Health
Dr. Rhoda Wanyenze explains how researchers can work more effectively with policymakers
Published
2 years agoon
By
Mak Editor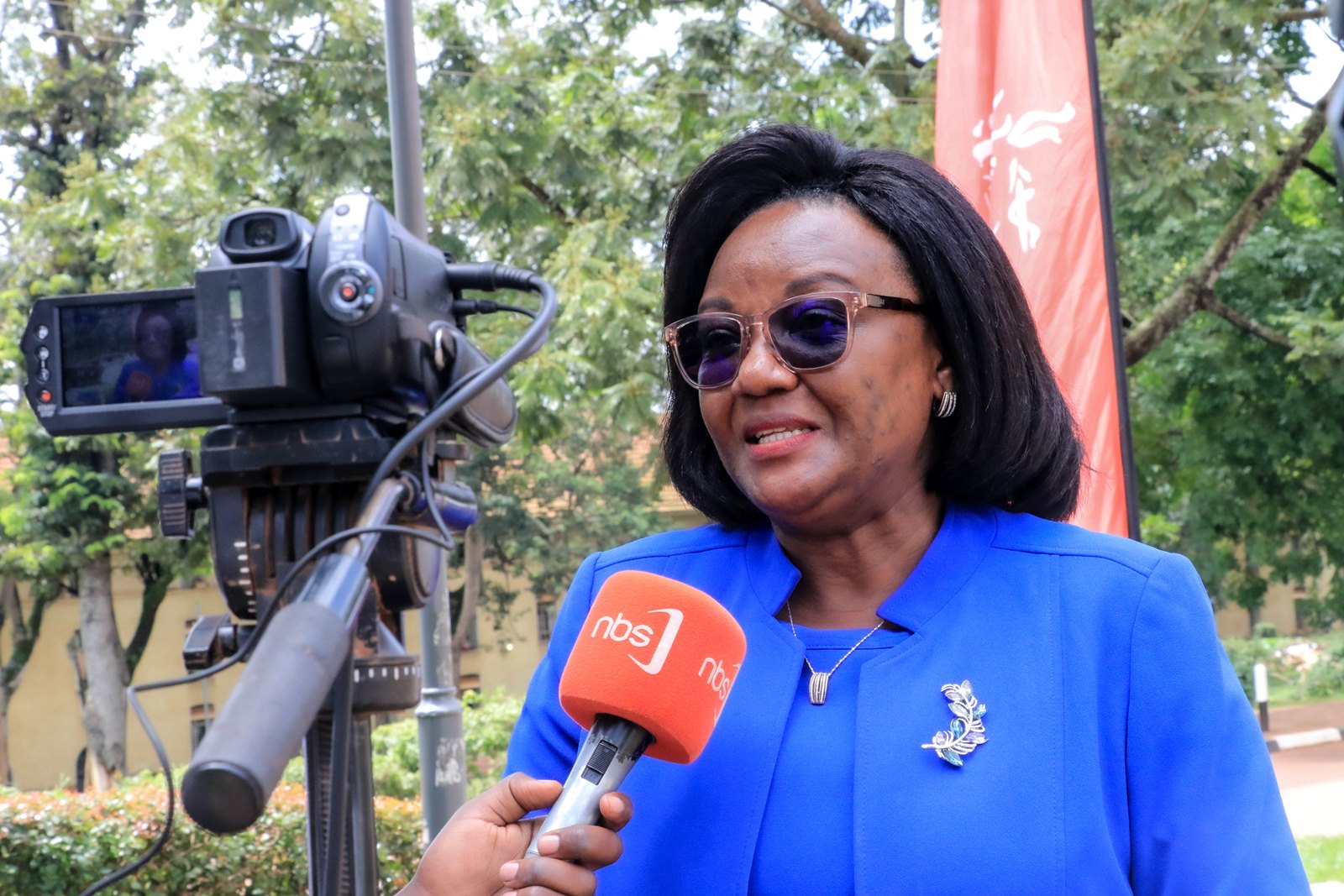
In advance of the World Health Summit Regional Meeting, we spoke with the Dean of Makerere University School of Public Health about how researchers and academics build trust and gain influence with decision makers
Ahead of this year’s World Health Summit Regional Meeting, we spoke with Dr. Rhoda Wanyenze, the Dean of Makerere University School of Public Health, about the theme of this year’s event – bridging the science-to-policy gap for global health.
Dr. Rhoda Wanyenze, who has collaborated with government health officials to develop evidence-based policies from HIV to COVID-19 and maternal and child health, said that researchers and policymakers can, among other things, “interpret the data together, make sure the interpretation is appropriate, and tease out the actions they’re going to take.”
Dr. Wanyenze, who is also a principal investigator for Exemplars in Global Health’s COVID-19 research, added: “Let the primary focus not just be the publication [of the research], but also, responding to [policymakers] needs and giving them information that they can use.”
Across sub-Saharan Africa, research institutions have been partnering with policymakers to help inform policy decisions for decades. For example, the Infectious Diseases Research Institute in Uganda and the Uganda Virus Research Institute supported the Ministry of Health through the COVID-19 pandemic and recent Ebola outbreak. In fact, during the 2022 Ebola epidemic, the Uganda Virus Research Institute repurposed some of its research laboratories to support the government’s disease response and diagnostics efforts.
Many of the continent’s universities, including the School of Public Health at the University of Kinshasa, the Muhimbili University of Health and Allied Sciences in Tanzania, the Cheikh Anta Diop University of Dakar, and the University of Zimbabwe, also have strong collaborative relationship with health officials. The University of Zimbabwe, for example, embeds some of its students within the country’s Ministry of Health.
The Makerere University School of Public Health has a similar track record of partnering with and helping inform policymakers in Uganda. To explore how researchers and academics can establish mutually beneficial relationships with policymakers ahead of the World Health Summit Regional Meeting on April 13 in Washington, D.C., Dr. Wanyenze offered her thoughts in an interview
Researchers often struggle to identify the best moment to reach out to policymakers. What does your experience tell you?
Dr. Wanyenze: You don’t wait until you’ve conceptualized the questions, then go to them when you are at the tail-end or when you are presenting the findings. After you present, they’ll ask, Did you also do this?’ And you’ll say, “No, I didn’t.’ And then they’ll ask, ‘Did you also do that?’ And you’ll say, ‘No, I didn’t do that either.’
Sometimes I find that we make a lot of assumptions about what they need to know. Before we even begin to craft our research questions, we need to understand what they’re struggling with and ensure that we are aligned to their needs as we gather evidence.
I’ll give you an example: several years ago, we were beginning to work out how we can move from traditional HIV testing methods to self-testing. We were working on designing a randomized controlled trial to test the effect of this. We had to speak with the Ministry of Health to understand: what is it that they worry about? What is it that would make them not want to adopt this policy?
We also didn’t have just the [Ugandan] Ministry of Health, we had other stakeholders, including people living with HIV, women living with HIV, and we could hear their voices loudly. ‘People will fight. We shall have divorces. We shall have violence.’ We had to think through carefully, if we are going to do this trial, we have to have sufficient mechanisms to deal with potential risks.
At the same time, we must collect this information in a bit more detail so that at the end of the day, we are not just saying, ‘This trial works,’ but we are saying, ‘It won’t cause harm, or if it causes harm, this is how you can mitigate it.’ We had to carefully do this trial with sufficient safety nets to respond to these issues. We had to think about the referral resources, for example, should we have any violence.
Then they told us, ‘We want to know the cost.’ Initially, we had not planned to include costing, but we had to integrate something that can support them to be able to make that decision.
Another example is research my team did on the impact of COVID on maintaining essential health services in Uganda. We presented to the Ministry of Health and its partners our proposed objectives and selected disease indicators to track in the maintenance of essential health services. They informed us that other partners were already working on some of the indicators such as HIV, TB, and maternal health. Rather than duplicate these indicators, they advised us to focus on other indicators which had not been addressed. We agreed to reorient the focus with the resources we had, to harmonize our work with other partners and ensure responsiveness to the needs of the Ministry of Health. Later, when the EHS continuity committee published updated guidelines on maintaining essential health services, it included recommendations based on our research.
How do you manage policymakers’ shifting needs and incorporate their feedback throughout the lifetime of your research?
Dr. Wanyenze: Interim feedback loops are critical to being sensitive to their needs. The challenge is you might not be funded to do everything they ask you to do, but sometimes you find things that are easy to integrate without necessarily spending much. It might involve a few more questions that you can address, with the resources that you have, and produce additional evidence that is needed by the ministry. The benefits are tremendous. By engaging them, they develop a sense of ownership. So that they feel, ‘This is our research.’ And they actually begin to say, ‘When are you giving us the results?’
How should researchers think about reporting out their results to policymakers?
Dr. Wanyenze: Working with policymakers through interpreting the implications of your work is really important. It can help when planning how to disseminate the work so that it is more meaningful.
For one project funded by the Global Fund – a partnership to enhance analytical capacity and data use in Eastern and Southern Africa called PERSuADE – we prioritized the areas for analysis with the Ministry of Health and then we worked with their teams and generated the evidence they needed. Then we were able to track what actions they’ve taken based on the findings.
If you work with the Ministry of Health and any other partners and you use their data or involve them in the data collection, analysis and interpretation, make sure that you include them as co-authors. A common challenge we have experienced is researchers who work with the ministries and other stakeholders publishing the findings without including them as authors or even informing them and sharing the findings.
How do things change if you are working with routine data the government collects?
Dr. Wanyenze: If you are working with data that the government routinely collects, you need to be engaged with policymakers in terms of how you’re going to use that data and that you are actually going to add value and do a good quality analysis that will help them answer their questions. Also, you need to be clear that you will not use their data for anything else without their permission. Sometimes researchers will get this data and they’re flying off and doing other things than what was originally agreed upon. And before you know it, they’ve published it without the government knowing. You need to ensure trust and a partnership that’s respectful.
What advice do you have for research organizations that currently do not have a relationship with the government but want to develop one. How can they establish a mutually beneficial and respectful relationship?
Dr. Wanyenze: Whether you want to work with a ministry of health or an NGO, the process is the same. You need to engage with them to clarify the partnership and expectations. There has to be benefit to the ministry or the NGO to want to work with you. The benefit often will be that you’re generating evidence that will add value to their decisions in a timely manner. You need to be responsive to their needs, to the extent possible.
How can researchers balance the need for quality research, which takes time, and the needs of policymakers, who often have pressing and time-sensitive needs.
Dr. Wanyenze: Timeliness is very important, but it should not compromise quality of the research. Sometimes the research takes long, and researchers will share their findings with policymakers when the findings have been overtaken by events and are no longer relevant. We sometimes prioritize some of their most critical questions and share preliminary findings as we finalize analyses for the rest of the study objectives and papers. Holding back the dissemination until the papers are written is a missed opportunity—we lose the opportunity for feedback from stakeholders to enhance the interpretation of the findings and to use the findings.
by Exemplars News — Originally published by exemplars.health
See original article here;
You may like
-


Strengthening Grants Management Through Institutional Collaboration and Capacity Building
-

Ugandan Study Flags Girls and Senior Students as a Mental Health High-Risk Group
-


Mak, HERS-EA Discuss Nurturing More Women Leaders
-
Call For Applications: PhD Fellowship Training Position
-


Makerere Hailed for Its Leadership in Health Policy and Knowledge Systems
-


Opening KNOSA Learning Forum at Mak
General
Strengthening Grants Management Through Institutional Collaboration and Capacity Building
Published
4 days agoon
July 15, 2025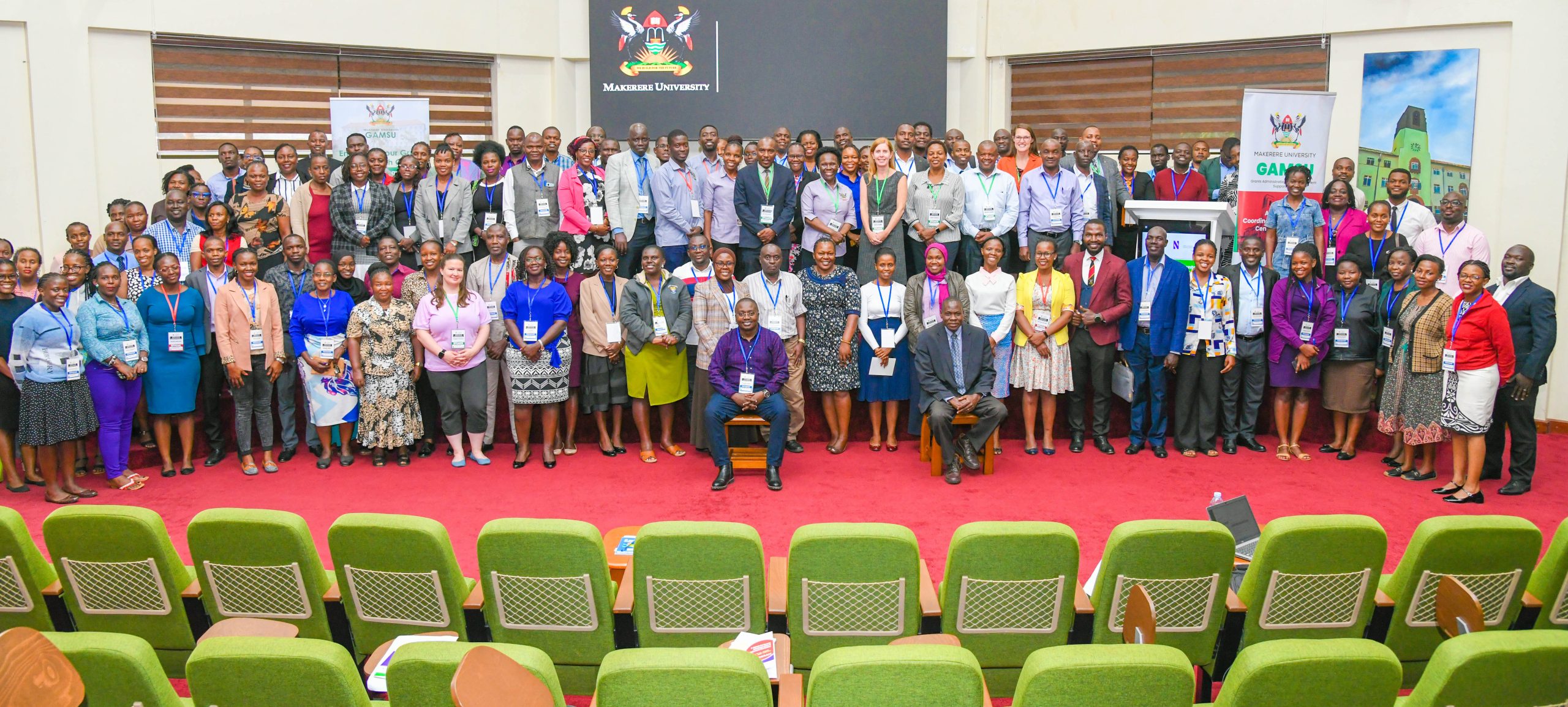
As the funding to the higher education sector keeps on reducing due to competing priorities, universities are implored to come up with structures and strategies to attract and win research grants.
Key findings indicate that universities with institutionalized grant management offices, strong and coordinated research teams are better positioned to effectively compete for grants.
Makerere University, in partnership with Northwestern University, is spearheading the E-SMAC G11 Grants Administration and Management workshop from 14th to 17th July 2025, aimed at strengthening grant management offices and systems among the participating universities and entities.
It is envisioned that through this capacity building approach, the workshop which brings onboard over 130 participants from different universities and entities, will address the knowledge and skills gaps among faculty, grant managers, administrators and support staff.
The participating universities and entities include: Makerere University, Uganda Christian University-Mukono, Soroti University, Gulu University, Clarke International University, King Ceasor University, Kyambogo University, Muni University, Mother Kevin University, Uganda Martyrs’ University-Nkozi, Ernest Cook University, Mbarara University of Science and Technology, University of Kisubi, Kabale University, Busitema University, BRAC University, Infectious Diseases Institute, Ministry of Health, and among others.
Makerere University and Northwestern University have built a strong partnership over the past decade through academic exchange, collaborative research, and capacity building initiatives. “Since 2020, the institutions have deepened their collaboration in research administration through the UASP fellowship, sharing best practices and co-developing of sustainable systems to strengthen research management,” said Prof. Sylvia Antonia Nakimera Nannyonga-Tamusuza, Head of Grants Administration and Management Support Unit (GAMSU) at Makerere University.
She informed the participants that Northwestern University has been instrumental in building the capacity of staff at Makerere University in grants writing, management and administration.
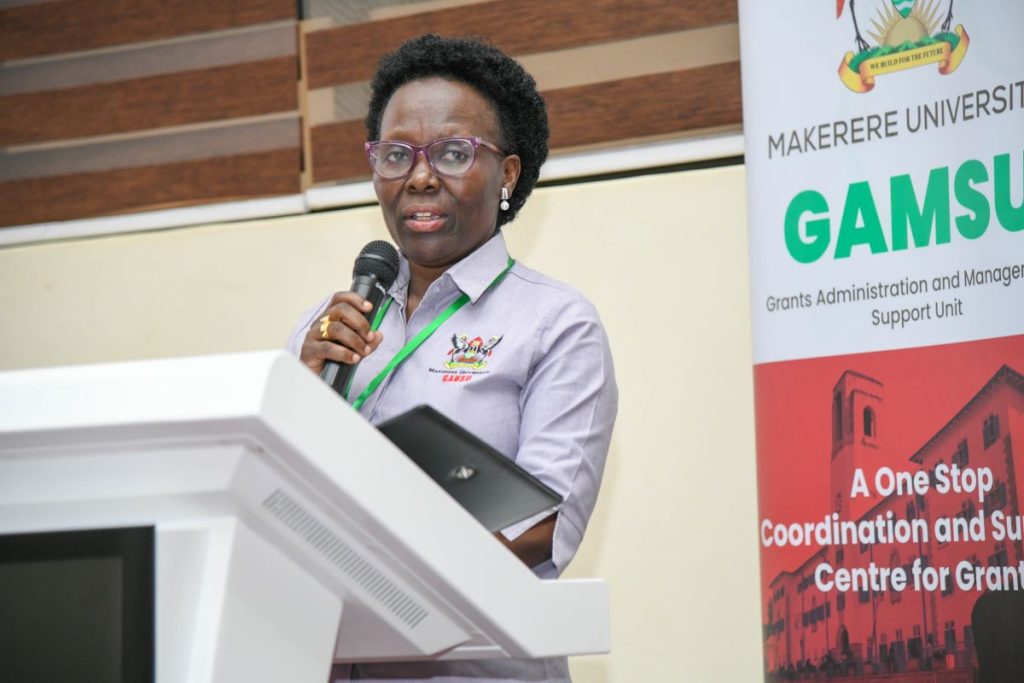

Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza testified that when she was appointed to head GAMSU, she received comprehensive training from Northwestern University, which enhanced her competences and expertise in the field. She acknowledged Kate Klein from Northwestern University for the mentorship that empowered her with valuable knowledge and skills. She reported that five (5) members of staff from Makerere University had been trained by Northwestern University in grants and research management.
Filled with joy, she introduced the team of experts from Northwestern University namely Kate Klein, Bethany Ekesa and Elizabeth Christian to Makerere University, and applauded them for accepting to be facilitators. Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza assured the workshop participants that the team from Northwestern University would not only train them, but would share best practices in grants management and administration as well as networking opportunities.
The training workshop is part of the Expanded Strengthening of Makerere University’s Research Administration Capacity (E-SMAC) program, which focuses on enhancing research administrative systems and staff capacity at Makerere University and its partner institutions. Mordecai Tayebwa is the Program Director and Principal Investigator of the E-SMAC program being implemented from July 2024 to December 2025. The program is funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
The workshop provides a platform to build faculty, grant managers and administrators capacity in grant writing and management, foster cross-functional collaboration across departments, strengthen understanding of budget creation, biosketch and funder systems, encourage mentorship and peer to peer learning, and lay a foundation for regular support.
The training tackles four broader themes namely Grants Introduction and Systems, Proposal Development, Capacity Building, and Outcomes and Forward Planning. It covers vital areas such as grant writing, budgeting, funder systems, compliance, and overall grant administration. It features practical sessions, mentorship opportunities, and collaborative learning, with the goal of strengthening pre-award and post-award grant management and improving research productivity and compliance.
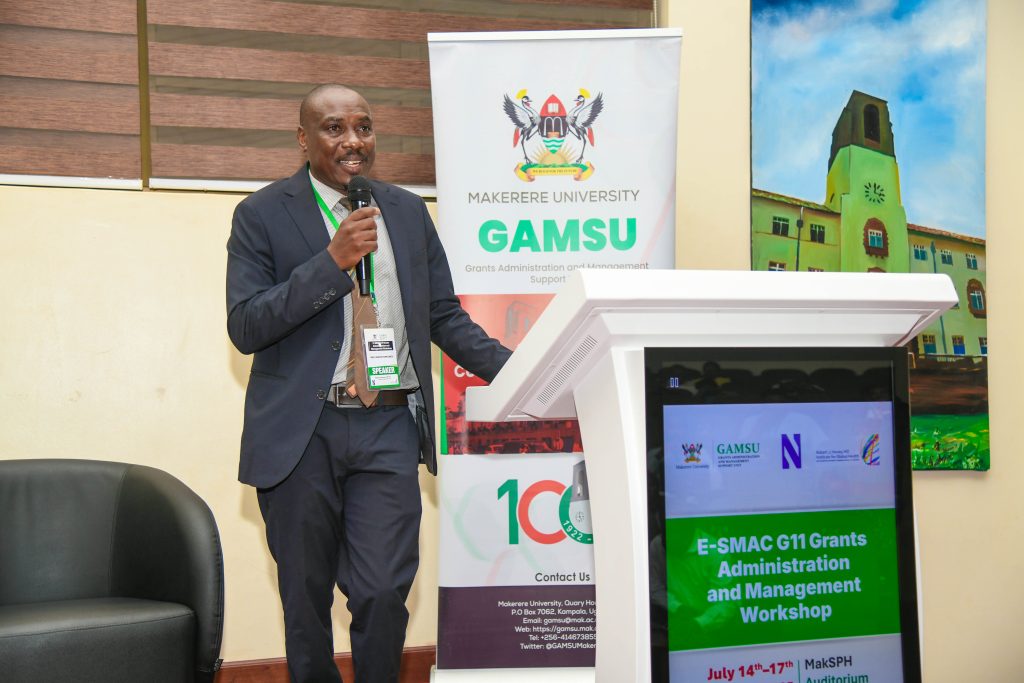

Opening the workshop, the Acting Deputy Vice Chancellor (Finance and Administration) at Makerere University, Prof. Winston Tumps Ireeta urged universities to institutionalize grant management offices and policies as well as strengthening research systems through collaborations.
Sharing his experience, Prof. Ireeta informed the participants that he was involved in the strategic discussion that led to the establishment of GAMSU at Makerere University. “We observed that Makerere University School of Public Health had established a grants office, which was instrumental in attracting and winning funds for research. We were inspired by this best practice. Thus, a comprehensive policy was developed to streamline and strengthen grants management across all colleges at the University,” he said.
Prof. Ireeta noted that Makerere University commits to being a research-driven institution, a strategic direction, that needs a strong funding base. ‘Research grants are therefore a key resource,” he said.
Stressing the importance of adhering to the technical details in the grants management processes, Prof. Ireeta appealed to the participants to be active listeners and maximally utilize the moment to learn from the experienced facilitators.

In the same vein, Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza, applauded the University Council and Management for the strategic direction undertaken to elevate GAMSU from a Unit to a Directorate. This points to the central role of the grants office in the life cycle of Makerere University. She pointed out that GAMSU reports to the Vice Chancellor through the Deputy Vice Chancellor (Finance and Administration).
Established by the University Council in 2020, GAMSU is a central office at Makerere University. It provides professional and coordinated services across the entire grant life-cycle-from identifying funding and developing proposals to ensuring compliance, project execution, financial oversight, and institutional capacity building. GAMSU works closely with academic and administrative staff to support competitive, well-managed and accountable research.
Focusing on the training workshop, Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza called upon the participants to utilize the golden opportunity to deepen their understanding of grants management in advancing research. She acknowledged the role of this collaboration in fostering mutual learning and the sharing of best practices, noting that such initiatives were key in ensuring that research conducted by universities aligns with global standards. She encouraged participants to engage fully in the workshop, collaborate with their peers, and build lasting connections to foster continuous learning.
The Administrative Director of the Havey Institute for Global Health at Northwestern University, Kate Klein, noted that grants administration goes beyond securing funding. She explained that grant administration is about building strong, sustainable systems that support researchers, facilitate collaboration, and ultimately contribute to solving global challenges.
Klein stated that grants administration and management require continuous learning, adaptability, and a strong foundation in regulatory and financial oversight.
“Collaborating and learning from one another is essential,” Klein stated. “When grants administration is effectively managed, it becomes a powerful catalyst for driving impactful change in research, ultimately advancing global initiatives that address the world’s most pressing challenges.”
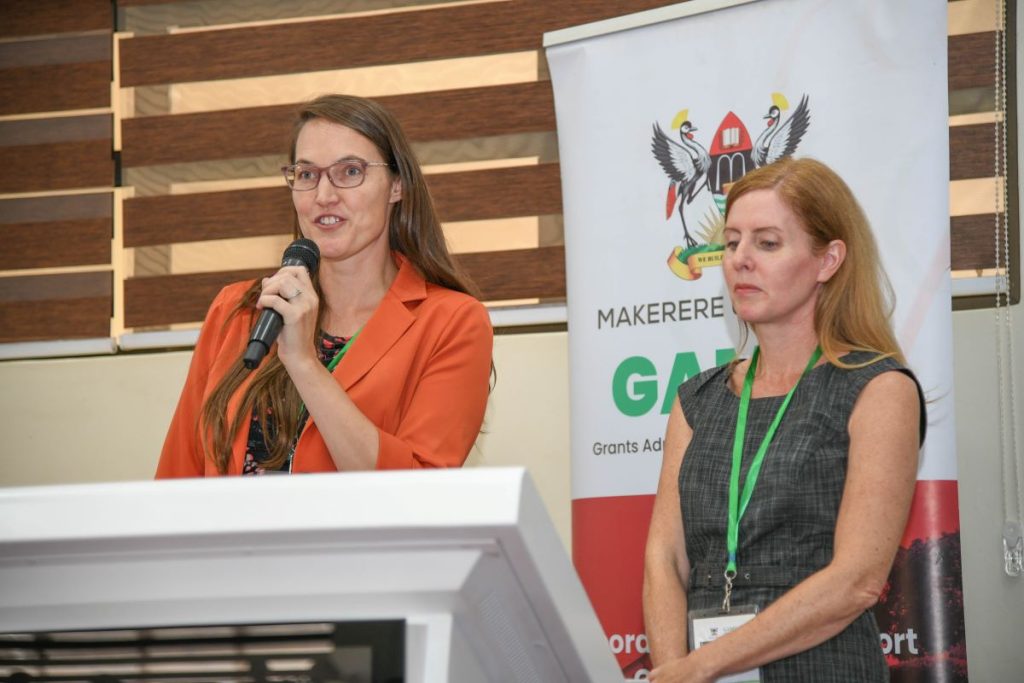

She urged participants to critically analyze their current systems and identify areas where improvements could be made. By doing so, they would be better positioned to manage grants effectively and maximize their impact. She guided that a research grants administrator should be able to design monitoring frameworks, liaising with funders to address grant-specific issues, coordinating compliance, budgeting and reporting to ensure timely and effective implementation.
Presenting the Existing Support Systems and Principal Investigator (PI) agreements, Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza pointed out the critical role of GAMSU in maximizing Makerere University’s access to grants. This is particularly important in the context of limited financial resources, where GAMSU ensures that the university effectively leverages available funding opportunities.
Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza explained that GAMSU ensures research projects align with the priorities of funders and comply with both institutional and external regulations. She emphasized that this alignment is essential for securing and managing grants successfully. She stated that oversight offered by GAMSU, helps streamline the process for researchers. She pointed out that grant management is a collaborative process, involving multiple stakeholders across the university, which ensures that the necessary expertise and support are in place to manage grants effectively.
Underscoring the importance of grant negotiations, particularly with sub-award grants, Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza clarified that such negotiations are most successful when managed at the institutional level, where GAMSU oversees the entire lifecycle of a grant-from identifying funding opportunities to post-award activities.
Harriet Nambooze, the Project Coordinator at Makerere University School of Health Sciences, provided participants with a detailed guide on navigating the National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant application process. She introduced essential tools such as Grants.gov, eRA Commons, SAM.gov and the NATO Commercial and Government Entity (NCAGE), which are critical for applying and receiving an NIH award.
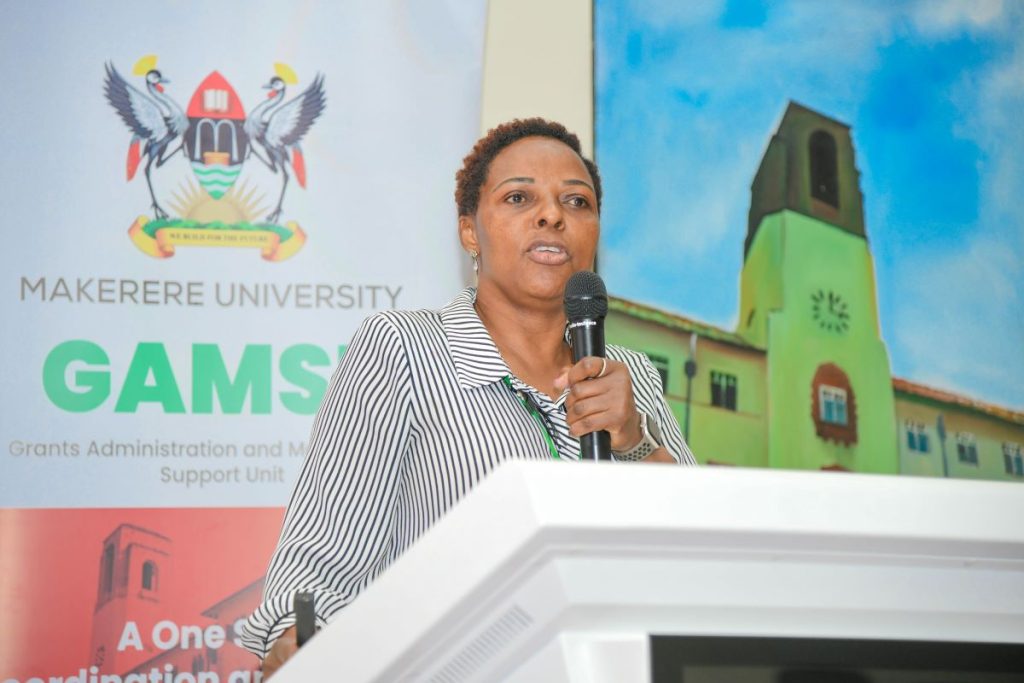

Nambooze stressed the importance of accurately setting up roles in the eRA Commons system, including Signing Official (SO), Principal Investigator (PI), Account Administrator (AA), and Administrative Official (AO), as well as ensuring that profiles are up-to-date across various systems.
She highlighted the necessity of adhering to NIH’s strict submission deadlines and maintaining active individual and institutional profiles to facilitate timely applications. She recommended that institutions should appoint multiple Signing Officials (SOs), to avoid any delays with the required submissions.
Presenting to the participants, Mordecai Tayebwa shared a detailed, step-by-step guide to starting a new grant application. He explained the key elements of the grant process, including the necessity of including a budget, adhering to specific formatting guidelines, and uploading required documents, such as the foreign justification for international projects.
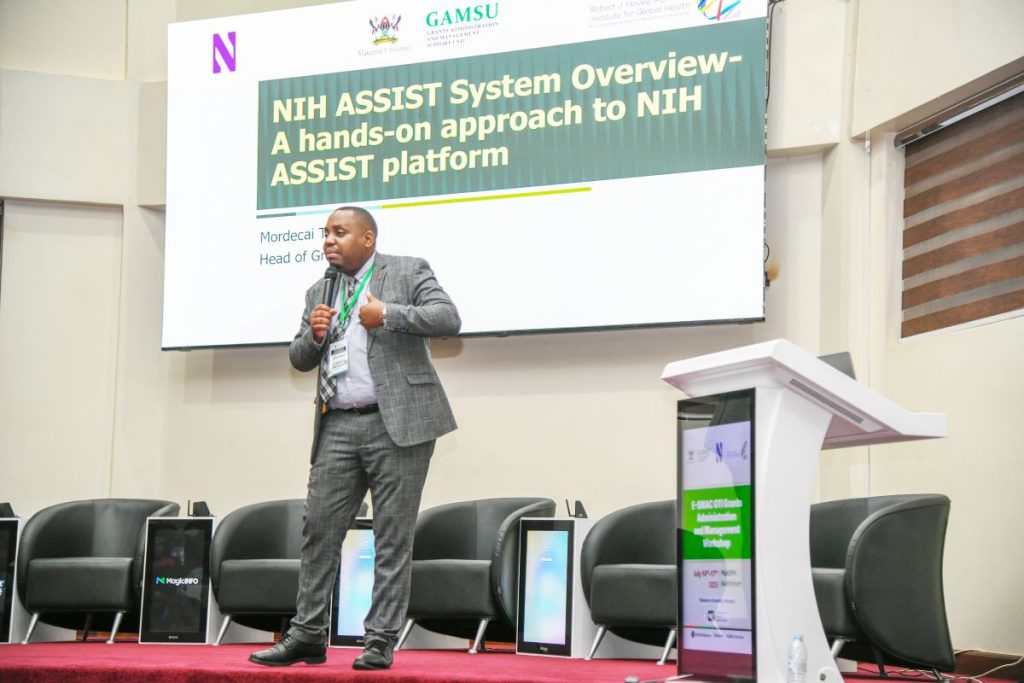

He pointed out the need of thoroughly verifying the application before submission to ascertain that all required documents are included. “This step is crucial to avoid errors that could delay or jeopardize the submission,” he said.
The first day of the workshop set a strong foundation for enhancing grant administration capacity among the participating universities. Participants were equipped with knowledge and skills in grant systems at the national and global levels.
Day two, will focus on topics such as reading funding opportunity announcements, tailoring writing, budget development and justification, sub-contract management, sub-recipient monitoring, and Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs).
On Day three, the participants will gain a deeper understanding of the Grants Office, financial management, internal controls and reporting, peer review process overview and project closeout.
On Day four, the participants will witness the launch of the MakGAP (Makerere University Grants Professional Initiative), listen to a keynote speech on grants management from the Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe, as well as presentations on professional growth through MakGAP, CRA Exam, and Global Research Administration Networks, and professional recognition of research managers and administrators in Africa and post evaluation.
The first day of the workshop set a strong foundation for enhancing grant administration capacity among the participating universities. Participants were equipped with knowledge and skills in grant systems at the national and global levels.
Day two, will focus on topics such as reading funding opportunity announcements, tailoring writing, budget development and justification, sub-contract management, sub-recipient monitoring, and Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs).
On Day three, the participants will gain a deeper understanding of the Grants Office, financial management, internal controls and reporting, peer review process overview and project closeout.
On Day four, the participants will witness the launch of the MakGAP (Makerere University Grants Professional Initiative), listen to a keynote speech on grants management from the Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe, as well as presentations on professional growth through MakGAP, CRA Exam, and Global Research Administration Networks, and professional recognition of research managers and administrators in Africa and post evaluation.
Health
Ugandan Study Flags Girls and Senior Students as a Mental Health High-Risk Group
Published
7 days agoon
July 12, 2025
Based on research led by Max Bobholz and colleagues from Makerere University in Uganda, Essentia Institute of Rural Health, and the Medical College of Wisconsin in the United States.
Adolescence is meant to be a time of holistic growth and self-discovery, but for many Ugandan teenagers, this period is becoming a season of silent mental health struggles. A new study published in PLOS Global Public Health has uncovered a silent but growing crisis: nearly one in five Ugandan secondary school students in the study areas have signs of an emotional disorder. These conditions included anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and adjustment disorders often involving excessive worry, sadness, fear, or mood instability. Also, one in 20 adolescents exhibited behavioral issues ranging from attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and oppositional defiant disorder to substance use and other risky behaviors like alcohol use.
The study, led by Max Bobholz, a PhD candidate in Public and Community Health at the Medical College of Wisconsin, surveyed a sample of 1,953 students aged 10 to 18 years enrolled in eight secondary schools in Iganga district in Eastern Uganda and Mukono district in Central Uganda. This was one of the most comprehensive efforts yet to understand the prevalence and drivers of mental health challenges among school-going Ugandan adolescents.
“We are looking at a generation facing a complex blend of stressors, namely, academic, social, and emotional,” says Bobholz. “Our findings show that certain groups are especially vulnerable, and schools need to be equipped to respond.”

This study results, published on June 12, 2025 was funded by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA), a government agency of the Swedish Ministry for Foreign Affairs, through the Makerere University Postdoctoral Fellowship to one of the investigators, Dr. Catherine Abbo. Other researchers included Julia Dickson-Gomez, Arthur Kiconco, Abdul R. Shour, Simon Kasasa, Laura D. Cassidy, and Ronald Anguzu.
According to the study, girls bear a higher emotional burden. Researchers found that female students had nearly two times higher odds of suffering from emotional disorders such as anxiety or depression than their male peers.
Dr. Catherine Abbo, an Adolescent Psychiatrist and Associate Professor at Makerere University, attributes this to both biological and socio-cultural factors. “Puberty brings hormonal shifts that can heighten emotional sensitivity,” she explains. “But just as importantly, Ugandan girls often face intense pressure to conform to gender roles while also navigating issues like body image, harassment, and future uncertainty.” The researchers are calling for gender-sensitive mental health interventions, particularly in schools, where early support could help mitigate long-term mental health issues.

Higher associations in older teens?
Age also emerged as a key associated factor, with each additional year increasing the odds of behavioral disorders by 20%. “As adolescents grow older, they are more prone to risk-taking, impulsivity, and resistance to authority,” explains Dr. Simon Kasasa, a senior lecturer and biostatistician at Makerere University School of Public Health.

“Combine that with academic pressure and identity-related stress, and it’s no surprise we’re seeing more conduct issues in late adolescence,” Dr. Ronald Anguzu, an Assistant Professor in the Institute for Health and Humanity at the Medical College of Wisconsin, added. This study raises critical questions about whether and how Ugandan secondary schools support older students as they transition toward adulthood.
The unseen influence of family mental health
The study also found that adolescents with a family history of mental illness had twice the odds of exhibiting behavioral problems compared to those without such a history.
“This speaks to the intersection of genetics and environment,” says Bobholz. “Living in a household with people affected by mental illness can mean instability, stigma, and lack of emotional support, all of which weigh heavily on a developing mind.”
The authors recommend that school mental health screening include family mental health history and advocate for greater collaboration between education and health sectors to support at-risk households.

Private schools: High marks, higher stress?
Interestingly, students in private schools had 1.4 times the odds of experiencing emotional disorders compared to those in public schools. Private schools, often seen as academic havens, may inadvertently be cultivating high-pressure environments. “There’s an assumption that better facilities mean better well-being,” says Dr. Abbo. “But intense academic competition, social isolation, and a lack of trained counselors can create emotional pressure cookers.”
Previous research in 47 secondary schools across five districts (Rakai, Kyotera, Masaka, Lwengo, and Kalungu) in southwestern Uganda found that economic and family support helped reduce absenteeism among adolescent girls in secondary schools. However, this support did not significantly improve behavior or reduce grade repetition. The region, which includes districts like Rakai and Masaka, also faces a higher burden of HIV, adding to the challenges young people experience.
Meanwhile, a review of data from 42 primary schools in Luwero District identified school-based mental health interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy and mindset-building approaches as being particularly effective. Researchers now suggest that integrating these strategies, along with efforts to reduce school violence, could go a long way in improving the mental health of Ugandan adolescents.
A-Level pressure: Academic ambition meets mental health strain
The study also found a correlation between advanced (A’level) education and increased risk of emotional disorders. “We selected one school district from each region based on population and past academic performance. As these students prepare for university or the job market, the pressure to succeed becomes enormous,” says Kasasa. “They’re facing a future full of uncertainty, with very little structured mental health support to help them cope.”

A wake-up call for Uganda’s education and health systems
The authors of this study assert the urgent need for school-based mental health programs, especially in private and A-level institutions. These programs should offer routine screening, emotional support, and training for teachers to recognize warning signs of mental health disorders.
Importantly, this study adds weight to calls for a national adolescent mental health policy, tailored to Uganda’s context, with interventions that bridge health, education, and social services.
“Our data shows that mental health challenges are not a fringe issue,” says Bobholz. “They are widespread, significant, and deeply tied to school, home, and society.”
The COVID-19 school closures between 2020 and 2022 deepened feelings of isolation and financial strain, with out-of-school adolescents reporting depression rates as high as 21.5% to 50% higher than their peers who remained in class, according to research published in February 2025. Yet Uganda invests less than 1% of its health budget in mental health, with just one psychiatrist per million people, leaving many teens to cope through cheap alcohol used by 28% of urban youth or untrained healers, as reported by the government paper The New Vision in April 2025. With only 26% of students completing lower secondary school and 35% of the population under age 24, these mental health challenges now pose a serious threat to the country’s future.
Mercy Akankunda of Proven Foundation, a Ugandan NGO supporting vulnerable groups, warns that mental health struggles are quietly eroding the well-being of the country’s youth, over 12 million strong and making up 35% of the population. “These teens are not just statistics. They are the future of Uganda, she asserts. If Uganda hopes to reap the dividends of its young population, addressing adolescent mental health must become and remain a national priority, not just for treatment, but for prevention, resilience, and hope.
Reference:
Bobholz, M., Dickson-Gomez, J., Abbo, C., Kiconco, A., Shour, A.R., Kasasa, S., Cassidy, L.D., & Anguzu, R. (2025). Correlates of behavioral and emotional disorders among school-going adolescents in Uganda. PLOS Global Public Health. Read the study here
Health
Call for Applications: Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR) Training Course
Published
1 week agoon
July 11, 2025By
Mak Editor
The Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR) Training Course, scheduled to take place from July 30th to August 1st, 2025, at the Makerere University College of Health Sciences’ Conference Room.
Background
The SUSTAIN: Advancing Makerere University Masters of Health Sciences in Bioethics program at Makerere University College of Health Sciences aims at developing and institutionalizing a mentorship program in research ethics that facilitates development of bioethics professionals and health researchers who are committed to the growth and application of research ethics in Uganda’s academic and research institutions to the highest possible degree. The Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR) course is one of the short courses that introduces trainees to a framework that involves application of established scientific, professional norms and ethical principles in the performance of all activities related to scientific research.
Course objectives
At the end of this course, trainees should be able to identify, manage and prevent research misconduct.
Course outline
Introduction to RCR; Introduction to Professionalism and Ethics; Human subject’s protection and regulatory framework in Uganda; Humane handling of animal research subjects; Conflict of interest;
Responsible laboratory practices; Mentor-mentee relationships; Collaborative research international, industry); Peer review; Research misconduct (including policies for handling misconduct); Community involvement during research in a low resource setting; Responsibility to society and environment; Responsible financial management; Data acquisition, management, sharing and ownership; Responsible authorship, publication and communication.
Target group
The Responsible Conduct of Research course is targeted at Researchers, Research administrators, Research assistants, Study coordinators, Graduate students and Student supervisors. Certificates will only be awarded to participants with 80% attendance.
Course fee: 205,000/=, or 56USD is payable.
The course fee will cater for meals and refreshments during the training period.
Payment & Registration procedure:
9030026194023, Stanbic Bank, Mulago, Makerere University Biomedical Research Center Limited
Dollar Currency:
9030026194147, Stanbic Bank, Mulago, Makerere University Biomedical Research Center Limited
Please Note: Share payment details on email/whatsup and a hardcopy deposit slip delivered on the first day of the training to Miriam Musazi, Department of anatomy, Bioethics Centre, Room C4,
Mob: +256 782 363 996/ +256 701 363 996, Email: mmusazi@gmail.com.
NB. Only those who will have paid by this date will be considered for the course
Venue: The training will take place at Makerere University College of Health Sciences’ Conference room
Trending
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoRe-advert: Admission to Undergraduate Programmes 2025/2026
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoRe-Advert for Applications for Diploma and Certificate Training
-

 General5 days ago
General5 days agoMakerere University Fees Waiver for 40 First Year Female Students 2025/2026
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoPress Statement on Ranking
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoCall for Applications: Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR) Training Course
