Health
Mak Researchers Design National Drowning Prevention Strategy
Published
5 years agoon
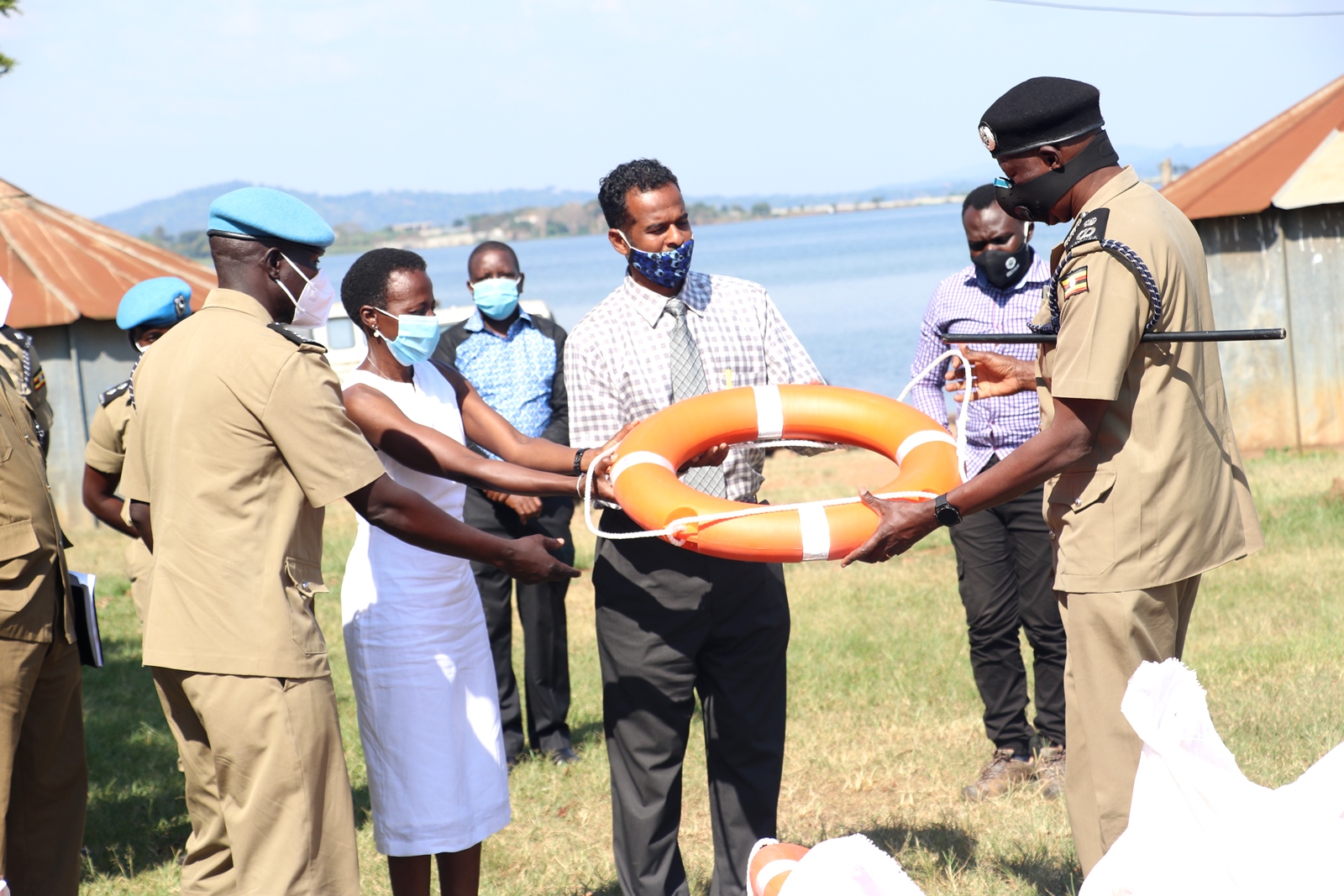

By Joseph Odoi
Makerere University researchers under Trauma, Injuries and Disability (TRIAD) Unit) have designed a national drowning prevention strategy. This strategy comes at a time when there is sky rocketing cases of drowning in Africa.
Globally, drowning is the third leading cause of unintentional injury death; accounting for 7% of all injuries. Over 90% of the estimated 322,000 annual global drowning deaths occur in low-and middle-income countries.
Although the burden of drowning is believed to be highest in the WHO-African region, data collection and surveillance for drowning in African countries is limited.
In bid to contribute to data driven interventions, Makerere University researchers carried out a study aimed at establishing the availability of drowning data in district-level sources and understanding the reporting of and record keeping on drowning in Uganda.
As part of the study titled: Drowning in Uganda; examining data from administrative sources, researchers engaged various health stakeholders who shared their experiences about drowning and how it can be prevented in communities.
It is upon that background that scholars designed a contextual appropriate strategy for drowning prevention in Uganda under the project titled; Drowning in Uganda; examining data from administrative sources.
According to the researchers, this drowning strategy is first ever in Uganda. ‘’it will be a national document that will guide all the efforts on drowning prevention in the country; and will avoid non-coordinated activities aimed at prevention of drowning. the strategy will also provide for monitoring and evaluation of all activities and interventions for drowning prevention in the country since there will be a government lead agency tasked with this responsibility’ ’explained Mr. Fredrick Oporia who is part of the study team
STRATEGIES TO PREVENT DROWNING
In this study published on semantics scholar among other journals, the researchers came up with the following strategies to counter drowning;
• Setting and enforcing safe boating regulations. • Providing incentives that encourage adherence to boating regulations related to not overloading transport boats and increasing enforcement of boating regulations. • Ensuring boats are fit for purpose and increasing regular inspection of the seaworthiness of boats. • Improving detection and dissemination of information about the weather. • Supporting increased availability and use of lifejackets through subsidy, lifejacket loaner programs, and free lifejacket distribution programs. • Increasing sensitization about safe boating practices, the importance of wearing lifejackets, and limiting alcohol and illicit drug use when boating. Community members, especially children, are vulnerable to drowning in unsafe water sources such as ditches, latrines, wells, and dams. Potential interventions could include: • Modifying access to wells and dams to prevent children or adults from falling in. • Installing boreholes and pumps to enable community members to draw water safely.
Providing safe rescue and resuscitation training to community members and conducting refresher trainings. • Developing and providing low-cost rescue equipment such as boat fenders (rubber and ropes tied to boat on all sides that can assist in the immediate rescue of individuals) and buoyant throwing aids.
To enable ongoing design, implementation, and evaluation of drowning prevention efforts, the researchers note that it is essential to collect data on drowning incidents. Reporting of and record keeping on drowning in Uganda should also be improve according to the researchers namely; Tessa Clemens, Frederick Oporia, Erin M Parker, Merissa, A Yellman, Michael F Ballesteros and Olive Kobusingye
Other Potential interventions highlighted by the researchers include: • Providing records officers with proper training, equipment, and appropriate storage facilities. • Sensitizing the public on the importance of reporting all drowning cases to authorities.
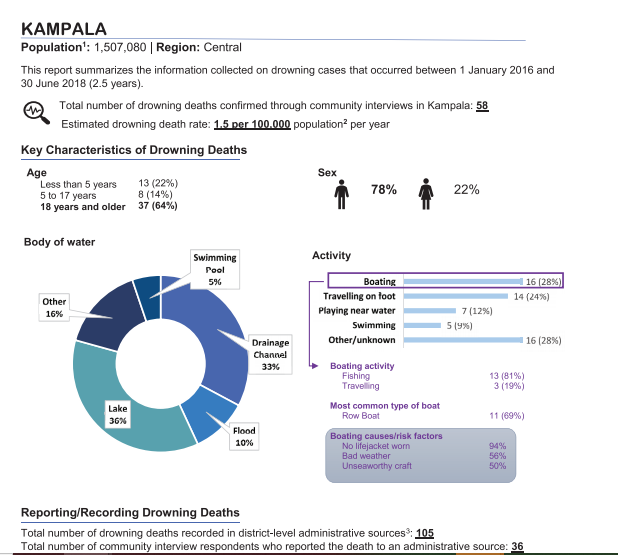
As part of their study findings, the researchers noted that; A total of 1435 fatal and non-fatal drowning cases were recorded; 1009 (70%) in lakeside districts and 426 (30%) in non-lakeside districts.
Of 1292 fatal cases, 1041 (81%) were identified in only one source. After deduplication, 1283 (89% of recorded cases; 1160 fatal, 123 non-fatal) unique drowning cases remained. Data completeness varied by source and variable.
On demographics, fatal victims were predominantly male (85%), and the average age was 24 years. In lakeside districts, 81% of fatal cases with a known activity at the time of drowning involved boating.
What were people doing when they drowned?
Activity at the time of drowning in lakeside districts and non-lakeside districts
• Overall, boating was by far the most common activity that people were engaged in at the time of the drowning incident.
• Other common activities were collecting water/watering cattle and travelling on foot.
• The most common activities that people engaged in prior to drowning were similar in lakeside and non-lakeside districts. However, in non-lakeside districts, more drowning deaths occurred as a result of collecting water or watering cattle than as a result of boating in those districts.
• Almost half (48%) of all drownings occurred while the person was engaged in an occupational activity.
Of the 1,063 people who died from boating-related drowning or suffered a severe boating related drowning incident but survived, 1,007 (95%) were not wearing a lifejacket at the time of the incident.
Bathing in water bodies: Study participants indicated that drowning sometimes occurs when people are bathing in lakes, ponds, swamps, and valley dams. People can unexpectedly slip into deep water from shallower areas or rocks.
Crossing flooded rivers and streams:
Attempting to cross flooded rivers and streams during the rainy season was another cause of drowning identified by study participants.
“Currently, people cross from makeshift bridges such as that of round poles. When the river overflows, it covers them. So, you can’t see them; so, you just start guessing: ‘the pole might be here or there’ and in case your guess is wrong, you automatically drown and you will be gone.” an Interview respondent in Kabale district explained
Delayed rescue attempts: Study participants identified the importance of timely rescue and resuscitation to prevent death from drowning. However, they also indicated that community members lack knowledge on how to rescue someone who is drowning.
Alcohol use: Several participants identified alcohol use as a key risk factor for drowning. Participants stated that alcohol use is common, especially in fishing communities. “We have a problem with alcoholism. Many of our colleagues go to the waters when their minds are a bit twisted by the alcohol and on some occasions, this has caused accidents and some of them have drowned just like that.” – Interview respondent, Nakasongola district.

When asked on strategies of preventing drowning, participants suggested the following strategies for preventing drowning:
• Provide affordable and high-quality lifejackets to all water transport users and fishing communities. • Increase sensitization of fishermen and all water transport users on the importance of using lifejackets and avoiding alcohol while boating. • Provide subsidies for large and motorized boats that can be used for safe water travel and fishing to replace small and low-quality boats that are currently in use.
Inspect boats regularly to ensure they are in good travelling condition. • Recruit and deploy more marine police units on all major water bodies to enhance security and quick response to drowning incidents. • Install boat fenders (rubber and ropes tied to boat on all sides) to assist with the immediate rescue of individuals who are involved in a drowning incident. • Provide frequent and safe ferry services to enable water travellers access to safe transportation across rivers and lakes. • Avoid fishing during the moonlight periods to minimize hippopotamus attacks which are more frequent at that time.
“I think these fishermen really need lifejackets for their work and also need to be sensitized on how to manage the engine of the boats that they use for their work. In most cases, these men just learn how to use these boats without having been trained first.” – Interview respondent, Rakai district. Swimming and basic rescue skills said
Moving forward, the researchers recommend that since; drowning is a multisectoral issue, and all stakeholders (local and national government, water transport, water sport, education, fishing, health, and law enforcement) should coordinate to develop a national water safety strategy and action plan.
MORE ABOUT THE STUDY
The study was conducted in 60 districts of Uganda for a period of 2.5 years (from January 1st, 2016 to June 30th, 2018). In the first phase, records concerning 1,435 drowning cases were found in the 60 study districts.
In the second phase, a total of 2,066 drowning cases were identified in 14 districts by community health workers and confirmed through individual interviews with witnesses/family members/friends and survivors of drowning. This work was funded by Bloomberg Philanthropies through the CDC Foundation
You may like
-


Makerere University Affirms E-Mobility Push with Fast-Charging Station Launch
-


82% Stressed: Uncovering the Hidden Mental Health Burden Among Kampala’s Taxi Drivers
-


Makerere University and International Partners Sign MoU for the 9th Kampala Geopolitics Conference
-


Farmers’ Preferences Drive Success in Tree-Planting, Duke Scholar Finds
-


AI SHOWDOWN: Careers Fair 2026 Kicks Off at Makerere
-


Makerere University Unveils Pre-Award Grants Management System
Health
82% Stressed: Uncovering the Hidden Mental Health Burden Among Kampala’s Taxi Drivers
Published
2 days agoon
March 12, 2026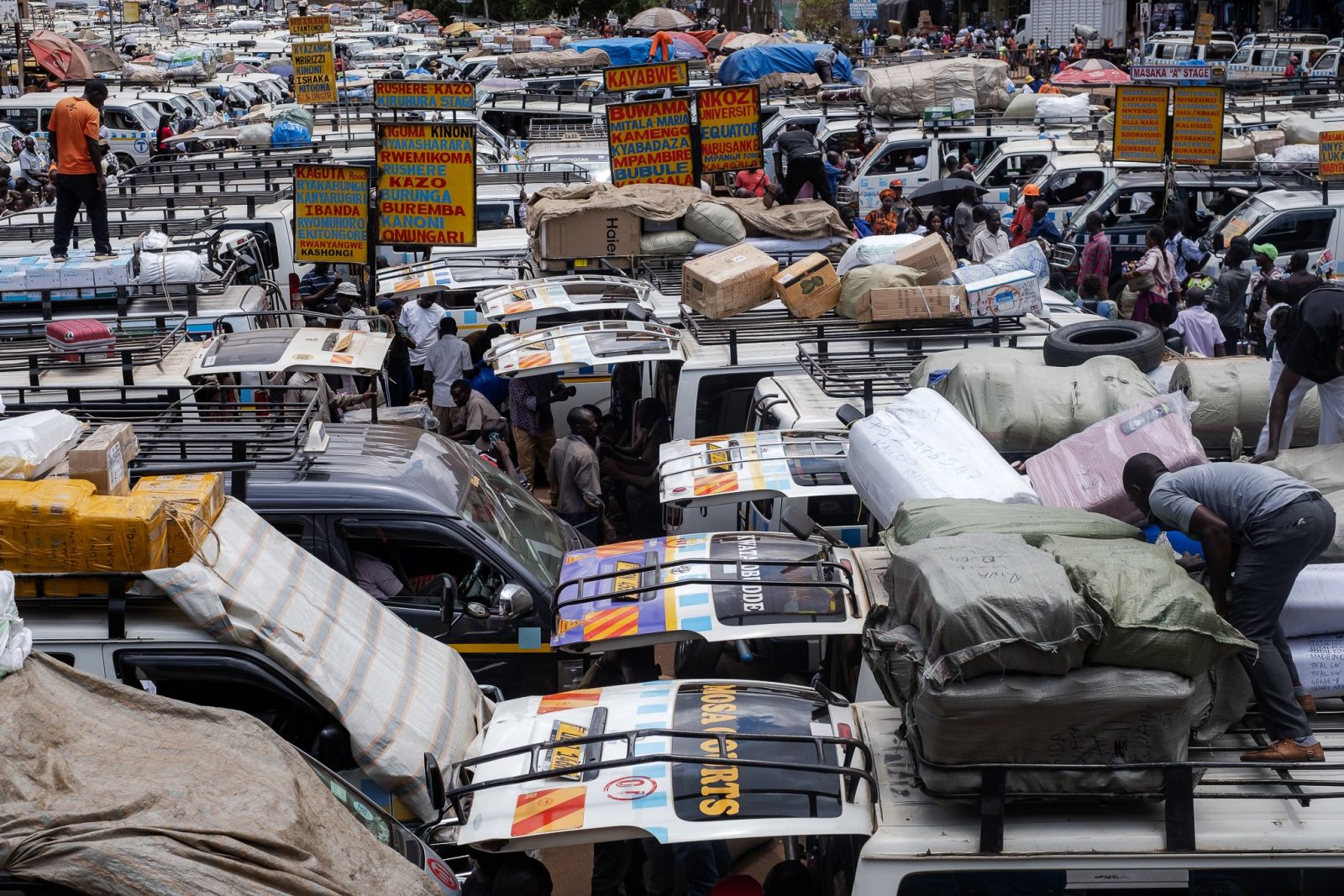
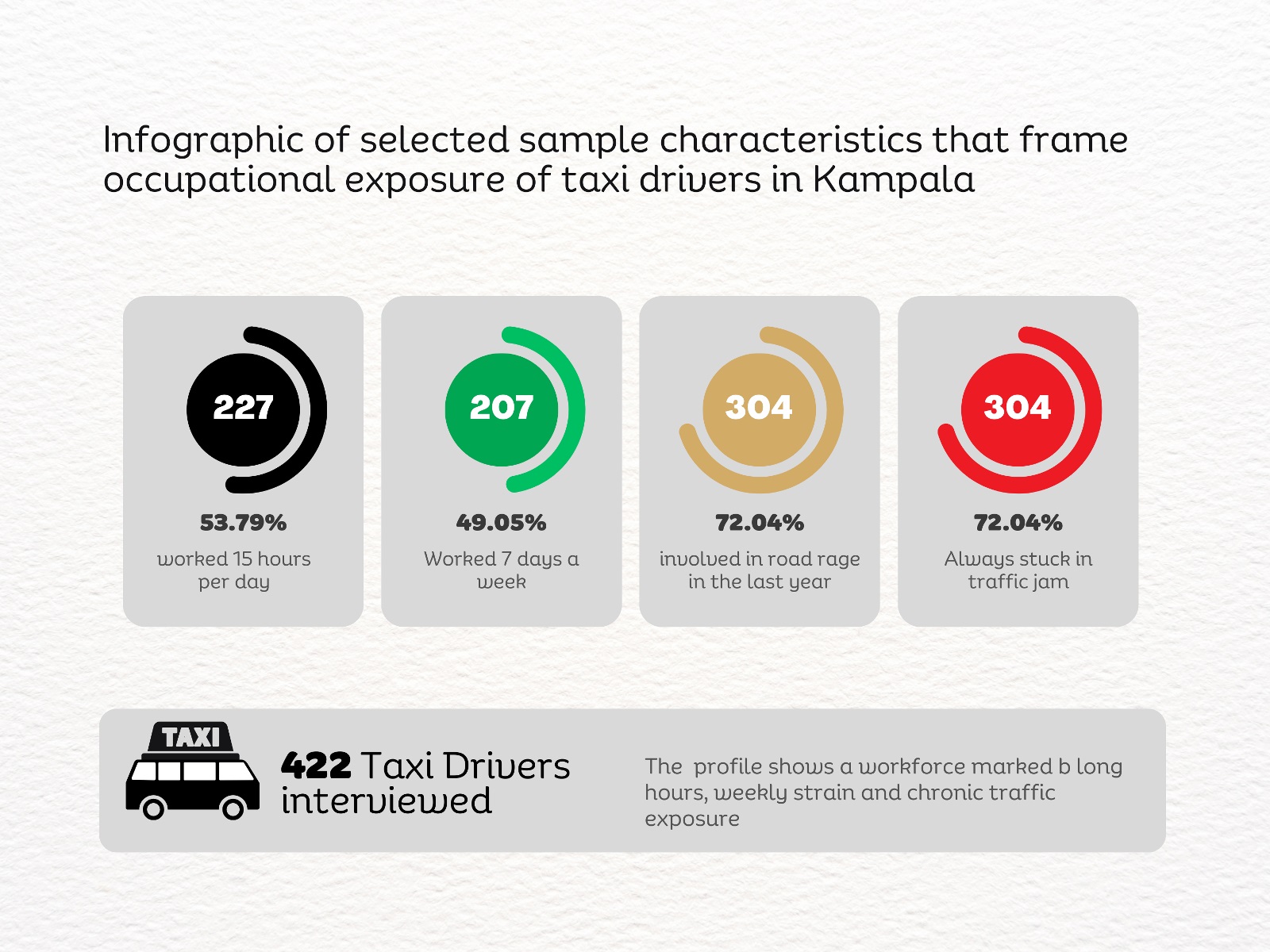
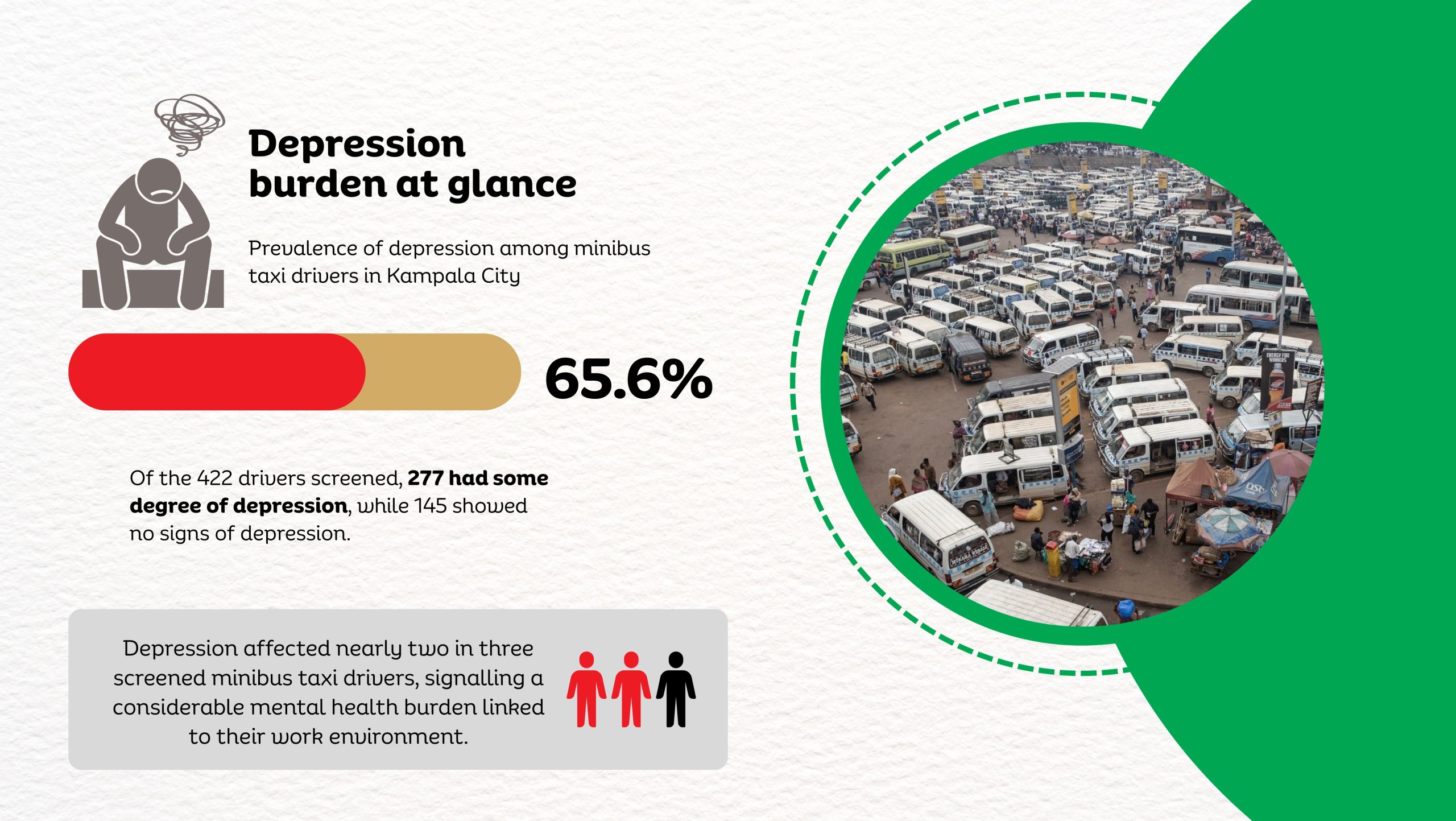
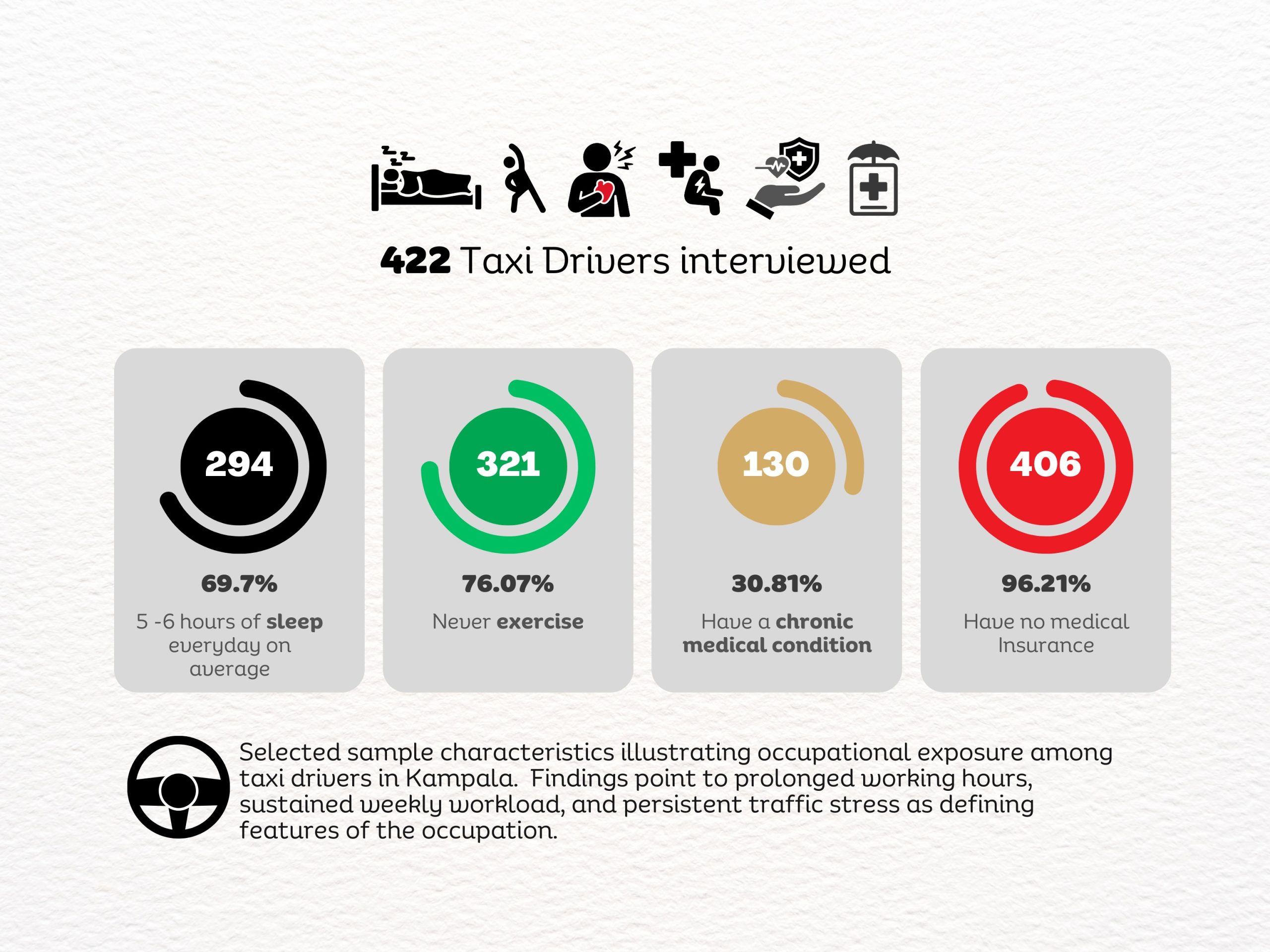
A new study by Dr. Linda Kyomuhendo Jovia, a medical doctor and graduate of the Master of Public Health programme at Makerere University School of Public Health, has found high levels of psychological distress among minibus taxi drivers operating in Kampala’s major taxi parks. In a cross-sectional survey of 422 drivers across Old, New, Kisenyi, Usafi, Namirembe, Nakawa, and Nateete parks, nearly two-thirds screened positive for symptoms of depression (65.6%), while anxiety affected more than 70%, and stress an estimated 82%. The findings point to a largely overlooked occupational health concern within the city’s informal transport sector, where long working hours, economic pressure, poor sleep, and prior road accidents were associated with higher levels of mental strain.
Before sunrise settles over Kampala, Old Taxi Park is already awake. White minibuses marked with the blue stripe of Uganda’s public service taxis sit jammed bumper to bumper, their noses pointed toward narrow exits that will soon release them into the city’s traffic. Dust clings to the windows. Torn seats peek through sliding doors. Diesel hangs low in the air. Conductors slap the metal sides of vans and shout destinations into the morning.
“Kireka! Banda! Bweyogerere!” The calls overlap until they become a steady roar.
Passengers squeeze through narrow corridors between vehicles where there was never meant to be walking space. Hawkers weave through the crowd with trays of roasted maize and boiled eggs. Somewhere, a small radio crackles. Nearby, two conductors argue over whose turn it is to load passengers. This scene is how Kampala wakes, in diesel fumes, shouted destinations, and the quiet urgency of people trying to earn a living before the traffic tightens its grip on the day.
Handwritten route boards fixed to the taxis signal their destinations: Masaka “A” Stage, Kaguta Road, Nakawa, Namirembe, Ntinda, Gayaza, Nansana, and Entebbe, guiding passengers through the organised chaos of the park. Behind every steering wheel sits someone doing the arithmetic of survival. Drivers wake before dawn to secure a place in the queue. For many, sleep is short, interrupted, and rarely restorative. The day stretches across long hours of traffic, uncertain earnings, rent, school fees, and taxi levies, including annual payments of about UGX 720,000. Passengers today mean dinner tonight. Yet inside the noise of the taxi parks, another story has remained largely invisible.
Across Uganda, an estimated 400,000 taxis move millions of passengers every day, forming the backbone of the country’s informal transport system. But almost nothing is known about the psychological toll on the drivers who keep it running.
That gap is what drew Dr. Kyomuhendo into Kampala’s taxi parks. What she uncovered were levels of depression, anxiety, and stress far higher than many had imagined.
A Medical Doctor Turning Toward Public Health
Born on 23 July 1994 to Mr. Muhigwa Lawrence and Ms. Kataito Jacqueline, Dr. Kyomuhendo grew up in Hoima District in western Uganda. Her early education took her from St. Christina Nursery School to Budo Junior School before she continued to Trinity College Nabbingo and later Mount Saint Mary’s College Namagunga for Advanced Level, where she studied Biology, Chemistry, and Mathematics.
In 2014, she earned a government scholarship through the Public Universities Joint Admissions Board and enrolled for a Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery at Busitema University, graduating in 2019.
During her medical internship at Masaka Regional Referral Hospital, she began noticing a troubling pattern in the cases arriving at the wards: road traffic injuries, complications of chronic diseases, severe malaria in children, and obstetric emergencies that might have been prevented with earlier intervention. Many of the crises doctors were treating, she realized, had begun long before patients reached the hospital. “They were symptoms of deeper problems,” she recalls.
Public health offered a way to investigate those underlying causes. In 2022, she enrolled in the Master of Public Health Distance programme at Makerere University School of Public Health, where students are trained to examine health problems not only at the bedside but across entire populations. Guided by Associate Professor Lynn Atuyambe, a respected scholar in Community Health and Behavioural Sciences at MakSPH, and Dr Juliet Kiguli, Senior Lecturer and public health anthropologist, the student’s work benefited from strong academic stewardship.

Uganda’s road transport system is dominated by motorcycles and 14-seater minibus taxis. About 15,000 operate in the Kampala Metropolitan Area alone.
These drivers navigate congested roads, pollution, erratic traffic patterns, and long working hours. Their workday often begins before dawn and stretches deep into the evening.
“They are important in Uganda’s transport industry,” Kyomuhendo said. “Yet they seem to be overlooked in our society.”
While commuting through Kampala during her studies, she began to notice the lives of taxi drivers. Arguments between passengers and conductors were common. When tensions rose, someone would eventually mutter the same question in Luganda.
“Oba abasajja ba takisi baabaki?” loosely to mean, ‘What is wrong with taxi men?’
The question lingered, and in June 2024, social media campaigns marking Men’s Mental Health Awareness Month pushed her to think about the issue differently. What if the behaviour many passengers dismissed as impatience or aggression was linked to something deeper? To her, taxi drivers seemed an unlikely but revealing group to study.
“They carry the responsibility for passengers’ lives every day,” she says. “Yet very little attention is paid to their own well-being.”
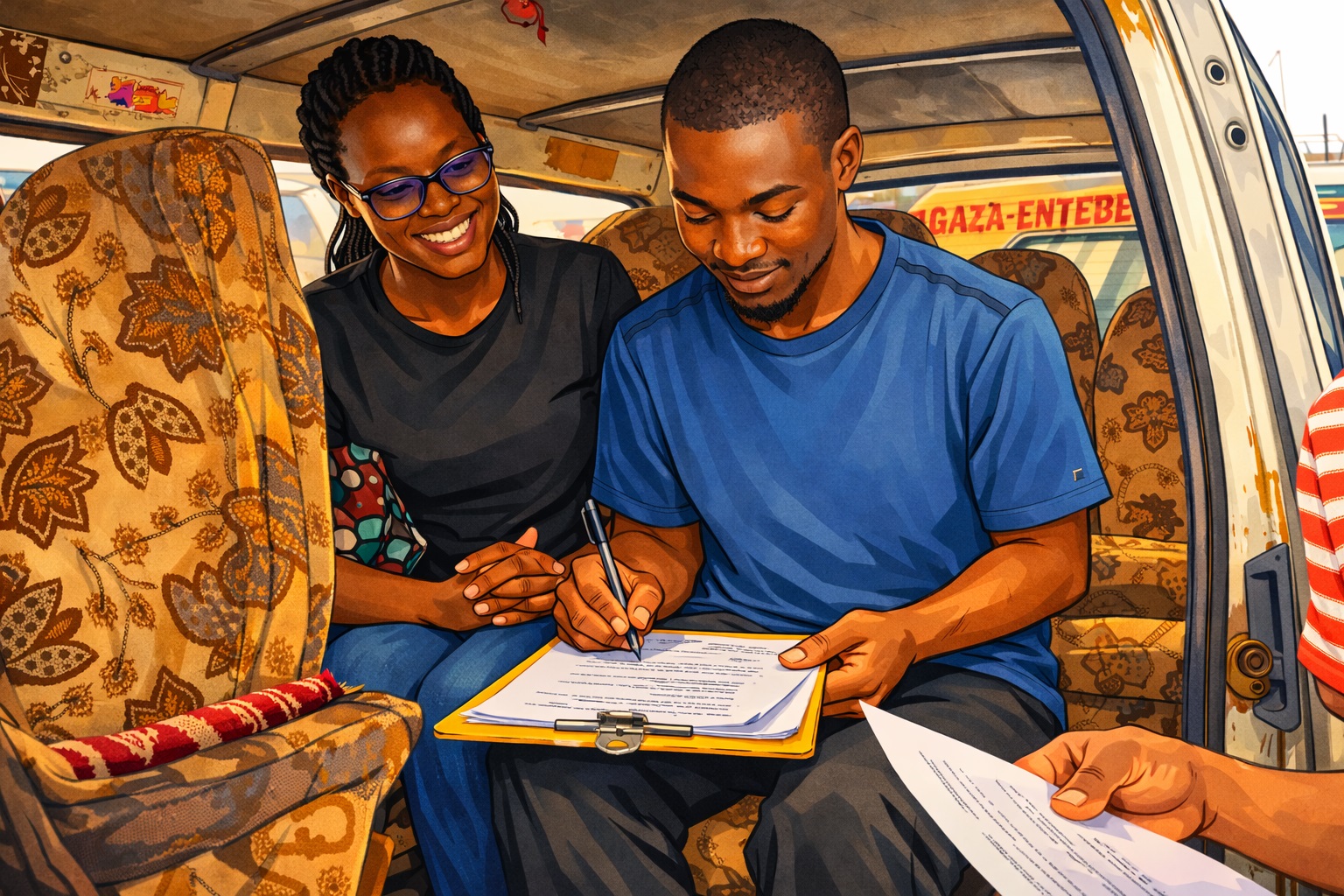

For instance, Kampala City Authority (KCCA) documents that between 2019 and 2024, geolocated crash data reveal a dangerous road environment in which Kampala’s taxi drivers operate daily. A total of 1,878 vulnerable road users, including pedestrians, motorcyclists, and cyclists, were killed in crashes involving motor vehicles, with buses and minibuses linked to 281 deaths, most of them pedestrians (147) and motorcycle occupants (131). Fatalities were heavily concentrated along major corridors such as Jinja Road, Kibuye–Natete Road, Bombo Road, and Ggaba Road, while for pedestrians, the most dangerous segments included Gayaza Roundabout (Kalerwe) and Kyebando Police Post along the Northern Bypass and Entebbe Road, where fatality densities reached 27–28 deaths per kilometer. These patterns highlight the high-risk traffic environments in which taxi drivers work, specifically busy arterial roads and bypass intersections where pedestrians, boda bodas, and public transport vehicles compete for space. These conditions contribute to the broader pressures that shape drivers’ safety, well-being, and mental health.
Research in the taxi parks
Her dissertation set out to answer two questions: how common are depression, anxiety, and stress among taxi drivers in Kampala, and what factors contribute to them? The study surveyed 422 male drivers across seven major taxi parks: Old, New, Kisenyi, Usafi, Namirembe, Nakawa, and Nateete, using a multistage sampling approach designed to ensure representation across the city’s transport hubs.
Participants completed structured interviews on socio-demographic, occupational, lifestyle, use of habit-forming substances, medical, and environmental factors. Mental well-being was assessed using the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale (DASS-21), a widely used screening tool in mental health research.
The data were analysed using statistical models that allowed Kyomuhendo to examine how occupational conditions, lifestyle factors, and health status interacted to shape mental well-being.
The study reflected the epidemiological training embedded in MakSPH’s Master of Public Health programmes, where students are encouraged to investigate real-world health challenges through evidence-based research.
Conducting interviews inside the taxi parks meant stepping into one of the most unpredictable environments in the city. “The atmosphere was survival for the fittest,” Kyomuhendo recalls.
Stories behind the statistics
The fieldwork brought moments that stayed with her long after the questionnaires were completed. One driver laughed when asked how he coped with stress. “I don’t drink or smoke,” he said, suggesting that multiple relationships were his way of managing the emotional strain of the job.
The answer was not in the questionnaire, and they both laughed. Yet the moment captured something deeper about life in the taxi parks: humour often hides exhaustion.
Another driver told her he had spent years buying herbal medicine for a hernia that never healed. Every month, he spent close to 100,000 shillings, hoping the treatment would eventually work. She advised him to seek hospital care, a conversation that stayed with her.
“Sometimes people spend far more trying to manage a problem than it would cost to treat it properly,” she explains.
When the data were analysed, nearly two-thirds of the drivers screened positive for symptoms of depression. More than 70 percent had symptoms of anxiety, and over 80 percent reported levels of stress. The psychological burden was far heavier than most people had assumed.
Several factors stood out. Drivers who had experienced road accidents in the previous year were significantly more likely to report depression. Chronic medical conditions and a family history of mental illness also increased the risk.
Sleep deprivation emerged as one of the most important predictors. Drivers who consistently slept fewer than seven hours per night were far more likely to report anxiety and stress. Also, economic security mattered. Drivers who owned their vehicles were substantially less likely to experience anxiety compared to those who rented taxis or paid daily remittance fees to vehicle owners. In other words, psychological distress followed the same lines as economic pressure.
More than a transport problem, and the silence around men’s mental health
The implications extend beyond the drivers themselves, she observed. Mental health affects concentration, reaction time, and decision-making. All abilities that are critical for safe driving in a city known for congestion, unpredictable traffic, and frequent road hazards, including flooding, among others.
“If drivers are anxious or sleep-deprived,” Kyomuhendo explains, “there is a risk they may struggle to follow traffic rules or respond quickly to hazards.”
In a transport system that carries millions of passengers daily, the well-being of drivers becomes a matter of public safety. The findings suggest that mental health among taxi drivers should be treated as both an occupational health issue and a transport policy concern.
During interviews, Kyomuhendo noticed another pattern. Few drivers openly described themselves as depressed or anxious. Instead, stress appeared through jokes, casual references to alcohol or relationships, or long pauses followed by silence.
Men’s mental health remains a difficult subject in many communities. “Men’s mental health is a serious public health issue that should not be ignored,” she says.
Breaking the stigma will require awareness campaigns, stronger occupational protections, and greater attention from both health authorities and transport regulators, she proposes.

A different way of seeing the city?
This research also changed how Kyomuhendo sees Kampala. Where passengers notice congestion or impatience, she now sees the pressures shaping the people behind the wheel. “It made me appreciate the men who show up every day and work hard despite their struggles,” she says.
One driver confided in her about the pressures of the job. “People will not help you unless they know the problems you are facing,” he said.
The city and its drivers
By late afternoon, the taxi parks are as crowded as they were in the morning. Conductors still shout destinations into the traffic. Engines idle in long rows of white vans waiting for passengers. Drivers lean against steering wheels, hoping the next arrival will finally fill the vehicle.
The city keeps moving because they do. Most passengers step into these taxis thinking only about where they are going—work, home, school, or the market. Few stop to consider the pressures carried by the people behind the wheel.
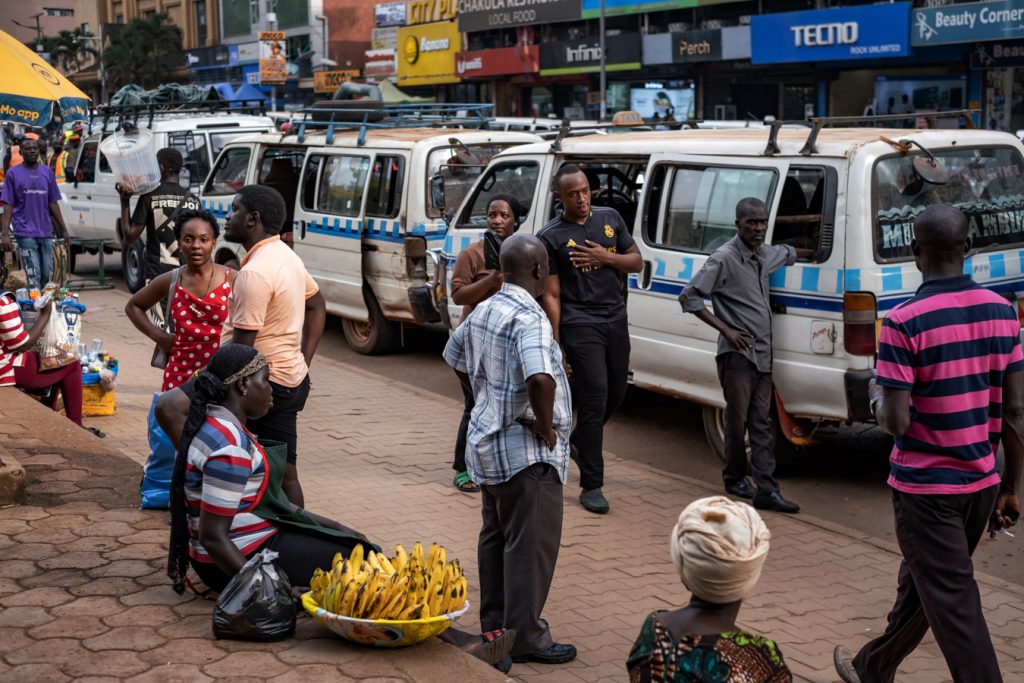
Yet Kyomuhendo’s research suggests that beneath the noise of the taxi parks and those car hoots on the streets lies something far quieter and far less visible: a level of stress, anxiety, and depression that touches not only the drivers themselves but also the safety of the passengers they carry and the communities they serve.
Each morning, the vans will still line up bumper-to-bumper. Conductors will still shout destinations into the traffic. Kampala will still climb inside and move.
If nearly half a million taxis keep Uganda moving every day, who is protecting the minds of the people behind the wheel?
Health
Makerere Graduation Underscores Investment in Africa’s Public Health Capacity
Published
1 week agoon
March 4, 2026
KAMPALA, 25 February 2026 — Higher education must move beyond awarding degrees to producing solutions for national and global crises, speakers said on Wednesday as Makerere University continued its 76th Graduation Ceremony, positioning universities as central actors in strengthening Africa’s public health capacity.
Addressing graduands on Wednesday, February 25, 2026, at Freedom Square, national leaders and university officials framed graduation not as a ceremonial endpoint but as an investment in workforce readiness, research leadership, and evidence-driven governance, particularly at a time when health systems across the continent face growing pressure from pandemics, demographic change, and climate-related risks.
The message resonated strongly through presentations from Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) and Makerere University College of Health Sciences (MakCHS), whose graduates enter professional service amid renewed global attention to health system resilience, scientific leadership, and locally generated research.
Delivering the commencement address on Day Two of Makerere University’s 76th Graduation Ceremony, Dr. Margaret Blick Kigozi, Board Chairperson of the Makerere University Endowment Fund, reflected on her graduation in 1976 during a period of national uncertainty under then-Chancellor President Idi Amin. She recalled leaving Uganda soon after with her young family, carrying “little more than education, values, and hope,” an experience she used to frame lessons on resilience, purpose, and responsibility in uncertain times.

Challenging graduates to rethink professional success, she reminded those entering health and life sciences that their training carries extraordinary influence.
“Power does not make you important; it makes you responsible,” she said. “You will decide who is listened to and who is dismissed, who waits and who is rushed through, who feels safe and who feels small. Your education has trained you to ask better questions, but your humanity must guide the answers. Behind every chart, every case, every experiment, there is life, and life deserves care, patience, and dignity.”
Throughout the ceremony, speakers returned to a common refrain: societies increasingly depend on evidence, and universities must produce professionals capable of translating knowledge into policy, practice, and community impact.
Across the four-day congregation, the University will award 9,295 degrees and diplomas, including 2,503 Master’s degrees, 6,343 Bachelor’s degrees, 206 Postgraduate Diplomas, and 30 Diplomas. But beyond the numbers, speakers repeatedly returned to a central question on how higher education can translate academic growth into national development and health security.
On day two, graduands were presented from the College of Natural Sciences, the College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Biosecurity, the College of Health Sciences, and the MakSPH, the latter positioned squarely within Africa’s ongoing struggle to expand its pool of trained epidemiologists, health systems researchers, and policy leaders.
Vice Chancellor Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe noted that Africa averages just 80 researchers per million people, compared to a global average of 1,081, warning that the human resource gap remains substantial.
“Today the School of Public Health presents graduands joining the field at a time when Africa faces a critical shortage of highly trained public health leaders,” he said.

The School of Public Health presented seven PhD candidates: Aber Harriet Odonga, Komakech Henry, Lubogo David, Nakisita Olivia, Namukose Samalie, Ntaro Moses, and Osuret Jimmy. It also graduated 195 Master’s students and 29 Bachelor of Environmental Health Science graduates, including four first-class honours recipients led by Phillip Acaye with a CGPA of 4.63.
Their research spans maternal and child health, epidemic preparedness, sanitation behaviour change, nutrition systems integration, and injury prevention, areas increasingly recognised as foundational to national development rather than peripheral health concerns.
University Chancellor Dr. Crispus Kiyonga emphasized that research must move beyond academic publication into policy and implementation.
“Research plays a very vital role in the development of any community,” he said, linking university scholarship directly to Uganda’s national development agenda.
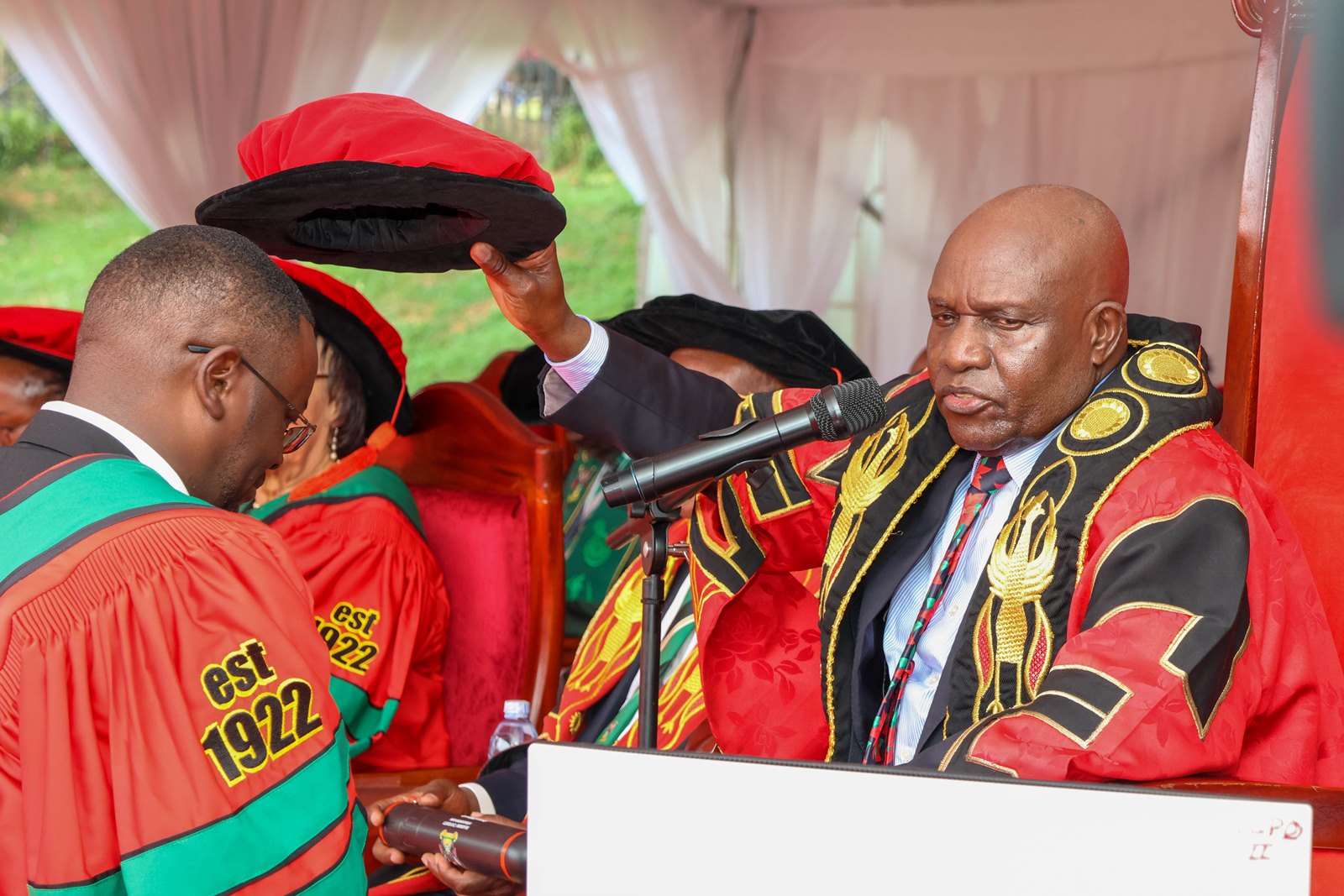

For public health education, that responsibility carries particular urgency. The COVID-19 pandemic, recurring disease outbreaks, and climate-linked health risks have exposed how deeply national stability depends on scientific capacity.
The chancellor hailed the Government of Uganda for committing UGX 30 billion through the Makerere University Research and Innovations Fund (MakRIF).
Mak Urged on More PhDs
Representing the First Lady and Minister of Education and Sports, State Minister Dr. Joyce Kaducu Moriku described doctoral training as central to Uganda’s research ambitions, noting government efforts to expand funding and modernize higher education systems.

“Universities must produce more PhDs to strengthen the national research agenda,” she said, adding that competence-based reforms aim to align training more closely with societal needs.
“More PhDs also mean the university is growing in academic leadership and an increase in research. So, keep the numbers growing, especially in Science, Technology, and Engineering,” she added.
The 213 PhDs conferred this year, a record, signal more than institutional expansion but a response to structural deficits.
Africa bears approximately 25% of the global disease burden but produces a disproportionately small share of global health research. The continent’s research density remains far below global averages. In this context, each doctoral graduate becomes not merely an academic achievement but a strategic asset.
A University Responding to Its Moment
For the School of Public Health, the graduation reflects a broader evolution in how public health training is conceived. Rather than focusing solely on the treatment of disease, the field increasingly addresses systems, sanitation, nutrition, behavioural change, surveillance, prevention, and climate change, areas where research directly shapes everyday life.
Recent MakSPH-led initiatives, including national HIV impact surveys and digital health system expansion, demonstrate how academic institutions increasingly function as implementation partners to the government rather than observers.
Over the past five years, MakSPH has supported the national scale-up of electronic medical records through the CDC-funded Monitoring and Evaluation Technical Support (MakSPH-METs) programme, and led the Third Uganda Population-Based HIV Impact Assessment (UPHIA 2024–2025), the first fully Ugandan-implemented national survey of its kind.
Launched in 2020, the METs program has supported the nationwide scale-up of UgandaEMR+, transitioning thousands of facilities to secure electronic medical records and deploying critical ICT infrastructure. In March 2026, these systems will be formally transitioned to the Ministry of Health, reflecting sustainable national ownership.
Health
Three MakSPH Faculty Honoured with Makerere University Research Excellence Awards 2026
Published
2 weeks agoon
March 2, 2026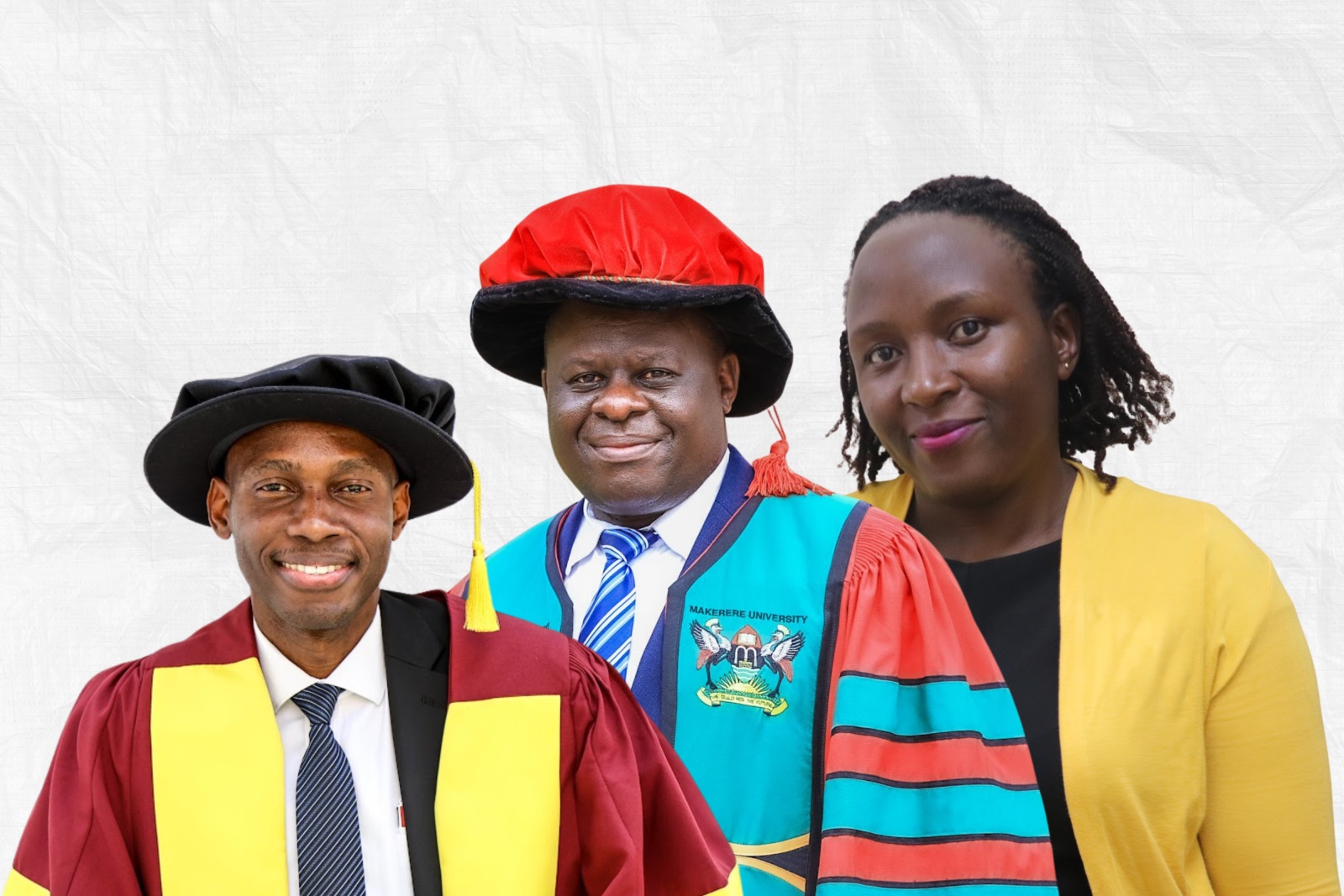
KAMPALA—Three faculty members from Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) have been recognised at the Makerere University Vice-Chancellor’s Research Excellence Awards 2026, highlighting the School’s expanding contribution to research leadership, scientific productivity, and policy-relevant scholarship across Africa.
Associate Professor Peter Kyobe Waiswa, Associate Professor David Musoke, and Juliana Namutundu received honours during the University’s 76th Graduation Ceremony at Freedom Square, where Makerere celebrated scholars whose work has demonstrated exceptional research achievement and impact beyond academia.

The annual awards, coordinated by the Directorate of Research, Innovation and Partnerships (DRIP), recognise faculty and staff whose scholarly output and leadership advance Makerere University’s ambition to become a research-led institution.
“This recognition celebrates sustained excellence in research productivity and contributions to knowledge that advance both national and global discourse,” Vice-Chancellor Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe said. “We are strengthening a culture where research does not remain confined to journals but translates into solutions for society.”
Among the university’s top researchers was Assoc. Prof. Peter Kyobe Waiswa, a health systems scientist whose work focuses on maternal, newborn, and child health. Waiswa ranked among Makerere’s overall top researchers after publishing 43 peer-reviewed papers in 2025, tying with three-time award winner Prof. Moses Kamya of the School of Medicine in the College of Health Sciences.
His research examines how health systems function at their most fragile moments, including childbirth, early life, and community-level care, addressing questions of equity, service delivery, and health system performance across Africa.
Also recognised was Dr. David Musoke, an Associate Professor of Disease Control, whose 25 publications earned distinction among senior career researchers. His work spans environmental health, community health systems, and implementation research, areas increasingly viewed as critical to preventing disease before it reaches hospitals.
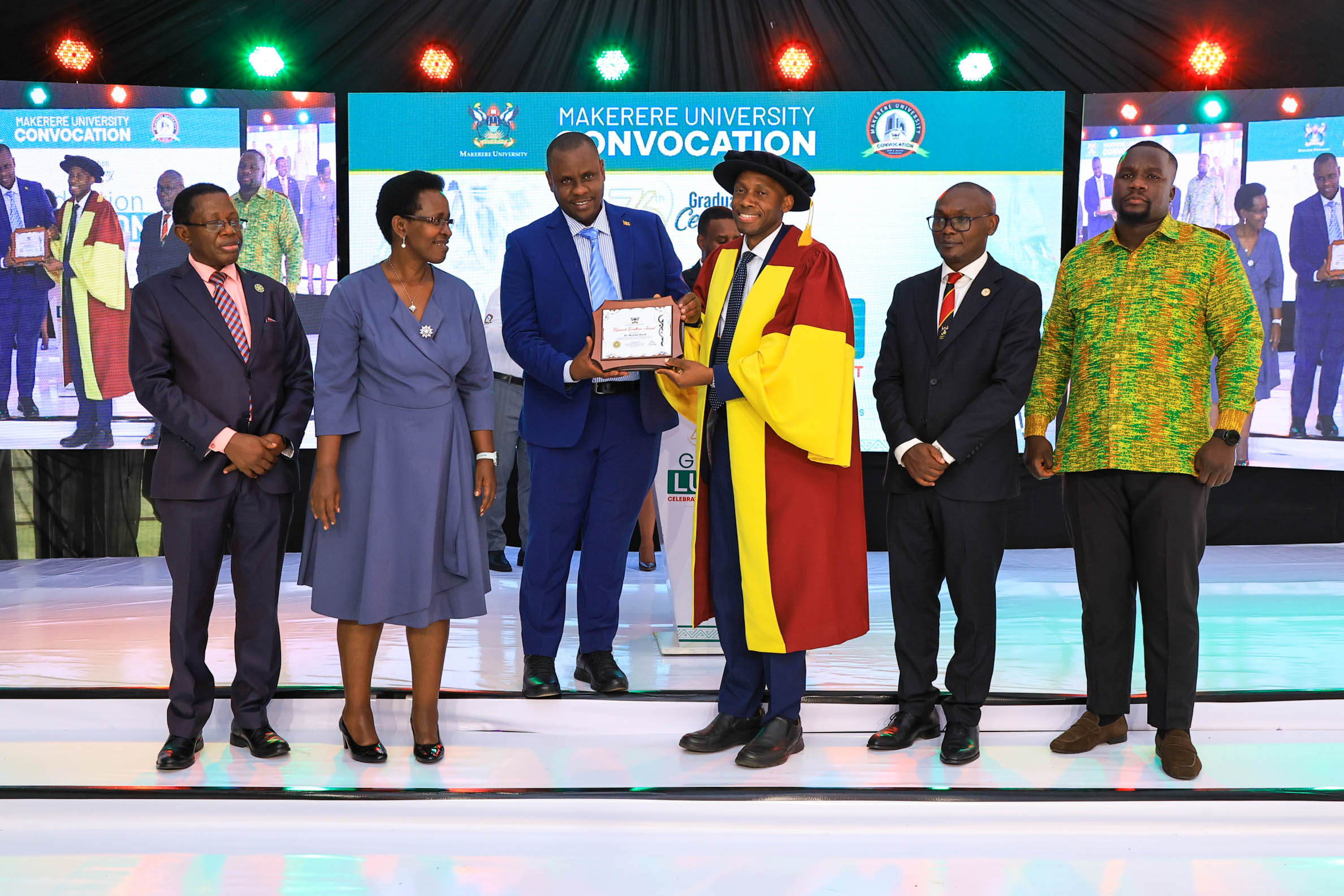

In the early-career category, Juliana Namutundu received recognition for emerging research leadership, reflecting Makerere’s effort to nurture the next generation of African scholars.
Together, the awards underscored MakSPH’s growing influence within Makerere’s research ecosystem, particularly in fields linking science directly to population wellbeing.
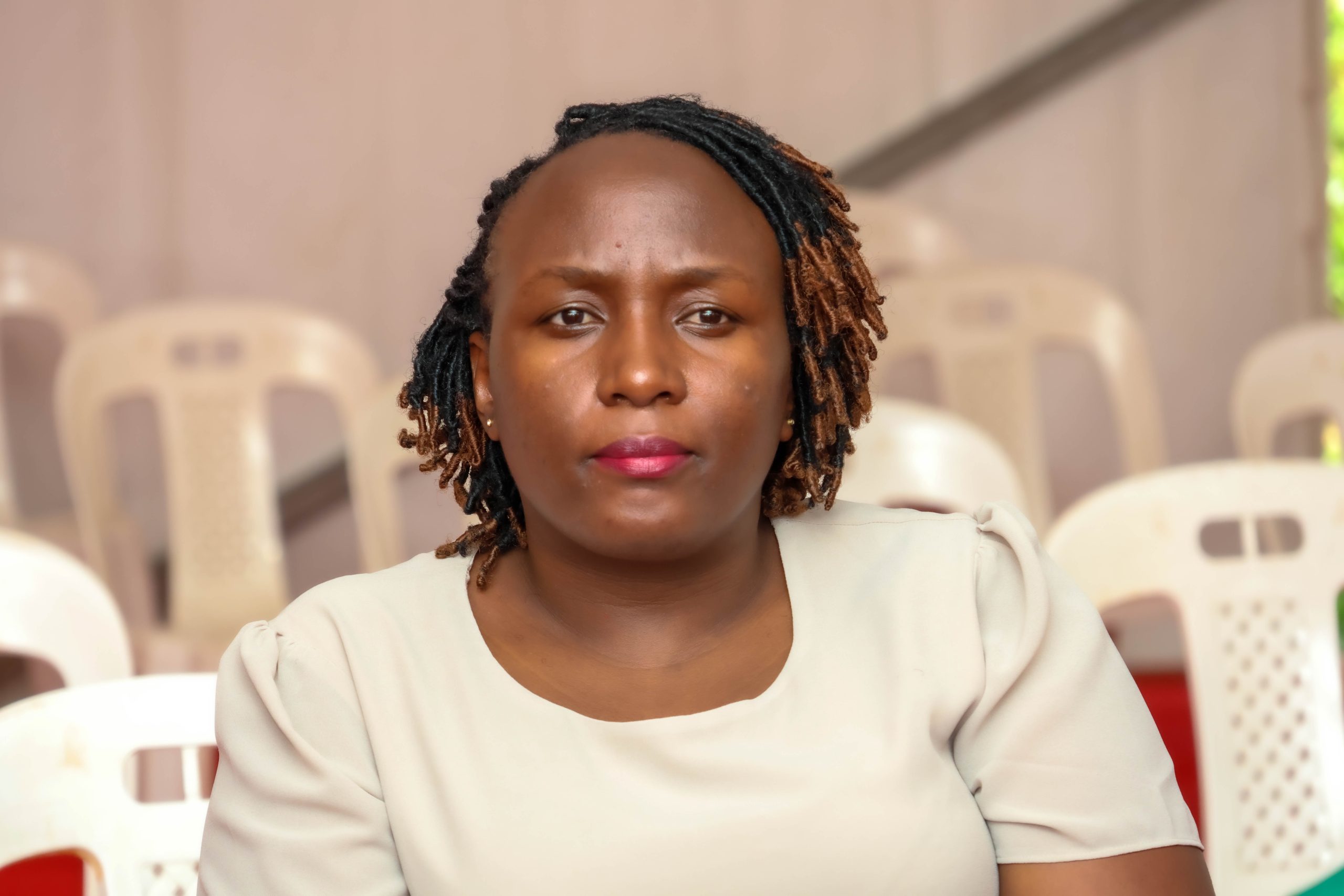

The Research Excellence Awards were established to encourage publication in high-impact journals while reinforcing Makerere’s ambition to become a globally competitive research university. Nominations are reviewed by the Board of Research and Graduate Training, chaired by Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Academic Affairs) Prof. Sarah Ssali.
Awardees were honoured during a graduation luncheon organised by the Makerere University Convocation, the institution’s alumni and staff association, which described the event as a celebration of “excellence and inspiring impact.”
The ceremony also recognised forms of scholarship extending beyond traditional academic publishing.
Dr. Geofrey Musinguzi, a research associate at the School of Public Health, was honoured for his book My Journey with Rectal Cancer, an account of diagnosis, treatment, and recovery that blends personal testimony with public health advocacy.
Diagnosed at age 44 while a visiting scholar at the University of Antwerp in Belgium, Musinguzi sought medical care after experiencing persistent symptoms, including rectal bleeding and back pain. His treatment involved surgeries, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and a year living with a colostomy bag.
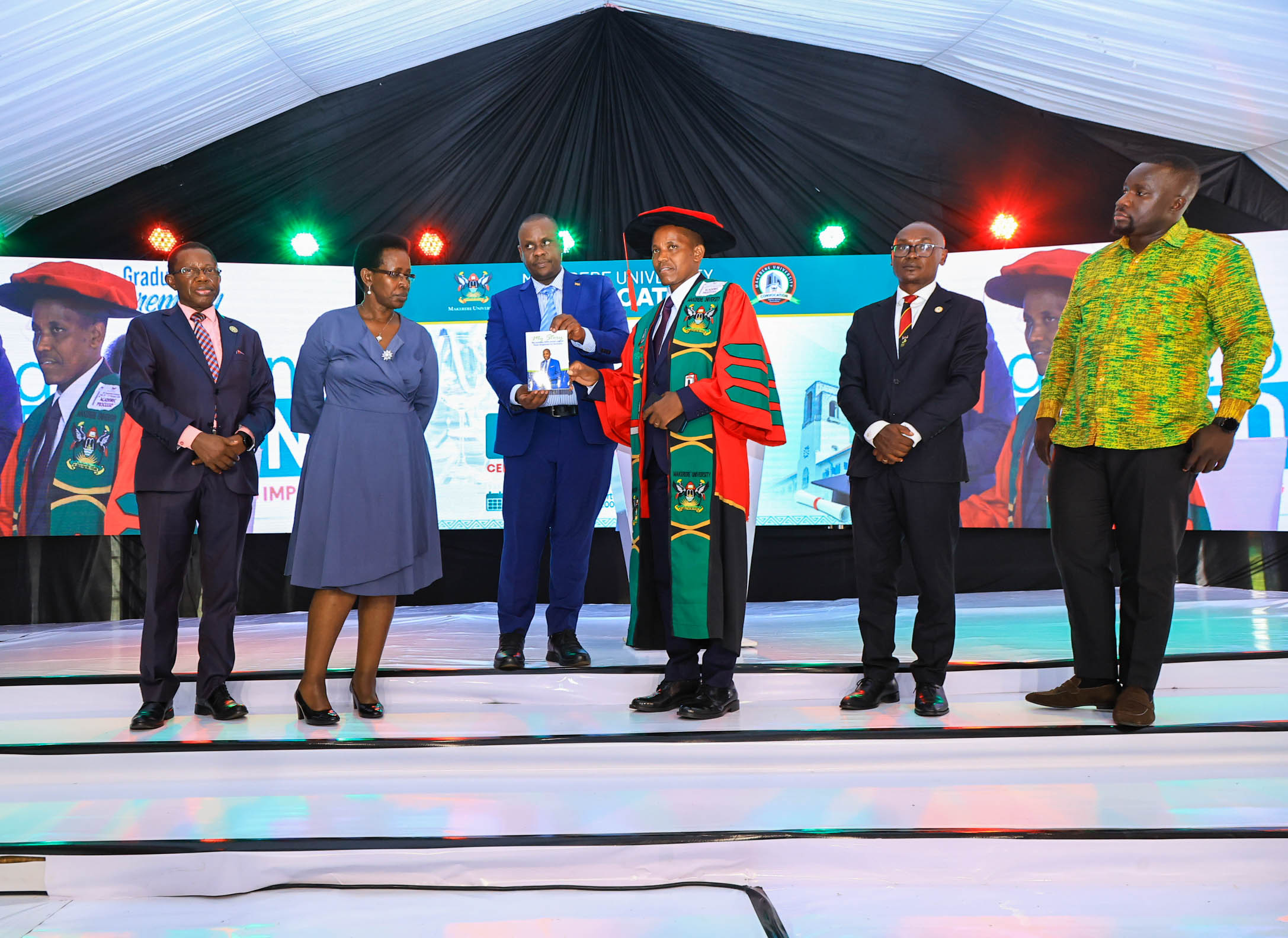

Rather than keeping the experience private, he documented it publicly to challenge cancer stigma and encourage early screening. The book, launched at the School of Public Health in August 2024, highlights how lived experience can shape public health awareness alongside scientific research.
The recognition reflects a broader understanding of research impact, one that includes scholarship capable of influencing behaviour as well as policy.
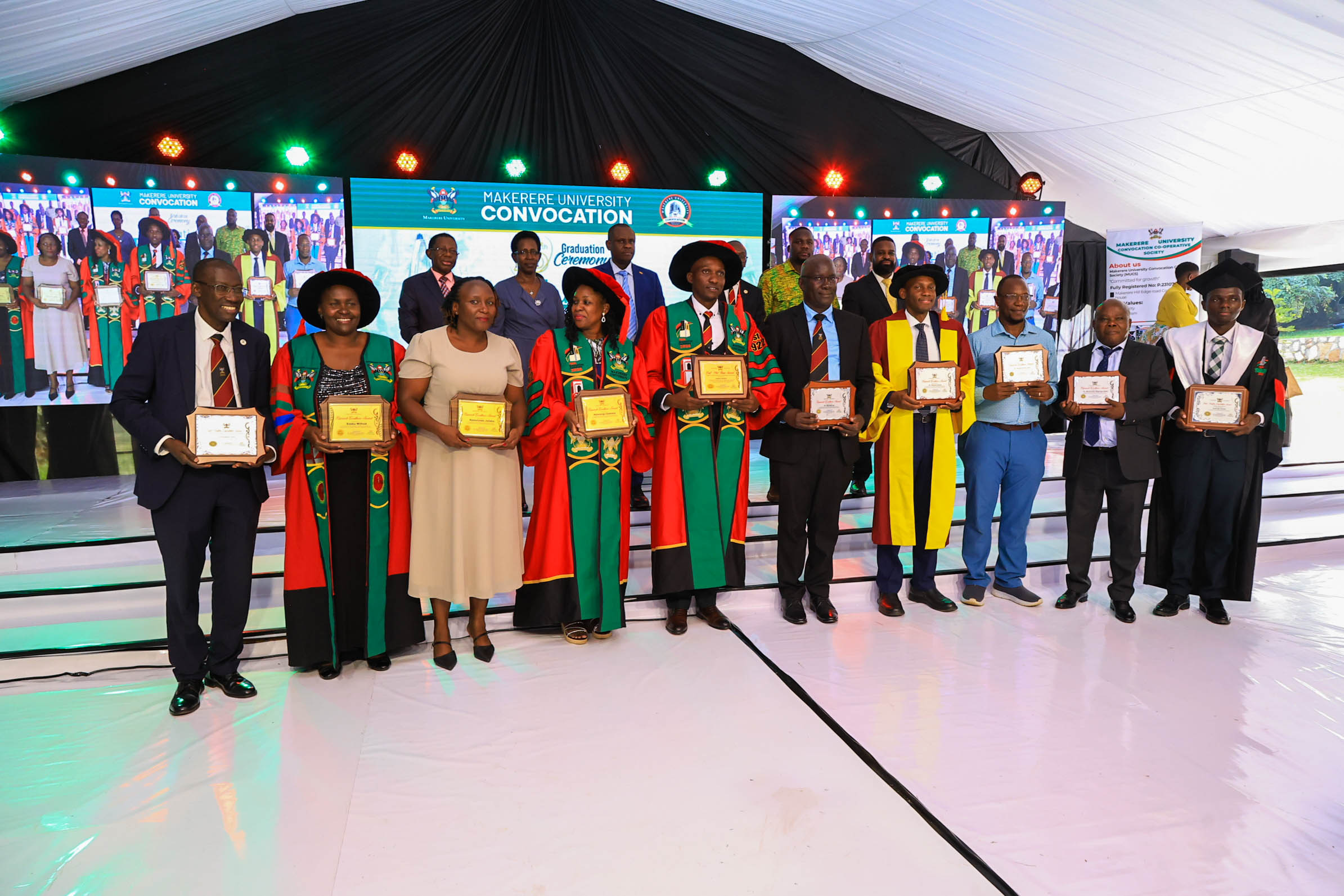

Makerere’s emphasis on research excellence comes as African universities face increasing pressure to produce locally grounded evidence while competing globally for visibility and funding. For MakSPH, whose work spans disease surveillance, environmental health, and health systems research, publication output increasingly serves as both academic currency and development infrastructure.
“These awards are part of our broader effort to position Makerere as a truly research-led institution,” Nawangwe said, adding that scholarship must remain aligned with national and regional priorities.
Trending
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMakerere University commemorates 13 transformative years of partnership with Mastercard Foundation
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMakerere University and World Bank Sign Partnership to Strengthen Environmental and Social Sustainability Capacity
