Agriculture & Environment
Academia & Local Govt. Officials in West Nile Sensitized on Forestry & Biodiversity Conservation
Published
4 years agoon
By
Jane Anyango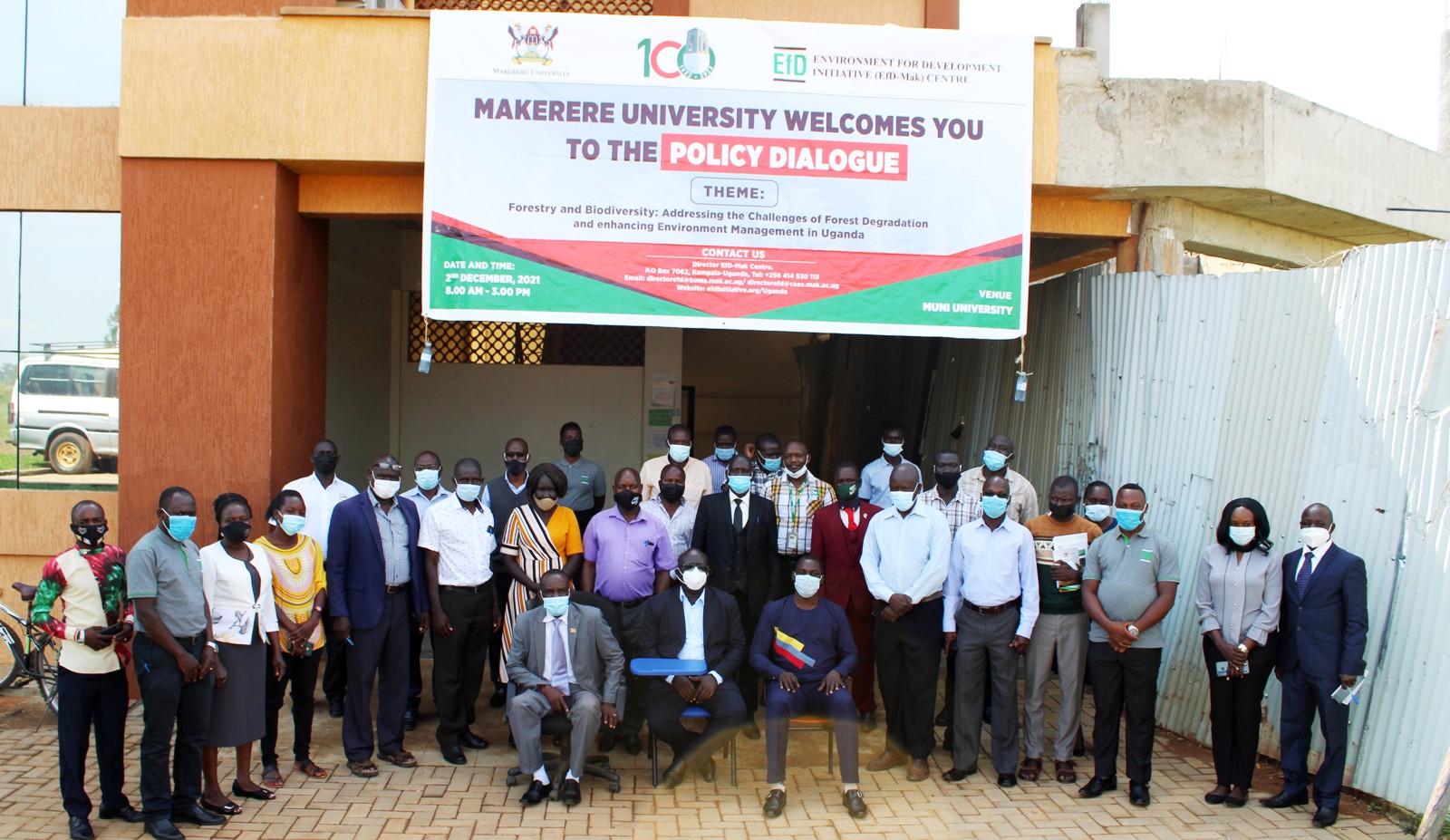
Over 60 participants comprising academia, local government officials, the private sector and civil society organization on 2nd December 2021 converged at Muni University in Arua district to dialogue on the status of forests and bio diversity in West Nile region of Uganda
The policy dialogue was organized by EfD-Mak Centre in collaboration with Muni University and Arua District Local Government under the theme, “Forestry and Biodiversity: Addressing the challenges of Forest Degradation and enhancing Environment Management in Uganda”.
Arua threatened by high Refugee influx and atrocities on the environment
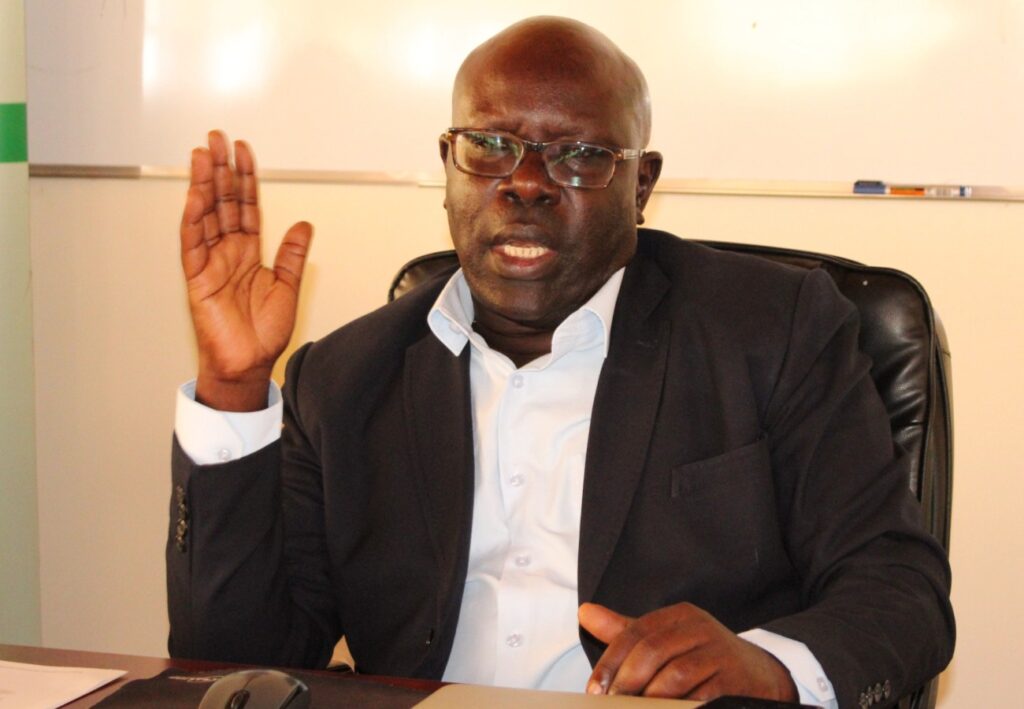
The Ag. Director EfD-Mak Centre Fred Kasalirwe said Arua was selected because a lot of atrocities committed on nature in the region and the fact that Arua Local Government has been at the fore front of this because it is the mother district for all.
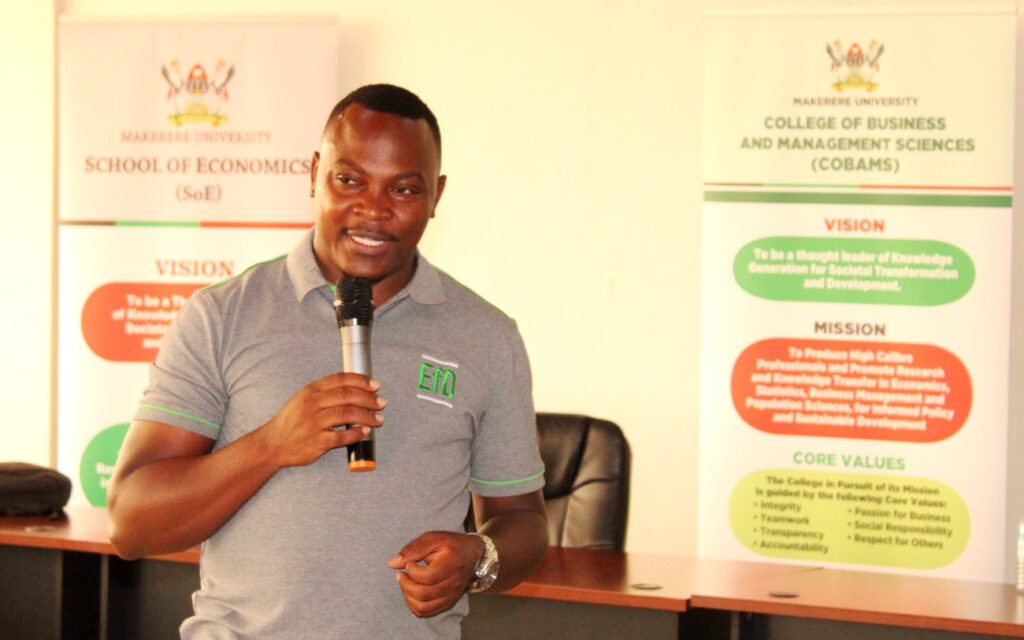

Kasalirwe said there is an influx of refugees and refugee settlements in the region who interface with nature directly because they lack alternative sources. Most of the charcoal and firewood supplied in Kampala and other towns come from West Nile and this has led to the loss of indigenous tree cover. Whoever tries to replace goes for eucalyptus and pine also impacting on the flora and fauna.
“One of the mandates of the centre is to reach out to policy makers and implementers and other stakeholders in the field of environment and natural resources because the policies are implemented at the local government levels. So reaching out to local governments helps to understand what is on ground and when we sit to make policy recommendations, we have voices from the lower local government levels.
The voices gathered from the engagement and debate will be taken up through drafted policy briefs and then we organize a national level dialogue with combined voices from all districts visited, identify policy gaps and engage the ministers and advocates who are parliamentary committees on environment, natural resources and agriculture to air out voices on the parliament floor,” said Kasalirwe.

Forest depletion in West Nile higher than the national rate
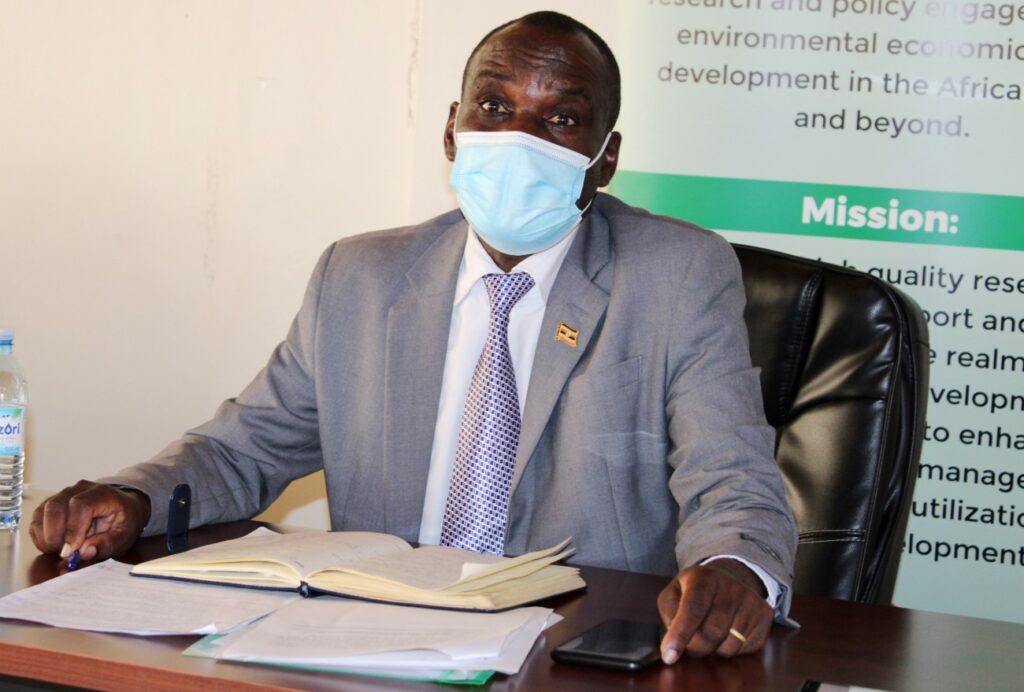
The representative of the Vice chancellor Muni University Prof. Robert Kajobe who is Dean school of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences said the degradation of the environment and forests in the region is relatively more that the national rate.
“We have over 40 years of degradation which has worsened. Uganda has 1.4million refugees and out these over 1million refugees are in West Nile alone. These added to the native population of 3 million culminates to 4 million people looking for materials for construction, fuel wood and charcoal and the toll is on the environment.
Before the refugee status West Nile was known for tobacco growing and the tobacco depleted the soil in the region for a long time because when they were curing tobacco they were using fuel wood selecting indigenous trees which were important with residual values leaving the ground bear”, the Vice Chancellor reported.
Prof. Kajobe decried that West Nile region used to have two rainy seasons (March to May) and another longer one (July to November or up to early December) but in the last three years, the region has had one season of drought from December up to may.

In addition he said there is scarcity of construction materials and fuel wood forcing women and girls to walk 3-5km looking for fuel wood and while hunting for wood, conflicts arise, they are bitten or raped.
The region he reported is experiencing food insecurity due to soil depletion caused by clearance of the forests and because of the drought, annual crops cannot do well while perennial crops like tea cocoa, banana and coffee are no more
Muni university pilots alternative fuel sources and revises curriculum
Muni university according to Prof. Kajobe has embarked on a number of research projects on sustainable and alternative use of the environment including a pilot project on biogas from feacal sludge as a main source of fuel for homes and institution to reduce pressure on forest cutting using sludge.
“The university has done studies on the severity of the problem and secondly we are designing courses in environment and natural resources to bring on board technical people locally both in Masters, Bachelors and Diploma to help in fixing the problem.

We are also partnering with organizations to provide information as technical backstopping to many local and international NGOs, created awareness through media and visited these areas and talked to the local communities to see that the problem is solved. Another key issue is the involvement of the district local government and technical people and political leaders to rally together and solve the problem.
District plans to mitigate forest and biodiversity degradation
The Chairman (LCV) Alfred Okuonzi called upon the District leadership to defend, identify and promote a conservation culture saying, all people know the importance of forests and natural resources in general.
The Chairman noted that a lot has been written and said but all has remained on paper due to lack of exemplary leadership at the district adding that time has come for the district to announce tree cutting in West Nile as an outbreak just like COVID-19 to attract the attention and financing from every stakeholder.
“With the outbreak of COVID-19, we saw vehicles and financial assistance flow to districts. But when trees are cut nothing is done. We need special funding to green the region. If we continue interfering with the environment supporting our livelihoods, the pattern of rains will continue to be distorted, agricultural production will continue to be affected leading to malnutrition and poor performance in schools”.

The district chairman expressed the need to put in place more staffing in the forest department to the level of Principal and senior forest officers as is in other sectors.
He said although government has injected resources in environmental protection, the resultant impact remain minimal largely due to poor leadership and uncontrolled reproduction increasing the population heavily dependent on the environment.
He said the district plans to spend resources on individual leaders and homesteads to ensure they plant trees, change people’s mindset and promote forest management. The district he said is engaging the National Forestry Authority to include district forest office in all the activities.
The Chairman said plans are underway to work with the Uganda National Roads Authority to provide seedlings to plant trees along the roads while the next two years will be dedicated as years of greening to restore the glory of Arua district.
He encouraged district technocrats to work with media to provide information to raise awareness and provide information and the media on the other hand, to package the messages in a way that change the mindset of the communities.

While closing the workshop, the Deputy Resident District Commissioner Ocen Robert underscored the importance of environment and forest in livelihood provision and in regulating the climate.
“I liked the statistics by one presenter who said a human being requires 700 kg of oxygen per year but one tree produces about 100 kg of oxygen. If one is to survive, you need to plant 7 trees and encourage every family member to plant 7 trees annually”
He proposed the need to come up with subsidies on alternative sources of energy such as electricity and solar and gas to make it more accessible and affordable to reduce stress on the forests.
He also proposed the need to discourage people using firewood – cured bricks and promote alternative building materials such as blocks from cement, the need to speak to local residents on the status and advantages of the forests such that conservation and protection begins right from the community level.He appealed to leaders to speak one language in order to succeed in implementation of the district ordinances.
You may like
-

Ugandan Study Flags Girls and Senior Students as a Mental Health High-Risk Group
-
Call For Applications: PhD Fellowship Training Position
-


Makerere Hailed for Its Leadership in Health Policy and Knowledge Systems
-


School of Business Conducts Strategic Leadership Training for Makerere University Managers
-


Makerere University, DFCU Bank Sign MoU to Advance Innovation, Student Leadership and Research
-


Advancing Regional Health Priorities Through the CARTA Research Hubs
Agriculture & Environment
Mak Moves to Revitalize Food Technology & Business Incubation Centre to Drive Innovation & Entrepreneurship
Published
5 hours agoon
July 14, 2025By
Mak Editor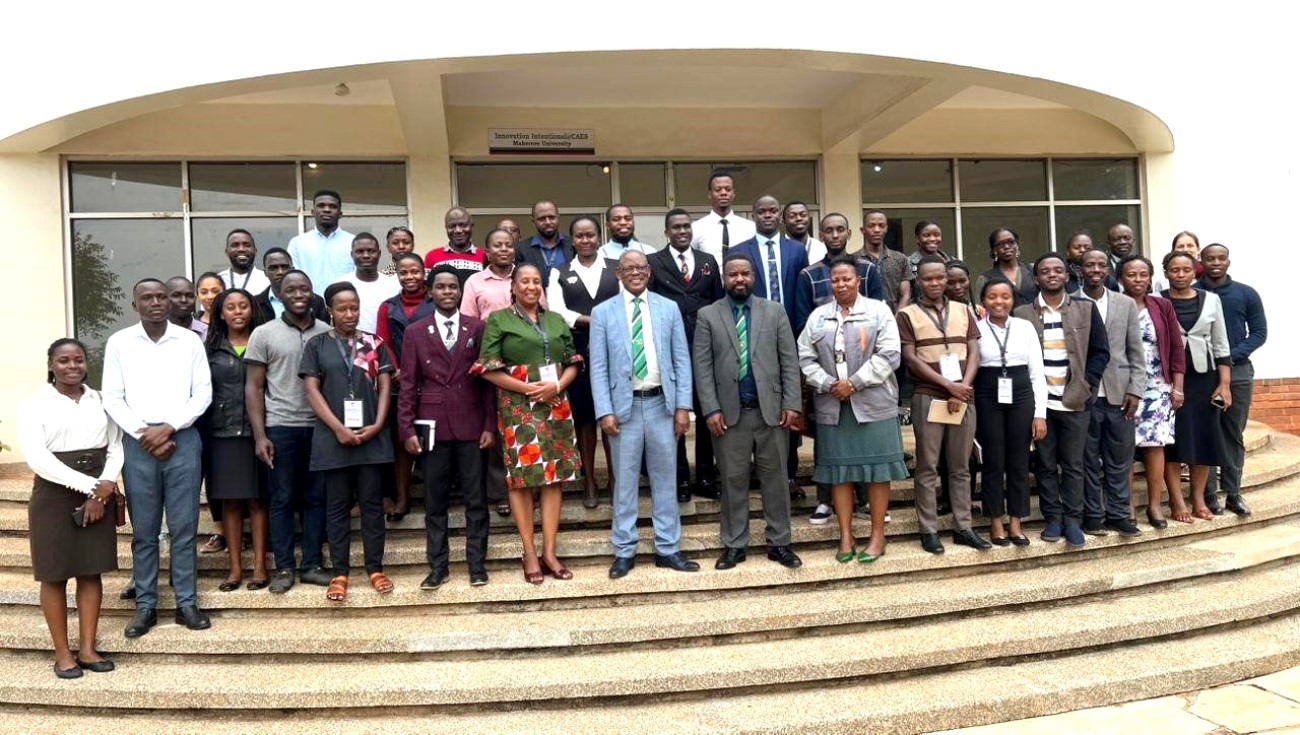
By Ssembogga Derrick
Makerere University marked a significant milestone on Thursday, 10th July 2025, with the launch of the revitalization programme for the Food Technology and Business Incubation Centre (FTBIC). This initiative is poised to position the FTBIC as a national hub for food innovation, student enterprise development, and agro-industrial transformation.
Hosted under the School of Food Technology, Nutrition and Bioengineering (SFTNB) at the College of the Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES), the revitalization of the FTBIC is intended to bridge the gap between academia and industry. “We aim to achieve this by supporting food-based start-ups, enhancing graduate entrepreneurship, and promoting the commercialization of research,” Dr Julia Kigozi, Dean, SFTNB explained. The project receives critical funding from the Makerere University Research and Innovations Fund (MakRIF), which consistently supports innovation and research-based development at the university.
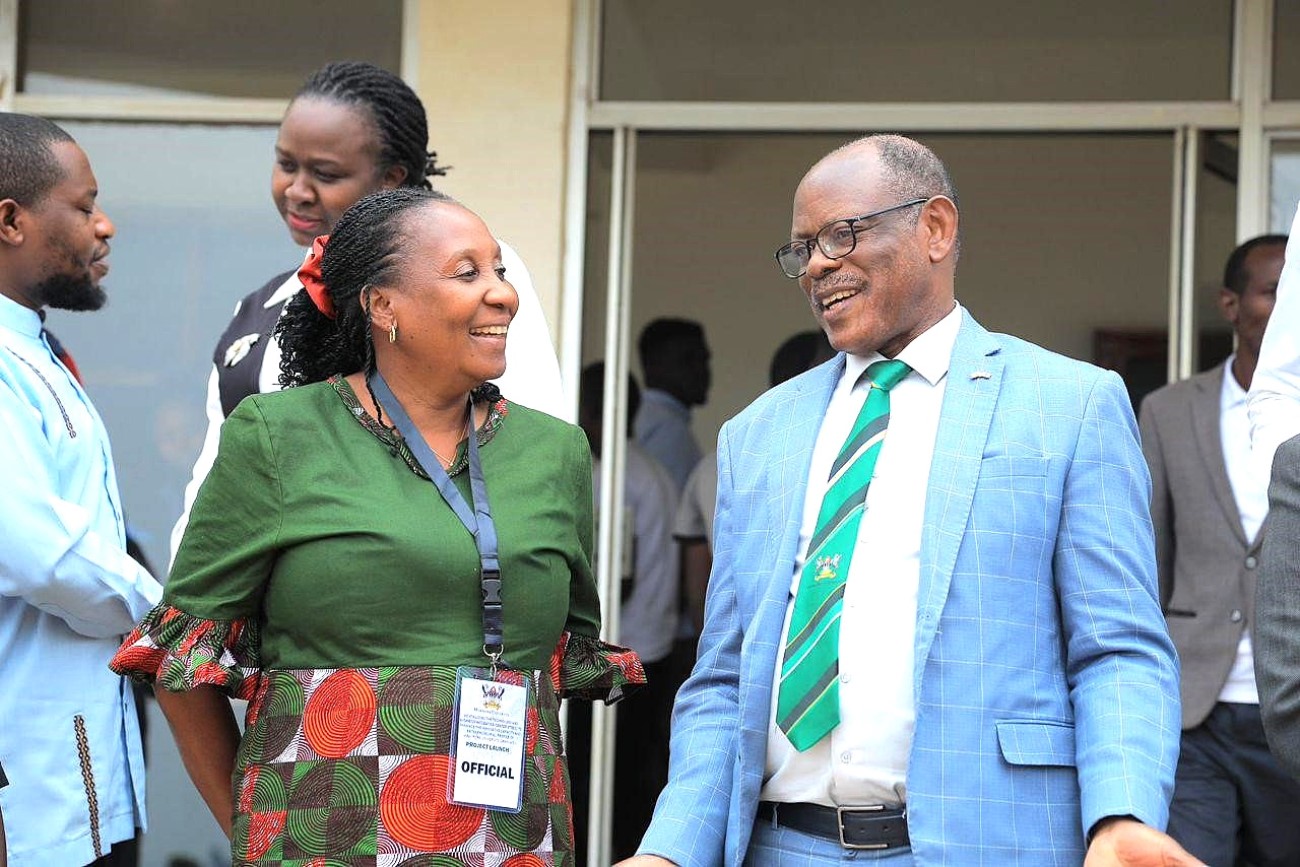

Unveiling a New Strategic Vision
The event, held under the theme “Revitalizing FTBIC to Unlock Innovation and Entrepreneurship Potential among Makerere University Graduates”, marked the official launch of the Centre’s revitalization programme to key stakeholders. It featured the presentation of FTBIC’s new strategic vision and direction, highlighting the commitment of the institution and its partners to fostering graduate entrepreneurship and innovation in food systems. The event also aimed to raise awareness of the Centre’s crucial role in supporting industry, research, and national development.
Participation of stakeholders
The launch attracted a vibrant and diverse audience of over 50 participants. Among the attendees were student representatives; partners from other incubation centers both within and outside Makerere University, including MIIC, UNIPOD, and DGI; as well as representatives from national innovation stakeholders such as Uganda Industrial Research Institute (UIRI) and StartHub Africa.
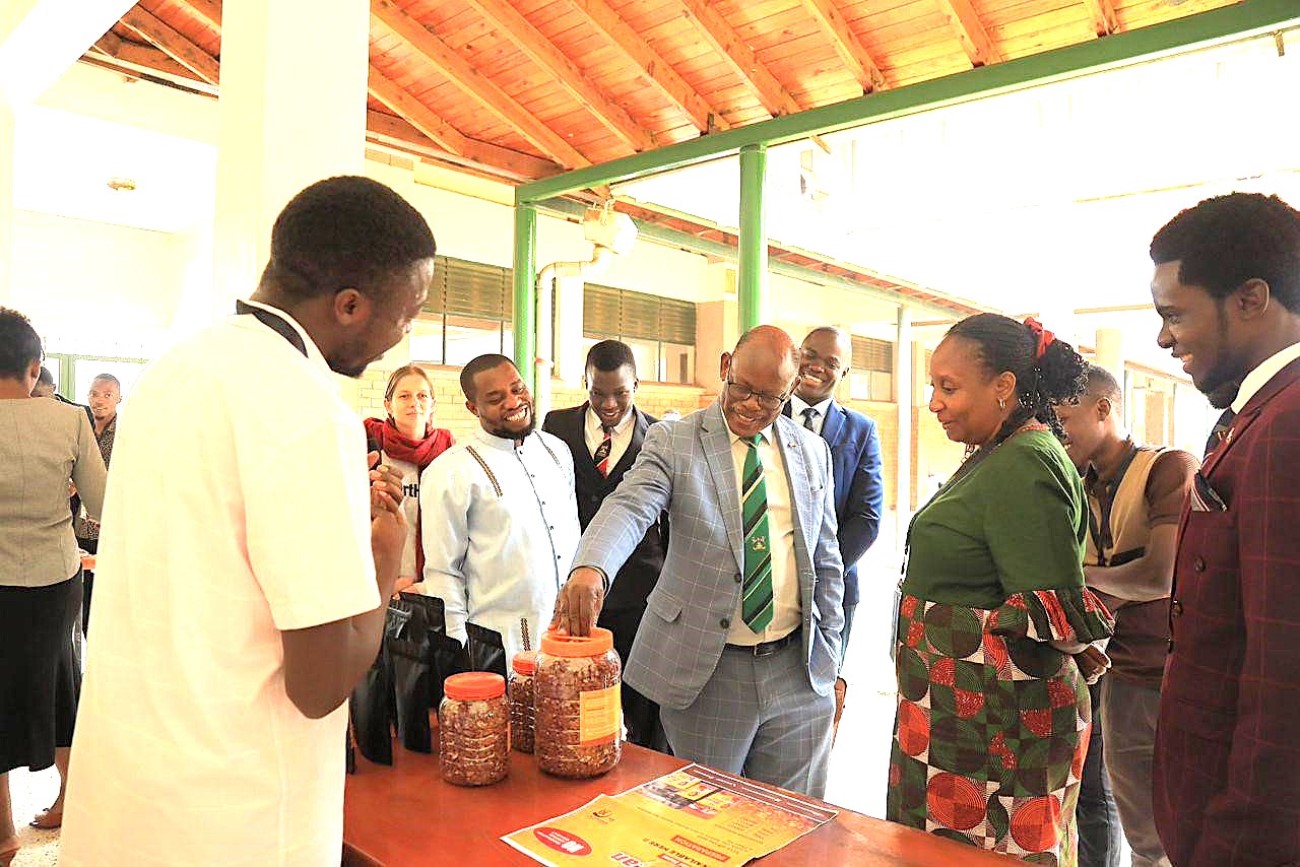

Most notably, the event was honored by the presence of the Vice Chancellor of Makerere University Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe. The Vice Chancellor commended the revitalization efforts, acknowledging the Centre’s immense potential to incubate hundreds of food-based start-ups and create employment opportunities for thousands of graduates. “The Centre is now well-positioned to become a flagship platform for innovation, employment creation, and agro-industrial development in Uganda and beyond. Makerere University remains committed to supporting such initiatives that align with national priorities and global development goals.”
The event featured the unveiling of the operational framework for the revitalized Centre, highlighting its commitment to innovation, entrepreneurship, and practical graduate training. Stakeholders in attendance expressed enthusiasm and pledged support for future collaboration, research, and product development initiatives aligned with national development priorities. The event also provided a platform to deepen partnerships with private sector actors and development organizations, reinforcing confidence in the Centre’s potential to serve as a national model for university-led incubation.

Agriculture & Environment
SophiA Project Upgrades Medical Infrastructure at Buvuma Health Centre IV, Trains Technicians for Maintenance Works
Published
5 days agoon
July 9, 2025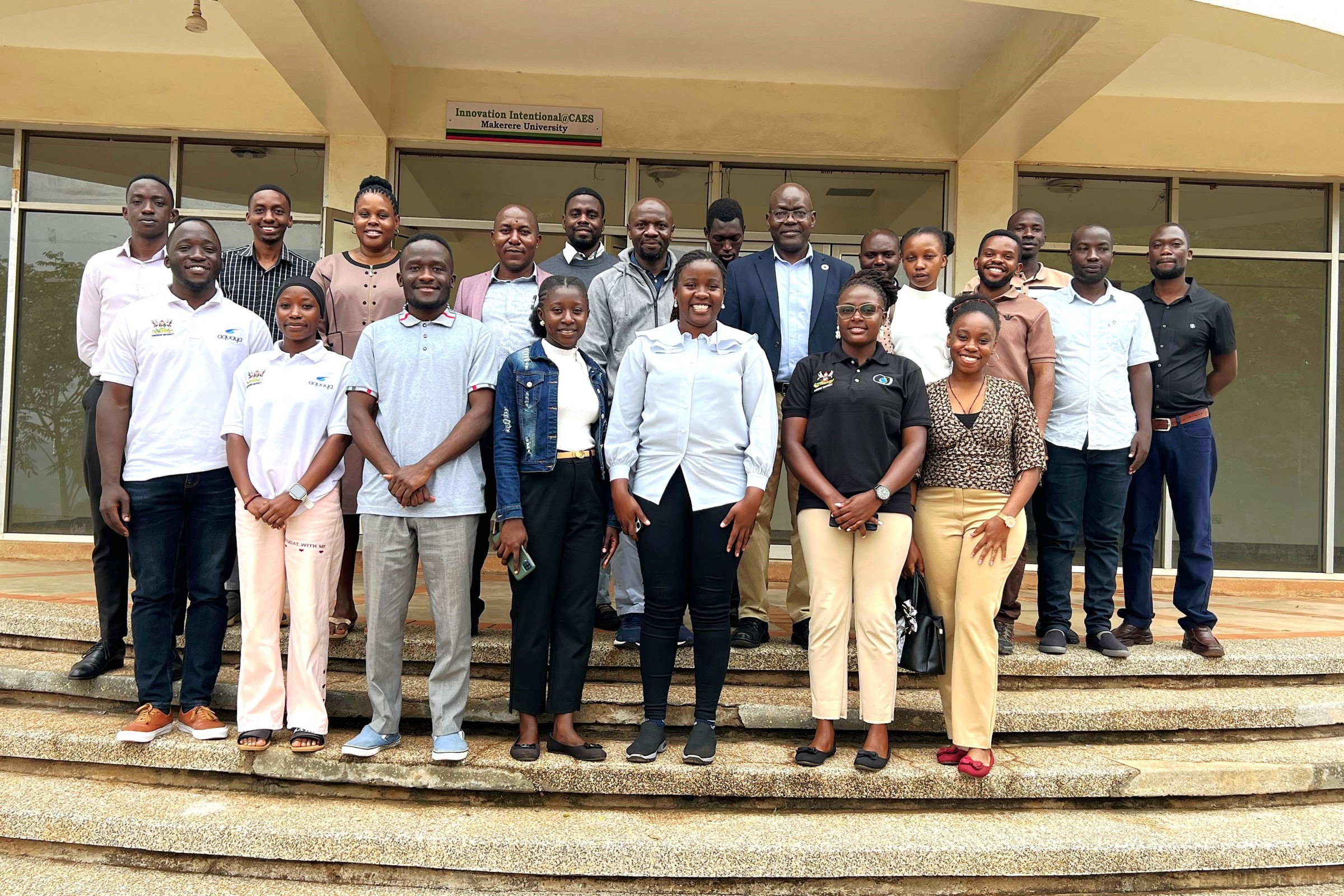
Overview of the Sustainable Off-Grid Solutions for Pharmacies and Hospitals in Africa (SophiA) Project
Despite ongoing urbanization across Africa, the majority of the population still resides in rural and remote areas, where infrastructure development remains limited. These regions face significant challenges such as lack of access to healthcare, education, clean water, and reliable electricity, contributing to higher rates of illness and poverty compared to urban centres. According to reports, Sub-Saharan Africa has approximately 120,000 public health facilities (22,000 hospitals and 98,000 health posts), of which around 26% lack any electricity access, and only 28% have reliable power supply.
Access to good healthcare is critical for sustainable development. However, many rural medical centres operate under harsh conditions – using polluted water, lacking cooling for medicines, and facing poor sanitation – largely due to unreliable electricity and water supply. Although half of the population in Sub-Saharan Africa lacks electricity, the region has abundant renewable energy potential that can be effectively harnessed through off-grid solar photovoltaic (PV) systems.

To address the above-mentioned challenges facing the African Continent, Makerere University in partnership with 13 organizations across Europe and Africa developed a project titled, “Sustainable Off-grid solutions for Pharmacies and Hospitals in Africa (SophiA)”. The five-year project that began on 1st October 2021 is funded by the European Union (Project: 101036836 – SophiA – H2020-LC-GD-2-3-2020). At Makerere University, the project is coordinated by Dr. Nicholas Kiggundu, Associate Professor in the Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES).
Piloted in Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Malawi, and Uganda, SophiA aims to provide sustainable off-grid energy solutions to rural and remote health facilities, fostering economic growth and ensuring equitable access to energy and healthcare. Using various technologies, such as photovoltaics, solar thermal, electrical and thermal storage, water treatment and natural refrigerants with low global warming potential, SophiA has developed and manufactured locally innovative, modular, affordable and efficient solar powered systems for providing:
- Safe and clean drinking water, free of bacteria and viruses, and deionised water for medical purposes;
- Hot water and steam production for thermal requirements of the hospitals;
- Cooling of medicines and food at +5°C;
- Low temperature storage of blood plasma and vaccines at -30°C;
- Ultra-low temperature storage of sensitive medication (e.g. some Covid-19 or Ebola vaccines) at -70°C.

In addition, PV MedPort, a simple and 100% solar-powered solution has been developed and tested as a mobile health care station in small remote areas in 4 different geographical conditions in Africa. The SophiA system has been manufactured in Africa and will provide, for the first-time, innovative solutions based on climate-friendly natural refrigerants to cover cooling demand for three different temperature ranges (-70°C, -30°C and +5°C). The system has been tested and demonstrated at four rural hospitals in remote regions throughout the African continent covering the major geographical regions and different climatic conditions in Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Malawi and Uganda.
SophiA Project initiatives in Uganda
In Uganda, all Health Centre IV hospitals with surgical theatres have been connected to the national grid except Buvuma Health Centre IV, which serves over 120,000 people scattered across 52 islands. Recognizing this gap, the Ministry of Health selected Buvuma Health Centre IV for the SophiA project to demonstrate sustainable off-grid solutions.

The SophiA System at Buvuma Health Centre IV provides the following services:
- Off-grid electricity supply
- Safe, clean drinking water for patients, staff, and the community
- Hot water and steam systems crucial for maternal care
- Solar-powered cooking and meal preparation
- Cooling systems for surgery and intensive care units
- Refrigeration for medicines at +5°C, blood plasma storage at -30°C, and ultra-low temperature storage (-70°C) for sensitive vaccines such as those for COVID-19 and Ebola
Training of Trainers Workshop
As the SophiA project approaches completion in September 2025, it is vital to establish a skilled pool of technicians capable of handling maintenance and minor repairs of the system components, including solar panels, water treatment units, generators, batteries, and cooking kits.

From June 23 to 27, 2025, Makerere University hosted a comprehensive Training of Trainers workshop. The training programme encompassed a diverse range of topics delivered by subject matter experts from institutions, including Makerere University (Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering – CAES, and the College of Engineering, Design, Art and Technology – CEDAT), Hochschule University of Applied Sciences, and Busitema University. Participants were carefully selected from diverse professional backgrounds, including recent engineering graduates from CAES and CEDAT, Makerere University, University technical staff, personnel from Kyambogo University, officials from Buvuma District Works and Health Departments, and electricians from Kampala City. The training sessions were conducted at Makerere University and Buvuma Health Centre IV Hospital.
Training Modules Included:
- Sustainable energy systems and their practical applications
- Energy generation and storage technologies
- Solar water heating: design, operation, maintenance, and performance optimization of solar water heaters, crop dryers, and concentrating solar heaters
- Solar PV technologies in Uganda: cell technology, system design, operations, maintenance, and hands-on practicals for standalone and grid-connected systems
- Public health implications of water quality
- Water treatment and quality management, including protocols, parameters, and case study on the MCDI treatment system
- Water quality testing methodologies
- Introduction to sustainable refrigeration and cooling technologies
- Environmental impact and safety considerations for refrigerants
- Refrigeration cycles and component overview
- Life cycle assessment of SophiA technologies
- Thermal energy storage within the SophiA system
- Steam as a productive energy source
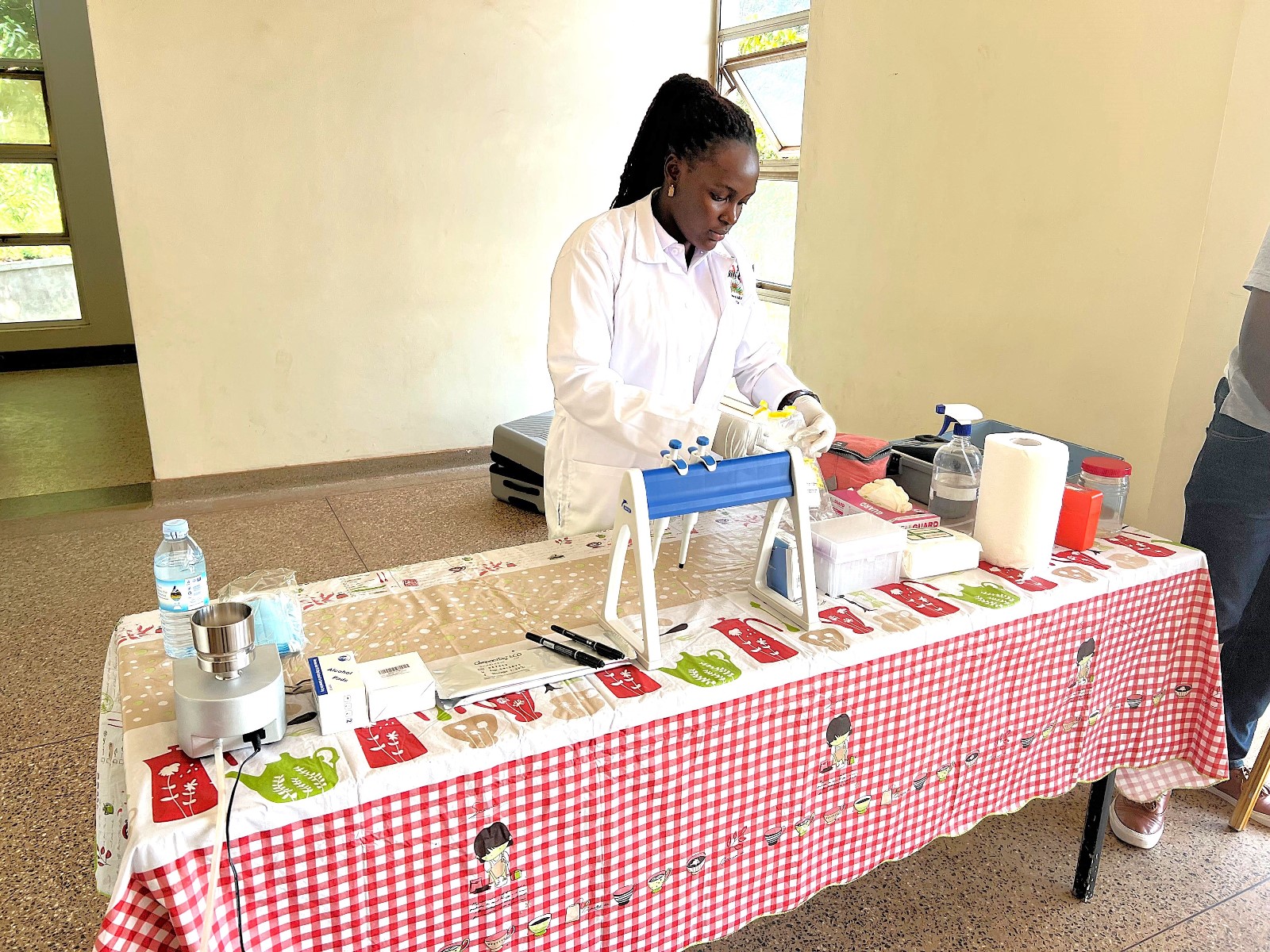

The Training Sessions
Day One: Introduction to foundational concepts in solar energy technologies
The first day of the SophiA Train the Trainers Workshop focused on building foundational knowledge in sustainable and solar energy systems. Led by Dr. Peter Tumutegyereize and Dr. Francis Mujjuni, participants explored a range of technologies and applications critical to clean energy deployment.
Key topics included:
Sustainable Energy Systems: Introduction to renewable energy systems including bioenergy, hydro, wind, geothermal, hydrogen fuel cells, and battery storage.
Solar Radiation & Geometry: Understanding solar constants, irradiance, and the impact of atmospheric conditions on solar performance.
Solar Thermal Technologies: Detailed look at solar water heating systems (FPCs and ETCs), maintenance, sizing, and solar dryers for agricultural and industrial use.
Photovoltaic (PV) Systems: Working principles, types of PV cells, performance factors, and diagnostics. Practical testing techniques and metrics like Voc, Isc, MPP, and PR were discussed.
Simulation & Application: Olivia Nakiwanuka demonstrated a PVsyst-based simulation of a 2.55 kWp standalone system for a conference hall, showing a high solar fraction (97.88%) and low LCOE (USD 0.03/kWh).

The sessions emphasized practical skills, performance analysis, and real-world application, equipping participants to train others and support solar adoption, especially in rural and off-grid settings.
Day Two: Water Treatment Technologies
The second day focused on water treatment technologies relevant to low-resource healthcare settings. Facilitated by Sneha De and Mr. Duc Dinh Ngoc from Hochschule Karlsruhe University, sessions covered technical, environmental, and operational challenges, with contributions from Dr. Joshua Wanyama on water quality management and Dr. Prossie Nakawuka on practical water testing.
Key challenges addressed included unreliable water supply and contamination in healthcare facilities, emphasizing the need for decentralized water treatment, especially in rural areas.
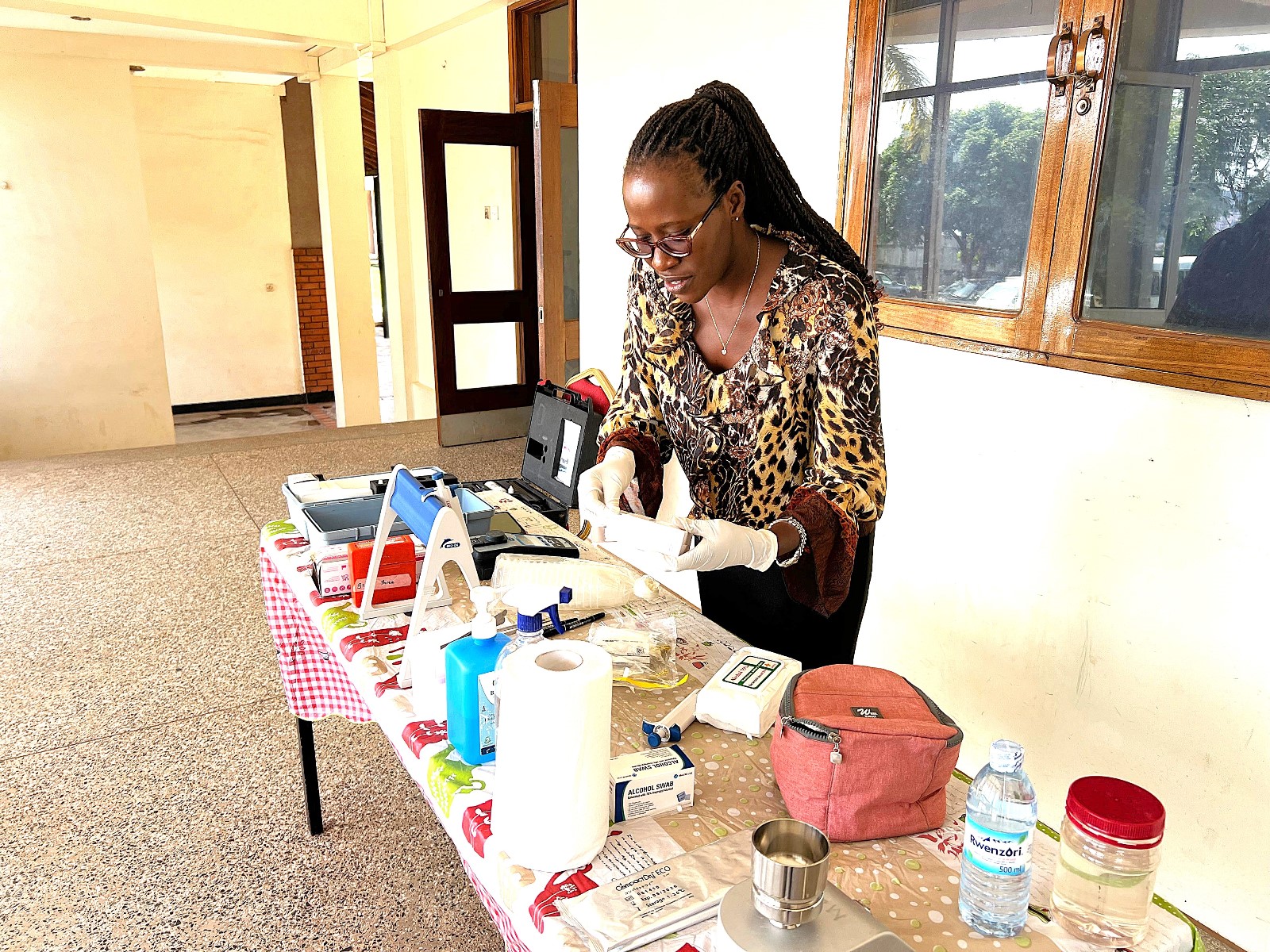

Sneha De reviewed biological and physical/chemical water treatment methods, highlighting technologies such as activated sludge, filtration, membrane bioreactors, and advanced disinfection techniques. The SophiA modular water treatment system, integrating ultrafiltration and membrane capacitive deionisation (MCDI), was introduced as a scalable solution for producing safe drinking and deionised water for medical use.
Mr. Duc Dinh Ngoc trained participants on the MCDI technology, an energy-efficient method for salt and fluoride removal suitable for low-salinity water.

Dr. Joshua Wanyama discussed the water quality management protocols, outlining key physical, chemical, and biological water parameters and monitoring strategies, including modern IoT-based tools, to ensure water safety and public health.
The day concluded with a hands-on lab session by Dr. Prossie Nakawuka, where participants practiced water quality testing using turbidimeters, incubators, and filtration techniques.
Overall, Day Two combined theoretical insights, technology demonstrations, and practical skills, preparing participants to implement sustainable water treatment and quality management systems in healthcare environments.

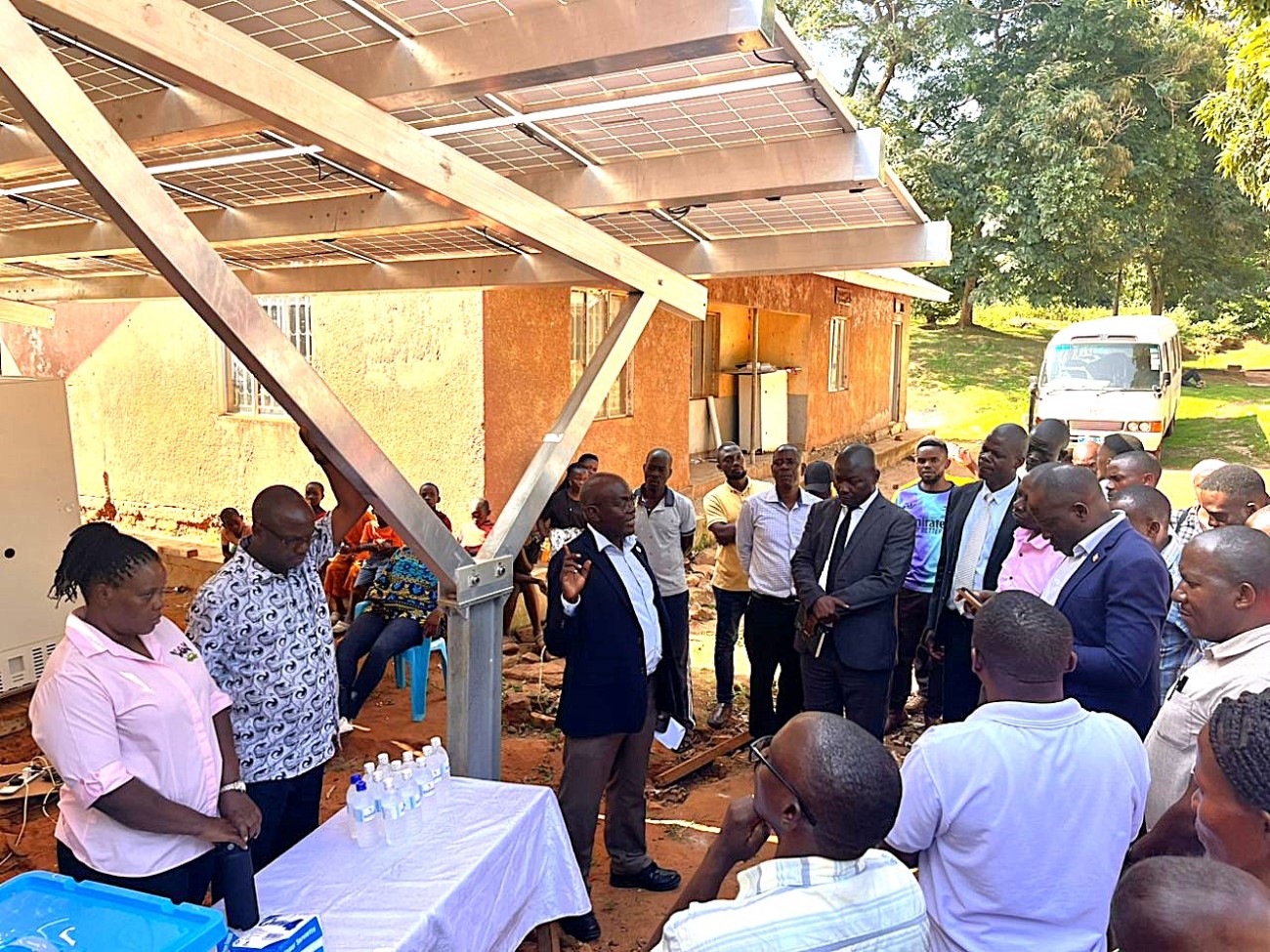
Day Three: Refrigeration and Cold Storage
The third day of the SophiA workshop focused on sustainable refrigeration and cold storage technologies tailored for healthcare in Sub-Saharan Africa. Experts discussed energy-efficient, climate-friendly cooling solutions vital for vaccine storage, medicines, and diagnostics, especially in off-grid and rural settings.
Key highlights included the introduction of solar-powered and biomass-based refrigeration systems, thermal energy storage methods, and the use of natural refrigerants like propane, ammonia, and CO₂ as environmentally safer alternatives. Presentations emphasized the critical role of refrigeration in healthcare and the urgent need to replace harmful chemicals with sustainable technologies.
Sessions covered real-world applications such as the SophiA cooling containers in Burkina Faso, safety protocols for flammable refrigerants, and the environmental and economic benefits of solar refrigeration systems assessed through life cycle analysis.

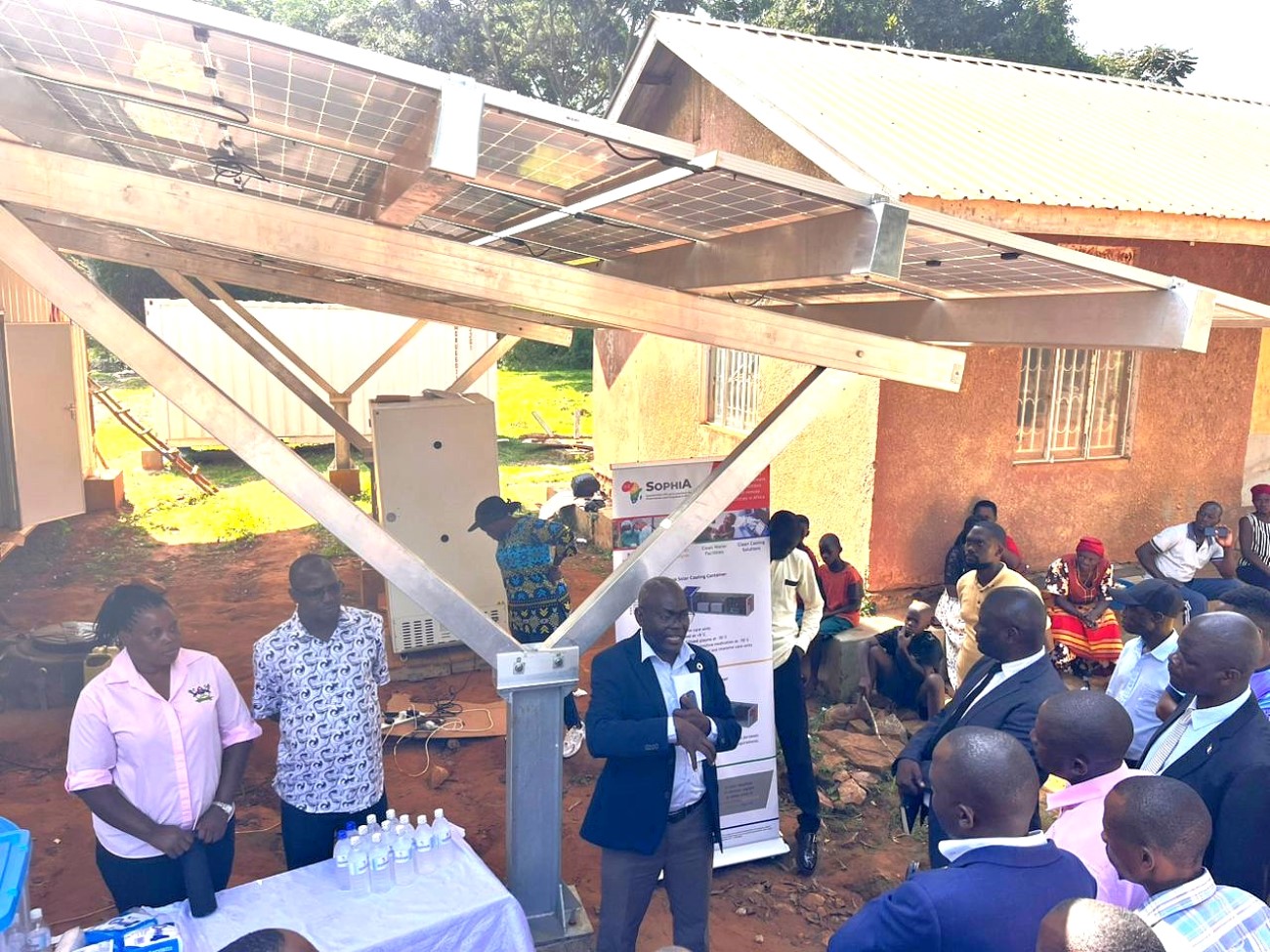
The day ended with an interactive quiz and discussion, reinforcing learning and encouraging participants to apply sustainable cooling practices in their communities.
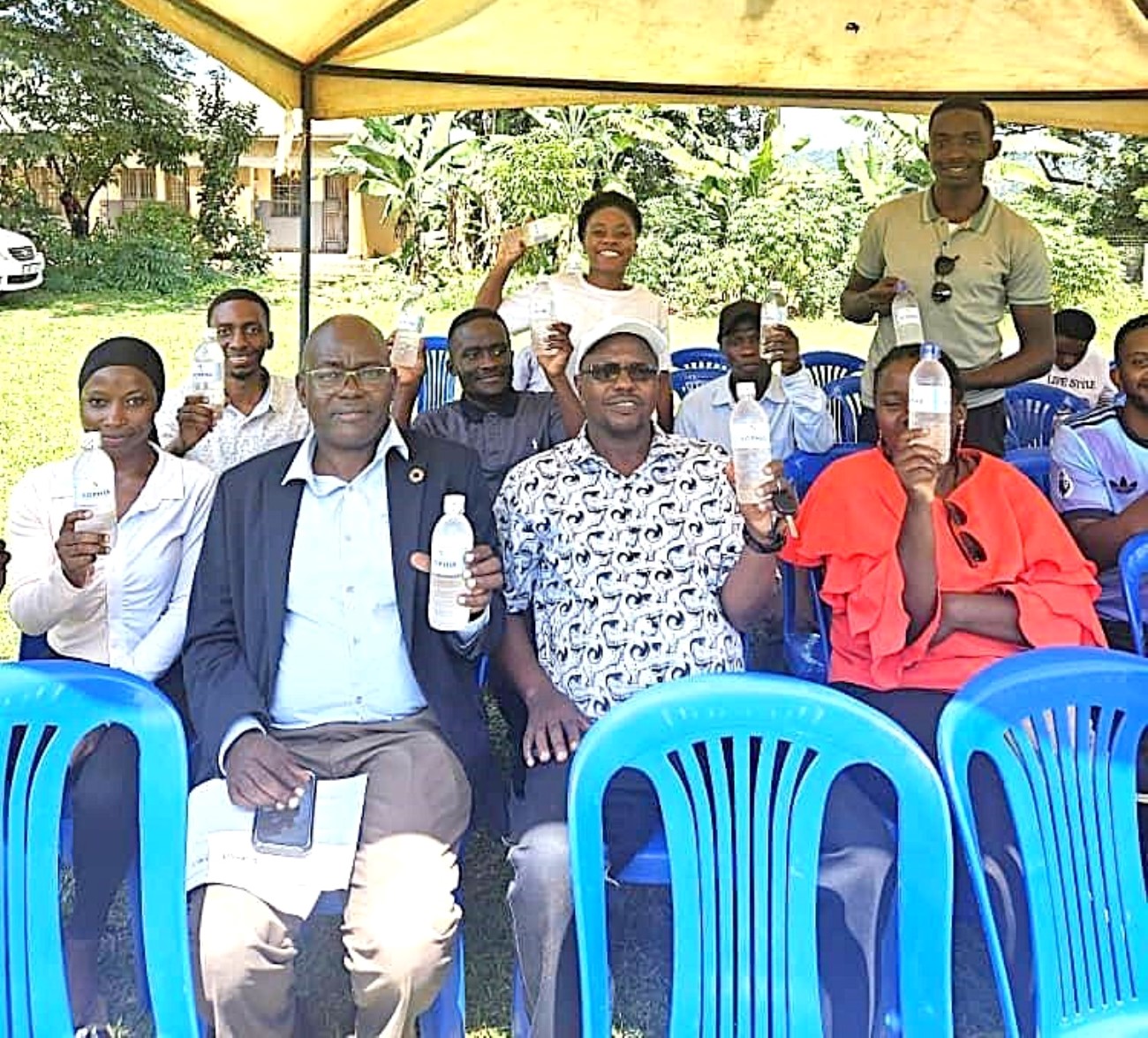
Day Four: World Refrigeration Day & Field Visit to Buvuma Island
The fourth day of the SophiA Train the Trainers workshop was dedicated to the celebration of the World Refrigeration Day and a field excursion to Buvuma Island, providing participants with a unique opportunity to witness the SophiA system in action. The day was coordinated by Dr. Sarah Bimbona and Dr. Nicholas Kiggundu, who led the delegation to Buvuma Health Centre IV, the pilot site for the SophiA installation in Uganda.

The visit served as both a practical extension of the previous day’s technical sessions and a community engagement event. Participants were able to observe the installed SophiA system, which integrates solar-powered refrigeration, water treatment and steam generation technologies designed for off-grid healthcare settings. During the visit, Dr. Kiggundu provided a detailed briefing to local stakeholders, including representatives from the Buvuma District Local Government, delegates from the Buganda Kingdom, and members of the local community. He explained how the SophiA system will enhance healthcare delivery on the island through reliable cold storage for vaccines and medicines, access to clean drinking water, and steam generated for cooking and use in the maternity wards.
As part of the long-term sustainability plan for the SophiA system, the launch of SophiA Water was announced, an entrepreneurial initiative designed to generate revenue locally for the operation and maintenance of the system.

The field trip ended with a certificate awarding ceremony in appreciation of the participants’ dedication and active engagement throughout the training programme.
Agriculture & Environment
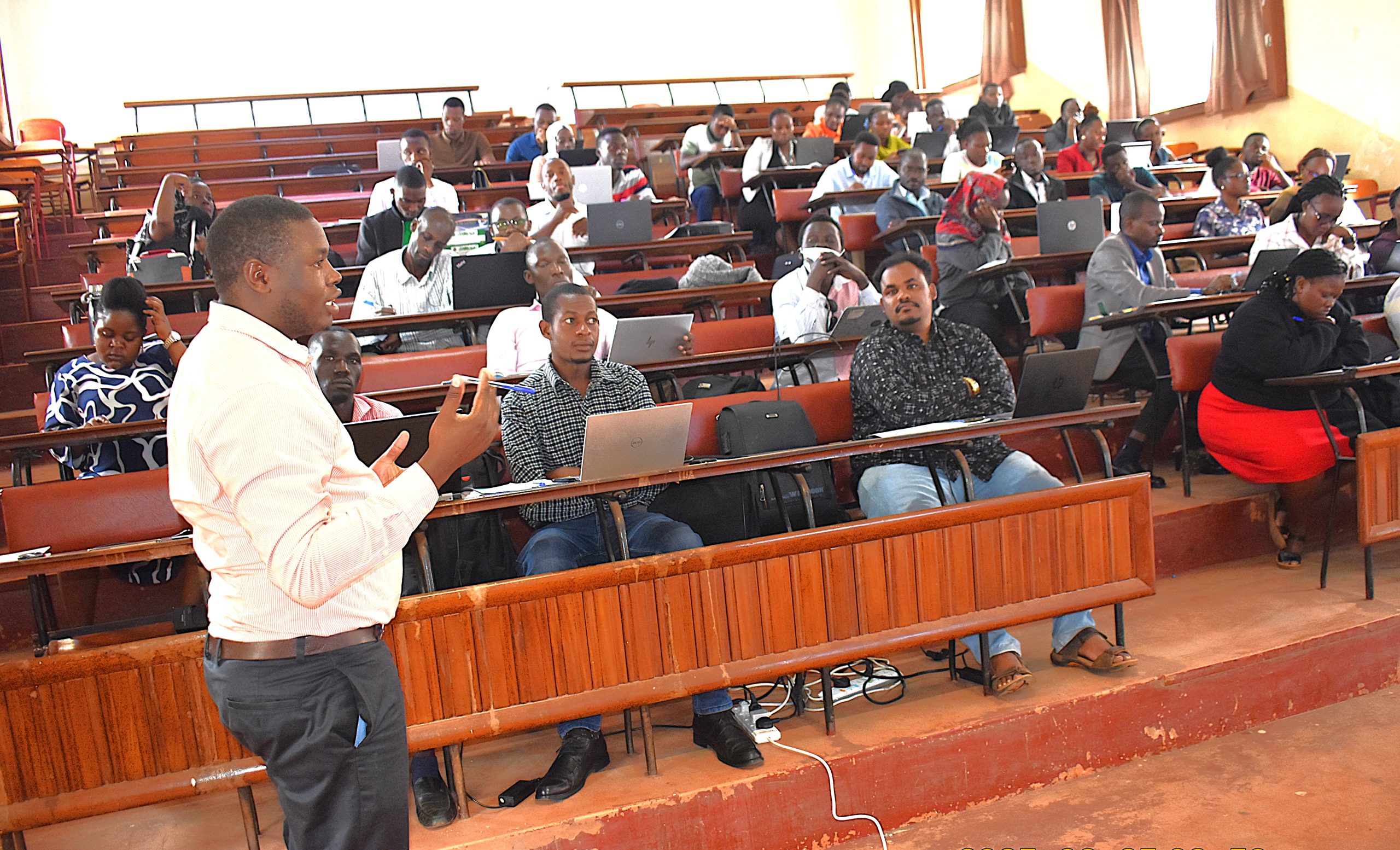
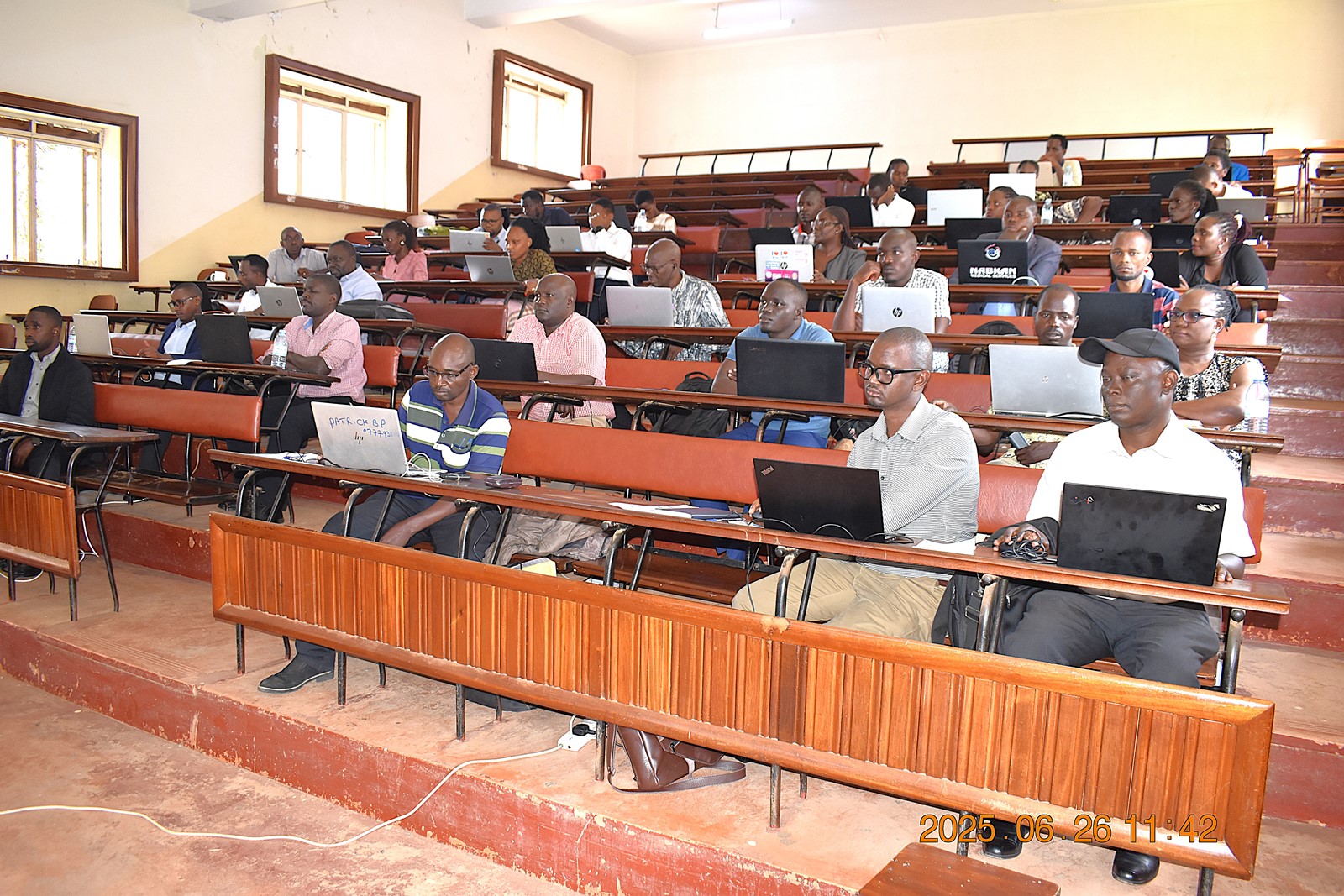
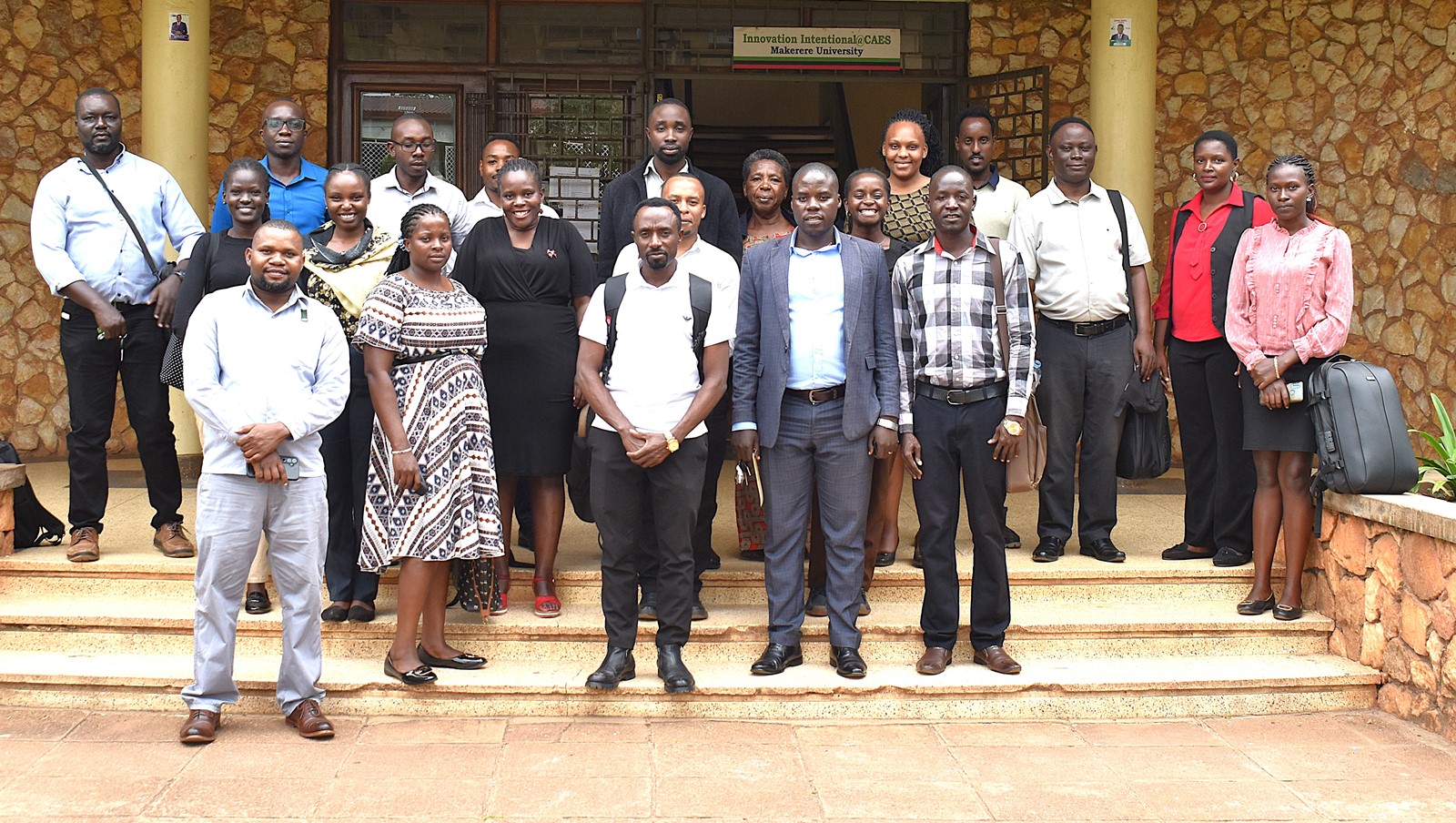
APRC Trains Graduate Students & Stakeholders in the Use of the African Agriculture Adaptation Atlas
Published
2 weeks agoon
July 3, 2025
The Agricultural Policy Research Centre (APRC), housed within the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES) at Makerere University, continues to play a pivotal role in shaping Uganda’s agricultural future through evidence-based policymaking. With a mission to ensure that agricultural policies are grounded in empirical research and data, APRC is actively investing in capacity-building initiatives that empower researchers, policymakers, and development actors.
In a significant stride toward building climate resilience in African agriculture, APRC recently organized a two-day intensive training workshop focused on the African Agriculture Adaptation Atlas (AAAA) – a state-of-the-art, web-based decision-support platform that facilitates the integration of climate data into agricultural planning and policy.

The workshop, held on Wednesday 25th and Thursday 26th June 2025 at the School of Agricultural Sciences, Makerere University, targeted two key groups: graduate students on the first day, and university faculty, government officials, and development practitioners on the second. This structure ensured tailored learning experiences for both emerging and seasoned professionals, helping to bridge the gap between academic research and real-world policy implementation.
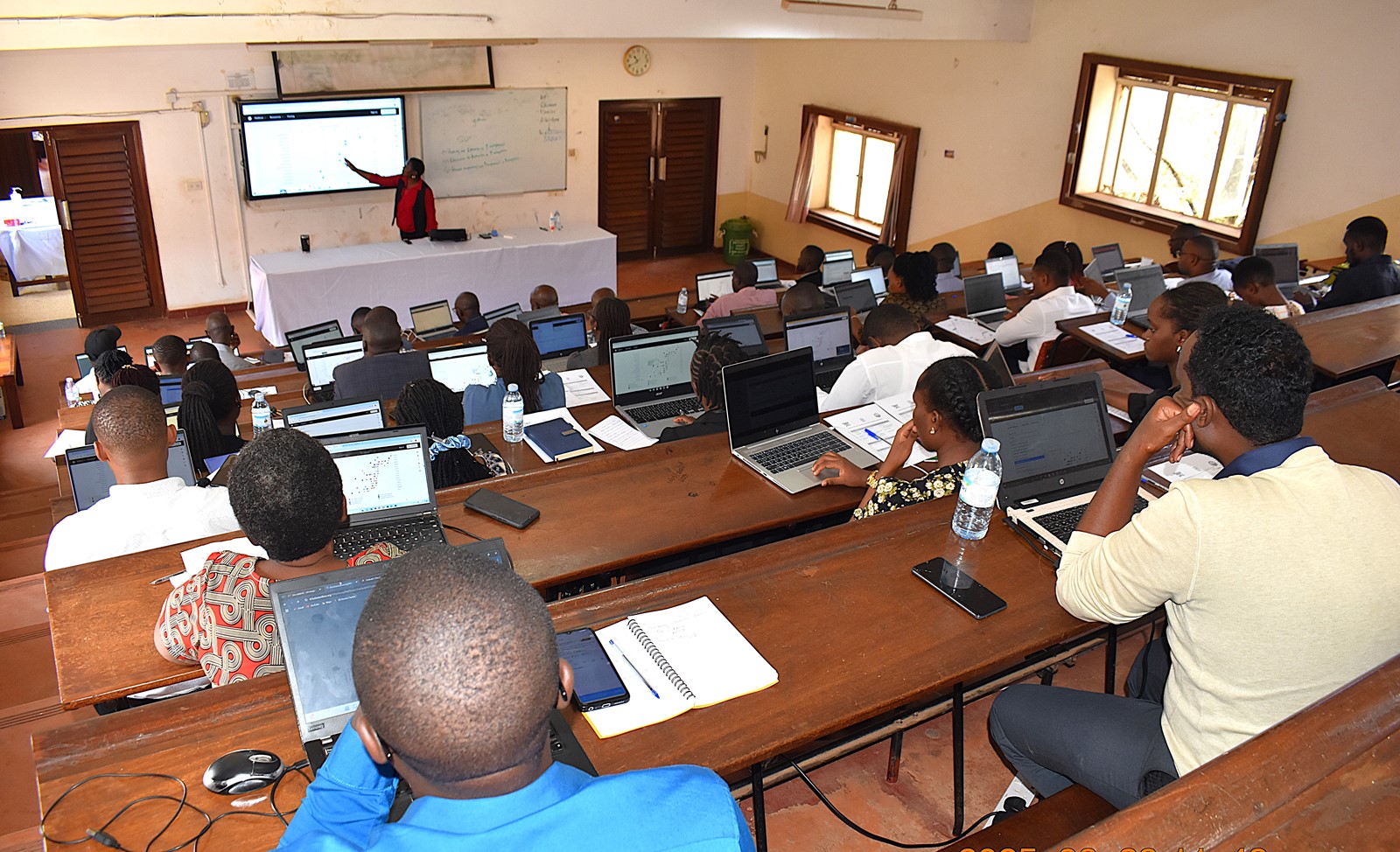
The African Agriculture Adaptation Atlas (AAAA) is designed to provide dynamic, data-rich visualizations that support informed decision-making in agriculture and food systems across the continent. Through interactive maps and analytical tools, users can explore projected climate impacts, evaluate risks, and identify localized, climate-smart adaptation strategies.

Throughout the sessions, participants received hands-on training in a broad range of AAAA functionalities, including:
- Leveraging the Atlas for research and policy communication: Enhancing the ability of scientists and policy actors to translate complex climate data into actionable insights;
- Assessing projected climate impacts and associated agricultural risks: Essential for forward-looking planning and risk mitigation;
- Identifying climate-smart investment options, with a particular focus on the livestock sector, which is especially vulnerable to climate shocks;
- Analysing gendered vulnerabilities: Examining how climate change disproportionately affects women in agricultural communities;
- Understanding the implications of heat stress on agricultural productivity: Supporting targeted interventions to protect producers and their livelihoods;
- Estimating the economic returns of adaptation strategies: Aiding in prioritizing investments and allocating limited resources effectively.

Prof. Bernard Bashaasha, the APRC Coordinator, emphasized the importance of the training in advancing Africa’s adaptation agenda. “As climate change continues to threaten food security and disrupt livelihoods across the continent, tools like the AAAA, and the skills to use them effectively are essential. They empower decision-makers to craft policies that are adaptive, inclusive, and rooted in science,” he noted.
The workshop was coordinated by Dr. Florence Rwiza, Lecturer in the Department of Agribusiness and Natural Resource Economics at CAES.
More photos from the Training






Trending
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoAdmission List to Bachelor of Education External (BED) 2025/26 -Private Sponsorship
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoUndergraduate Admission List Self Sponsorship Scheme 2025/2026
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoRe-advert: Admission to Undergraduate Programmes 2025/2026
-
 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoAdmission Lists -Disability and District Quota Schemes 2025/26
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoDiploma/Degree Holders Scheme – Self Sponsorship Admission Lists 2025/26
