs at all levels, supporting collaborative efforts to regulate excessive alcohol and drug abuse, establishing rehabilitation centers where feasible, and implementing interventions that engage male miners in promoting sexual behavior change and responsible parenthood.
Testimonies from adolescent girls and women empowered by the Women RISE project:
This being the end of the project dissemination, the participants listened to powerful testimonies from some of the adolescent girls and young women whose life was positively transformed through the Women RISE project. The transformation has had multiplier effects extending to uplifting the livelihoods of children, families and communities, where these girls and women conduct their work.

“We were monitored, trained in financial literacy and saving, entrepreneurship and equipped with life skills. We have created alternative sources of income. We have been transformed and empowered to lead better lives,” testified some of the adolescent girls and young women amidst applause from the stakeholders.
One participant emphasized that the support from partners and stakeholders is crucial for sustaining this momentum. It was disclosed that plans are already in place to expand the reach of the project, to integrate community health and education systems, and address new challenges that may arise in these rapidly growing districts.
Courtesy of the Women RISE project, the young people speak with confidence. They are in position to speak publicly and advocate for the needs of their peers. Many are making informed decisions about their lives, choosing to abstain from unprotected sex, using family planning methods, and making more assertive decisions about relationships. One participant mentioned, “I have learned that protecting my life is essential. I don’t go with anyone. I ask myself, ‘Who am I going with? What is his health status?”
Another young person shared, “This program changed my life. I was tested for HIV, and I am now confident in my decision not to engage with any man before knowing his status. Abstinence is my choice.”
What does this say about resilience? These young people have demonstrated remarkable growth and are now capable of standing resiliently in case of future crises. They have learned how to manage businesses, with many having multiple income streams. One notable success story is a young person who, after dropping out of school due to teenage pregnancy, financed her child’s delivery using proceeds from her business and she testified that she went back to school to complete her studies.

Peer mentorship has contributed to both personal and community resilience. Through these programs, young people have built self-esteem and empathy while advocating for others. One peer mentor said, “I have made many new friends. Even older people trust me, and I am able to help them, even escorting them to health facilities when necessary.”
Initiatives being undertaken by the Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development:
Addressing the stakeholders, Mr. Fred Ngabirano, Commissioner for Youth and Children Affairs at the Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development highlighted the power of grassroots transformation in fostering economic and social development.
He emphasized the commitment of the Government of Uganda to addressing social challenges and creating sustainable opportunities for young people and women in vulnerable sectors. He said that among the various initiatives under the Ministry’s mandate is the Juakali Center, which plays a crucial role in identifying and supporting women and young people in their economic journeys. “Once we organize groups of young people, we collaborate with Juakali to provide them with opportunities,” he explained.
As the project beneficiaries shared their transformational experiences, Mr. Ngabirano highlighted key lessons drawn from their testimonies. He emphasized that transformation is not solely reliant on financial aid, but rather on effective strategic planning, capacity development and resource management.
“Some individuals have received venture capital funds such as Youth Livelihood Programme, but have not made significant progress. This raises an important question—what is the key to success? The answer lies in effective financial planning and passion-driven work; it is about how well you plan and utilize what you have,” he remarked.
The Commissioner emphasized the importance of passion in professional and entrepreneurial success, saying, “If someone lacks passion for what they do, no amount of facilitation will drive success.” He thus lauded the young entrepreneurs who have followed their passion—whether in hairdressing, the grocery business, or other trades—and have, as a result, seen remarkable progress in their endeavors.
Mr. Ngabirano called for prioritizing human resource development as a means to transform people. He elaborated that investing in developing human potential should be a key focus. As the government continues to collaborate with academic institutions and grassroots organizations, Mr. Ngabirano stated that the future of youth and women empowerment remains promising.
Strategies being undertaken by the Ministry of Health:
Dr. Allan Kasozi from the Division of Adolescent Health at the Ministry of Health highlighted the pressing health challenges faced by young people, particularly those engaged in artisanal mining. He stressed the urgent need for targeted interventions to protect vulnerable youth working in hazardous conditions. Dr. Kasozi revealed that the Ministry of Health is finalizing the Adolescent Health Hosted Implementation Plan, a comprehensive strategic document that will guide adolescent health policies and interventions for the next five years. He underscored the importance of targeted service delivery, ensuring that healthcare efforts effectively reach both remote areas and the most at-risk populations.
Dr. Kasozi expressed his deep appreciation for the resilience and hard work of all stakeholders involved in the Women RISE project research, acknowledging the critical insights it has provided. He emphasized that while policymakers may not always have the opportunity to closely observe the daily realities of young miners, this research has shed light on crucial issues that demand immediate attention.
“The findings from this study, alongside the voices of young people, have been incredibly enlightening. These insights will play a pivotal role in shaping our strategies at the Ministry of Health to effectively tackle the challenges faced by adolescent populations, particularly those in vulnerable sectors like artisanal mining,” he stated.
He credited the project research team for their invaluable contributions, noting that their work provides vital evidence to inform better health planning for Uganda’s youth. “This research presents an opportunity for us to lead with informed solutions. It reinforces the need for a multi-faceted approach to adolescent health, ensuring that young people, regardless of their circumstances, receive the care and support they need.”
Contribution from the Ministry of Local Government:
Mr. Rashid Biruma from the Ministry of Local Government who represented the Commissioner for Local Council Development, Mr. Swizin Mugyema stated the critical role of research in addressing national challenges. He acknowledged the existence of numerous problems facing the country and highlighted that the identification of specific issues through research is crucial in finding solutions. He noted that the workshop had provided valuable insights into the scale of the challenges, which extend beyond the specific areas being discussed.
One major issue raised during the workshop was the problem of child labour in mines. Mr. Biruma referred to this as a significant concern, particularly due to its association with crimes and children in conflict with the law. He praised the Ministry of Labour, Gender, and Social Development for its efforts in rehabilitating children involved in such activities, particularly through diversion programs aimed at reintegrating them into society.
“Child labour is associated to various related issues, including crime and children in conflict with the law. This is a critical issue that requires urgent attention, and we must explore ways to address and redress it. We are grateful for the support from the Ministry, which is assisting us, particularly through diversion programs aimed at rehabilitating children involved in criminal activities,” he said.
In addition to tackling child labour, Mr. Biruma highlighted the importance of leadership, particularly at the local government level. He reiterated that the Ministry of Local Government would continue ensuring compliance with legal frameworks and enforcement of rights.
Education, both formal and civic, was another point of emphasis. He encouraged the use of established community structures to promote civic education, stressing that awareness and community engagement are crucial to the success of these initiatives. He also urged the dissemination of information to local government officials to ensure compliance with community engagement strategies.
Presentation of findings on sexual behaviours of young male artisanal miners in Kassanda District:
In a study conducted by Ms. Patience Natwijuka, a Master of Science student funded by the project and her team at Makerere University, critical insights have been revealed regarding the sexual behaviors and factors influencing consistent condom use among adolescent and young male artisanal miners in Kassanda District, Central Uganda. The research, which focused on mining sites in Kagaba and Kayonza, sheds light on the health risks faced by this vulnerable population and highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions.
The study, which involved a survey of 304 male participants aged 15 to 24 years, sought to assess sexual activity, multiple sexual partnerships, transactional sex, and socioeconomic determinants affecting condom use. The findings paint a stark picture of the realities young miners face, emphasizing the intersection of economic vulnerability, risky behaviors, and health outcomes.
One of the most alarming findings was that the median age of first sexual intercourse among these young miners was 16 years. On average, they reported having 16 lifetime sexual partners, with around 8 sexual partners in the last 12 months alone. Such patterns of sexual activity significantly heighten the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and HIV, raising concerns about the well-being of these young workers.
The study revealed that 24% of respondents had contracted an STI in the past year, while 55% engaged in multiple sexual partnerships. Additionally, 11% reported involvement in transactional sex, where economic hardships often push them into high-risk relationships. Compounding the risks, 56% of the adolescents reported alcohol use, a factor known to impair judgment and contribute to risky sexual behaviors.
A deeper analysis of the factors affecting consistent condom use revealed that marital status and parental survival played significant roles. Married or cohabiting young miners were less likely to use condoms consistently compared to their single counterparts. The findings highlighted the need for strategies to ensure that all young people irrespective of survival status of parents, receive guidance on safer sex.
Given these findings, Ms. Natwijuka and her research team strongly recommend the implementation of comprehensive health education programs in mining areas. These programs should focus on raising awareness about HIV, STIs, and the importance of condom use among young artisanal miners. Her study serves as a wake-up call to all stakeholders, urging collaborative efforts to safeguard the well-being of young artisanal miners and mitigate the rising health crisis in Uganda’s mining communities.
Way Forward:
Prof. Kwagala shared that education remains a key pillar in the discussions, with a strong focus on empowering adolescent girls and boys in mining districts. Notably, districts such as Kassanda have made significant strides by offering vocational training opportunities, equipping young people with practical skills for a sustainable future. These initiatives have enabled many, particularly those from disadvantaged backgrounds, to return to school or enroll in vocational institutions, providing them with viable alternatives beyond the mining industry and fostering long-term economic empowerment.
While the challenges remain, the commitment from district leaders to continue building on the project’s successes is clear. One participant emphasized that the support from partners and stakeholders is crucial for sustaining this momentum. Plans are already in place to expand the reach of the project, to further integrate community health and education systems, and address new challenges that may arise in these rapidly growing districts.
In Kassanda, for example, district leaders are focused on ensuring that more adolescent girls and boys have access to the resources they need to succeed. With the involvement of more partners and stakeholders, including local schools, health facilities, and NGOs, there is confidence that the district will continue to make progress in addressing the needs of its young people.
Prof. Kwagala emphasized that an integrated, community-driven approach is key to addressing mining community challenges. She noted that peer mentorship and education are empowering youth to advocate for safer practices and healthier lifestyles. While challenges remain, she highlighted the collective effort of local leaders, project partners, and youth as a model for lasting change. With continued commitment, the project aims to create a lasting impact, fostering healthier and more resilient generations.
She noted that outreach efforts to schools are underway to address the alarming dropout rates among girls, many of whom face early pregnancies, mining work, or repeated pregnancies. Prof. Kwagala highlighted that some girls become pregnant as early as 12 years old, stressing the urgency of interventions to create better opportunities for them.
Prof. Kwagala explained that several initiatives are in place to keep girls in school. For instance, peer mentors in Kassanda have reached out to 720 pupils. These provide age-appropriate education on menstrual hygiene, abstinence, and other essential health topics. The impact on schools has been ignificant, with peer educators playing a key role in engaging parents as well and in guiding children to health facilities for necessary services.
Prof. Kwagala highlighted the vital role of private-public partnerships in the program’s success, where partnership with an NGO and public health facility providers in partnership with trained peer mentors, through outreach or mobile clinics facilitated delivery of services like counseling, PEP, contraceptives, STI testing, HIV testing, and ARVs. This has led to increased service utilization and referrals among young people, fostering trust in these resources. She also emphasized the importance of mobile clinics in reaching remote communities with limited access to healthcare. These clinics have successfully built trust and confidence, offering a more accessible and reliable healthcare option.
You may like
-


Mastercard Foundation Scholars Urged to Embrace Mentorship for Career Growth
-


Makerere University Students Triumph in National Conservation Competition
-


Mak Cooperative Society holds AGM: Growth, Transparency and Member Welfare Take Centre Stage
-


From Campus to Community: Universities Lead Teso in Fight Against Greenhouse Gas Emissions
-


Makerere University Launches Short Course to Strengthen Climate Change Reporting
-


Makerere University and World Bank Sign Partnership to Strengthen Environmental and Social Sustainability Capacity
Business & Management
Public Lecture on Research Collaboration across borders presents enormous opportunities to researchers, faculty and students
Published
1 week agoon
March 3, 2026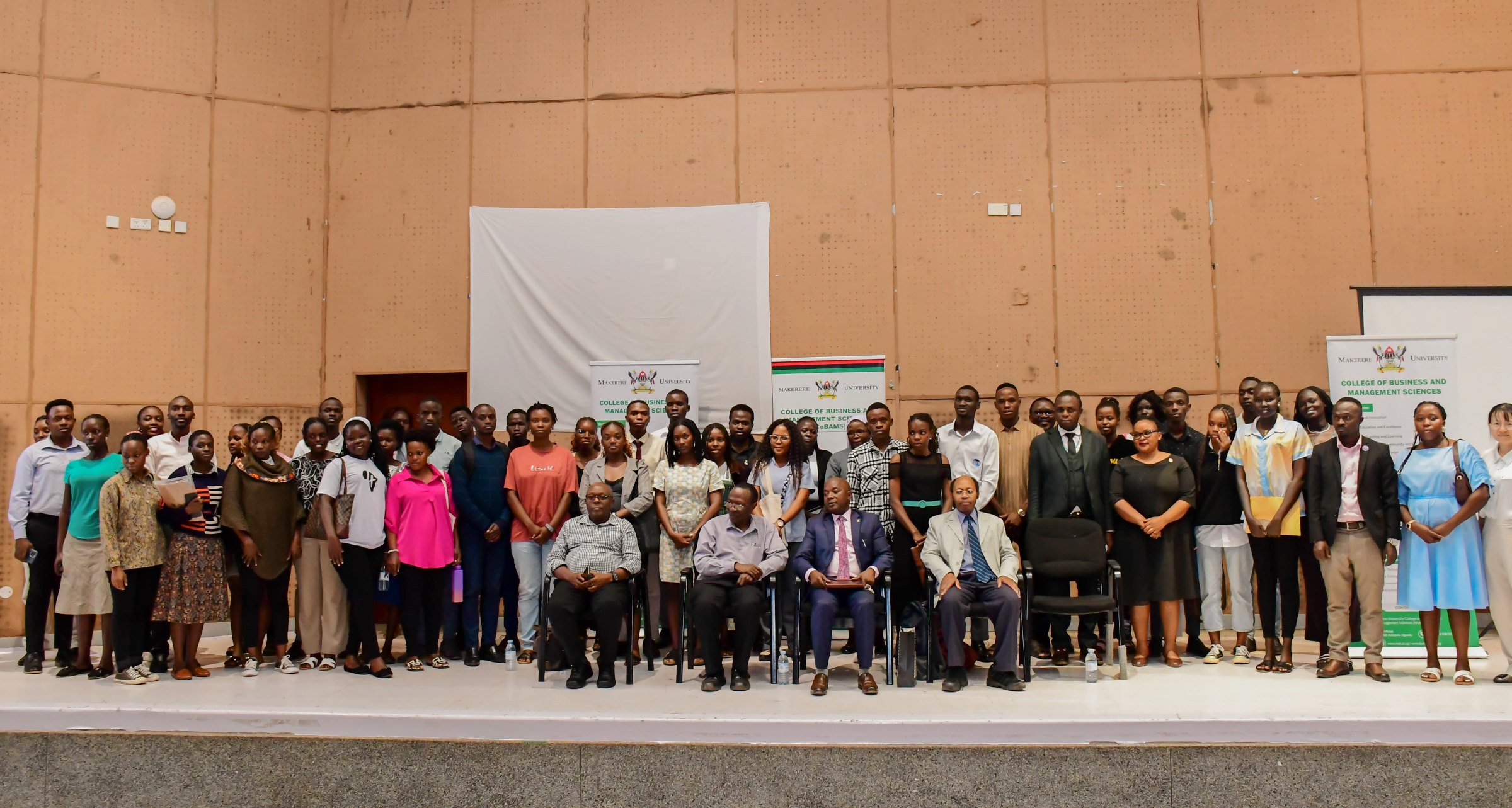

Delivering the public lecture, titled: Research Collaboration across borders, Prof. Ken Kamoche from Nottingham University, urged researchers at Makerere University, to undertake research that will strengthen and empower Africa, including fields that are ignored.
“My research has focused on those pertinent issues and fields that are always ignored. I call upon you to re-consider undertaking research in the fields of knowledge management, innovations, indigenous knowledge, identity, artificial intelligence (AI) and Africa at large,” said Prof. Kamoche.
Acknowledging that he had undertaken tremendous research and publication in human resource management and organizational studies, Prof. Kamoche testified that he took a paradigm shift to focus on the values that underpin the organizational behaviour.
Held at Makerere University Yusuf Lule Central Teaching Facility Auditorium on 3rd March 2026, the public lecture attracted faculty from Makerere University, Kyambogo University, Uganda Christian University, administrators, researchers, and students. Before heading to the public lecture, Prof. Kamoche held a discipline-specific meeting with academic staff at the School of Business under the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS) at Makerere University.
The Africa Research Group: Fostering Global Scholarly Engagement and Capacity Building
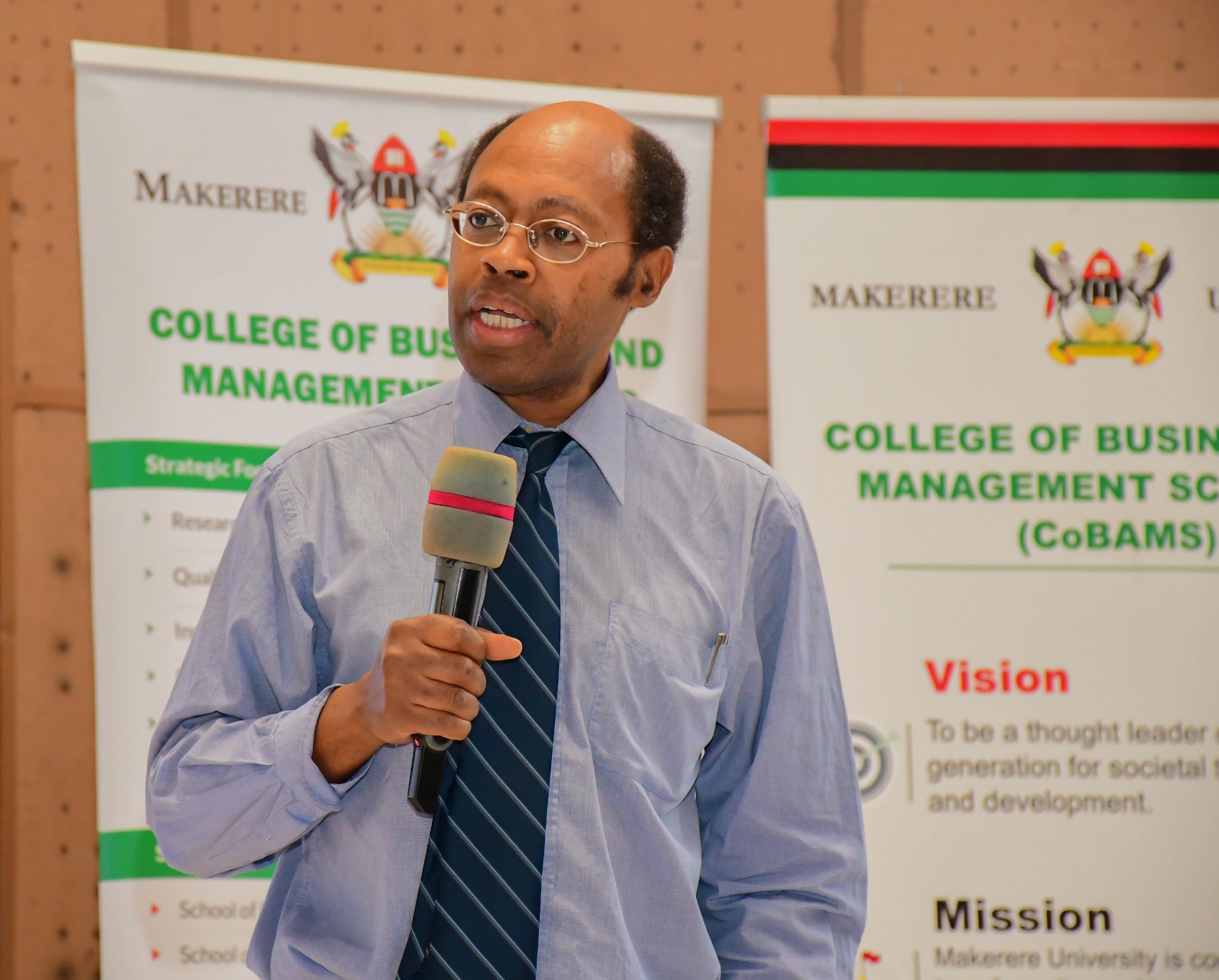

Prof. Kamoche highlighted the establishment of the Africa Research Group to address the gap in engagement between scholars in Africa and their counterparts in Europe, Asia, and North America.
Established in 2012, the Africa Research Group at Nottingham University Business School provides a platform to spur knowledge transfer across disciplines and continents.
“I am here to inspire you to do research. If you are looking for a platform, I invite you to utilize the Africa Research Group. We have been able to give researchers from Africa a voice. We welcome research students at all levels,” Prof. Kamoche said.
He pointed out that the Africa Research Group provides mentorship to postgraduate and early-career researchers, supports doctoral supervision, joint publications, and funding applications. Prof. Kamoche encouraged students and faculty members to participate in future activities and pursue collaborative research opportunities.
What inspires Prof. Kamoche?
Responding to a question from the students who admired his commitment to research, publication, authorship, Prof. Kamoche said: “The desire to make a difference and share knowledge with others, and make an impact.”
Research collaboration
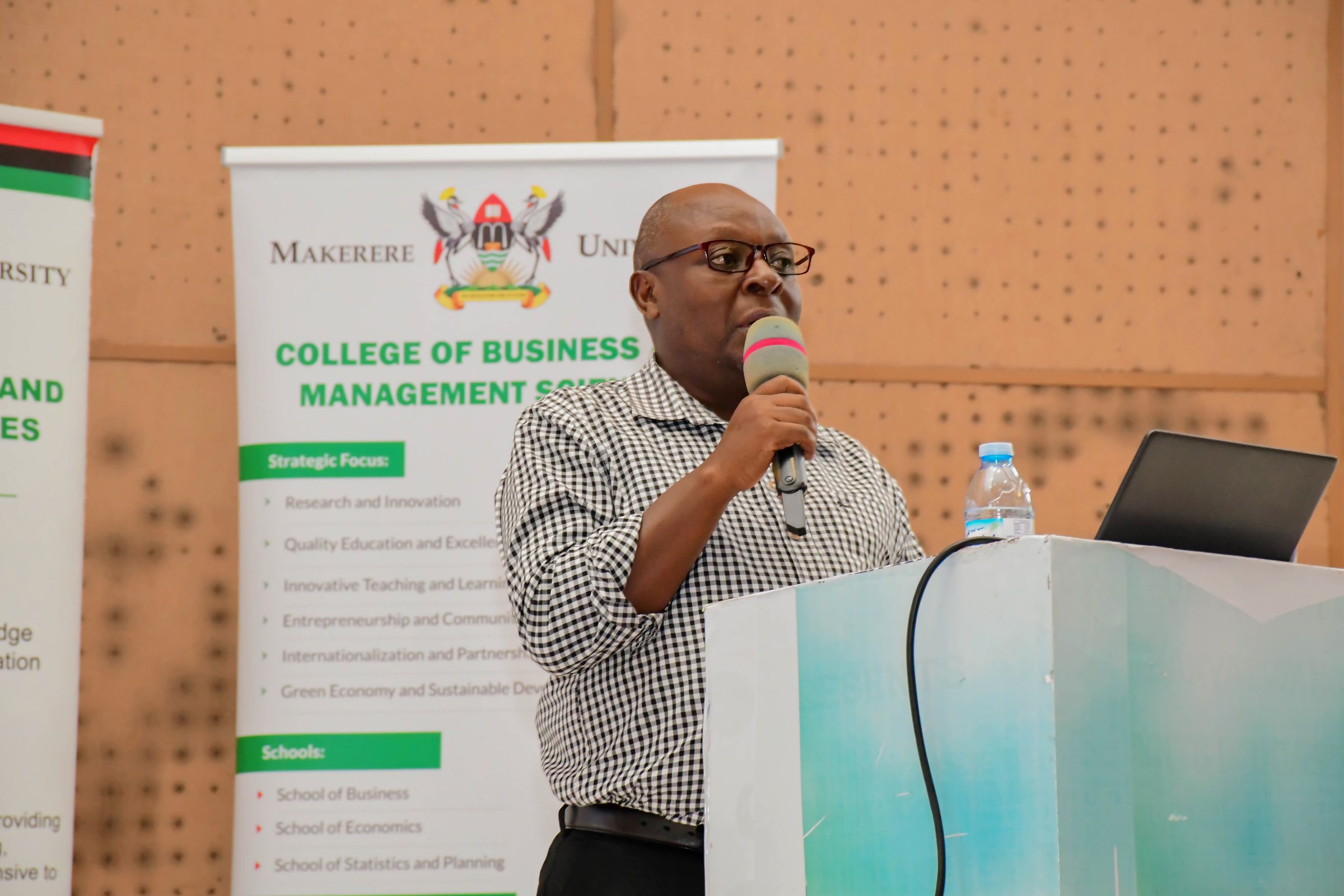

During the public lecture, Dr. Christopher Muganga, Dr. Seperia Wanyama, and Dr. Anthony Tibaingana from the School of Business, and Dr. John Mushomi from the School of Statistics and Planning, emphasized the importance of research and collaboration in the transformation of countries and societies in general. The members of faculty stressed the importance of knowledge sharing and exchange of ideas, authorship and publication, mentorship, joint research undertakings and networking.

Global academic collaboration
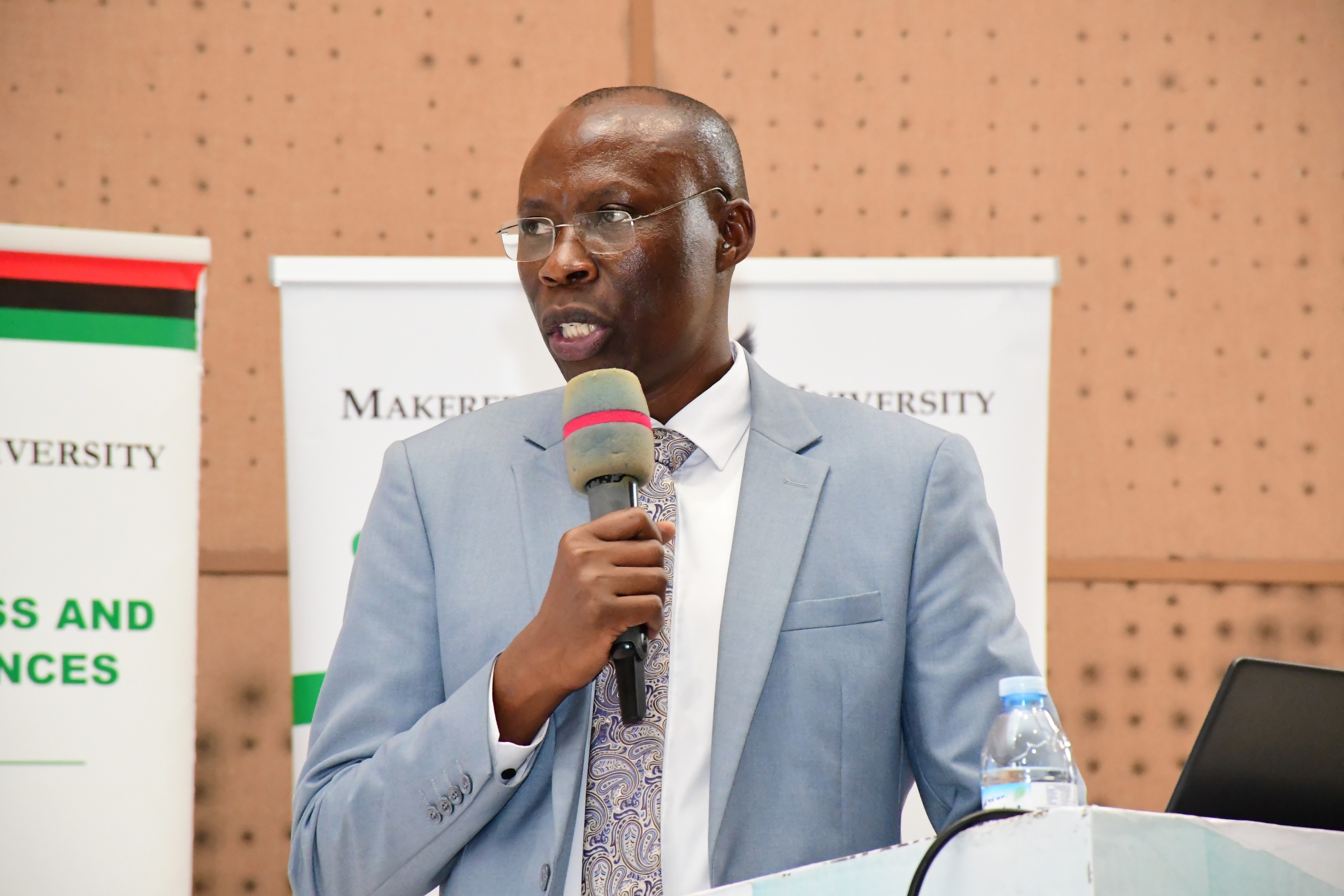

Dr. Seperia Wanyama highlighted the significance of the public lecture in creating opportunities for collaboration, knowledge exchange, and the collective advancement of academic and societal understanding.
“The event serves as a platform for fostering diversity in academia, bringing together researchers, students, and administrators to engage in shared learning,” he said.
He applauded Prof. Ken Kamoche for his distinguished contributions global academic collaboration and research. He credited Prof. Kamoche for his willingness to share valuable insights on research collaboration across borders. He urged participants to remain active and engaged throughout the session.
Talent Management and Cross-Continental Collaboration
Prof. Kamoche commended Makerere University for hosting him, reflecting on the golden opportunity to engage with students, faculty, and researchers. He shared insights from his extensive academic journey, research contributions, and initiatives to strengthen collaboration across Africa, Asia, and the West.
Reflecting on talent management and organizational leadership, Prof. Kamoche noted that he has maintained a strong focus on leveraging his international experiences to foster cross-continental academic collaborations and address challenges relevant to both African and global contexts.
Focusing on talent management, Prof. Kamoche shared insights from his extensive research, explaining how organizations often take an “exclusive” approach, concentrating resources on a small group of high-performing individuals seen as the main drivers of value. He also highlighted a different perspective: the “inclusive” approach, which recognizes that every employee has unique skills that can contribute to the organization’s success.
Using recent research in Kenya’s banking sector, published in the South African Journal of Human Resource Management, Prof. Kamoche illustrated how talent management connects closely with innovation, employee engagement, and confidence. His findings indicated that while high performers are essential, sustainable success comes from balancing focus on star performers with developing the wider workforce.
Prof. Kamoche reflected on earlier studies conducted in Hong Kong, which examined the experiences of employees identified as “high potential.” He noted that being labeled talented can be a double-edged sword, creating pressure, high expectations, and sometimes causing employees to rethink their career priorities over time.
Comparative Insights on Asian Management and Strategic African Partnerships
Prof. Kamoche shared insights from his comparative research on Asian management practices, tracing his academic interest in Asia back to his graduate studies at Oxford. There, he examined Japanese management systems at a time when Japan’s economic model was admired worldwide. Through interviews with senior human resource executives in major Japanese corporations, he sought to understand the foundations of their organizational success.
Prof. Kamoche observed that while African countries are familiar with Western business systems, their understanding of Asian management philosophies remains limited. His research highlighted key differences in operational practices, particularly in areas such as time management and efficiency.
“Some Chinese infrastructure projects run continuously, reflecting a highly results-driven approach,” he noted. He acknowledged challenges raised by local employees regarding cultural differences, labor practices, and the need for more equitable engagement.
Prof. Kamoche emphasized that Chinese investment in Africa is far from uniform, encompassing state-owned enterprises, private firms, and long-term individual entrepreneurs. “African countries must strategically leverage these partnerships to maximize both economic and social benefits while protecting local interests,” he argued.
Dr. Anthony Tibaingana commends Prof. Kamoche’s Scholarly Impact
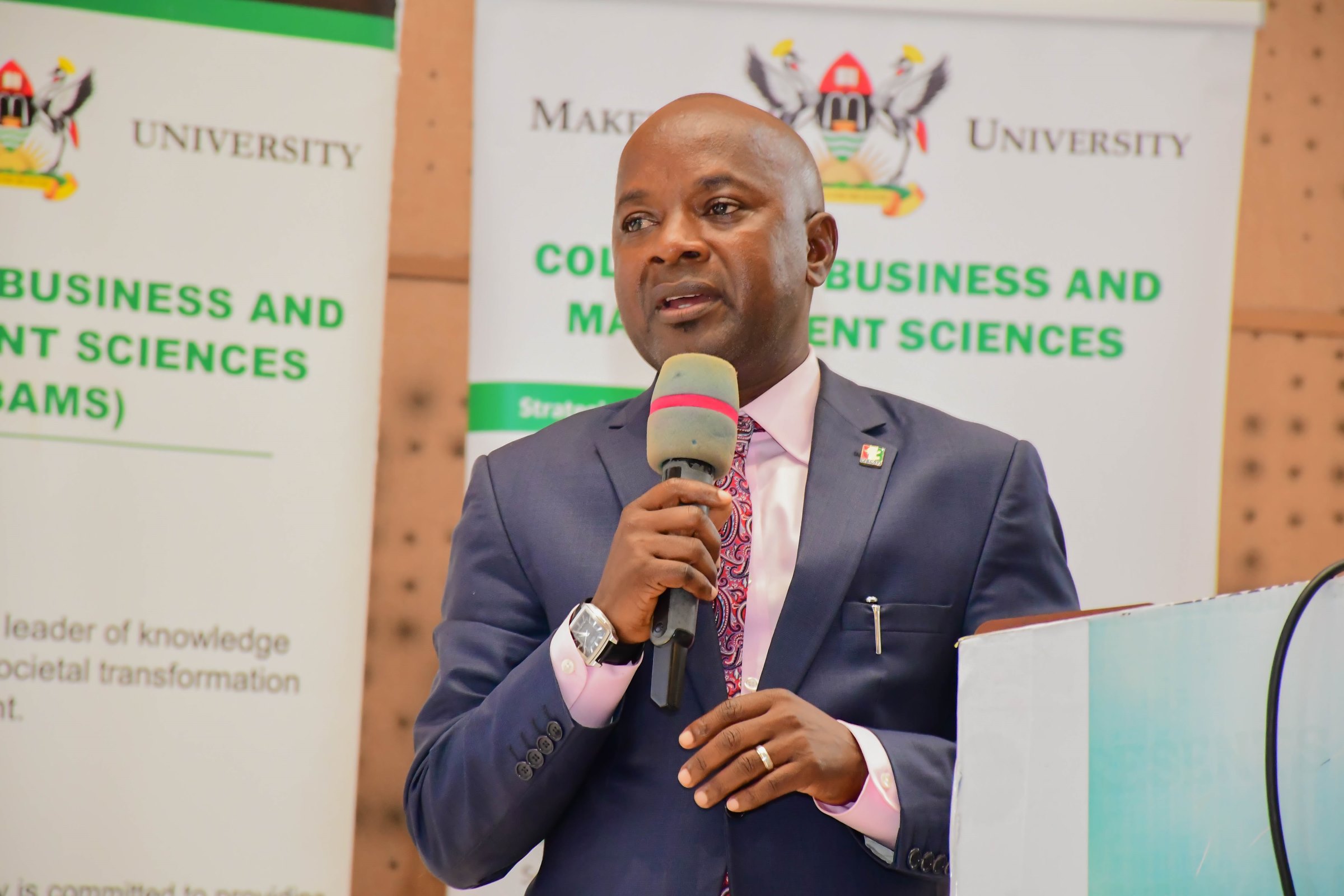

The Acting Dean of the School of Business, Dr. Anthony Tibaingana, lauded Prof. Kamoche for delivering an insightful lecture at Makerere University, describing the presentation as an exceptional exposition of knowledge and scholarship.
Dr. Tibaingana highlighted the significance of Prof. Kamoche’s return to Africa, describing it as a meaningful reconnection with his roots and a contribution to the continent’s intellectual growth.
The Acting Dean commended the depth of the presentation, particularly its insights into human resource management, leadership, and talent development. He emphasized that Africa, with its youthful population, presents both opportunity and responsibility for scholars to generate research-based solutions to the continent’s challenges.
He underscored the need for academia to address pressing issues such as leadership gaps, institutional weaknesses, and talent retention within universities and organizations.
Dr. Tibaingana encouraged faculty and students to continue engaging through research networks and ongoing conversations facilitated by the Africa Research Group at Nottingham University Business School.

He reaffirmed the university’s commitment to teaching, research, and community outreach, noting that such engagements contribute to long-term academic partnerships and future institutional growth.
Moderated by Dr. Christopher Muganga from the School of Business, the public lecture concluded with the presentation of Makerere University Souvenirs to Prof. Kamoche and networking engagements with students.

Monica Meeme contributed to this story as a Guest Writer
Business & Management
Thirty Public Officers Certified in Integrated Regulatory Cost-Benefit Analysis
Published
1 week agoon
March 3, 2026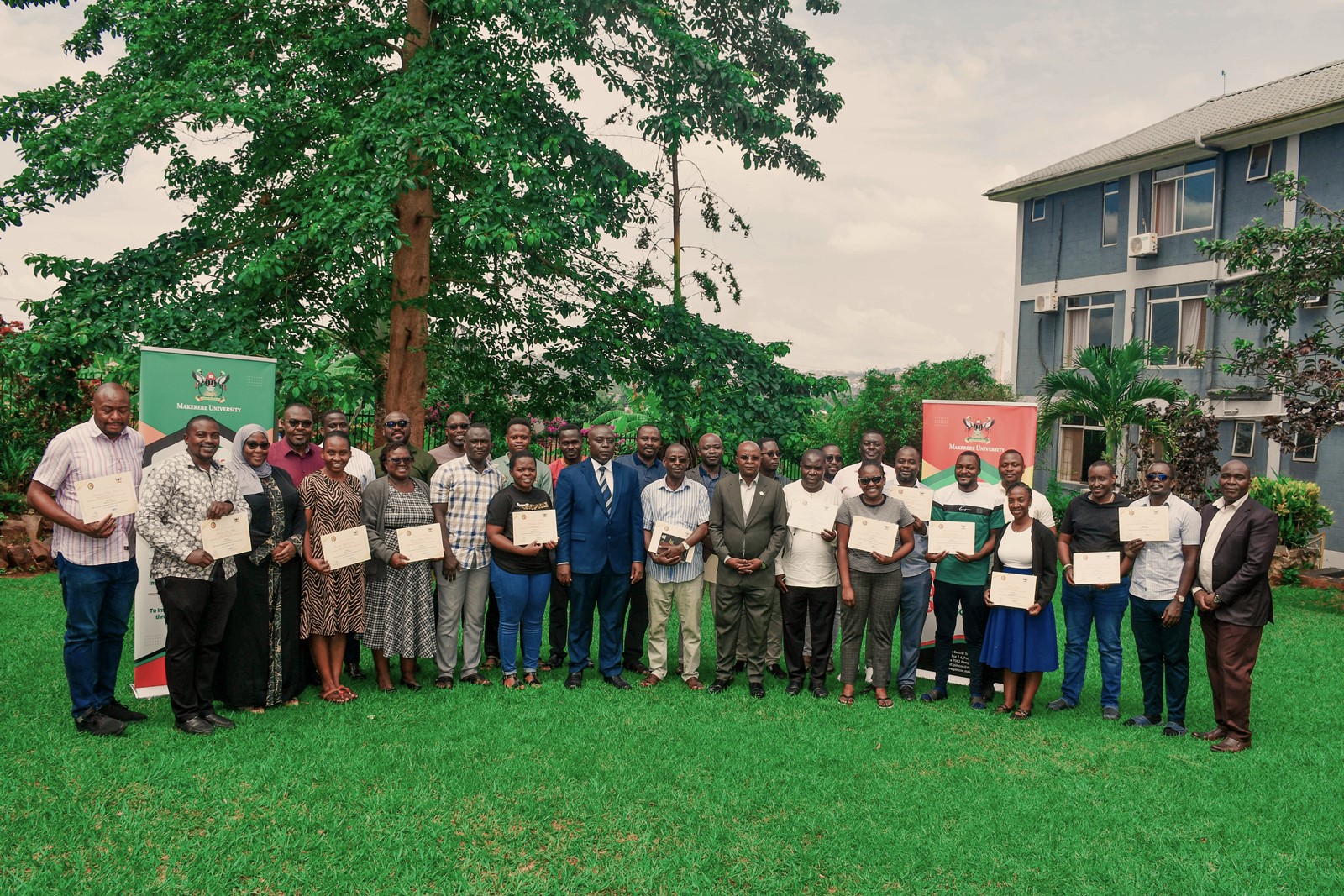
Thirty public officers from various Ministries, Departments and Agencies (MDAs) have successfully completed a two-week intensive training in Integrated Regulatory Cost-Benefit Analysis (IRCBA), culminating in the award of certificates at a closing ceremony held on 27th February 2026 at the Pearl on the Nile Hotel in Jinja.
The training was jointly organized by the Public Investment Management Centre of Excellence at Makerere University and the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development (MoFPED), in collaboration with the Infrastructure and Social Services Department (ISSD) and the National Planning Authority (NPA). It focused on operationalizing the Revised Guidelines for the Issuance of Certificates of Financial Implication (CFIs), which came into effect on 1st July 2025.
A Strategic Reform for Fiscal Credibility
In closing remarks delivered on by Commissioner Paul Patrick Mwanja behalf of the Permanent Secretary/Secretary to the Treasury, participants were commended for undertaking the training during a demanding budget cycle, when many MDAs are simultaneously preparing the FY 2026/27 Budget, executing the FY 2025/26 Budget, and implementing the National Development Plan IV and the Tenfold Growth Strategy.

The PS/ST emphasized that the revised Guidelines mark a significant shift toward a more transparent, data-driven, consultative, and analytically rigorous approach to evaluating policy and legislative proposals. Participants were equipped to assess fiscal implications, evaluate economic and socio-economic impacts, analyze distributional effects, and address uncertainty using structured analytical tools.
They were reminded that training alone is not sufficient, the real test lies in consistent application. As members of the third cohort, they were challenged to serve as reform ambassadors, championing evidence-based policymaking and strengthening analytical standards across government.
Bridging Academia and Public Service
Delivering the official closing remarks, the Director of the PIM Centre of Excellence, Prof. Edward Bbaale, commended participants for their active engagement and unwavering commitment throughout the training.
He described the programme as both timely and strategic, designed to equip officers with practical tools to prepare robust Statements of Financial Implication (SFIs) that support credible issuance of CFIs. He noted that strong financial analysis enhances fiscal discipline, policy coherence, and the overall quality of legislation and public policy in Uganda.
Prof. Bbaale underscored the longstanding partnership between Makerere University and the Ministry of Finance, highlighting how it continues to bridge academia and public service by combining analytical rigor with practical policy experience. He emphasized that the collaborative model — bringing together faculty from the College of Business and Management Sciences and practitioners from Government, reflects the core vision of the PIM Centre of Excellence: strengthening national systems through evidence-based policymaking.
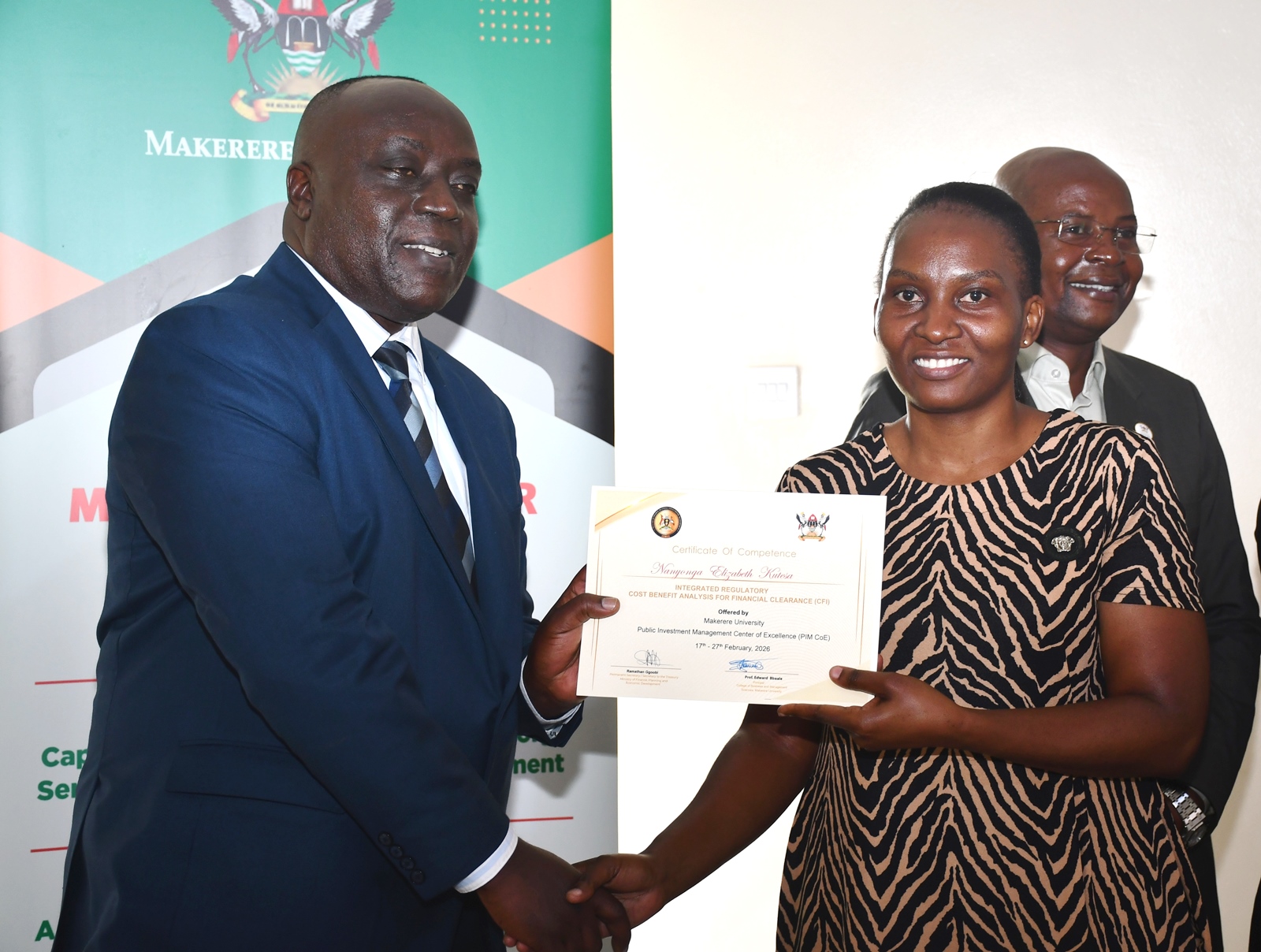

During the two weeks, participants gained hands-on experience in applying cost-benefit analysis across four critical dimensions: budgetary analysis, socio-economic analysis, distributive impacts, and risk assessment. Prof. Bbaale encouraged them to return to their institutions as agents of transformation, improving evaluation frameworks, strengthening regulatory decisions, and ensuring that public interventions deliver value for money and long-term development impact.
He also reaffirmed the Centre’s broader mandate beyond training, noting its recent support to the revision of Development Committee Guidelines, assessment of public investment performance since NDP I, and hosting of the Second Public Investment Management Conference in August 2025.”
Building from “Zero Kilometre”
Earlier, the Manager of the PIM Centre of Excellence highlighted the practical approach adopted during the training. Participants began with blank Excel sheets and built analytical models from scratch, likened to the engineering concept of starting at “zero kilometre,” where construction begins from the very starting point and progresses step by step.
The interactive sessions enabled participants from diverse disciplines, including policy analysts, planners and statisticians, to interrogate assumptions, refine costing approaches, and debate implementation and enforcement frameworks. Their sector-specific insights enriched the learning process and strengthened the analytical models developed.
The Manager noted that excellence is not about knowing everything, but about bringing together the right expertise. Facilitators from MoFPED, NPA, the Office of the President, and Makerere University ensured that theory remained grounded in practical government realities.
Participants Applaud Practical and Engaging Sessions
Speaking on behalf of the cohort, a participant described the training as highly engaging and transformative. The combination of theory and practical application, coupled with patient facilitation, allowed officers from varied professional backgrounds to learn from one another.

The participant highlighted the final day’s discussions as the most impactful, expressing confidence that the knowledge gained would enhance policy analysis and improve the quality of programmes and projects across MDAs.
Certificates Awarded
The ceremony concluded with the award of certificates to all 30 participants in recognition of their successful completion of the IRCBA training. The certification marks another milestone in Government’s effort to build a critical mass of experts capable of institutionalizing rigorous financial and economic analysis in public policy processes.
As the workshop was formally declared closed, participants were encouraged to apply their newly acquired skills consistently, mentor colleagues, and contribute to strengthening fiscal governance across Government.
The PIM Centre of Excellence reaffirmed its commitment to continuous research, policy advisory support, and capacity building as Uganda advances toward more credible, transparent, and sustainable public decision-making.
Business & Management
Botswana Delegation Visits Makerere’s Public Investment Management Centre to Study Sustainable Training Model
Published
1 week agoon
March 3, 2026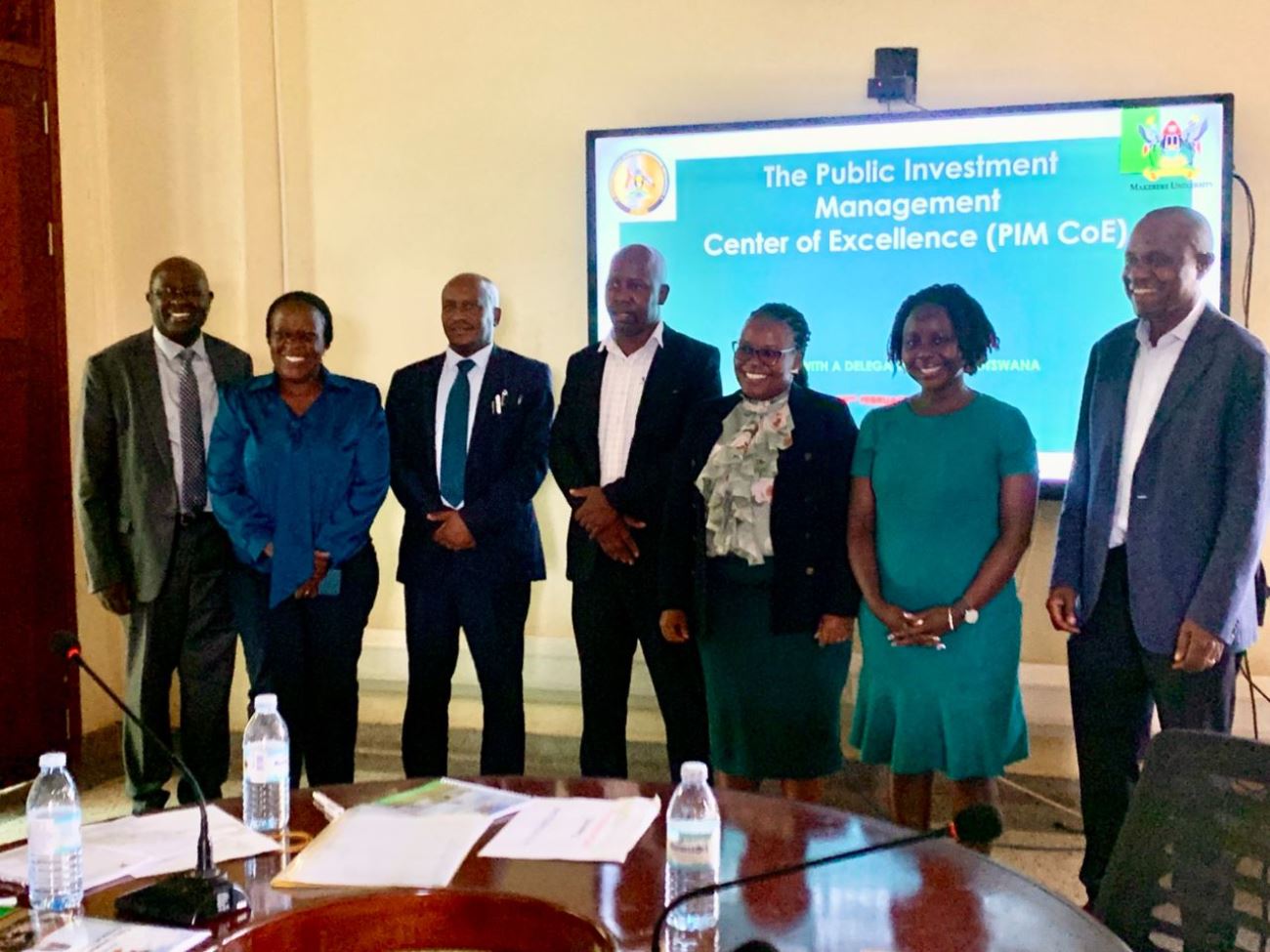
Kampala, Uganda – 25 February 2026
A delegation from Botswana’s public investments sector on 25th February 2026 visited Makerere University’s Public Investment Management Centre of Excellence to benchmark its sustainable training model and draw lessons from Uganda’s well-established Public Investment Management (PIM) framework.
The team, composed of specialists in public investments, is exploring ways to strengthen capacity within Botswana’s public sector institutions. The delegation underscored the importance of structured and sustainable capacity-building programmes, noting that effective public investment management is central to driving national development and ensuring value for money in public projects.
During the engagement, the Botswana team sought to understand the Centre’s operational model, including how it designs and delivers training programmes that remain impactful over time. Particular interest was placed on the Centre’s approach to sustainable training delivery, the documentation of challenges and successes, and mechanisms used to ensure that public officers acquire long-term, practical skills that translate into improved project planning, appraisal, and implementation.
The visiting delegation commended Uganda’s commitment to institutionalizing PIM training and emphasized that cross-country learning is vital for strengthening public financial management systems across Africa. They observed that Uganda’s experience offers practical insights into building a resilient and responsive PIM framework anchored in continuous professional development.
As part of their recommendations, the delegation proposed the introduction of a hybrid training model to enhance accessibility for international participants. Under this approach, the theoretical components of PIM courses would be delivered online, allowing participants to engage remotely from Botswana and other countries. This would then be followed by in-person sessions in Uganda focused on hands-on, experiential learning at the Centre.
According to the delegation, such a model would significantly reduce travel costs and time while preserving the value of face-to-face practical training. The hybrid approach would also provide flexibility for busy public officers, enabling them to balance professional responsibilities with structured learning.
The visit further strengthened regional collaboration and reaffirmed the role of Uganda’s Public Investment Management Centre of Excellence as a hub for capacity development in public investment management across the continent.
Trending
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 Agriculture & Environment2 weeks ago
Agriculture & Environment2 weeks agoCAES Presents Overall Best Performing Student in the Sciences & a Record 28 PhDs at the 76th Graduation Ceremony
-

 General5 days ago
General5 days agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
-

 Natural Sciences2 weeks ago
Natural Sciences2 weeks agoMak 76th Graduation Ceremony: CoNAS Presents 16 PhDs & Best Performing Male Student in the Sciences
