General
In Memory and Honor of Professor John Tuhe Kakitahi’s illustrious legacy | 16-02-1940 to 15-05-2024
Published
2 years agoon
By
Mak Editor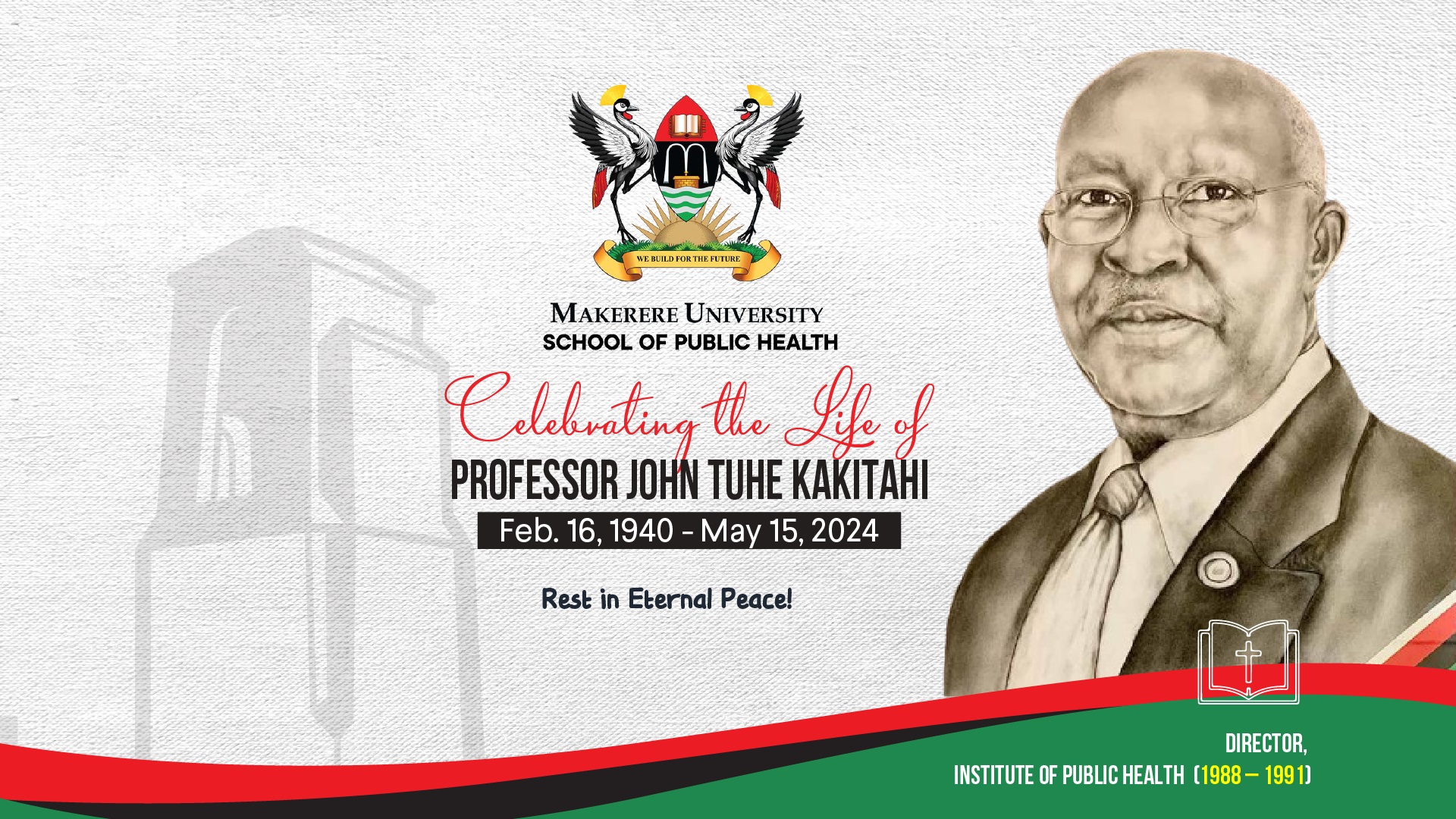
Professor John Tuhe Kakitahi, a luminary in the field of public health nutrition has left an indelible mark on the landscape of healthcare in Uganda and beyond. At the age of 84, Professor Kakitahi was called to heaven this morning at Mulago Hospital.
Today, we celebrate a man who from his early career years, demonstrated exceptional intellect, clinical acumen, passion and complete dedication to combating hunger, malnutrition and human suffering. Throughout his tenure at Institute of Public Health (IPH), Dr. Kakitahi’s contributions were manifold. He in addition to teaching and mentorship conducted field investigations and community outreaches to improve human nutrition and maternal-child health. Kakitahi’s contribution and influence in nutrition transcended borders, as he represented Uganda with distinction at various international forums.
As a lecturer and public health nutritionist, Prof. Kakitahi established and headed Mwana mugimu nutrition center in Mulago hospital in the 1990s. Mwanamujimu became pivotal in treating kwashiorkor aided by support from Rotary International. He later established additional nutritional units and sites throughout Uganda.
In 2008, he served as Deputy Principal of the Makerere University College of Health Sciences.

But Who was Kakitahi?
Prof. John Tuhe Kakitahi was born on February 16, 1940. His university appointment came in March 1973. Now, picture Dr. Kakitahi as a hardworking, intellectual house surgeon with clinical acumen who was a good clinician, pediatrician, researcher, and nutritionist. In the early years of his career at the Department of Preventive Medicine, he collaborated with individuals such as the late Prof. Suleiman Jabir Farsey and Professor Joseph Sekyala Winter Lutwama (RIP), who was the first African to hold the title of Head of the Department of Preventive Medicine. The individuals he collaborated with provided an accurate portrayal of his character.
From 1948 until 1958, Dr. Kakitahi studied primary education at Kigezi High School. He studied Secondary O’Level at Busoga College Mwiri from 1957 to 1961 and ‘A’ level at Kings College Budo from 1962 to 1963. In 1964, he attended Makerere University and earned an MBChB in 1970.
Kakitahi was Senior Casualty Officer in New Mulago Hospital’s Casualty Department for 1.5 years before enrolling in IPH’s Diploma Course in Public Health. He managed department operations and provided emergency patient treatment. The Senior House Officer position at Mulago Hospital was Dr. Kakitahi’s first job after his internship. For 1.5 years, he oversaw casualty department patient care and administration. He also managed the Nurses Health Unit for a similar time, exhibiting his healthcare administration versatility and dedication.
Kakitahi also ran a Nutritional Rehabilitation Clinic at Kasangati Health Centre, providing critical services to the community. He also helped the Pediatrics Department in managing the Old Mulago Hospital’s Nutrition Ward. He intensively treated acutely malnourished children, contributing significantly to their care and recovery.
In 1968-1969, he worked in the Lymphoma treatment center and Solid Tumor Centre during school breaks. He took part in research on chemotherapy treatment for cancer patients as well.
Using his medical background, he joined the Institute of Public Health (IPH) in 1972 and earned a Diploma in Public Health in 1973.
In 1973, he joined Makerere University Service as an IPH Lecturer. He passionately taught human nutrition to undergraduate and postgraduate students, particularly Diploma in Public Health students, as part of the Maternal Child Health and Nutrition teaching programme. His focus was on MCH field investigations, particularly the Ankole PPP.
On July 1, 1977, Dr. Kakitahi became a senior lecturer. Later, for 45 days, Dr. Kakitahi replaced Dr. Kakande as IPH director on June 22, 1987. He was sitting in for the then director, Professor Namboze, who was on a special assignment for the Health Policy Review Commission. On August 1, 1984, he was appointed as an Associate Professor at the Institute of Public Health. On September 18, 1989, Dr. Kakitahi assumed the position of Head of the Institute of Public Health for a two-year term.
Dr. Kakitahi’s remarkable journey is interwoven with stories of dedication, expertise, and significant impact. As a young medical practitioner, he worked as a Medical Officer at Makerere Students Health Centre for several months in 1973, shortly after being hired as a Lecturer at IPH, where he laid the groundwork for the transformation of the then-Sickbay into the current University Hospital. Dr. Kakitahi pursued excellence by finishing his MSc in Nutrition at Cambridge on a WHO scholarship from 1974 to 1976. His abilities and commitment made him a well-known member of the Uganda Medical Association and the British Nutrition Society, both of which promote health locally and globally.
In 1977, he successfully represented Uganda at the 27th WHO Regional Committee for Africa in Brazzaville, Congo. This was the first of several significant appointments, including leading the Mwanamugimu Nutrition Unit in 1980 and representing Uganda at international gatherings such as the Inter-Country Nutrition Workshop in Gaborone, Botswana, and the WHO Regional Committee for Africa in Accra, Ghana, and Libreville, Gabon.
In May 1985, he accompanied the Minister of Health to the 38th World Health Assembly, where Uganda demonstrated its commitment to global health and nutrition programmes. In 1991, he organised Kampala’s first public discussion on Urban Health, Environment, and Health, solidifying his reputation as a community and occupational health visionary.
Throughout his career, Dr. Kakitahi provided expert consultancy services to the Food and Agriculture Organization and participated in numerous nutrition review missions aimed at combating hunger and malnutrition. These missions, organized by WHO, UNICEF, and other organizations, took place in countries such as Ethiopia, Malawi, Zambia, Kenya, Seychelles, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Tanzania, and Lesotho as part of the Nutrition and Human Resources for Health Mission.
Dr. Kakitahi and his Role in Establishing the Mwana mugimu nutrition center
Mwana mugimu nutrition center was set up with support from Rotary International. Rotary International recognized it as the best nutritional unit in the East African region, and was related to the Save the Children Fund, which provided administrative and financial support. This support in the 1990s led to the establishment of similar nutritional units and sites throughout the country. Later, Princess Royal Anne Elizabeth Alice Louise visited the programme and recognised it as a successful Save the Children programme.
Mwanamugimu has its roots in a Luganda proverb (Mwanamugimu ava ku ngozi) that means “A healthy child comes from a healthy mother.”
In Uganda in the 1970s and 1980s, Dr. John Kakitahi led nutritional work. After treating children for severe acute malnutrition without success, Dr. Kakitahi, like many Ugandan doctors, became passionate about prevention. Kakitahi, like Prof. Namboze, left pediatrics early to study public health at the Makerere University Institute of Public Health, now known as the School of Public Health. When Amin’s repression and violence against Ugandans escalated in 1973, they recruited Kakitahi as a lecturer, and he took over the MRC Unit after Roger Whitehead and Paget Stanfield left.
Whitehead, the MRC’s senior scientist under Dean Stanfield, was instrumental in Mwanamugimu and its extension to the Luteete Health Center. Whitehead and other MRC Unit researchers were first skeptical of the Mwanamugimu program, but its public health ethic shaped their thinking and approach.
Whitehead and Stanfield, codirectors of the unit, initiated a research program to reframe nutrition as a science and practice of health promotion, influenced by Mwanamugimu’s hybrid public health model.
They renamed the MRC facility the Child Nutrition Unit, omitting “infantile” and “malnutrition,” and announced a longitudinal nutritional health study for rural village children during the unit’s extension opening on July 17, 1969, by the then-Deputy Minister of Health, Mr. S. W. Uringi.
Kakitahi struggled to run the unit without knowing the study program or how to get basic biochemical test reagents. Few medical supplies and the difficulties of fixing equipment and getting replacement parts prevented the MRC from continuing to operate as a research institution. Whitehead and the Dunn Nutrition Unit at Cambridge (which Whitehead then directed) helped Kakitahi travel abroad for nutrition training, escape the rising violence temporarily. After finishing his training in 1976, Kakitahi “plucked some courage and came back” to Uganda and took over the Mwanamugimu Unit.
Kakitahi kept the unit running with his personal vehicle and what he could spare from his increasingly meager salary, and he and Latimer Musoke, who had taken over as Chair of Pediatrics after Stanfield’s departure, launched a program to train public health workers and extend the Mwanamugimu program’s preventive promise to rural areas.
Kakitahi’s return from Cambridge coincided with the huge increase in violence when Israel attacked Uganda’s main airport at Entebbe. A Tel Aviv-Paris flight was hijacked in June 1976 and diverted to Entebbe with Amin’s consent. In a predawn raid a week later, Israeli forces rescued the hostages and killed the hijackers and twenty of Amin’s men.
Mwanamugimu promoted health and welfare in Amin’s Uganda during a medical shortage. The amazing endurance of the Mwanamugimu initiative illustrates what is often lost in simplistic stereotypes depicting Africa as a continent in crisis. Mwanamugimu’s growth throughout Uganda’s darkest hour demonstrates the need of long-term public health programming and biomedical knowledge. Musoke and Kakitahi were graduates of East Africa’s top medical and educational schools and were able to use their skills to do well in their periods of uncertainty. Kakitahi was one of a generation of medical students trained to increase Ugandan physician population. Mwanamugimu’s modest infrastructure, technology, and a flexible framework made it a local program that could survive resource constraints.
Kakitahi and his colleagues, in collaboration with village health workers, also known as “Ssalango,” conducted door-to-door visits in a specific area to provide community members with information, support, and essential medical care. Ssalango, who commenced working at the Luteete Health Centre in 1978, stated that one of their primary responsibilities was to identify children exhibiting stunted growth. Ssalango and other community health experts educated mothers and guardians on malnutrition and how to assess nutritional status using arm circumference. Similar to the significant women who received training at Mwanamugimu, they instructed individuals on how to prepare kitobero in their own homes using ingredients that were readily available and commonly used in their daily meals. In addition to this early intervention, community health workers were in a favourable position to do follow-up visits to prevent slightly malnourished children from progressing towards “kwashiorkor.”
Kakitahi and Latimer Musoke showed what long-term infrastructure and knowledge can do by expanding on prior public health programming and medical services. Kakitahi revitalized Mwanamugimu and expanded the nutrition scout program after Amin. Funding was needed to rebuild facilities, restore the Nutrition Rehabilitation Program, and boost outreach. In 1983, Rotary International awarded Kakitahi a $245,000 “Health, Hunger and Humanity” grant to reinstate all parts of the central Mwanamugimu Unit in Mulago, including medical training, and begin the “second phase.” The second phase revived nutritional initiatives at Kayunga, Luteete, and Kasangati satellites. It was projected they served 650,000 people by 1984.
Kakitahi then established outreach initiatives at health centers in Mbale, Jinja, Bugembe, Kitovu, Ibanda, Kabale, Kisoro, and Gulu, which required an intermediate owing to Northern insecurity. Mwanamugimu Nutrition Services, a national program founded by Kakitahi, was based on these eleven satellites.
Kakitahi envisioned a public health programme to boost the health of a new national population. A Rotary International delegation visited Uganda in 1985 and was so impressed with the program and its local reception that the organization made a rare exception to their one-time financing policy. Kakitahi assumed this was Rotary International’s last grant and stretched this second disbursement over three years. After Rotary International returned in 1987, another exception and grant were provided, bringing the total support to $980,000 from 1983 to 1992.50 Despite political turmoil, Kakitahi restored and expanded Mwanamugimu Nutrition Services.
Kakitahi, who had been trying to expand Mwanamugimu nutrition programs to remote regions, became “frustrated” when he could no longer secure funds in the early 1990s due to the IMF and World Bank’s Structural Adjustment Policies (SAPs). After realizing he “didn’t have any money to continue,” WHO colleagues urged Kakitahi to create a health worker training program for newly independent Namibia. Uganda’s nutritional programming changed when Kakitahi left in dissatisfaction over structural adjustment’s lack of resources.
According to several observers, Ugandans regarded their national health system as “the demoralization of health workers” since many left when structural transformation proved difficult. Through Amin and the Bush War, Kakitahi stayed in Uganda.
Jennifer Tappan, a historian of Global Health in Africa and author of The Riddle of Malnutrition: The Long Arc of Biomedical and Public Health, calls John Kakitahi and his colleagues, Latimer Musoke, Ssalango, and Gladys Stokes, “awe-inspiring.”
Because of biomedical knowledge, competence, and infrastructure—the underpinnings of a national health system—Mwanamugimu survived. Thus, Mwanamugimu could become a fully local project, which, along with its clear worth, explains its amazing resilience.
Professor Tappan notes that “Kakitahi, his colleagues, and the influencers who kept Mwanamugimu alive illustrate the return on long-term investments in national systems of medical provision, which can then serve as the foundation for flexible and resilient public health programming, programming that can promote health and wellbeing in ways that increase rather than undermine sovereignty and the right to health that all people deserve.”
Compiled by Communications Office -MakSPH
You may like
-


82% Stressed: Uncovering the Hidden Mental Health Burden Among Kampala’s Taxi Drivers
-


Makerere Graduation Underscores Investment in Africa’s Public Health Capacity
-


Three MakSPH Faculty Honoured with Makerere University Research Excellence Awards 2026
-


Makerere’s 76th Graduation Ceremony: CHS showcases research strength with 26 PhD Graduates
-


Medical graduates urged to uphold Ethical values
-


MakSPH Environmental Health Graduates Trained to Prevent Disease at Its Source
General
Makerere University Affirms E-Mobility Push with Fast-Charging Station Launch
Published
1 day agoon
March 13, 2026By
Mak Editor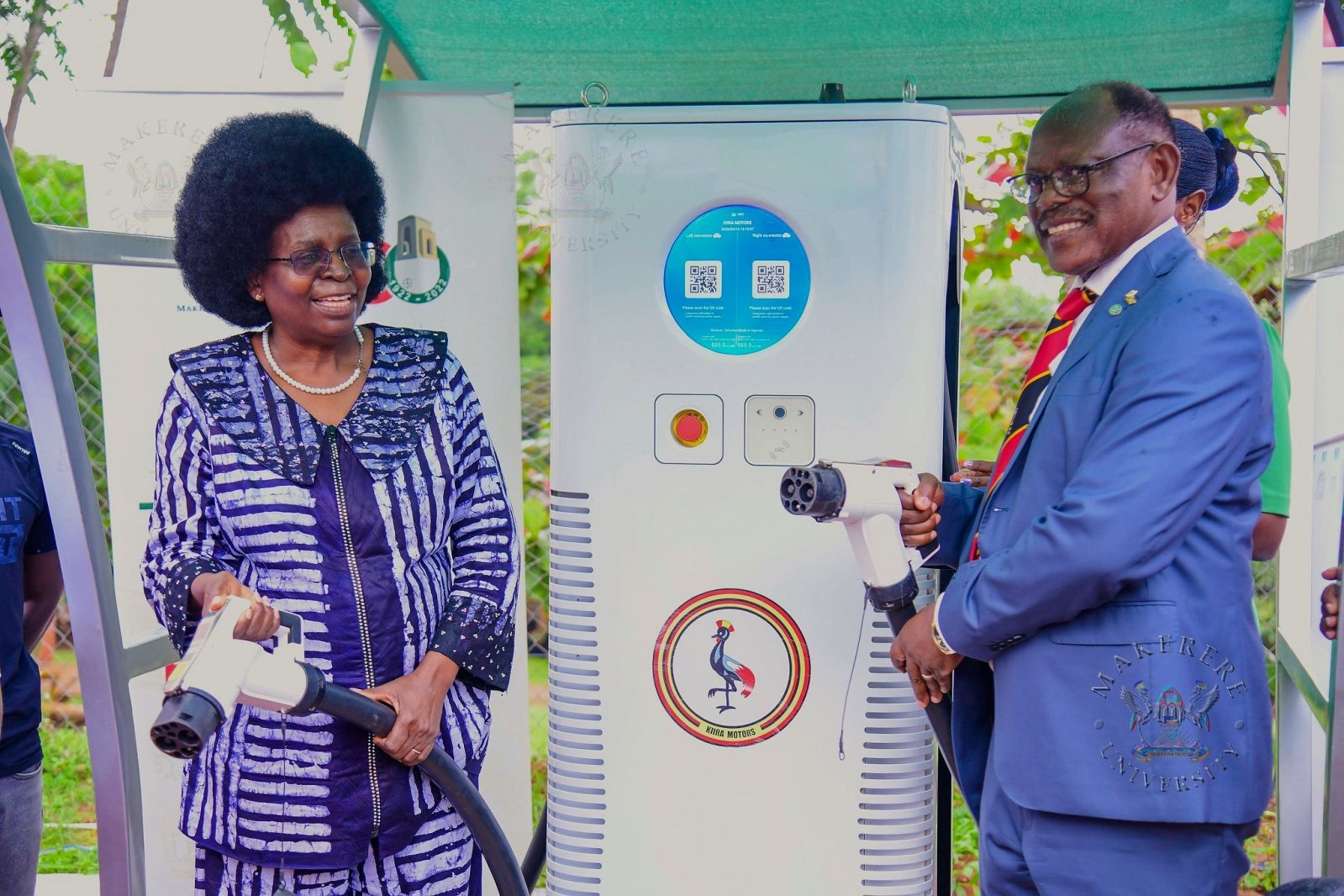
In a landmark event symbolizing Uganda’s stride towards sustainable transportation, Hon. Dr. Monica Musenero Masanza, Minister of Science, Technology, and Innovation, commissioned the first Electric Fast-Charging Station at Makerere University on Friday 13th March 2026. The ceremony, held at the Senate Building Parking Lot, marks a pivotal moment in the nation’s e-mobility journey, blending academic innovation with industrial application and governmental support.
The station, a DC Fast Charger C6-180 installed in collaboration with Kiira Motors Corporation (KMC), is designed to power electric vehicles efficiently, supporting Uganda’s shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. This setup ensures high-power DC charging ideal for fleet operations.
Hon. Dr. Musenero, in her keynote remarks, highlighted the profound significance of the occasion, tracing its roots back to 2011 when Makerere unveiled the Kiira EV – Uganda’s first electric vehicle prototype. “This infrastructure is the physical manifestation of a journey that began on this very hill nearly two decades ago,” she stated, emphasizing how the university’s initial proof-of-concept challenged skepticism about Africa’s role in automotive technology.

The event, she noted, completes a narrative full circle, with the birthplace of the Kiira EV now hosting the infrastructure to sustain a modern electric fleet. The commissioning aligns seamlessly with Uganda’s National E-Mobility Strategy, which aims to localize 65% of the e-mobility value chain by 2040 and create over 500,000 high-quality green jobs.
Hon. Dr. Musenero underscored the strategy’s focus on reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels while enhancing environmental well-being. “We are transforming Uganda into a net source of e-mobility solutions,” she declared, pointing to the potential for Ugandan intellect to produce vehicle parts and charging systems domestically.
In his remarks at the event, the Vice Chancellor Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe described the launch as a “multi-faceted achievement,” not only advancing the institution’s inclusive agenda but also setting an example for public institutions in adopting e-mobility. In so doing, Makerere University has positioned itself at the forefront of this transition.
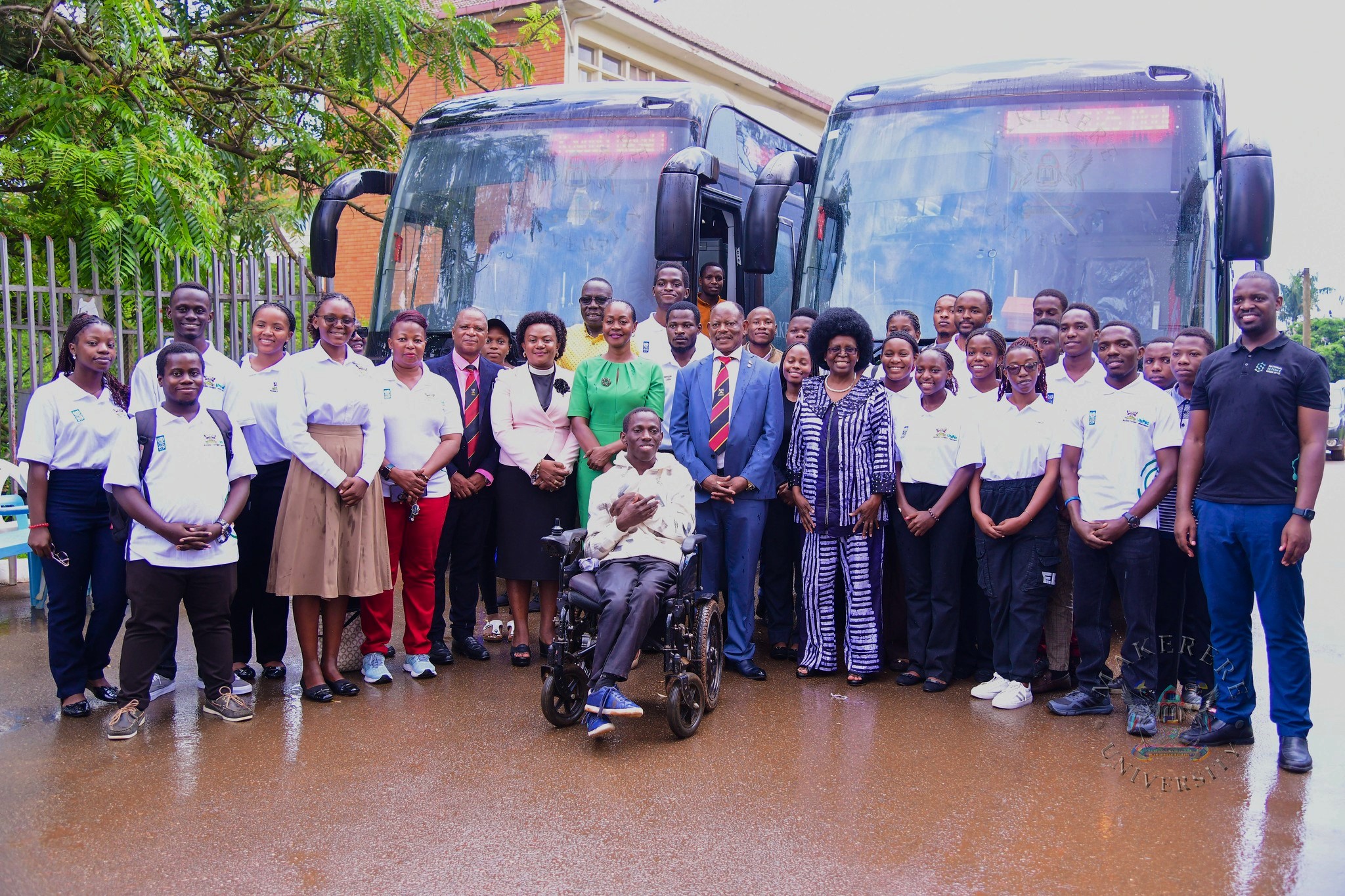
On September 26, 2025, President Yoweri Museveni commissioned the Kiira Vehicle Plant in Jinja and handed over three Kiira Motors Corporation (KMC) buses to Makerere University to enhance staff and student mobility. The fleet included two diesel-powered Kayoola Coaches and one electric Kayoola EVS 8.5m bus donated by KMC specifically to aid the movement of differently-abled staff and students. This move demonstrates academia’s capacity to integrate home-grown solutions into daily operations, impacting the economy through practical science.
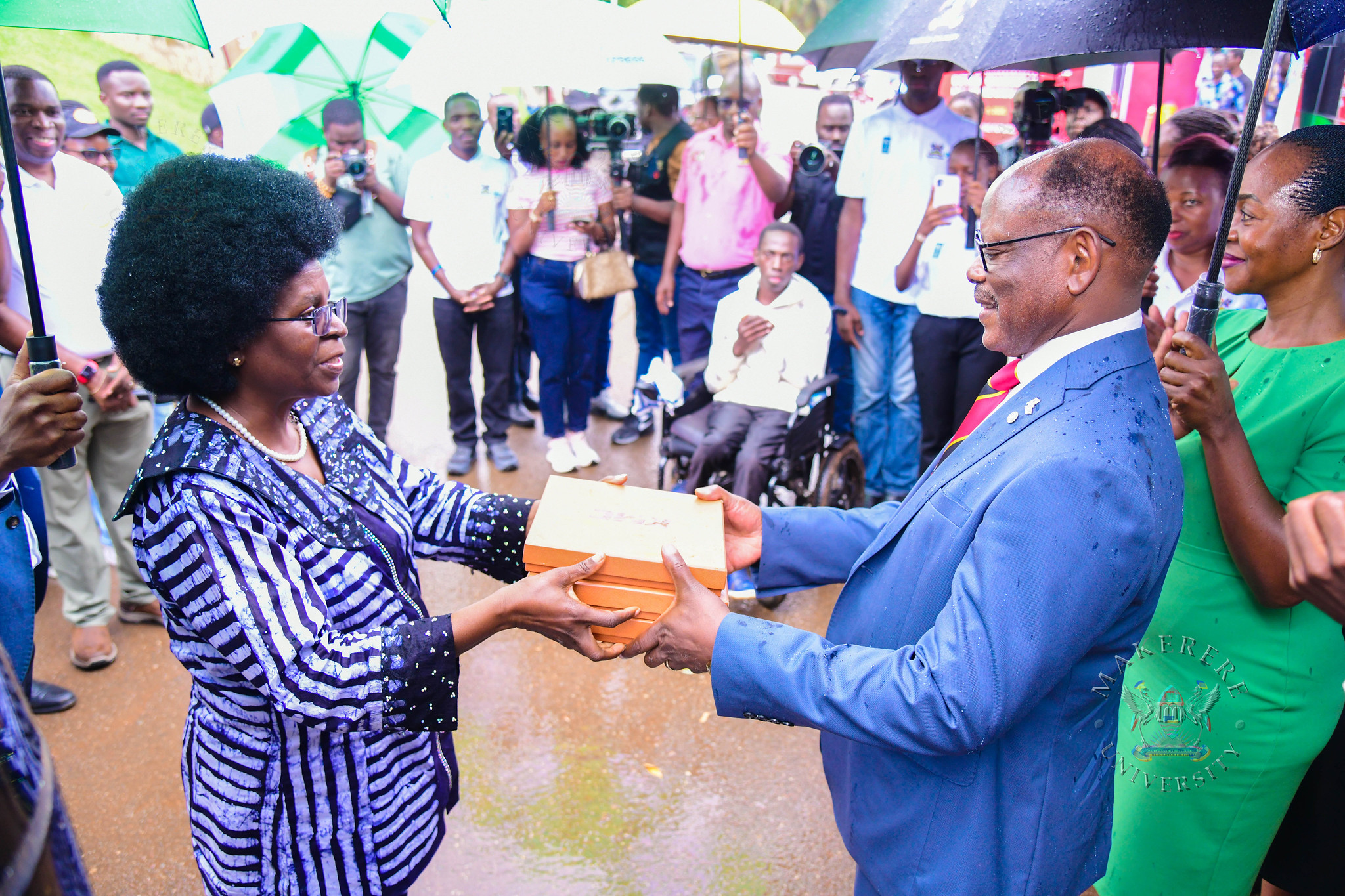

The commissioning of the fast-charging station is rooted in a long history of collaboration. The Kiira Electric Vehicle Project, hatched in the former Faculty of Technology, has evolved into a national movement for automotive manufacturing. Hon. Dr. Musenero praised this progression: “We have moved beyond proving that an electric vehicle can be built in Uganda. We are now ensuring our electric vehicles are deployed across the continent, solving Africa’s mobility problems.”
Academia’s role remains central, as Hon. Dr. Musenero elaborated. While government provides policy frameworks and the private sector offers capital, universities supply the essential knowledge. The E-Mobility Skilling Programme at Makerere University‘s Innovation Pod (Mak-UniPod) is training the next generation of electric vehicle engineers, who are tackling “moonshot projects” to redefine urban transport. Research into optimizing local resources, such as Uganda’s lithium and cobalt deposits for battery production, is also underway.
A key environmental highlight of this development is Uganda’s renewable energy advantage. With over 95% of the national grid powered by hydroelectric dams, every charge at this station utilizes clean energy. “We are using our own water to power our own vehicles, keeping our wealth within our economy rather than exporting it to purchase foreign oil,” Hon. Dr. Musenero remarked, framing the launch as Uganda plugging into the global renewable shift. She pledged the Science, Technology, and Innovation (STI) Secretariat’s continued collaboration with Makerere University, KMC, and partners to proliferate such stations across Kampala and beyond.
Addressing Makerere students, Hon. Dr. Musenero issued a challenge: “See this charging station as a symbol of your own potential. The engineers who built the first Kiira EV were once sitting exactly where you are. They did not wait for permission to be great.” She urged them to leverage available resources to innovate, building on a legacy that has shifted national conversations.
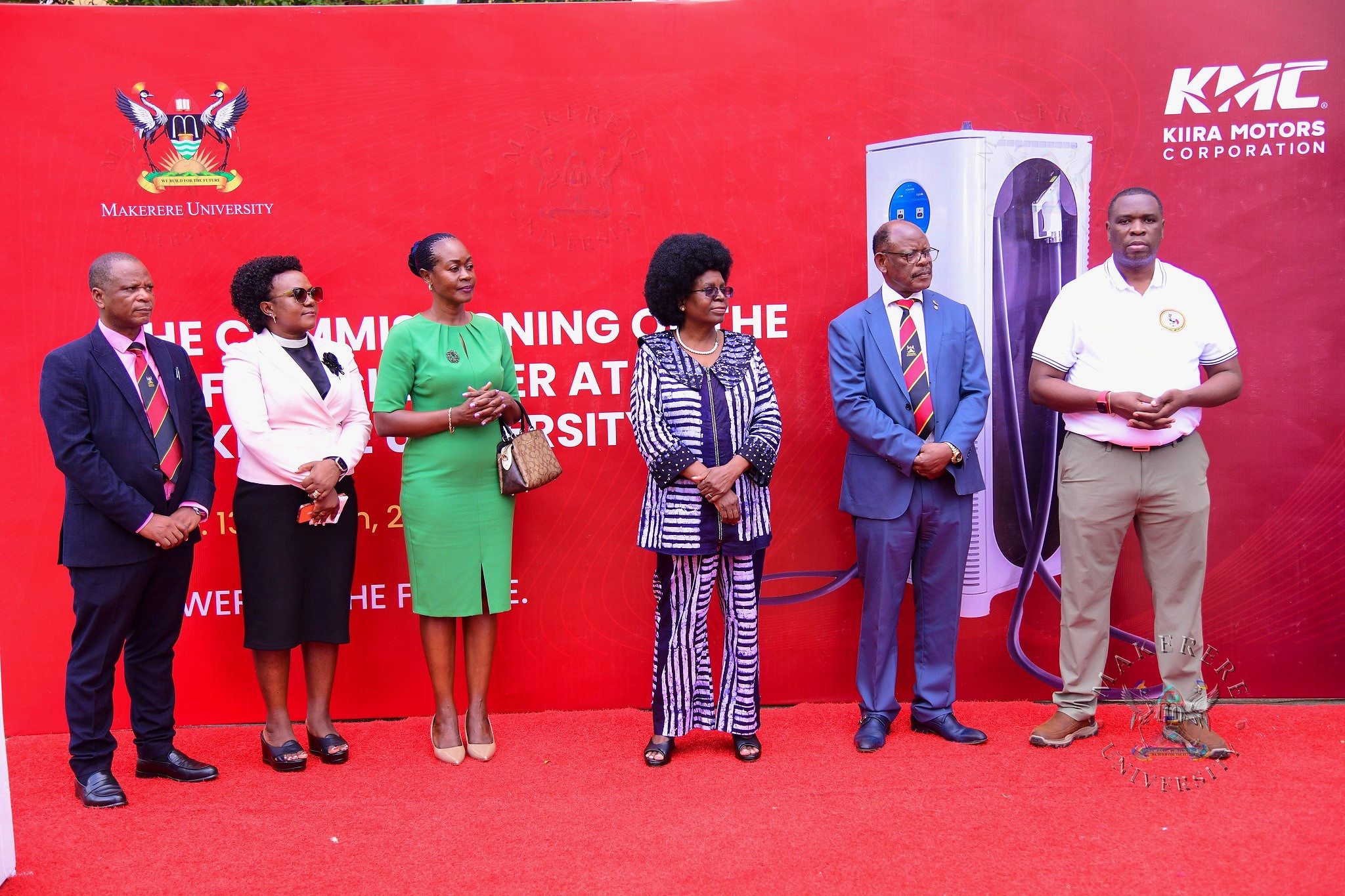

The event drew distinguished guests, including Members of Management, Eng. Paul Isaac Musasizi, KMC’s CEO and his management team, private sector partners, development agencies, and university faculty.
Looking ahead, this launch propels Uganda towards a “Qualitative Leap” in its economy, as Hon. Dr. Musenero described. By fostering innovation and investing in young minds, the nation aims to lead in technological advancement. The station not only powers vehicles but ignites progress, ensuring Uganda remains at the forefront of Africa’s e-mobility revolution.
As the ceremony which was intermittently “blessed” by drizzles drew to a close, the feeling of hope for a cleaner, self-reliant future – one charged by Ugandan ingenuity, was unmistakable.
General
Makerere University and International Partners Sign MoU for the 9th Kampala Geopolitics Conference
Published
2 days agoon
March 12, 2026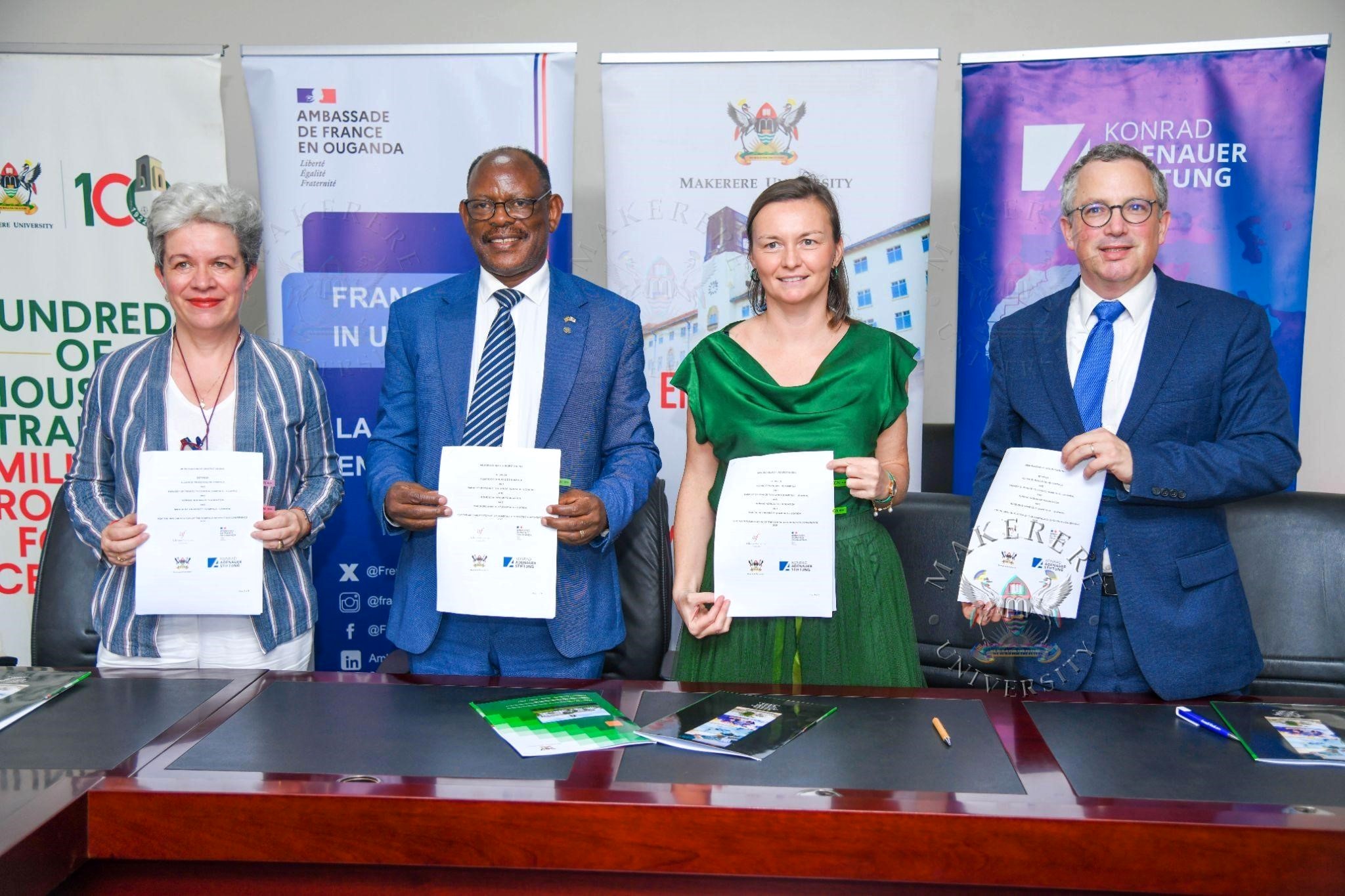
Makerere University, on 10th March, 2026, signed a Memorandum of Understanding with the Embassy of France in Uganda, the Konrad Adenauer Foundation (KAS), and Alliance Française de Kampala to organize the 9th edition of the Kampala Geopolitics Conference (KGC), scheduled to take place on 15–16 April 2026 at Makerere University.
The signing formalizes the continued partnership that has established the Kampala Geopolitics Conference as one of the region’s leading platforms for dialogue on global affairs, bringing together scholars, policymakers, civil society leaders, and students to debate the major geopolitical and socio-economic transformations shaping the world.
The conference, inspired by the Nantes Geopolitics Conference in France, was first launched in Kampala in 2018 and has since grown into a unique intellectual space for cross-continental exchange between Africa and Europe.
A Platform for Ideas, Dialogue, and Youth Engagement
Speaking at the signing ceremony, Makerere University Vice Chancellor, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe, emphasized the importance of the Kampala Geopolitics Conference as a platform that connects academic discourse with global policy conversations while empowering students to engage with the complex challenges shaping the international system.

The Vice Chancellor noted that hosting the conference reflects Makerere University’s long-standing commitment to fostering intellectual exchange and positioning the institution as a hub for regional and global dialogue.
“Makerere University is proud to host the Kampala Geopolitics Conference because it creates an important platform for debate and exchange on the global issues shaping our world, while giving our students the opportunity to engage directly with leading thinkers and policymakers,” said Prof. Nawangwe.
Prof. Nawangwe further commended the Embassy of France in Uganda, the Konrad Adenauer Foundation, and Alliance Française de Kampala for their continued collaboration with Makerere University in organizing the conference over the years. He expressed confidence that the 2026 edition will once again provide a dynamic platform for dialogue, bringing together scholars, policymakers, and students to examine the geopolitical trends shaping Africa and the wider world.
Speaking at the signing ceremony, H.E. Virginie Leroy, Ambassador of France to Uganda, highlighted the significance of the conference as a platform that encourages dialogue on global issues while empowering young people to participate in shaping the future.
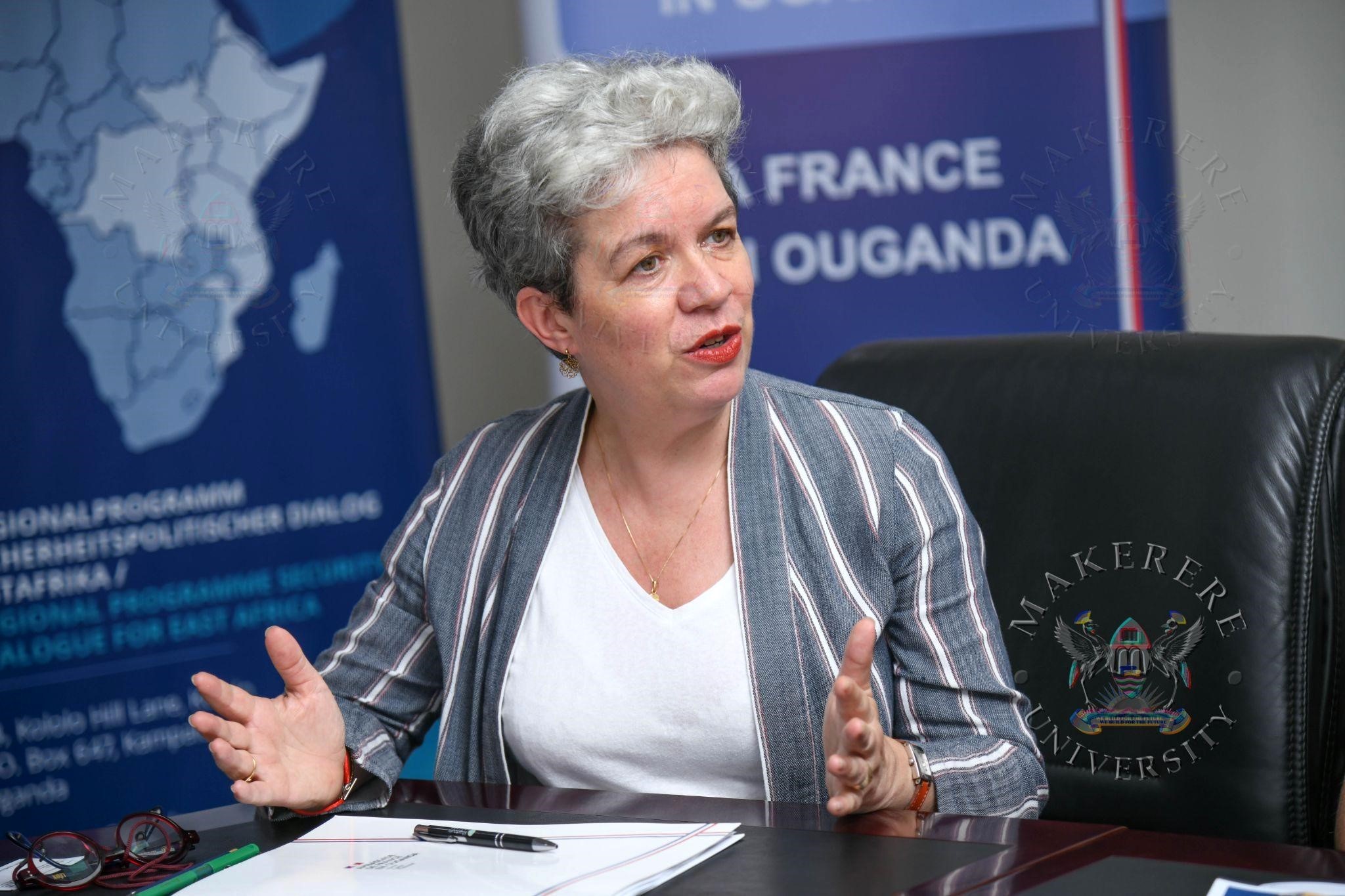

Since its inception, the Kampala Geopolitics Conference has created opportunities for students, researchers, policymakers, and entrepreneurs to engage with some of the most pressing global debates. The Ambassador noted that the curiosity and engagement of Ugandan students have become one of the defining features of the conference.
“This conference has become a unique space where students, researchers, policymakers and civil society exchange ideas on the major transformations shaping our world,” Ambassador Leroy said, adding that the event demonstrates the intellectual vitality of Uganda’s youth and the strength of the partnerships that sustain it.
Strengthening Partnerships for Global Dialogue
The Konrad Adenauer Foundation, a long-standing partner in the initiative, reaffirmed its commitment to supporting platforms that foster meaningful discussions on international affairs and regional dynamics.
Speaking during the ceremony, Anna Reismann, Director of the Konrad Adenauer Foundation in Uganda, emphasized the importance of the conference in connecting local perspectives with global debates.
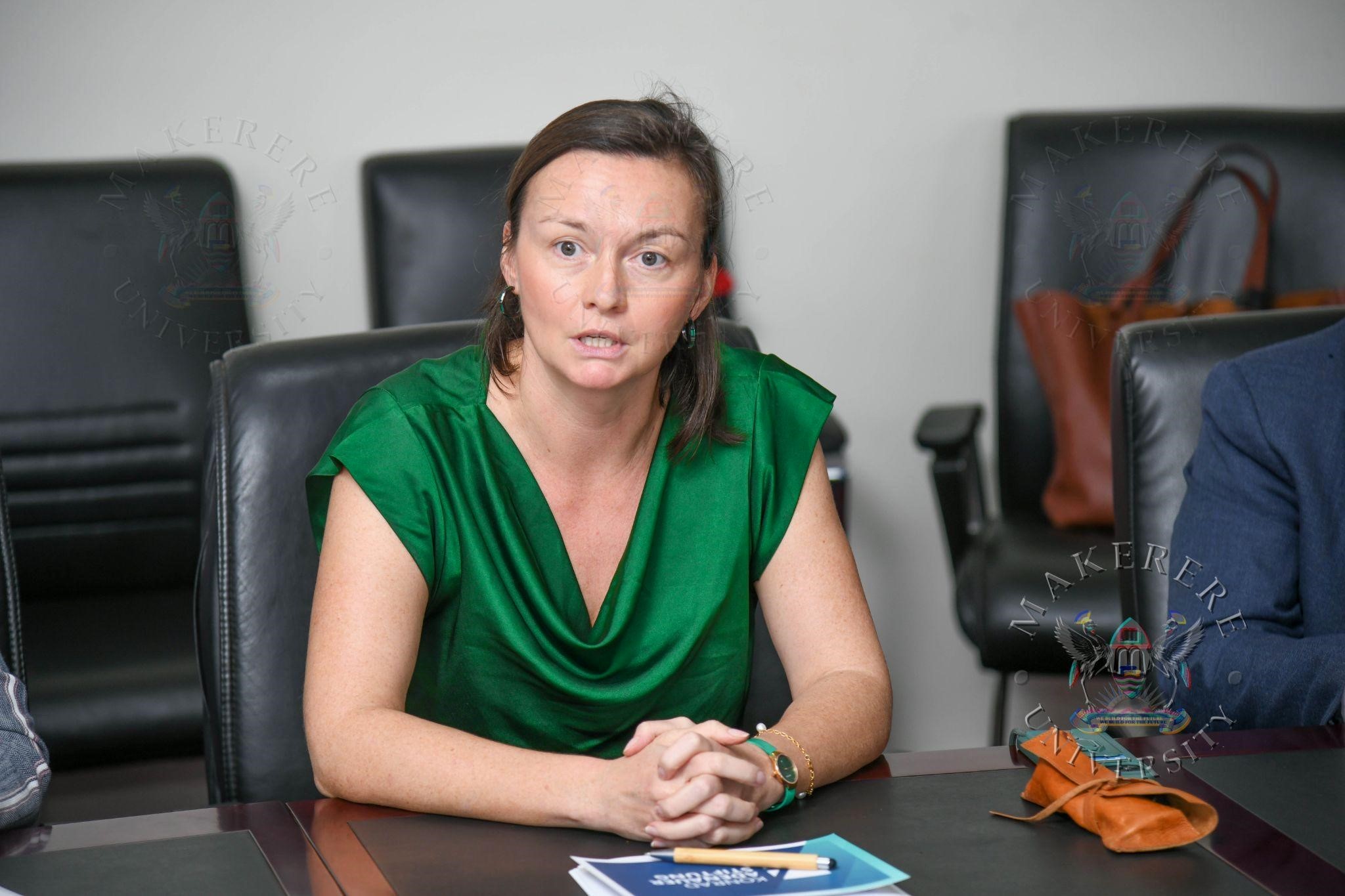

She noted that Africa has increasingly become a focal point in global geopolitics, attracting engagement from a wide range of international actors through investments, trade, security cooperation, and diplomatic partnerships. While these engagements create new opportunities for economic growth and technological advancement, they also raise important questions about sustainability, governance, and the terms of international cooperation.
According to Reismann, the conference provides an important forum to examine these issues and to encourage dialogue that bridges academic perspectives with practical policy considerations.
The 2026 edition of the Kampala Geopolitics Conference will focus on key global and regional issues shaping international relations and development.
Among the themes to be explored are the future of development cooperation, particularly as global aid dynamics evolve and countries explore more sustainable and balanced partnerships. Another panel will examine youth and public policy in Africa, recognizing the critical role that young people play in shaping governance, innovation, and development across the continent.
With Africa home to the youngest population in the world, discussions will highlight the importance of ensuring that young people are not only beneficiaries of public policies but also active contributors to their design and implementation.
Makerere University at the Centre of Global Conversations
Hosting the conference reflects Makerere University’s continued commitment to fostering intellectual exchange and positioning the institution as a hub for regional and international dialogue.
Through its partnerships with global institutions such as the Embassy of France, the Konrad Adenauer Foundation, and Alliance Française de Kampala, Makerere continues to create platforms that connect academic knowledge with policy discussions and real-world challenges.
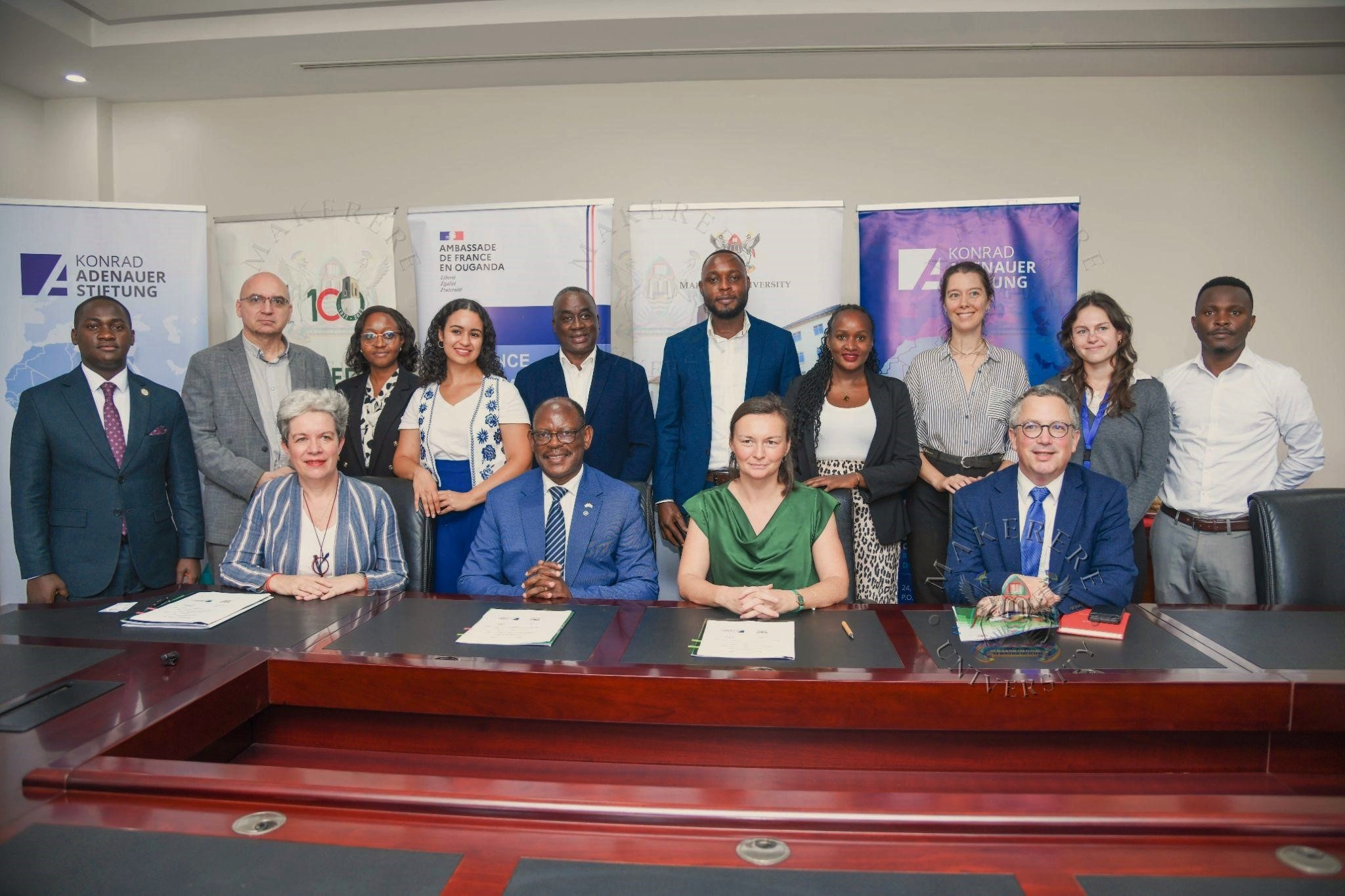

The Kampala Geopolitics Conference is expected to once again bring together leading experts, scholars, and practitioners from across Africa and Europe, while providing students with a rare opportunity to engage directly with global debates.
As preparations for the 2026 edition gather momentum, the partners expressed confidence that the conference will continue to inspire critical thinking, encourage dialogue across disciplines and generations, and strengthen cooperation between Africa and its international partners.
Caroline Kainomugisha is the Communications Officer, Advancement Office, Makerere University.
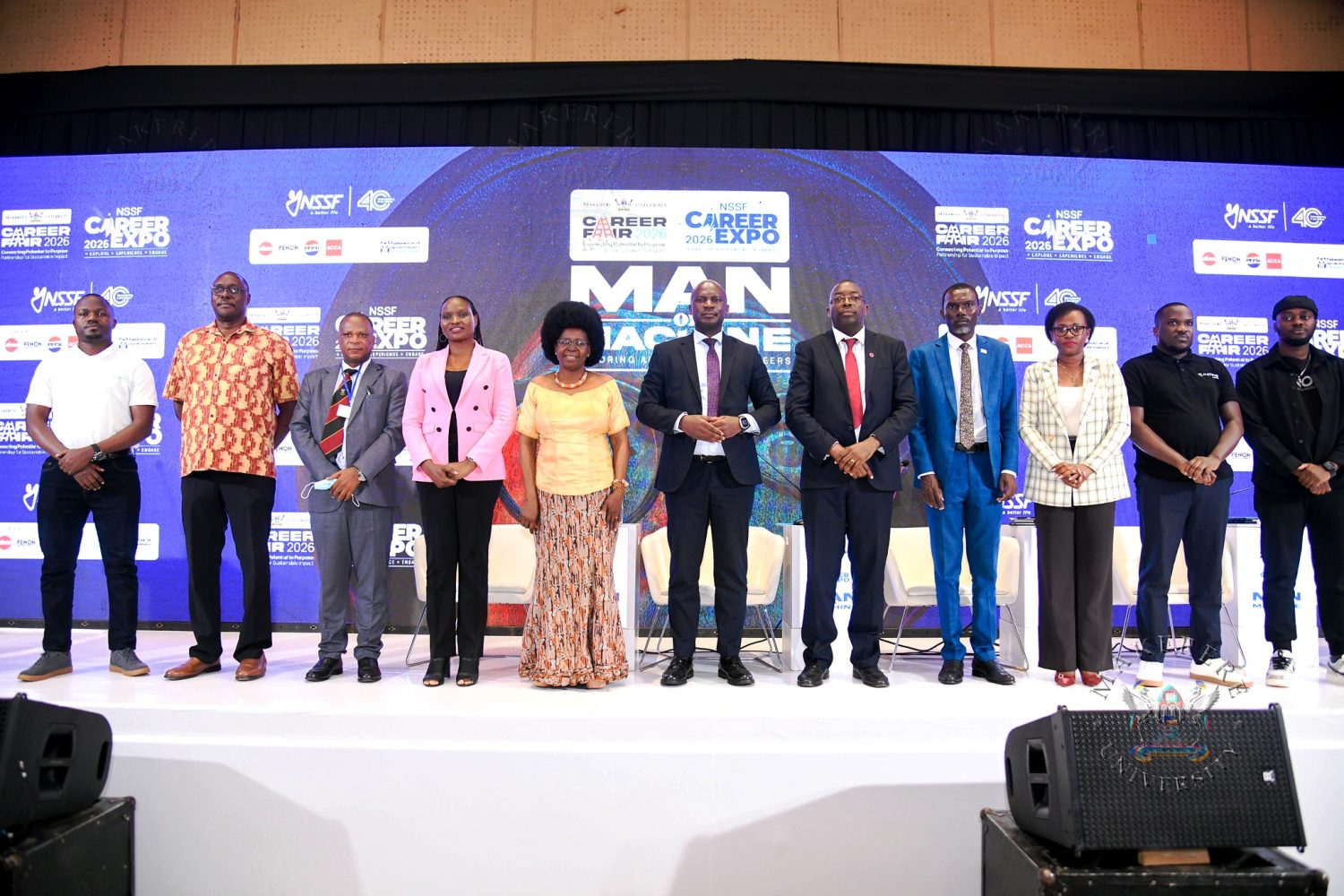

Makerere University has kicked off the three-day Careers Fair 2026, bringing together students, industry leaders, and policymakers to discuss the future of work in the era of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
The first day of the expo, held under the theme “Man or Machine: Exploring AI’s Impact on Careers” and sponsored by the National Social Security Fund (NSSF), explored the impact of AI on industries and careers.
The annual expo offers career guidance, job opportunities, entrepreneurship training, and networking platforms for students. It builds on previous themes focused on employability, innovation, and adapting to rapidly changing work environments.
In her keynote address, Hon. Dr. Monica Musenero Masanza, Minister for Science, Technology and Innovation, stressed the need for Uganda to strategically position itself in the digital economy.
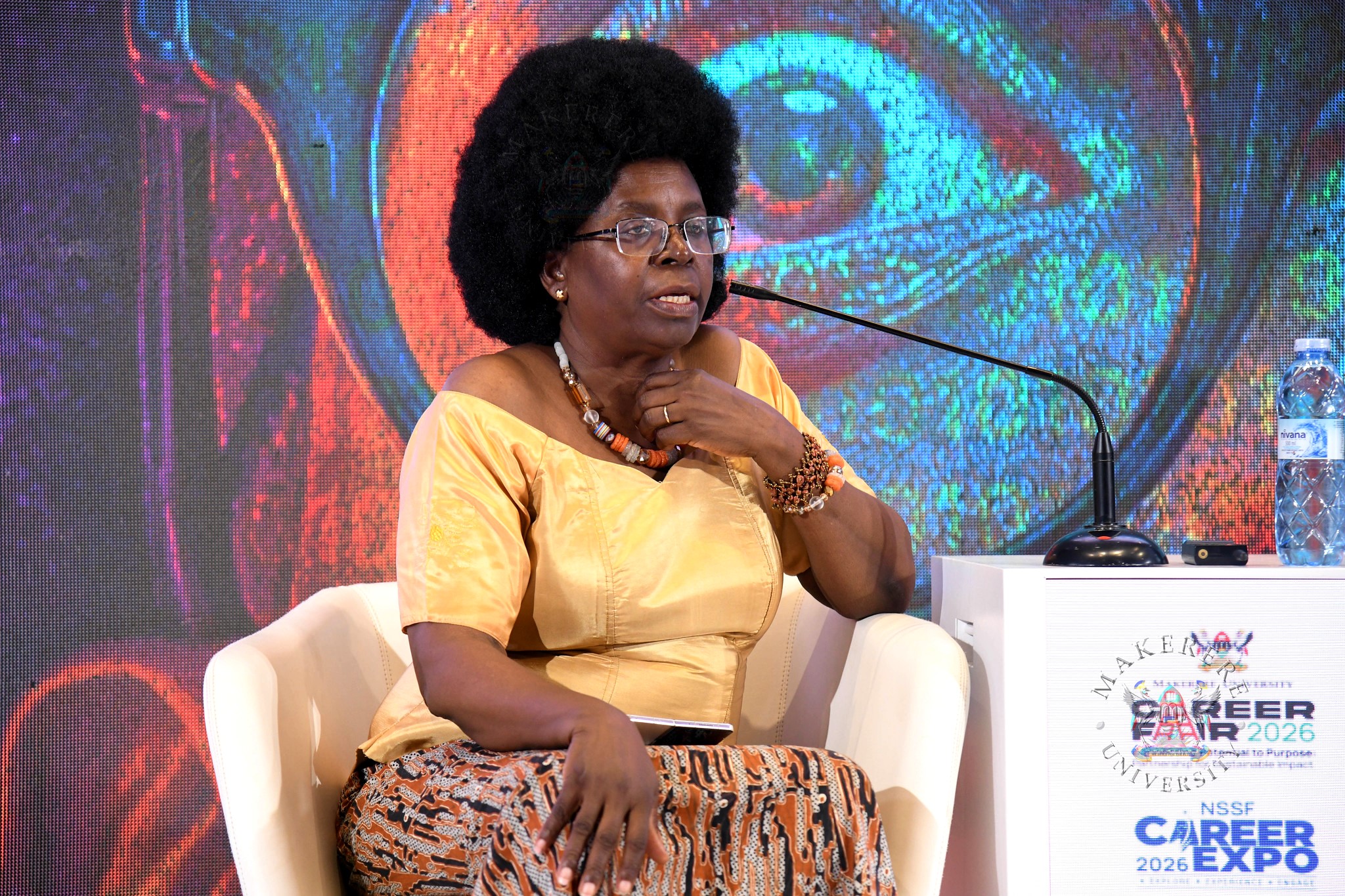

She noted that Africa missed the first and second industrial revolutions and warned that the current digital revolution could also bypass the continent if deliberate efforts are not made to participate in it.
“Africa was just here, minding her own business, hunting her animals, resting. A distant industrial revolution impacted us very negatively,” she said, referencing the slave trade and colonization that followed the first industrial revolution.
The minister emphasized that Uganda must focus on producing digital goods and services rather than merely consuming them.
“We are still down there, but we are facing up. We must give Uganda a clear chance at sustainable and progressive transformation,” she said.
She observed that Uganda’s digital economy is currently skewed toward consumption, resulting in significant financial outflows.

“Our net flow in this digital economy, including AI, is negative. We are losing money, jobs, and opportunities,” she added.
Musenero urged young people to move beyond simply using digital tools and instead focus on creating value.
“Mind or machine, it must give us a positive economic voice. Whichever one gives us that, we should go for it,” she said.
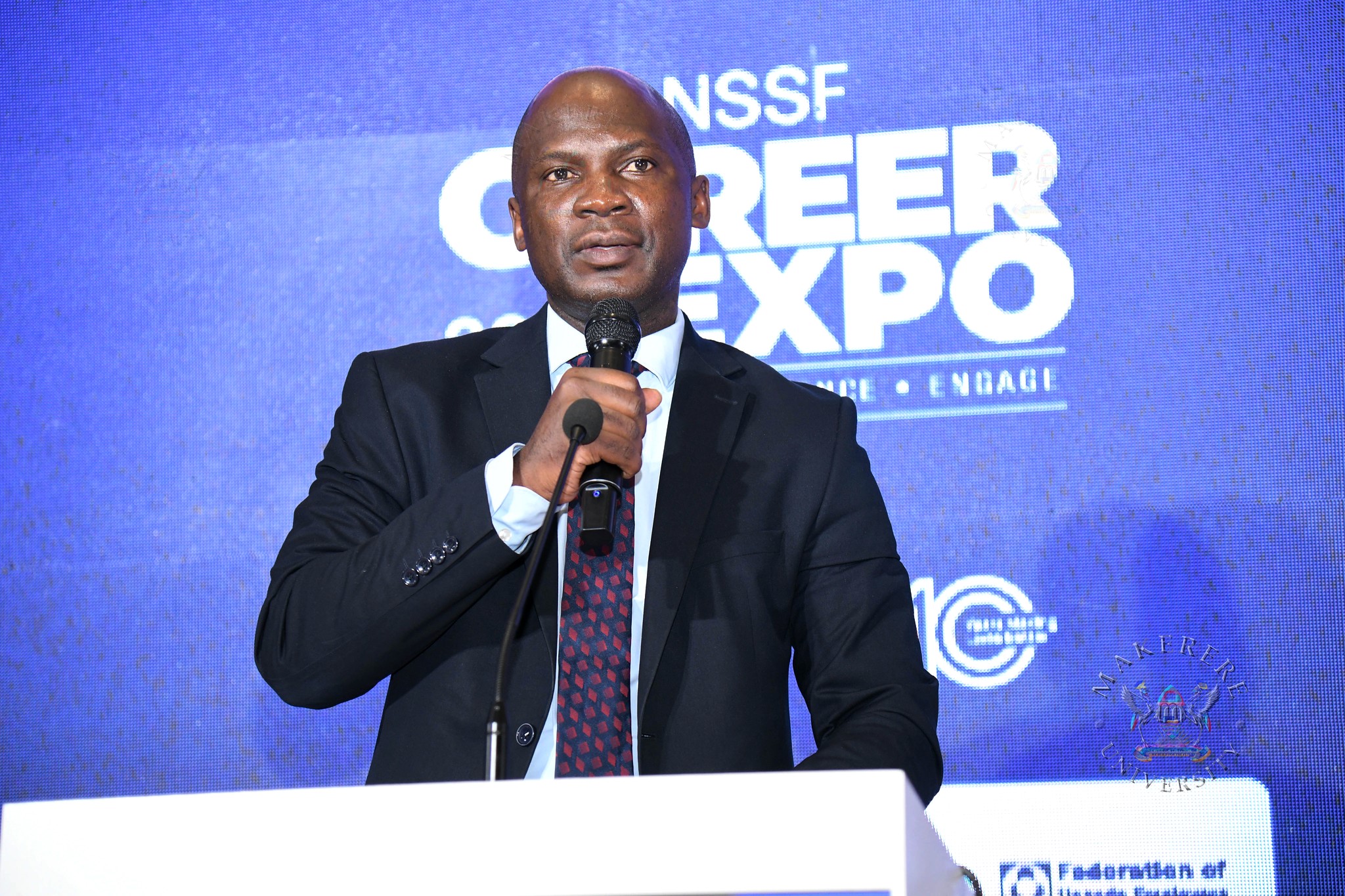
Speaking on behalf of the Vice Chancellor, Professor Moses Musinguzi, the Principal of the College of Engineering, Design, Art and Technology acknowledged the inevitability of Artificial Intelligence in modern society and urged stakeholders to focus on harnessing its potential.

“The general consensus worldwide is that we cannot condemn AI. Instead, we should see how we can make better and more productive use of it,” he said.
Musinguzi highlighted some of the challenges posed by AI in academia, noting that students can easily generate answers within minutes, potentially undermining the learning process.
“A student using AI can generate your answer in less than a minute. And that’s not what we want. We want to impart knowledge and skills to students,” he stressed.
He encouraged institutions to adopt AI responsibly while maintaining the core objective of producing skilled graduates.

“We are now trying to see better methods of using AI while still maintaining the objective of producing students who have the skills and knowledge to advance the world,” Musinguzi said.
He further noted that AI will inevitably affect traditional careers, making adaptation essential.
“If we don’t innovate, there is a threat that we shall be exterminated,” he warned, urging students to embrace innovation and contribute to Africa’s development.
Earlier, Lameck Kavuma from AI Studio Uganda explained the fundamentals of AI, describing it as a system built on pattern recognition and mathematical models that predict the next word or action.
“AI is all about pattern recognition,” he said, noting that the technology still has limitations, particularly when dealing with noise or changes in context.

Kavuma observed that AI has existed since the 1990s in forms such as spam filters and recommender systems. However, recent advances in generative AI now allow machines to process long texts and hold conversations, making it appear as though AI is crossing into traditionally human roles.
He emphasized that AI could level the playing field by increasing productivity and removing traditional barriers to access.
“AI is a leveler. It removes gatekeepers,” Kavuma said.
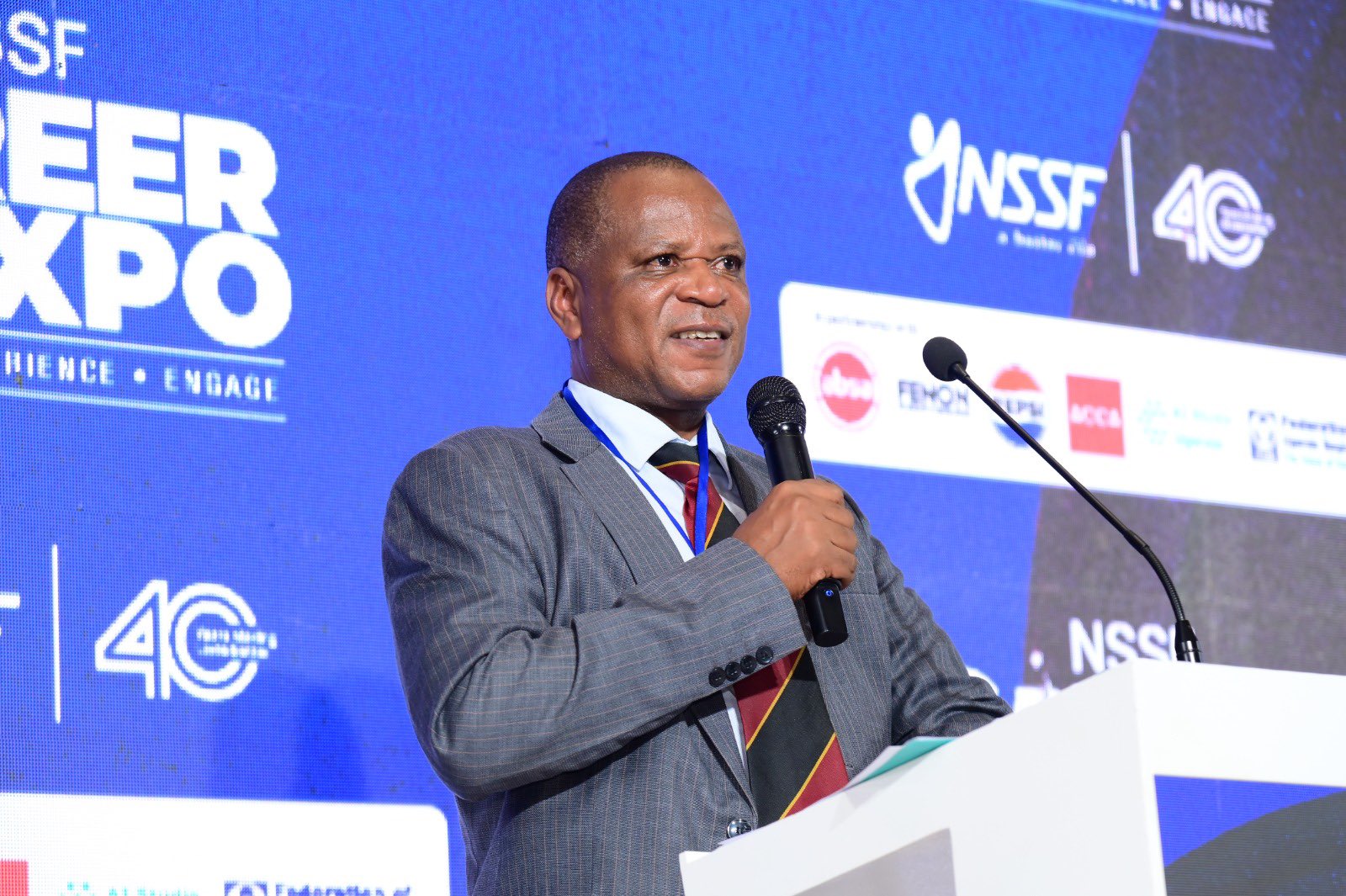
On his part, Gerald Paul Kasato, Deputy Managing Director of NSSF, stressed the importance of collaboration between humans and machines.
“The future is not about humans competing with machines. It is about humans learning how to work with machines,” he said.
Kasato noted that AI, automation, and digital technologies are rapidly reshaping the workplace and creating new opportunities.
“AI, automation, and digital technologies will transform industries, but they will also create new careers, new businesses, and new opportunities,” he said.

He urged students to equip themselves with the right skills, mindset, and adaptability to thrive in the evolving job market.
“The real challenge is ensuring that young people are equipped with the right skills, mindset, and adaptability to thrive in this new world,” Kasato emphasized.
Kasato revealed that NSSF continues to promote financial literacy among young people, with more than 130,000 students registered and over UGX 235 billion saved.
“The future belongs to those who are curious, adaptable, innovative, and willing to continuously learn,” he said.
Also speaking at the event, Michael Ssegwaya, Executive Director and Chief Financial Officer at ABSA Bank, emphasized the need to adapt to a rapidly changing world driven by AI.
“The world is changing, and the banking sector is also changing. We handle millions of transactions, many of which are processed through AI systems,” he said.
Ssegwaya encouraged students to use AI tools to enhance productivity while maintaining independent thinking.
“I told my daughter, you can use AI, but your answers should not look like they came directly from AI. I need you to think and think differently,” he said.
He also highlighted ABSA’s “Ready to Work” program, which aims to prepare students for the evolving job market.
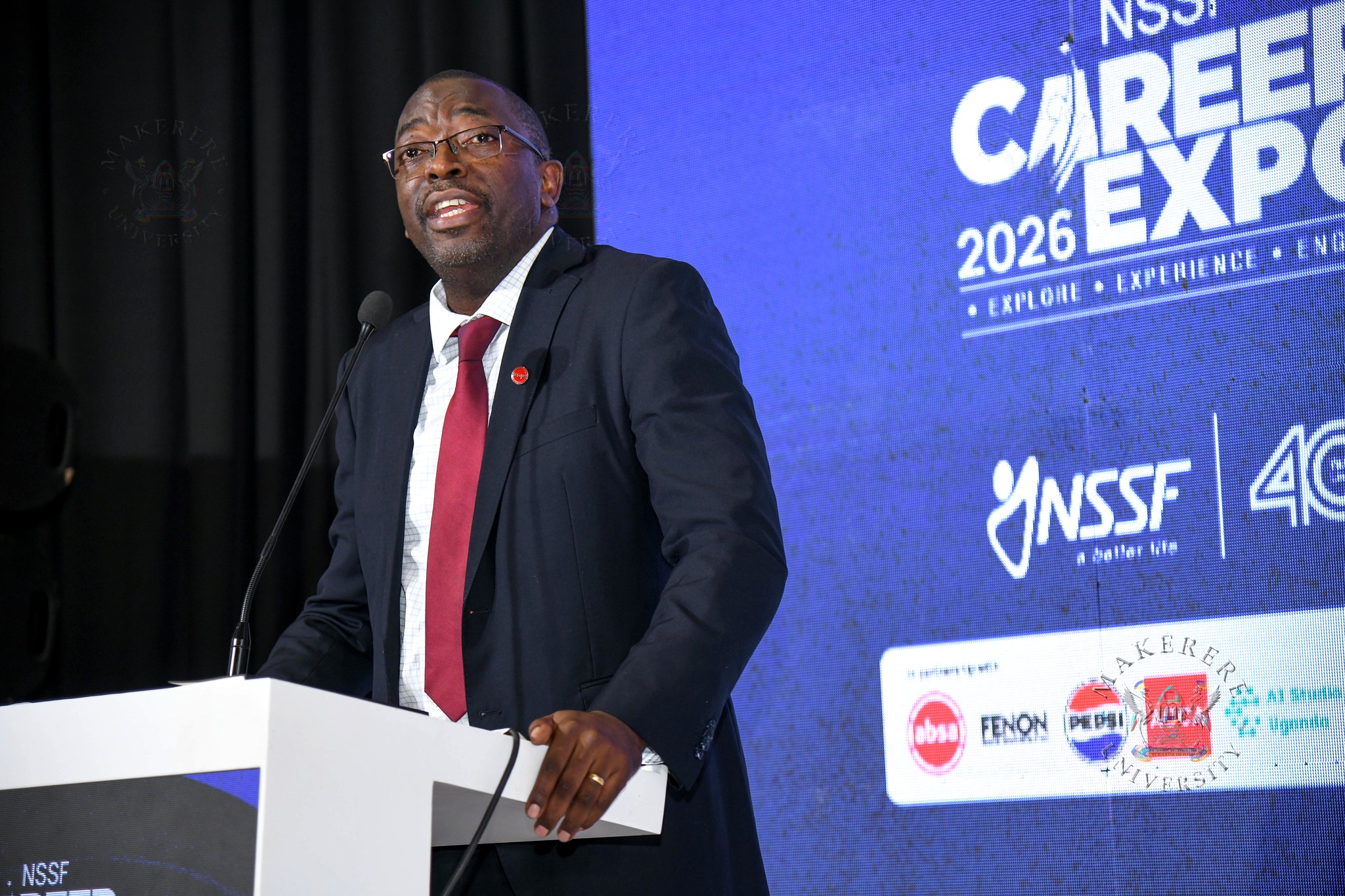

Ssegwaya urged students to develop skills such as creativity, communication, and empathy, which are less likely to be replaced by machines.
“Critical thinking is going to be important. Creativity may not necessarily be replaced,” he said.
He challenged students to become job creators rather than job seekers.
“I hope you are going to the university to become a job creator and not just a job seeker,” he added.
Similarly, Charlotte Kukunda from ACCA highlighted the need for professionals to adapt to the rapidly evolving technological landscape.
“The pace of change in AI is phenomenal, and it is also scary,” she said.
Kukunda revealed that ACCA is reimagining its qualification structure to include employability modules such as entrepreneurship, digital technology, and innovation.

“We have included optional employability modules so that students can choose what makes sense for their career paths,” she explained.
ACCA’s revised qualification, set to launch in June and September 2027, will emphasize skills such as data analysis, financial investment, and sustainability reporting.
She encouraged students to embrace AI while strengthening human intelligence.
“Accountants are embracing artificial intelligence and exploring its potential while paying attention to the risks,” she said.
Meanwhile, Douglas Opio, Executive Director of the Federation of Uganda Employers, challenged students to consider becoming employers.
“We have an acute shortage of employers,” he said.
Opio emphasized the importance of strong theoretical foundations, describing theory as the basis for practical innovation.

“Theory is like the operating system of practice,” he noted.
He urged students to view skills as a renewable resource that can drive growth and innovation.
“AI must be part of the skill set that you actively look for,” he added.
The NSSF Career Expo, launched in 2010, aims to bridge the gap between education and employment by equipping students and graduates with the skills, knowledge, and networks needed to thrive in the modern workforce.
The event promotes a culture of saving, innovation, and entrepreneurship while bringing job opportunities closer to students.

Key features of the expo include career guidance and counseling, job opportunities, entrepreneurship training, mentorship, and networking platforms. This year’s expo is being held in 15 universities across Uganda, including Makerere University, Kyambogo University, and Uganda Martyrs University, Nkozi.
Trending
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMakerere University commemorates 13 transformative years of partnership with Mastercard Foundation
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMakerere University and World Bank Sign Partnership to Strengthen Environmental and Social Sustainability Capacity
