General
First Makerere Workshop on Social Systems & Computation
Published
15 years agoon
Summary Top researchers from Northwestern University (Chicago), University of British Columbia (Vancouver) and Makerere (Kampala) are teaming up to offer a workshop on cutting-edge methods for computational modeling of social systems, algorithm design, and machine learning. The sessions will take place between December 3rd and 10th, and there is no cost for attendance; however, registration is mandatory.
Summary Top researchers from Northwestern University (Chicago), University of British Columbia (Vancouver) and Makerere (Kampala) are teaming up to offer a workshop on cutting-edge methods for computational modeling of social systems, algorithm design, and machine learning. The sessions will take place between December 3rd and 10th, and there is no cost for attendance; however, registration is mandatory.
Attendance is limited to academic staff working at a Ugandan university; students doing research in related areas may also be given special permission to attend if space permits. Participants will have the opportunity to publish papers in official, reviewed workshop proceedings at a later date. A certificate of completion will be provided to participants who attend at least two thirds of workshop sessions.
Overview Traditionally, computer science has viewed data as coming from either an adversarial source or from nature itself, giving rise to worst-case and average-case design and analysis of optimization algorithms. In recent years with the advent of modern technologies like the Internet, it has become increasingly apparent that neither of these assumptions reflects reality. Data is neither adversarial nor average, but rather inputs to algorithms are constructed by a diverse set of self-interested agents in an economy, all aiming to maximize their own happiness. Thus the raw data is often not available to an algorithm designer, but must be solicited from the agents–that is, the designer faces an economic constraint. The primary goal of this workshop is to explore the implications of this observation. We will study the performance of algorithms in the presence of utility-maximizing agents and ask whether alternate designs might create incentives for agents to act more optimally. Simultaneously, we will look at other more traditional optimization problems such as approximation and learning and techniques to solve them, pointing out that these may often be leveraged to solve issues in the economic setting.
Related Research Areas Computer Science Theory; Artificial Intelligence; Economics; Business
Format The workshop will consist of six 3-hour lectures, plus meal/breakout sessions for informal research discussion. Spaces are strictly limited, and attendees must pre-register. We will aim to select topics and session times that are best for our participants. To register, and to indicate your preferences for topics and dates, please complete the survey at http://www.surveymonkey.com/s/WWGMKZG.
List of Candidate Topics The workshop will consist of up to six of the following twelve topics.
Introduction to Game Theory
Game theory is the mathematical study of interaction among independent, self-interested agents. It has been applied to disciplines as diverse as economics, political science, biology, psychology, linguistics—and computer science. This tutorial will introduce what has become the dominant branch of game theory, called noncooperative game theory, and will specifically describe normal-form games, a canonical representation in this discipline. The tutorial will be motivated by the question: "In a strategic interaction, what joint outcomes make sense?"
Voting Theory
Voting (or "Social Choice") theory adopts a“designer perspective” to multiagent systems, asking what rules should be put in place by the authority (the “designer”) orchestrating a set of agents. Specifically, how should a central authority pool the preferences of different agents so as to best reflect the wishes of the population as a whole? (Contrast this with Game Theory, whichadopts what might be called the “agent perspective”: its focus is on making statements about how agents should or would act in a given situation.) This tutorial will describe famous voting rules, show problems with them, and explain Arrow's famous impossibility result.
Mechanism Design and Auctions
Social choice theory is nonstrategic: it takes the preferences of agents as given, and investigates ways in which they can be aggregated. But of course those preferences are usually not known. Instead, agents must be asked to declare them, which they may do dishonestly. Since as a designer you wish to find an optimal outcome with respect to the agents’ true preferences (e.g., electing a leader that truly reflects the agents’ preferences), optimizing with respect to the declared preferences will not in general achieve the objective. This tutorial will introduce Mechanism Design, the study of identifying socially desirable protocols for making decisions in such settings. It will describe the core principles behind this theory, and explain the famous "Vickrey-Clarke-Groves" mechanism, an ingenious technique for selecting globally-utility-maximizing outcomes even among selfish agents. It will also describe Auction Theory, the most famous application of mechanism design. Auctions are mechanisms that decide who should receive a scarce resource, and that impose payments upon some or all participants, based on agents' "bids".
Constraint Satisfaction Problem Solving
This hands-on tutorial will teach participants about solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems using search and constraint propagation techniques. This is a representation language from artificial intelligence, used to describe problems in scheduling, circuit verification, DNA structure prediction, vehicle routing, and many other practical problems. The tutorial will consider the problem of solving Sudoku puzzles as a running example. By the end of the session, participants will have written software (in Python) capable of solving any Sudoku puzzle in less than a second.
Bayesian methods and Probabilisitic Inference
Bayesian methods are commonly used for recognising patterns and making predictions in the fields of medicine, economics, finance and engineering, powering all manner of applications from fingerprint recognition to spam filters to robotic self-driving cars. This session will show how principles of probability can be used when making inferences from large datasets, covering issues such as prior knowledge and hyperpriors, the construction of "belief networks", and nonparametric methods such as Gaussian processes. Several applications will be demonstrated.
Computer Vision
It is useful to be able to automatically answer questions about an image, such as "is this the face of person X?", "how many cars are there on this street?" or "is there anything unusual about this x-ray?". This session will look at some of the current state of the art in computer vision techniques, including methods for representing the information in an image (feature extraction), and to recognise objects in an image given such a representation. We will particularly spend some time looking at approaches which have been found to work well empirically on object recognition, such as generalised Hough transforms, boosted cascades of Haar wavelet classifiers, and visual bag-of-words methods. Locally relevant applications in crop disease diagnosis, parasite detection in blood samples and traffic monitoring will be demonstrated as illustrating examples.
Learning Causal Structure from Data
Until a few decades ago, it was thought to be impossible to learn causes and effects from purely observational data without doing experiments. Sometimes, however, it is impossible to do experiments (e.g. in some branches of genetics), or experiments may be costly or unethical (e.g. situations in climate change or medicine), so the emergence of computational methods for distinguishing causes, effects and confounding variables is likely to have wide implications. Some principles are now understood for learning the causal structure between different variables, and this session will explain the most successful current approaches, their possibilities and their limitations.
Internet Search and Monetization
The internet is one of the most fundamental and important applications of computer science. Central to its existence are search engines which enable us to find content on the web. This module focuses on the algorithms like PageRank that these search engines use to help us find webpages. It also studies how these engines make money through advertising.
Social Networks
Social networks describe the structure of interpersonal relationships and have many alarmingly predictable properties. While most people have just a few friends, most social networks have at least a few very popular people. Furthermore, most people are closely linked to every other person so that a message (or an idea or a disease) can spread rapidly throughout the network. Finally, social networks tend to be fairly clustered — i.e., if two people share a common friend it is quite likely that they are also friends. This module will discuss the typical structures of social networks, models that explain these structures, and the impact of these structures on activities in the social network such as message routing or the adoption of new technologies.
Two-Sided Matching Markets
Many markets involve two “sides'' that wish to be matched to one another. For example, a marriage market matches women to men; a job market matches workers to employers. In such settings, people on each side have strict preferences over the options on the other side of the market. Hence, a woman Julie may like David best, John second best, and Christopher third. David on the other hand may prefer Mary to Julie. In such settings, what matches might we expect to form? Can these matches be computed by a centralized algorithm, a match-maker for example, and what are the corresponding incentives of the participants? These questions are of fundamental importance as such centralized algorithms are in use in many important markets. In many countries, medical students are matched to hospitals using such algorithms, or school children to schools.
Approximation Algorithms
In the field of algorithms, many tasks turn out to be computationally difficult. That is, the time to complete the task is fundamentally large compared to the size of the problem. For example, consider the problem of finding the optimal way to visit 10 cities, visiting each exactly once. To minimize travel time, one could test all possible travel schedules, but for 10 cities there are already 3.5M of them! Unfortunately, there is not a significantly quicker way to find the optimal solution. However, one can find an approximately optimal solution quickly. That is, with just a few things to check, one can design a schedule that takes at most 50% more time than the optimal one. In this module we showcase a few general techniques for computing approximate solutions to hard problems, including the use of randomization and linear programming.
Graph Theory
A graph is a combinatorial object consisting of nodes and edges, and is a extremely valuable abstraction of many practical problems. For example, nodes might represent jobs and edges might connect pairs of jobs that can not be performed simultaneously. Alternatively, nodes might represent electronic components on a circuit board and edges the wiring that connects them. Many questions that arise in such domains can be cast as an optimization question in the corresponding graph. The number of workers required to complete all jobs in fixed time frame in the first example is at its heart a graph coloring problem. Asking whether one can lay out the circuit board so no two wires cross becomes the problem of determining which graphs have planar representations. This course defines graphs, shows how to solve a few fundamental graph problems, and applies them to practical settings.
Speaker Bios
Nicole Immorlica is an assistant professor in the Economics Group of Northwestern University's EECS department in Chicago, IL, USA. She joined Northwestern in Fall 2008 after postdoctoral positions at Microsoft Research in Seattle, Washington, USA and Centruum voor Wiskunde en Informatica (CWI) in Amsterdam, The Netherlands. She received her Ph.D. from MIT in Boston, MA, USA, in 2005 under the joint supervision of Erik Demaine and David Karger. Her main research area is algorithmic game theory where she investigates economic and social implications of modern technologies including social networks, advertising auctions, and online auction design.
Kevin Leyton-Brown is an associate professor in computer science at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada. He received a B.Sc. from McMaster University (1998), and an M.Sc. and PhD from Stanford University (2001; 2003). Much of his work is at the intersection of computer science and microeconomics, addressing computational problems in economic contexts and incentive issues in multiagent systems. He also studies the application of machine learning to the automated design and analysis of algorithms for solving hard computational problems.
John Quinn is a Senior Lecturer in Computer Science at Makerere University. He received a BA in Computer Science from the University of Cambridge (2000) and a PhD from the University of Edinburgh (2007). He coordinates the Machine Learning Group at Makerere, and his research interests are in pattern recognition and computer vision particularly applied to developing world problems.
You may like
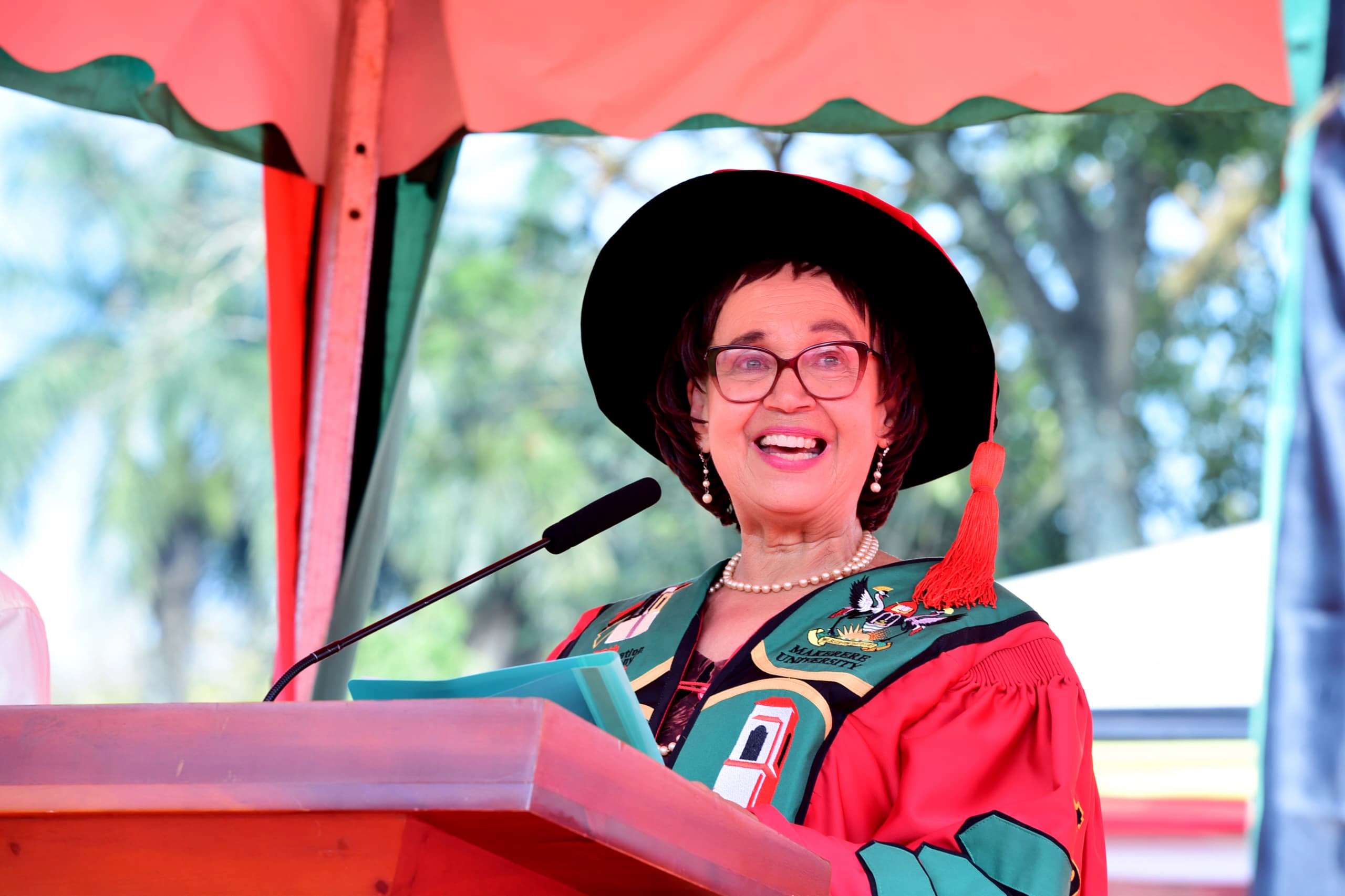

The Board Chairperson of the Makerere University Endowment Fund (MakEF), Dr. Margaret Blick Kigozi, has urged graduands in Health and Life Sciences to uphold professional ethics and serve humanity with diligence and compassion.
Her appeal came during the passing out of graduates from the College of Natural Sciences (CoNAS), the College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Bio-Security (CoVAB), the College of Health Sciences (CHS) and the School of Public Health (SPH) on Day Two of the 76th Graduation Ceremony of Makerere University.
“Class of 2026, you are now part of the Makerere legacy. Wherever you go clinics, laboratories, farms, boardrooms, or classrooms, you carry this institution with you. Serve your patients with skill and compassion. Care for animals and communities responsibly. Question boldly and keep learning,” Dr Kigozi, said.
Delivering the commencement address, Dr. Kigozi lauded the graduates for their dedication to careers that directly impact lives and communities. She encouraged them to use their knowledge generously and exercise their power gently.
“Your education has trained you to ask better questions. Your humanity must guide the answers. Never forget that behind every chart, every case, every animal, every experiment, there is life. And life deserves care, patience, and dignity. Give every person you come in contact with care, patience and dignity,” Dr Kigozi, noted.
As the graduates embark on their professional journeys, Dr. Kigozi emphasized the importance of cultivating basic business acumen and financial literacy to ensure sustainability in their work.

“You do not need to become accountants but you must be able to read the essentials: understand simple financial statements, budgets and key metrics so you can judge whether a clinic, lab, or program is sustainable. You are encouraged to start your business. There are numerous investment opportunities in your areas of training. You can provide services to our people and create jobs,” Dr Kigozi, said.
She shared candidly how, when she first stepped into leadership, she realised she did not understand balance sheets or budgets well enough. So, she returned to Makerere for short courses to strengthen herself.
“A well-run Hospital, clinic or lab delivers better outcomes, attracts staff, and secures funding. Business savvy is not only about profit, it’s about sustainability and the freedom to serve ethically and effectively. Carry clinical skill with business sense so your work endures and grows,” Dr. Kigozi, noted.
Quoting renowned writer and producer Shonda Rhimes, creator of Grey’s Anatomy, who once reflected that succeeding in one area of life can sometimes mean falling short in another, Dr. Kigozi encouraged women graduates to intentionally balance professional ambition with family responsibilities.
“When one area thrives, another is often under strain. When Navio was graduating from school I had to manage the Presidential Investor Round Table on the same day as Executive Director Uganda Investment Authority. I chose my job and delegated his siblings to attend Navios graduation. I learnt from this. I choose family always after that thing you achieve once and keep forever,” Dr Kigozi, said.
In his speech, the Prof Barnabas Nawangwe, the Vice Chancellor, informed the congregation that Makerere’s ranking on all university ranking platforms has remained stable, placing Makerere among the top 10 African universities and within the top 4.5% globally.
“In the Times Higher Education global ranking, Makerere University made a formidable jump from the 1200-1500 bracket to the 800-1000 bracket. This was no mean achievement and I congratulate all members of the Makerere Community on this stellar performance,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
General
Graduation marks the next phase of accountability, graduates told
Published
2 days agoon
February 25, 2026
“A degree is not a finish line. Graduation is not the end of learning, It is the beginning of accountability,” Prof. Nicholas Ozor, the Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network Nairobi, Kenya (ATPS), said.
Delivering a keynote address under the theme ‘Knowledge with purpose’, during Makerere University’s 76th graduation ceremony on Tuesday 24th February, Prof Ozor, challenged graduates to see their degrees not as status symbols, but as instruments of responsibility.
In his speech, he painted a candid picture of the world the graduates are stepping into, one marked by climate change, technological disruption, inequality, food insecurity and the rapid spread of misinformation. Yet rather than framing these challenges as obstacles, he described them as opportunities for purposeful leadership.
“Into this world, you step, armed with knowledge, credentials, and potential. Your degrees do not make you better than others. They make you responsible for others,” Prof Ozor, said.
Addressing graduands from College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES)
College of Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS), College of Education and External Studies (CEES) and School of Law (SoL), Prof. Ozor tailored his message to each field of study.
To graduates of the School of Law, he described the legal profession as a moral calling, urging them to use the law to protect the vulnerable and uphold justice with courage.
“Uganda, Africa, and the world do not need lawyers who only know how to argue. They need lawyers who know why they argue. Use the law to protect the weak, not intimidate them. Use your knowledge to defend justice, not delay it. Let integrity define your reputation not merely your résumé,” Prof Ozor, said.
For graduands who might feel that shortcuts will be tempting and silence will feel safer than truth, Prof. Ozor reminded them that justice does not need clever people, but courageous ones.
To the College of Education and External Studies, he underscored the transformative power of teachers, reminding them that classrooms shape nations long before policies do.
“Every nation rises and falls on the quality of its teachers. Never underestimate the power of a classroom. Teach not only for examinations, but for understanding. Teach not only content, but character. Teach learners how to think not what to think. Education is quiet work but its impact echoes across generations,” Prof Ozor, noted.
He called upon graduands from the College of Computing and Information Sciences, to use technology to solve African problems, not merely to imitate foreign solutions.
“Technology is powerful, but it is not neutral. Every line of code carries values. Every system you design affects real lives. Build for inclusion. Build for accessibility. Build for truth. Do not let innovation outrun ethics. The future will not belong to those who know the most technology, but to those who use it wisely,” He noted.
During the ceremony, Prof Ozor announced that the African Technology Policy Studies Network is offering PhD scholarships and postdoctoral fellowships in Artificial Intelligence, inviting deeper collaboration with Makerere.
For graduates of the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, he highlighted their critical role at the intersection of sustainability and survival, calling on them to blend indigenous knowledge with scientific innovation to secure Africa’s food systems and protect its ecosystems.
In closing, he reminded graduands that their integrity will open doors their degrees cannot, their humility will teach them lessons success never will, and their resilience will matter more than their grades.
Five principles to be remembered:
- Embrace lifelong learning. The world changes too fast for static knowledge.
- Choose purpose over comfort. Impact matters more than income.
- Build character before career. Skills get you hired; character sustains you.
- Serve something larger than yourself. Give back to your communities and your country.
- Believe in Africa, and act. Do not wait for solutions from elsewhere. Be the solution.
General
Over 9,200 to graduate at Makerere University’s 76th Graduation
Published
2 days agoon
February 24, 2026
Pomp and colour defined the opening day of the Makerere University’s 76th Graduation Ceremony as thousands gathered to celebrate academic excellence and new beginnings.
The historic ceremony has brought together scholars, families, friends and industry partners in a vibrant celebration of achievement and possibility. Throughout the four-day event, the University will confer degrees and award diplomas to 9,295 graduands in recognition of their dedication and hard work.
Among the graduates, 213 will receive Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degrees, 2,503 will graduate with Master’s degrees, and 6,343 will earn Bachelor’s degrees. In addition, 206 students will graduate with postgraduate diplomas, while 30 will be awarded undergraduate diplomas.
Of the total number of graduands, 4,262 are female and 5,033 are male. According to Vice Chancellor, this marks the first time in 15 years that male graduands have outnumbered their female counterparts.
The best overall graduand in the Sciences, Esther Ziribaggwa, graduated on the opening day with the Bachelor of Agricultural and Rural Innovation and an impressive Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) of 4.77.
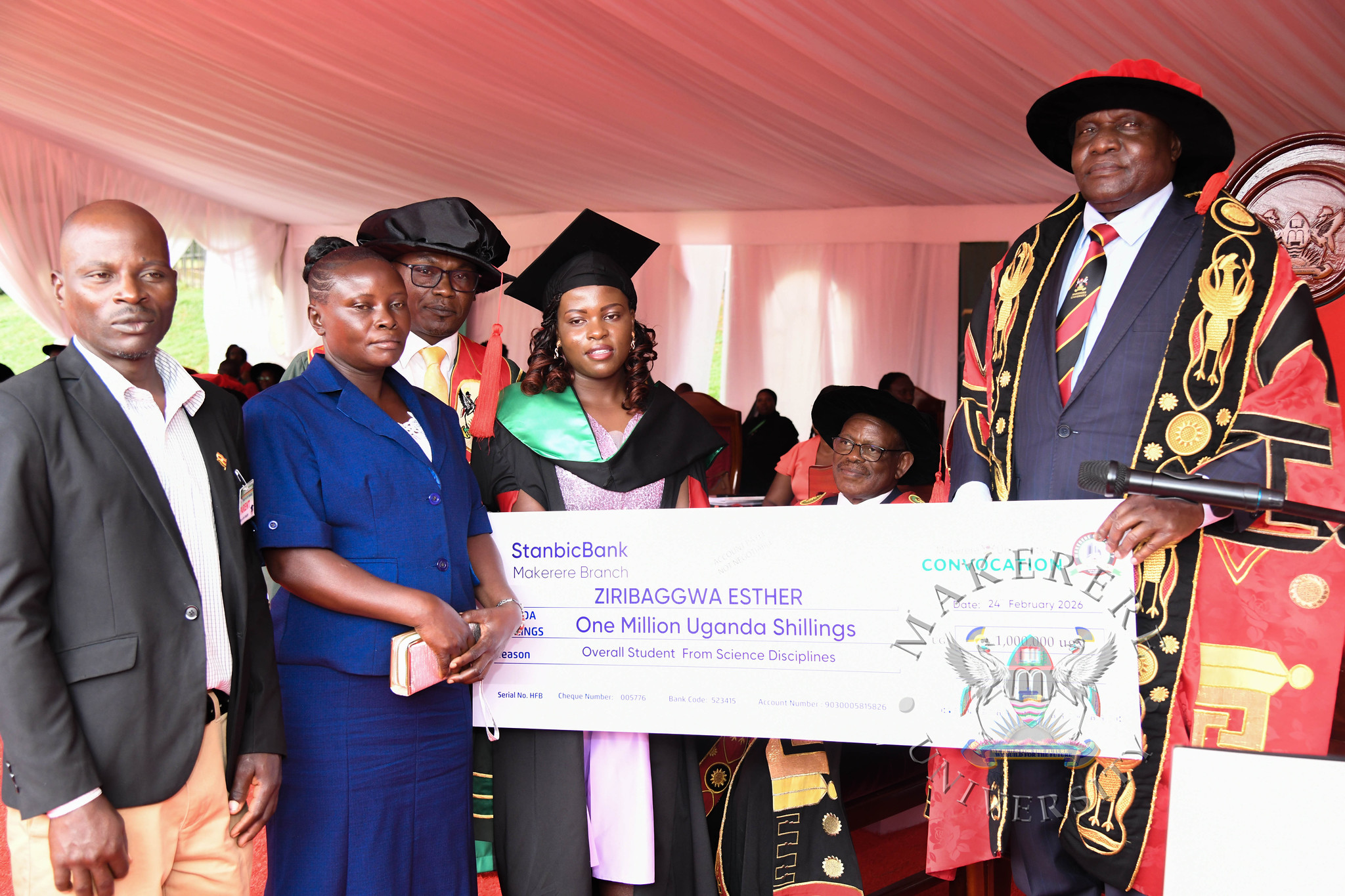
The ceremony marks a proud moment for Makerere University as it continues to nurture top-tier professionals across diverse fields.
While presiding over the graduation, the State Minister for Primary Education, Hon. Dr. Joyce Moriku Kaducu, on behalf of the First Lady and Minister of Education and Sports, Hon. Janet Kataaha Museveni, pointed out that Makerere University is a model institution, where leaders are nurtured, scholars are sharpened, and where dreams have been given direction.
In her address, Hon. Museveni, highlighted Government’s deliberate investment in research, innovation, and infrastructure to strengthen higher education in Uganda.
“The establishment of the Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund (RIF), supports high-impact research and innovation that directly contributes to national priorities and development. Through this initiative, thousands of researchers and innovators have pursued practical, scalable solutions that are transforming communities and key sectors across Uganda,” Mrs Museveni, said.
The Minister also noted that Parliament’s approved a USD 162 million concessional loan to upgrade science, technology, and innovation infrastructure at Makerere University. The funding will facilitate the construction of modern laboratories, smart classrooms, and state-of-the-art facilities for Engineering and Health Sciences, investments expected to position the University firmly within the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
“Government has embarked on the construction of a National Stadium at Makerere University and other institutions of higher learning across the country. This will promote physical education, strengthen talent identification, and boost investment in the sports sector,”
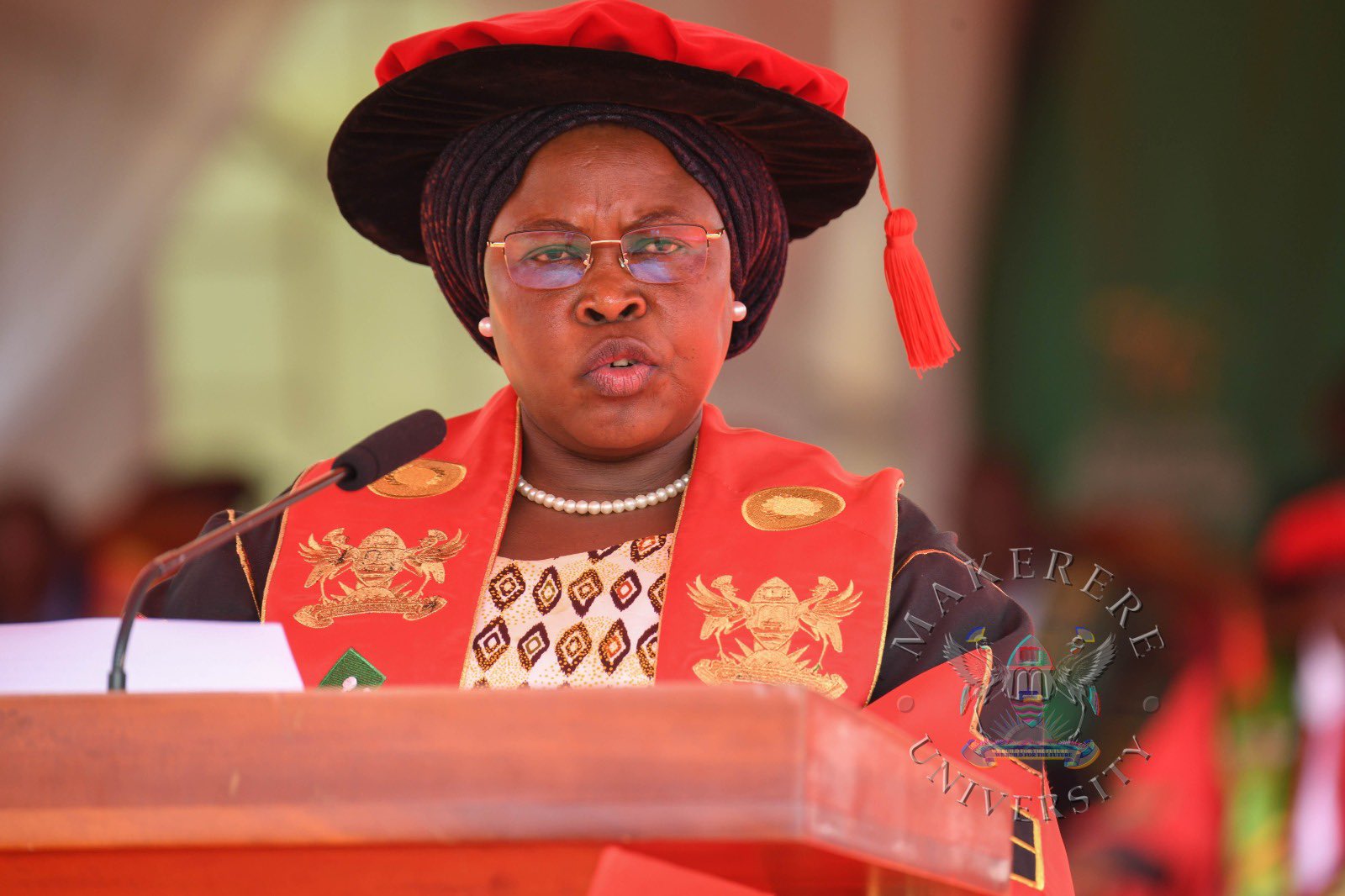

Turning to the graduands, the Minister encouraged them to see themselves not merely as job seekers, but as job creators and solution-makers.
Uganda and Africa need innovators who will modernize agriculture; engineers who will build quality infrastructure; healthcare professionals who will strengthen health systems; and educators who will inspire the next generation,” the Honourable Minister said.
She reminded graduates that they are entering a rapidly changing world shaped by Artificial Intelligence, climate change, and shifting global markets. To thrive, she advised them to remain adaptable, creative, and committed to lifelong learning.
She also encouraged graduates interested in entrepreneurship to tap into the Government’s Parish Development Model, which provides community-based financing and production support.
Quoting Proverbs 3:5–6, the Minister urged the graduates to trust in God as they embark on their next chapter.
She extended special appreciation to the Mastercard Foundation for its 13-year partnership with Makerere University in expanding access to education and empowering young people in Uganda and beyond.
In his speech, the Chancellor of Makerere University, Dr Crispus Kiyonga, urged graduands to harness research, innovation and technology to drive Uganda’s transformation.
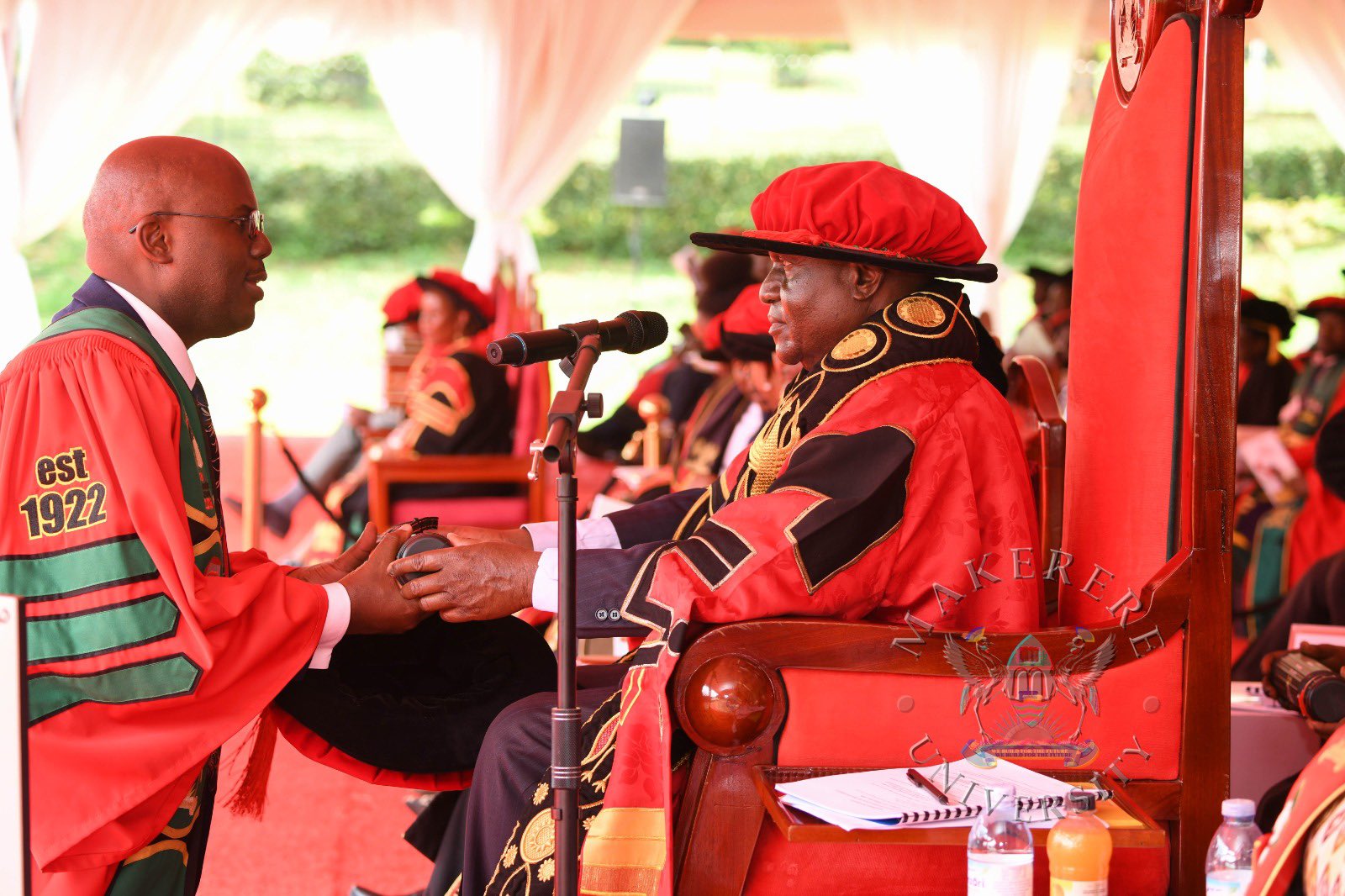

“This is a milestone in your lives. You have invested time, discipline and hard work to attain these qualifications. It is important that you derive value from this achievement, not only for yourselves, but for your families and for society.” Dr Kiyonga, said.
Dr. Kiyonga expressed gratitude to the Government of Uganda for its continued financial support to the University, particularly the funding allocated under MakRIF, which he described as critical in strengthening the institution’s research capacity.
“Research plays a very vital role in the development of any community. Makerere as the oldest University in the country is doing a significant amount of research, However, more work is required to mobilize additional resources to further strengthen research at the University.” Dr Kiyonga, noted.
Acknowledging the challenges of a competitive job market, Dr. Kiyonga encouraged graduates to think beyond traditional employment pathways.
“It is true that the job market may not absorb all of you immediately. But the knowledge you have acquired is empowering. You can create work for yourselves, individually or in teams.” Dr Kiyonga, said.
He advised the graduands to embrace discipline, integrity and adaptability in the workplace, and to take advantage of technology and digital platforms to innovate and respond to societal challenges.
“Every development challenge presents an opportunity. Believe that you can apply your knowledge to create solutions with impact.” He said.
Addressing the congregation, the Vice Chancellor, Prof Barnabas Nawangwe, congratulated the graduands, particularly staff and societal leaders on their respective achievements.
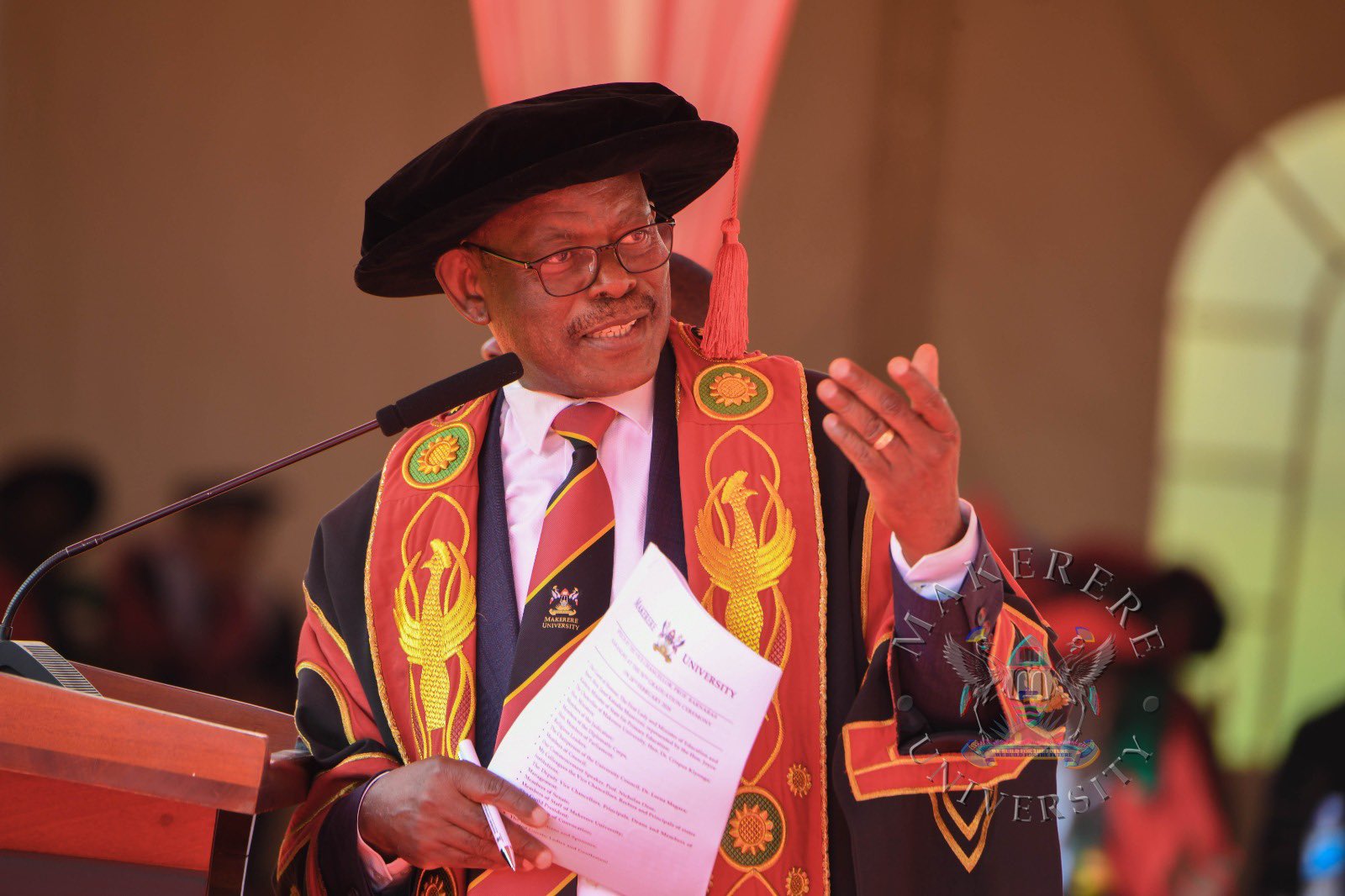

“I congratulate all our graduands upon reaching this milestone. In a special way I congratulate the members of staff, Ministers, and Members of Parliament that are graduating today as well as children and spouses of members of staff,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
In his speech, Prof Nawangwe, recognized outstanding PhD students, particularly members of staff. who completed their PhDs in record time without even taking leave from their duties.
He called upon graduates not to despise humble beginnings but rather reflect on the immense opportunities around them and rise to the occasion as entrepreneurs.
“You are all graduating with disciplines that are needed by society. We have equipped you with the knowledge and skills that will make you employable or create your own businesses and employ others. Do not despair if you cannot find employment. Instead, reflect on the immense opportunities around you and rise to the occasion as an entrepreneur,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
Prof Nawangwe called upon the graduands of PhDs to use their degrees to transform the African continent.
“As you leave the gates of Makerere I urge you to put to good use the knowledge you have received from one of the best universities in the World to improve yourselves, your families, your communities, your Country and humanity. Let people see you and know that you are a Makerere alumnus because of the way you carry yourself in society with dignity and integrity. Put your trust in God and honour your parents and opportunities will be opened for you,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
Delivering a key note address, Prof. Nicholas Ozor, the Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network Nairobi, Kenya ((ATPS). Reminded the graduates that a degree is not a finish line but the beginning of accountability. “The world is a complex, fast changing and deeply unequal. Degrees make you responsible for others not better than them,” Prof Ozor, said.
Trending
-

 Humanities & Social Sciences4 days ago
Humanities & Social Sciences4 days agoMeet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 Agriculture & Environment6 days ago
Agriculture & Environment6 days agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
-

 General3 days ago
General3 days ago76th Graduation Highlights
