Agriculture & Environment
SophiA Project Upgrades Medical Infrastructure at Buvuma Health Centre IV, Trains Technicians for Maintenance Works
Published
8 months agoon
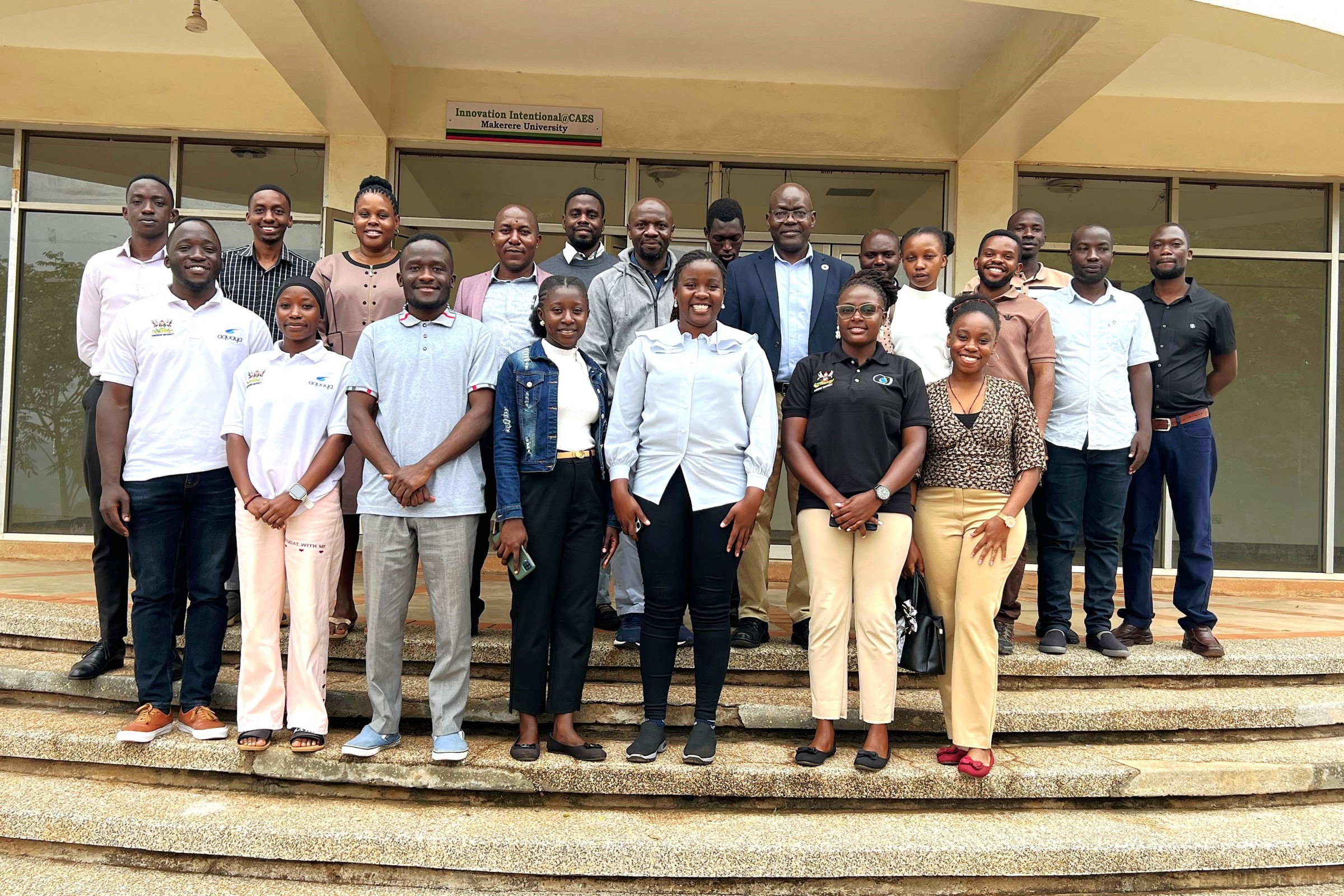

Overview of the Sustainable Off-Grid Solutions for Pharmacies and Hospitals in Africa (SophiA) Project
Despite ongoing urbanization across Africa, the majority of the population still resides in rural and remote areas, where infrastructure development remains limited. These regions face significant challenges such as lack of access to healthcare, education, clean water, and reliable electricity, contributing to higher rates of illness and poverty compared to urban centres. According to reports, Sub-Saharan Africa has approximately 120,000 public health facilities (22,000 hospitals and 98,000 health posts), of which around 26% lack any electricity access, and only 28% have reliable power supply.
Access to good healthcare is critical for sustainable development. However, many rural medical centres operate under harsh conditions – using polluted water, lacking cooling for medicines, and facing poor sanitation – largely due to unreliable electricity and water supply. Although half of the population in Sub-Saharan Africa lacks electricity, the region has abundant renewable energy potential that can be effectively harnessed through off-grid solar photovoltaic (PV) systems.
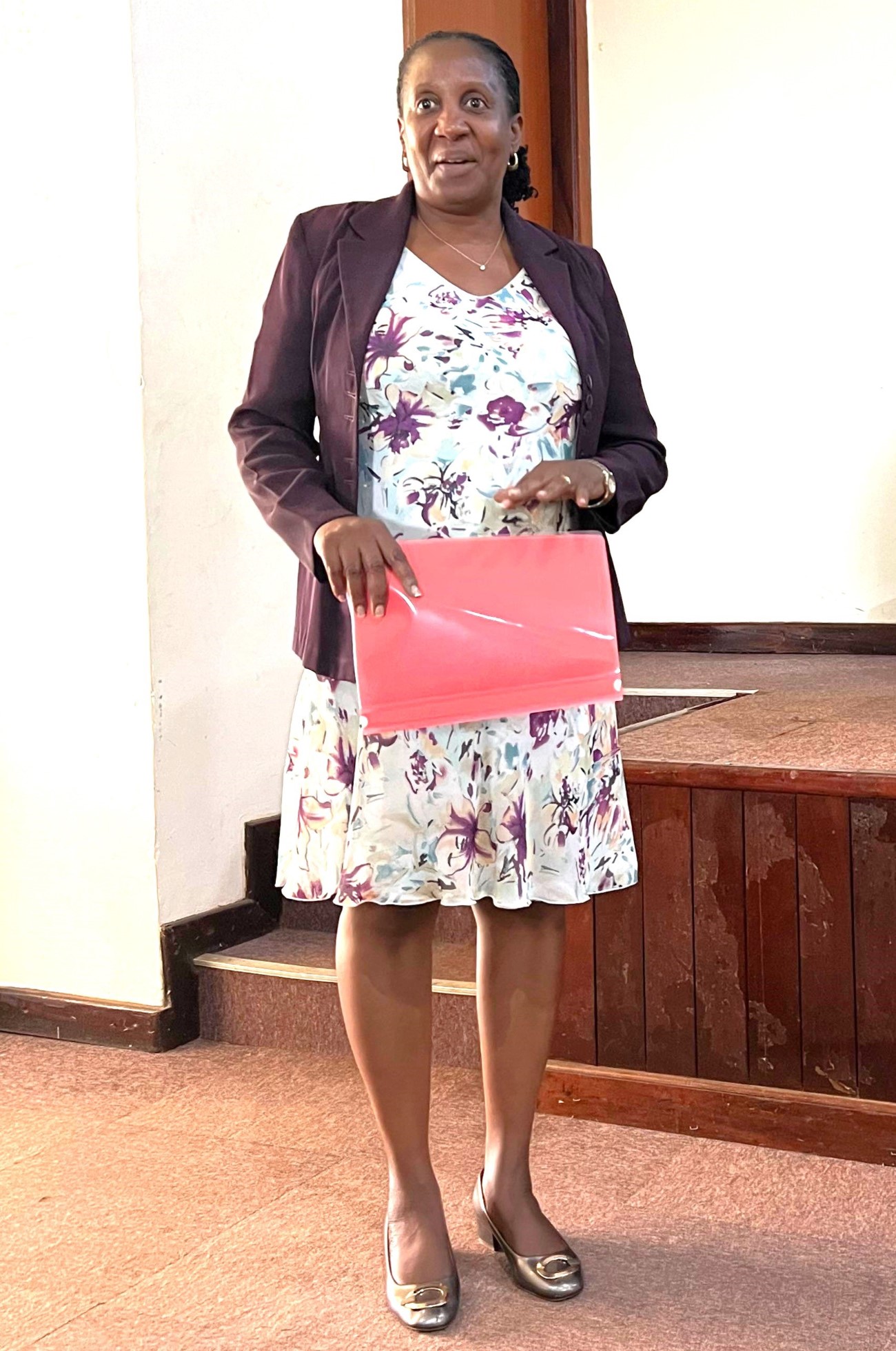

To address the above-mentioned challenges facing the African Continent, Makerere University in partnership with 13 organizations across Europe and Africa developed a project titled, “Sustainable Off-grid solutions for Pharmacies and Hospitals in Africa (SophiA)”. The five-year project that began on 1st October 2021 is funded by the European Union (Project: 101036836 – SophiA – H2020-LC-GD-2-3-2020). At Makerere University, the project is coordinated by Dr. Nicholas Kiggundu, Associate Professor in the Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES).
Piloted in Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Malawi, and Uganda, SophiA aims to provide sustainable off-grid energy solutions to rural and remote health facilities, fostering economic growth and ensuring equitable access to energy and healthcare. Using various technologies, such as photovoltaics, solar thermal, electrical and thermal storage, water treatment and natural refrigerants with low global warming potential, SophiA has developed and manufactured locally innovative, modular, affordable and efficient solar powered systems for providing:
- Safe and clean drinking water, free of bacteria and viruses, and deionised water for medical purposes;
- Hot water and steam production for thermal requirements of the hospitals;
- Cooling of medicines and food at +5°C;
- Low temperature storage of blood plasma and vaccines at -30°C;
- Ultra-low temperature storage of sensitive medication (e.g. some Covid-19 or Ebola vaccines) at -70°C.

In addition, PV MedPort, a simple and 100% solar-powered solution has been developed and tested as a mobile health care station in small remote areas in 4 different geographical conditions in Africa. The SophiA system has been manufactured in Africa and will provide, for the first-time, innovative solutions based on climate-friendly natural refrigerants to cover cooling demand for three different temperature ranges (-70°C, -30°C and +5°C). The system has been tested and demonstrated at four rural hospitals in remote regions throughout the African continent covering the major geographical regions and different climatic conditions in Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Malawi and Uganda.
SophiA Project initiatives in Uganda
In Uganda, all Health Centre IV hospitals with surgical theatres have been connected to the national grid except Buvuma Health Centre IV, which serves over 120,000 people scattered across 52 islands. Recognizing this gap, the Ministry of Health selected Buvuma Health Centre IV for the SophiA project to demonstrate sustainable off-grid solutions.
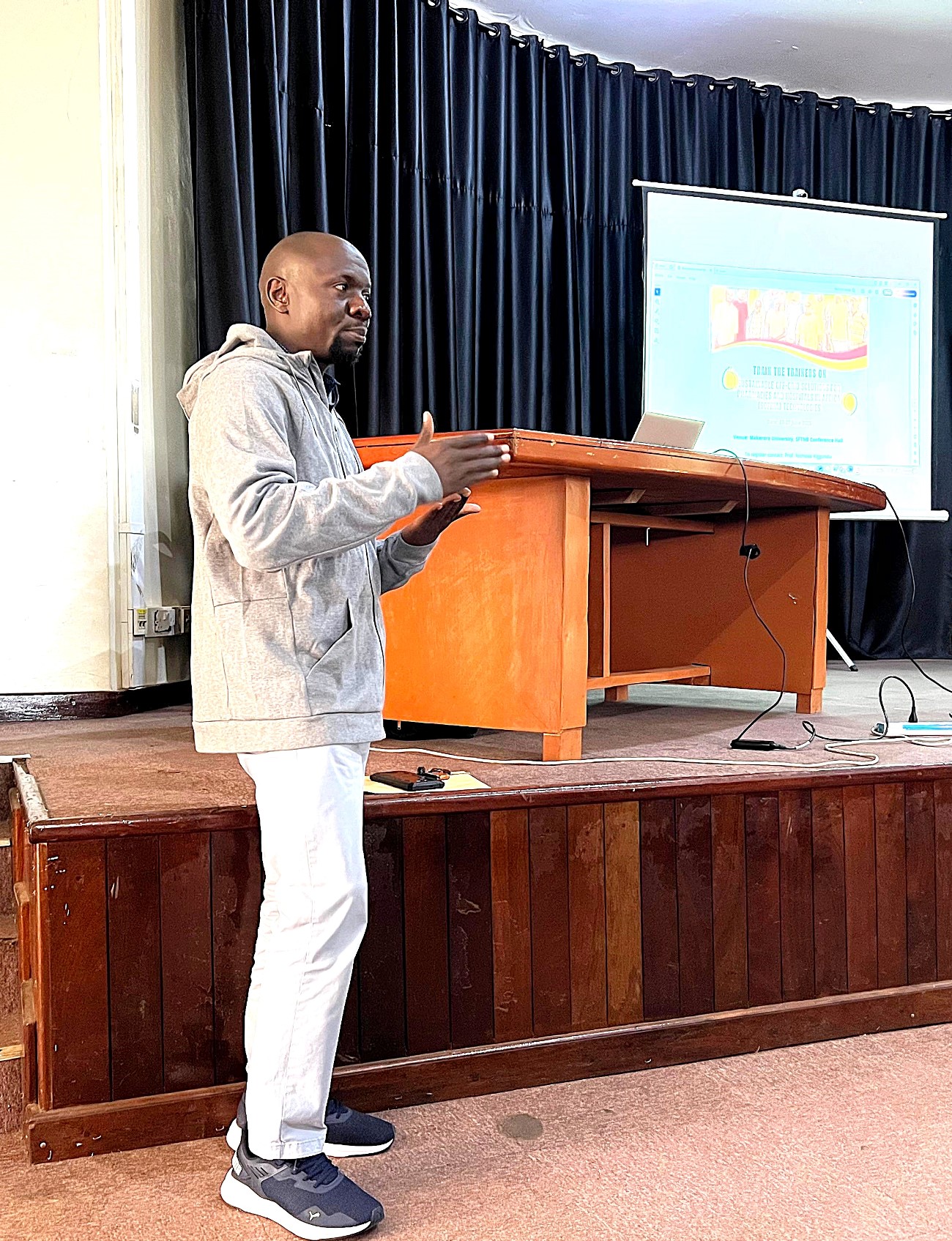

The SophiA System at Buvuma Health Centre IV provides the following services:
- Off-grid electricity supply
- Safe, clean drinking water for patients, staff, and the community
- Hot water and steam systems crucial for maternal care
- Solar-powered cooking and meal preparation
- Cooling systems for surgery and intensive care units
- Refrigeration for medicines at +5°C, blood plasma storage at -30°C, and ultra-low temperature storage (-70°C) for sensitive vaccines such as those for COVID-19 and Ebola
Training of Trainers Workshop
As the SophiA project approaches completion in September 2025, it is vital to establish a skilled pool of technicians capable of handling maintenance and minor repairs of the system components, including solar panels, water treatment units, generators, batteries, and cooking kits.
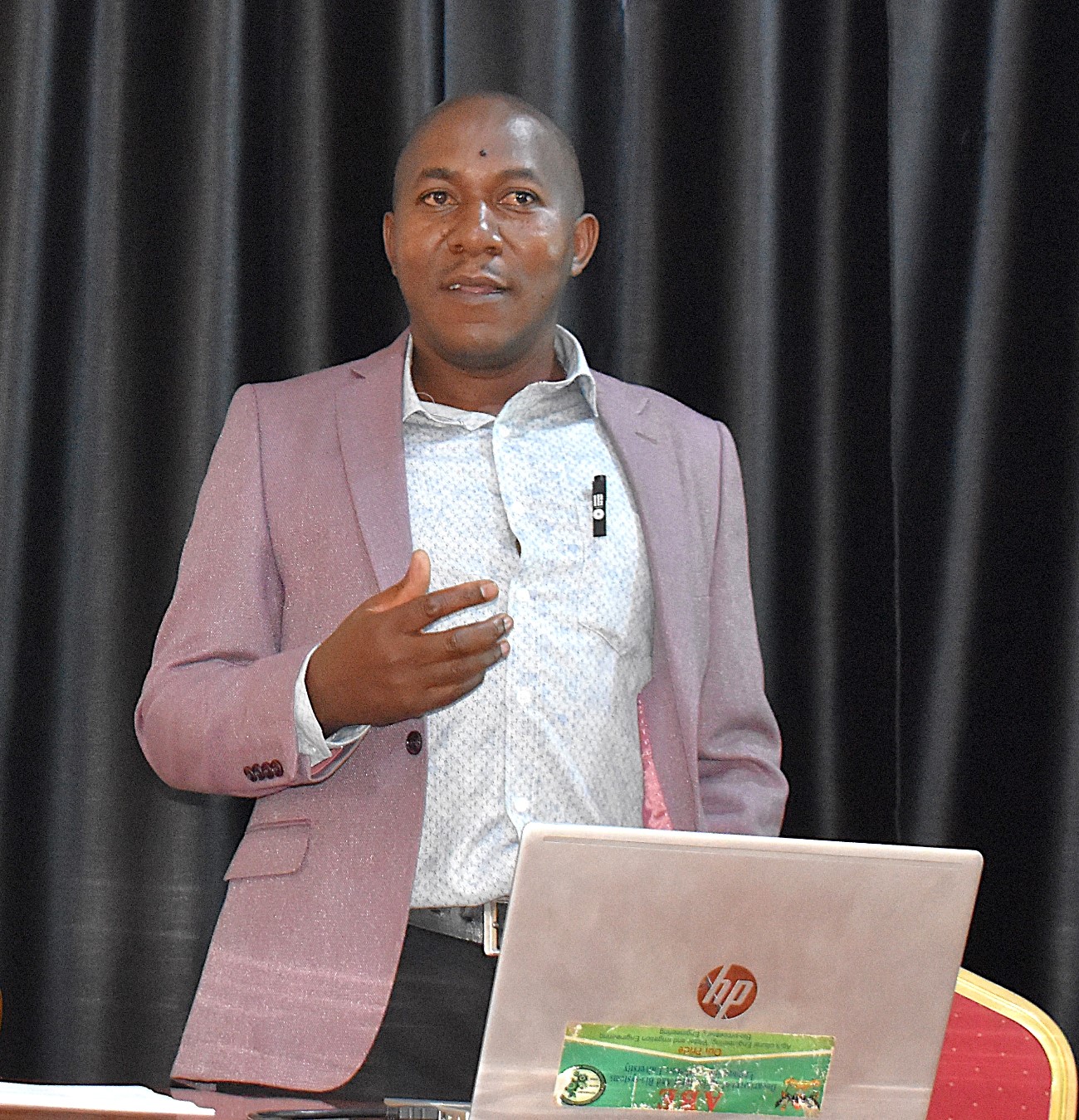

From June 23 to 27, 2025, Makerere University hosted a comprehensive Training of Trainers workshop. The training programme encompassed a diverse range of topics delivered by subject matter experts from institutions, including Makerere University (Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering – CAES, and the College of Engineering, Design, Art and Technology – CEDAT), Hochschule University of Applied Sciences, and Busitema University. Participants were carefully selected from diverse professional backgrounds, including recent engineering graduates from CAES and CEDAT, Makerere University, University technical staff, personnel from Kyambogo University, officials from Buvuma District Works and Health Departments, and electricians from Kampala City. The training sessions were conducted at Makerere University and Buvuma Health Centre IV Hospital.
Training Modules Included:
- Sustainable energy systems and their practical applications
- Energy generation and storage technologies
- Solar water heating: design, operation, maintenance, and performance optimization of solar water heaters, crop dryers, and concentrating solar heaters
- Solar PV technologies in Uganda: cell technology, system design, operations, maintenance, and hands-on practicals for standalone and grid-connected systems
- Public health implications of water quality
- Water treatment and quality management, including protocols, parameters, and case study on the MCDI treatment system
- Water quality testing methodologies
- Introduction to sustainable refrigeration and cooling technologies
- Environmental impact and safety considerations for refrigerants
- Refrigeration cycles and component overview
- Life cycle assessment of SophiA technologies
- Thermal energy storage within the SophiA system
- Steam as a productive energy source
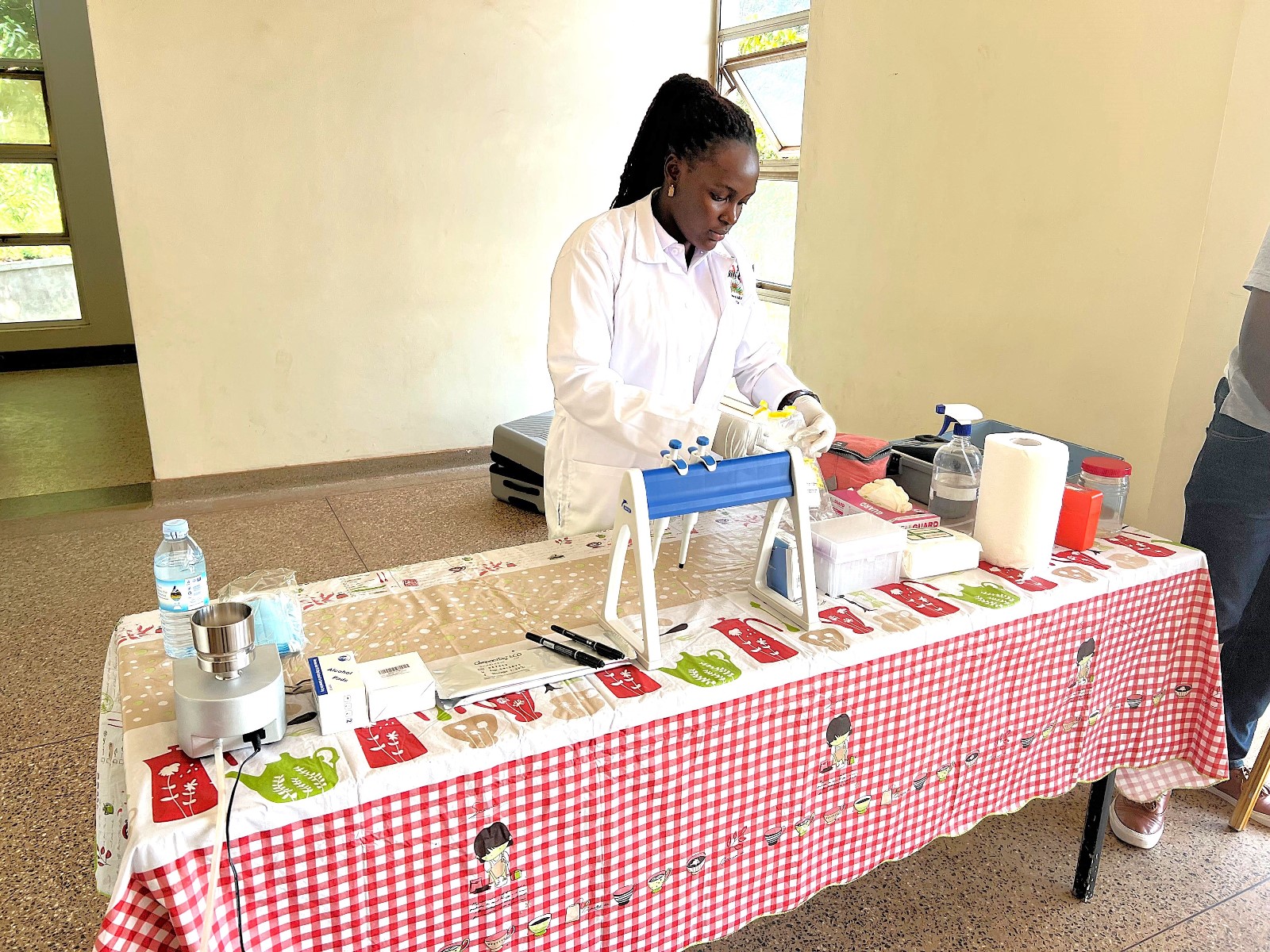

The Training Sessions
Day One: Introduction to foundational concepts in solar energy technologies
The first day of the SophiA Train the Trainers Workshop focused on building foundational knowledge in sustainable and solar energy systems. Led by Dr. Peter Tumutegyereize and Dr. Francis Mujjuni, participants explored a range of technologies and applications critical to clean energy deployment.
Key topics included:
Sustainable Energy Systems: Introduction to renewable energy systems including bioenergy, hydro, wind, geothermal, hydrogen fuel cells, and battery storage.
Solar Radiation & Geometry: Understanding solar constants, irradiance, and the impact of atmospheric conditions on solar performance.
Solar Thermal Technologies: Detailed look at solar water heating systems (FPCs and ETCs), maintenance, sizing, and solar dryers for agricultural and industrial use.
Photovoltaic (PV) Systems: Working principles, types of PV cells, performance factors, and diagnostics. Practical testing techniques and metrics like Voc, Isc, MPP, and PR were discussed.
Simulation & Application: Olivia Nakiwanuka demonstrated a PVsyst-based simulation of a 2.55 kWp standalone system for a conference hall, showing a high solar fraction (97.88%) and low LCOE (USD 0.03/kWh).

The sessions emphasized practical skills, performance analysis, and real-world application, equipping participants to train others and support solar adoption, especially in rural and off-grid settings.
Day Two: Water Treatment Technologies
The second day focused on water treatment technologies relevant to low-resource healthcare settings. Facilitated by Sneha De and Mr. Duc Dinh Ngoc from Hochschule Karlsruhe University, sessions covered technical, environmental, and operational challenges, with contributions from Dr. Joshua Wanyama on water quality management and Dr. Prossie Nakawuka on practical water testing.
Key challenges addressed included unreliable water supply and contamination in healthcare facilities, emphasizing the need for decentralized water treatment, especially in rural areas.
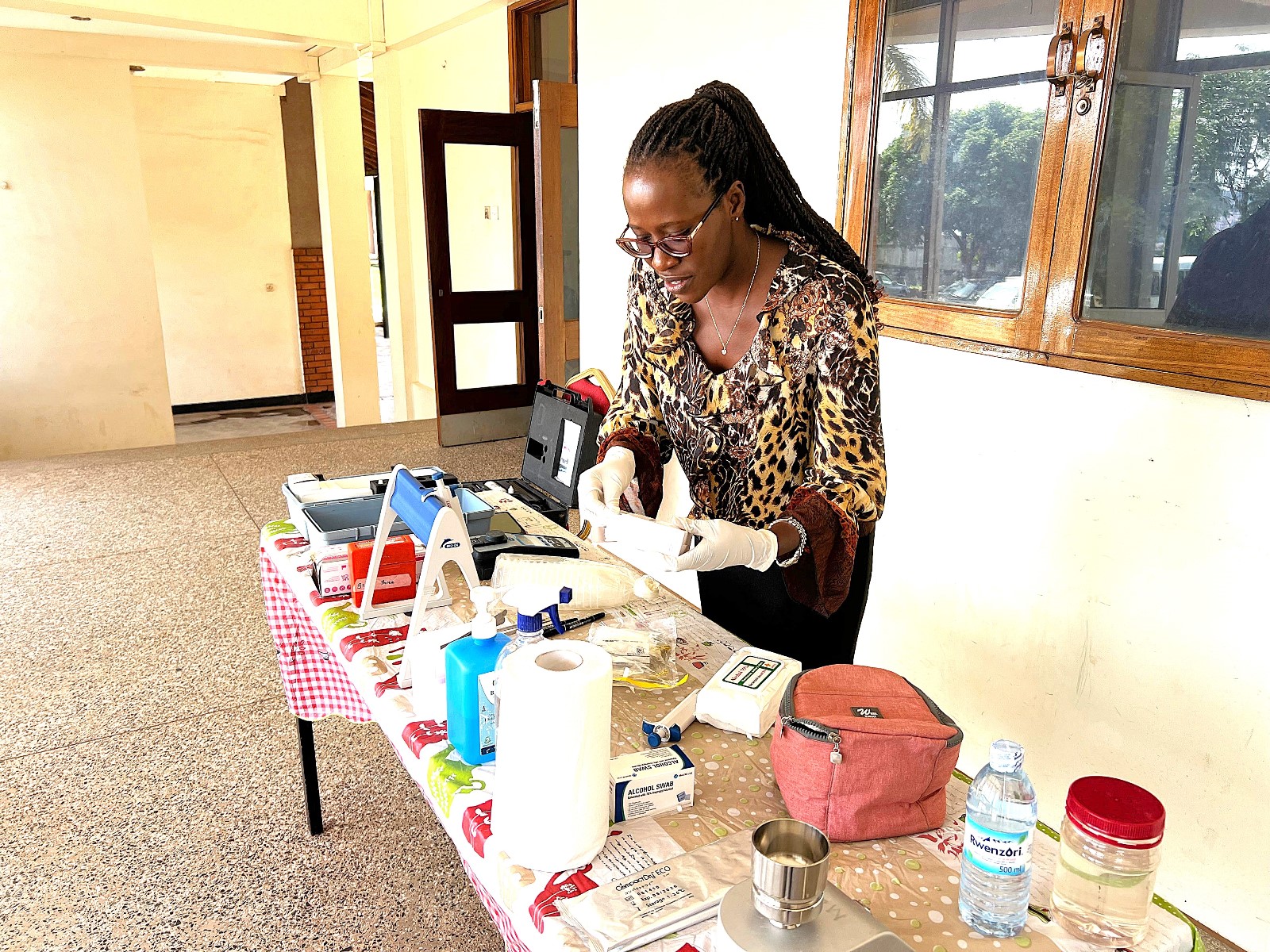

Sneha De reviewed biological and physical/chemical water treatment methods, highlighting technologies such as activated sludge, filtration, membrane bioreactors, and advanced disinfection techniques. The SophiA modular water treatment system, integrating ultrafiltration and membrane capacitive deionisation (MCDI), was introduced as a scalable solution for producing safe drinking and deionised water for medical use.
Mr. Duc Dinh Ngoc trained participants on the MCDI technology, an energy-efficient method for salt and fluoride removal suitable for low-salinity water.

Dr. Joshua Wanyama discussed the water quality management protocols, outlining key physical, chemical, and biological water parameters and monitoring strategies, including modern IoT-based tools, to ensure water safety and public health.
The day concluded with a hands-on lab session by Dr. Prossie Nakawuka, where participants practiced water quality testing using turbidimeters, incubators, and filtration techniques.
Overall, Day Two combined theoretical insights, technology demonstrations, and practical skills, preparing participants to implement sustainable water treatment and quality management systems in healthcare environments.

Day Three: Refrigeration and Cold Storage
The third day of the SophiA workshop focused on sustainable refrigeration and cold storage technologies tailored for healthcare in Sub-Saharan Africa. Experts discussed energy-efficient, climate-friendly cooling solutions vital for vaccine storage, medicines, and diagnostics, especially in off-grid and rural settings.
Key highlights included the introduction of solar-powered and biomass-based refrigeration systems, thermal energy storage methods, and the use of natural refrigerants like propane, ammonia, and CO₂ as environmentally safer alternatives. Presentations emphasized the critical role of refrigeration in healthcare and the urgent need to replace harmful chemicals with sustainable technologies.
Sessions covered real-world applications such as the SophiA cooling containers in Burkina Faso, safety protocols for flammable refrigerants, and the environmental and economic benefits of solar refrigeration systems assessed through life cycle analysis.

The day ended with an interactive quiz and discussion, reinforcing learning and encouraging participants to apply sustainable cooling practices in their communities.
Day Four: World Refrigeration Day & Field Visit to Buvuma Island
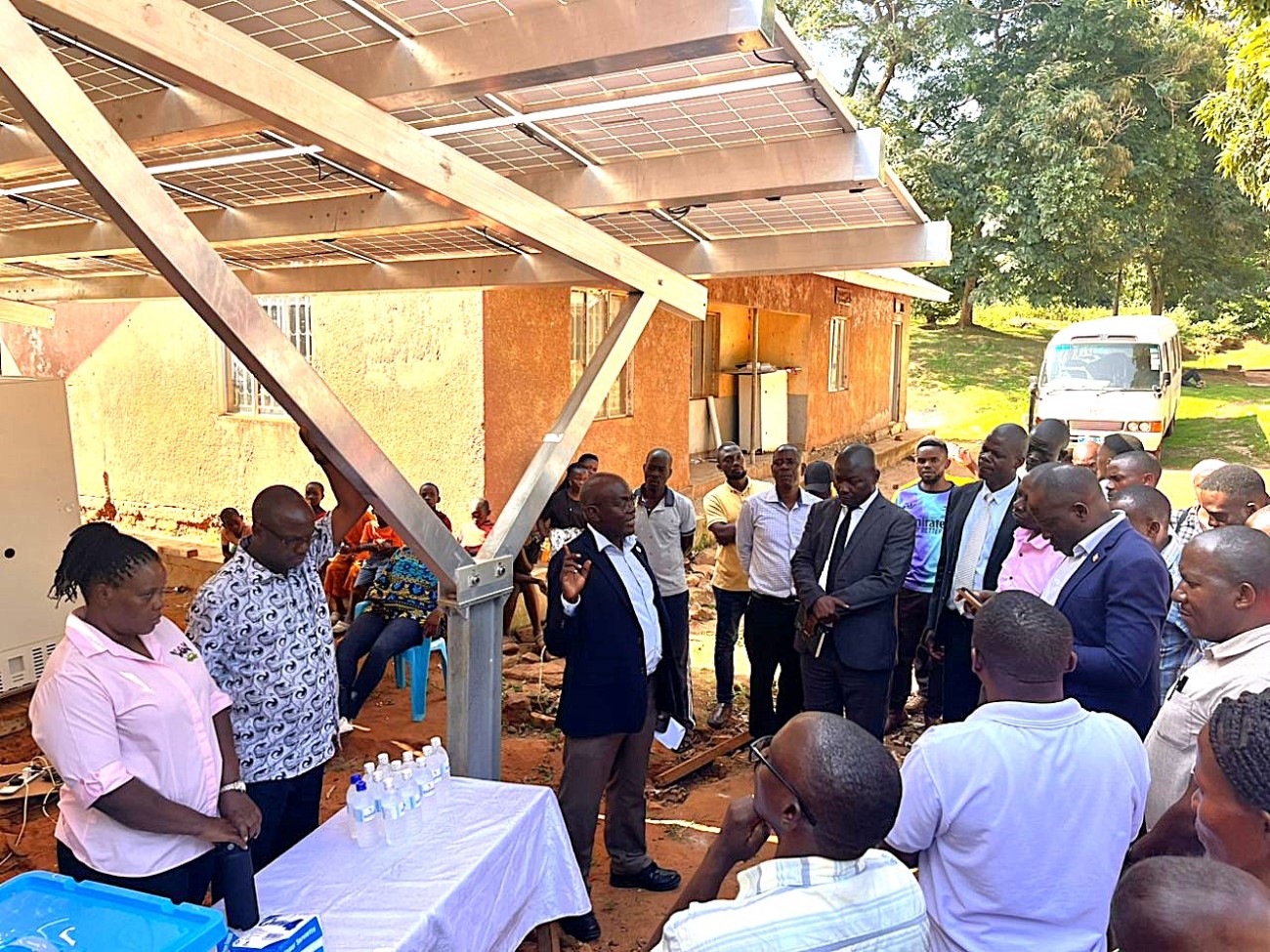
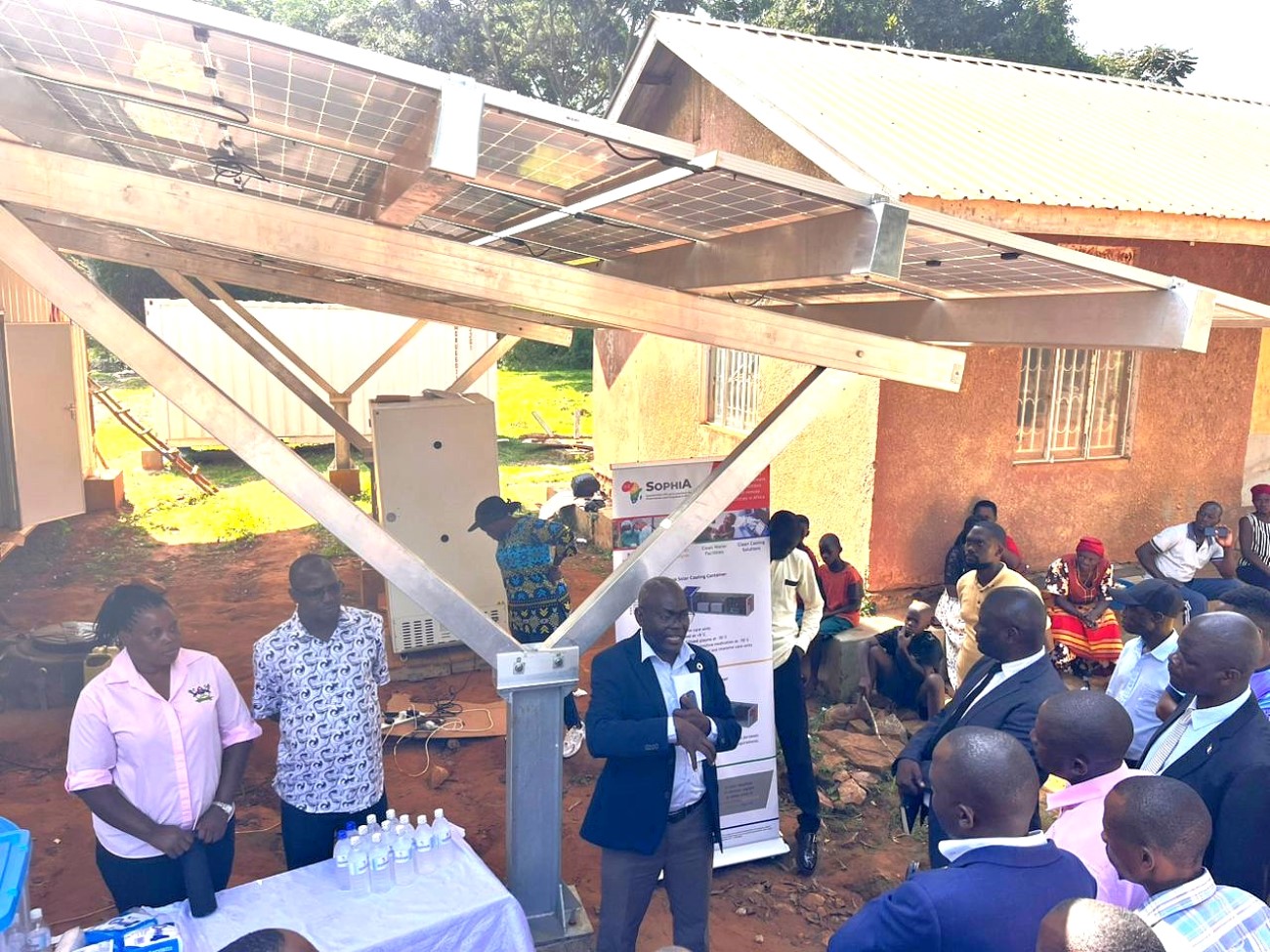
The fourth day of the SophiA Train the Trainers workshop was dedicated to the celebration of the World Refrigeration Day and a field excursion to Buvuma Island, providing participants with a unique opportunity to witness the SophiA system in action. The day was coordinated by Dr. Sarah Bimbona and Dr. Nicholas Kiggundu, who led the delegation to Buvuma Health Centre IV, the pilot site for the SophiA installation in Uganda.

The visit served as both a practical extension of the previous day’s technical sessions and a community engagement event. Participants were able to observe the installed SophiA system, which integrates solar-powered refrigeration, water treatment and steam generation technologies designed for off-grid healthcare settings. During the visit, Dr. Kiggundu provided a detailed briefing to local stakeholders, including representatives from the Buvuma District Local Government, delegates from the Buganda Kingdom, and members of the local community. He explained how the SophiA system will enhance healthcare delivery on the island through reliable cold storage for vaccines and medicines, access to clean drinking water, and steam generated for cooking and use in the maternity wards.
As part of the long-term sustainability plan for the SophiA system, the launch of SophiA Water was announced, an entrepreneurial initiative designed to generate revenue locally for the operation and maintenance of the system.
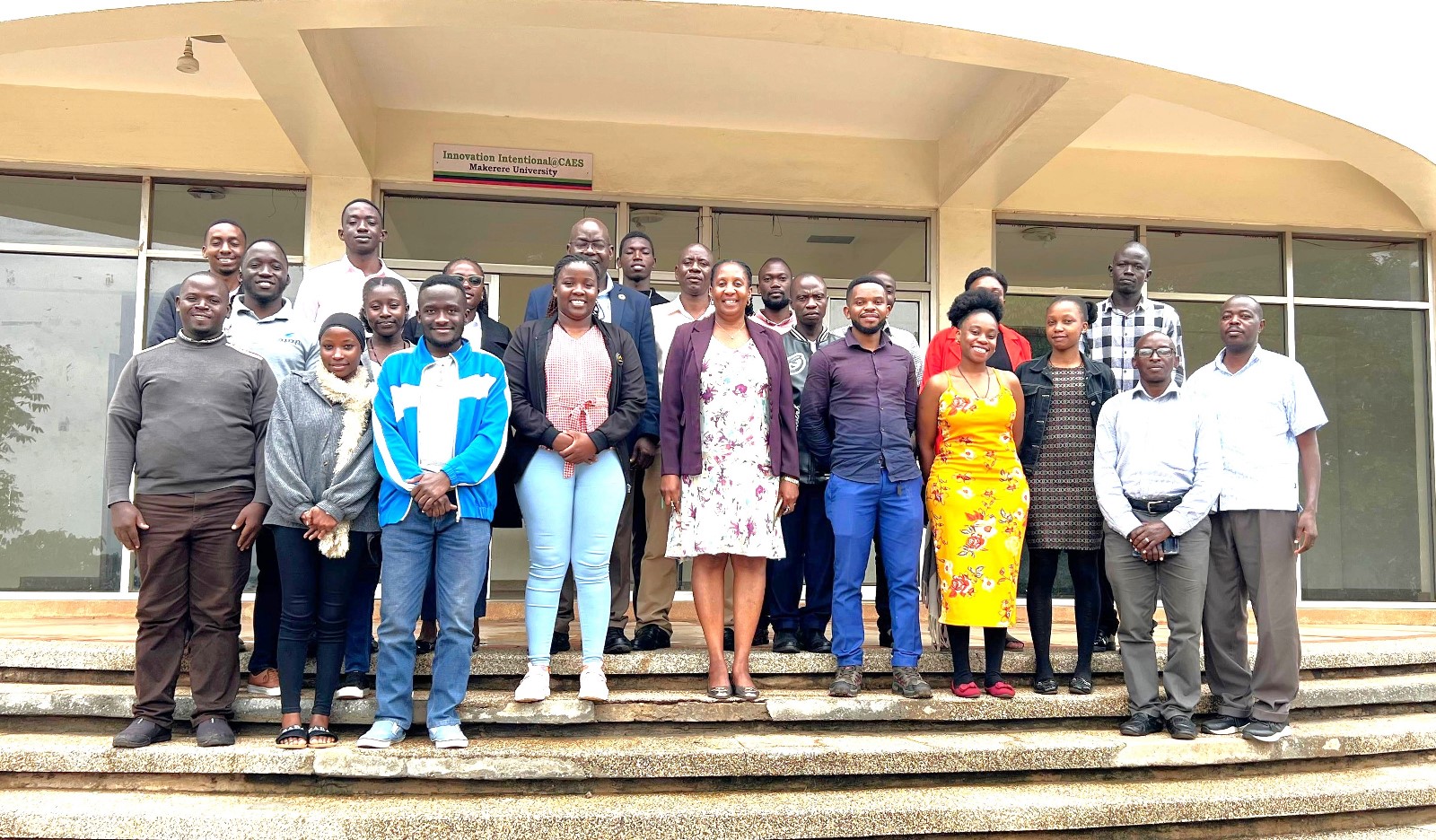

The field trip ended with a certificate awarding ceremony in appreciation of the participants’ dedication and active engagement throughout the training programme.
You may like
-


Meet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-


Makerere University School of Public Health Graduates First Cohort of Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Short Course
-


Climate variability found to shape malaria trends in Yumbe District
-


Mak hosts First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling
-


Uganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-


Makerere University Researchers Release New Soybean Variety, MakSoy 7N
Agriculture & Environment
Mak hosts First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling
Published
4 days agoon
February 20, 2026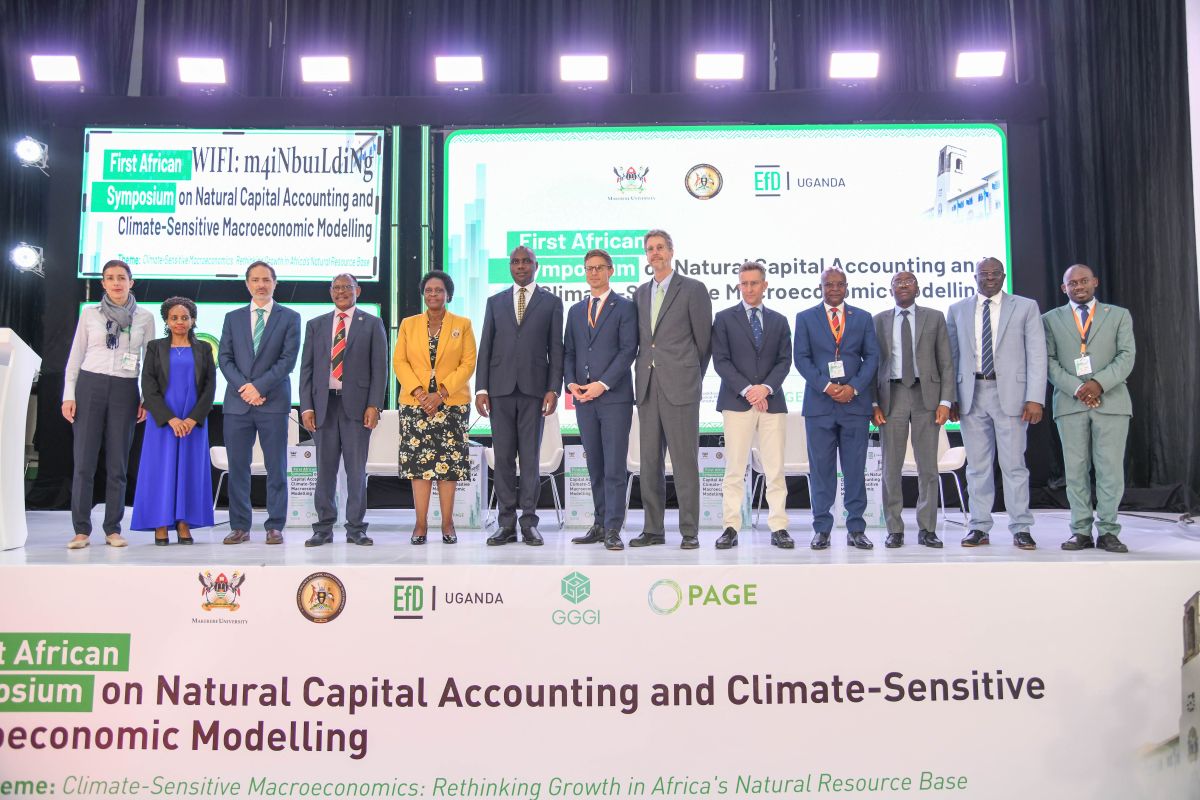
African economies are increasingly exposed to climate-related shocks that threaten development gains, fiscal sustainability, and macroeconomic stability. From extreme weather events and biodiversity loss to the depletion of natural capital, climate risks are reshaping economic realities across the continent. Yet many macroeconomic frameworks used in public finance and planning continue to overlook climate and nature-related risks and the long-term benefits of resilience and adaptation investments.
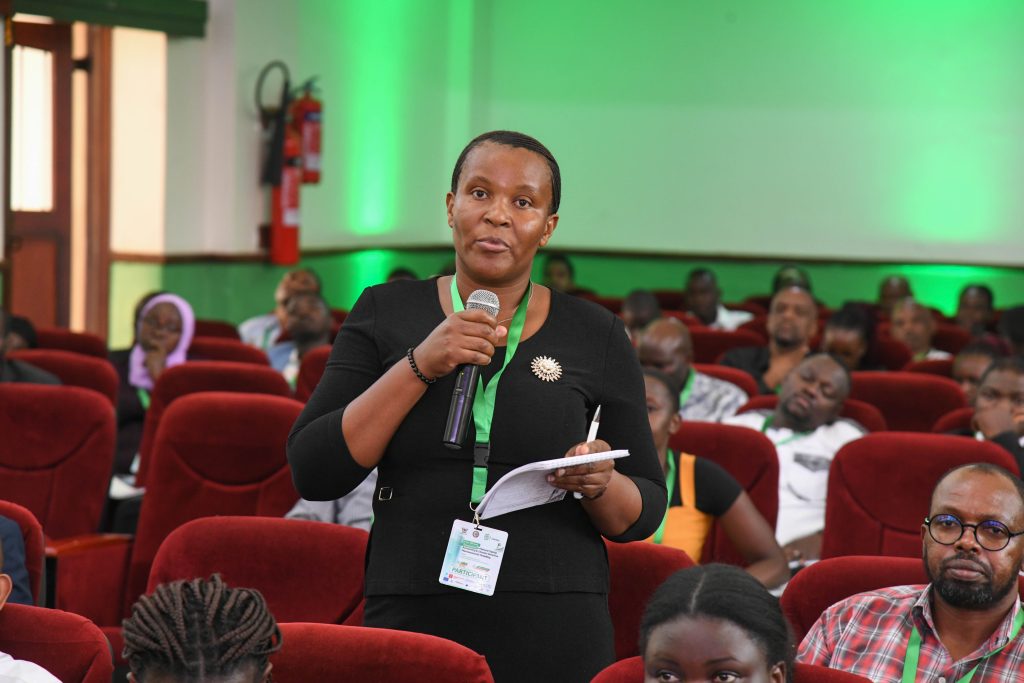
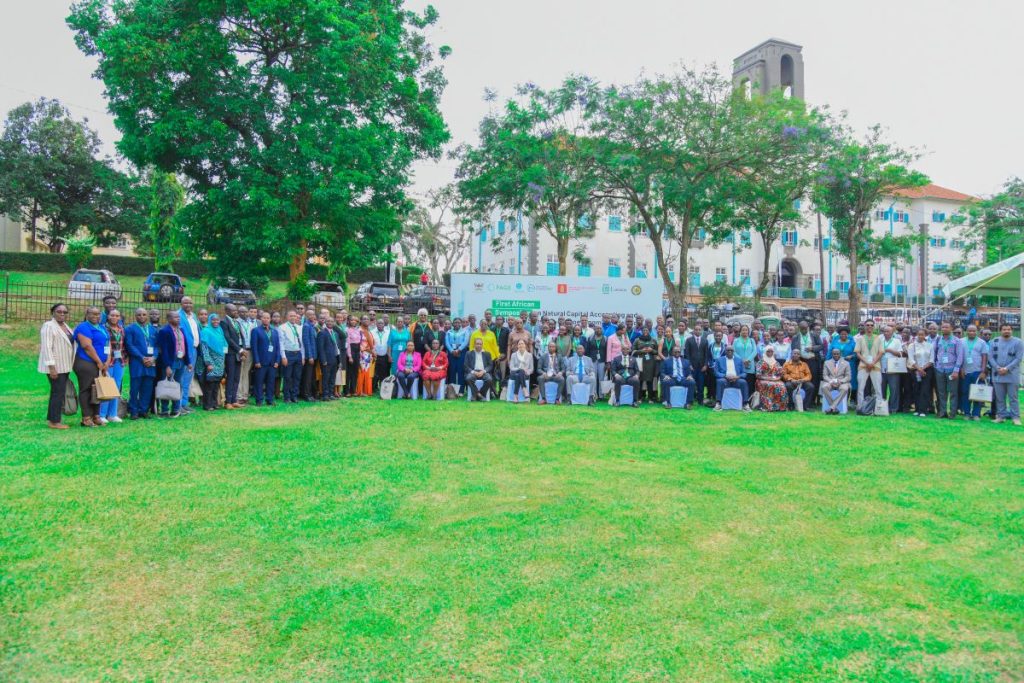
To address this emerging reality, over 250 participants from Africa, Europe and beyond, convened at Makerere University – Kampala, on the 12th and 13th of February 2026, to participate in the First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling.
Following the theme, “Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomics: Rethinking Growth in Africa’s Natural Resource Base, the hybrid symposium organized by Makerere University through the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling (CEACM) within the School of Economics, under the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS), the Environment for Development Initiative (EfD), and the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development (MoFPED) in Uganda, brought onboard ministers, leading economists and planners, researchers, policy makers, the academia, development partners, climate change experts and the media.
The Symposium being the first of its kind on the continent, reflected Africa’s growing determination to work collectively in confronting shared development challenges, building on recent momentum such as the formation of Pan-African Finance Ministers Forum for Climate Action (PAFMCA).
Featuring speeches and presentations from notable speakers and partners, a keynote address on Natura Capital Accounting and Climate Change Nexus in Africa and their impact on Fiscal Policy, panel discussions, expert opinions, and exhibition kiosks (World Café), the symposium presented a platform to strengthen Africa’s analytical and institutional capacity to integrate climate and natural capital considerations into macroeconomic and fiscal policy.
Vice Chancellor underscores the role of universities
Welcoming the delegates to Makerere University, the Vice Chancellor-Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe emphasized that universities must lead innovation and collaborative research efforts to support collective climate change mitigation across the continent.
In the same vein, he advocated for strong collaboration between universities in Africa and government Ministries. “Makerere’s collaboration with the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, stands as a shining example of how academia and government can strengthen economic management,” he said.
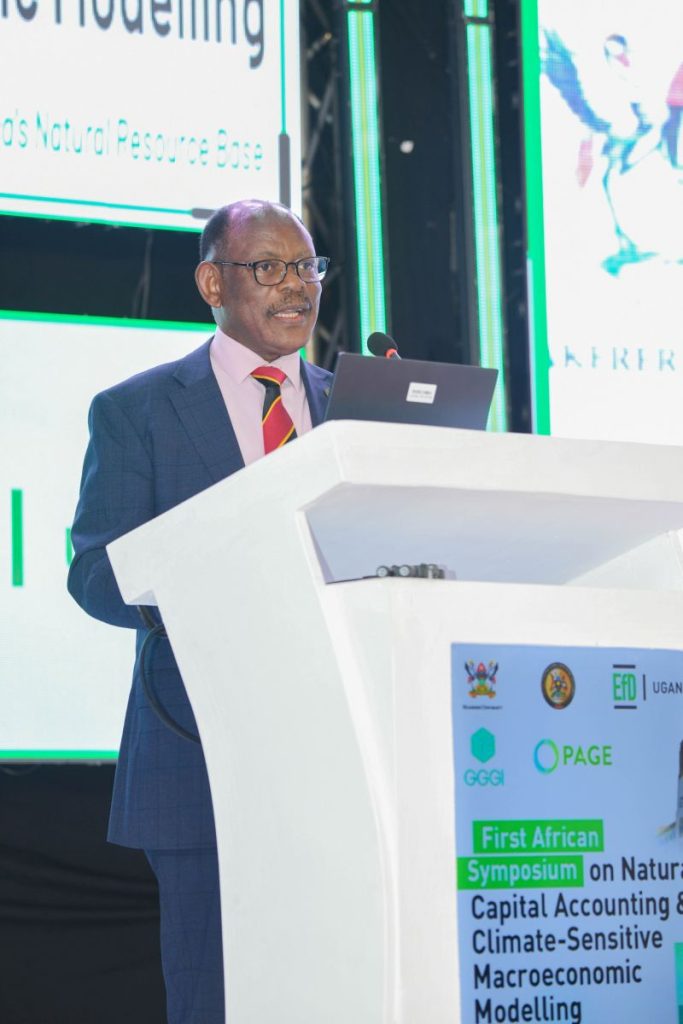

Prof. Nawangwe revealed that the collaboration between Makerere University and the Ministry, has strengthened macroeconomic modelling, fiscal policy analysis, and technical capacity within government. In addition, the partnership led to the establishment of the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling, bridging academic scholarship with real-world policy application.
“We have jointly established the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling. The Centre (established in August 2025) is anchored within the School of Economics in the Department of Policy and Development Economics, under the Master of Science in Economic Policy and Investment Modelling, a program jointly facilitated by Makerere University, the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development and the Bank of Uganda,” he mentioned.
Climate and Economic transformation are inseparable
The Vice Chancellor highlighted the critical intersection between economic transformation and environmental sustainability, noting that economies in Africa, heavily dependent on natural resources, face unprecedented pressures from climate shocks, biodiversity loss, and environmental degradation. Convinced that economic growth cannot be pursued in isolation from climate and environmental realities, he stressed the importance of integrating natural capital accounting and climate considerations into national development strategies.
Prof. Nawangwe advocated for shared responsibility of universities, research institutions, and policymakers to develop innovative analytical tools, responsive policy frameworks, and strong institutional capacities that promote sustainable growth while safeguarding environmental assets for future generations.
The Vice Chancellor commended UN PAGE and the Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI) for funding the symposium, as well as, other stakeholders namely the European Union and the Coalition of Finance Ministers for Climate Action (CoFMCA), Ministry of Water and Environment (MoWE), National Planning Authority (NPA), Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS), the National Environment Management Authority (NEMA) for being reliable partners.
Integrating Climate into Fiscal Policy
During the opening ceremony, the Minister of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, Hon. Matia Kasaija underscored the urgency of embedding climate considerations into economic planning.
“As Ministers of Finance, we are often confronted with difficult trade-offs. Our task is to balance the needs of today with sustainability for future generations,” said Hon. Kasaija, in a speech read by Hon. Henry Musasizi, the Minister of State for Finance (General Duties).
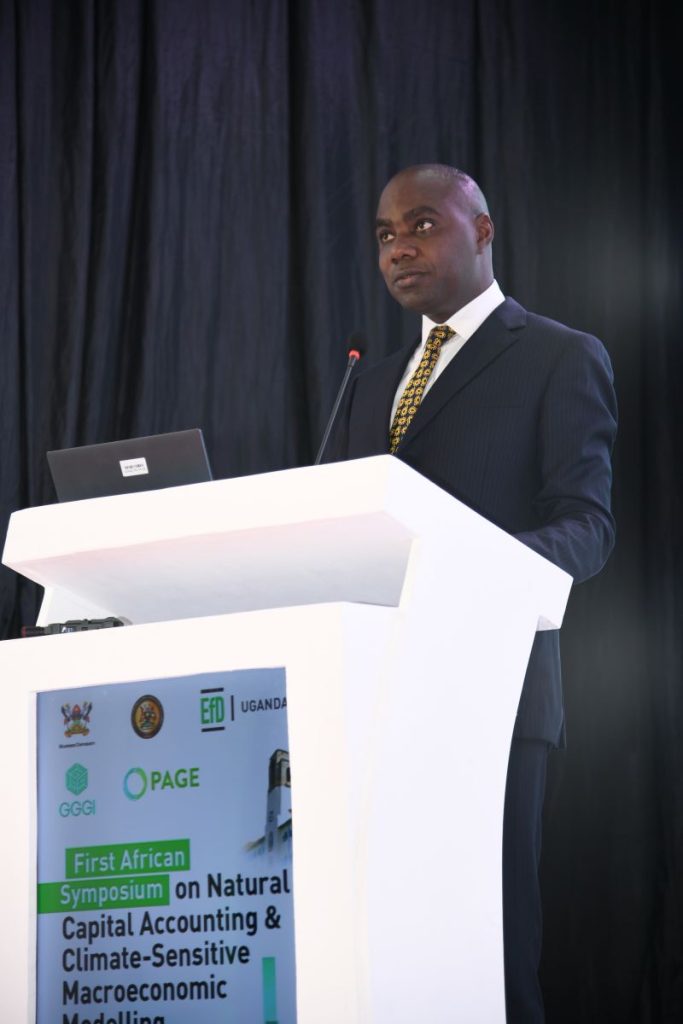

The Minister guided that traditional macroeconomic models focusing only on growth, inflation, and fiscal balance are inadequate in an era of climate shocks. He affirmed that African economies are facing interconnected challenges which directly impact economic growth. He stressed that traditional macroeconomic frameworks must evolve to systematically incorporate environmental degradation and climate shocks, whose consequences can no longer be ignored in policy analysis.
“For countries such as Uganda, whose development prospects are closely linked to natural resources and the climate-sensitive sectors, these challenges are not abstract. They affect livelihoods, public finances and long-term economic resilience,” he mentioned.
The Minister emphasized that natural capital accounting and climate-sensitive macroeconomic modelling are vital for valuing natural assets, assessing environmental costs, and guiding sound investment decisions.
Protecting Africa’s Natural Capital
Hon. Beatrice Atim Anywar, Minister of State for Environment, emphasized the urgent need to protect Africa’s ecosystems. “Africa stands at a defining crossroads. Our economies remain anchored in natural capital—forests, water resources, biodiversity, land, and ecosystems—which sustain life, generate fiscal revenue, and underpin development,” she said.
She warned that climate-related shocks are already undermining growth and public investment. “Floods, droughts, land degradation, biodiversity loss, and water stress are no longer distant risks. They are present realities, already affecting productivity and macroeconomic stability,” she said.
She emphasized the need for improved economic models that account for environmental and climate risks: “Traditional macroeconomic frameworks have not adequately captured climate risks or the long-term economic benefits of resilience and adaptation. This limits our ability to make informed policy decisions as Africa pursues economic transformation, energy security, and fiscal stability,” she stated.
Hon. Anywar highlighted collaboration with GIZ, Makerere University, and government ministries, which led to the development of the MONCAP (Model for Natural Capital Policy Assessment). “This tool is being used to assess natural capital assets for climate change, energy transition, and their linkages to the macroeconomy. It supports budgeting by estimating the cost of depleted natural capital assets,” she said.
“Water security, forest conservation, ecosystem restoration, and climate adaptation are not costs. They are investments in Uganda’s long-term economic stability, productivity, and prosperity.”
Stakeholders urged to transform climate threats into opportunities
Adam Sparre Spliid, the Deputy Head of Mission, Danish Embassy said: “Integrating climate risk and natural capital into our macroeconomics frameworks is not only academic exercise, it is a massive de-risking strategy for private investment. By bridging the gap between government policy and planning, academia and research, and the private markets, we transform climate threats into tangible opportunities.”
Sustainability includes youth, jobs and human well-being
Dr. Steven Stone, Chair of the UN PAGE Management Board, emphasized that sustainability extends beyond the environment to encompass youth, jobs, economic growth, and human well-being. “While the environment is Africa’s foundational source of wealth, sustainable development requires balancing ecological stewardship with economic progress, including income and employment for the youth which are critical priorities for countries such as Uganda.”
Dr. Stone highlighted that UN PAGE, originating from the Rio+20 Conference, supports climate-sensitive economic policy in Africa, emphasizing that dialogue, scenario-building, cross-sector collaboration, and strong partnerships are key to advancing sustainable, inclusive, and climate-resilient development.
Africa’s Wealth Declining
In the keynote address titled, Natural Capital Accounting and Climate Change Nexus in Africa and their Impact on Fiscal Policy, Paul Jonathan Martin, Manager of Environmental Operations at the World Bank for Eastern and Southern Africa, and a specialist with over 30 years in climate and natural resources, warned that Africa’s overall wealth is under threat due to declining renewable natural capital.
“Produced capital has increased by 20%, human capital by a third, but renewable capital has declined by 30%,” Martin said. “When combined, Africa’s overall wealth trajectory has been weakening since 2010.”
He stressed that natural resources must be treated as economic assets requiring systematic accounting: “Africa’s rich natural resources are fundamental for sustainable development,” he said.
Citing examples from Ethiopia and Kenya, he highlighted successful integration of natural capital into public investment and budget decisions. “In Ethiopia, there are payments for ecosystems and investment prioritization tools. In Kenya, natural capital accounting integration into budgets has strengthened public investments. Climate change has deep, cascading effects across sectors, but Africa has major potential to lead climate solutions,” he said.

Martin also highlighted the economic benefits of climate adaptation: “From 2020–2050, the cumulative effect of adaptation on Uganda’s GDP is positive. Without action, under a dry/hot climate future, GDP could significantly deviate from projected growth paths.”
Drawing on insights from over 70 country climate and development reports produced by the World Bank, the keynote speaker highlighted the profound macroeconomic impacts of climate change across Africa. He stressed the importance of integrating climate and natural capital into macroeconomic planning. He noted that Africa’s forests, water systems, and biodiversity are vital for sustainable development but face growing threats from climate change, environmental degradation, and climate-related disasters that undermine productivity, public investment, and economic stability.
He observed that traditional macroeconomic models often fail to capture the value of natural assets and regulating ecosystem services, which are critical to both economic stability and resilience but are largely excluded from GDP calculations.
Africa-Led Solutions
Prof. Edward Bbaale, Principal, College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS), stressed the importance of developing African-led solutions. “We need to champion the Africa-led model. We need approaches that fit our unique context. Africa is not here to take in other frameworks blindly,” he said.
By supporting research, training, policy dialogue and modelling innovation, the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling (CEACM) positions Makerere University as a regional hub for advancing climate-sensitive macroeconomic policy across Africa.
He highlighted CEACM’s capacity-building programs: “Our goal is to ensure African Ministries of Finance have home-grown expertise to integrate climate and natural capital considerations into fiscal and macroeconomic policy. This is critical for long-term resilience and sustainable development,” he said.
The Principal explained that establishment of independent research centres enables Makerere University to go beyond traditional academic instruction and focus deeply on societal challenges, particularly those related to climate change, environmental degradation, and biodiversity loss.

He reported that the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling is structured to advance methodological innovation, develop new data systems, and strengthen climate-sensitive macroeconomic tools that are tailored to the African context.
MONCAP Model for Policy Assessment
Dr. Peter Babyenda, a member of faculty at CoBAMS, demonstrated MONCAP (Model for Natural Capital Policy Assessment), which integrates climate and natural capital variables into fiscal and macroeconomic planning.
“MONCAP allows policymakers to estimate the economic cost of depleting natural assets such as forests, wetlands, and water resources. It helps simulate policy options and determine how investments in natural capital yield long-term benefits,” Babyenda said. “We came up with this model to aid the Ministry of Water and Environment. This model is open—you can extend it,” he added.

He highlighted capacity-building initiatives, including short courses and the Master of Science in Macroeconomic and Investment Modelling, designed to train economists to incorporate natural capital and climate into policy planning.
International Perspectives
Sweetman Liam, Ireland’s Finance Minister, highlighted the economic value of ecosystems: “There is a deeper value of landscapes in flood prevention and biodiversity. Decision-making was informed, and people started understanding economic value,” he said.
Prof. Chukwuone Nnaemeka of the University of Nigeria emphasized collaboration with national statistical agencies: “We coordinate with the National Bureau of Statistics to develop natural capital accounting metrics. Increase the use of Natural Capital Accounting in decision-making,” he stated.
Technical and Parallel Sessions
The afternoon session featured three parallel sessions focusing on Natural Capital Accounting Methodologies and Best Practices, Climate-Sensitive Fiscal and Economic Modelling, and Natural Capital Accounting and Model Uptake and Use.
Drawing on diverse expertise, the panels highlighted innovative approaches and demonstrated that natural capital is not an environmental afterthought, but a central pillar of sustainable economic and policy planning.
The first day of the African Symposium drew to a close with interactive exhibitions at the World Café, where case studies and practical demonstrations highlighted innovative approaches to integrating climate and natural capital into economic planning. Participants actively engaged in discussions and networking, forging collaborations that promise to advance climate-sensitive fiscal and development strategies across Africa, setting a strong and optimistic tone for the days ahead.
Agriculture & Environment
Uganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
Published
4 days agoon
February 20, 2026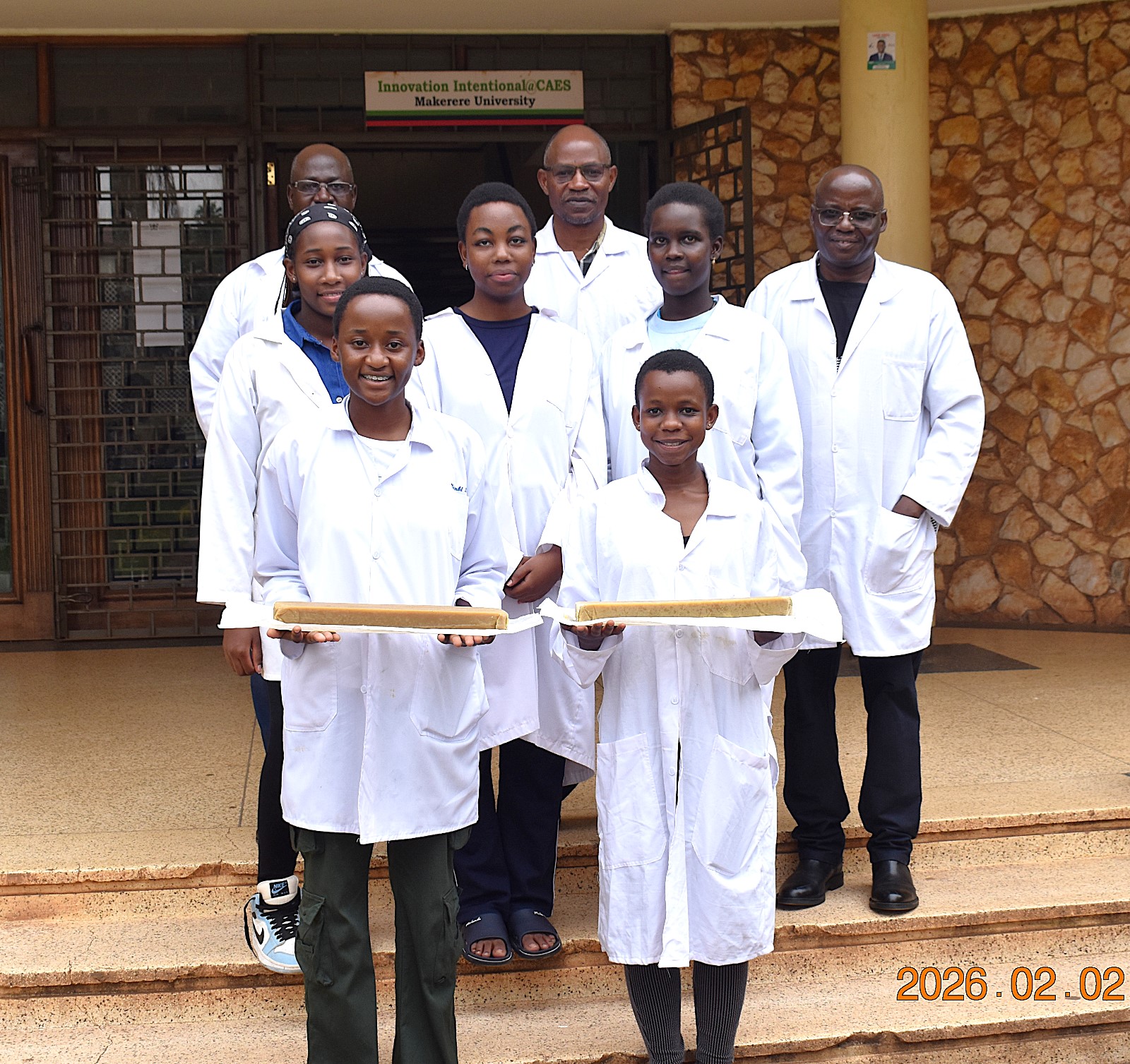
*****The students were supervised by researchers from the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES) at Makerere University, led by Prof. Fred Kabi.
The garbage challenge
With urbanization rates rising rapidly across Uganda, municipal solid garbage generation in the country’s cities is projected to increase by more than 40 percent by 2050. The growing burden of unmanaged garbage, particularly organic garbage, continues to pose environmental and public health risks, underscoring the urgent need for innovative and sustainable solutions.
It is against this backdrop that Senior Four students of Uganda Martyrs Secondary School Namugongo undertook a project to demonstrate how local market garbage challenges can be transformed into opportunities for sustainable development.
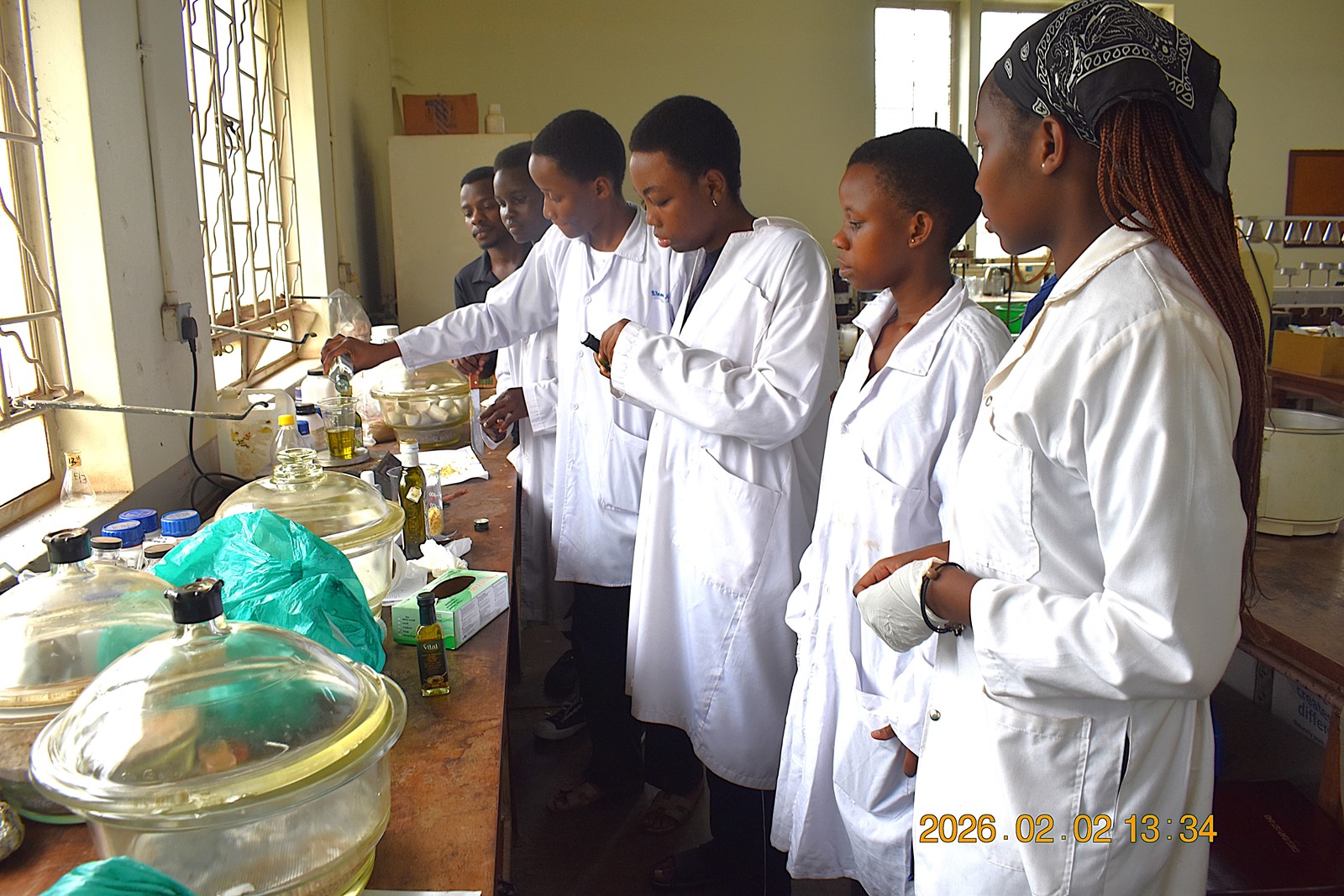

Addressing the garbage Challenge
As part of their academic project under the competence-based curriculum, the students were tasked with identifying real-world challenges within their communities and developing practical solutions using locally available resources. Through research and field observations, they identified poor garbage management, particularly the accumulation of organic waste at major dumping sites such as Kiteezi Landfill, as a critical issue.
At these sites, unsorted solid garbage often accumulates uncontrollably, sometimes leading to collapses that pose serious environmental and public health risks including water contamination by leachates, persistent foul odors, and disease outbreaks.
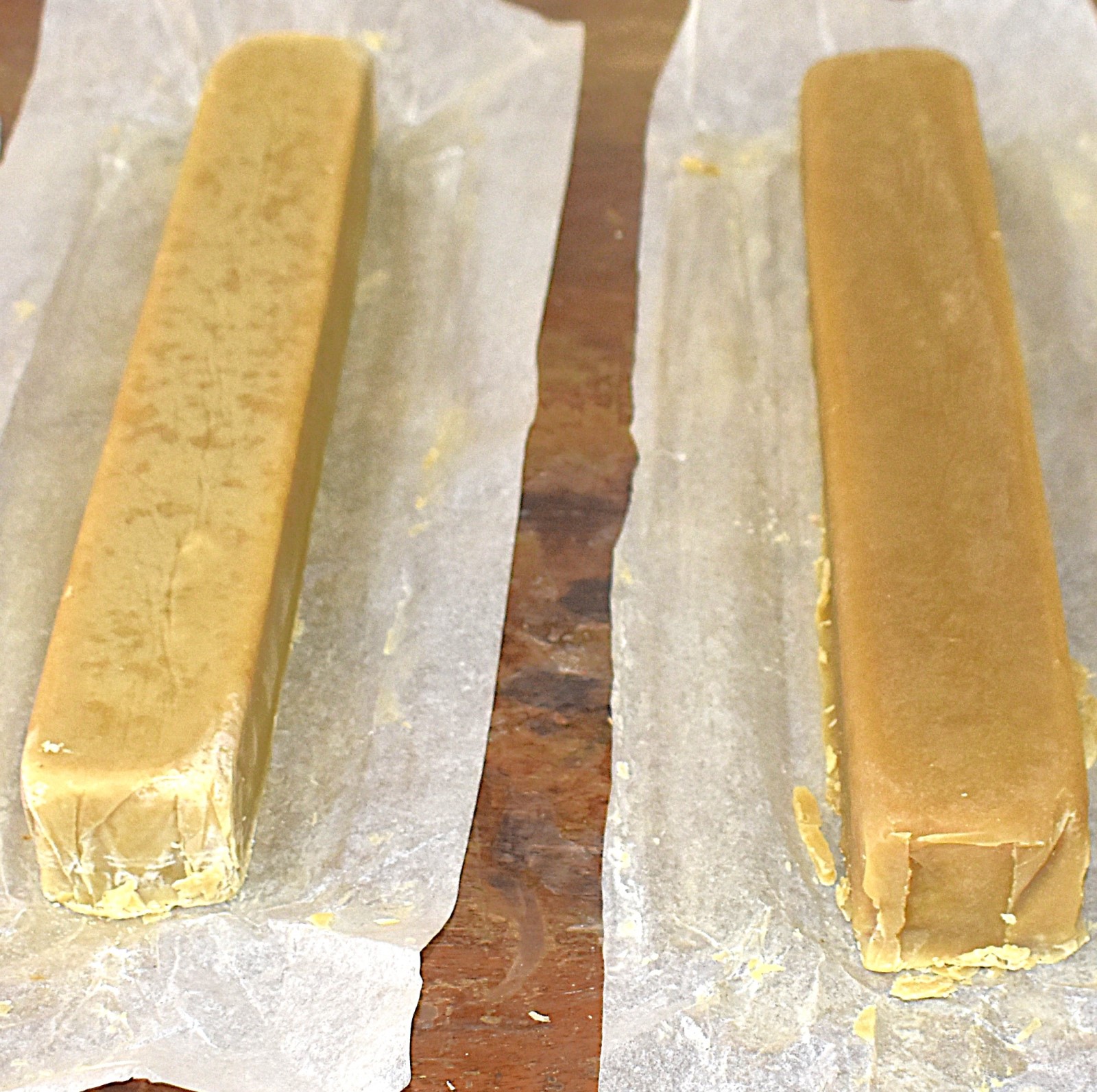

Rather than solely viewing solid market garbage as a problem, the students recognized its untapped potential within the biodegradable fraction of market garbage streams. Their innovative solution was to convert organic solid market waste (biodegradable garbage) into an industrial raw material for soap production by utilizing saprophagous Black Soldier Fly larvae (BSFL) to accumulate lipids and applying the scientific process of saponification.
Makerere University Support to the project
The students’ project was supervised by Prof. Fred Kabi together with technicians from the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES) at Makerere University. Prof. Kabi and his team have been actively researching on Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) as a bio-waste management technology capable of converting biodegradable solid municipal garbage and farm waste into valuable by-products such as organic fertilizers, animal feeds, soap, and biodiesel.
Working in collaboration with Ento Organic Farm Uganda Ltd, the researchers have demonstrated how insect-based waste conversion systems can support a circular economy by transforming biodegradable waste into industrial raw materials.
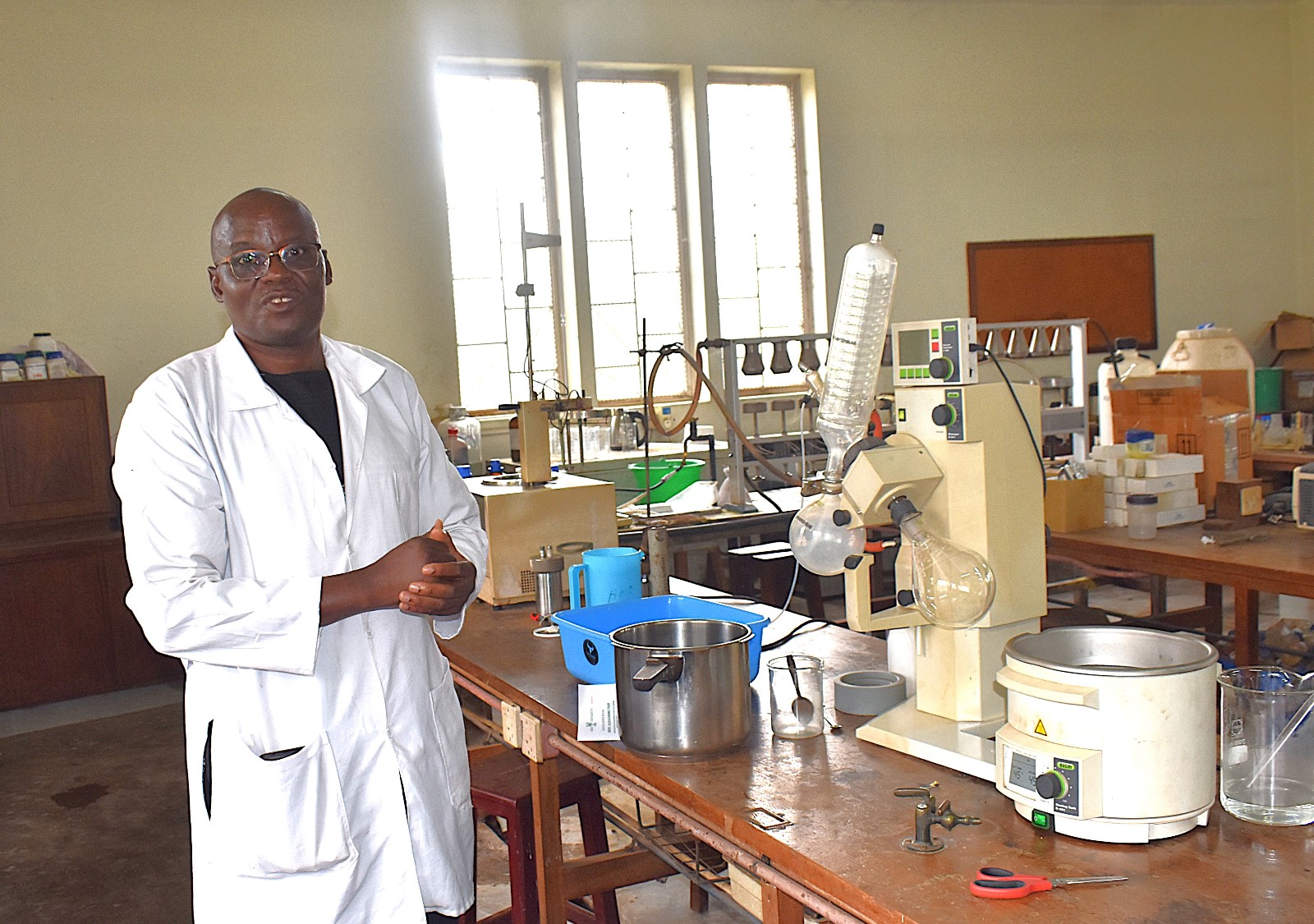

According to Prof. Kabi, the five young garbage entrepreneurs (students) began their project by collecting information on household garbage management practices. After analyzing the data, they engaged stakeholders along the garbage value chain to brainstorm all-inclusive, source-based waste management strategies.
“The students developed a solution that links efficient waste management at garbage generation source to support production of organic fertilizer, insect protein for animal feeds, and soap, which is only possible with biodegradable garbage,” Prof. Kabi explained. “This approach of the Competence Based Curriculum (CBC) for lower secondary schools supports the concept of taking Makerere University to the community of budding scientists while promoting sustainable community development through a circular economy.”
From Market Waste to Soap Bars
The Team leader, Ms. Ivy Stephanie Kitali explained the step-by-step scientific process behind the project. The students began by collecting organic waste from local markets, which was then shredded to prepare it for the larvae as a substrate. “Black Soldier Fly larvae were then introduced to the prepared waste. The larvae efficiently consumed the organic matter, greatly reducing its volume while accumulating lipids (fats) in their bodies. After maturation, we separated the larvae from the remaining waste, euthanized through blanching and dried it. Oil was then extracted from the dried larvae using ethanol as a solvent. This lipid-rich oil became the primary ingredient or raw material for soap production. To enhance the final product, the larvae oil was blended with minute quantity of sunflower oil before adding sodium hydroxide, initiating saponification, the chemical reaction that transforms fats and oils into soap,” she explained. The process ultimately yielded usable bars of soap derived entirely from what had once been discarded as unwanted market waste/garbage.

Building Skills and Sustainable Innovation
Beyond producing soap, the project provided students with hands-on training in scientific research, waste management techniques, bio-chemistry, and sustainable innovation. They gained practical exposure to insect-based biotechnology and learned how environmental challenges can be addressed through science-driven by entrepreneurship.
Agriculture & Environment
Makerere University Researchers Release New Soybean Variety, MakSoy 7N
Published
5 days agoon
February 19, 2026
The National Variety Release Committee (NVRC) has officially approved Maksoy 7N, the latest soybean variety developed by the Makerere University Centre for Soybean Improvement and Development (MAKCSID) in the Department of Crop Science and Horticulture, College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences at Makerere University. The approval was announced during the committee’s 47th meeting at the National Agricultural Research Laboratories (NARL) in Kawanda on 13th February 2026.
The NVRC, chaired by Dr. Joseph Kikafunda, is composed of stakeholders from the Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry, and Fisheries (MAAIF), research institutes, seed regulatory agencies, farmers’ organizations, and private seed companies. The committee evaluates new crop varieties for performance and traits before official release, helping to enhance national food security.
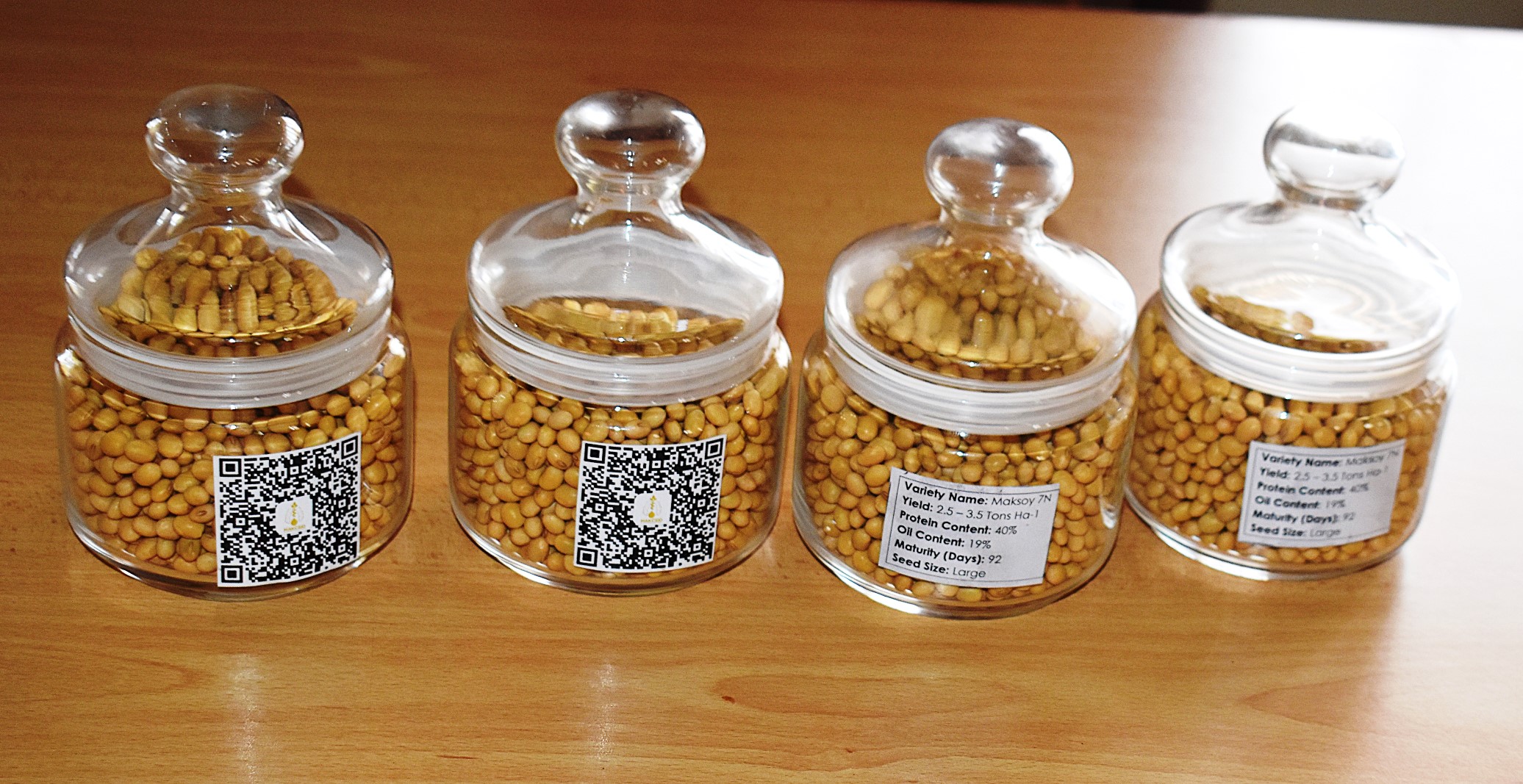

Rigorous Testing Confirms Superior Performance
MakSoy 7N, a cross between 6N and SG underwent extensive Distinctive, Uniformity, and Stability (DUS) testing across multiple seasons and locations in Uganda, including Kabanyolo (Wakiso), Nakabango (Jinja), Ngetta ZARDI (Lira), Abi ZARDI (Arua), Bulindi ZARDI (Hoima), and Mubuku Irrigation Scheme (Kasese).
The trials were conducted in accordance with the Seeds and Plant Act, Cap. 41 and the UPOV guidelines.
Results showed that the variety is clearly distinct from its closest reference, Maksoy 3N, in pod color, stem hair, and seed hilum, with uniformity meeting the 1% off-type standard, and stability confirmed across locations and seasons. On-farm trials were conducted to test performance under farmers’ management and to determine farmer preferences. Following these findings, the National Seed Certification Service (NSCS) recommended Maksoy 7N for release, providing farmers with a high-yielding and soybean rust-resistant variety.

Key Reasons Behind the Development of MakSoy 7N
Soybean plays a critical role in nutrition and income generation, offering 40% protein and 20% oil. It is used in human food, livestock feed, agro-industrial applications, and soil fertility improvement, supporting climate-smart agriculture and reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers. It also breaks pests life cycle if included in the cropping system.
Maksoy 7N was developed to address yield stagnation, rising disease pressure (including soybean rust), and growing national and regional demand for high-performing varieties. Advanced yield trials across six locations – Kabanyolo (Central), Nakabango (Eastern), Bulindi (Mid-West), Ngetta (Northern), Abi (West Nile), and Mubuku (Western) – demonstrated the variety’s strong performance in both multi-environment trials and participatory on-farm evaluations.

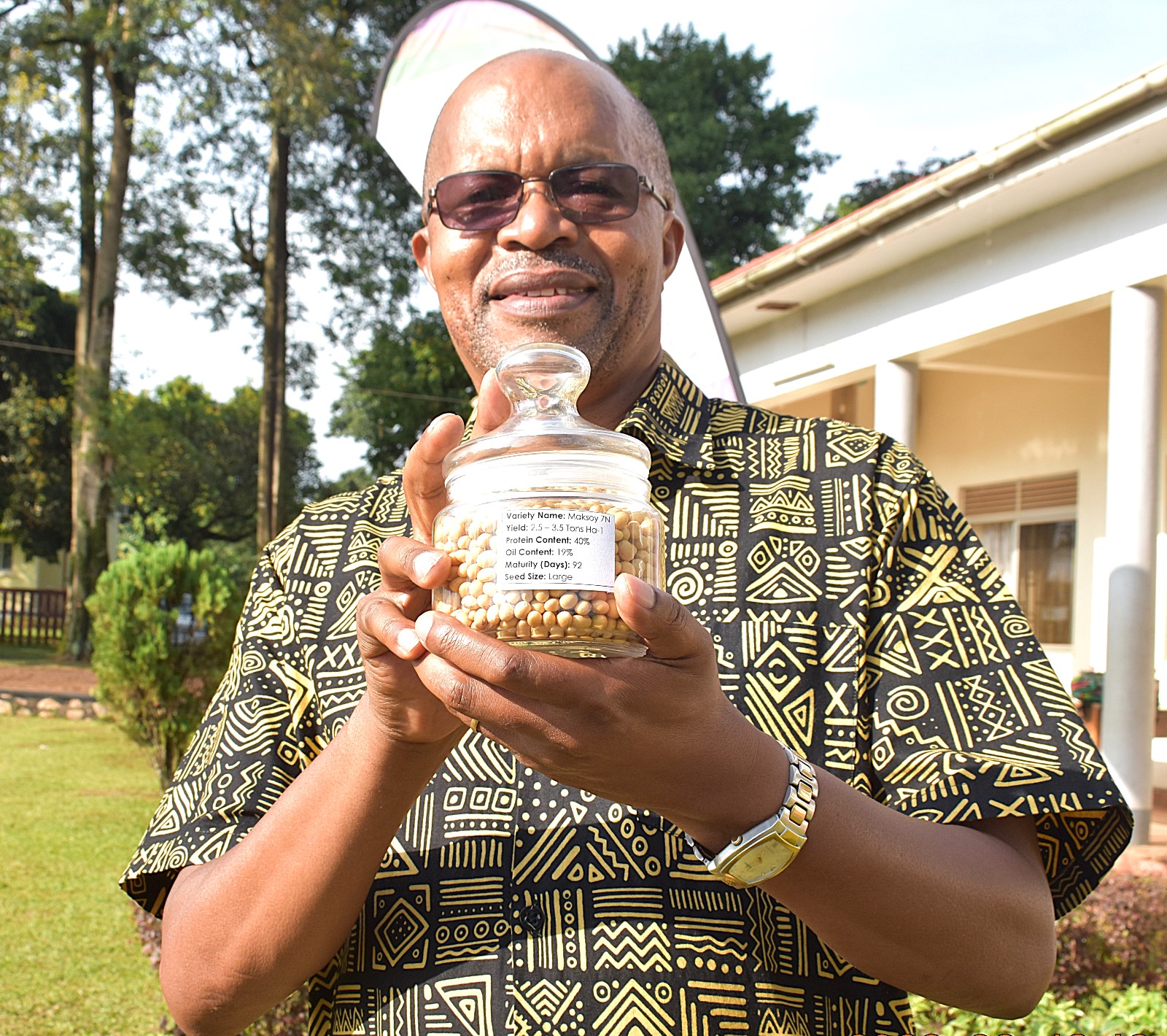
According to Prof. Phinehas Tukamuhabwa, Principal Investigator and Director of MAKCSID, Maksoy 7N demonstrates strong resistance to soybean rust and outstanding agronomic performance. The variety yields between 3-3.5 tons per hectare and matures in approximately three months. Maksoy 7N is expected to enhance national soybean productivity, increase smallholder farmer incomes, and strengthen Uganda’s soybean value chain.
Maksoy 7N joins six previously released high-yielding varieties (Maksoy 1N–6N). Impact studies by the Vegetable Oil Development Project (VODP) reveal that 93% of Ugandan soybean farmers plant Maksoy soybean varieties.

Appreciation to the partners
Prof. Tukamuhabwa expressed gratitude to the local and international development partners for their invaluable support to the project. These partners include the Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries (MAAIF), the National Oil Seeds Project(NOSP) and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) who funded the research. Other research partners include the National Agricultural Research Organization (NARO), the Regional Universities Forum for Capacity Building in Agriculture (RUFORUM), Integrated Seed and Sector Development Uganda (ISSD Uganda), Soybean Africa Ltd, Makerere University Animal Science Laboratory, Soybean Innovation Lab, International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA), and the host farmers who participated in the on-farm trials.
He also appreciated the Makerere University administration for the support extended to MAKCSID.
Honoring the Research Team
Addressing the meeting, Dr. Kikafunda, Chair of the National Variety Release Committee, praised the research team for their exceptional achievements and steadfast dedication to enhancing the nation’s food security. He emphasized the importance of their work in driving agricultural innovation and urged them to prioritize the rapid multiplication and widespread distribution of the new varieties, ensuring they reach the farmers and contribute to increased productivity and improved livelihoods across the country.
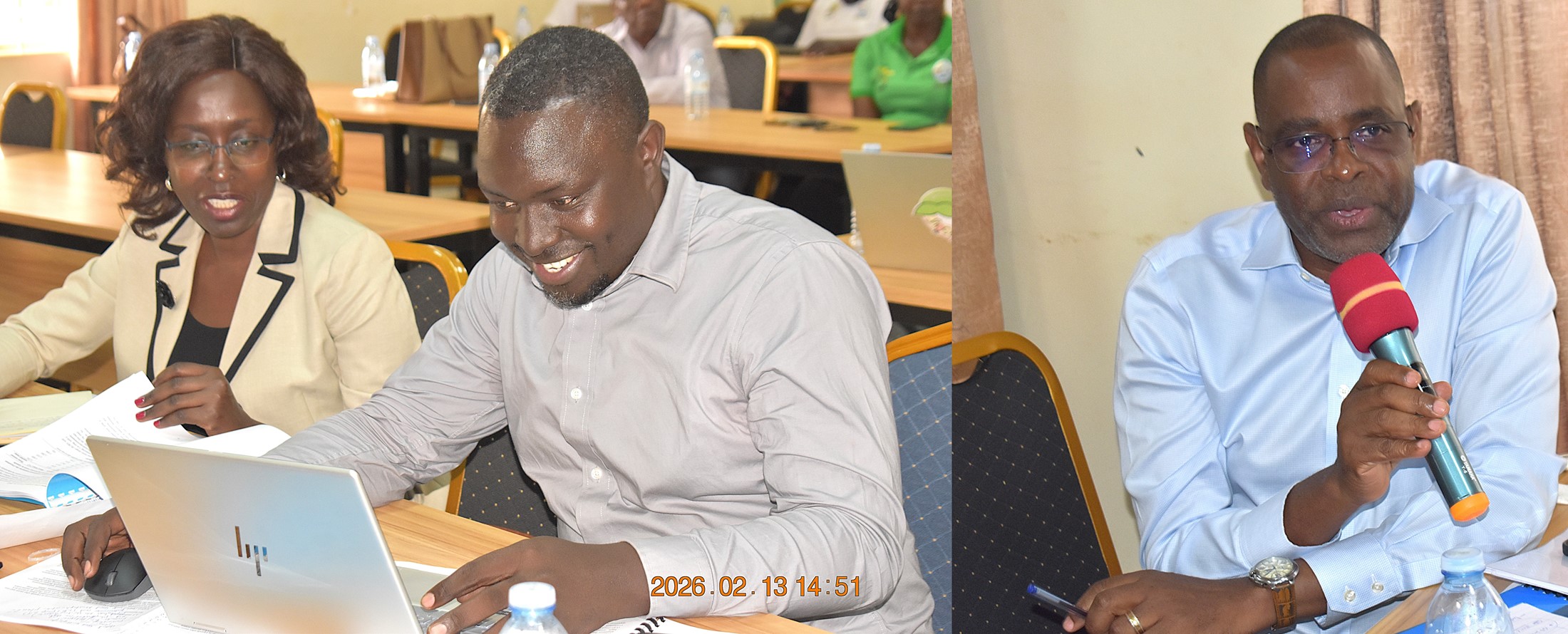

In her remarks, Dr. Mildred Ochwo Ssemakula, Head of the Department of Crop Science and Horticulture at the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES), Makerere University, and member of the National Variety Release Committee, lauded the team for their commitment in developing the new variety, MakSoy 7N. “This is the result of over eight years of dedicated effort. The previous variety, MakSoy 6N, was released in 2017. I deeply appreciate the team’s dedication to field activities. I also commend the former Principal of CAES, Prof. Bashaasha, for his contribution in making the MakCSID a reality, and the current Principal, Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga, for her continued support to the Centre.”
Dr. Ochwo further recognized the pivotal role of Makerere University, particularly CAES, in training critical human resources for the country, noting that most innovators and personnel in key agricultural organizations are graduates of CAES.

The Soybean research team includes:
- Prof. Phinehas Tukamuhabwa – Breeder & Team Leader
- Dr. Tonny Obua – Breeder
- Prof. Jeninah Karungi – Entomologist
- Dr. Geoffrey Tusiime – Pathologist
- Dr. Thomas Odong – Data Scientist
- Dr. Dennis Okii – Data Scientist/Germplasm Research
- Ms. Mercy Namara – Seed Scientist
- Mr. Alex Malaala – Agronomist
- Mr. George Yiga – Nursery Manager
- Mr. Jordan Uworthrwoth – Germplasm Maintenance
Approval of the Sweet Potato and Sorghum Varieties from NARO and NASECO
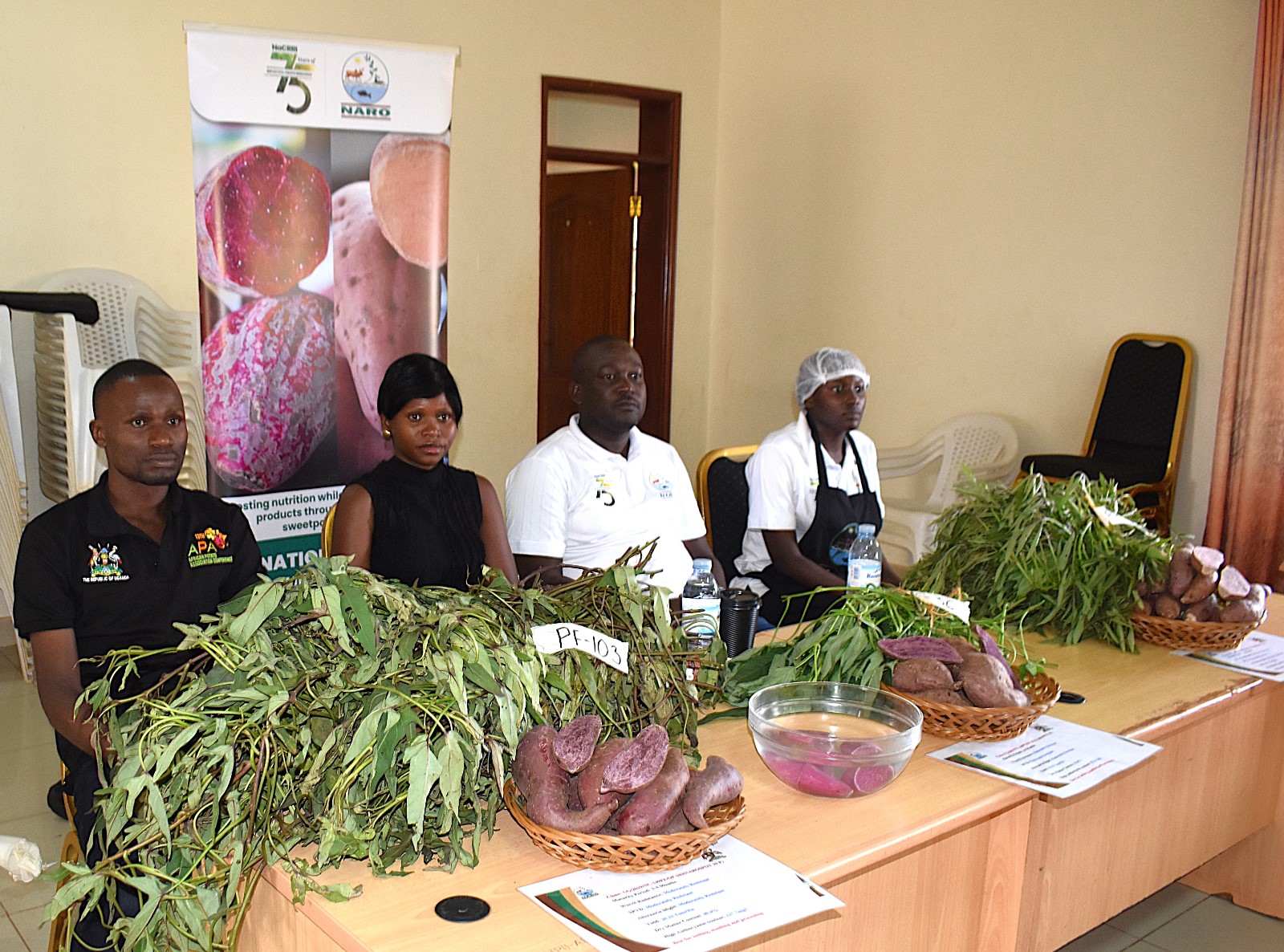
At the same event, the Committee approved three purple-fleshed sweet potato varieties – NAROSPOT 8P, 9P, and 10P – developed by the National Agricultural Research Organization (NARO). These varieties are credited for their high yields, strong disease resistance, and abundant provitamin A content. With a short growing period of just three to four months, these sweet potatoes allow farmers to achieve multiple harvests annually, boosting both productivity and profitability.

The committee also approved two high-yielding sorghum hybrid varieties, NS1 (Tongo) and NS5 (Tara), from NASECO (1996) (U) Ltd. These varieties are versatile, suitable not only for food consumption but also for livestock feed, bioethanol production, and brewing. Early reports indicate strong adoption rates among farmers, which is expected to reduce dependence on imported hybrid seeds and strengthen the local agricultural seed industry.
More photos from the event



Trending
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoAptitude Exam (Paper 1) Results for the Mature Age Entry Scheme 2026/2027
-

 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoFor Youth by Youth – Call for Second Cohort Applications
-

 Agriculture & Environment4 days ago
Agriculture & Environment4 days agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
