Engineering, Art & Tech
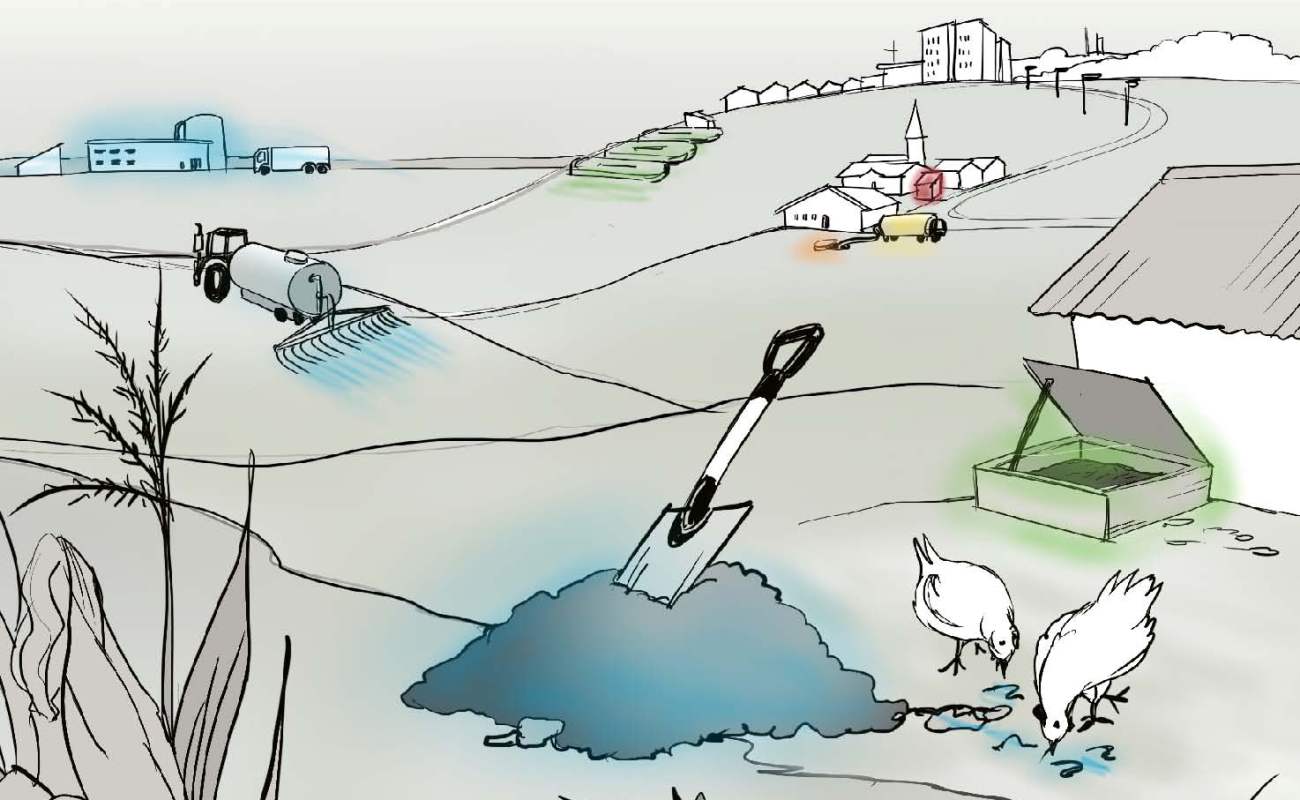
Guide to Sanitation Resource Recovery Products & Technologies
Engineering, Art & Tech
CEDAT and KOICA Partner to Advance E-Learning at Makerere University
Engineering, Art & Tech
Uganda Urged to Strengthen OSHE Enforcement Amid Rising Workplace Injuries
Engineering, Art & Tech
Makerere University and Nile Basin Discourse Partner on Water Resource Management Initiative
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoMature Age Scheme Exam Results for 2025/2026
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoFreshers’ Joining Instructions 2025/2026
-

 General2 days ago
General2 days agoUndergraduate Admission List Self Sponsorship Scheme 2025/2026
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMastercard Foundation Board pays its inaugural visit to Makerere University
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoUVCF Makes Case for HEAC Programme















