Agriculture & Environment
Mak, GoU &World Bank Partner to Build Capacity in Public Investment Management
Published
4 years agoon

By Jane Anyango
About 20 staff from the School of Economics, the National Planning Authority (NPA) and the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development (MoFPED) convened at Essella Country Hotel in Wakiso district for a one-week (13th -17th September, 2021) Training of Trainers (ToT) to build capacity in Public Investment Management (PIM).
The training was officially opened by the Principal, Makerere University College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS) Assoc. Prof. Eria Hisali on behalf of the University Management.
The training was organized by the World Bank-funded Makerere University Centre of Excellence in Public Investment Management (PIM CoE) in the School of Economics (SoE), College of Business and Management Studies (CoBAMS).
The training was conducted by paired up facilitators from Government of Uganda (GoU) and Makerere University who have built capacity in the area of PIM system and processes and moved to Queens University in Canada while others have built their capacities locally.
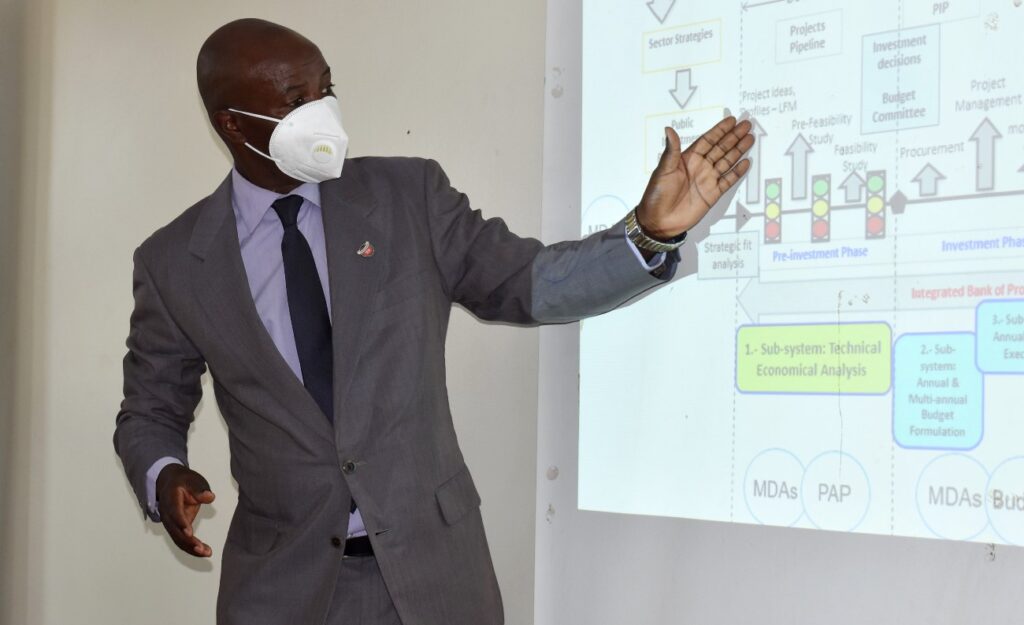

The training emanates from a diagnostic study undertaken by MoFPED and the World Bank in conjunction with School of Economics where weaknesses in the Public Investment Management Systems and Processes were identified.
Part of the weaknesses identified were lack of capacity in project appraisals which is a complex analysis that involves rigorous economic analysis using conversion factors and shadow prices, which are not conventional in the daily economics known.
Some of the aspects covered during this Training of Trainers included: An overview of the PIM System and processes in Uganda, Project Concept Note Presentation, Project Profile presentation, Public Private Partnerships. Integrated Bank of Projects, Integrated Project Appraisal and Economic Analysis of Projects.

The Principal Investigator Makerere University PIM CoE Prof. Edward Bbaale who is also Dean School of Economics said, as a result of the glaring challenges, interventions were mapped out to establish the PIM CoE that brought on board the Ministry of Finance, the National Planning Authority and the University in a collaborative initiative.
“Out of that, we competed and received a grant from the World Bank to establish a PIM CoE with the mandate to undertake training, research and advisory services in the area of Public Investment Management.
This training is part of the mandate for which the PIM CoE is established. We are trying to increase on a number of trainers. Initially four staff from the School of Economics have undergone training organized by the Ministry of Finance and the World Bank in the area of Public Investment Management and we feel that the four are not enough to undertake this type of training.

This type of training we are having is a training of trainers with the main intention of increasing the number of trainers in Public Investment Management. Thanks to the World Bank for the grant that is delivering the output and also thanks to the Ministry of Finance for the great partnership”, Prof. Bbaale said.
While officially opening the training, the Principal CoBAMS, Assoc. Prof. Eria Hisali thanked the management of PIM CoE for the numerous activities they have been undertaking over the past one year.
The Principal appreciated the entire management of MoFPED for the support extended to Makerere University, and trainers and participants for interesting themselves in this training program.
“When this initiative was started a couple of years ago, it seemed to be a farfetched idea but I am extremely happy that we can now see some tangible results. Thank you so much for remaining committed and I really hope and look forward to a lot more.

I appreciate the unwavering support from the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development. They have been participating in the training and playing a key role in having the PIM CoE get to where we are.
The support we got from the World Bank was with a very strong backing from the Ministry of finance. So, we thank you so much and we can only look forward to a stronger collaboration and partnership”, Assoc. Prof. Hisali appreciated.
Dr. Hisali described the PIM CoE as an important initiative whose strategic feet is located within the strategic focus of the college for the next 5-10 years.
“We have taken steps to establish flagship activities. Our focus currently is to have at least one flagship activity at each school. These flagship activities are going to be the main vehicle for engagement with policy makers out there and the community.

At the School of Economics we started with the Centre for Macro-economic Modelling and works are ongoing and this is yet another initiative that can fit within these flagship activities which takes us to the community and policy makers”, the Principal said.
Over the next five to ten years, Prof. Hisali reported that, the college will be keenly focused on enhancing the capacity of all staff including academic, administrative and support staff.
He said, starting the last Financial Year, the college rolled out an initiative requiring every academic staff to pick at the minimum of two new methodological areas.
The college he said trained staff in Impact Evaluation and has been running a modules in Computer Programming and Object Oriented Programming in Stata. In addition Dr. Hisali said, the college is also running a series of modules in Economic Modelling, Advanced Time Series while the School of Business will be commencing capacity building in Event Study Modelling.
Dr. Hisali said that with the support from the Ministry of Finance, NPA and other players in the public and private sectors, there is an ongoing effort to start a graduate degree program in PIMS and to integrate some of these materials into the university curriculum at the undergraduate and graduate levels.

The Principal advised that as government and university embark on this training, it should not be looked at as the end in itself but rather something going to equip all the partners to make bigger contributions.
One of the things Prof. Hisali proposed was the need to take up the idea of a policy lab where on a quarterly basis, the academia, Ministry of Finance, NPA and other stakeholders in PIM should be able to sit together, pick up a topical issue and take off half a day and deliberate on it fully and either make policy suggestions or agree on areas that might require further study in order to come up with meaningful policy interventions in this field.
The second idea proposed by the Principal was getting students on board as the easiest way of getting the multipliers. Dr. Hisali advised that as the university integrates the materials in the curriculum and wait for the degree program, there can be a shortcut where graduate students are encouraged to take up topics for their dissertations and encouraged to pick and use these important tools and in that way, the multiplier will increase and become bigger.
The other issue on taking up multipliers according to Dr. Hisali would be undertaking some studies like computation of shadows and parameters .In this regard, he said, the university can again collaborate with the Ministry to fund a few of these studies in groups.

Dr. Hisali reported that the college has been supporting some research and publications for the last five years but it is now having conversations on the possibility of changing the modality of that support and focus on putting together those resources to support research projects that will be using some of the new tools being learnt.
“So we will be moving away from the old approach to a new dispensation where we look into the methodology you are using and once convinced that it fits within these new areas we are trying to build capacity then we support. So the little facilitation at the college level will be biased towards initiatives like this and then definitely the tools of economic analysis that you are picking through this training will be one of those areas we want to support,” Prof. Hisali said.
Dr. Hisali expressed the university commitment to continue supporting and to ensure that these initiatives succeed saying, management was already in discussion with the ministry to ensure that the PIM CoE can be sustained not to end with the World Bank support.

The Commissioner for Projects and Public Investments in the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development Hannington Ashaba said Public Investment Management largely involve system, institutions, processes that government uses to appraise public investments to ensure that only tangible and viable projects are implemented to give better returns and to make sure that they contribute to the national development agenda.
Commissioner Ashaba said government has been implementing a number of PIM reforms and notable among them is to build capacity across government to ensure that they have in-country capacity that enables government ministries to do feasibility studies such that only viable projects can be included in the budget and government plan.
“It is on the basis of that that we think that working Makerere University School of Economics will help churn a large number of professionals in PIMS that will be very impactful in supporting government especially under the National Development Plan III which is focusing on core infrastructure projects that will propel the country to a middle class economy”, Mr. Ashaba said.
The commissioner said some of the challenges government is facing in PIMS go beyond capacity to include the fact that Uganda as a developing country has resource constraints. Ashaba told participants that the money is not enough so, it must be rationalized and allocated to only projects with bigger impact that will generate growth and revenue to repair the national debt.
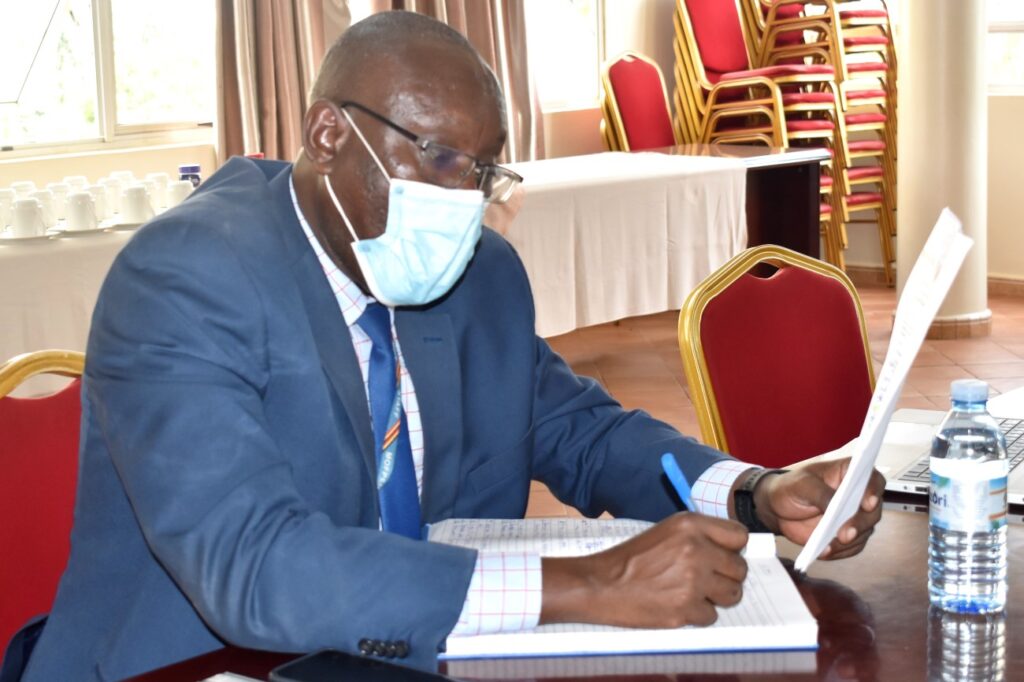

Mr. Ashaba said besides the budget constraints, there is need to ensure that government is working as a whole to solve the coordination issue in the way projects are identified, prepared and studied such that by the time a decision to undertake a project is reached, it is really a project well-grounded to guarantee proper implementation, coordination and completion on time not to escalate costs.
“ Makerere is coming in at the right time when we are deepening the PIM reforms and we think that the academia especially the School of Economics which is setting up a PIM CoE will ensure that some of the curriculum includes PIMS aspects to ensure that graduates churned out are clearly well grounded in public investment.
But also two, we have a gap of evidence around public investment. So, if Makerere could help in undertaking topical studies, that would help generate evidence on how investment contribute to growth and also may be identify most of impactful projects where we need to deepen some of the interventions around PIMS” the commissioner stated.
Mr. Ashaba was also optimistic that the University PIM CoE will not only help government in capacity building and conducting topical studies and research but, also come in handy to act as independent reviewers of government so that they can give independent advice on viability of some of the projects so that they can assist government in taking decisions on some public investments.
The Manager Makerere University PIM CoE Dr. Willy Kagarura said the aim of the center is to train people locally and internally so as to improve what is delivered to the students to be relevant on the job market.
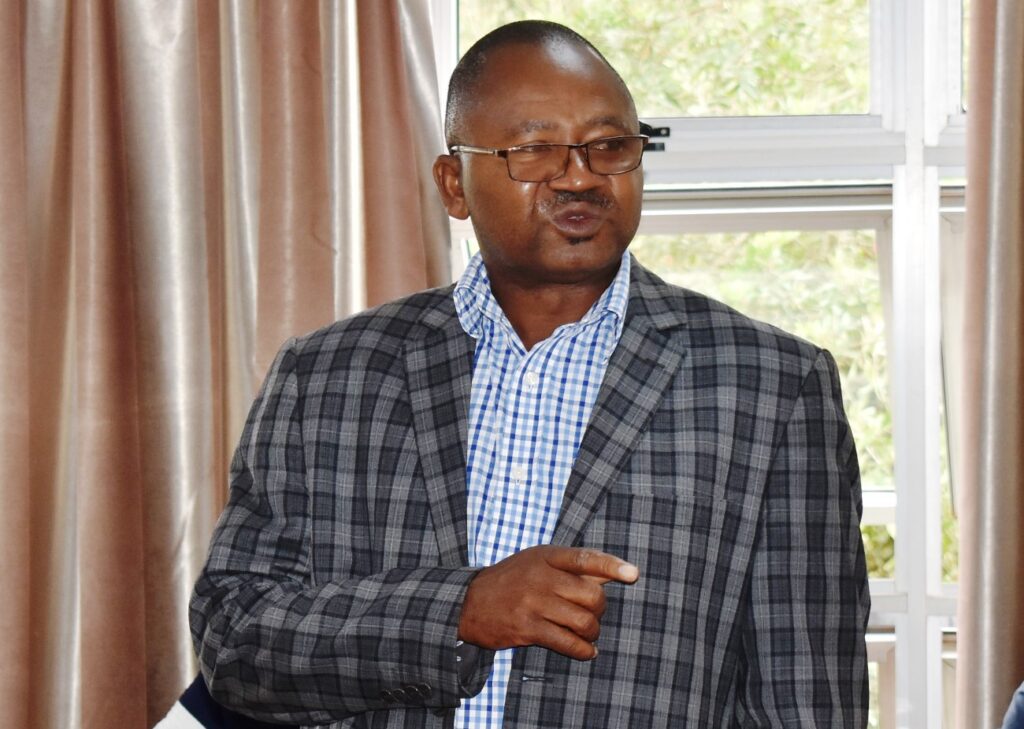

“Four people have been on this training with the Ministry of Finance. We want to extend our capacity at our school to deliver the mantle and train people in government offices and our students so that they don’t face challenges when out of the university.
We are continuing to update ourselves to international levels and in October 2021, we are supposed to go to Queens University but some four people have been admitted to attend the Queens University training so that we build capacity at that level, then our graduates here will be skilled continuously up the international standards.” Dr. Kagarura explained.
Another centre mandate according to Dr. Kagarura is to develop short and long term Public Investment Management curriculum and materials. He said, with the support of the Ministry of Finance, the short term courses, materials and curriculum used in the ToT training were developed.
Dr. Kagarura also reported that as part of the mandate, the center has trained government practitioners in Munyonyo and was now partnering with Ministry of Finance in partly delivering that.
“In conducting research, two impact evaluation studies have commenced and there is another study to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on Public Investment Management framework in Uganda. The other one is to roll out training and awareness to other universities where the trainees will be used to go to other universities”, Dr. Kagarura added.
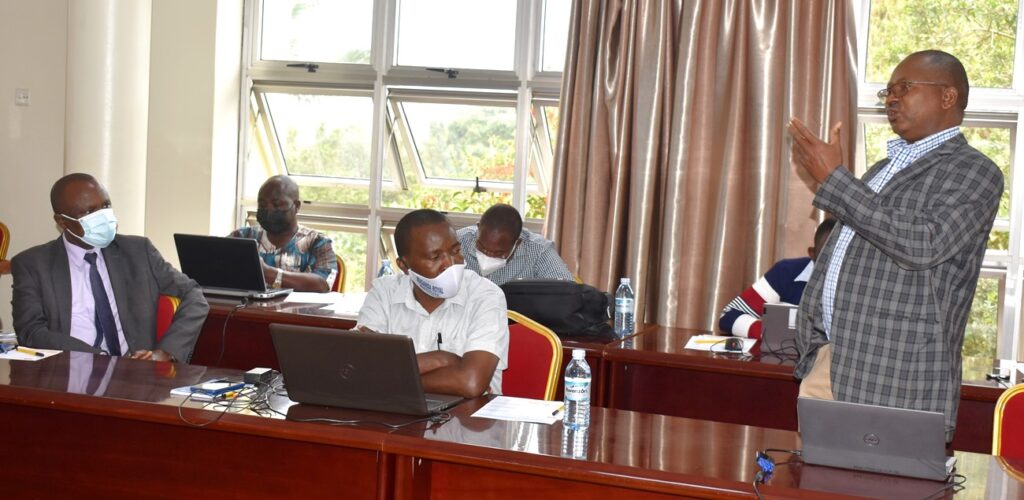

Dr. Kagarura also reported that the centre has established an office for sustainably managing the trainings and was in touch with the Institute of Public Management to have an accreditation as an approved training entity so that once people train, they do exams from the Institute of Public Management and get a certificate. This will easy recruitment of interested people and service delivery.
Besides the funder’s conditions and the COVID-19 Lock down that partly delayed the commencement of the center activities, Dr. Kagurura decried the tedious process in the PPDA that hampered the center activities. He said the Centre activities planned to start in 2017 delayed till September 2020 due to multiple approvals in the PPDA.
“We need to establish the loss incurred through this PPDA processes to our economy. If I can get a laptop at the market at shs 3 million, through PPDA it will take a year in hustles and approvals and get it at shs.9 million or lowest at Shs. 7million, this is just a laptop, what about the roads! So processes are a problem”, Dr. Kagarura submitted.
He said despite the COVID-19 lock down, the trainings were conducted online with interruptions of connectivity. Dr. Kagarura called upon the, donors, University, college, Ministry of finance, NPA and other partners for support to ensure the centre is sustained beyond the World Bank funding.
Jane Anyango is the Principal Communication Officer, College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES)
You may like
-


Support Staff Trained to Promote Safety of Students and Stakeholders
-


Call for Applications: Short Course in Molecular Diagnostics March 2026
-


VC Opens Training for MoKCC Officials on Safeguards in Procurement
-


For Youth by Youth – Call for Second Cohort Applications
-


Building Skills for Better Public Investments: PIM Centre Trains Public Sector Economists
-


Call for PhD Student Fellowships under H-DATA
Agriculture & Environment
From Adversity to Excellence: The Inspiring Journey of Makerere’s Best Science Student, Esther Ziribaggwa
Published
2 weeks agoon
February 6, 2026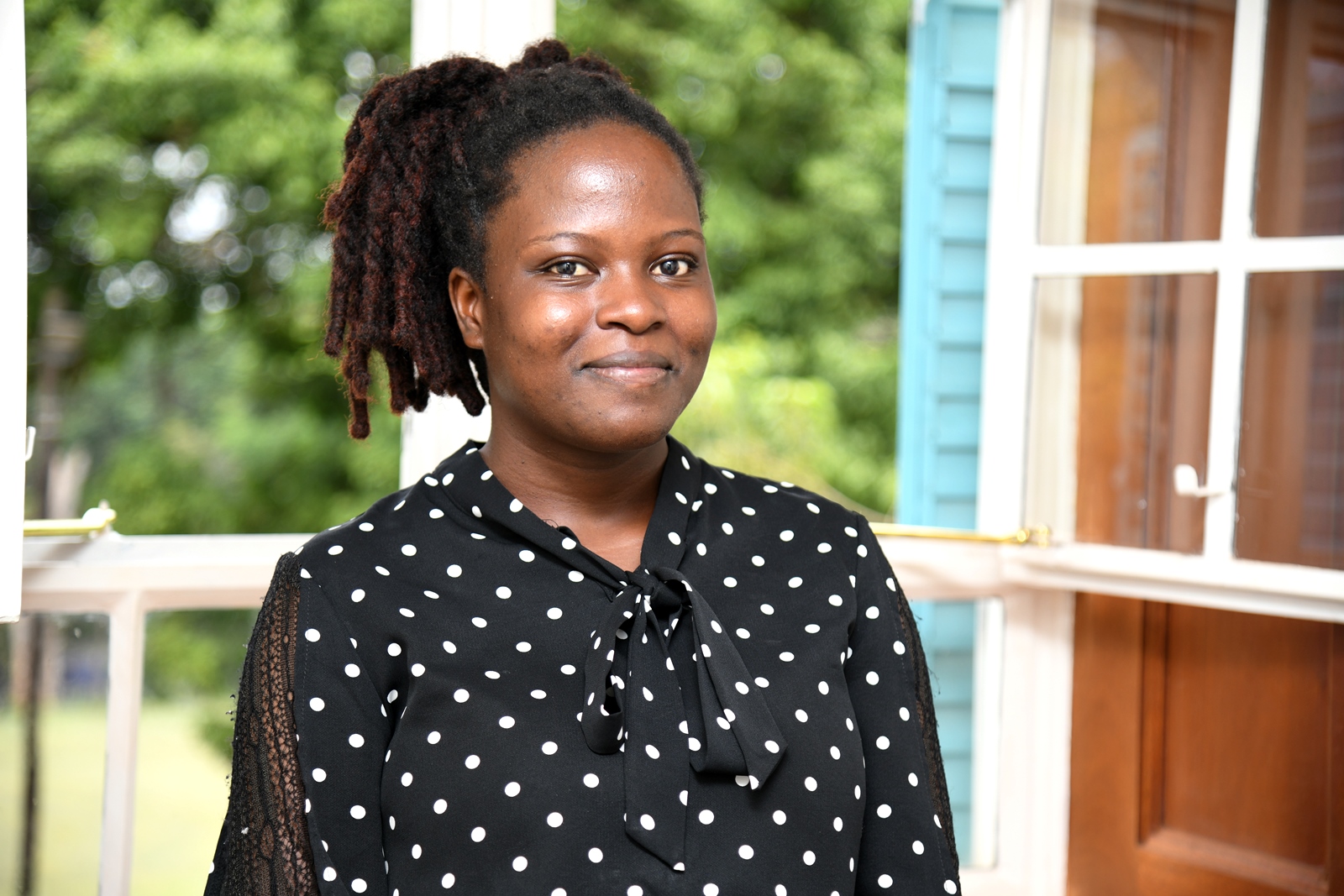
Growing up in Nkonge Village, Kyampisi Sub County in Mukono District, Esther Ziribaggwa learned early the meaning of resilience.
Born to Mr. Musisi Godfrey, a farmer, and Ms. Babirye Resty, a market vendor in Seeta, Mukono District, her journey from humble beginnings to becoming Makerere University’s top-performing student in the Sciences is a testament to her determination, hard work, and unwavering faith. She attained a CGPA of 4.77 in the Bachelor of Agricultural and Rural Innovation, a programme taught at the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES). She will be graduating from Makerere University on 24th February 2026, the first day of the 76th graduation ceremony.
Educational Journey and Navigating the Financial Hurdles to remain in School
Ziribaggwa’s journey to academic excellence has not been smooth. But her parents’ sacrifices laid the foundation for her dreams, even as life presented relentless challenges.
She began her education at Frobel Day and Boarding Primary School and later joined Seeta Boarding Primary School, where she excelled with 9 aggregates in her Primary Leaving Examinations. However, the transition to secondary school presented challenges that tested her resolve.
She joined Mpoma Royal College in Mukono District alongside her sister, who had scored 12 aggregates. Shortly after starting Senior One, their father fell seriously ill, requiring an intestinal surgery, and could not continue to work. With the family unable to pay school fees, both sisters dropped out for a year. It was only through the compassion of the school bursar and the then Head Teacher, Ms. Namazzi Connie, who reduced their fees from 800,000 to 380,000 Uganda Shillings, that Ziribaggwa and her sister were able to return. “The year out of school was a huge setback,” she recalls, “but I focused on catching up. I knew I couldn’t waste this second chance.” Her perseverance paid off. Despite the lost year, she completed her O’ Level with 25 aggregates in eight subjects.
Her A’ Level years were marked by similar challenges. Due to financial constraints, Ziribaggwa attended three different schools. She initially enrolled at Seat of Wisdom Boarding School in Kayunga but was forced to leave when her family could no longer afford the fees. At the time, her father, the family’s sole breadwinner, had undergone a second operation and was unable to work. Her mother, a market vendor, stepped in to support her education and transferred her to Paul Mukasa Day and Boarding Secondary School in Mukono District as a day student. However, the long daily commute was exhausting, leading to a final transfer to Godmark High School in Mukono District where she completed her A’ Level in 2019 with 15 points in Geography, Economics, Agriculture, and Subsidiary Mathematics.
After completing secondary school, Ziribaggwa waited two years before joining university due to financial constraints. Although she had been admitted under the private sponsorship scheme to pursue a Bachelor of Statistics, she was unable to raise the required tuition. Following the outbreak of COVID-19 and the subsequent lockdown, an opportunity arose for her to obtain government sponsorship. At the time, there were no Senior Six leavers, prompting Makerere University to invite applications from candidates who had completed Senior Six within a specified period. The cut-off points across programmes were lowered, enabling her to secure government sponsorship to pursue a Bachelor of Agricultural and Rural Innovation.
Appreciation
She is deeply grateful to the Almighty, her parents, and everyone who supported her educational journey. She is specifically thankful to the Government of Uganda for sponsoring her university education, and to Ms. Namazzi Connie, her O-Level Head Teacher, for subsidizing her school fees. She is also grateful to all her lecturers at CAES and Jesus is King Ministry under the Makerere University Christian Union.
Message of Resilience to Fellow Students
To the students navigating similar challenges, Ziribaggwa shares a message of encouragement. “Never let your situation break you. There’s always going to be challenges, sometimes pushing you to what feels like a point of no return. But those moments should not define your future – they are a test of your resilience. Strive to outgrow them and become a better person, even when the journey feels impossible.”
Career and Aspirations
Ziribaggwa currently works in the extension division of Slow Food Uganda, an agricultural organization based in Mukono District, where her work focuses on women and youth. Although her dream was to become a medical doctor, her love for agriculture has grown over time and does not regret taking on this path. She aspires to become a Senior Agricultural Officer in the country, with the goal of improving farming conditions, particularly in the rural communities. Growing up in a farming community exposed her to many challenges faced by farmers, including unpredictable weather conditions that necessitate irrigation support, and improper use of agrochemical inputs, which pose risks to both soil quality and human health.
Ziribaggwa hopes to pursue further studies in crop and soil science. She draws inspiration from exemplary leaders like Hon. Rebecca Kadaga, former Speaker of the Parliament of Uganda, and First Deputy Prime Minister and Minister for East African Community Affairs. “I have always admired her for being hardworking, resilient, and eloquent,” she says, seeking to emulate these qualities in her own journey.
Agriculture & Environment
Call for Applications: QCF Postdoctoral Research Fellowships
Published
4 weeks agoon
January 20, 2026
Makerere University’s Department of Geography, Geo-informatics and Climatic Sciences in partnership with Quadrature Climate Foundation and Red Cross Red Crescent Climate Centre are seeking two fellows for Quadrature Climate Foundation (QCF) Fellowship Programme. This is a two-year post-doctoral programme fully funded by QCF, which is an independent charitable foundation working for a greener and fairer future. Applications for the two-year post-doctoral fellowship are invited from individuals with demonstrated interest and expertise in locally led adaptation to climate change research. This initiative is a unique and excellent opportunity to expand the network of interested individuals with researchers and decision-makers, as well as deliver action-oriented research to inform policy and practice. Depending on their interest, each applicant should choose one of the two thematic areas offered under the fellowship program:
- Knowledge co-creation for locally led adaptation to climate change
- Decentralised decision making for effective climate change adaptation and resilience
The Fellow working on the Thematic Area 1: knowledge co-creation for locally adaptation will explore collaborative learning processes (including informal learning) for climate change adaptation among smallholder farmers with focus on Uganda, with linkages to related work in Bangladesh, Mozambique and Nepal. The overall intention is to generate understanding of how decision making processes, across scales, can be linked to local and context specific knowledge systems and process for epistemic just adaptation. The key research questions are:
- What does the process of co-creating knowledge for locally led climate change adaptation look like in a rural smallholder farming setting of a Least Developed Country (LDC)?
- What are the possibilities, promises and pitfalls of knowledge co-creation for locally led adaptation planning?
The research will intentionally contribute to methodological and practice advances in co-creation of knowledge for locally led climate change adaptation.
The research on Thematic Area 2: decentralised decision making for effective adaptation and resilience will undertake scientific interrogation of a climate finance mechanism that has been designed for locally led adaptation and resilience in Uganda. The Fellow will largely focus on testing selected assumptions behind the design of the mechanism. The key questions are:
- How does effective locally led climate change adaptation and resilience building investment decision making look like in practice?
- What works and how does it work? What does not work and why?
Key considerations in the research will include local leadership, inclusion, context specificity, cross-scale, and capability strengthening. The targeted contributions of the fellowship include improved knowledge management for climate resilience planning and decision-making, strengthened evidence-based research-policy-practice dialogues, framework(s) for integrating local and experiential knowledges in resilience building investment decision making processes, among others.
The Fellows will be based, full-time, at Makerere University, Kampala as a core member of the team working on locally led adaptation and resilience. Their work will be conducted under the auspices of the Least Developed Countries Universities Consortium on Climate Change (LUCCC) through which Makerere University is engaged in research and knowledge management collaborations. The Fellowships will focus on Uganda, but with deliberate linkages across LDCs, which might necessitate travels for in-person working meetings.
Roles and responsibilities of the Postdoctoral Research Fellow
The Fellow will be highly motivated to work with a transdisciplinary research team, grow their research expertise, engage with climate change researchers, decision-makers, practitioners and generate different categories of publications. Makerere University will appoint a locally based mentor to the Fellow to provide professional development support. Where needed, the Fellow will participate in teaching and community outreach activities including knowledge sharing in ways that foster collaborative research for adaptation policy and practice.
Requirements:
- A PhD, awarded within the previous three years, in a related discipline (e.g., geography, climate and society, sustainability, adaptation governance, epistemic justice, climate finance).
- Knowledge and experience of locally led adaptation in the agriculture sector.
- Experience in synthesizing and managing datasets and literature.
- Experience in, and knowledgeable of, participatory and collaborative action-oriented research methodologies and tools.
- Demonstrated ability to produce research information products for different audiences.
- Excellent written and verbal communication skills in English
- Demonstrated interest and experience in transdisciplinary collaborations across-scales including with local communities, decision-makers and practitioners in LDCs
- Experience in giving international oral presentations and interest in public communication for wide-ranging categories of audiences
- Data and information visualisation skills will be an added advantage
Application requirements:
Applicants should submit a single PDF with: (i) an application letter not longer than 2 pages that includes indication of theme of interest, a description of research interests, research expertise, and an explanation of how they can work as part of the transdisciplinary research team in line with the fellowship objectives described above; (ii) a CV including a publication list; (iii) copies of academic transcripts and/or certificates; (iv) an example of written work; (v) email addresses of two references who have been directly involved in their PhD research.
Applicants must submit the PDF application document to colocal.caes@mak.ac.ug. Please type “LUCCC PDR Application: COLOCAL-Makerere” as the subject line of the email.
Closing date
Midnight (GMT+3) on 27th February, 2026 or until the position is filled.
Selection process
Eligible and complete applications will be considered followed by communication with short-listed applicants. Makerere University, in consultation with Quadrature Climate Foundation and the Red Cross Red Crescent Climate Centre, will conduct interviews of the short-listed applicants.
If you have not heard from Makerere University within two months of the deadline, please assume your application has been unsuccessful.
Contact details for enquiries about this post-doc fellowship: colocal.caes@mak.ac.ug
Makerere University reserves the right to
- Disqualify ineligible, incomplete and/or inappropriate applications;
- Change the conditions of the award or to make no awards at all
-The QCF Fellowship Programme is a two-year, post-doctoral programme fully funded by Quadrature Climate Foundation (QCF).
-Quadrature Climate Foundation is an independent charitable foundation working for a greener and fairer future. For more information on QCF, please visit qc.foundation.
Agriculture & Environment
Mak-CAES Trains Small-Scale Processors on Soybean Value Addition & Product Development
Published
2 months agoon
December 16, 2025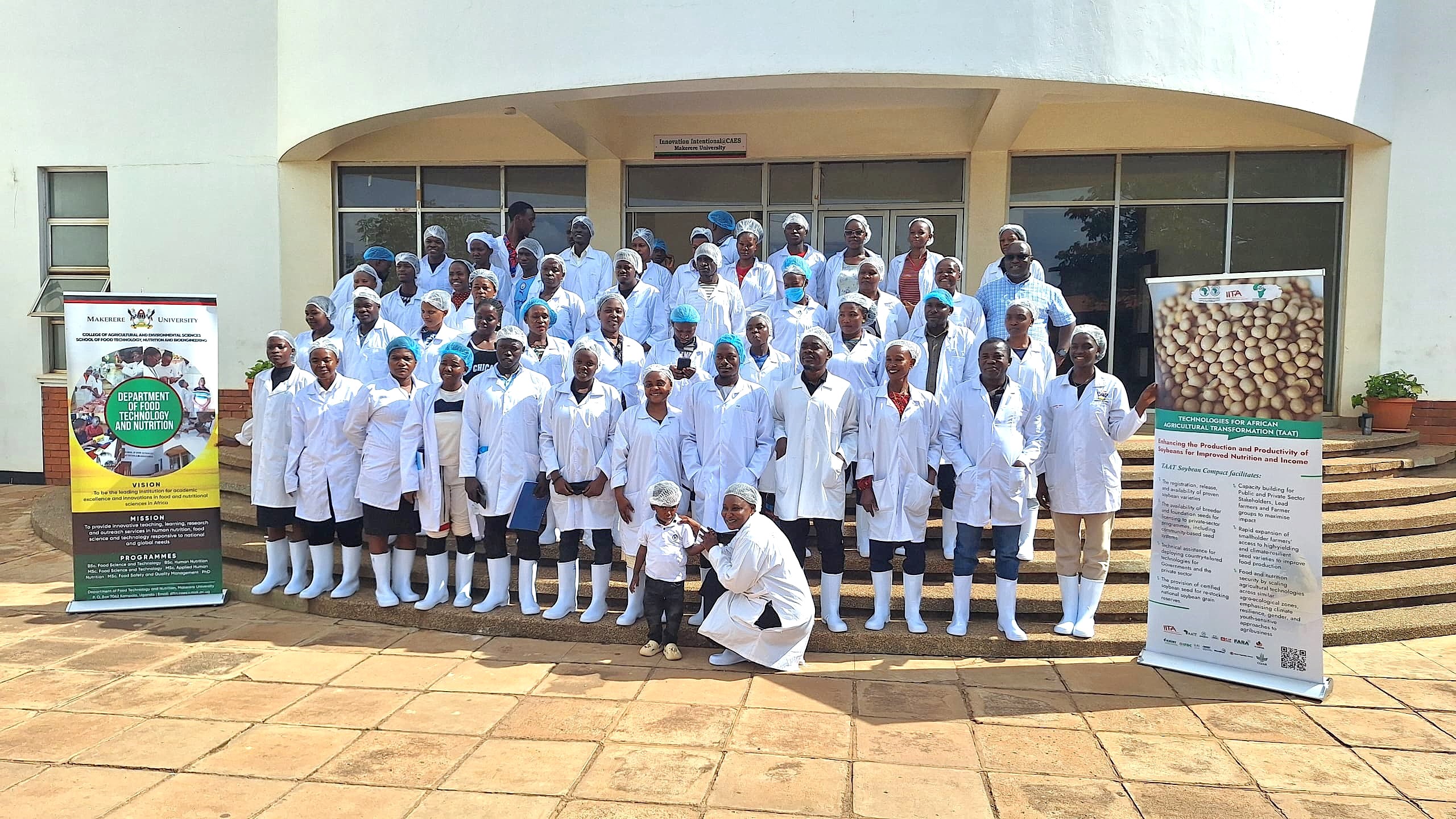
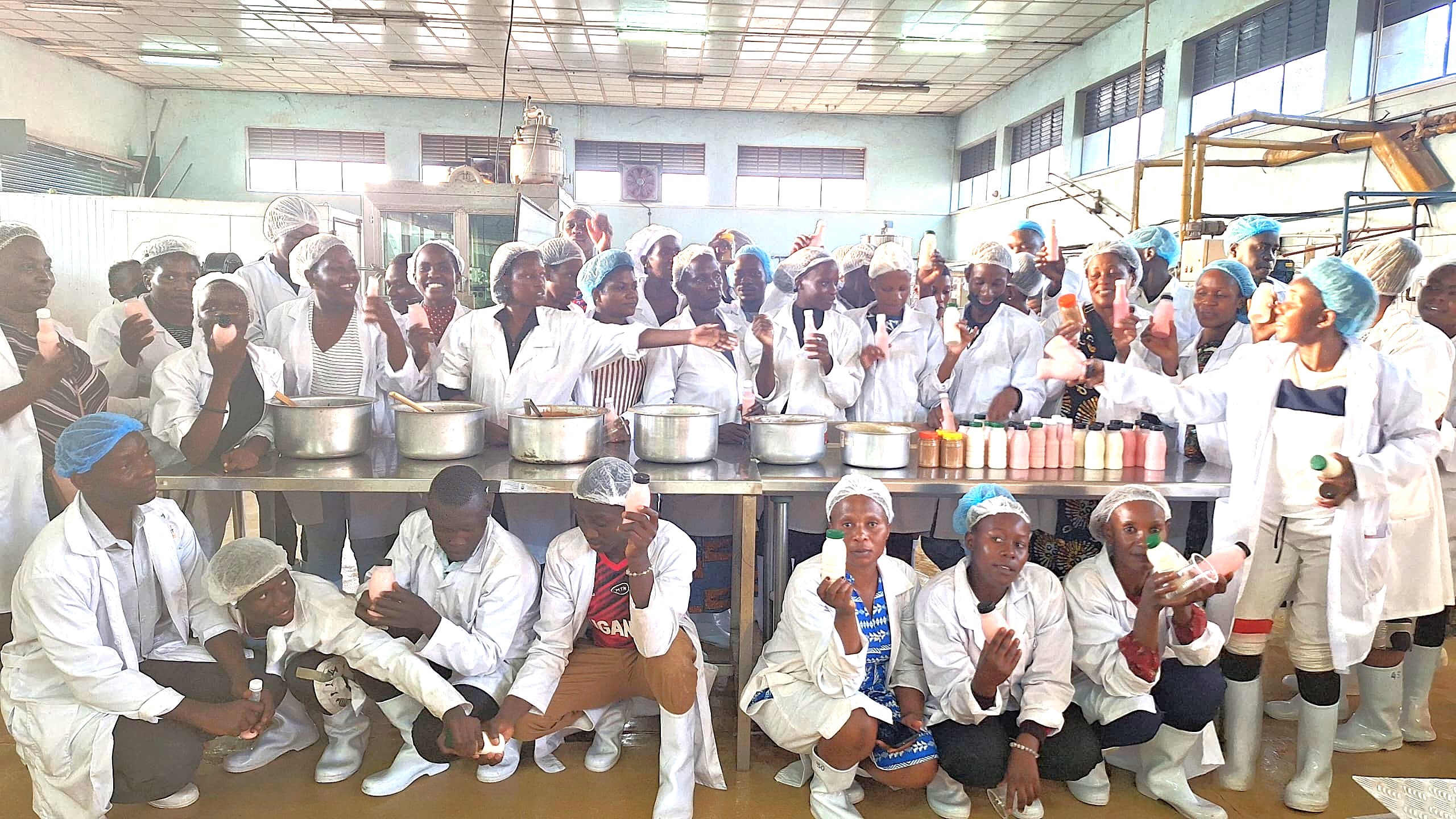
The Department of Food Technology and Nutrition (DFTN), Makerere University, in collaboration with Smart Foods Uganda Ltd, successfully conducted a five-day intensive training on soybean value addition and product development from 24th to 28th November 2025. The training was implemented with support from IITA Uganda under the Training for African Agricultural Transformation (TAAT) Soy Compact Project, aimed at strengthening agro-processing capacities and promoting soybean utilization for improved nutrition and livelihoods.
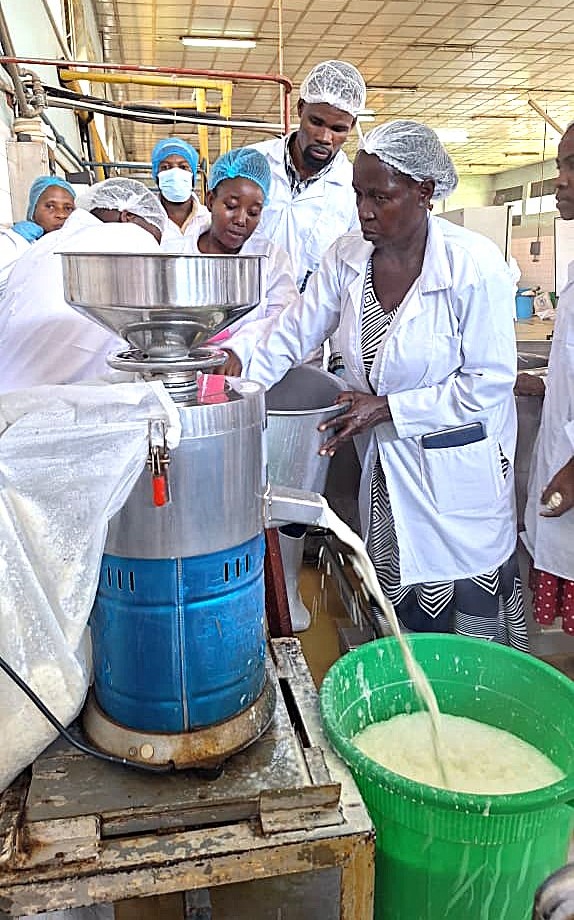

The training program was highly practical and skills-oriented, featuring extensive hands-on sessions designed to equip participants with applicable processing and product development competencies. Most of the practical activities were hosted at Makerere University’s Food Technology and Business Incubation Centre (FTBIC). Participants also benefited from an industry exposure and experiential learning session at Smart Foods Uganda Ltd in Bweyogerere, where they gained first-hand insights into commercial-scale soybean processing operations, quality control systems, and product marketing strategies.

Key thematic areas and technologies covered during the training included soybean nutrition and associated health benefits; assessment of quality attributes of soybeans and soy-based products; application of Good Hygiene Practices (GHP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP); and processing of high-quality soy products. Practical sessions focused on the production of soymilk, tofu, soy yoghurt, soy flour, and soy coffee, as well as the formulation of soy-fortified composite porridge flours. Participants were also trained in the development of various soy-based bakery products, including bread, mandazi, daddies, and baghia. In addition, sessions on marketing, branding and positioning of soy products, as well as UNBS certification requirements and documentation, were conducted to enhance market readiness and regulatory compliance.
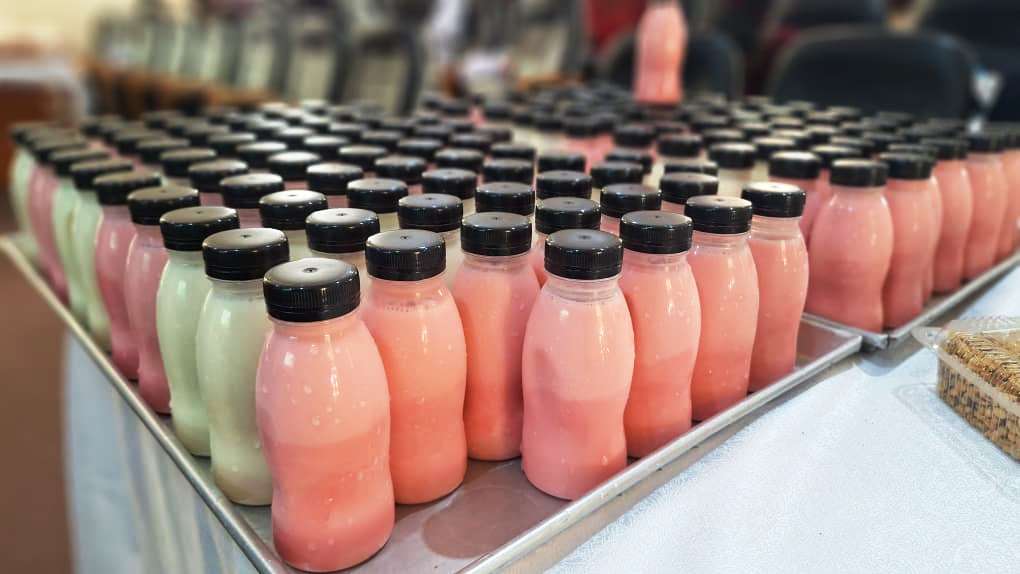

The training attracted a total of 57 participants, comprising small-scale soybean processors and graduating university students, thereby fostering knowledge exchange between academia and industry. Overall, the training contributed significantly to building technical capacity in soybean value addition, promoting entrepreneurship, and supporting the development of nutritious, market-oriented soy-based products in Uganda. The School of Food Technology, Nutrition, and Bioengineering, under the leadership of Dr. Julia Kigozi (Dean), conducts periodical trainings for agro-processors across the country to enhance technical capacity, improve product quality, and promote the adoption of modern, safe, and sustainable food processing practices. These trainings are designed to equip agro-processors with practical skills in food safety, quality assurance, value addition, post-harvest handling, nutrition, and bioengineering innovations, thereby enabling them to meet national and international standards. Through this outreach, the School contributes to strengthening agro-industrial development, reducing post-harvest losses, supporting entrepreneurship, and improving food and nutrition security while fostering stronger linkages between academia, industry, and communities.

Trending
-

 Agriculture & Environment2 weeks ago
Agriculture & Environment2 weeks agoFrom Adversity to Excellence: The Inspiring Journey of Makerere’s Best Science Student, Esther Ziribaggwa
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoAptitude Exam (Paper 1) Results for the Mature Age Entry Scheme 2026/2027
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoDr. Samalie Namukose and the Quiet Work of Making Nutrition Count
-

 Research2 weeks ago
Research2 weeks agoCall for PhD Student Fellowships under H-DATA
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoHow Jimmy Osuret Turned Childhood Trauma into Evidence for Safer School Crossings
