Education
Research shows need for training of staff and students on online learning
Published
3 years agoon

Learners were found to be unsatisfied with Blended learning pedagogy
Education is no longer just about putting pen to paper and memorizing facts. Today, innovative educators in higher education are improving learning through technology, as evidenced by the rapid adoption of technology-assisted teaching methods and blended learning (BL) models.
Blended learning integrates technology and digital media with traditional instructor-led classroom activities, giving students more flexibility to customize their learning experiences.
Although Blended learning has existed in Makerere University since 1991 in the Department of Open and Distance learning, this mode of teaching only recently became common place owing to the Covid-19 pandemic.

Following the Covid-19 lockdown, which resulted in the closure of the education sector, Makerere University was forced to adopt emergency Online and Distance e-learning (ODeL). The university since 2019 has adopted blended learning across all disciplines in the university.
The power of blended learning methods, however, lies in their ability to improve the student experience. It is against this background that a team of researchers set out to evaluate blended learning at Makerere University. Led by Arthur Mugisha, the Principal Investigator, the team set out to study how students understood the blended learning pedagogy, how they used BL during the pandemic, how respondents found BL, peer’s opinions on BL excitement and how BL could be made more exciting.
The study conducted for from December 2021 until July 2022 showed that 66% of the students/ respondents claimed to have a clear understanding of BL pedagogy to be a mixture of face to face and online modes of teaching and learning.

However, only 36% of the respondents found BL to be exciting due to: the flexibility and convenience it brings in the learning, the opportunity to be exposed to new learning technologies like zoom, reduced transport-accommodation-meal costs and disease spread, self-paced learning through downloaded materials, act of bringing the University closer to the communities and competence-based learning leading to promotion at places of work and unfortunately the ability to cheat exams.
The other percentage of 64% was not excited about BL because of the challenges it posed such as; consumption of data, poor network connectivity, length of exams (more than 24 hours), absence of a clear timetable, system failures and technology illiteracy among other things.
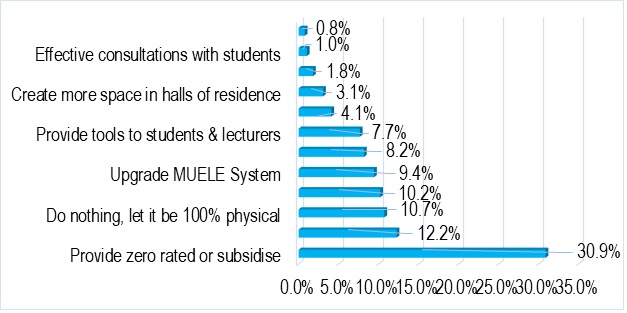
The students made some suggestions which they hope will make BL more exciting. These include a zero-rated system, upgrading the MUELE system (Makerere University E-learning Environment) and training for lecturers and students among other things.

The research team also evaluated the readiness of learners for BL pedagogy as well as the forms of learner support received. Only about 42% reported to have received training on the use of online platforms while 19% reported having received financial assistance, data/Wi-Fi and study gadgets from friends and relatives.
Research also showed that 51% of the respondents were and are ready to take on BL for continuity while 49% were skeptical and critical making them reluctant to embrace BL
An evaluation of the use of MUELE showed that 82.5% of the respondents found it difficult to navigate the teaching platform. About 98.5% could not join a group on MUELE. The students reported that they did not find the platform user friendly. This, Mr Arthur Mugisha said, calls for some changes on the learning platform.
Learners were found to be unsatisfied with Blended learning pedagogy.
Over 90% of the students reported not to have received guidance from their lecturers while also feedback on coursework submitted was also slow. It was also noted that majority of the students that required practical/ clinical experiences never received them during the online learning. Results showed that about 80% of the students were disappointed with the online examination system.
Some of the challenges identified with Blended learning are listed in the table below.
| BL challenges during Covid-19 | Frequency | Percentage |
| High cost of data | 231 | 29.6% |
| Poor network | 218 | 27.9% |
| No or little practical sessions | 42 | 5.4% |
| Acquisition of learning devices and their functionality | 41 | 5.2% |
| Other interruptions in environment | 41 | 5.2% |
| Difficulty in accessing MUELE | 40 | 5.1% |
| Limited screen sharing by lecturers | 37 | 4.7% |
| System inefficiencies | 33 | 4.2% |
| Unreliable power/electricity supply | 30 | 3.8% |
| Lack of a clear timetable to follow | 21 | 2.7% |
| Poor communication/misinformation | 19 | 2.4% |
| Unnecessary movements-staggered reporting with associated costs | 10 | 1.3% |
| Disruptions from unmuted Microphones | 8 | 1.0% |
| Virus leading to jamming and hanging | 4 | 0.5% |
| Less time during exams/inconsistencies in timing | 3 | 0.4% |
| Low motivation for online study | 2 | 0.3% |
| Phishing or frequent adverts | 1 | 0.1% |
| Total | 781 | 100% |
The learners also identified some possible solutions to the challenges. These include;
| Potential solutions to BL challenges | Frequency | Percentage |
| Reduce data costs | 166 | 31.9% |
| Go back to face-to-face | 107 | 20.5% |
| Stabilise internet or network connectivity | 69 | 13.2% |
| MUELE system improvement/upgrade | 50 | 9.6% |
| Provide compliant learning gadgets | 27 | 5.2% |
| Lecturers should fully be available online | 24 | 4.6% |
| Improve learner support systems | 22 | 4.2% |
| Provide more flexible time tabling | 13 | 2.5% |
| BL is good except for practicals | 12 | 2.3% |
| Explore other platforms beyond MUELE | 6 | 1.2% |
| Create central information repositories | 6 | 1.2% |
| Provide reliable alternative power sources | 6 | 1.2% |
| Host should regulated unmuted microphones | 4 | 0.8% |
| Consult students during decision making | 4 | 0.8% |
| Provide more time to submit online exams | 3 | 0.6% |
| Create BL regional centres of Excellence | 2 | 0.4% |
| Total | 521 | 100.0% |
The research study recommended BL must be practiced but also improved. Other recommendations include;
- Once practiced, BL should cut cross both academic and non-academic units of the University.
- Top Makerere University management needs to take interest in adequately financing and staffing the Institute of Open, Distance and eLearning
- On ensuring number 3 above, there is need to attach ODeL specialists (champions) to each of the University units with clear terms of reference.
- It is hoped that in the near future regional BL centres of excellence will be created and specialists attached to support off-campus BL activities.
- In regard to regional BL centres of excellence, subsidising players who provide alternatives to hydro power to ensure that the remotest of learners is able to participate in BL.
- Introduce a basic BL course for both lecturers and learners
- Promote the Bring-Your-Own-Device approach for sustainability. Communicate it to the students’ community, parents and/or sponsors

While speaking during the dissemination workshop, NCHE director of Quality Assurance, Dr Pius Achang who represented the Ed of NCHE, Prof. Mary Okwakol, called on Makerere University to extend support to other institutions of learning because “while NCHE rolled out e-learning, acceptability has been hard”. He hoped that the findings of the research will inform policy on blended learning.
On his part, the Deputy Vice Chancellor (Finance and administration) Prof. Henry Alinaitwe, who represented the VC called for continued training of both staff and students in an effort to improve BL uptake. He called on CEES to offer training to all staff inform of teacher training for many lecturers have no teacher training experience.
The Principal of CEES, Prof. Anthony Muwagga Mugagga, called on the government to fund the evaluation of blended learning across the country. The government called on the College of education to support e-learning during the lockdown so it is important that an evaluation of that mode of teaching be done. He thanked the government of Uganda for its continued support to research as the university moves towards becoming a research-led institution. Prof. Mugagga called on the Ministry of Education and Sports to support the collect with ICT equipment as well as support he IODEL centre so that it can offer training in BL across the country.

He called for uptake of digital technologies but also warned against its dangers such as spread of pornographic materials.
The Director of IODel, Prof. Paul Muyinda Birevu, noted that a similar evaluation among teaching staff had been done so it was important for the team to evaluate the students’ uptake and affordances of blended learning.
Dr. Stephen Wandera, from MakRIF congratulated the project team upon winning the grant and successfully disseminating the findings. He called on the improvement of MUELE to make it for interactive for both staff and students. He encouraged the PI to offer some policy guidance on Blended learning.
PROJECT TEAM
- Arthur Mugisha
- Prof. Paul Birevu Muyinda
- Dr. Joshua Bateeze _ KCCA
- Dr. Harriet Najjemba
- Dr. Robert Ayine- NCHE
- Prof. Jessica Norah Aguti – Busitema University
Project Admin
Rose Akanya
You may like
-


Makerere University commemorates 13 transformative years of partnership with Mastercard Foundation
-


200 UVTAB students graduate: CEES emphasizes Skills, Integrity and Community Impact
-


CAES Presents Overall Best Performing Student in the Sciences & a Record 28 PhDs at the 76th Graduation Ceremony
-


Graduation marks the next phase of accountability, graduates told
-


Over 9,200 to graduate at Makerere University’s 76th Graduation
-


Mak 76th Graduation Ceremony: CEES Celebrates Academic Excellence, with 27 PhDs
Education
200 UVTAB students graduate: CEES emphasizes Skills, Integrity and Community Impact
Published
5 days agoon
February 28, 2026
28th February 2026– On 28th Feb 2026, 200 students examined by the Uganda Vocational and Technical Assessment Board (UVTAB) were awarded National Diplomas and Certificates during the 7th graduation ceremony organized by the Centre for Lifelong Learning (CLL) under the College of Education and External Studies (CEES) at Makerere University.
The occasion marked a significant milestone not only for the graduates, but also for the university’s expanding lifelong learning and technical education mandate.
Speakers described the ceremony as a celebration of partnership, and the growing recognition of skills-based education as a driver of national transformation.

The celebration brought onboard graduands, parents and guardians. At the ceremony, the Principal of CEES, Prof. Anthony Muwagga Mugagga was represented by Prof. Paul Muyinda Birevu, the Director of the Institute of Open, Distance and e-Learning. The following University officials also graced the ceremony: Dr. Harriet Nabushawo-Dean, School of Distance and Lifelong Learning, Dr. Marjorie Batiibwe-Head, Department of Science, Technical and Vocational Education, Dr. Oscar Mugula-National Coordinator, Centre for Lifelong Learning, Dr. Rose Atugonza-former Coordinator of the Centre, and members of staff at the Centre for Lifelong Learning.

Vice Chancellor congratulates UVTAB graduates
The Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe conveyed his regards, and congratulated the students, the Centre for Lifelong Learning under College of Education and External Studies (CEES), as well as, the College of Engineering, Design, Art and Technology (CEDAT) upon this academic milestone built on partnership, skills development, and lifelong learning.
In a special way, Prof. Nawangwe credited the students, supervisors, and instructors for undertaking the real-life project, which led to the construction of the wall fence at Makerere College School.
The wall fence constructed by students pursuing the National Diploma for Architecture, and Civil Engineering, was unveiled on 12th November 2025, and handed over to the Head Teacher of Makerere College School, Dr. Martin Muyingo.
A Milestone Built on Sacrifice and Partnership

Addressing the congregation of graduates, parents, guardians, instructors, and invited guests, Dr. Oscar Mugula, the National Coordinator of the Centre for Lifelong Learning, acknowledged the sacrifices made by families.
“Today is not only about certificates and diplomas,” he said. “It is about the journey you have walked — the sleepless nights, the tuition sacrifices, the encouragement, and the belief that education changes lives.”
He thanked parents and guardians for standing by the students throughout their studies, describing their investment in education as one that yields long-term dividends for families and communities.
The graduation ceremony underscored the importance of institutional collaboration. Dr. Mugula extended gratitude to the leadership and management of CEDAT for the strong partnership that has enabled the Centre for Lifelong Learning to train and mentor students effectively. He commended instructors and trainers whose dedication shaped the graduates’ academic and professional growth.
“Our instructors have not only taught content,” he noted. “They have moulded character, built competence, and instilled discipline.”
Skills and Entrepreneurship are the New Currency
The Principal of CEES, Prof. Anthony Muwagga Mugagga, in a speech read by Prof. Paul Muyinda Birevu, the Director of the Institute of Open, Distance and e-Learning, emphasized that the qualifications awarded represent more than academic success — they signify practical competence.
“These qualifications certify knowledge, and affirm your ability to apply what you have learned in real-world contexts.”
The Principal reminded graduates that technical and vocational education is inherently practical, designed to solve problems and respond to industry demands.
“You are entering society at a time when skills are the new currency,” he stated. “Uganda needs technicians, innovators, engineers, administrators, planners, and entrepreneurs who can deliver results.”
The graduates received awards in diverse fields, including architecture, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, accountancy, public administration and management, business administration and management, and project planning and management.
Embracing entrepreneurship
Prof. Mugagga called upon the graduates to embrace entrepreneurship. “Entrepreneurship begins with identifying the need of your society/community. I encourage you to master your craft/skill, and learn to work with teams, and develop a positive attitude towards work,” he said.
Graduation as the Beginning of Responsibility
While celebrating academic achievement, speakers cautioned graduates against viewing graduation as the final destination. “Today marks the end of one chapter,” Prof. Mugagga observed, “but it is the beginning of responsibility.”
He urged them to pursue mastery in their respective disciplines, emphasising that competence must go beyond minimum standards. “Be the graduate who says, ‘Give me the task, and I will deliver,’” he challenged.

Graduates were encouraged to build professional identities anchored in integrity, reliability, and innovation. They were advised to maintain professional networks formed during their studies and to continue learning in order to remain relevant in a rapidly evolving global environment.
Dr. Mugula echoed this call, describing the graduates as “designers of change and leaders of tomorrow.” “You have crossed a bridge,” he said. “What lies ahead depends on the choices you make from today.”
Recognized Qualifications and Standards for further education
A key highlight of the ceremony was the reaffirmation that the diplomas and certificates awarded are nationally and internationally recognised under the Government of Uganda through UVTAB.
“The custodian of these awards is the Government of Uganda,” Dr. Mugula emphasized. “These qualifications meet standards required for further education and professional advancement.”
He encouraged graduates not to stop at the diploma or certificate level, but to consider advancing to degree programs locally and internationally. “A new journey begins today,” he said. “Plan for your dream degree. Take yourself to the next level.”
The message resonated strongly with students who had progressed from certificate level to diploma level — a transition celebrated during the ceremony as a testament to determination and growth.
Recognising Academic Excellence
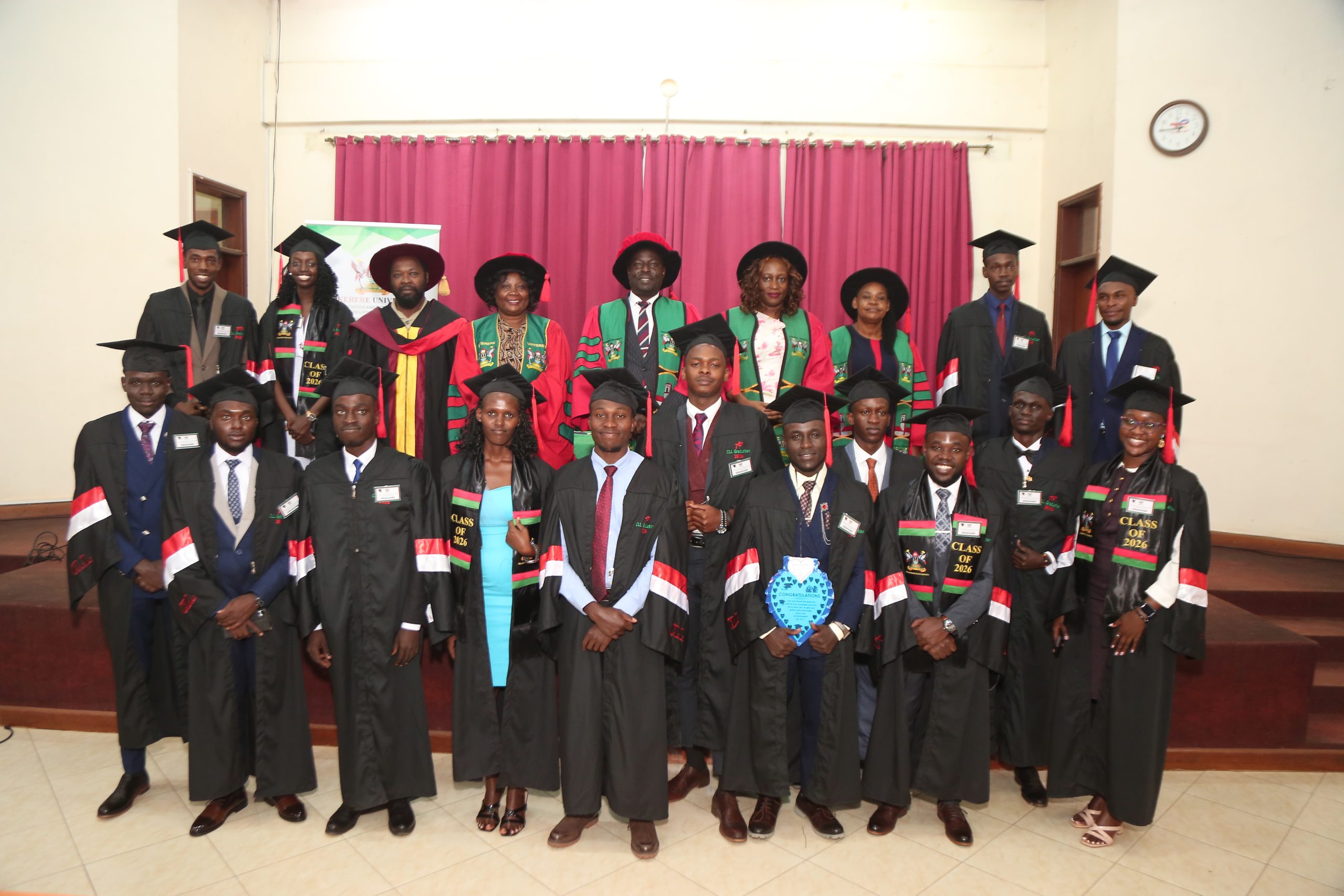

The ceremony also celebrated outstanding performers who graduated with First-Class Diplomas (GPA 4.4–5.0).
Among those recognised were:
Diploma in Public Administration
• Giibwa Dennise Kivumbi (4.63)
• Hussein Omar (4.41)
• Ssentale Peter (4.50)
National Diploma in Business Management
• Oyella Vivian Mildred (4.48)
National Diploma in Accountancy
• Nakiboneka Ritah (4.43)
• Nabaasa Annah (4.65)
• Olupot Jorem Dominic (4.42)
• Mulindwa Ashraf (4.53)
National Diploma in Civil Engineering
• Masaakate Joshua Robinson (4.53)
• Tamale Arafah (4.51)
• Kulumba Anwar (4.59)
Their achievement was met with applause from the audience, serving as inspiration to fellow graduates.
Giving Back to the Community
Beyond personal advancement, graduates were urged to remain ambassadors of the Centre for Lifelong Learning. “Most young people out there are not aware of these opportunities,” Dr. Mugula said. “Guide them. Encourage them to seek institutions whose qualifications are recognised.”
He called upon graduates to mentor others, share knowledge, and uplift communities. “That is how we build a stronger society,” he said. “You have come, you have seen, you have experienced. Now help others to benefit.”
The Centre’s motto — “Taking the University to the Communities and bringing the Communities to the University” — was highlighted as a reflection of its outreach philosophy. Established in 1953 as the Department of Extra-Mural Studies, the Centre has evolved into Makerere’s primary unit for community training and lifelong learning initiatives.
Character, Discipline, and Faith
In addition to academic and professional counsel, speakers emphasised moral grounding and discipline.
Graduates were advised to uphold integrity in their workplaces, avoid shortcuts, and resist societal pressures that undermine professionalism. “Your character will sustain your success,” Prof. Muyinda Birevu remarked. “Skills will open doors, but integrity will keep you in the room.”.
A Growing Role in Uganda’s TVET Landscape
The ceremony reflected Uganda’s broader efforts to strengthen Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET). The partnership between Makerere University and UVTAB demonstrates how universities and national assessment bodies can collaborate to expand access to quality, standards-based technical education.
Speakers commended the government for supporting TVET reforms and reaffirmed Makerere’s commitment to inclusive education pathways that serve both traditional and non-traditional learners.
As industries evolve and technology reshapes economies, the demand for competent, adaptable professionals continues to grow. The graduates, drawn from multiple disciplines, are positioned to contribute meaningfully to national development.
Looking Ahead
For the 200 graduates, the ceremony symbolised achievement earned through hard work and perseverance. Yet, as repeatedly emphasised, it also marked a beginning.
They leave equipped with recognised qualifications, practical training, and the encouragement of mentors and families. They carry the responsibility to apply their knowledge ethically, pursue continuous improvement, and uplift their communities.
As the event drew to a close, the central message remained clear: Graduation is not merely a celebration of past effort — it is a launchpad for future impact.
“Go out and seek jobs with confidence — you have the skills,” Prof. Muyinda Birevu told them. “Create jobs with courage — you have the innovation.”
With that charge, applause filled the hall, marking not just the award of diplomas, but the commissioning of a new cohort of skilled professionals ready to transform society.
Education
Mak 76th Graduation Ceremony: CEES Celebrates Academic Excellence, with 27 PhDs
Published
1 week agoon
February 24, 2026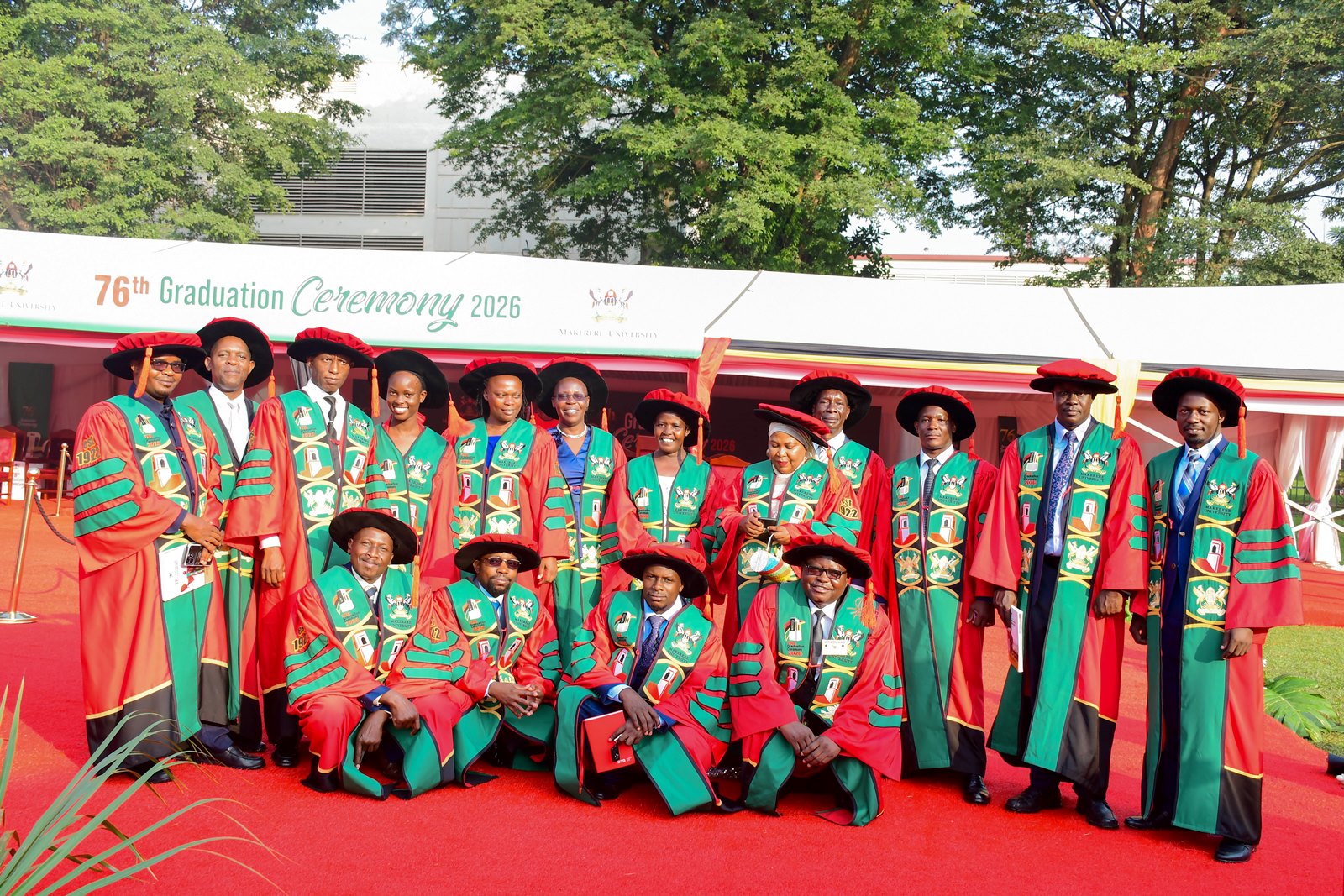
24th February 2026– Makerere University officially commenced its 76th Graduation Ceremony, setting the stage for a four-day celebration of academic excellence scheduled to run until 27th February 2026. The landmark event brought together government and university officials, faculty, staff, graduands, parents and guardians, development partners, and the media, in a vibrant display of achievement. A total of 9,295 graduands were presented by the respective colleges for the conferment of degrees and the award of diplomas and certificates.
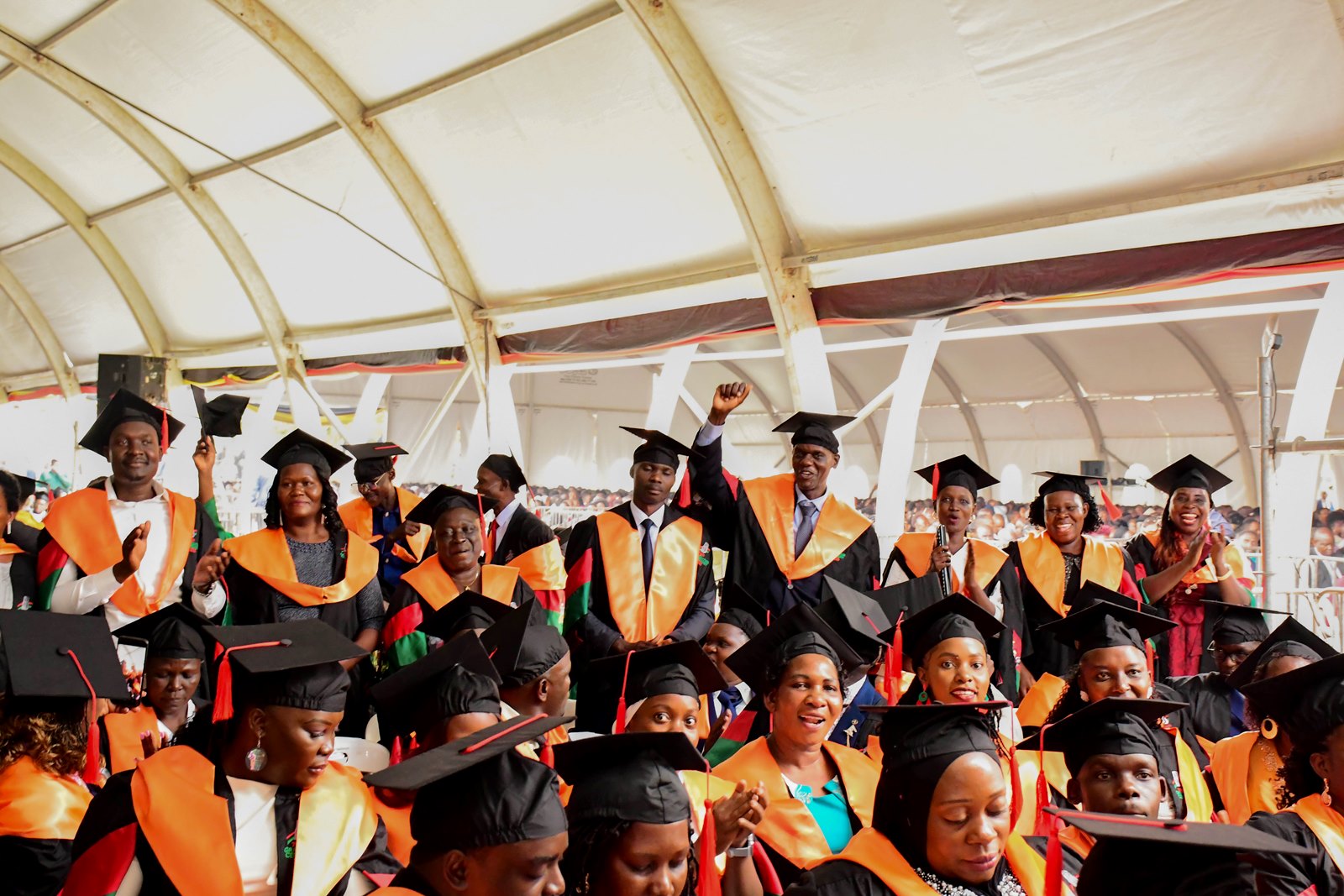

On the first day, presided over by the Chancellor, Hon. Dr. Crispus Kiyonga, the congregation at the Freedom Square witnessed Principals, Deputy Principals, Deans and faculty presenting students for graduation from the following colleges: Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES), Education and External Studies (CEES), Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS) and the School of Law.
CEES Graduation Statistics
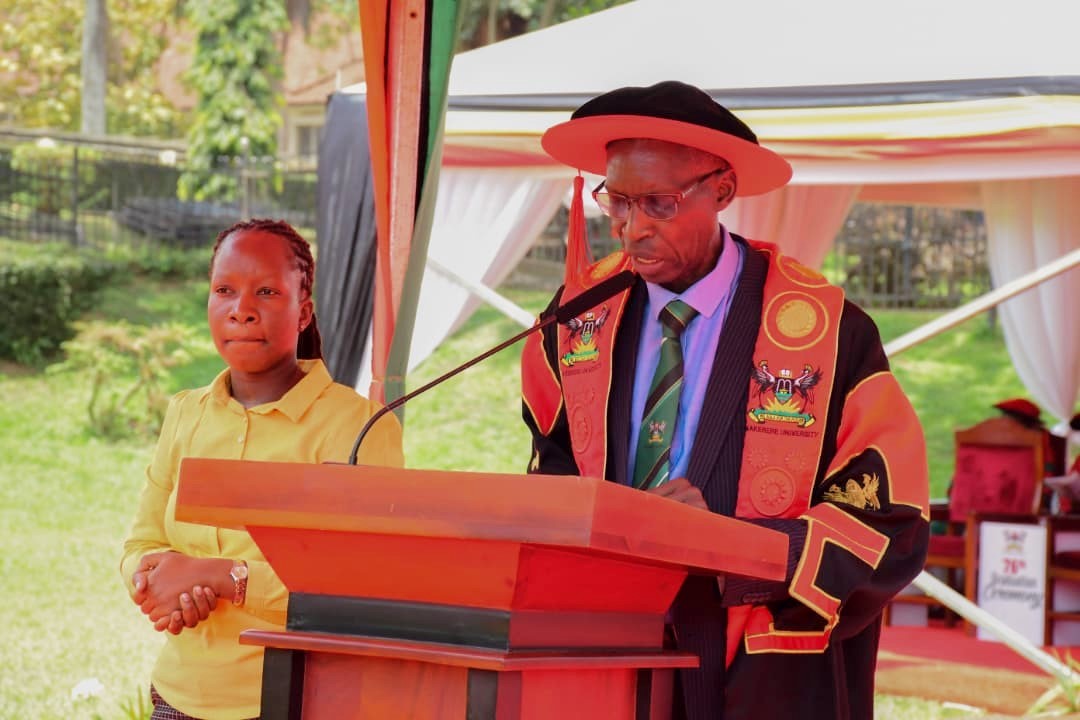

The College of Education and External Studies (CEES) presented 824 graduands for the conferment of degrees and the award of diplomas. These included 27 Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degrees, 106 Master’s degrees, 111 Postgraduate Diplomas, 572 Bachelor’s degrees, and 8 Diplomas—a reflection of the College’s strong postgraduate research profile and its continued investment in advancing professional and teacher education.
CEES champions digital transformation and Competence-Based Education
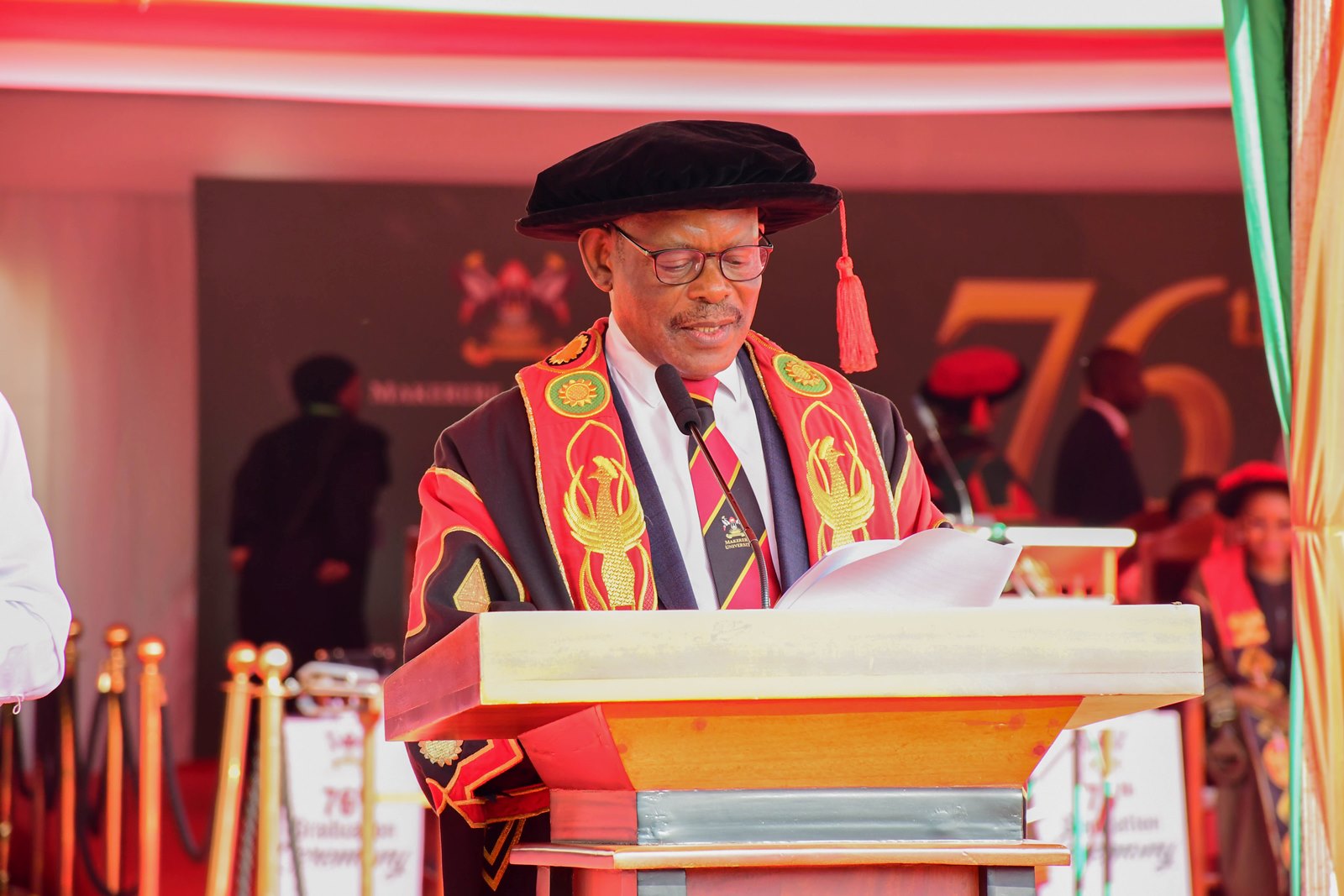

Addressing the congregation, the Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe, underscored the strategic role of the College of Education and External Studies (CEES) in driving the University’s digital and pedagogical transformation. He observed that CEES has remained at the forefront of championing Makerere’s digital agenda, notably through the institutionalisation of the Institute of Open, Distance and eLearning.
“The College of Education and External Studies continues to play a pivotal role in Makerere University’s digital and pedagogical transformation by Championing the digital transformation of Makerere University. In pursuit of digital transformation, Makerere University institutionalised the Institute of Open, Distance, and eLearning effective January 1, 2025. The College, through the Institute of Open, Distance, and eLearning, in collaboration with the College of Engineering, Design, Art and Technology (CEDAT), is implementing a KOICA-funded project aimed at enhancing the distance education environment at Makerere University,” Prof. Nawangwe said.
The Vice Chancellor noted that the initiative reflects Makerere’s deliberate shift towards innovative, technology-enabled learning models designed to expand access, enhance quality, and position the University as a leader in digital higher education in the region.
He explained that the initiative has already yielded significant milestones, including the development and approval of a 10-year Distance Education Master Plan (2025–2035), the construction of a four-storey Open, Distance and eLearning Centre, and the capacity building of academic staff in multimedia e-content production.
He emphasized that these efforts, alongside the ongoing Phase II of the eLearning Initiative supported by the Mastercard Foundation, demonstrate Makerere’s resolve to integrate online and face-to-face learning in expanding access to quality higher education.
Affirming CEES’ growing continental stature, the Vice Chancellor applauded the College for its leadership in advancing Competence-Based Education (CBE) across Africa. He reported that in 2025, CEES successfully coordinated eight partner institutions and secured a prestigious €1 million ERASMUS+ grant to spearhead the institutionalisation of CBE in East and West Africa.
Through the Transitioning Higher Education Regulators and Universities to Competence-Based Education (TRUCE) initiative, he noted, the College is working collaboratively with regulatory bodies, universities, and industry stakeholders to realign teaching methodologies, assessment frameworks, and digital integration towards demonstrable learner competencies that respond to labour-market demands and societal priorities.
Graduates urged on entrepreneurship and employment
To the graduates, Prof. Nawangwe reminded them of the prestige and responsibility that comes with a Makerere degree, “You are graduating with a degree from one of the best universities on earth. We have equipped you with the knowledge and skills that will make you employable or create your own businesses and employ others. Do not despair if you cannot find employment; instead reflect on the immense opportunities around you and rise to the occasion as an entrepreneur. Do not despise humble beginnings. To the graduands of PhDs, you are now global science citizens. Africa expects much from you. Use your degree to transform our Continent.”
Funding of Research and Innovation
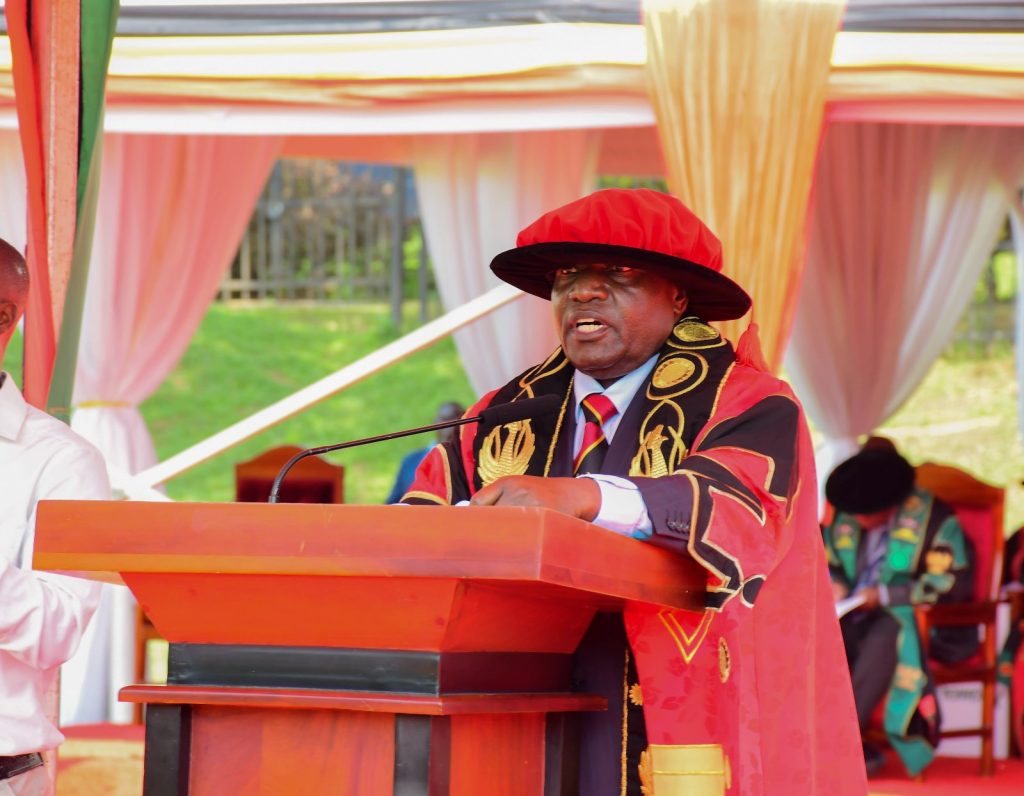

The Chancellor, Hon. Dr. Crispus Kiyonga stated that research plays a very vital role in the development of any community. In this regard, the Chancellor thanked the government of Uganda for committing UGX 30 Billion through the Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund (MakRIF). He lauded the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation Secretariat-Office of the President for supporting research initiatives at Makerere University aimed at promoting home grown solutions to our various challenges.
The Chancellor called upon the graduates to tap into opportunities at the University to broaden their knowledge on the world, communities and societies.
Government Commits USD 162 million concessional loan for Laboratory and Infrastructural development, orders shift to Competence-Based Education.
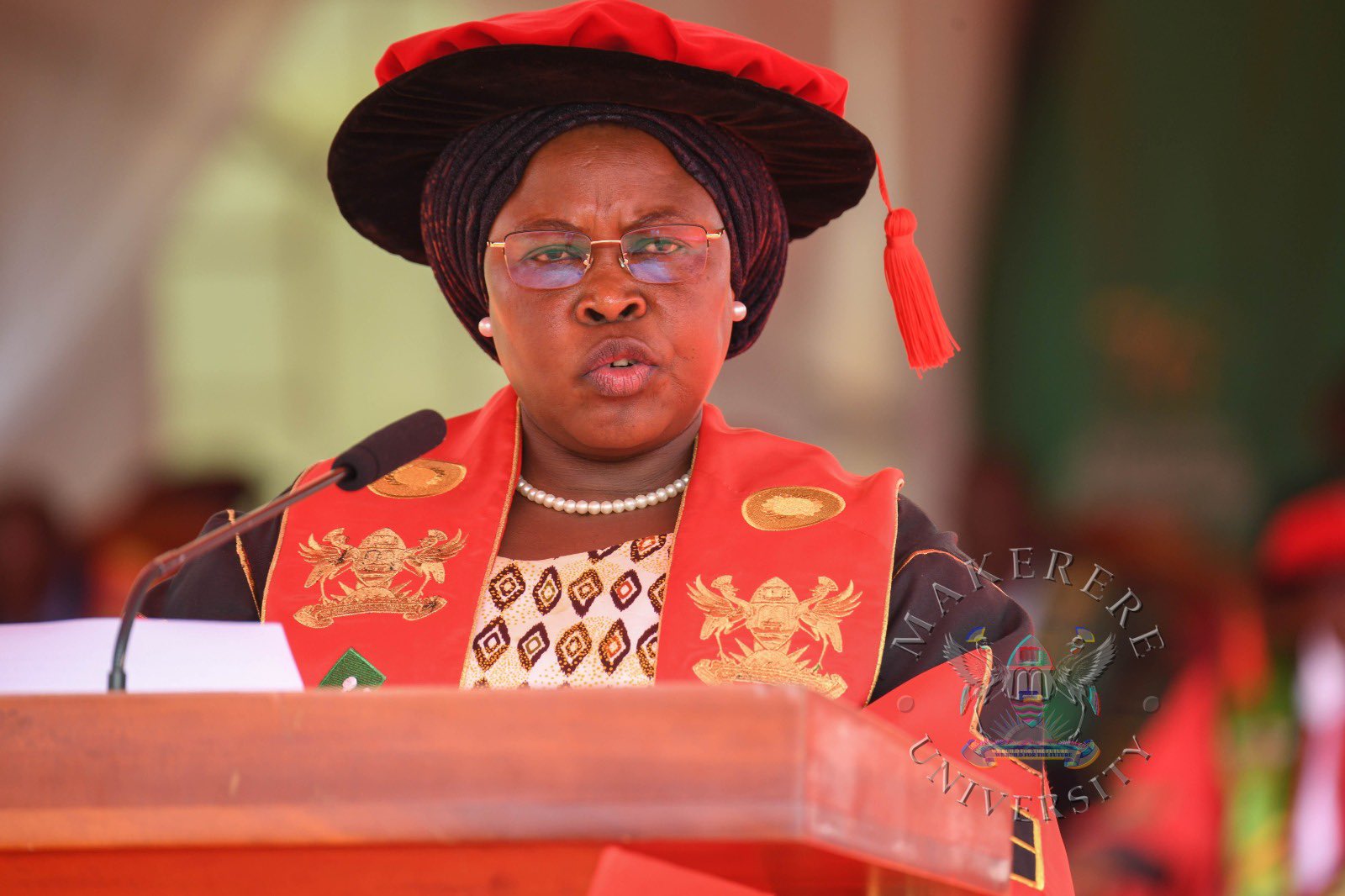

The Guest of Honour, Hon. Janet Kataaha Museveni, Minister of Education and Sports and First Lady of Uganda, represented by State Minister for Primary Education, Hon. Dr. Joyce Moriku Kaducu, commended Makerere University for its pivotal role in nurturing leaders, sharpening scholars, and giving direction to dreams. She congratulated the University Council, management, staff, and graduands for their dedication, noting that Makerere continues to serve as a model institution for academic excellence and national development.
Addressing the transition to Competence-Based Education, the Minister restated the directive that all higher education institutions must prepare for full implementation of Competence-Based Education and Training by July 2027. She urged Makerere University, and particularly CEES, to lead in curriculum reform, staff training, and infrastructure development to ensure graduates are equipped with practical skills, innovation, and problem-solving abilities.
“As we celebrate today’s achievements, we must also look far to the future. I reiterate a key directive from the Ministry of Education and Sports: all institutions of higher learning must prepare for the full implementation of Competence-Based Education and Training by July 2027. This is not merely a policy change; it is a fundamental shift in how we prepare our graduates. We are moving toward a model that emphasizes practical skills, innovation, and problem-solving. I request the Vice Chancellor and your team to lead the way in curriculum reform, staff training, and infrastructure development to make Competence-Based Education (CBE) a reality,” she said.
The Minister highlighted the Government’s deliberate investments in higher education, particularly in research, innovation, infrastructure, and academic development. She underscored key initiatives including the Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund (Mak-RIF), which supports high-impact research and innovation addressing national priorities, and the USD 162 million concessional loan for modernizing university infrastructure, including state-of-the-art laboratories and smart classrooms. The minister reaffirmed the Government’s commitment to strengthening higher education through research funding, digital transformation, and strategic partnerships, emphasizing that universities must not only produce graduates but also solution-makers and job creators.
In her message to the graduands, the minister urged graduands to use their degrees to solve problems and create jobs, emphasizing the need for innovators, engineers, healthcare professionals, and educators. She encouraged them to stay adaptable, creative, ethical, and committed to lifelong learning, while seizing opportunities like the Parish Development Model to drive sustainable community transformation.
Commencement Speaker encourages Knowledge with Purpose and Service with Integrity
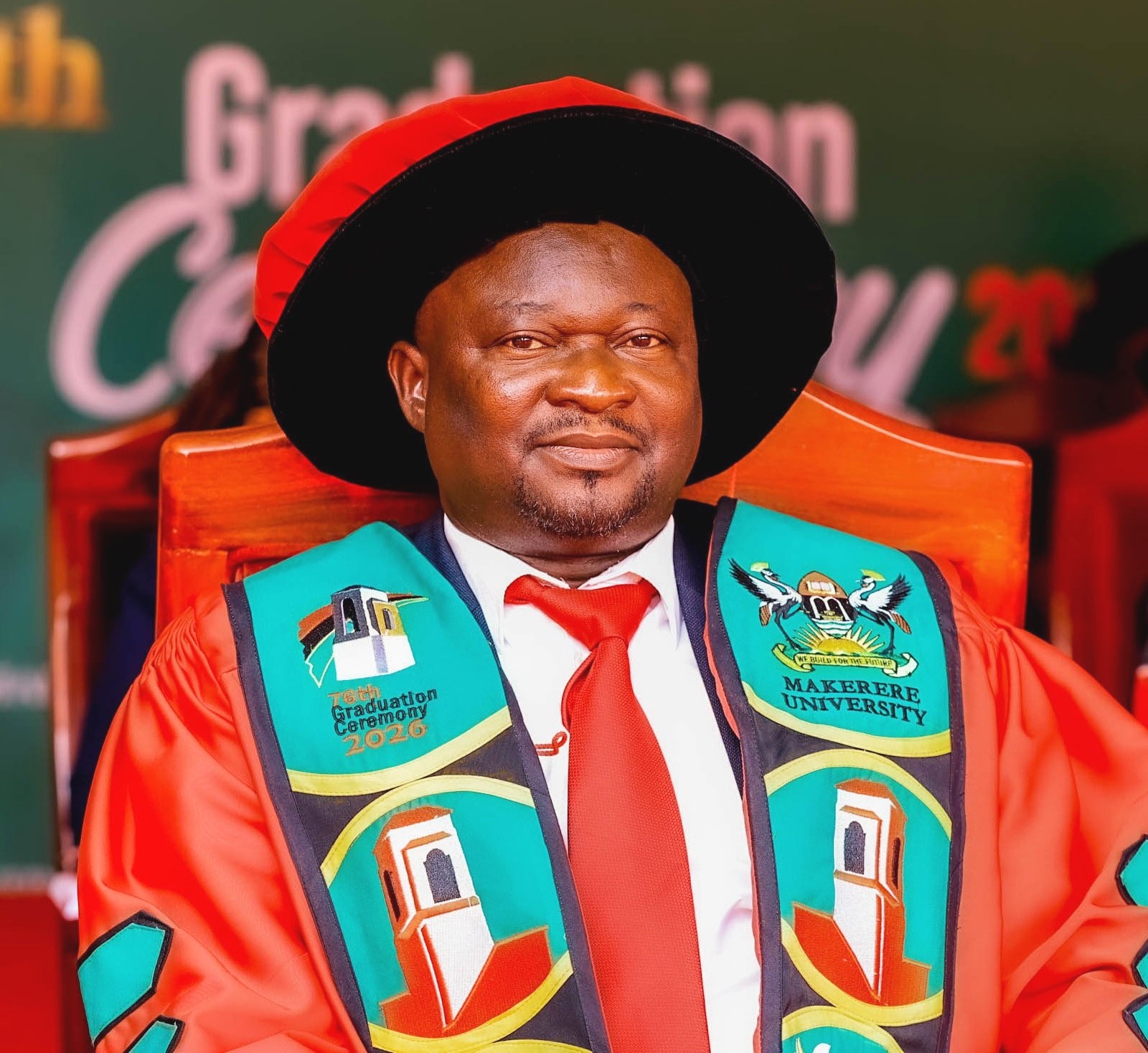

Delivering the commencement address under the theme “Knowledge with Purpose, Service with Integrity”, Prof. Nicholas Ozor, Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network, reminded graduates that Makerere University has long been a beacon of scholarship and a home for thinkers, innovators, reformers, and leaders. From its halls have emerged presidents, jurists, scientists, educators, technologists, and agricultural pioneers whose work has shaped Uganda, the continent, and the world. Prof. Ozor informed graduands of the storied legacy they had joined, marking both the end of one chapter and the beginning of another; one that demands knowledge, courage, creativity, integrity, and service.
“From these halls have emerged presidents, jurists, scientists, educators, technologists, and agricultural pioneers whose ideas have shaped not only Uganda, but the continent and the world. Among those who studied here are former Presidents such as Julius Nyerere, Mwai Kibaki, Milton Obote, Benjamin Mkapa, and Joseph Kabila. Graduates, today you join this storied legacy of a great citadel of learning. This moment did not come cheaply. It was earned through late nights, failed attempts, financial strain, resilience, and persistence. Today we celebrate your achievement—but even more, we recognize your responsibility,” he articulated.
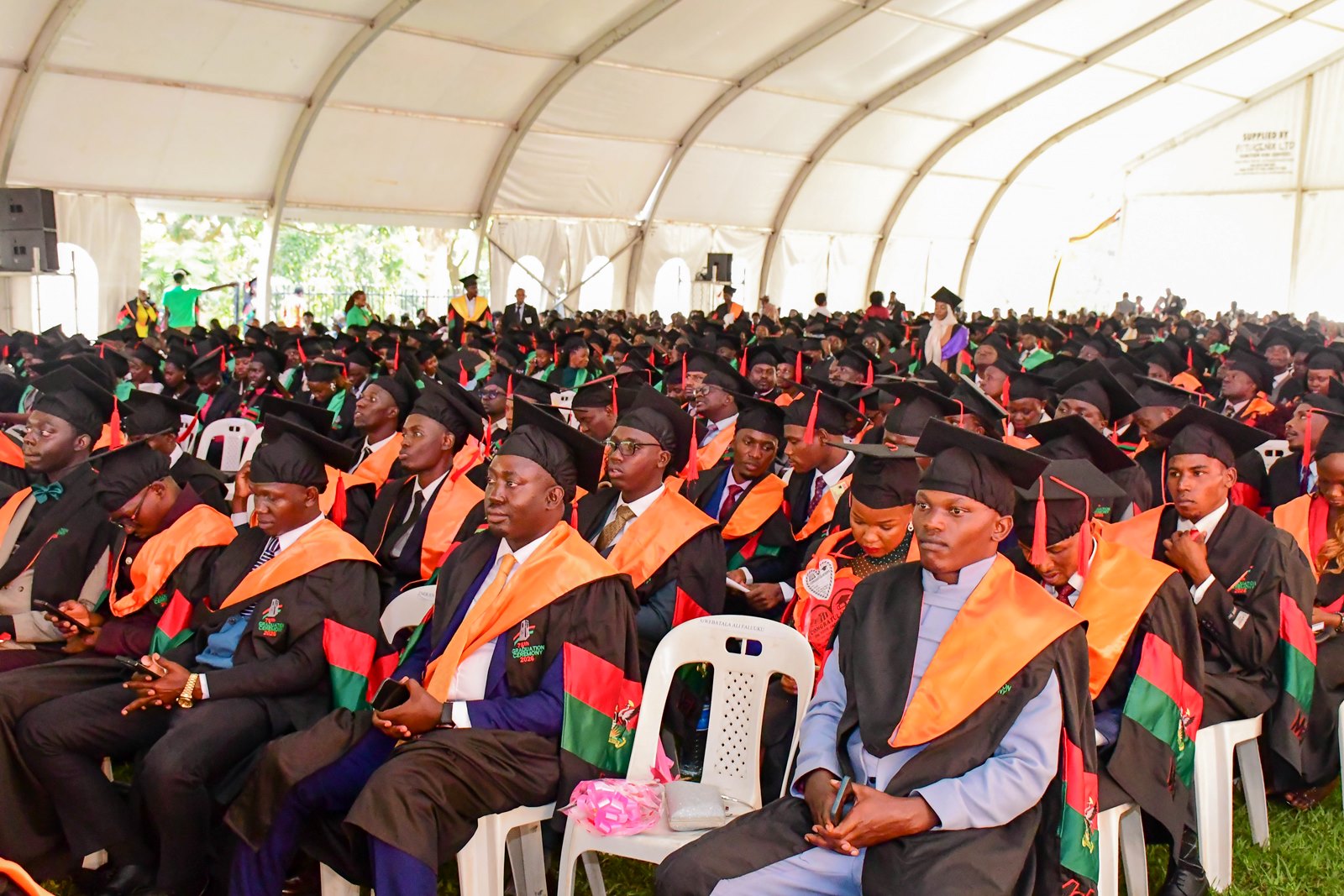

Addressing the CEES graduands, he emphasized that they are custodians of the future, noting that the quality of teachers directly shapes the future of nations. He urged them to never underestimate the power of the classroom, to teach not only for examinations but for understanding, to teach both content and character, and to cultivate critical thinking rather than rote knowledge. He described education as quiet work whose impact echoes across generations.
Beyond CEES, Prof. Ozor delivered key lessons for all graduates, stressing that character, integrity, humility, and resilience will outlast certificates and grades. He encouraged them to embrace lifelong learning, choose purpose over comfort, build character before career, serve something larger than themselves, and believe in Africa by taking initiative to solve its challenges. He pointed out that failure is part of growth, urging them to let it refine rather than define them.
He acknowledged the sacrifices of parents and guardians, noting that their financial, emotional, and spiritual support is embedded in every certificate awarded. Prof. Ozor concluded with a call for graduates to carry the values of Makerere into the world, whether in government, private sector, civil society, academia, or entrepreneurship. He encouraged them to build justice, minds, systems, and sustainable futures, honoring their families, their nation, and the University itself, reminding them that the future is watching and waiting for their contribution.
Photo Credit: Christopher Kaahwa – Communications Practitioner
Education
Facilitating Access and Participation through Higher Education Access Programmes and Connected Education for Students with Refugee Backgrounds: A Global South Delphi Study
Published
3 months agoon
December 19, 2025
On 17th December 2025, a Delphi workshop was convened at Kampala Kolping Hotel, providing a collaborative platform for dialogue on standardisation and harmonisation of Higher Education Access Programmes (HEAP) across institutions, alongside strategies for portability and verification on demand through a HEAP Digital Passport. Discussions centered on accreditation, diversification of delivery and learner support, and future scenarios for HEAP and Connected Education.
Expert panelists underscored the urgent need for:
- Standardised HEAP frameworks across universities to ensure consistency in admission pathways.
- Harmonisation of HEAP curricula, duration, and procedures to eliminate barriers that hinder access and transition.
- Development of a HEAP Digital Passport enabling portability of credentials, secure digital verification, and integration with national qualification frameworks and international recognition systems.
Uganda, is one of the leading refugee-hosting countries with inclusive education policies, faces challenges in ensuring equitable access and participation for students with refugee backgrounds. While some universities offer HEAP as a bridging programme for marginalized learners, variations in programme design, delivery, and support systems still exist, which may lead to violations of accreditation. This calls for urgent standardisation and harmonisation to strengthen HEAP as a recognized transitional pathway into higher education.

Funded by Education Beyond Borders, researchers from Makerere University and the University of Edinburgh engaged stakeholders from public and private universities in Uganda through participatory workshops and expert meetings. This Delphi Workshop aimed providing a collaborative platform for dialogue on standardisation and harmonisation of Higher Education Access Programmes (HEAP) across institutions, alongside strategies for portability and verification on demand through a HEAP Digital Passport. Discussions centered on accreditation, diversification of delivery and learner support, and future scenarios for HEAP and Connected Education. The project is led by Dr. Rovincer Najjuma (Principal Investigator), with co-PIs Dr. Rebecca Nambi and Dr. Michael Gallagher.
Listening to experiences and co-creating solutions
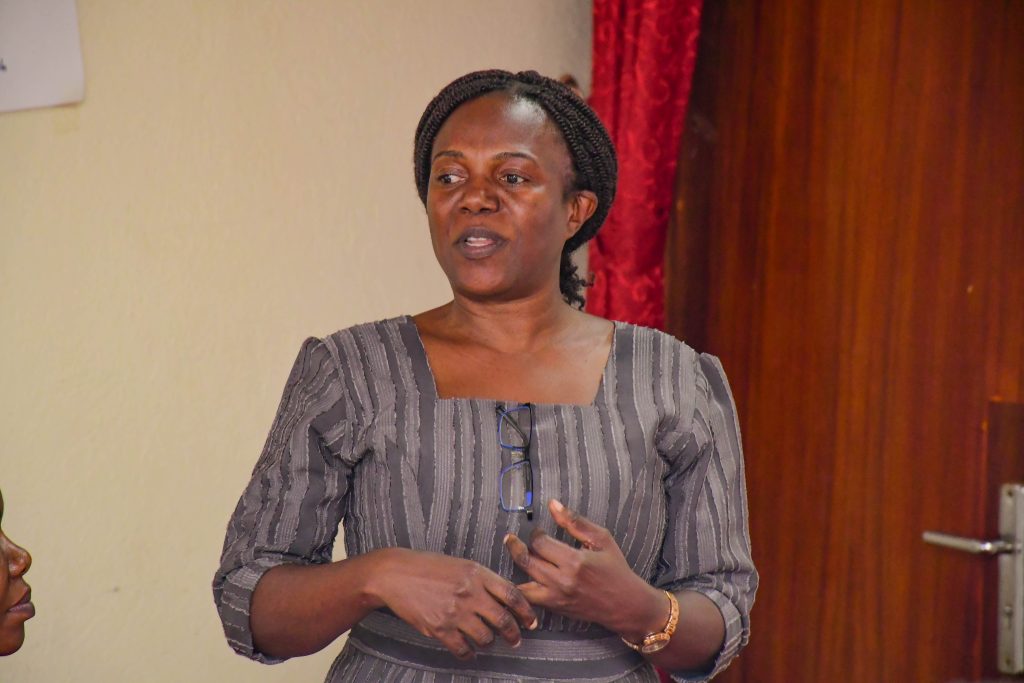

Opening the workshop, Dr. Rebecca Nambi, a Senior Lecturer at Makerere University and Co-Investigator of the project, emphasized that the engagement was not about formal presentations, but about listening to experiences of students with refugee backgrounds that have accessed Higher Education using the HEAP programme and co-creating solutions with Expert Panelists.
Highlighting the persistent disparities in refugee participation in higher education, Dr. Nambi explained that while global and national efforts often focus on primary and secondary education, higher education remains critically under-supported. Drawing on years of research, she observed that refugee participation in higher education has historically stood at three percent (3%), later improving to about seven percent (7%), leaving the highest number of refugees excluded.
“Where do they go if they do not transition to higher education?” she asked. “Who supports them and how do institutions respond when learners arrive with disrupted educational trajectories?”
Shift from mere documentation of marginalization and adversity to practical interventions
Dr. Nambi underscored the importance of moving beyond research that merely documents marginalizationa and adversity. She advocated for practical interventions that improve systems for people with refugee backgrounds and strengthening education for host communities. “Addressing refugee education is part of a broader global agenda shaped by migration, conflict, and labour mobility in several countries.”
Dr. Nambi emphasized that HEAP provides a legitimate pathway for students with refugee backgrounds, and the ongoing adjustments aim to align the program with national standards and student needs.
Central to the discussion was the concept of connected learning, which promotes flexible, blended, and digitally supported education pathways that link learners across institutions, resources, locations, and systems.
Referencing the Makerere University E-Learning Environment (MUELE) as a key enabler of digital and interactive learning between lecturers and students at Makerere University, Dr. Nambi urged other universities to explore such a digital approach to catalyze the delivery of HEAP programmes. She noted that connected education is not solely about technology, but about harmonization, recognition, and collaboration among universities and regulators.
Comparing public and private universities, Dr. Nambi observed that private universities often have more flexible access pathways, and urged that documentation of students’ experiences of HEAP is critical to understanding gaps in provision, delivery and support
“Much of our work has involved examining how Makerere University and other universities are handling access for vulnerable students. We want to document lived experiences, analyze what is working and what is not, and generate evidence that can inform policy and institutional practice,” Dr. Nambi explained.
HEAP Emerging Challenges, lived experiences and future
Moderating one of the key sessions, Dr. Rovincer Najjuma, the Principal Investigator and a Lecturer in Digital Education and the Global South at the University of Edinburgh, guided participants through delphi workshop activities; these included engaging panelists in articulating expectations, uncertainities and risks, and developing future scenarios for HEAP accreditation, diversification of delivery and support and connected education.

Using participatory methods, participants shared insights through post-it notes and group reflections, capturing perspectives from expert panelists, HEI administrators, and students with refugee backgrounds. Dr. Najjuma encouraged an open dialogue, ensuring that student voices, particularly those with refugee backgrounds were centred in the conversation by encouraging them to share their experiences and journeys of participating in HEAP programmes.
The panelists acknowledged that while the HEAC has changed the nomenclature from HEAC to HEAP, programmatic provisions need to evolve, to address the inconsistencies that remain with respect to how institutions implement HEAP, duration, curriculum, and transfer of HEAP credit across institutions. Panelists shared about the critical gaps in awareness, mentorship, orientation, and institutional readiness to implement HEAP in ways that support refugee learners effectively.

On the issues faced by students with refugee status, participants identified several recurring challenges affecting access to and participation in higher education. These included low awareness of the HEAP programmes, fragmented and uncoordinated information dissemination, and difficulties in credential recognition and transfer across institutions and country host-country education systems.
Students highlighted low self-esteem, identity struggles, and stigma, especially where access programmes are perceived as inferior to Advanced High School Certificates. They also cited financial barriers, limited digital access, mental health challenges, and lack of learner-centred teaching approaches.
Key outcomes from the workshop
Panelists outlined key expectations to strengthen access and participation, which included the development of a standardized national HEAP curriculum, with clear and uniform entry requirements, and seamless credit transfer across institutions and host countries, facilitated by the development of HEAP Digital Passport.
Mentorship emerged as a cornerstone of learner support, alongside extended orientation programmes, life skills training, and entrepreneurial education. Participants emphasized the need for blended and online learning, supported by affordable internet access and institutional investment in digital infrastructure.
Policy coherence, stakeholder engagement in policy formulation, and timely communication of reforms were identified as essential for successful implementation. Participants called for gender-sensitive curricula, student representation structures, humane and trauma-informed teaching staff, and adequate learning resources, including reference materials.
HEAP: A Structured Pathway to Higher Education
Dr. Gidraf Joseph Wanjala, Principal of the College of Education, Open and Distance Learning at Kampala International University, highlighted the evolution of access programs in Uganda.
“Historically, the higher education access framework was known as the Higher Education Access Certificate (HEAC). Last year, it was updated to the Higher Education Access Program (HEAP), reflecting a shift from a certificate to a full program, approved by the Ministry of Education and Sports,” Dr. Wanjala said.

He explained that HEAP provides structured pathways for students to progress from diploma to bachelor degree levels, from mature entry to degree programs, and from senior secondary school to higher education. “This program is inclusive of refugee students and all marginalized groups, provided there is funding and space. HEAP supports students not just academically, but also through orientation programs, mental health training, reproductive health education, and gender-responsive support,” Dr Wanjala stated.
Challenging Misconceptions
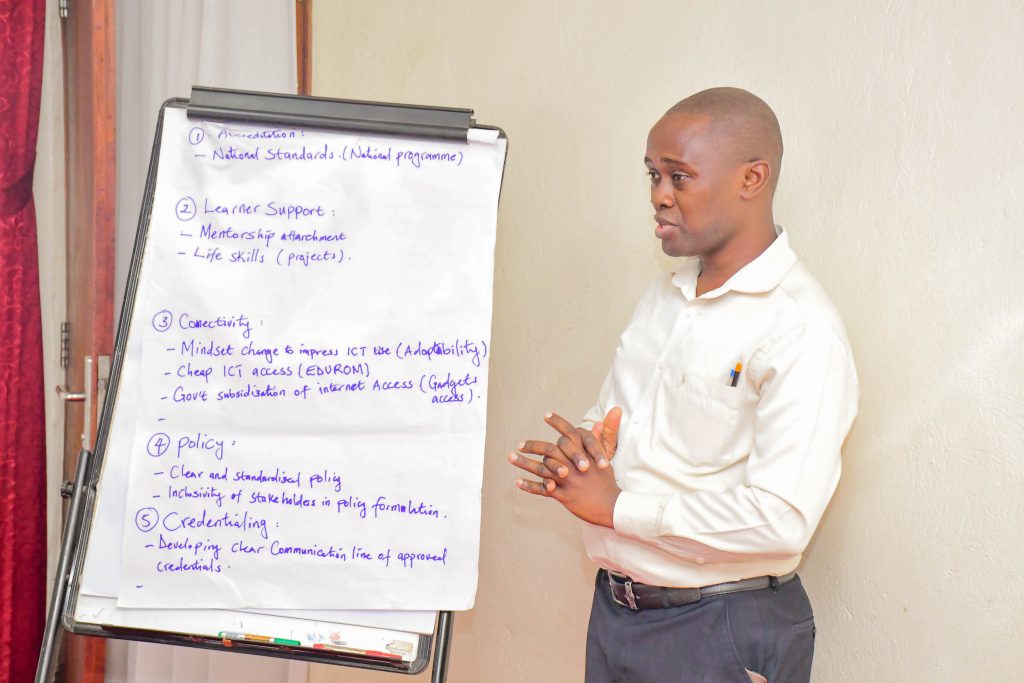

Dr. Derrick Ssekajugo, Chair of the Special Purpose Committee on Academics and Acting Principal of the College of Economics and Management at Kampala International University, addressed public misconceptions about HEAP.
“Some perceive HEAP—or previously HEAC—as only for students who could not succeed in secondary school. That is not the case. For instance, we have students who initially studied Education but through HEAP transitioned into medicine. Today, they are fully qualified professionals,” Dr. Ssekajugo said.
He also highlighted the pedagogical shift from teacher-centred to learner-centred approaches in secondary education and the need for universities to adapt. “Students entering HEAP come with diverse learning experiences, and universities must adjust to integrate them effectively into competency-based programs,” he noted.
Dr. Ssekajugo added that benchmarking with both local and international institutions is critical to identify gaps and best practices, which inform ongoing program improvements and policy reforms.
HEAP and standardization, accessibility and inclusivity
Sharing their vision for HEAP, panelists recommended standardization, accessibility, inclusivity and foundational nature of HEAP. They advocated for a competence-based HEAP, with a standardized curriculum, offline and online access to resource books and materials, diversification of delivery and support through blended learning and a HEAP Digital Passport for portability and verification on demand.
Trending
-

 General4 hours ago
General4 hours agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 Humanities & Social Sciences1 week ago
Humanities & Social Sciences1 week agoMeet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-

 General4 hours ago
General4 hours agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week ago76th Graduation Highlights
-

 Agriculture & Environment2 weeks ago
Agriculture & Environment2 weeks agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
