General
Call For Contribution To Mak@100 Book Chapters
Published
4 years agoon

INTRODUCTION
Makerere University (Mak) is due to celebrate a century of existence in 2022. Among the significant highlights of these centenary celebrations, the University plans to publish an easy-to-read and well-documented book that critically reviews its successes in living to the Motto: “We Build for the Future”, since its inception in 1922 as a technical institute. Under this theme, the book will address several sub-themes and issues such as: How Makerere has met the changing East African market needs for skilled labour since 1922 and how, as a premier regional university, it is now positioned to develop research leadership in the region; whether or not Makerere has sustained its research leadership status as a postcolonial university that had influenced other sub-Saharan universities, and how this is reflected in the curricula What are the new courses that have emerged to locate Makerere as a nation-building institution? What ground-breaking researches and knowledge is being produced in the University? What has been the relationship between the University and the states it was built to serve, and how has this affected Makerere‘s performance over the years? Since a university that has come of age is assessed based on its ability to be independent/autonomous, how has Makerere performed? What funding strategies are in place in this regard? What has emerged as Makerere‘s identity: an ivory tower or a service university that offers service to empower the hinterlands? What are Makerere‘s overall influence and image in the region, and what explains this? What would Makerere like to become in the next 100 years? These are some of the broad questions to guide the formulation of thoughts for the chapters from diverse disciplinary perspectives.
EDITORS: ABK Kasozi, Josephine Ahikire and Dominica Dipio
BOOK TIMELINE
Submission of abstracts (Max. 500 words): December 31, 2021
Submission of draft chapters (Max 10,000 words): March 30, 2022
Submission of Final Chapters: June 30, 2022
Book Publication – June to October 2022
Send abstracts to: mak100.bookproject[at]mak.ac.ug
Copy to: josephine.ahikire[at]mak.ac.ug, abkkasozi[at]yahoo.com, ahikirejosephine[at]gmail.com
THE THEMES AND BROAD AREAS OF FOCUS
Section 1: Providing skilled human resources for East African Society
(i)The technical school which opened in 1921
The colonial state established Makerere Technical School to produce low-level technicians. The school taught skills needed by the East African countries of Kenya, Uganda, Tanganyika, and Zanzibar. Students were taught carpentry, building, general mechanics, and some tailoring. Many of the trainees were absorbed by the E. African states and their markets. The question to answer by writers for this section is: What was the trajectory of the technical school and its offshoots in enhancing the lifestyles of the people of East Africa?
(ii) Makerere College and Kampala Technical College
A formal College was founded in 1922 as “Uganda Technical College”, but in the same year, the College was renamed Makerere College, teaching technical subjects and courses in education and the arts. The writers on this section should focus on the demands for skilled labour; what Makerere was called upon to deliver, and whether Makerere truly built the future of the parties involved. In 1928, vocational courses were separated from the College and were transferred to “Kampala Technical College”. What became of the latter College, and were vocational courses wholly divorced from the university system?
(iii) Makerere graduates to university status, 1949
The 1945 Judge Asquith’s Report on higher education gave the blueprint for establishing institutions of higher learning in British African colonies to provide high-level African civil servants such as doctors, engineers, agriculturalists, a few lawyers, and production of knowledge through research to the colonial states. In 1949, the institution became Makerere College, the University of East Africa, giving certificates of the University of London. When Makerere became a university, it assumed, like other universities, multiple functions. These functions included the production of knowledge for development, skilled and thinking individuals who would use known wisdom to create better knowledge and improve themselves and their societies. The University College was expected to be the leading teaching and innovation centre in East Africa. The areas to review in this section are the expectations of the colonial officers and their African collaborators who worked hard to establish the University. Did the institution fulfil those expectations? Did their aims go beyond human resource production? How did the production of graduates by Makerere change East African society in the eleven years before independence? The writers should assess the colonial workforce needs from 1935 to 1960, find out what Makerere was called upon to produce and whether it achieved those targets.
(iv) Skills needed for independent East Africa
In the period 1950 to 1963, Makerere remained the only University College for East Africa. There was an increased demand for educated graduates in almost all disciplines, including science and humanities-based ones. Makerere was called upon to produce graduates to increase educated Africans in the civil service and the private sector.
The education Makerere was giving was ideology-free, which Kenya and Uganda did not object to. But Tanzania felt that the instruction given must enhance patriotism and service to communities. Chapters dealing with topics in this section must review the needs of the three East African states in the period 1950 to 1965 and assess the place of Makerere therein.
(v) Skills needed for the digital age
From around 1980 through the current period, the digital age has transformed how goods and services are produced and delivered. It is only those societies that use technology that are likely to sustain a reasonable standard of living. To what extent has Makerere transformed its activities to exploit the digital age for itself and the society it serves.
Section II: Production of knowledge through research and innovation
When Makerere became a university, it was expected to produce and expand knowledge by providing researchers with facilities for creating, disseminating, storing information and data for use by society and institutions of higher learning. Although not emphasized as its primary task, the Asquith Report identified research as one of the functions of the various university colleges the British Empire was to establish in Africa. Has Makerere contributed to knowledge, the development and improvement of the thinking capacity of its target areas? Writers on this section have several sub-themes and therefore chapters to think about, including:
- Writers, poets, and actors
In the period 1950 to 1970, Makerere-based writers contributed to the dissemination of knowledge. These writers included Ngugi was Thiong’o, Okot p’Btek, Peter Nazareth, Ali Mazrui, Audrey Richards, Paul Theroux, V.S. Naipaul, Mahmood Mamdani, Samwiri Karugire, Mathia M. Kiwanuka, Phares Mutibwa and others. A chapter to assess the contribution to knowledge by Makerere staff and students in this period would say a lot about how the university contributed to building an informed society in East Africa.
- Visual Artists
Since 1940, the Margaret Trowell School of Fine has produced artists whose work has contributed to the shaping of Makerere University’s social consciousness. It has documented Makerere’s challenges and successes over the years. The art works, both in storage in the Makerere Art Gallery and those in private and public spaces, reveal Makerere as an enduring institution which has used every opportunity to push its research agenda. Artists such as Gregory Maloba, Sam Ntiro, Elimo Njau, Francis Nnaggenda and Kefa Ssempangi have, through their work, provided a variety of perspectives on Makerere’s history. A narrative of Makerere University’s journey of ten decades through the lens of Makerere Artists is proposed.
- Knowledge production
There was a lot of knowledge produced at the East African Institute of Social Research (now MISR), the Medical School and the Faculty of Agriculture from 1950 to 1970. A survey of what was achieved in research at Makerere in that period would add to our knowledge of the institution’s contribution to knowledge in East Africa.
- Management of research and post-graduate production
Management of research and production of high-level person power such as PhD holders is a topic that a book on the achievements of Makerere should highlight. To what extent has Makerere contributed to developing high-level human resources and creating the next generation of knowledge producers?
Section III: Makerere’s contribution to democratic governance and the building of social institutions in East Africa
Universities contribute to democratic governance and the building of social and political institutions by equipping their graduates with the intellectual skills to understand and analyze social and political issues before taking appropriate positions. Makerere has supplied East Africa with political leaders, including presidents, prime ministers, ministers, judges and journalists. Writers of chapters in this section might organize these achievements by roles such as:
- Political leaders
- Religious leaders
- Institutional developers
- Famous politicians and political thinkers
Section IV: Makerere’s contribution to the economic development of East Africa
Universities support economic growth by the general training of the labour force and providing knowledge linked to a country’s innovation system. This is more so now when most critical development is knowledge-based; universities should be the reservoirs of intellectuals and experts. To what extent has Makerere supplied the market with skills and knowledge to move East African economies forward? Writers for this section need to have a thorough understanding of East African economies and the extent to which the university has influenced their performances.
Section V: Makerere and Curriculum Development in East Africa
Universities strengthen lower levels of education by training the needed teaching personnel and triggering relevant curriculum changes at the lower levels of education. Lower-level syllabuses are structured to fit into the admission requirements of universities. The question to ask is: To what extent has Makerere influenced what is taught at the lower levels of education? Should Makerere take credit or blame for the slow curriculum development and the failure of Africanising what is taught in East African schools and universities?
Section VI: Challenges
There are several challenges to Makerere’s ability to build the future for a society that contributors must investigate if readers are to participate in appreciating the successes or failures of Makerere University.
- Governance of the University
The governance of a university is key to the delivery of good higher education. Like other universities, Makerere has passed through several hiccups in its desire to provide higher education.
Though it is difficult to govern institutions differently — or better – than the way society is managed, we expect higher education institutions to handle themselves well, to be autonomous but at the same time accountable to the public in the way they manage their financial and academic processes. Higher education institutions, particularly universities, must accept the Government as the final protector of the public good in higher education to achieve autonomy and accountability. In Uganda the oversight roles of the Auditor General for financial matters and the National Council for Higher Education must be accepted. At the same time, governments must understand that universities perform best when they are institutionally free and protected from state micromanagement. The writers in this section must survey the history of how the University has been governed and how it has passed through the East African region’s various political storms since 1922.
- The university and the Uganda state
The history of the current university in Uganda is tied to, and reflects, the rocky history of the Uganda state since the 1945 anti-colonial riots. The Ugandan university has prospered and declined amidst the fortunes of the Uganda state. Like other African countries, university education was introduced in Uganda to create an intelligent collaborating elite to manage the colonial state. After independence, the post-colonial leaders were determined to build a collaborating middle class and avoid the emergence of a hostile educated elite. A well-researched chapter on the university’s relations with the state between 1922 and 2022 would be an excellent monument to reveal how Makerere survived and built a society in that period.
- Funding of the University, 1922-2022
The funding of Makerere is key to understanding almost all the challenges the university has faced in the past and is meeting now. Writers for this section should study the model the colonial state used in funding Makerere; its subsequent alteration by the 1970 Act to a state-driven one; the failure of the state to finance the institution fully; the throwing of the university to the waves of the market in the 1980s; the subsequent shortage of funds and the impact of the Structural Adjustment “Conditionalities” on Makerere.[1] Although the state allowed the market to operate in the financing of Makerere, the state retained its power to control the institution’s financial policy. Currently, most public universities have accumulated deficits. After such a review, it is necessary to point out what went right or wrong and what course the institution should take in financing all its activities.
- Staff and Student strikes
Writers on this section should review staff and student strikes at Makerere, beginning with the 1928 and 1952 food strikes to the many activists from the 1980s when the university implemented neoliberal policies to the current period.[2] The core causes of these strikes are funding, relations with external forces and mismanagement. To write Makerere’s contribution to society, we must study its problems, shortcoming and the constraints under which it operates.
- The type of University Makerere has been and should be in the next century
Carol Sucherman poses an interesting question, which Mahmood Mamdani grappled with at the University of Cape Town.[3] Has Makerere been a foreign (European) university in Africa or an African university? In his many speeches in Parliament, Abu Mayanja emphasized the Africanisation of the curriculum as a basis of decolonizing the minds of Ugandan youths.[4] It seems that this is an area where Makerere has not entirely constructed ideas for Africanising the University. But we cannot blame the institution for this failure. The current African university was an outgrowth of the European university. Universities as chartered communities of learners, teachers and knowledge producers developed over time from the Islamic through the medieval and enlightenment periods. Some of the earliest centres of learning included Athens ((500-300 BC), Alexandria (288 BC- 650 AD), Qarawiyyin (859 -), Al-Azhar 970-) and Timbuktu (C12th – C18th). Many of these learning centres became corporate entities when rulers gave them charters or guarantees of freedom to teach and search for knowledge unhindered. The original aim of many universities founded in Europe before 1800 was to produce and defend the values and social legitimation of the founders of a given institution. The modern western university evolved out of religious centres of learning, mainly Christian Cathedral schools for the clergy. These included Bologna (1088), Salamanca (1134), Paris (1150), Oxford (1167), Cambridge (1209) and others. Later, other disciplines were added to theology for study as scholars realized that the development of the mind involved the mastery of multiple domains (Newman,1907). Al-Azhar, founded earlier in 970AD in Egypt, stuck to only religious teaching and research until the C19th.
In Uganda and many post-colonial states, higher education imitated and followed western traditions. Almost all university studies delivered at Makerere followed and were certified by a western institution, the University of London, whose certificates Makerere graduates received until 1963. The administration of the university and its curriculum followed and was never allowed to undermine the colonial administration, and any dissenting lecturers (like Mary Parker, who criticized the colonial policies of Kenya in her lectures) were not permitted to teach. With independence, it was expected that Makerere would develop a robust institutional personality, chart its course by defining what type of university it wished to be and serve society accordingly.
Umar Kakumba (PhD)
DEPUTY VICE CHANCELLOR (ACADEMIC AFFAIRS)/
CHAIRPERSON, MAK@100 PROGRAMME SUB-COMMITTEE
[1] Mamdani, Mahmood (2007). Scholars in the Marketplace: The Dilemmas of Neo-Liberal Reform at Makerere University, 1989-2005. Kampala: Fountain Publishers.
[2] Byaruhanga, Fredrick Karuhanga (2006). Student Power in Africa’s Education: A Case Study of Makerere University. New York: Routledge, Tailor and Francis Group
[3] Sicherman, Carol (2005). Becoming an African University: Makerere 1922-2000. Kampala: Fountain Publishers
[4] Abu K. Mayanja: Several speeches in Parliament e.g Hansard: “Motion: 1965/66 – Estimates of Expenditure”, 6th July 1965, p. 2802; Hansard: “Motion – Address in Reply to the Presidential Speech.” January7, 1966 pp. 295 – 297; Hansard: Motion: Estimates of Expenditure- Ministry of Education, 6th July 1965, pp.2799-2806.
You may like
-


Mak Selected to Host Alliance for African Partnership Africa Office
-


Mak hosts First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling
-


Strengthening Global Partnerships to Advance Research, Innovation, and Graduate Training: Makerere University Hosts Delegation from the University of Warwick
-


Makerere Launches Scholarly Guide, Calls for Increased Research, Publication and Innovation in Africa
-


When Birth Becomes the Most Dangerous Moment, Wanduru & the Work of Making Labour Safer
-


How Jimmy Osuret Turned Childhood Trauma into Evidence for Safer School Crossings
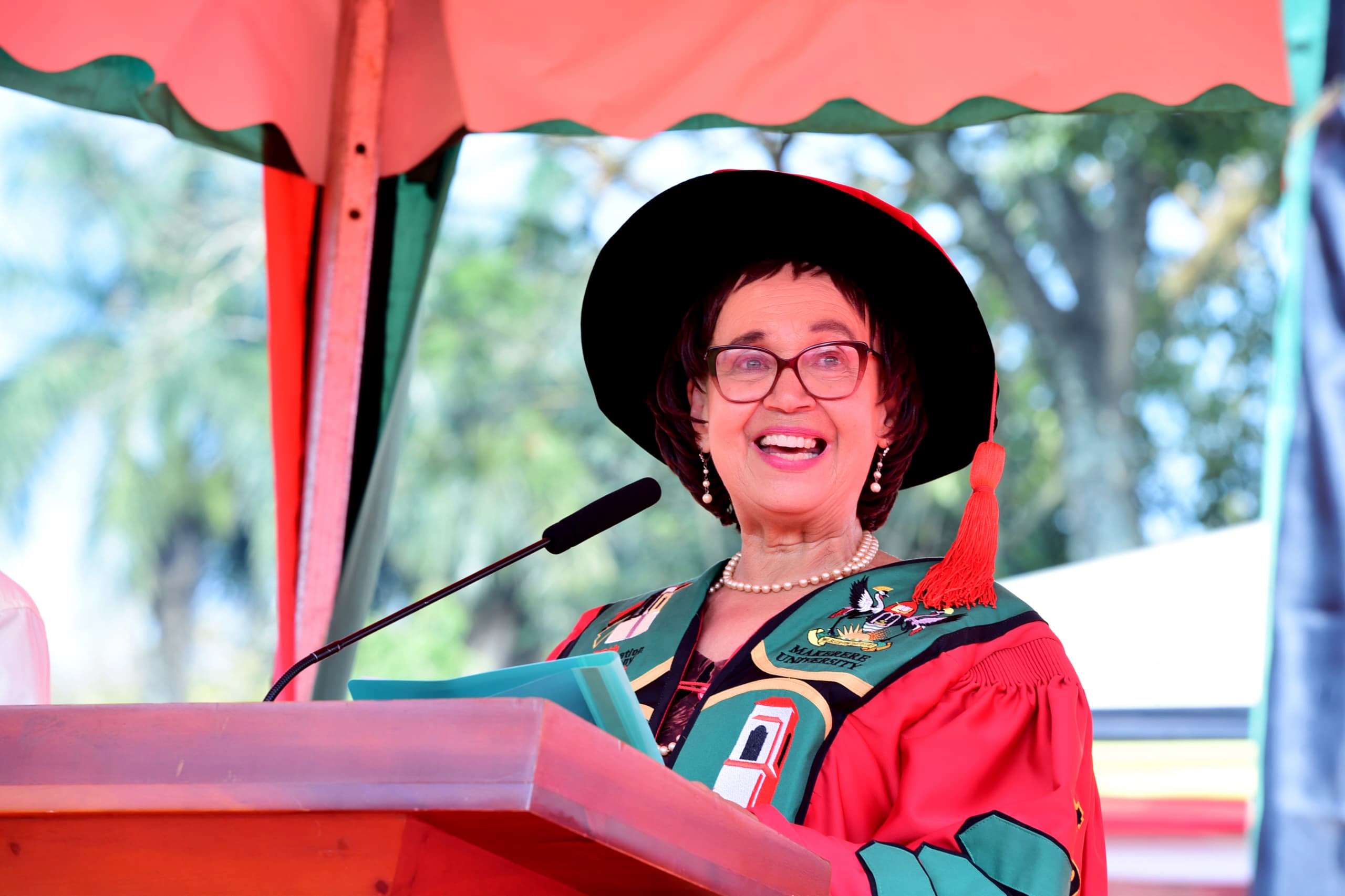

The Board Chairperson of the Makerere University Endowment Fund (MakEF), Dr. Margaret Blick Kigozi, has urged graduands in Health and Life Sciences to uphold professional ethics and serve humanity with diligence and compassion.
Her appeal came during the passing out of graduates from the College of Natural Sciences (CoNAS), the College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Bio-Security (CoVAB), the College of Health Sciences (CHS) and the School of Public Health (SPH) on Day Two of the 76th Graduation Ceremony of Makerere University.
“Class of 2026, you are now part of the Makerere legacy. Wherever you go clinics, laboratories, farms, boardrooms, or classrooms, you carry this institution with you. Serve your patients with skill and compassion. Care for animals and communities responsibly. Question boldly and keep learning,” Dr Kigozi, said.
Delivering the commencement address, Dr. Kigozi lauded the graduates for their dedication to careers that directly impact lives and communities. She encouraged them to use their knowledge generously and exercise their power gently.
“Your education has trained you to ask better questions. Your humanity must guide the answers. Never forget that behind every chart, every case, every animal, every experiment, there is life. And life deserves care, patience, and dignity. Give every person you come in contact with care, patience and dignity,” Dr Kigozi, noted.
As the graduates embark on their professional journeys, Dr. Kigozi emphasized the importance of cultivating basic business acumen and financial literacy to ensure sustainability in their work.

“You do not need to become accountants but you must be able to read the essentials: understand simple financial statements, budgets and key metrics so you can judge whether a clinic, lab, or program is sustainable. You are encouraged to start your business. There are numerous investment opportunities in your areas of training. You can provide services to our people and create jobs,” Dr Kigozi, said.
She shared candidly how, when she first stepped into leadership, she realised she did not understand balance sheets or budgets well enough. So, she returned to Makerere for short courses to strengthen herself.
“A well-run Hospital, clinic or lab delivers better outcomes, attracts staff, and secures funding. Business savvy is not only about profit, it’s about sustainability and the freedom to serve ethically and effectively. Carry clinical skill with business sense so your work endures and grows,” Dr. Kigozi, noted.
Quoting renowned writer and producer Shonda Rhimes, creator of Grey’s Anatomy, who once reflected that succeeding in one area of life can sometimes mean falling short in another, Dr. Kigozi encouraged women graduates to intentionally balance professional ambition with family responsibilities.
“When one area thrives, another is often under strain. When Navio was graduating from school I had to manage the Presidential Investor Round Table on the same day as Executive Director Uganda Investment Authority. I chose my job and delegated his siblings to attend Navios graduation. I learnt from this. I choose family always after that thing you achieve once and keep forever,” Dr Kigozi, said.
In his speech, the Prof Barnabas Nawangwe, the Vice Chancellor, informed the congregation that Makerere’s ranking on all university ranking platforms has remained stable, placing Makerere among the top 10 African universities and within the top 4.5% globally.
“In the Times Higher Education global ranking, Makerere University made a formidable jump from the 1200-1500 bracket to the 800-1000 bracket. This was no mean achievement and I congratulate all members of the Makerere Community on this stellar performance,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
General
Graduation marks the next phase of accountability, graduates told
Published
2 days agoon
February 25, 2026
“A degree is not a finish line. Graduation is not the end of learning, It is the beginning of accountability,” Prof. Nicholas Ozor, the Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network Nairobi, Kenya (ATPS), said.
Delivering a keynote address under the theme ‘Knowledge with purpose’, during Makerere University’s 76th graduation ceremony on Tuesday 24th February, Prof Ozor, challenged graduates to see their degrees not as status symbols, but as instruments of responsibility.
In his speech, he painted a candid picture of the world the graduates are stepping into, one marked by climate change, technological disruption, inequality, food insecurity and the rapid spread of misinformation. Yet rather than framing these challenges as obstacles, he described them as opportunities for purposeful leadership.
“Into this world, you step, armed with knowledge, credentials, and potential. Your degrees do not make you better than others. They make you responsible for others,” Prof Ozor, said.
Addressing graduands from College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES)
College of Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS), College of Education and External Studies (CEES) and School of Law (SoL), Prof. Ozor tailored his message to each field of study.
To graduates of the School of Law, he described the legal profession as a moral calling, urging them to use the law to protect the vulnerable and uphold justice with courage.
“Uganda, Africa, and the world do not need lawyers who only know how to argue. They need lawyers who know why they argue. Use the law to protect the weak, not intimidate them. Use your knowledge to defend justice, not delay it. Let integrity define your reputation not merely your résumé,” Prof Ozor, said.
For graduands who might feel that shortcuts will be tempting and silence will feel safer than truth, Prof. Ozor reminded them that justice does not need clever people, but courageous ones.
To the College of Education and External Studies, he underscored the transformative power of teachers, reminding them that classrooms shape nations long before policies do.
“Every nation rises and falls on the quality of its teachers. Never underestimate the power of a classroom. Teach not only for examinations, but for understanding. Teach not only content, but character. Teach learners how to think not what to think. Education is quiet work but its impact echoes across generations,” Prof Ozor, noted.
He called upon graduands from the College of Computing and Information Sciences, to use technology to solve African problems, not merely to imitate foreign solutions.
“Technology is powerful, but it is not neutral. Every line of code carries values. Every system you design affects real lives. Build for inclusion. Build for accessibility. Build for truth. Do not let innovation outrun ethics. The future will not belong to those who know the most technology, but to those who use it wisely,” He noted.
During the ceremony, Prof Ozor announced that the African Technology Policy Studies Network is offering PhD scholarships and postdoctoral fellowships in Artificial Intelligence, inviting deeper collaboration with Makerere.
For graduates of the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, he highlighted their critical role at the intersection of sustainability and survival, calling on them to blend indigenous knowledge with scientific innovation to secure Africa’s food systems and protect its ecosystems.
In closing, he reminded graduands that their integrity will open doors their degrees cannot, their humility will teach them lessons success never will, and their resilience will matter more than their grades.
Five principles to be remembered:
- Embrace lifelong learning. The world changes too fast for static knowledge.
- Choose purpose over comfort. Impact matters more than income.
- Build character before career. Skills get you hired; character sustains you.
- Serve something larger than yourself. Give back to your communities and your country.
- Believe in Africa, and act. Do not wait for solutions from elsewhere. Be the solution.
General
Over 9,200 to graduate at Makerere University’s 76th Graduation
Published
3 days agoon
February 24, 2026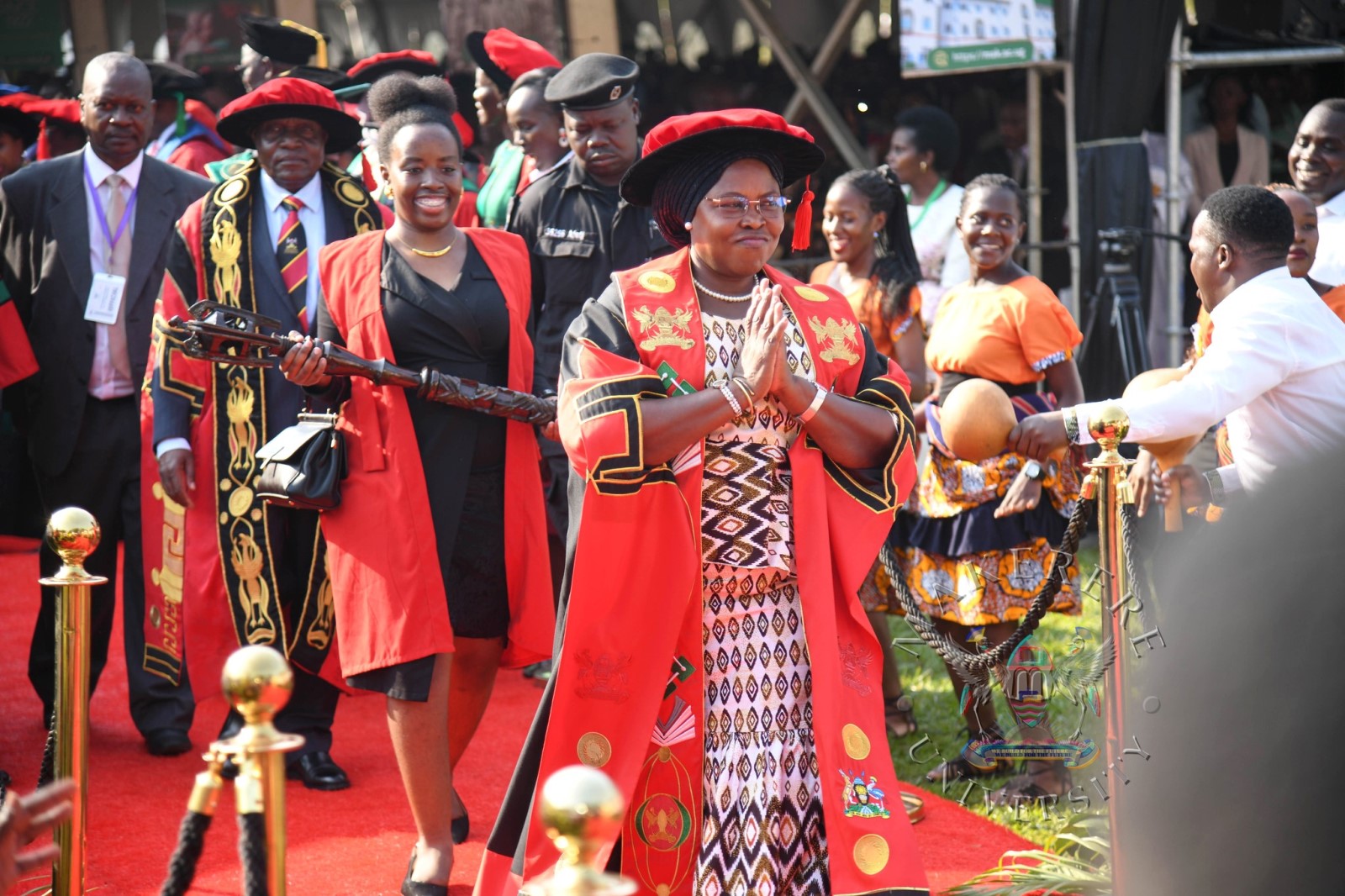
Pomp and colour defined the opening day of the Makerere University’s 76th Graduation Ceremony as thousands gathered to celebrate academic excellence and new beginnings.
The historic ceremony has brought together scholars, families, friends and industry partners in a vibrant celebration of achievement and possibility. Throughout the four-day event, the University will confer degrees and award diplomas to 9,295 graduands in recognition of their dedication and hard work.
Among the graduates, 213 will receive Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degrees, 2,503 will graduate with Master’s degrees, and 6,343 will earn Bachelor’s degrees. In addition, 206 students will graduate with postgraduate diplomas, while 30 will be awarded undergraduate diplomas.
Of the total number of graduands, 4,262 are female and 5,033 are male. According to Vice Chancellor, this marks the first time in 15 years that male graduands have outnumbered their female counterparts.
The best overall graduand in the Sciences, Esther Ziribaggwa, graduated on the opening day with the Bachelor of Agricultural and Rural Innovation and an impressive Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) of 4.77.
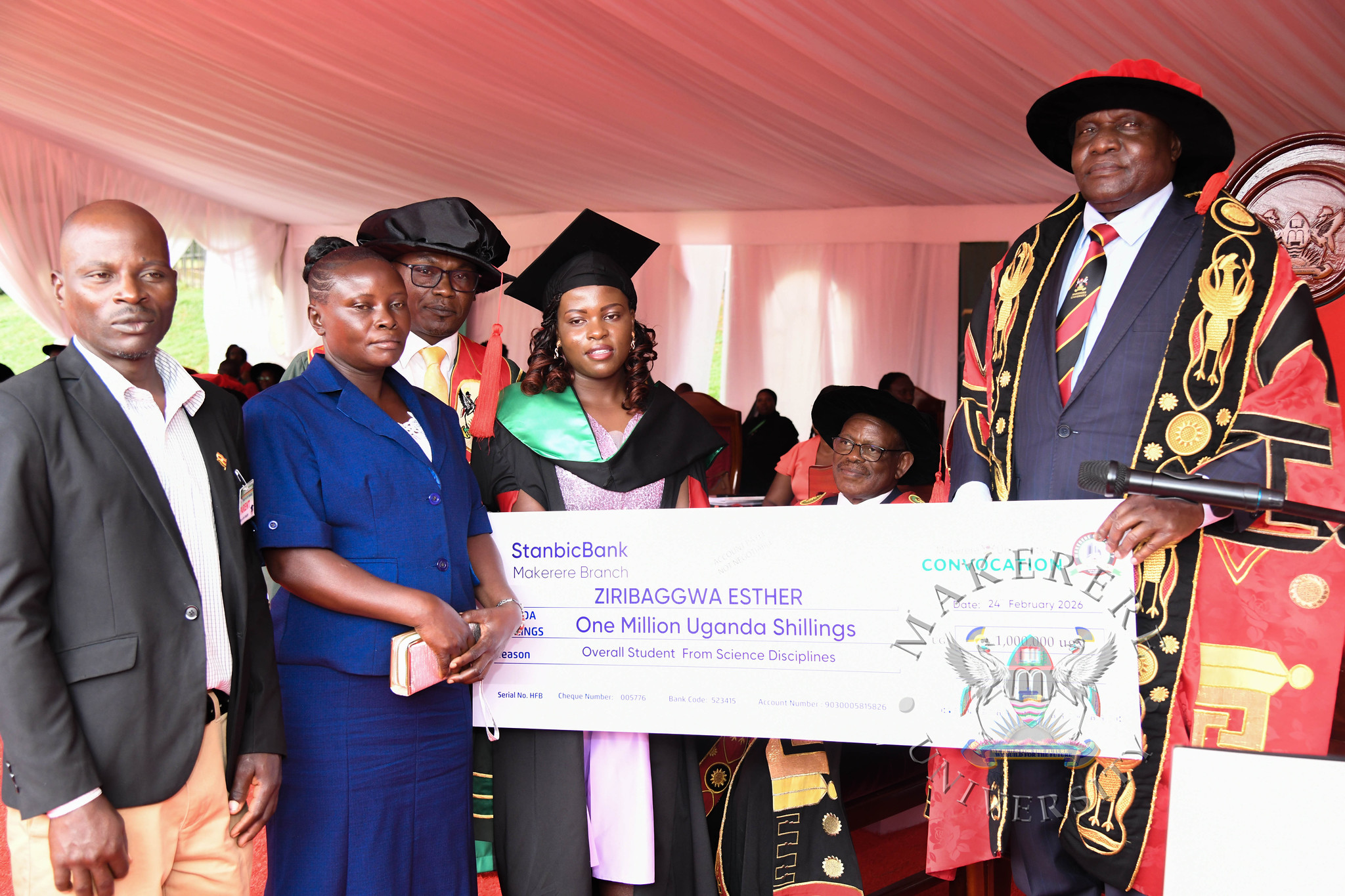
The ceremony marks a proud moment for Makerere University as it continues to nurture top-tier professionals across diverse fields.
While presiding over the graduation, the State Minister for Primary Education, Hon. Dr. Joyce Moriku Kaducu, on behalf of the First Lady and Minister of Education and Sports, Hon. Janet Kataaha Museveni, pointed out that Makerere University is a model institution, where leaders are nurtured, scholars are sharpened, and where dreams have been given direction.
In her address, Hon. Museveni, highlighted Government’s deliberate investment in research, innovation, and infrastructure to strengthen higher education in Uganda.
“The establishment of the Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund (RIF), supports high-impact research and innovation that directly contributes to national priorities and development. Through this initiative, thousands of researchers and innovators have pursued practical, scalable solutions that are transforming communities and key sectors across Uganda,” Mrs Museveni, said.
The Minister also noted that Parliament’s approved a USD 162 million concessional loan to upgrade science, technology, and innovation infrastructure at Makerere University. The funding will facilitate the construction of modern laboratories, smart classrooms, and state-of-the-art facilities for Engineering and Health Sciences, investments expected to position the University firmly within the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
“Government has embarked on the construction of a National Stadium at Makerere University and other institutions of higher learning across the country. This will promote physical education, strengthen talent identification, and boost investment in the sports sector,”
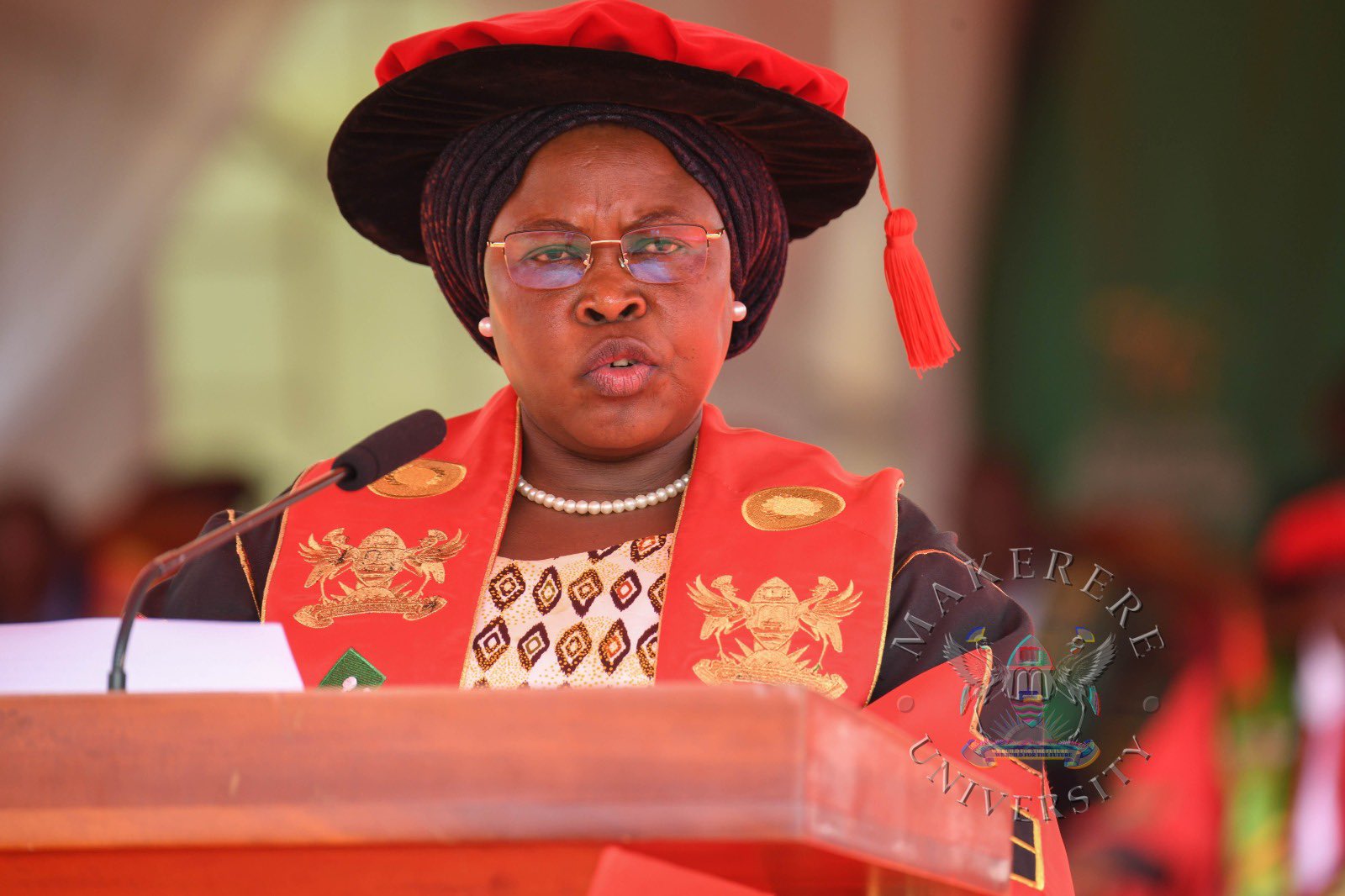

Turning to the graduands, the Minister encouraged them to see themselves not merely as job seekers, but as job creators and solution-makers.
Uganda and Africa need innovators who will modernize agriculture; engineers who will build quality infrastructure; healthcare professionals who will strengthen health systems; and educators who will inspire the next generation,” the Honourable Minister said.
She reminded graduates that they are entering a rapidly changing world shaped by Artificial Intelligence, climate change, and shifting global markets. To thrive, she advised them to remain adaptable, creative, and committed to lifelong learning.
She also encouraged graduates interested in entrepreneurship to tap into the Government’s Parish Development Model, which provides community-based financing and production support.
Quoting Proverbs 3:5–6, the Minister urged the graduates to trust in God as they embark on their next chapter.
She extended special appreciation to the Mastercard Foundation for its 13-year partnership with Makerere University in expanding access to education and empowering young people in Uganda and beyond.
In his speech, the Chancellor of Makerere University, Dr Crispus Kiyonga, urged graduands to harness research, innovation and technology to drive Uganda’s transformation.
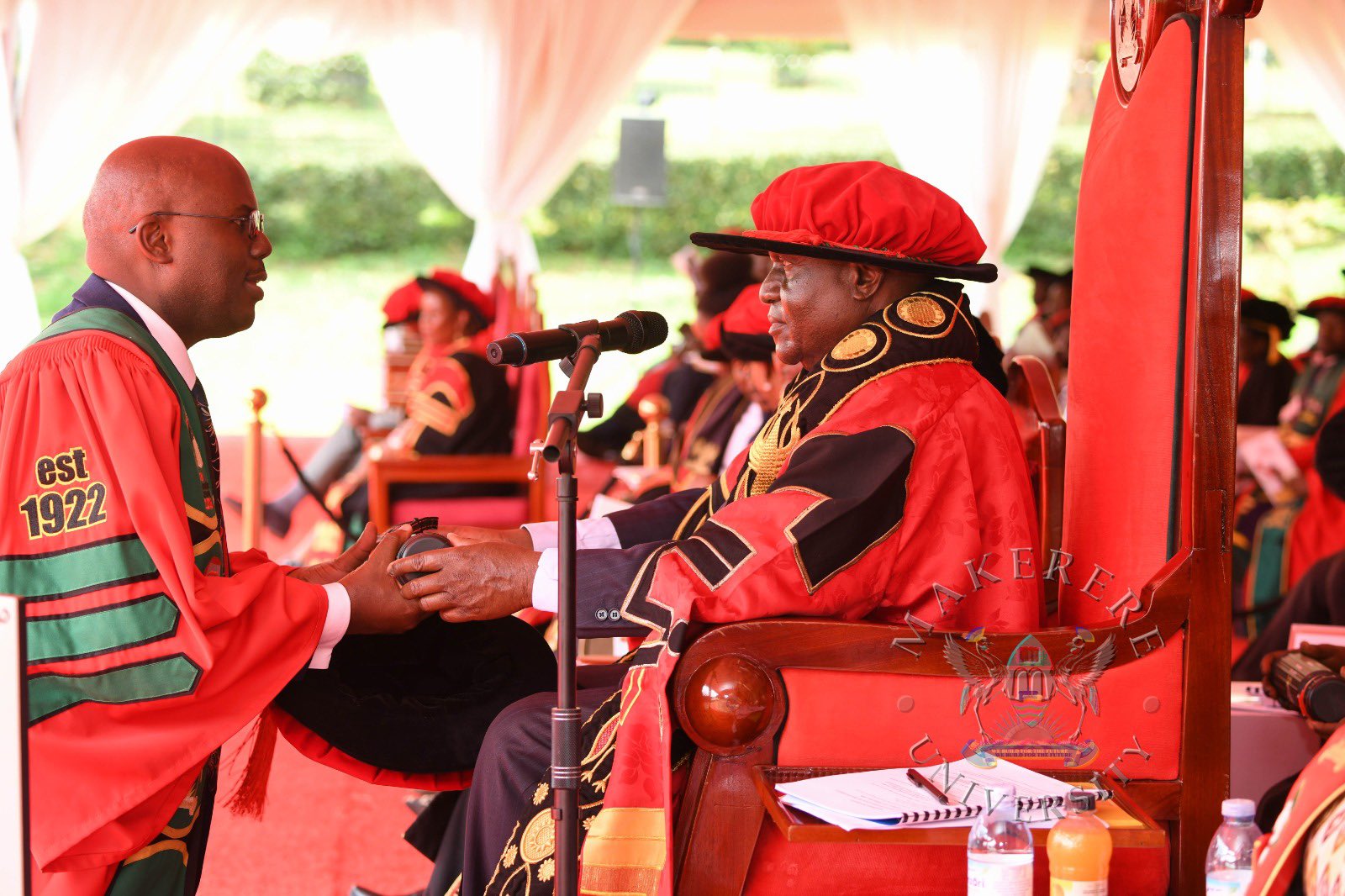

“This is a milestone in your lives. You have invested time, discipline and hard work to attain these qualifications. It is important that you derive value from this achievement, not only for yourselves, but for your families and for society.” Dr Kiyonga, said.
Dr. Kiyonga expressed gratitude to the Government of Uganda for its continued financial support to the University, particularly the funding allocated under MakRIF, which he described as critical in strengthening the institution’s research capacity.
“Research plays a very vital role in the development of any community. Makerere as the oldest University in the country is doing a significant amount of research, However, more work is required to mobilize additional resources to further strengthen research at the University.” Dr Kiyonga, noted.
Acknowledging the challenges of a competitive job market, Dr. Kiyonga encouraged graduates to think beyond traditional employment pathways.
“It is true that the job market may not absorb all of you immediately. But the knowledge you have acquired is empowering. You can create work for yourselves, individually or in teams.” Dr Kiyonga, said.
He advised the graduands to embrace discipline, integrity and adaptability in the workplace, and to take advantage of technology and digital platforms to innovate and respond to societal challenges.
“Every development challenge presents an opportunity. Believe that you can apply your knowledge to create solutions with impact.” He said.
Addressing the congregation, the Vice Chancellor, Prof Barnabas Nawangwe, congratulated the graduands, particularly staff and societal leaders on their respective achievements.
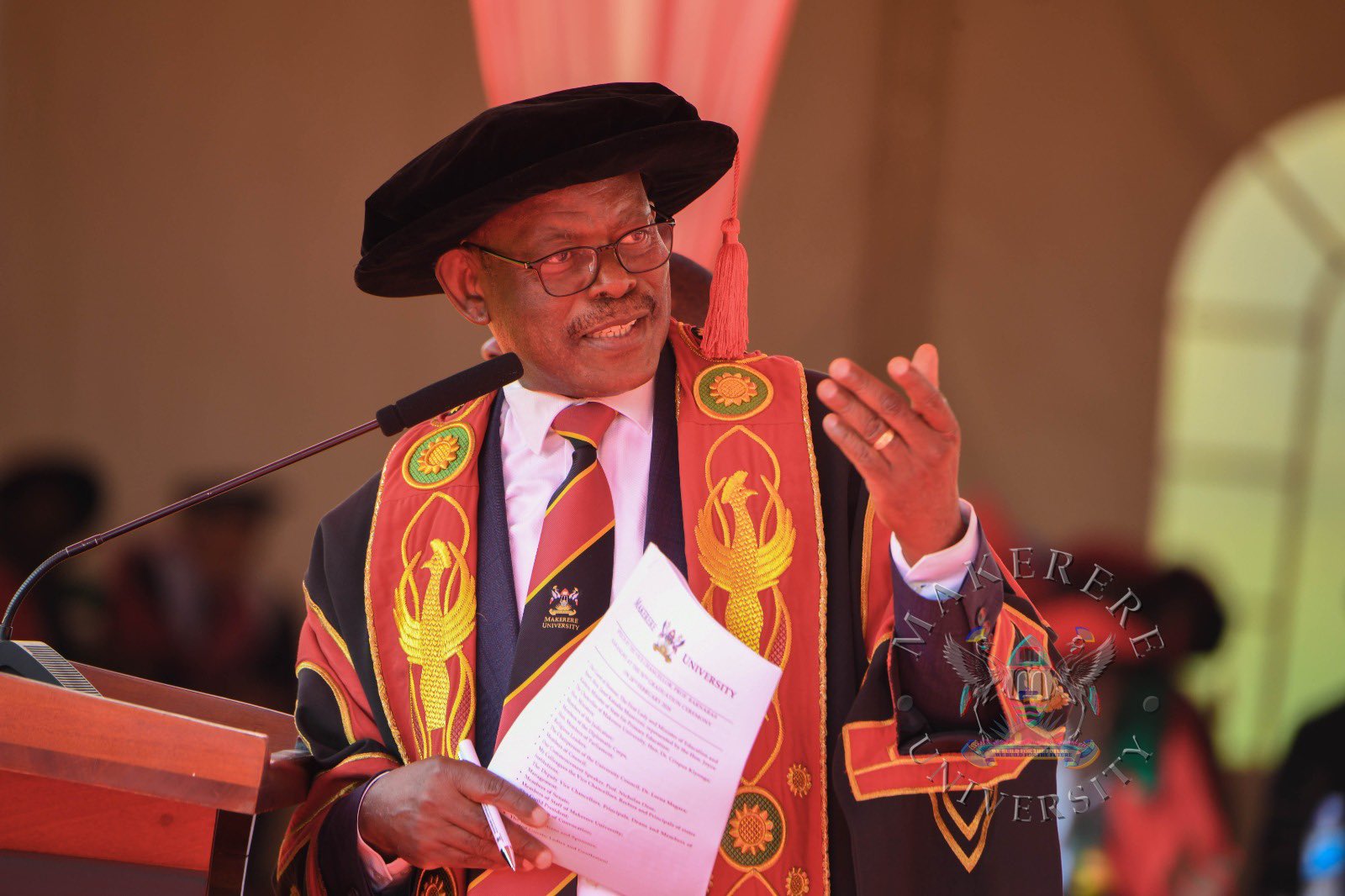

“I congratulate all our graduands upon reaching this milestone. In a special way I congratulate the members of staff, Ministers, and Members of Parliament that are graduating today as well as children and spouses of members of staff,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
In his speech, Prof Nawangwe, recognized outstanding PhD students, particularly members of staff. who completed their PhDs in record time without even taking leave from their duties.
He called upon graduates not to despise humble beginnings but rather reflect on the immense opportunities around them and rise to the occasion as entrepreneurs.
“You are all graduating with disciplines that are needed by society. We have equipped you with the knowledge and skills that will make you employable or create your own businesses and employ others. Do not despair if you cannot find employment. Instead, reflect on the immense opportunities around you and rise to the occasion as an entrepreneur,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
Prof Nawangwe called upon the graduands of PhDs to use their degrees to transform the African continent.
“As you leave the gates of Makerere I urge you to put to good use the knowledge you have received from one of the best universities in the World to improve yourselves, your families, your communities, your Country and humanity. Let people see you and know that you are a Makerere alumnus because of the way you carry yourself in society with dignity and integrity. Put your trust in God and honour your parents and opportunities will be opened for you,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
Delivering a key note address, Prof. Nicholas Ozor, the Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network Nairobi, Kenya ((ATPS). Reminded the graduates that a degree is not a finish line but the beginning of accountability. “The world is a complex, fast changing and deeply unequal. Degrees make you responsible for others not better than them,” Prof Ozor, said.
Trending
-

 Humanities & Social Sciences4 days ago
Humanities & Social Sciences4 days agoMeet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 Agriculture & Environment1 week ago
Agriculture & Environment1 week agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-

 General3 days ago
General3 days ago76th Graduation Highlights
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
