Health
Uganda Newborn Programme Shifts the Paradigm of Newborn Care
Published
3 months agoon
By
Mak Editor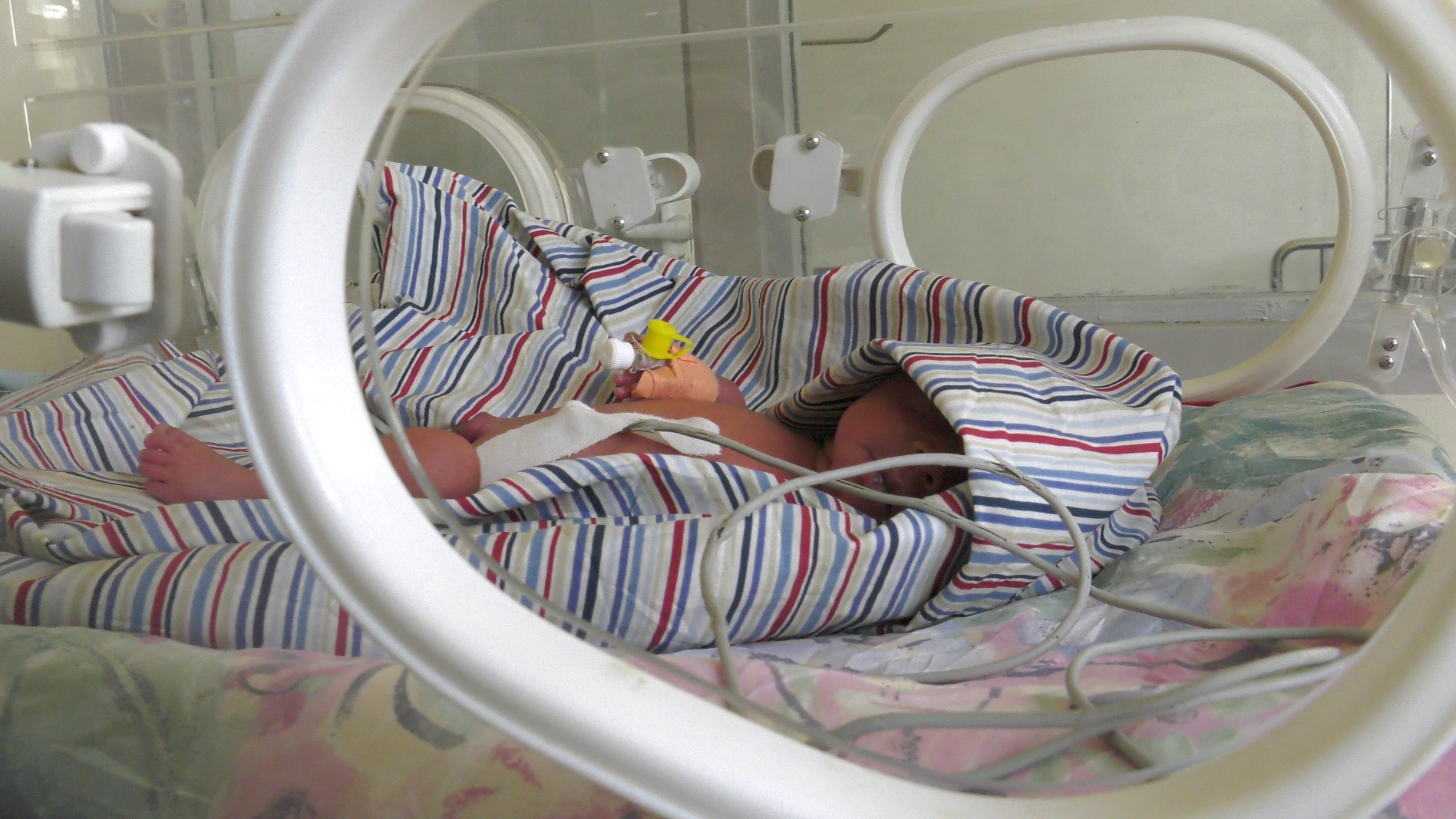
By Joseph Odoi
Every newborn deserves the best start to life. Yet, in Uganda, the burden of newborn morbidity and mortality remains high. The newborn mortality rate stands at 22 deaths per 1000 live births (UDHS 2022). According to most recent UN annual estimates, Uganda records 62,000 deaths around the time of birth. Of these, 32,000 are neonatal deaths, 26,000 are stillbirths and 4,800 are maternal deaths. Majority of the newborn deaths occur within the first week after delivery- a period considered very vulnerable for both the mother and baby.
Uganda’s high fertility rate translates to about 1.7 million births per year; and of these 250,000 babies need special newborn care as they are either born too small or fall sick within the first month of life. This has placed a huge burden on the country and strained the already limited investment for neonatal care.
Despite national efforts, newborn deaths continue to account for nearly half of all under-five deaths in Uganda, according to the Uganda Demographic and Health Survey (UDHS) 2022.
To contribute to addressing this challenge, a coalition of institutions namely; Makerere University School of Public Health, Baylor Foundation Uganda, Adara Development Uganda, Nsambya Hospital, and the Ministry of Health with funding from ELMA Philanthropies launched a national health systems strengthening initiative known as the Uganda Newborn Programme (UNP) in 2022. This program uses a regional approach to improve newborn care in three regions of Uganda namely Kampala, North Central and Western regions.
According to Dr. Monica Okuga, the Uganda Newborn Programme Coordinator at Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH), the Uganda Newborn Programme (UNP) made huge strides in providing quality newborn care in 36 health facilities across the three regions of Uganda.
Uganda New Born Programme Achievements
‘’Under the UNP, there have been so far many achievements. Institutional neonatal mortality rate has reduced in the facilities where the program is implemented and this has contributed to overall reduction in neonatal mortality in the regions. For example, Institutional neonatal mortality reduced to 7/1000 and 2/1000 live births by the end of Year 2, down from the baseline rates of 8.4/1000 and 11.9/1000 in Bunyoro and Tooro, representing reductions of 16.7% and 85.3% respectively’’ Dr. Okuga stated.

Dr. Okuga further explained that, ‘’Overall asphyxia case fatality rates across program areas have also reduced from 8.9% to 5%; adherence to infection prevention and control measures has improved across the facilities; and the quality of newborn care provided has also improved.
In addition to revamping many newborn care units, Dr. Okuga revealed that the programme supported the construction of newborn care units, citing Kyegegwa Hospital, Buliisa General Hospital, Masindi General Hospital, and Kyangwali HCIV.
In line with the SDGs programme objectives, specifically SDG 3; Good Health and Well-Being, Makerere University School of Public Health, together with partners including the National Planning Authority (NPA), UNICEF, FHI360, and the Ministry of Health, produced the Situation Analysis of Newborn Health in Uganda-2023 update.

This document has now been taken up by the Ministry of Health and is being used to develop a strategy for implementing the suggested recommendations therein, as well as costing the investment for improving newborn health in Uganda.
The previous newborn situation analysis was conducted 17 years ago in 2008’’ she explained of programme contribution at a multi-sectoral level

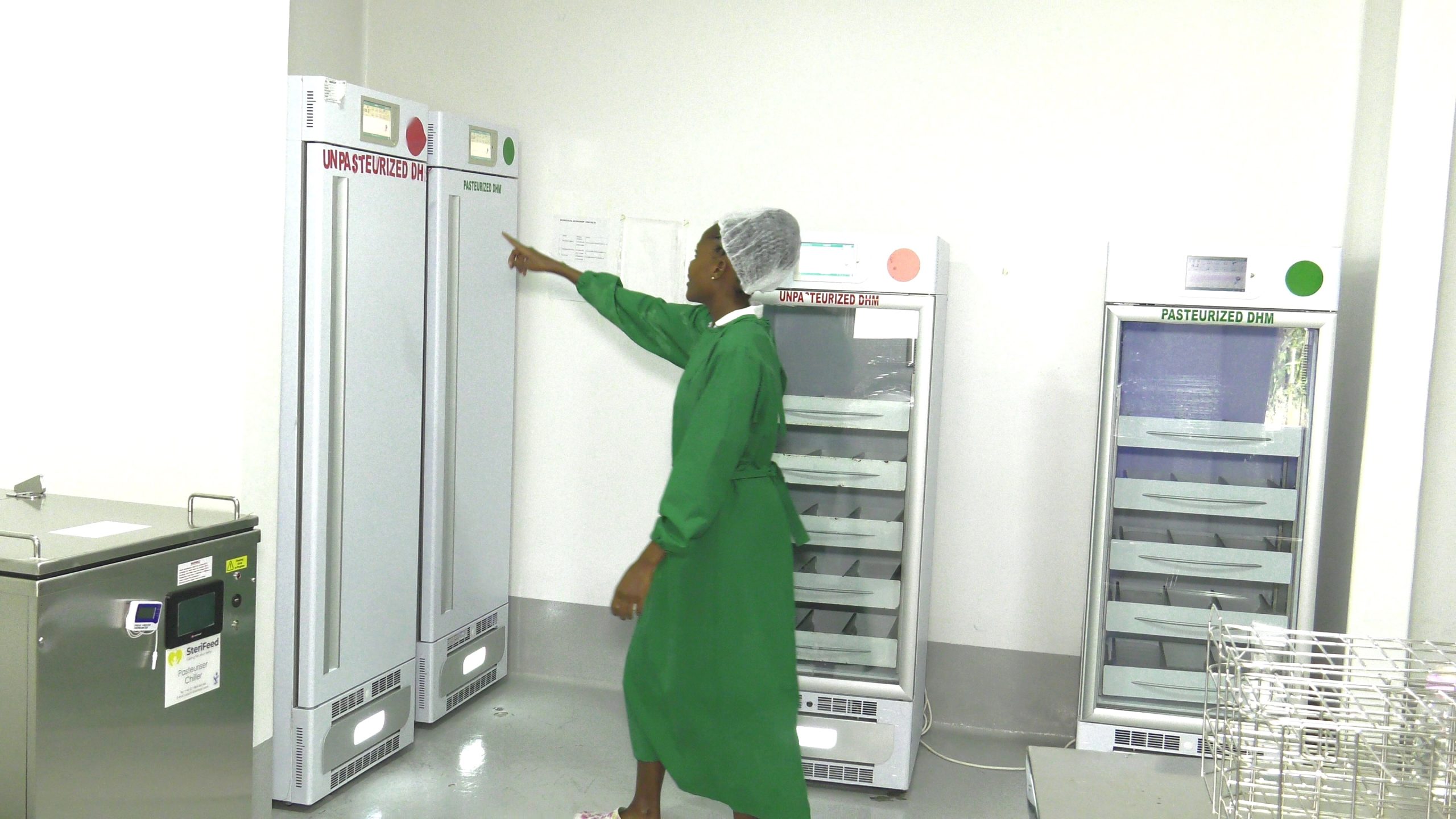
Establishment of Uganda’s First Breast Milk Bank
Still under this programme, the first ever Breast Milk bank was established at Nsambya hospital with other donor milk satellite sites at Mengo, Rubaga, Kibuli and Naguru hospitals in Kampala. This donor breast milk has benefited over 275 babies across Kampala and its neighboring districts.

Hospital-to-Home (H2H) Initiative
Another innovation that has been scaled up through the programme is the Hospital to Home (H2H) initiative by Adara Uganda. While many newborn interventions focus primarily on in-hospital care, the Uganda Newborn Programme, in partnership with Adara Development Uganda, pioneered the Hospital-to-Home (H2H) Model, extending its newborn care continuum to the household level. This innovative model ensures that high-risk newborns continue to receive vital support after hospital discharge, addressing the gaps in follow-up care that are common in low-resource settings.
According to Beatrice Niyonshaba, Deputy Director of Maternal, Newborn, and Child Health at Adara Development; “In Uganda, many families struggle to return for follow-up visits due to cost, transport challenges, and lack of caregiver awareness. The H2H model addresses this by involving caregivers early, equipping them with knowledge on newborn danger signs, and ensuring post-discharge follow-up through community health systems like village health teams.”
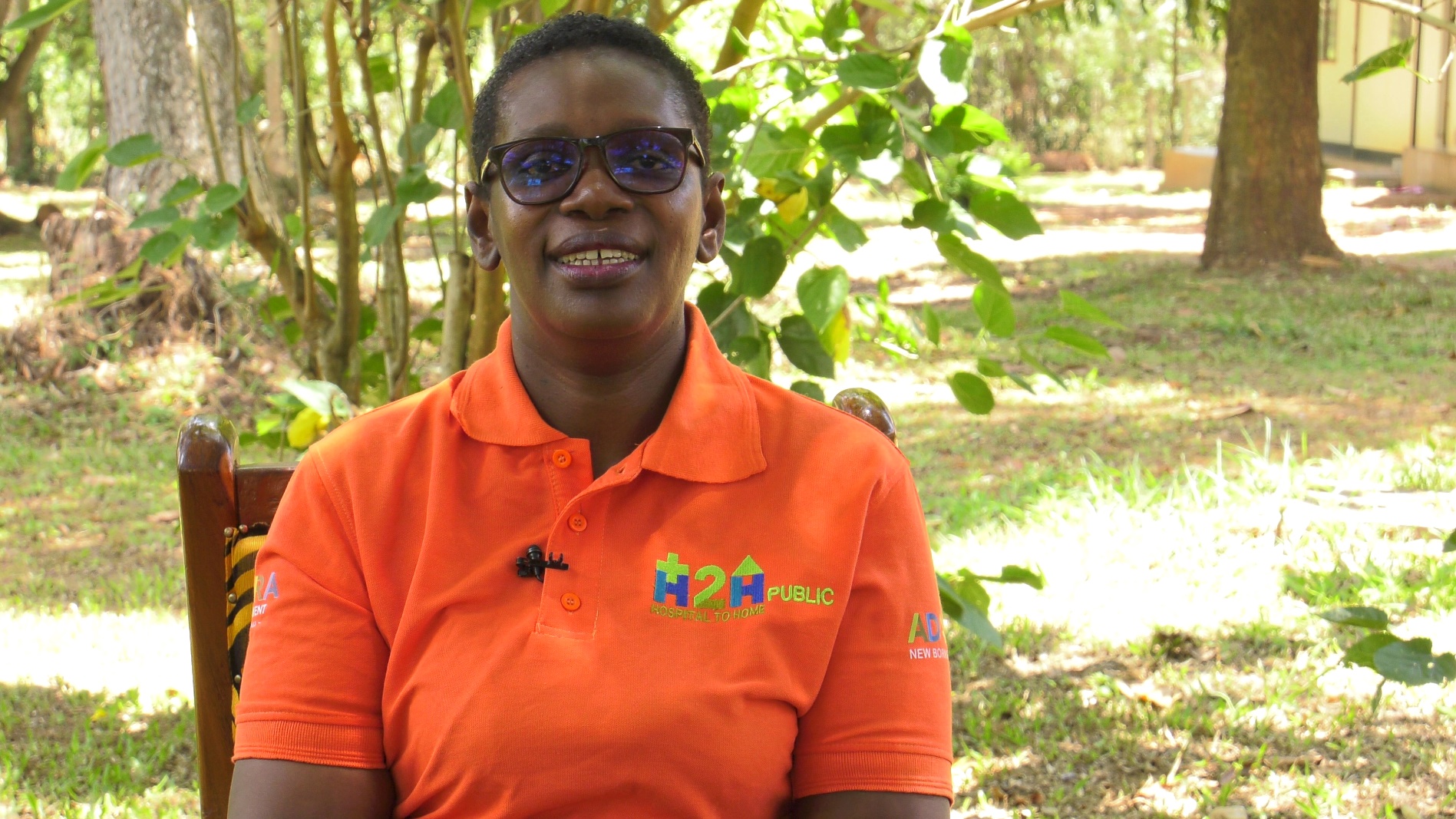

She adds, “The model not only reduces post-discharge mortality but also builds trust and ownership among families, which is critical but often an overlooked aspect of newborn survival in low-income settings. ‘’We also run regular community sensitization and awareness initiatives about the causes and survivability of small and sick newborns, preventative measures, as well as the services”. The model was initially piloted at Kiwoko Hospital, with strong support from both healthcare staff and the community. This phase allowed for continuous refinement and strengthening of the model, ensuring it met the needs of both families and healthcare providers.’’ Ms. Niyonshaba explained of the H2H Model uniqueness
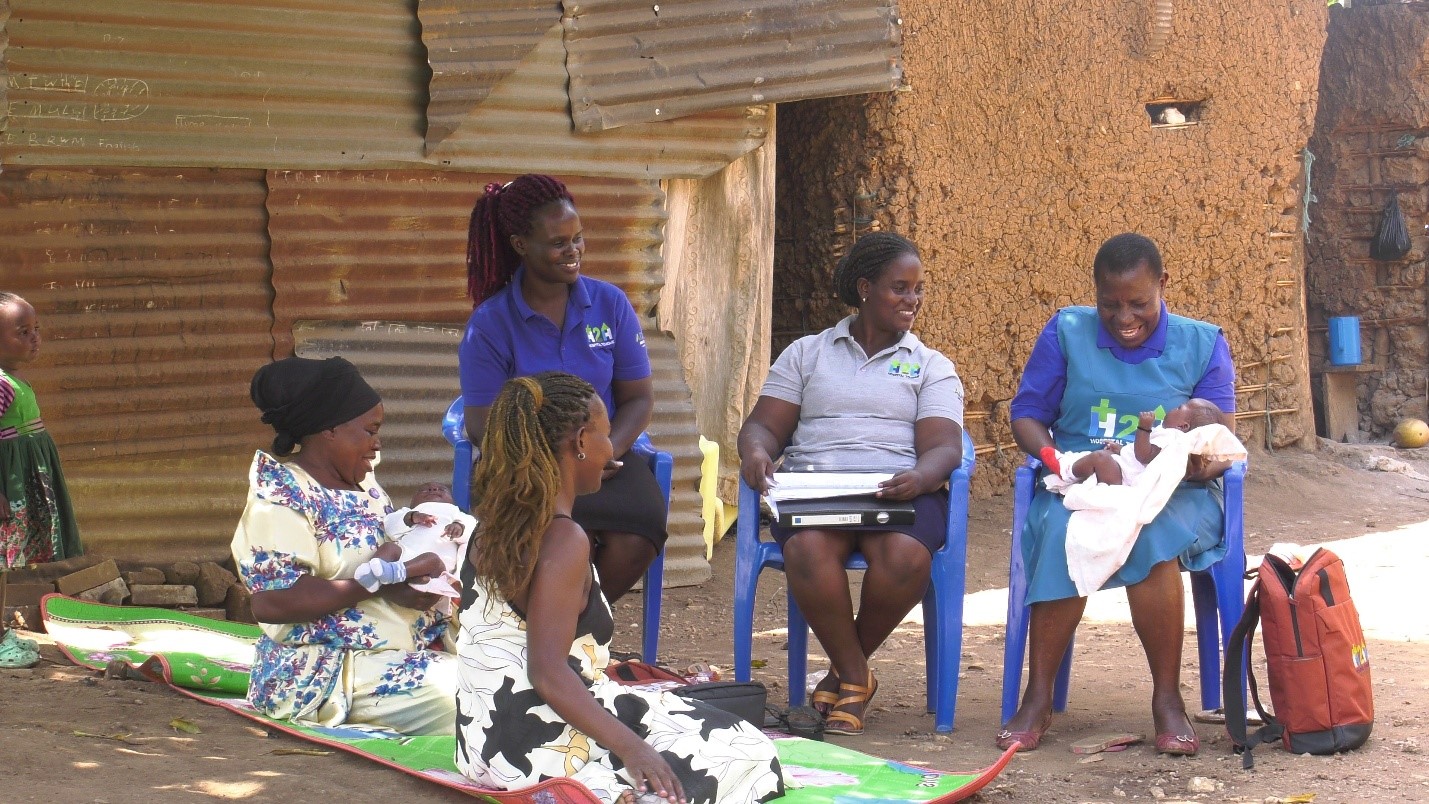

Currently, the model is being implemented in Nakaseke hospital, a government facility. This will provide insights for scale up to other government facilities. The programme has seen tremendous success due to the engagement and motivation of CHWs, who are provided with incentives, extensive training, and ongoing support. Regular check-ins and monthly meetings ensure these workers remain accountable and connected to the Programme’s objectives.
Challenges in Newborn Care
According to Dr. Monica Okuga and Prof. Peter Waiswa, the Uganda Newborn Programme team lead from MakSPH, in spite of the many achievements, several challenges persist. They explain that many health facilities in Uganda were built without infrastructure to support Newborn Care Units (NCUs). There are no standard floor plans for these units. In many facilities, the neonatal care units are housed in improvised rooms, while in some cases, completely new NCUs are built.
However, even where NCUs are present, they are often let down by an unstable power supply, despite the fact that most equipment in the NCUs require consistent electricity to function. In addition, there are other health system challenges such as insufficient drug supplies from the government, inadequate staffing, and the low involvement of medical officers in neonatal care. Internal rotation of already trained nurses to other units further worsens the situation. Other issues include untimely or late referrals of mothers and babies, as well as challenges with the low quality of data produced in these units.
In terms of lessons learnt while implementing the UNP, The Uganda Newborn Programme team observed and noted several key lessons during the implementation of the programme
- The importance of leadership engagement in the uptake of interventions is very critical. The leaders to be engaged not only include those at the facility level but also those at the district level. The support of political district leaders such as the Chief Administrative Officer (CAO) is also very crucial. One way of engagement is through sharing performance dashboards with key indicators to the District Health Officers (DHOs), CAO, and Health Facility In-charges.
- There is a need for continuous engagement of district leadership for sustainability in public health facilities, especially the human resource aspect for established Newborn Care Units (NCUs).
- There is a need to intervene across the board/spectrum of the health system. Addressing one challenge, for example, the provision of equipment, may not result in the required benefits without addressing human resources and skills.
- Using a regional approach to care, which includes all hospitals and high-volume health centres, is a more rapid and cost-effective way to scale up maternal and newborn care. It also improves access, quality, and referral, thus reducing unnecessary mortality.
- Regional Local Maternity and Neonatal Systems (LMNS) provide avenues/platforms to share lessons and share feedback to teams/facilities on gaps identified.
- Targeted mentorships not only maintain skills but also support teams in innovating for problem-solving.
- Continuous engagement of medical officers in facilities creates buy-in and brings them on board to support and bridge gaps in newborn care in the neonatal care units.
In terms of sustainability, the team stated that the programme’s design took into account the potential for continuation beyond the initial funding from ELMA Philanthropies. From the outset, the Ministry of Health was actively involved in the co-creation of the programme. The programme also made effective use of existing staff and infrastructure to enhance the quality of newborn care. While there was occasional catalytic provisions of drugs and equipment, the programme primarily relied on the government’s drug supply and delivery systems to ensure long-term sustainability.
About The Uganda Newborn Programme (UNP)
The Uganda Newborn Programme (UNP) has been actively working since its launch in July 2022, with the goal of significantly improving the care for small and sick newborns across the country. With support from ELMA Philanthropies, the programme has brought together a consortium of partners, including Makerere University School of Public Health, Baylor Uganda, Adara Uganda, and Nsambya Hospital, in collaboration with the Ministry of Health.
The programme is focusing on 20 high-burden districts across three regions of Uganda ie Western, Kampala, and North-Central, serving approximately 1.5 million births annually. Since its inception, the programme has been making strides in enhancing the capacity of health facilities, including the refurbishment and equipping of 30 specialized neonatal care units. These units are designed to meet the needs of small and sick newborns, in line with the National Essential Newborn Care (NEST) Toolkit.
Key activities that have been rolled out include
- Training and mentorship of Health Workers; More than 800 health workers have been trained and mentored in essential neonatal care practices such as neonatal resuscitation, Kangaroo Mother Care (KMC), Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP), and infection prevention and control. This has significantly improved the clinical competencies of healthcare providers in the management of small and sick newborns.
- Strengthening Infection Prevention and Control; The programme has focused on improving infection control measures at hospitals, which is critical in managing the high rates of sepsis and other infections among newborns.
- Effective implementation of newborn resuscitation and warm transport: This includes establishing standardized protocols and providing essential equipment like mabu bags plus masks, CPAP machines
- Improving Data Utilization; Efforts have also been made to ensure that health workers are using data-driven evidence for decision-making. Monthly perinatal death audits and support for data quality review have allowed for continuous improvement in service delivery.
- Enhanced Postnatal Care; Community-based postnatal care using Village Health Teams (VHTs) being trained to conduct home visits for newborns discharged from neonatal units. This helps ensure that infants receive timely follow-up care in the critical days after discharge.
The programme is set to run up to July 2025, and by then, it aims to have reached 120,000 small and sick newborns, helping to reduce newborn mortality by 40% in the target regions.
You may like
-


Call for Applications: Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR) Training Course
-
Call For Applications: PhD Fellowship Training Position
-


Makerere Hailed for Its Leadership in Health Policy and Knowledge Systems
-


NCBA Commits UGX 1.45 Billion to Makerere Marathon, Pledges Five-Year Support for Inclusive Education
-


Mak Marathon Unveils NCBA as Platinum Sponsor
-


SophiA Project Upgrades Medical Infrastructure at Buvuma Health Centre IV, Trains Technicians for Maintenance Works
Health
Call for Applications: Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR) Training Course
Published
2 days agoon
July 11, 2025By
Mak Editor
The Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR) Training Course, scheduled to take place from July 30th to August 1st, 2025, at the Makerere University College of Health Sciences’ Conference Room.
Background
The SUSTAIN: Advancing Makerere University Masters of Health Sciences in Bioethics program at Makerere University College of Health Sciences aims at developing and institutionalizing a mentorship program in research ethics that facilitates development of bioethics professionals and health researchers who are committed to the growth and application of research ethics in Uganda’s academic and research institutions to the highest possible degree. The Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR) course is one of the short courses that introduces trainees to a framework that involves application of established scientific, professional norms and ethical principles in the performance of all activities related to scientific research.
Course objectives
At the end of this course, trainees should be able to identify, manage and prevent research misconduct.
Course outline
Introduction to RCR; Introduction to Professionalism and Ethics; Human subject’s protection and regulatory framework in Uganda; Humane handling of animal research subjects; Conflict of interest;
Responsible laboratory practices; Mentor-mentee relationships; Collaborative research international, industry); Peer review; Research misconduct (including policies for handling misconduct); Community involvement during research in a low resource setting; Responsibility to society and environment; Responsible financial management; Data acquisition, management, sharing and ownership; Responsible authorship, publication and communication.
Target group
The Responsible Conduct of Research course is targeted at Researchers, Research administrators, Research assistants, Study coordinators, Graduate students and Student supervisors. Certificates will only be awarded to participants with 80% attendance.
Course fee: 205,000/=, or 56USD is payable.
The course fee will cater for meals and refreshments during the training period.
Payment & Registration procedure:
9030026194023, Stanbic Bank, Mulago, Makerere University Biomedical Research Center Limited
Dollar Currency:
9030026194147, Stanbic Bank, Mulago, Makerere University Biomedical Research Center Limited
Please Note: Share payment details on email/whatsup and a hardcopy deposit slip delivered on the first day of the training to Miriam Musazi, Department of anatomy, Bioethics Centre, Room C4,
Mob: +256 782 363 996/ +256 701 363 996, Email: mmusazi@gmail.com.
NB. Only those who will have paid by this date will be considered for the course
Venue: The training will take place at Makerere University College of Health Sciences’ Conference room
Health
Call For Applications: PhD Fellowship Training Position
Published
3 days agoon
July 10, 2025By
Mak Editor
Background:
Makerere University College of Health Sciences (MakCHS), Kampala, Uganda and Global Health Uganda (GHU); in collaboration with other research consortium partner institutions, including, Kenya Medical Research Institute (KEMRI), Kisumu, Kenya; Training and Research Unit of Excellence (TRUE), Blantyre, Malawi; University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway; University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands; and Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine (LSTM), UK have been conducting clinical research on Malaria Chemoprevention. This research has focused on Malaria Chemoprevention in vulnerable patient populations, including children with severe anaemia, children with sickle cell anaemia and pregnant women. As an example, two of our recently completed studies are “The post-discharge malaria chemoprevention in children with severe anaemia [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33264546/] and Malaria chemoprevention in children with sickle cell anaemia [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39718172/]”.
With support from the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) body, the consortium is expanding these studies to children with severe acute malnutrition, by conducting a large multi-centre randomized controlled trial entitled “Chemoprevention of malaria in the postdischarge management of children with severe acute malnutrition in Malawi and Uganda”.
In Uganda, the study will be conducted at one or two of their study sites in Jinja Regional Referral Hospital, Hoima Regional Referral Hospital or Kitgum General Hospital. Makerere University College of Health Sciences (MakCHS) and Uganda and Global Health Uganda (GHU) seek to appoint a full-time PhD Fellow, on this study. This will be a 4-year post, tenured at Makerere University and hosted at MakCHS.
Expectations of the PhD fellowship:
The PhD fellow will:
- Be a part of the main trial team, and participate fully in its implementation. However, he/she will be expected to design and develop his/her PhD research project, nested in the main trial.
- The area of study will be around “interactions between anaemia and severe acute malnutrition (SAM) in children or the interactions between malaria and severe acute malnutrition in children”.
- Conduct rigorous research, leading to high quality scientific publications.
- Submit a full research concept and obtain registration in the University by end of year-one. As such, there be an initial appointment for one year, renewable upon satisfactory performance.
- Academic mentorship and supervision will be provided by the research consortium (see above – composed of national and international researchers).
- Doctoral scholarly support and training environment, as well as didactic training in research methods and scientific writing skills will be provided by Makerere University.
- The funding support will cover tuition and a competitive monthly stipend for 4 years, scientific conferences fees/travel and other research-related costs.
Prospective candidates must:
- Hold Master’s of Medicine in Paediatrics and Child Health from a recognized university, and licensed to practice medicine in Uganda by the UMDPC.
- Possess undergraduate training in Medicine and Surgery (MBChB/MBBS/MD).
- Willingness to fully commit time and effort to their PhD studies, expected to start immediately
- Candidate should not hold other/concurrent fellowships
- Having publication experience will be an added advantage.
- Be highly motivated and willing to commit to a career in research and academia.
Application procedure:
Interested applicants should submit their application and supportive documents – listed here below, in one PDF document, in an email titled “PDMC-SAM–PhD Fellowship Application” to hr@globalhealthuganda.org [and cc – chdc.desk@mak.ac.ug] by 25th July 2025. The documents should include the following:
- An application letter (Max. 1 page)
- Motivation statement (Max. 500 words)
- CV (Max. 2 pages), including a list of publications
- Two (2) recommendation letters
- Academic transcripts and certificates for all university qualifications
- A synopsis focusing on the proposed PhD research work, describing briefly what is already known/burden, challenges, the gaps and potential interventions (include references) [Max. 800 words].
Health
Makerere Hailed for Its Leadership in Health Policy and Knowledge Systems
Published
4 days agoon
July 9, 2025
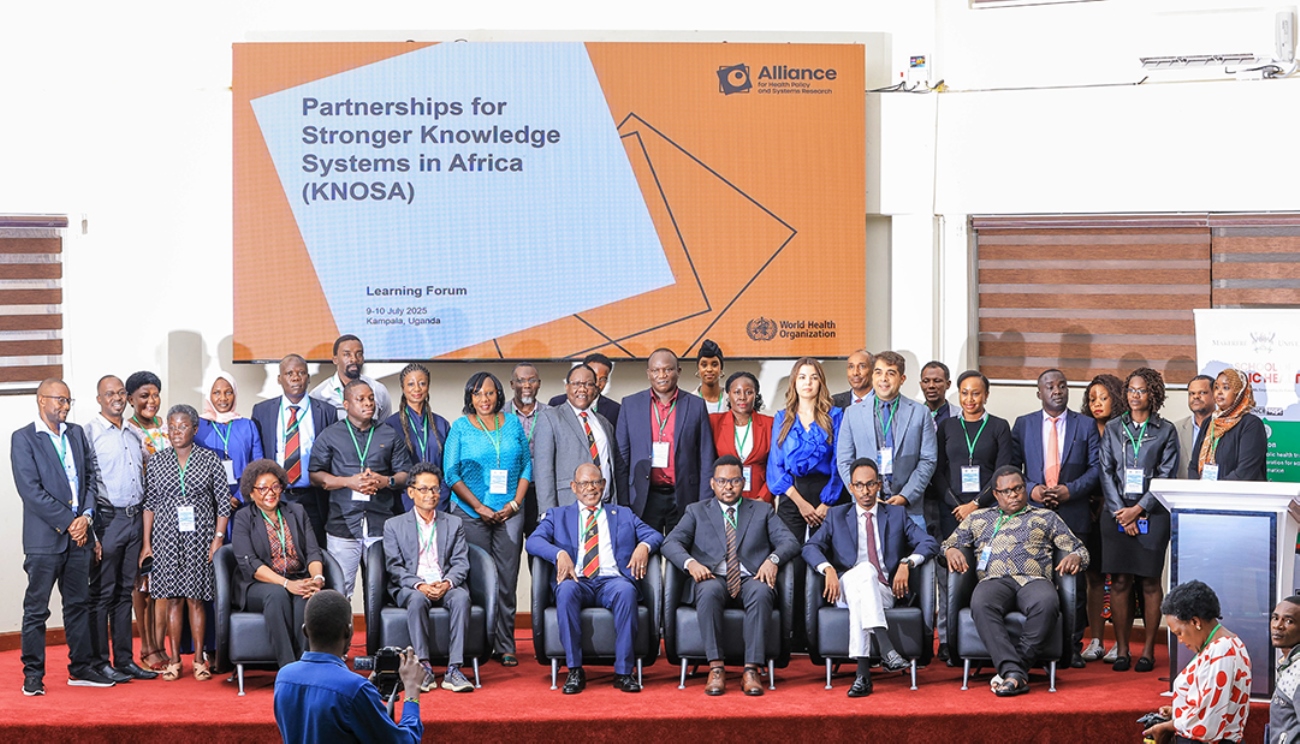
KAMPALA, July 9, 2025 — Makerere University has been hailed as a continental and global leader in health policy and systems research. This recognition came during the Partnerships for Stronger Knowledge Systems in Africa (KNOSA) Learning Forum, held July 8–10, 2025, hosted by Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) with support from the WHO Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research.
Delegates from Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, and Somalia applauded Makerere’s role in advancing evidence-informed policymaking and strengthening national knowledge systems. The forum highlighted the institution’s trusted leadership, practical research, and commitment to driving real change.
Dr. Kumanan Rasanathan, Executive Director of the WHO Alliance, praised Makerere’s long-standing role in bridging research and policy:
“You are a shining beacon on the continent and for the world,” he said. “In this moment of crisis, where every health investment must be efficient and equitable, Makerere’s leadership matters more than ever.”
He emphasized the Alliance’s 25-year partnership with Makerere: “We know Makerere University very well. My predecessors have worked with the Alliance since its inception in the 1990s. Makerere has been especially instrumental in advancing the field of health policy and systems.”
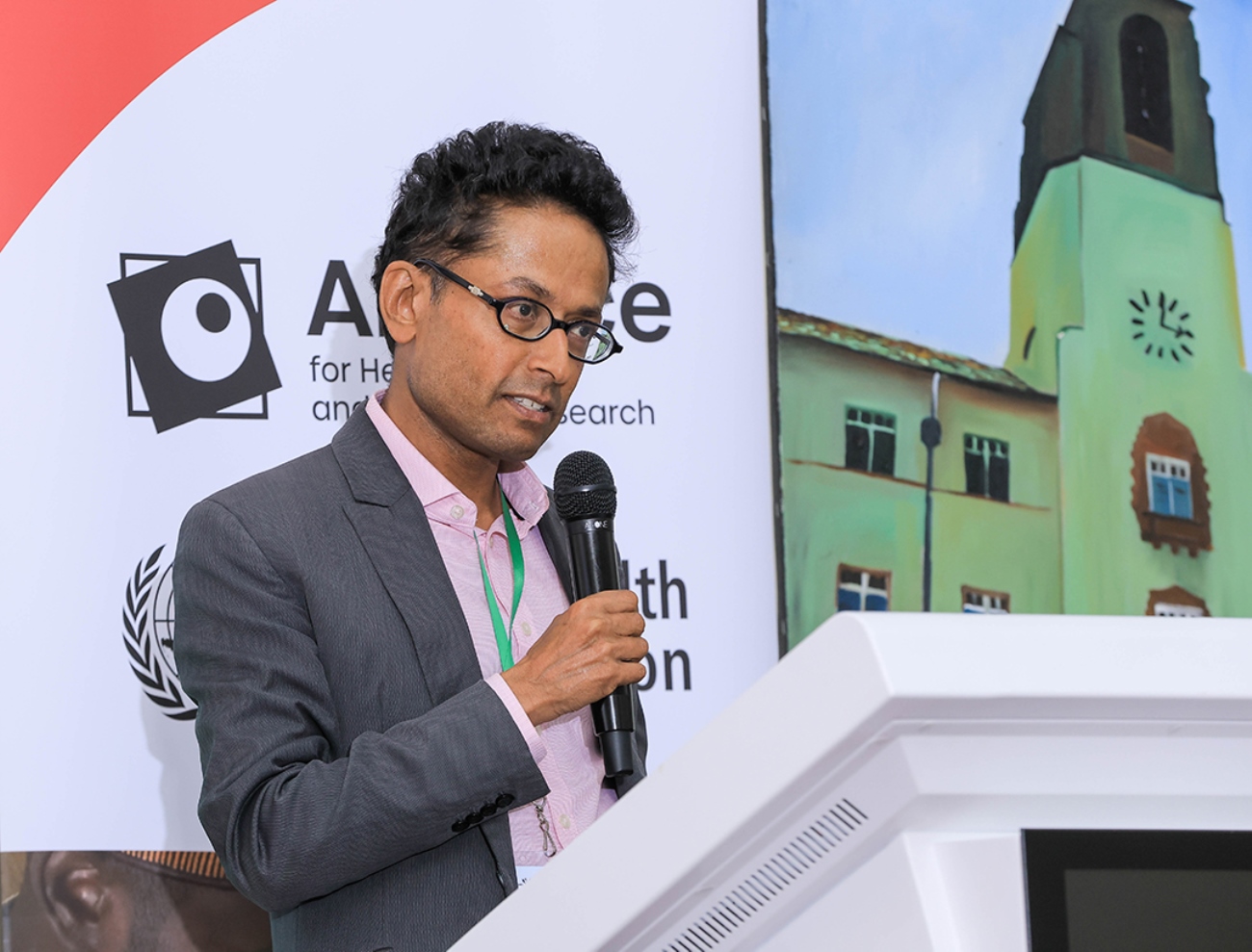

Dr. Rasanathan called for a move away from siloed approaches toward more adaptive, coherent systems. He reaffirmed WHO’s commitment to supporting regional initiatives like KNOSA that are driving this shift across Africa.

In the face of current funding cuts, Dr. Christine Musanhu of the WHO Uganda Country Office echoed these sentiments with a stern call to action: “In times of uncertainty, we need national systems that not only generate evidence but also understand and communicate it in ways that drive real change.”
She warned of tightening budgets, citing an 11% cut (roughly $67 million) in global funding for Uganda’s public health programs. “We are being asked to do more with less,” she said, urging countries to reprogram resources towards high-impact, evidence-based interventions.
Adding that, “Evidence must go beyond routine data—it is a measure of transformation.”

This year’s KNOSA forum focused on sharing country-level progress, refining evaluation approaches, enhancing communication products, including scientific publications, and engaging more deliberately with Uganda’s wider policy and research ecosystem.
Makerere University Vice Chancellor Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe, while sharing the institutional vision, called for African universities to lead from the front in addressing health and development challenges: “We can do all the research in the world, but unless it moves beyond our laptops and lecture rooms into real decision-making spaces, it won’t change lives.”
He noted that Makerere contributes over 80% of Uganda’s academic output and praised MakSPH and the College of Health Sciences (MakCHS) for innovations that have shaped responses to HIV, Ebola, and COVID-19. “Our work, backed by partnerships with government and global collaborators, is proof that African universities must lead from the front.”
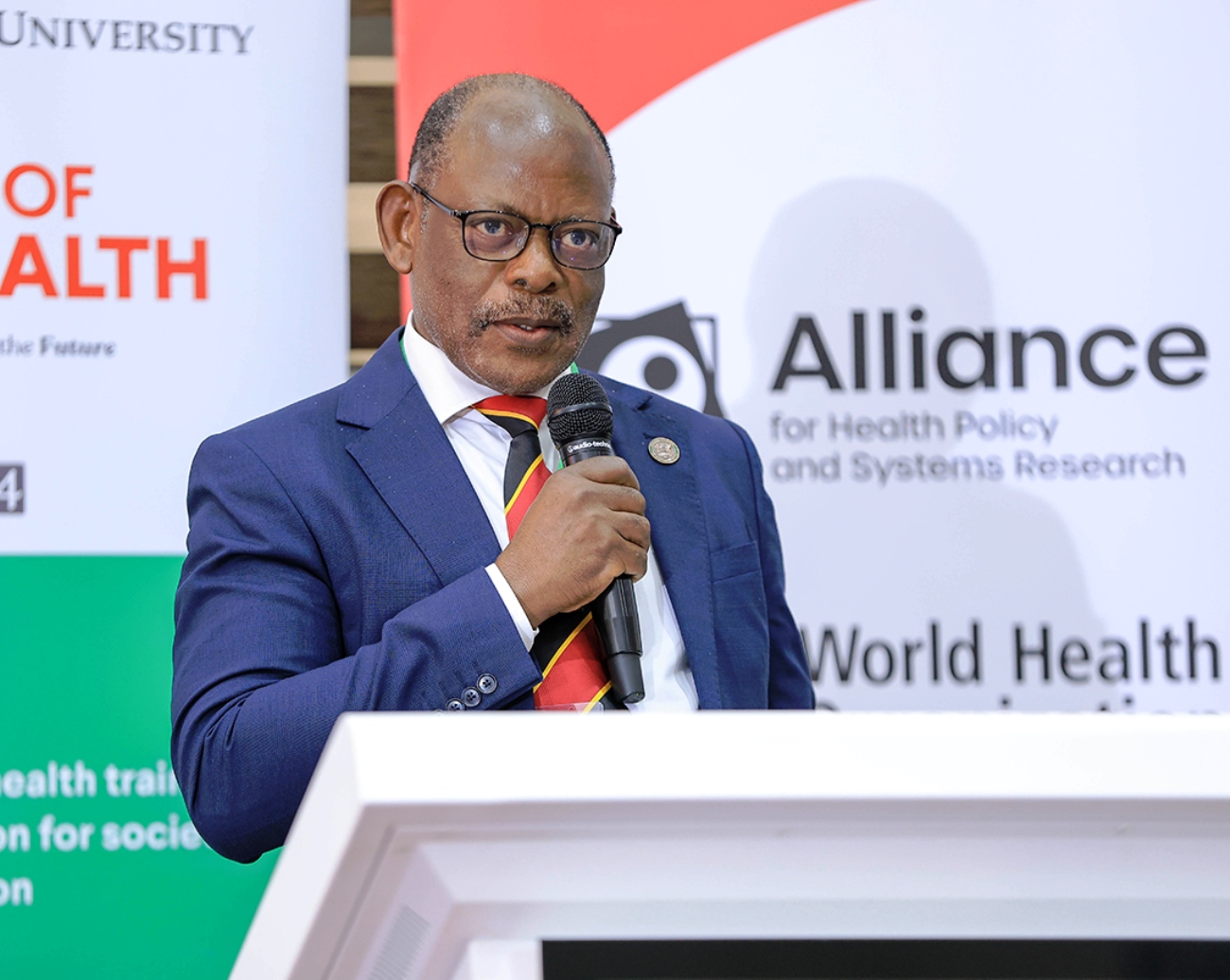

Professor Nawangwe urged deeper collaboration within KNOSA: “Our continent is interconnected. We cannot afford to work in silos. We are stronger together.”
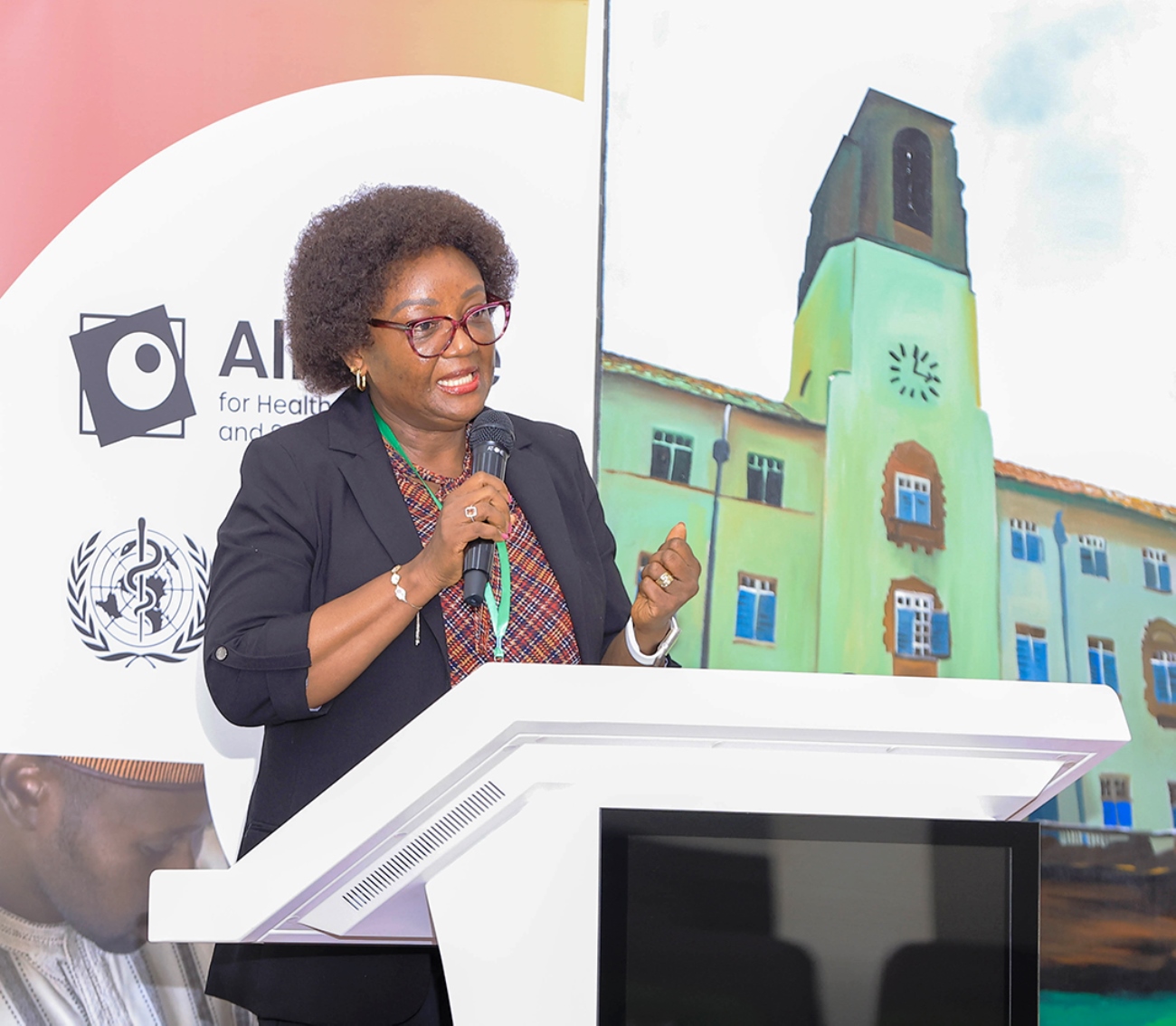
Dr. Aku Kwamie, the unit head at the WHO-Alliance, noted that there is a need for partners to shift their thinking regarding policy. She particularly shared three critical transitions to institutionalize evidence use: embedding knowledge within institutions, not just individuals; linking research directly to decision-making; and advancing from isolated academic work to system-level thinking. These shifts, she noted, are essential for embedding evidence into routine governance.

Professor Freddie Ssengooba, a Health Policy and Knowledge Systems expert at MakSPH, reaffirmed Makerere University’s regional leadership in the field and stressed the urgency for African countries to take full ownership of their health systems considering the shifting funding landscape:
“Health policy and knowledge systems research may not be as prominent as epidemiology or disease control,” he said, “but it’s central to how we harvest and connect knowledge with policy and resources. When the vaccine is here and the evidence is clear, that’s when they come to us, asking, “How do we achieve over 80% coverage?”

He praised KNOSA for helping elevate the field’s relevance: “There’s real appreciation for the work we do—not just with Uganda’s Ministry of Health, but across the region.”
Recalling the early collaboration with WHO, he said, “Back in 1997–98, a few of us, myself included, responded to an initial call and began what has now become a long-standing relationship with the WHO Alliance.”
“The Alliance is building capacity across Africa to ensure that research doesn’t stop at findings but goes on to shape decision-making and society,” he disclosed.
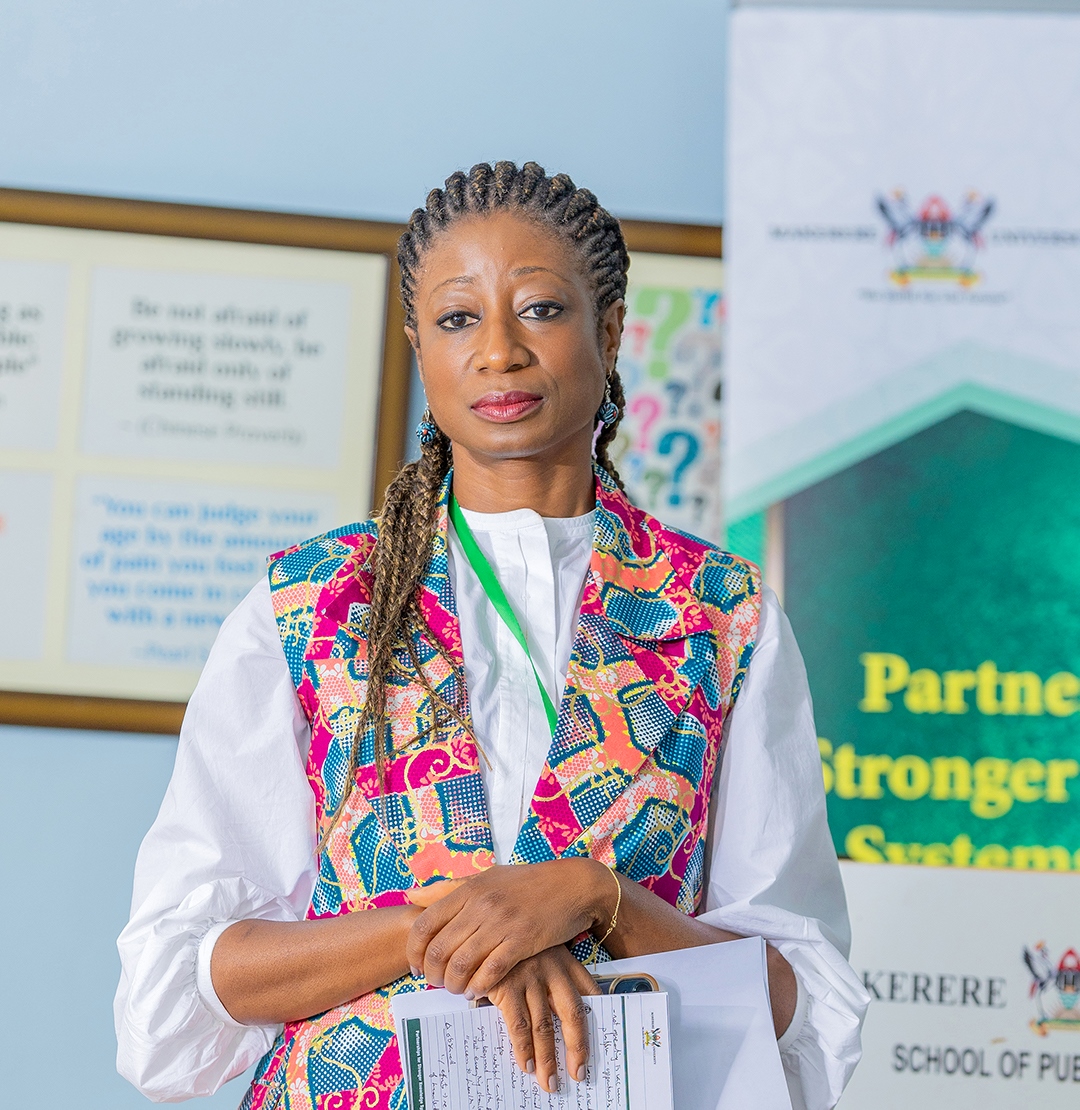
Professor Rhoda Wanyenze, the Dean of MakSPH, is currently ambitiously driving her colleagues, staff, and partners to embrace the culture of evidence use. She reiterated the School’s commitment to leading in evidence translation: “I’ve often told the Vice Chancellor—we at the School of Public Health are not in an ivory tower. We are deeply connected to real-world problems.”

To her, the need for a clear framework to improve engagement with decision-makers and address uneven success in research translation has never been greater than now: “Yes, we publish in high-impact journals. But the question is, what change happened because of your evidence?”
“I would love to see the School lead in developing a framework that showcases what we’ve done well and identifies where we can grow.”
She also acknowledged Prof. Ssengooba’s influence in broadening the lens on knowledge management: “You’ve challenged us to think beyond institutions, to consider networks and systems. That’s a gap we must fill.”

Trending
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoAdmission List to Bachelor of Education External (BED) 2025/26 -Private Sponsorship
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoUndergraduate Admission List Self Sponsorship Scheme 2025/2026
-

 General5 days ago
General5 days agoRe-advert: Admission to Undergraduate Programmes 2025/2026
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoAdmission Lists for – Bachelor of Laws 2025-26
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoDiploma/Degree Holders Scheme – Self Sponsorship Admission Lists 2025/26
