General
Frederick Kyazze: The Unwavering Custodian of Mak’s Transcripts Office
Published
11 years agoon

Frederick Mbabaali Kyazze speaks with firmness as he shares his life-changing experience at Makerere University. The 62 year old senior citizen of average height, dark complexion and a lean frame has recently retired from Makerere University after fourteen years of dedicated service as a Senior Assistant Registrar. Tiny wrinkles of untold wisdom are beginning to form on his face. His eyes are a deep haven of thoughts and exude intelligence. He turns up for this interview in a neatly pressed cream suit, which reminds me that neat suits have been his trademark over the years. He begins to speak, carefully choosing his words.
Joining the Transcripts Office
In the year 2000, Kyazze joined Makerere University as an Assistant Registrar, Senate Division. After only six months, the hardworking man was assigned a bigger responsibility to head the Transcripts Office. His immediate Supervisor at the time, who later became Academic Registrar of Makerere University Mr. Amos Olar Odur, referred to this move as a vote of confidence in Kyazze. He was subsequently duly appointed to the rank of Senior Assistant Registrar.
“At that time, there was a general public outcry about transcripts in Makerere University. I recall a famous joke on one of the local FM stations that ‘okufuna transcript e Makerere, bakutuma mu ggulu,’ loosely translated as ‘it is easier to go to heaven than to get a transcript from Makerere University.’ Now as Head of the Transcripts Office, I knew it was time to roll up my sleeves and get to serious work; and I resolved to endeavour to not only do good, but do it well too,” Kyazze reminisces.
“I received a letter transferring me to the Transcripts Office with immediate effect. At about 2:00pm, I entered my new office and started work, without induction. My predecessor, Rose Bwire, was also needed in another unit immediately. I take this opportunity to kindly request the concerned officials to pay attention to induction of new officers when transfers are made. I had some challenges in adjusting to my new role minus induction but with the guidance of a few colleagues, I later found my way around,” he says. This new development came with additional responsibilities for Kyazze.
It is then that Kyazze learnt of the various hindrances to fast acquisition of transcripts at Makerere University. Cases of missing/misplaced marks, late submission of marks and submission of incomplete marks were the most common reasons for delayed transcripts. Kyazze would have to face the students one after another and explain to them that everything possible was being done to process their transcripts. He and his team, would then work backwards to resolve the issue with the relevant department. But this did not always go well with the affected students, some of whom would throw insults at him. It is from such incidents that the then Acting Academic Registrar (AR), Sebastian Ngobi referred to him as the punching bag of Makerere University. “This nick-name was because whoever had issues with their transcript came to me. A student would not know which lecturer or department had not submitted results in time. I was the face of the University and I took the punches. I could not reveal to the students where the problem lay even when I knew it. I used to call myself the devil that the public loves to hate,” he recalls with nostalgia.
Transformation of the Transcripts Office
Kyazze shares that most of the Department’s operations were manual at the time. Ordinary typewriters were used to inscribe on the transcripts. Faculties submitted results manually on a results sheet. This contributed to further delays in processing transcripts. Nonetheless, Kyazze inspired his team to do their best in the circumstances. But in 2003, the Academic Registrar’s Department started automating its processes.
In 2009, Kyazze became the Acting Deputy Registrar in charge of the Examinations and Transcripts Division. This was an internal arrangement in the AR’s Department, pending confirmation from the Human Resource Directorate. This new role required Kyazze to timetable university wide examinations, draft budgets for these exams and writing to the various Faculties requesting them to nominate external examiners. Nonetheless, he continued to help out in the Transcripts office too.
Kyazze recalls that in 2009, the then Acting Vice Chancellor, Prof. Venansius Baryamureeba walked into his office and directed that transcripts be ready for issuing on graduation day. “This was the beginning of major change. We worked so hard even on 26th December to ensure that transcripts for the January 2010 graduation ceremony were ready. I am glad that by graduation, we had 80% of the transcripts ready. The remaining 20% were processed shortly afterwards. Commendably, the VC made sure that we were properly and promptly rewarded for these extra hours and we felt so motivated,” he narrates with a smile. Early processing of transcripts now became a culture and continues to date, save for few problem cases. Kyazze partly attributes this to the computerized management of data.
Another transformation has been in the date the Academic transcript bears. Initially since the 1980s, transcripts would carry the date of graduation, but this has since been revised to the date of completion since graduation comes much later in the following year and this led to delays in issuing definitive transcripts. Only the certificate bears the date of graduation.
During his tenure, Kyazze initiated improved furnishing and equipping of the transcripts office. “We produce transcripts massively. With time, I realized that storage of these transcripts was becoming a challenge. Since at that time the AR’s Department was managing its own budget, I proposed procurement of more filing cabinets across the department and this was done,” he explains in reference to the permanently fixed cabinets.
Paradoxically with the massive production of transcripts, thousands remain uncollected. The AR’s department continues to call out to graduates to pick their transcripts spurning as far back as the 1990s
Memorable moments
During his tenure at Makerere University, Kyazze has interacted with and served people from all walks of life. He vividly recalls a time when he attended to Cardinal Emmanuel Wamala. “A colleague, Simon Sagala who was the Manager of the University Printery at the time, came running and informed me that Cardinal Wamala was in the queue with students waiting to see me. I requested that the Cardinal be ushered in. He was here on behalf of a Priest from Kabale, whose transcript was urgently needed in Rome. I was able to help the Cardinal that very day,” says Kyazze. He also recalls having attended to the former Minister of Education, Hon. Geraldine Namirembe Bitamazire and former Deputy Chief Justice Leticia Kikonyogo, who were personally inquiring about their children’s transcripts. He is particularly happy that his signature is out there on thousands of transcripts. “This is a legacy that I am so proud of. I know my name will be remembered occasionally by these people and I am grateful to God for the opportunity to have served,” he says.
Lessons learnt
For the time spent at Makerere University serving students, staff and the public, Kyazze has learnt that it is imperative to remain ethical and composed in all situations. “I have learnt that it is important to stick to ethics and guard against compromise. For example, some people would come here requesting that the date of birth on their transcripts be changed to suit their needs and I would tell it straight to their faces that this cannot be done, no matter what they wanted to offer in return or the position they held in society. Some would get angry, throw insults and slam the door on their way out, but I eventually got used to these outbursts and stuck to my principles,” asserts Kyazze.
Kyazze has had to handle numerous sensitive investigation cases related to forged academic qualifications and transcripts. He has also had to turn up as a key witness in lawsuits filed against Makerere University in relation to transcripts. He affirms that integrity and sticking to his principles has bailed him out in times like these.
The Family man
Kyazze is a proud father of four; two boys and two girls. He has single-handedly raised his children since his dear wife, Betty Kyazze, passed on in 2002. “Fortunately I had been the type of father who leaves work and heads home straight away. This has allowed me ample time to groom my children,” he says. Two of his children have since graduated and the other two are steadily following suit. In his free time, Kyazze will be found glued to a current affairs program or watching a television documentary. He also has a deep passion for reading on a wide variety of topics.
What next after retirement?
Kyazze has now retired from Makerere University after what he describes as a successful career. He is nonetheless concerned about the delays in receiving retirement packages at Makerere University. “It is a challenge when Staff members retire and their funds are not released on time. So one finds oneself struggling with a number of expenses and sometimes their retirement projects freeze,” he explains.
Nonetheless, this highly schooled French and German tutor has aggressively plunged into offering consultancy services in higher education and languages. Kyazze also proof-reads and edits manuscripts in English, French, Luganda and German for publishing.
Kyazze’s former roles at Makerere University have since been taken over by Richard Byarugaba, who is also in charge of the Transcripts Office and closely worked with Kyazze for over three years.
Kyazze the Professional Teacher
Frederick Mbabaali Kyazze is a teacher by profession and graduated from Makerere University with a Bachelor’s Degree and Concurrent Diploma in Education in 1977. He specialized in languages (French and German). Kyazze had wanted to study law but this was hampered by a Government directive following the turbulent political times of the 1970s. “I recall that the Asians and many expatriate teachers had been expelled from Uganda, so there was a dire need for teachers. The late President Idi Amin’s government gave a directive that a large quota of admitted students be channeled into teaching. One afternoon in 1974 the then Minister of Education, Brigadier Barnabas Kili, came and harangued us in the Makerere University Main Building, telling us that we were to become teachers whether we wanted it or not, thus ‘conscripting’ us into the teaching army ” he narrates in a low tone.
Kyazze then opted to teach German since he had studied it at Bachelors, to broaden his A-level choice of History, French and Literature in English. At first, Kyazze was not allowed to take German as a teaching subject since he was a beginner, but with his excellent grades, the then Dean of Education, Prof. Rukare reasoned that Kyazze be given a chance.
Kyazze graduated from Makerere University to teach languages in Secondary Schools. He taught German in Kibuli Secondary School and Mengo Senior School concurrently (1977 -1980). He also taught French at Kampala High School and Trinity College Nabbingo.
“In 1982 the Head of the German Department at Makerere University, Dr. Jörg Braunert came looking for me. He asked if I could teach German at Makerere University. I had passed German with flying colours, under the guidance of Frau Ingrid Hills and Dr. Brigitte Kochan, my lecturers. I obliged and returned to Makerere as a Teaching Assistant,” he explains. He was given a two year renewable contract, which was later renewed thrice. Kyazze says he indelibly profited from teaching French and German because this enabled him to secure scholarships to attend short term training and refresher courses in France (1977 and 1983), Burundi (1989) and Germany (1978, 1991 and 1995). He has also participated in numerous annual East African German Teachers’ Seminars under Nairobi’s Goethe Institut’s auspices.
Kyazze later stopped teaching and enrolled for a Masters in French at Makerere University. Upon graduating with a Masters in 1997, Kyazze returned to the classroom to teach languages in secondary school. He was one of the most sought after French examiners by Uganda National Examinations Board (UNEB).
In 1999, Makerere University advertised for administrative jobs in the Academic Registrar’s Department. This signaled a shift in career for the illustrious Frederick Kyazze Mbabaali. He set foot in the AR’s Department, where he has left an unquestionable legacy.
Article by Marion Alina
You may like
General
Makerere University and International Partners Sign MoU for the 9th Kampala Geopolitics Conference
Published
16 hours agoon
March 12, 2026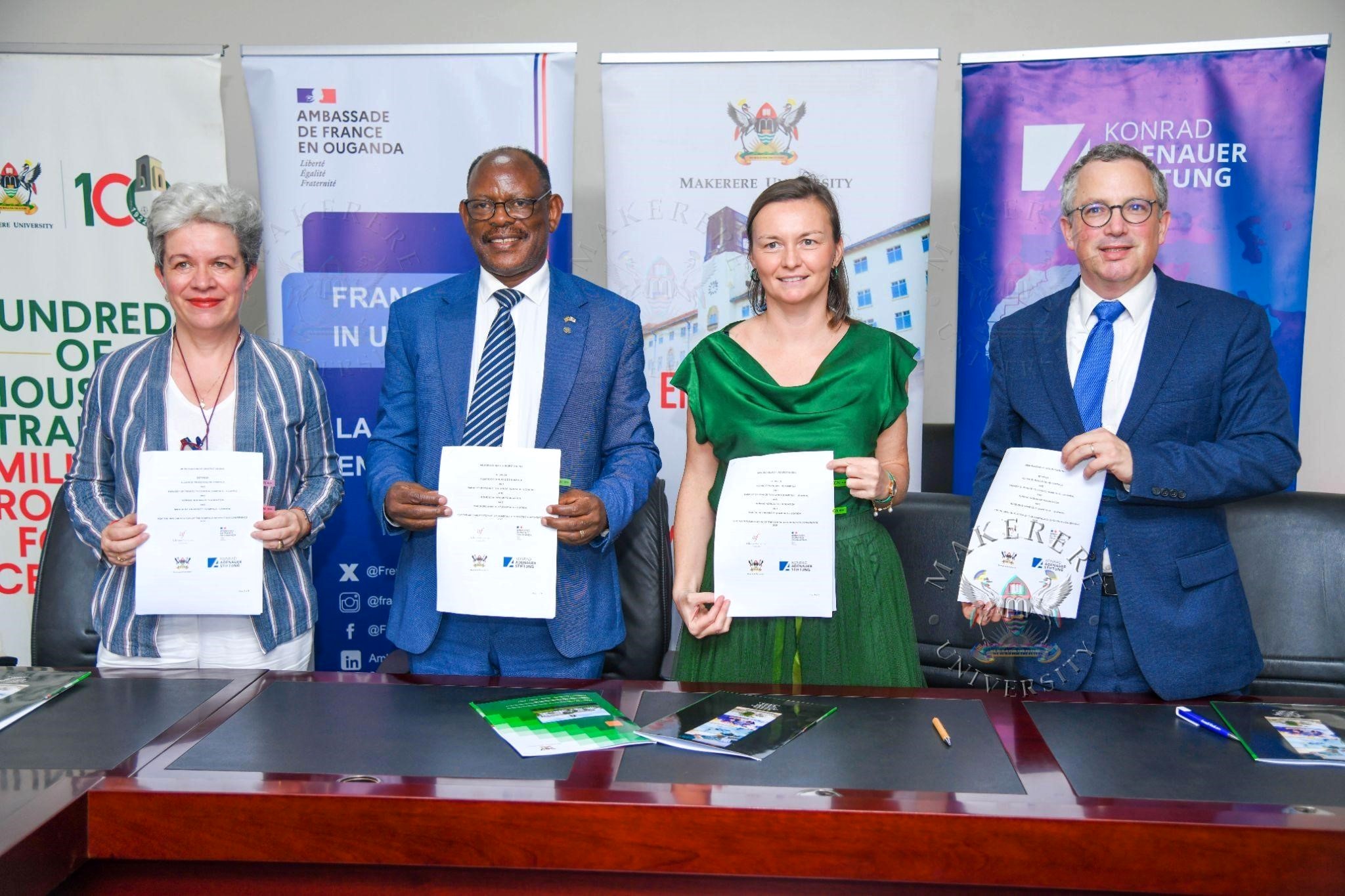
Makerere University, on 10th March, 2026, signed a Memorandum of Understanding with the Embassy of France in Uganda, the Konrad Adenauer Foundation (KAS), and Alliance Française de Kampala to organize the 9th edition of the Kampala Geopolitics Conference (KGC), scheduled to take place on 15–16 April 2026 at Makerere University.
The signing formalizes the continued partnership that has established the Kampala Geopolitics Conference as one of the region’s leading platforms for dialogue on global affairs, bringing together scholars, policymakers, civil society leaders, and students to debate the major geopolitical and socio-economic transformations shaping the world.
The conference, inspired by the Nantes Geopolitics Conference in France, was first launched in Kampala in 2018 and has since grown into a unique intellectual space for cross-continental exchange between Africa and Europe.
A Platform for Ideas, Dialogue, and Youth Engagement
Speaking at the signing ceremony, Makerere University Vice Chancellor, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe, emphasized the importance of the Kampala Geopolitics Conference as a platform that connects academic discourse with global policy conversations while empowering students to engage with the complex challenges shaping the international system.

The Vice Chancellor noted that hosting the conference reflects Makerere University’s long-standing commitment to fostering intellectual exchange and positioning the institution as a hub for regional and global dialogue.
“Makerere University is proud to host the Kampala Geopolitics Conference because it creates an important platform for debate and exchange on the global issues shaping our world, while giving our students the opportunity to engage directly with leading thinkers and policymakers,” said Prof. Nawangwe.
Prof. Nawangwe further commended the Embassy of France in Uganda, the Konrad Adenauer Foundation, and Alliance Française de Kampala for their continued collaboration with Makerere University in organizing the conference over the years. He expressed confidence that the 2026 edition will once again provide a dynamic platform for dialogue, bringing together scholars, policymakers, and students to examine the geopolitical trends shaping Africa and the wider world.
Speaking at the signing ceremony, H.E. Virginie Leroy, Ambassador of France to Uganda, highlighted the significance of the conference as a platform that encourages dialogue on global issues while empowering young people to participate in shaping the future.
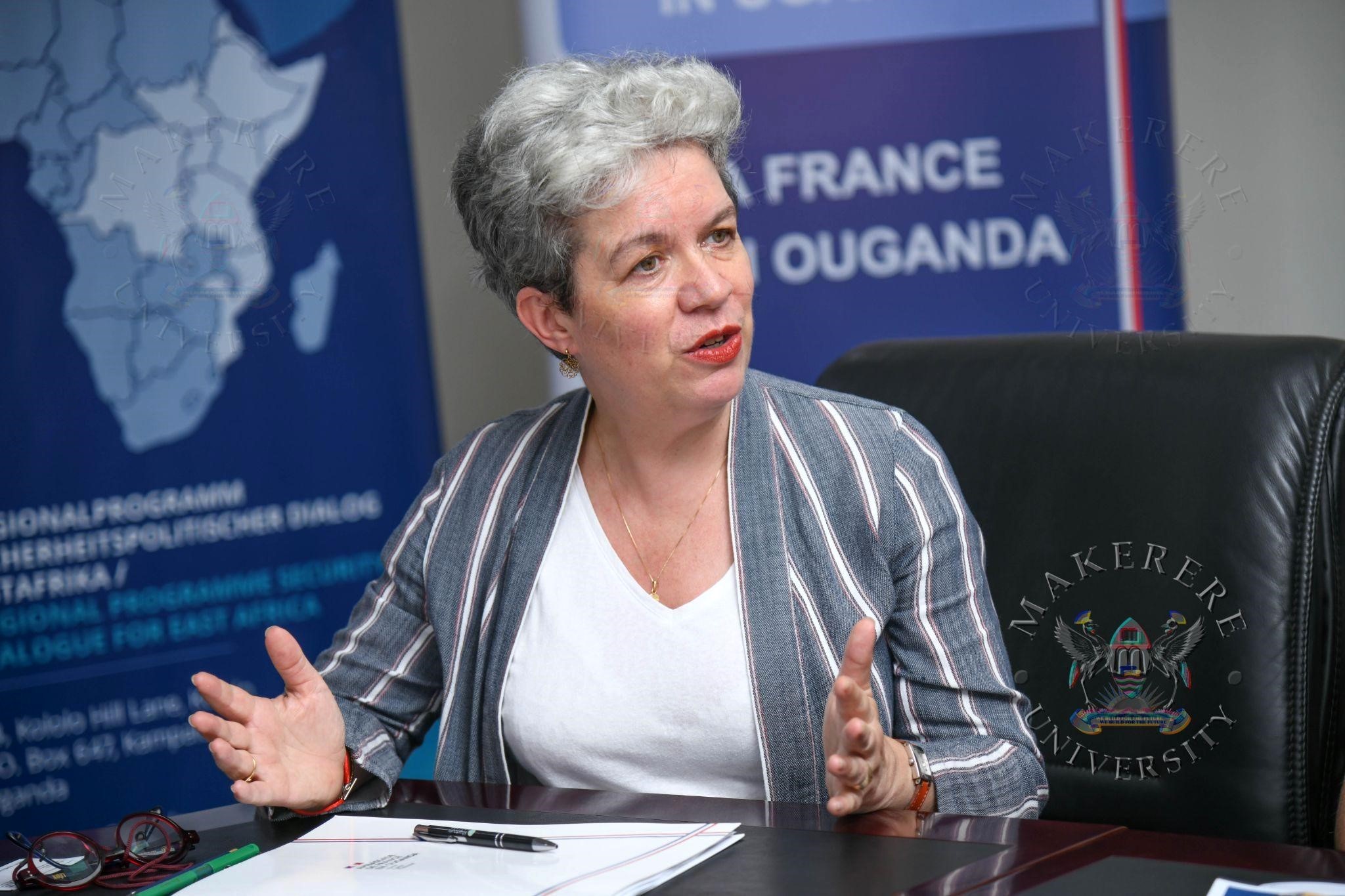

Since its inception, the Kampala Geopolitics Conference has created opportunities for students, researchers, policymakers, and entrepreneurs to engage with some of the most pressing global debates. The Ambassador noted that the curiosity and engagement of Ugandan students have become one of the defining features of the conference.
“This conference has become a unique space where students, researchers, policymakers and civil society exchange ideas on the major transformations shaping our world,” Ambassador Leroy said, adding that the event demonstrates the intellectual vitality of Uganda’s youth and the strength of the partnerships that sustain it.
Strengthening Partnerships for Global Dialogue
The Konrad Adenauer Foundation, a long-standing partner in the initiative, reaffirmed its commitment to supporting platforms that foster meaningful discussions on international affairs and regional dynamics.
Speaking during the ceremony, Anna Reismann, Director of the Konrad Adenauer Foundation in Uganda, emphasized the importance of the conference in connecting local perspectives with global debates.
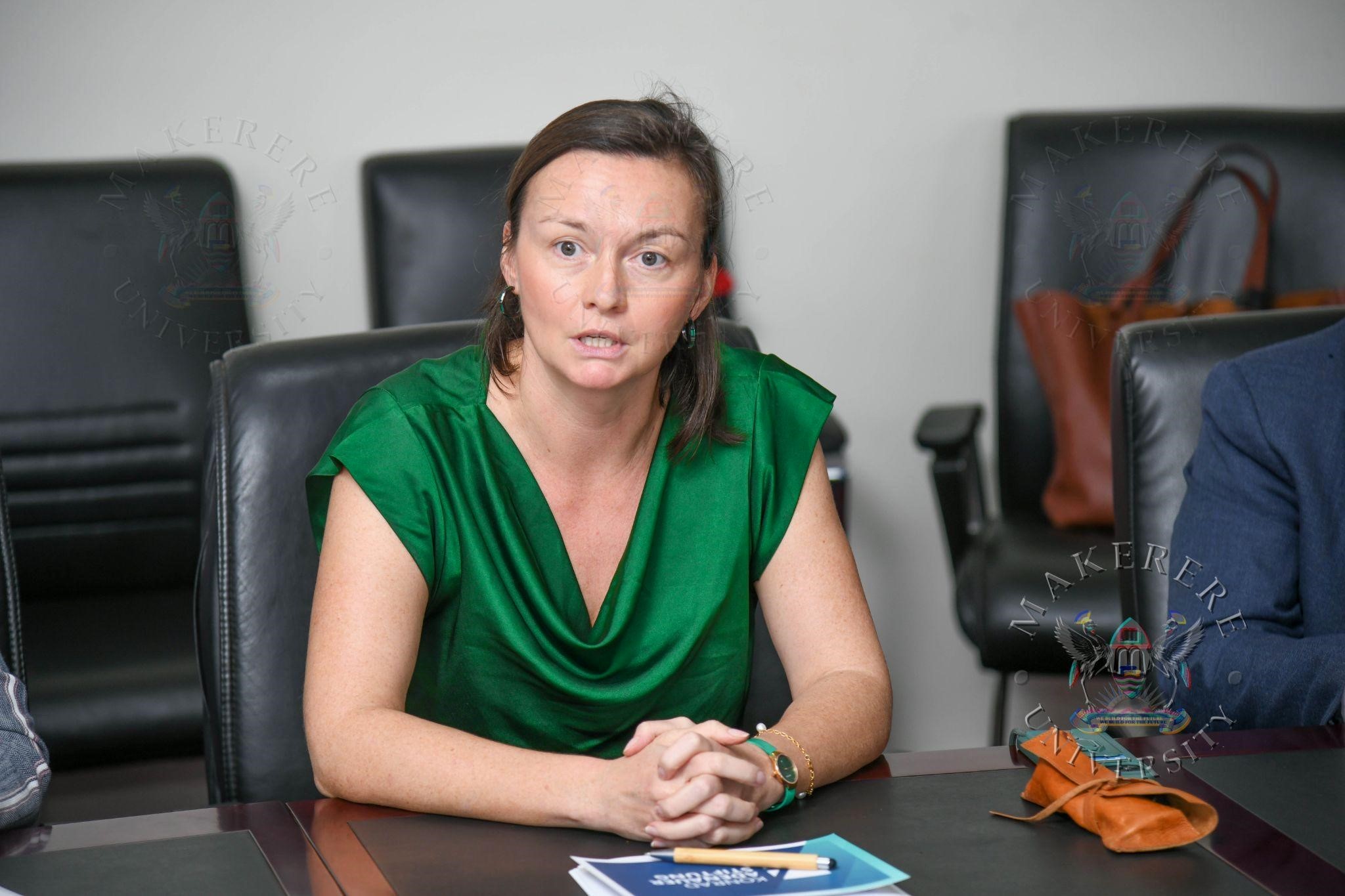

She noted that Africa has increasingly become a focal point in global geopolitics, attracting engagement from a wide range of international actors through investments, trade, security cooperation, and diplomatic partnerships. While these engagements create new opportunities for economic growth and technological advancement, they also raise important questions about sustainability, governance, and the terms of international cooperation.
According to Reismann, the conference provides an important forum to examine these issues and to encourage dialogue that bridges academic perspectives with practical policy considerations.
The 2026 edition of the Kampala Geopolitics Conference will focus on key global and regional issues shaping international relations and development.
Among the themes to be explored are the future of development cooperation, particularly as global aid dynamics evolve and countries explore more sustainable and balanced partnerships. Another panel will examine youth and public policy in Africa, recognizing the critical role that young people play in shaping governance, innovation, and development across the continent.
With Africa home to the youngest population in the world, discussions will highlight the importance of ensuring that young people are not only beneficiaries of public policies but also active contributors to their design and implementation.
Makerere University at the Centre of Global Conversations
Hosting the conference reflects Makerere University’s continued commitment to fostering intellectual exchange and positioning the institution as a hub for regional and international dialogue.
Through its partnerships with global institutions such as the Embassy of France, the Konrad Adenauer Foundation, and Alliance Française de Kampala, Makerere continues to create platforms that connect academic knowledge with policy discussions and real-world challenges.
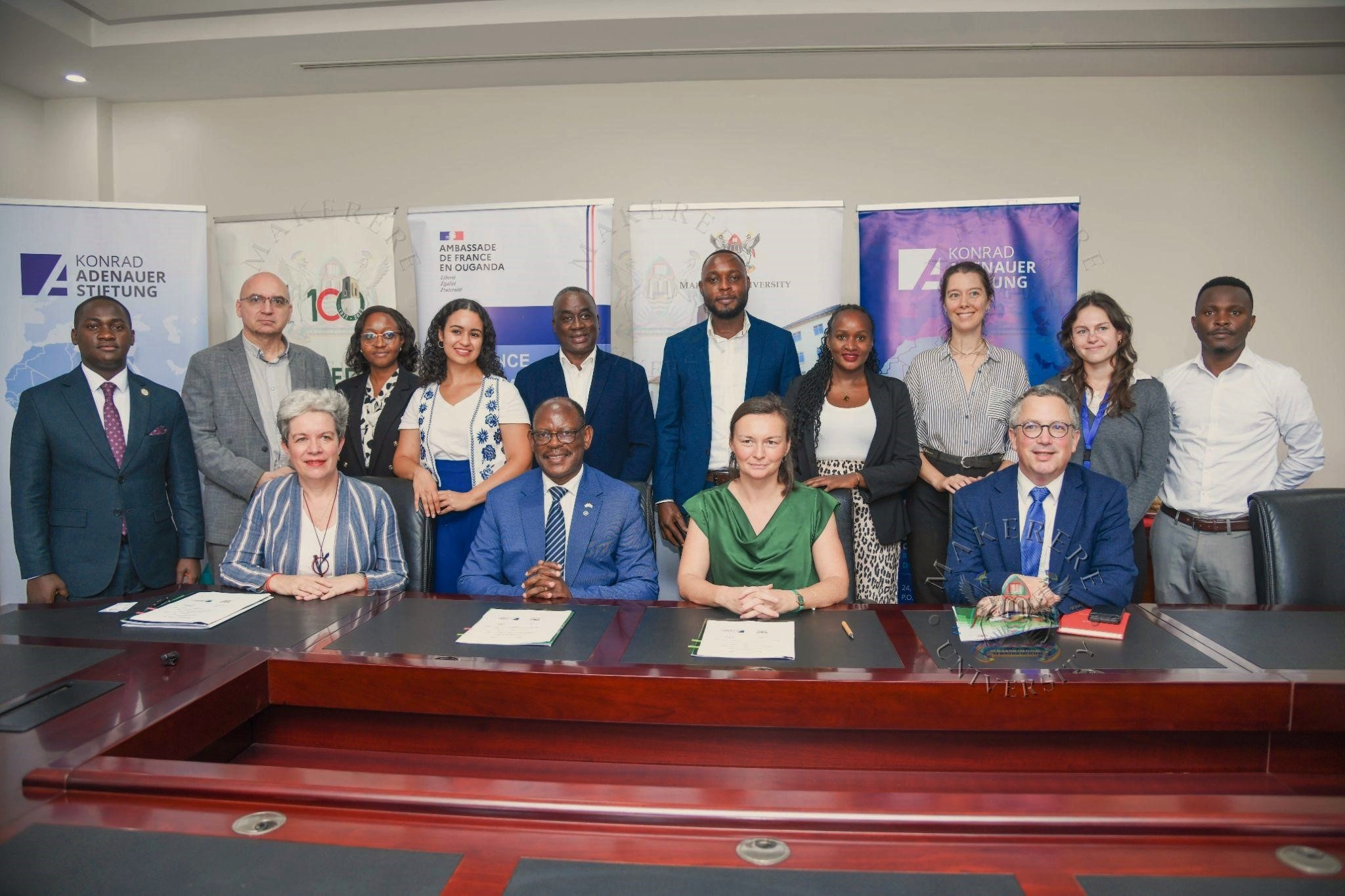

The Kampala Geopolitics Conference is expected to once again bring together leading experts, scholars, and practitioners from across Africa and Europe, while providing students with a rare opportunity to engage directly with global debates.
As preparations for the 2026 edition gather momentum, the partners expressed confidence that the conference will continue to inspire critical thinking, encourage dialogue across disciplines and generations, and strengthen cooperation between Africa and its international partners.
Caroline Kainomugisha is the Communications Officer, Advancement Office, Makerere University.
General
Makerere University Unveils Pre-Award Grants Management System
Published
2 days agoon
March 11, 2026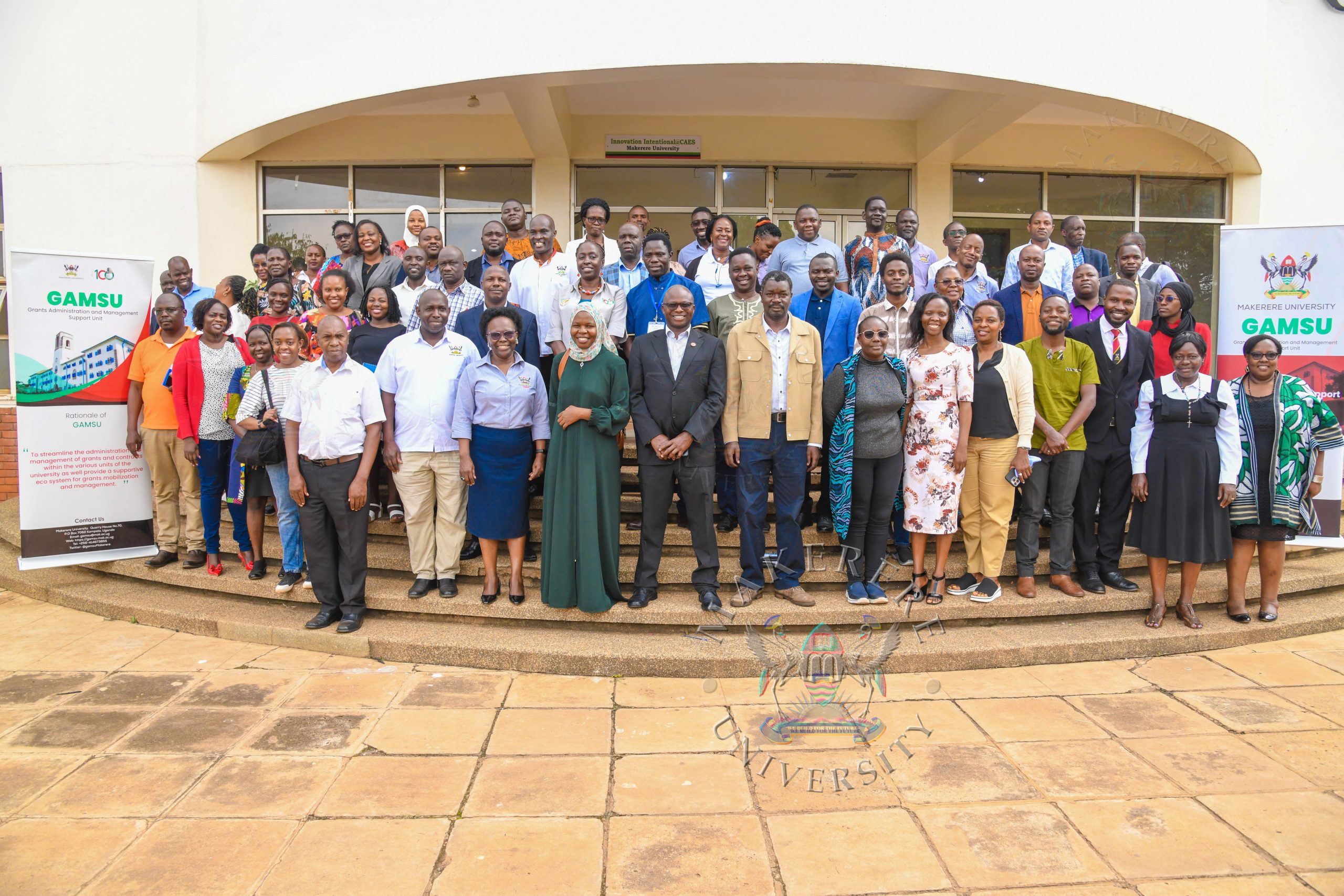
Following successful development of the Integrated Electronic Pre-Award Grants Management System for Sponsored Research, the Grants Administration and Management Support Unit (GAMSU) at Makerere University held a dissemination workshop, to onboard the University leadership, principal investigators, researchers, staff and partner institutions.
Held on Friday 6th March 2026, the dissemination workshop provided a platform to demonstrate the Integrated Electronic Pre-Award Grants Management System for sponsored research at Makerere University, and to receive instant feedback from physical and virtual participants.
Participants were drawn from the University leadership, including the Deputy Vice-Chancellor for Finance and Administration, the University Secretary, the Director-Graduate Training, Director-Research, Partnerships and Networking, Principals, Deputy Principals, Deans, Heads of Department, Principal Investigators, researchers, Heads of Administrative Units, representatives from international partner institutions, and members of the Grants Management Steering Committee (GMSC).
Welcoming the internal and external stakeholders to the dissemination workshop, the Head of GAMSU, Prof. Sylvia Antonia Nakimera Nannyonga-Tamusuza, emphasized that feedback from the participants was a vital step, that would not only enrich the grants management and administration processes, but also contribute to refining the system.
Expressing GAMSU’s commitment to the automation of the entire grants cycle, Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza credited the University leadership, the research project team members, and the different units within Makerere University, as well as, international partners, for the support rendered to GAMSU in developing the system.
The Integrated Electronic Pre-Award Grants Management System
Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza highlighted that the initiative responds to growing global competition for research funding and longstanding administrative challenges that researchers have faced when accessing and managing grants.
This digital initiative is designed to modernise how the institution handles research funding applications and administrative workflows before awards are granted. The system, aims to streamline the entire grant application lifecycle — from identifying funding opportunities to proposal preparation, compliance review, reporting, and closeout management.
Recognition of the Project team
Headed by Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza (Principal Investigator), the project team members include the following: Denis Michael Wamala (I.T Specialist), Prof. Helen Nambalirwa Nkabala (Senior Researcher-GMSC), Prof. Charles Masembe (Senior researcher-GMSC), Ivan Mutyaba (Grants Administrator-IREX Alumnus), Mordecai Tayebwa (Grants Manager-IREX Alumnus, Esther Kabinga (Legal Affairs Advisor), Innocent Tumwebaze (Early-Career researcher), Caroline Nabwire (Grants Administrator-GAMSU), Harriet Nambooze (Senior Grants Administrator) , and Victor Chris Watasa (System’s Design Consultant).
Acknowledgment of funding partners
The development of the Integrated Pre-Award Grants Management System was supported by the International Research and Exchange Board (IREX) through funding from the Carnegie Corporation of New York, with additional contributions from Makerere University.
Institutional leadership welcomes system development
On behalf of the University Management, the Acting Deputy Vice Chancellor (Finance and Administration), Prof. Winston Tumps Ireeta, lauded the Principal Investigator, Prof.Sylvia Antonia Nakimera Nannyonga-Tamusuza and her project team, for the development of the system aimed at digitizing the pre-award grant processes at Makerere University.
Opening the dissemination workshop, Prof. Ireeta, who doubles as the Chairperson of the Grants Management Steering Committee (GMSC), highlighted that the Integrated Electronic Pre-Award Grants Management System, would significantly benefit Makerere University and the researchers.
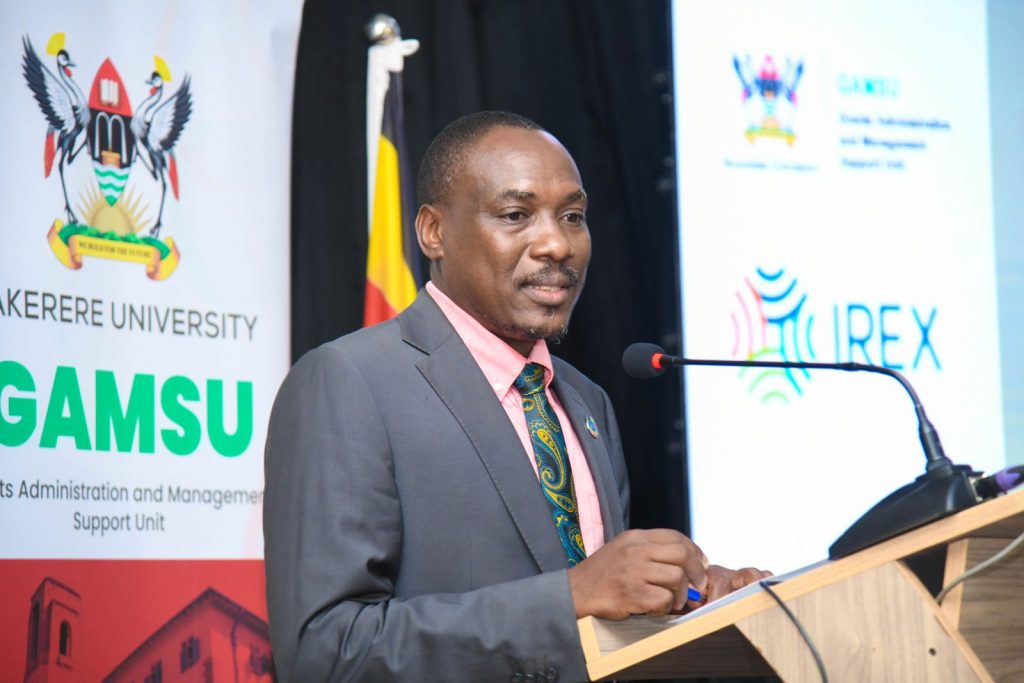

Prof. Ireeta emphasized that as Makerere University continues to implement its research agenda, the funding question becomes paramount. Acknowledging that funding through grants significantly facilitates research undertakings at Makerere University, Prof. Ireeta underscored the value of the Integrated Electronic Pre-Award Grants Management System, as an excellent addition, to existing processes aimed at amplifying the research profile of the University, as well as, streamlining grants management and administration.
“If we maximally utilize the system, the University and its researchers will be better placed to apply, attract and win grants, which will definitely boost the grant and research profile of this institution,” he said.
He encouraged the participants to actively follow the proceedings, and provide constructive input during the feedback session, in order to contribute to the refinement of the system.
Format of the dissemination workshop
The dissemination workshop featured a series of presentations including: Makerere University’s Strategic Research Direction; the Context of Administration and Management of Grants at Makerere University; Project Overview; Purpose and Objectives of the workshop; Overview of the Pre-Award Grants System Development; Technical demonstration of the system; and the Discussion and Stakeholder Feedback session.
The benefits of the system and the challenges it seeks to address
Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza, Head of GAMSU and Principal Investigator of the project, explained that the electronic pre-award system addresses several structural challenges in research grant management.
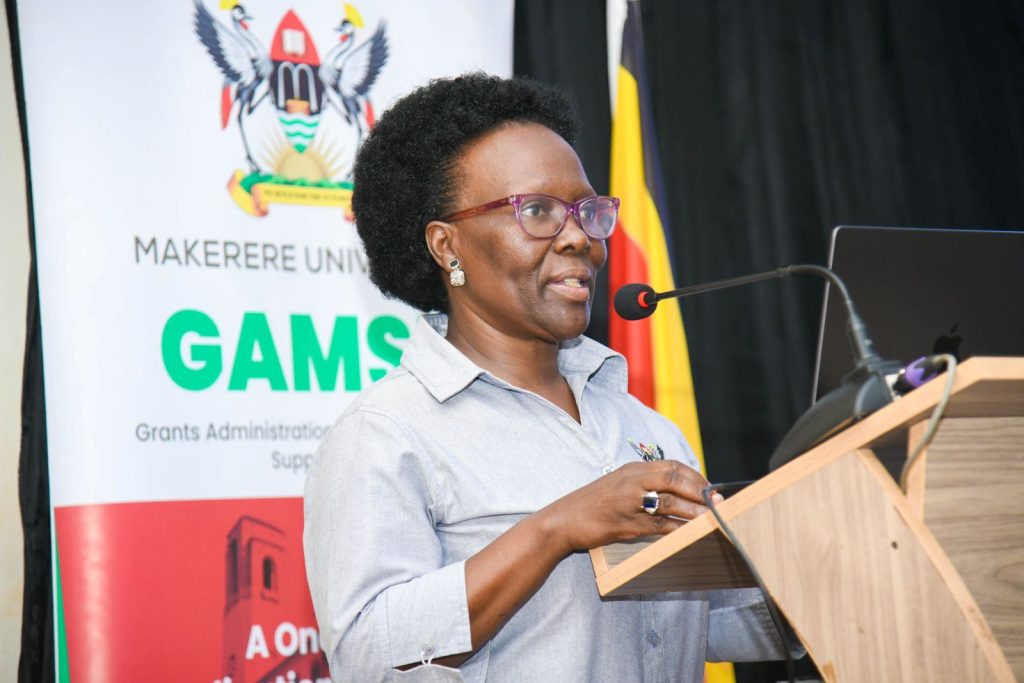

She said Makerere University faces increasing global competition for research funding. “Grants have become highly competitive, and we need stronger institutional strategies to support our researchers,” she said.
According to Prof. Nannyonga-Tamusuza, the previous grant management environment was fragmented because different university units operated independent systems. The new platform seeks to streamline processes and support database-driven decision-making for capacity building and institutional planning.
She explained that the system is designed to support researchers even before they begin writing proposals. “Understanding the funder’s requirements is critical. If a researcher does not clearly understand what the funder is asking for, even a well-written proposal may fail to secure funding,” she said.
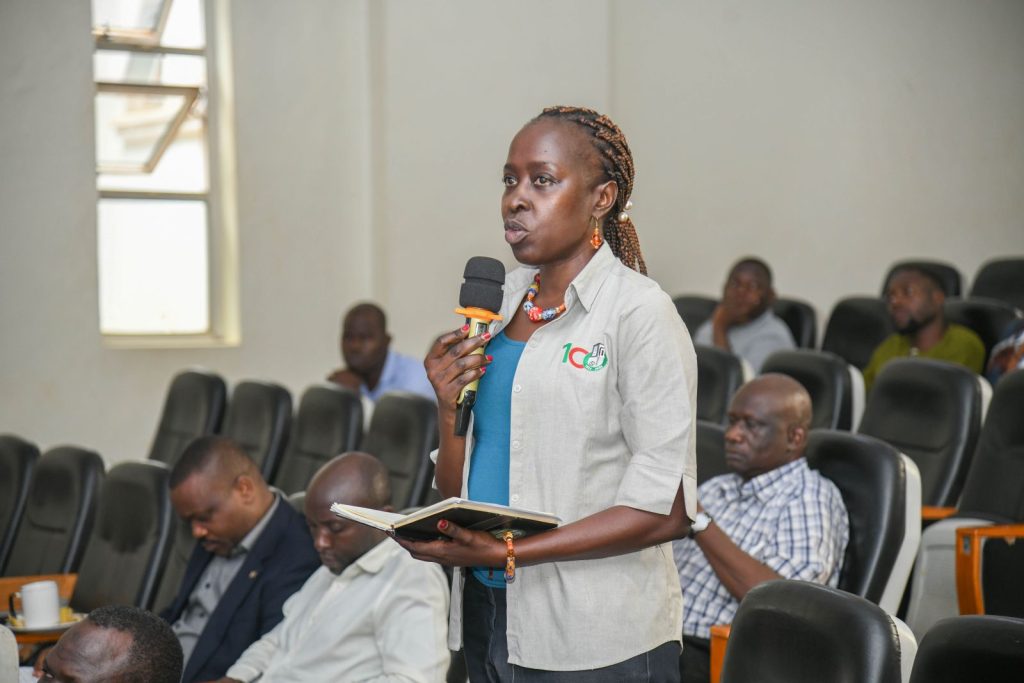

The Head of GAMSU stressed that transparency and accountability were central goals of the system. “With proper work logs and documentation, we can demonstrate accountability in grant administration,” she added.
She noted that principal investigators often require institutional documents such as audit reports and registration information when applying for grants. Centralised data storage, she said, would make such information more accessible.
Support for researchers, not replacement for individual applications
Prof. Nannyonga-Tamuzusa clarified that the system does not eliminate individual grant applications. “GAMSU is providing support to researchers. We want our staff to compete favourably within the global research community,” she said.
She explained that academic staff operate at different career levels. “Some staff are new to research grant applications and may need guidance. Others are experienced. Our role is to provide support whenever it is needed,” she stated
Addressing challenges in grant administration
The Head of GAMSU identified several challenges motivating the system’s development. These include: increasing international competition for research funding, fragmented awareness of funding opportunities across university units, limited coordination between researchers, colleges, and administrative structures, capacity gaps in grant proposal development, heavy reliance on manual administrative processes and limited institutional data for strategic planning.
She pointed out that GAMSU’s role is coordination, compliance, and institutional oversight rather than revenue collection.
Leaders and Researchers urged to adhere to university policies
Presenting the Context of Administration and Management of Grants at Makerere University, Mr. Yusuf Kiranda-University Secretary, articulated that the University Council, approved the Grants Administration and Management Policy in 2020, which provides governance guidance for research funding management. He appealed to participants to always read and make reference to the policy on matters pertaining to grants management and administration.

The University Secretary emphasized that research funds secured through grants are managed on behalf of Makerere University and the Government of Uganda. He therefore, urged researchers and principal investigators to uphold transparency and accountability when managing grant resources. “Funds acquired through grants must be accounted for within stipulated timelines and must demonstrate value for money,” said Mr. Kiranda.
In the same vein, he called upon research teams to follow the university’s human resource recruitment guidelines when appointing project staff.
Mr. Kiranda highlighted the importance of registering all grants managed across university units with GAMSU, noting that centralised oversight supports institutional accountability.
Director of Research highlights strategic research direction
Prof. Robert Wamala, Director of Research, Innovation and Partnerships (DRIP), presented the university’s strategic research agenda. He observed that university partnerships have sometimes been underutilised due to the absence of supporting infrastructure, such as the pre-award system.
The university’s research mandate includes promoting research coordination, strengthening innovation capacity, supporting technology transfer, and mobilising research funding.

Prof. Wamala said the university’s research strategy is guided by a 10-year institutional development plan aligned with Uganda’s National Development Plans. “The vision is to build a sustainable, research-led university that produces a highly productive academic workforce and versatile graduates,” he said.
Priority research themes
In his presentation, Prof. Wamala outlined Makerere University’s nine (9) priority research areas for the next five years. These include: Health and health systems; Sustainable urbanisation and housing; Governance, social justice, and equity; Agricultural transformation and food security, Education systems development; Economic growth, business, and innovation; Climate change and natural resource management; Cultural heritage; and Science, engineering, and technology.
Prof. Wamala encouraged researchers to align proposals with these institutional priorities. He urged academic staff to access university policies available on the official website (https://policies.mak.ac.ug)
Graduate training and institutional coordination
Prof. Julius Kikooma, Director of Graduate Training, said the establishment of GAMSU represents a major cultural shift in research administration.
He explained that earlier academic practice required researchers to independently search for funding opportunities and manage grants. “While that approach sometimes produced successful researchers, it also resulted in inconsistencies in proposal preparation and accountability reporting,” he said.

Prof. Kikooma emphasized the importance of institutional systems in meeting changing donor compliance requirements. He stated that grant writing involves two equally important components. “Approximately 50 percent depends on scientific proposal quality, while the other 50 percent depends on institutional compliance and administrative coordination,” he said.
He encouraged researchers to integrate GAMSU early in proposal development rather than treating the unit as a final review office.
Strategic investment in research competitiveness
In a document presented by Ms. Ritah Namisango, Prof. Charles Masembe-a member of the research team outlined the project overview, purpose, and workshop objectives, including system dissemination, stakeholder engagement, and functionality demonstration.
He stated that the electronic pre-award grants system is a strategic investment in Makerere University’s future research competitiveness. The digital transformation in grant administration will improve efficiency, strengthen accountability, and enhance access to funding opportunities.
Deputy Principal of CoBAMS applauds GAMSU Contributing to the discussion and stakeholder feedback session, the Deputy Principal of the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS), Associate Professor James Wokadala, commended GAMSU for the development of the system aimed at increasing the chances of winning grants. He appealed to GAMSU to cascade the training to the various units within the University.
General
Mastercard Foundation Scholars Urged to Embrace Mentorship for Career Growth
Published
2 days agoon
March 10, 2026
Mastercard Foundation Scholars have been encouraged to embrace mentorship programmes as a way of maximising opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Mentorship is a professional relationship in which an experienced person (the mentor) supports another (the mentee) in developing specific skills and knowledge that enhance both professional and personal growth.
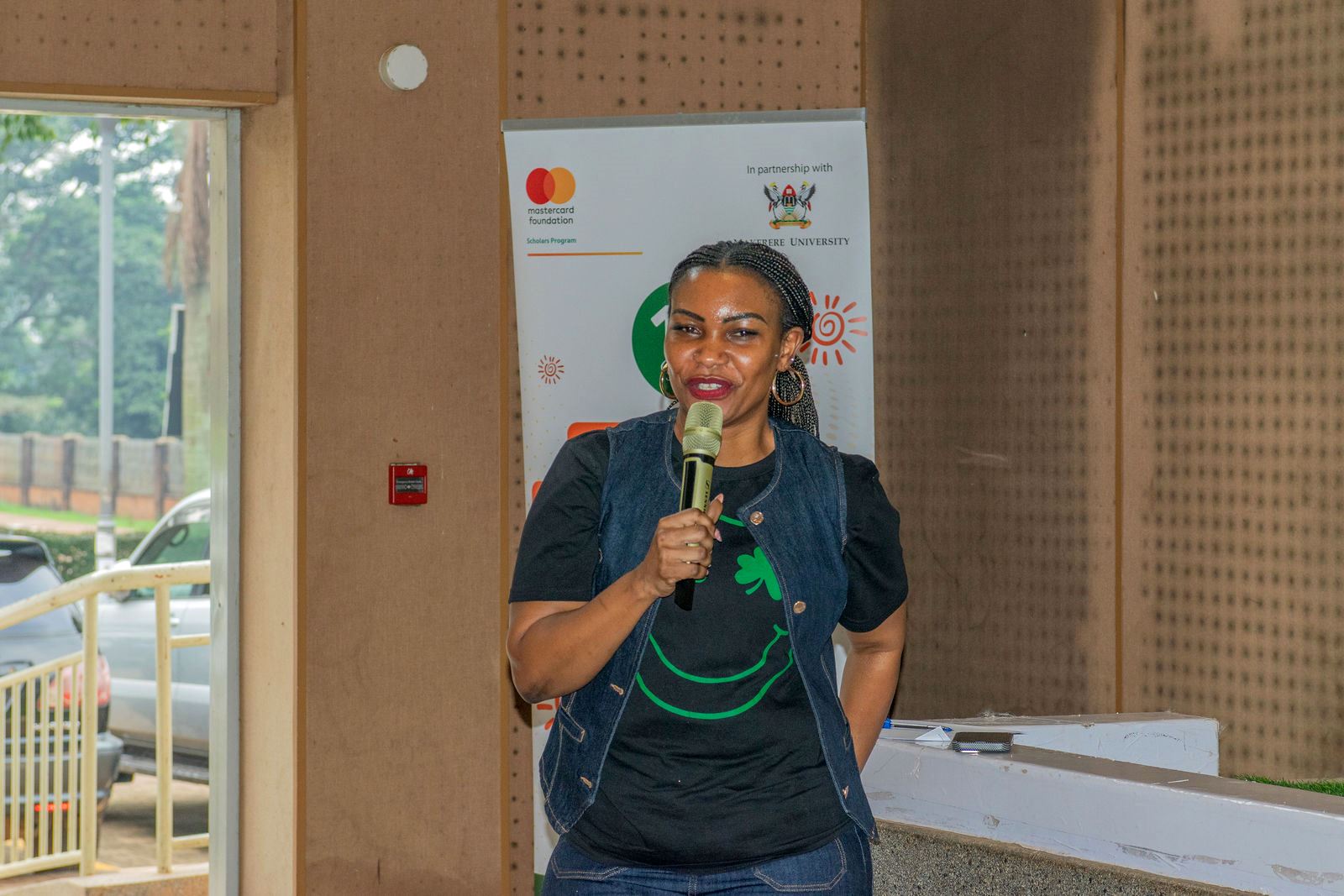
While speaking at a Mentor–Mentee matching session held on Saturday at the Central Teaching Facility, Mr Steven Langa, a counsellor and director at Family Life Network, told scholars that mentorship plays a pivotal role in preparing the next generation of leaders capable of transforming Uganda and Africa.
“We live at a very challenging time in history, a time when Uganda and Africa have to rise up to the occasion to provide leadership, professional excellence and innovation,” Mr Langa, said.

In his presentation, Mr Langa explained that a mentor is not a parent, therapist, or romantic partner, but rather a coach who helps the mentee build essential skills.
“The mentoring relationship is built on mutual trust, respect and communication and involves both parties meeting regularly to exchange ideas, discuss progress and set goals for further development. A mentor does not need to know, or to provide all the answers; instead, the mentor encourages the mentee to use their available resources to identify solutions,” Mr Langa, noted.
Speaking at the same event, Ms Eva Nabasumba, the Principal Academics and Career Development Officer at the Mastercard Foundation Scholars Program, encouraged scholars to build strong relationships with their mentors, which could later provide credible referees for employment, scholarships and other opportunities.

She highlighted several benefits of mentorship for mentees, including gaining advice, knowledge and insights from experienced professionals; developing professional communication skills; building valuable industry networks; engaging in employment-related conversations; exploring career pathways; and learning strategies for job searches, résumé writing and interviews.
During the session, mentors introduced themselves to their new mentees, allowing scholars to identify and connect with suitable mentors. Some of the mentors are doctors, teachers, counsellors, engineer’s business people and Accountants.
Apollo Mulondo, one of the mentors, urged scholars to take the mentorship opportunity seriously and respect the time and commitment of their mentors.
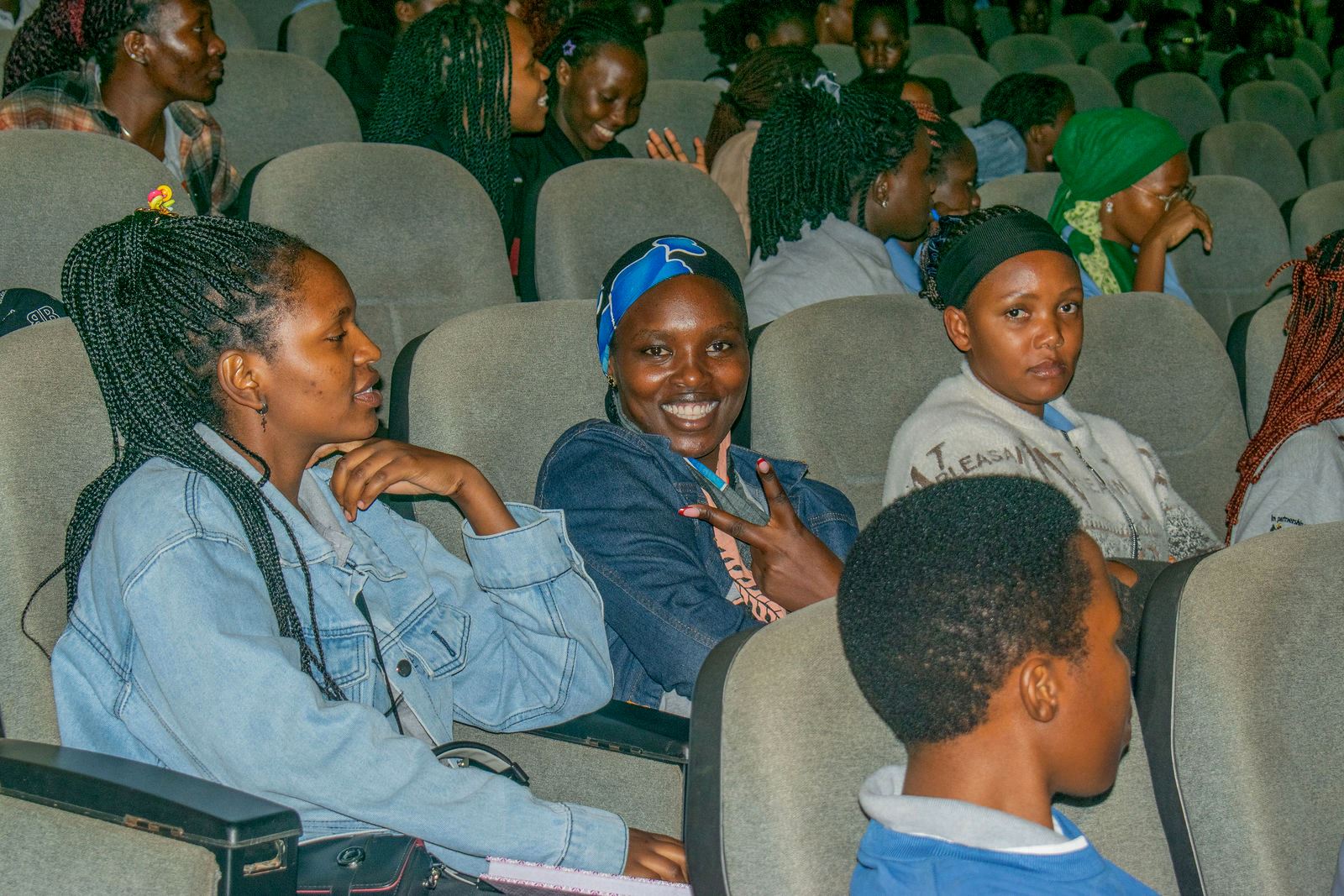
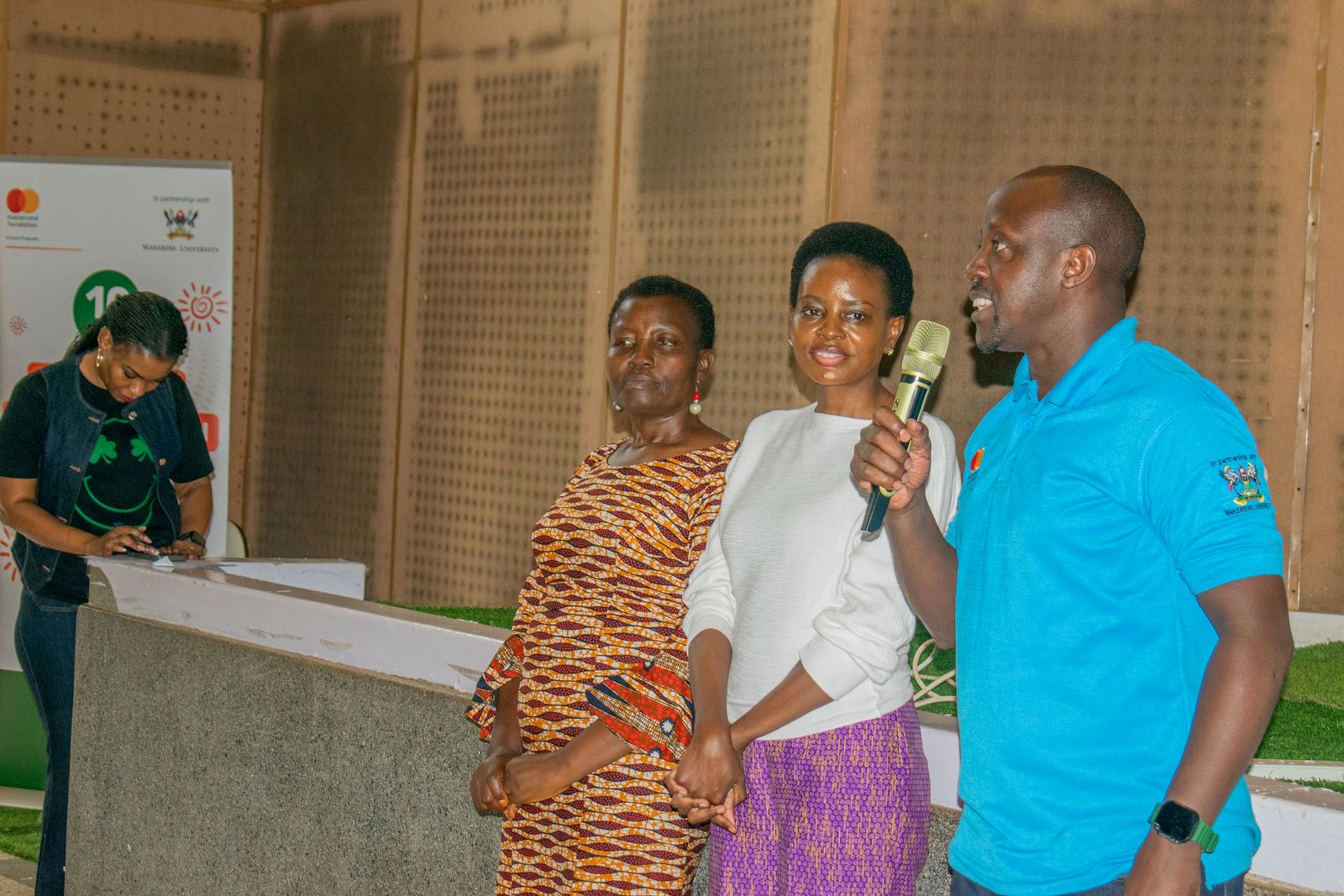
“Some of us are who we are today because of our mentors. Our offices are always open to you, so feel free to visit anytime. It does not matter what your background is you can make it,” Mulondo said.
The mentor–mentee matching session enabled scholars to interact with professionals from different fields, giving them an opportunity to identify mentors whose experience aligns with their academic and career aspirations. The engagement also created a platform for scholars to begin building networks that will support their growth beyond the university.
Trending
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMakerere University commemorates 13 transformative years of partnership with Mastercard Foundation
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMak News Magazine: February 2026
