General
Julius Nyerere Youth Festival 2025: A Call to Action for Africa’s Next Generation of Change Makers
Published
10 months agoon
By
Mak Editor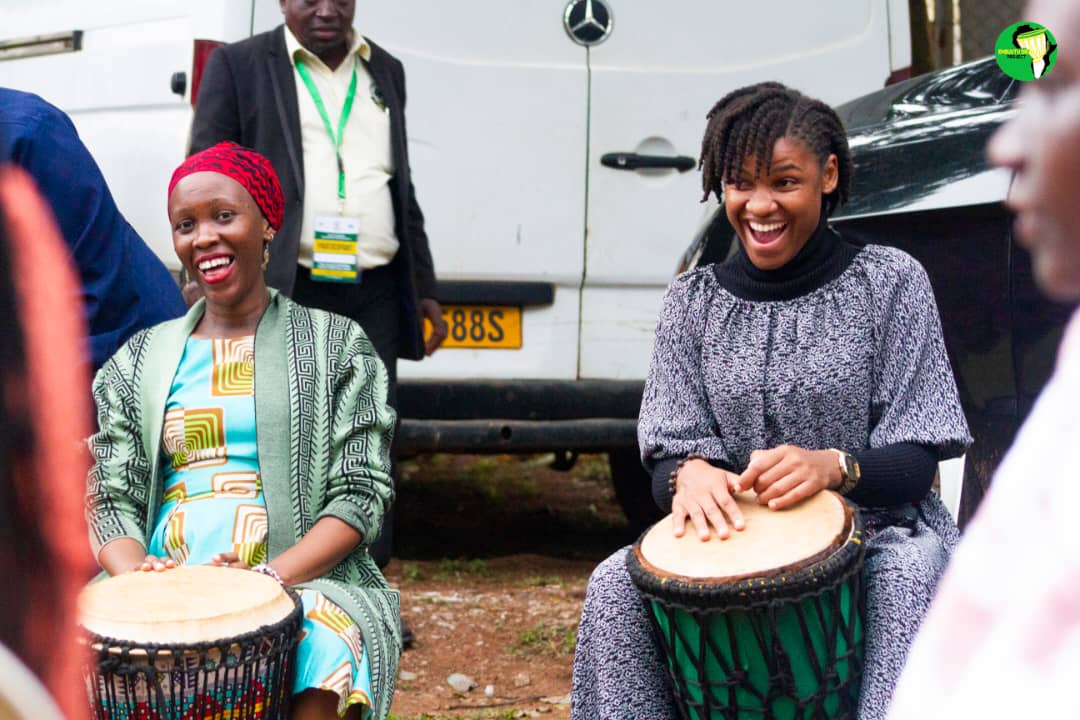
On April 15th and 16th, 2025, the Julius Nyerere Leadership Centre (JNLC) at Makerere University hosted the Julius Nyerere Youth Festival 2025—a powerful and transformative gathering that moved beyond a simple celebration of Mwalimu Nyerere’s legacy to issue a bold call to action for Africa’s emerging generation of leaders and visionaries.
Held under the theme “Our Heritage, Our Voice: Culture, Innovation, and Servant Leadership,” the festival became a dynamic platform where young people were empowered to reimagine leadership, embrace civic responsibility, and commit to sustainable development. Grounded in the enduring ideals of Mwalimu Julius Nyerere—whose birthday, April 13th, is remembered across the continent as a symbol of Pan-African unity and ethical leadership—the event revived his vision, bringing it into conversation with the urgent challenges and opportunities facing African youth today.
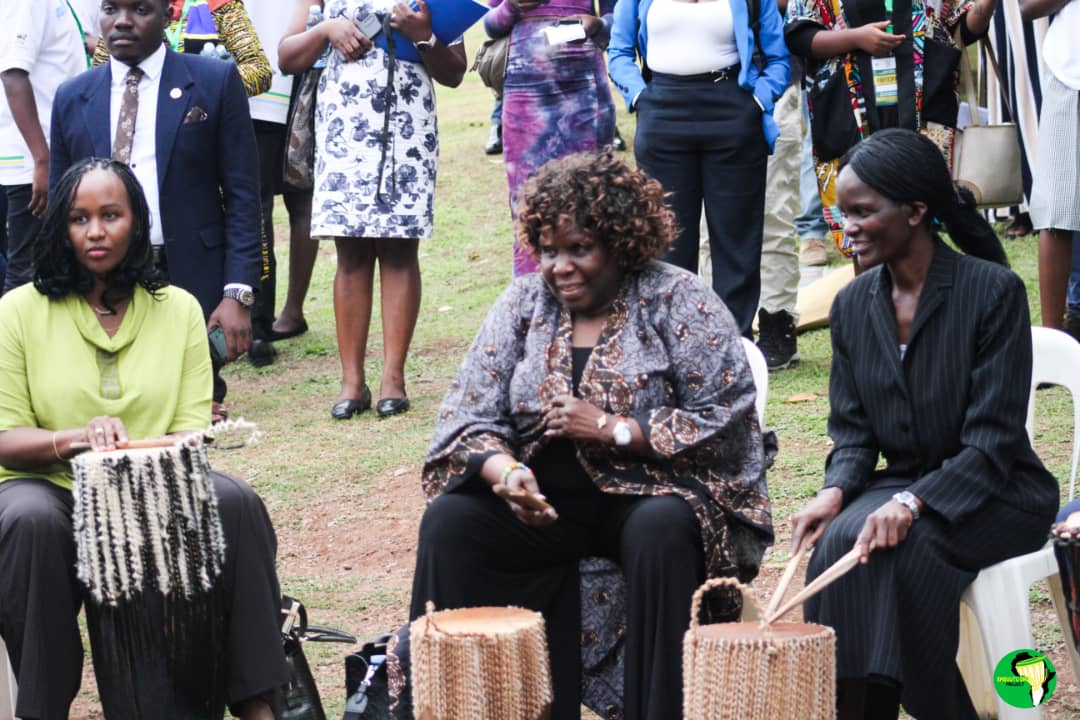
One of the Festival’s most memorable highlights was the evocative evening event titled “Voices in the Night,” hosted at the JNLC. Set around a fireside, this intimate session combined poetry, spoken word, and honest conversation. It brought together an intergenerational mix of participants—including student leaders, poets, scholars, and even members of Mwalimu Nyerere’s family—creating a space where ideas, memories, and aspirations could be shared in the spirit of reflection and solidarity.
During this gathering, Dr. Nansozi Muwanga, Executive Director of JNLC, reminded the audience that servant leadership is not just a nostalgic ideal—it is a living, evolving practice that must respond to the demands of today’s world. She underscored the Centre’s commitment to integrating culture and innovation into its work, noting:
“While servant leadership and culture are very central to what we do, we have also come to realize the need to bridge these values with innovation.”

She emphasized that innovation is essential for keeping Africa’s heritage alive and relevant—especially in a rapidly changing world. Celebrating the diverse youth-led enterprises showcased at the festival—from local coffee brands to handmade art pieces—Dr. Muwanga commended the spirit of creativity. However, she challenged participants to further explore the digital space, expressing hope that future festivals would highlight youth-led tech innovations as well.
In closing, she issued a heartfelt appeal to young people across the continent: to honour Africa’s heritage, but also to dare to reimagine its future—through bold ideas, digital tools, and servant leadership rooted in humility, empathy and action.
She called for leadership grounded in cultural understanding and community-based solutions. While acknowledging the impact of affirmative action in enabling more female students to access higher education, she also advocated for a more nuanced and balanced approach—one that responds to the evolving needs of both girls and boys in today’s society.
Ms. Butiku Sangu, Head of the Languages and Culture Department at the National Leadership Institute (NALI) in Kyankwanzi, anchored her message in the philosophy of Ujamaa and the essence of Africanness. She urged young people to critically re-examine their cultural foundations in the face of increasing global homogenization. True African leadership, she emphasized, must be deeply rooted in indigenous values—values that have sustained communities for generations.
Challenging the common assertion that socialism and African ideologies have failed, Ms. Sangu reframed Ujamaa not as a rigid political doctrine, but as a cultural and moral compass.
“The fact that socialism backfired in Europe was their problem,” she said. “Here in Africa, Ujamaa is a way of life.”

Rejecting intellectual colonialism, she encouraged youth to embrace unity and self-reliance as essential tenets of Nyerere’s vision. She went further to link culture with innovation, identifying mindset change as the most radical and necessary form of innovation.
At NALI, she explained, education is not about political indoctrination, but about decolonizing the mind—instilling pride in African history, language, and lived experiences.
“We teach Fikra—African thought,” she noted, warning that teaching young people that Africanness has failed only plants seeds of defeat and self-doubt.
She concluded with a powerful affirmation: authentic leadership begins with cultural clarity and confidence. Reclaiming African identity, she argued, is the foundation for building an innovative and self-determined future—crafted in Africa’s own image, not in the shadow of others.
The evening was further enriched by the presence of Dr. Susan Kiguli, a celebrated poet and literary scholar at Makerere University. During the “Voices in the Night” session, she spoke eloquently about the power of the spoken word, urging youth to embrace their authentic voices.
“Writing and performing is communication,” she declared. “And there is nothing stronger than the Word.”
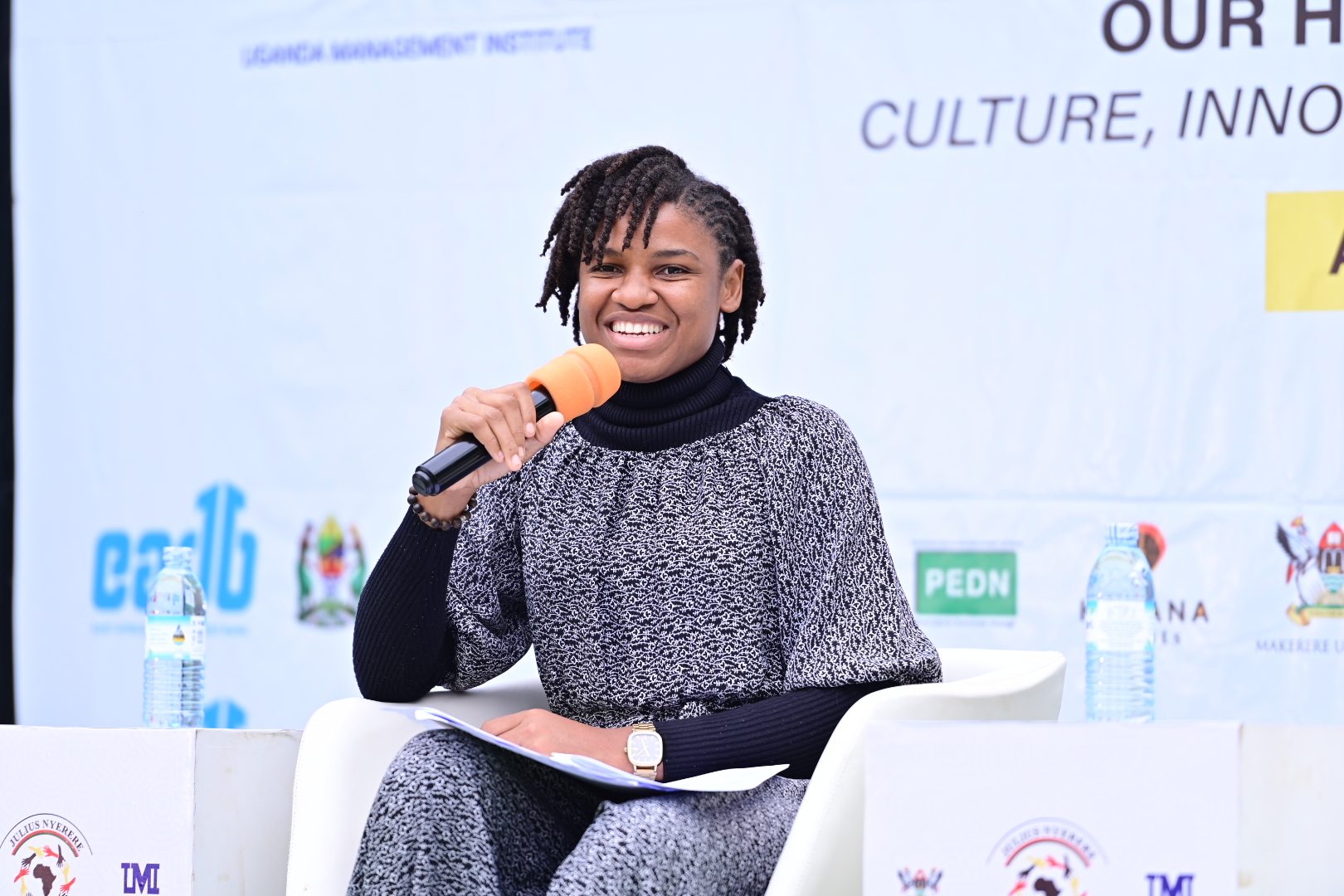

Even when it seems no one is listening, she encouraged the audience, “Some of the words may just ring—sometime, somewhere.”
Dr. Kiguli paid tribute to Mwalimu Julius Nyerere not only as a historic leader, but as a lasting teacher.
“Julius Nyerere was named by the people who saw his work. We call him Mwalimu, and it means teacher. Even when he’s not here, he’s still teaching.”
She shared a poignant moment from 1999, recalling how she was asked by the then Deputy Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Epelu Opio, to write a poem in honor of Nyerere shortly after his passing. The piece, written in under a day and titled “Mwalimu Nyerere in Memoriam,” was later sent to his family and the people of Tanzania.
In the poem, Dr. Kiguli honors Nyerere as a Pan-African beacon whose influence transcends borders and generations. She describes him as “a walking stick for Africa,” “a trailblazer of African unity,” and “a champion of justice.” She links him with fellow visionaries like Kwame Nkrumah and Patrice Lumumba, framing him as a “framer of our regard” whose light touched Uganda, South Africa, Burundi, and beyond.
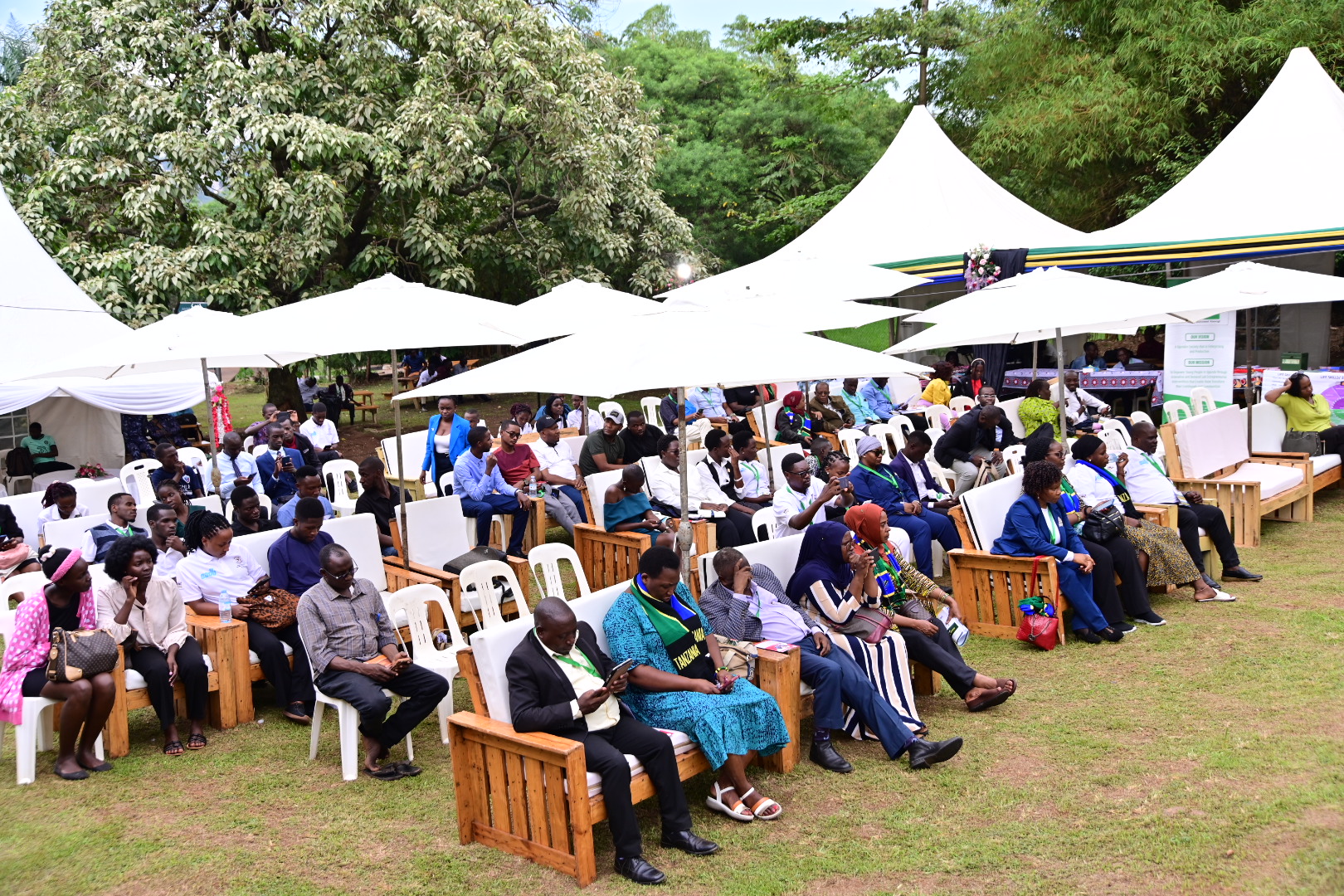

As night deepened, Mr. Kagayi Ngobi, one of Uganda’s most dynamic spoken word poets, electrified the audience with his powerful poem, “But why am I telling you this in English?” Delivered with raw energy and emotional depth, his performance tackled the pain of post-colonial identity, the failures of African governance, and the struggle for cultural reclamation.
“A poem is like a person—it never ages,” he mused.
With scathing yet loving critique, Kagayi challenged the erasure of African languages and condemned the education systems that alienate children from their roots. Lines like “Sadness is me, not knowing what I need to know to know who I am” resonated deeply, reflecting the wounds of historical disconnection. Yet his poem also celebrated small acts of resistance—like eating a roadside Rolex—as symbols of enduring cultural pride.
In a moving poetic interlude, Grace Deborah Mirembe, a Bachelor of Arts in Education student majoring in Literature and English at Makerere University, performed her original poem, “When Africa Rises.” Her verses envisioned a Pan-African renaissance rooted in solidarity and identity. She painted a vibrant picture of a united Africa—linked across cities and diasporas, from Kingston to Kinshasa, Harlem to Harare.
“We are not lost… we are flowering… we are kin,” she declared.

Her work invoked the spirits of Nkrumah, Sankara, Lumumba, and Nyerere—not as relics, but as guides lighting Africa’s path forward. Her final words captured the heartbeat of the Festival:
“Africa is yesterday’s story, today’s voice, tomorrow’s promise… One people, One pulse, One power.”
This message was echoed by Ms. Faith Martha Atieno, a fellow Literature and English student at Makerere University, in her compelling poem, “A Letter to My African Friend.” Her piece radiated ancestral pride and resilience, reminding the audience of the unbreakable strength woven into African identity.
“Women were fearless warriors,” she declared, uplifting the often-forgotten heroines of history.
Ms. Atieno offered a defiant stand against identity erasure, proclaiming with resolve:
“It’s not breaking any time soon.”
The fireside evening closed on a powerful note with Ms. Aisha Nyerere, Mwalimu Nyerere’s great-granddaughter based in Canada, who recited her poem “Ode to Kanga.” Through this evocative tribute to the traditional East African fabric, she wove together memory, identity, and belonging. The Kanga, she said, was not just cloth—it was a quiet matriarch, a keeper of history and love.
It clothed brides, absorbed tears, cradled infants, and stood silently through generations.
Even folded away in distant lands, the Kanga waited—to reconnect, to remind, to reclaim. Through it, Ms. Aisha Nyerere affirmed her place in the lineage of African heritage, showing that distance could not unravel the threads of identity.
As twilight descended on the Julius Nyerere Leadership Centre, Dr. Nansozi Muwanga rose with quiet grace and gratitude. She thanked the participants for their presence, for sharing in a day woven with dialogue, poetry, and purpose.
“Thank you so much for being with us today—for giving us your time,” she said. “I hope you are going home with something meaningful to carry forward.”

Bringing the Festival to a close, Dr. S. Kasozi-Mulindwa, Chairperson of the JNLC Board of Directors, delivered final remarks rich in reflection and encouragement. He spoke of the profound inspiration drawn from the energy, creativity, and courage of young people—affirming that their engagement breathes fresh life into the enduring legacy of Mwalimu Nyerere.
He extended heartfelt thanks to the JNLC team, especially Dr. Muwanga, whose visionary leadership made the Festival possible. He also acknowledged the contributions of sponsors, partners, and innovators who participated in the exhibition, whose collective efforts helped shape a space of learning, growth, and unity.
“This festival,” he concluded, “has not only remembered Mwalimu—it has reawakened him in each of us.”
You may like
-


Mak hosts First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling
-


Strengthening Global Partnerships to Advance Research, Innovation, and Graduate Training: Makerere University Hosts Delegation from the University of Warwick
-


Olivia Nakisita and the Quiet Urgency of Adolescent Refugee Health
-


First African Symposium underscores the role of the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling
-


Makerere Launches Scholarly Guide, Calls for Increased Research, Publication and Innovation in Africa
-


How Jimmy Osuret Turned Childhood Trauma into Evidence for Safer School Crossings
General
Over 9,200 to graduate at Makerere University’s 76th Graduation
Published
6 hours agoon
February 24, 2026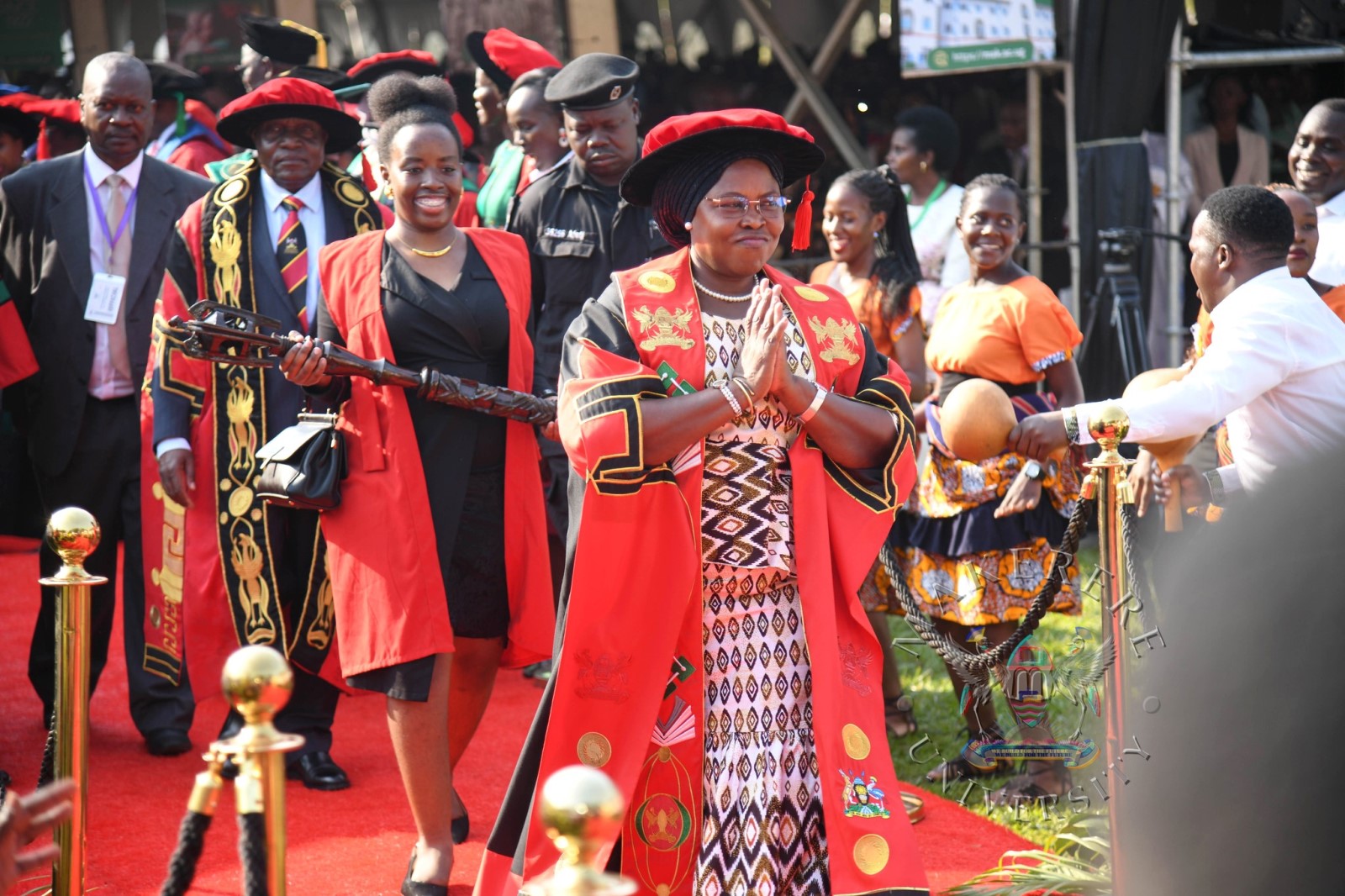
Pomp and colour defined the opening day of the Makerere University’s 76th Graduation Ceremony as thousands gathered to celebrate academic excellence and new beginnings.
The historic ceremony has brought together scholars, families, friends and industry partners in a vibrant celebration of achievement and possibility. Throughout the four-day event, the University will confer degrees and award diplomas to 9,295 graduands in recognition of their dedication and hard work.
Among the graduates, 213 will receive Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degrees, 2,503 will graduate with Master’s degrees, and 6,343 will earn Bachelor’s degrees. In addition, 206 students will graduate with postgraduate diplomas, while 30 will be awarded undergraduate diplomas.
Of the total number of graduands, 4,262 are female and 5,033 are male. According to Vice Chancellor, this marks the first time in 15 years that male graduands have outnumbered their female counterparts.
The best overall graduand in the Sciences, Esther Ziribaggwa, graduated on the opening day with the Bachelor of Agricultural and Rural Innovation and an impressive Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) of 4.77.
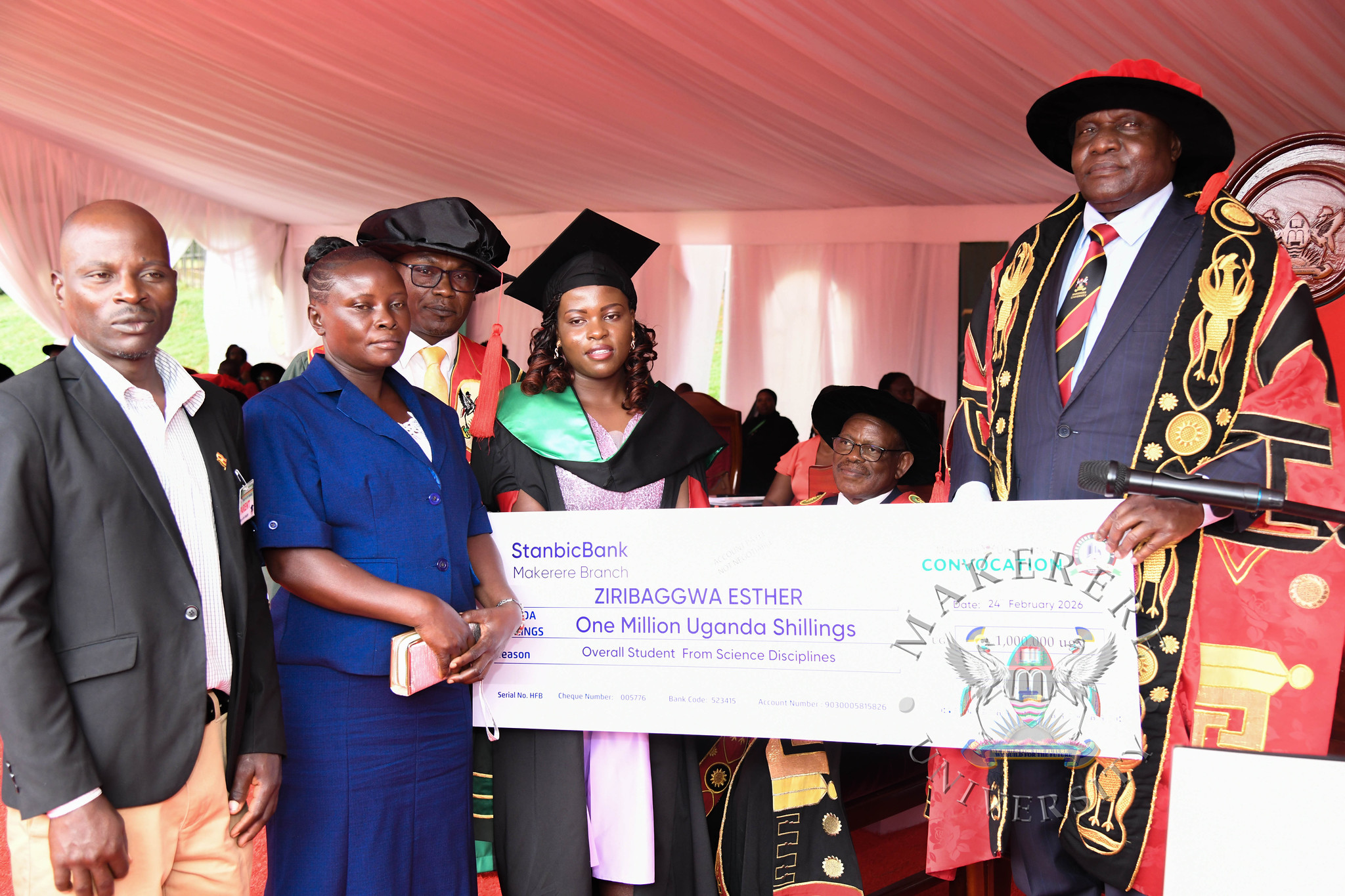
The ceremony marks a proud moment for Makerere University as it continues to nurture top-tier professionals across diverse fields.
While presiding over the graduation, the State Minister for Primary Education, Hon. Dr. Joyce Moriku Kaducu, on behalf of the First Lady and Minister of Education and Sports, Hon. Janet Kataaha Museveni, pointed out that Makerere University is a model institution, where leaders are nurtured, scholars are sharpened, and where dreams have been given direction.
In her address, Hon. Museveni, highlighted Government’s deliberate investment in research, innovation, and infrastructure to strengthen higher education in Uganda.
“The establishment of the Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund (RIF), supports high-impact research and innovation that directly contributes to national priorities and development. Through this initiative, thousands of researchers and innovators have pursued practical, scalable solutions that are transforming communities and key sectors across Uganda,” Mrs Museveni, said.
The Minister also noted that Parliament’s approved a USD 162 million concessional loan to upgrade science, technology, and innovation infrastructure at Makerere University. The funding will facilitate the construction of modern laboratories, smart classrooms, and state-of-the-art facilities for Engineering and Health Sciences, investments expected to position the University firmly within the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
“Government has embarked on the construction of a National Stadium at Makerere University and other institutions of higher learning across the country. This will promote physical education, strengthen talent identification, and boost investment in the sports sector,”
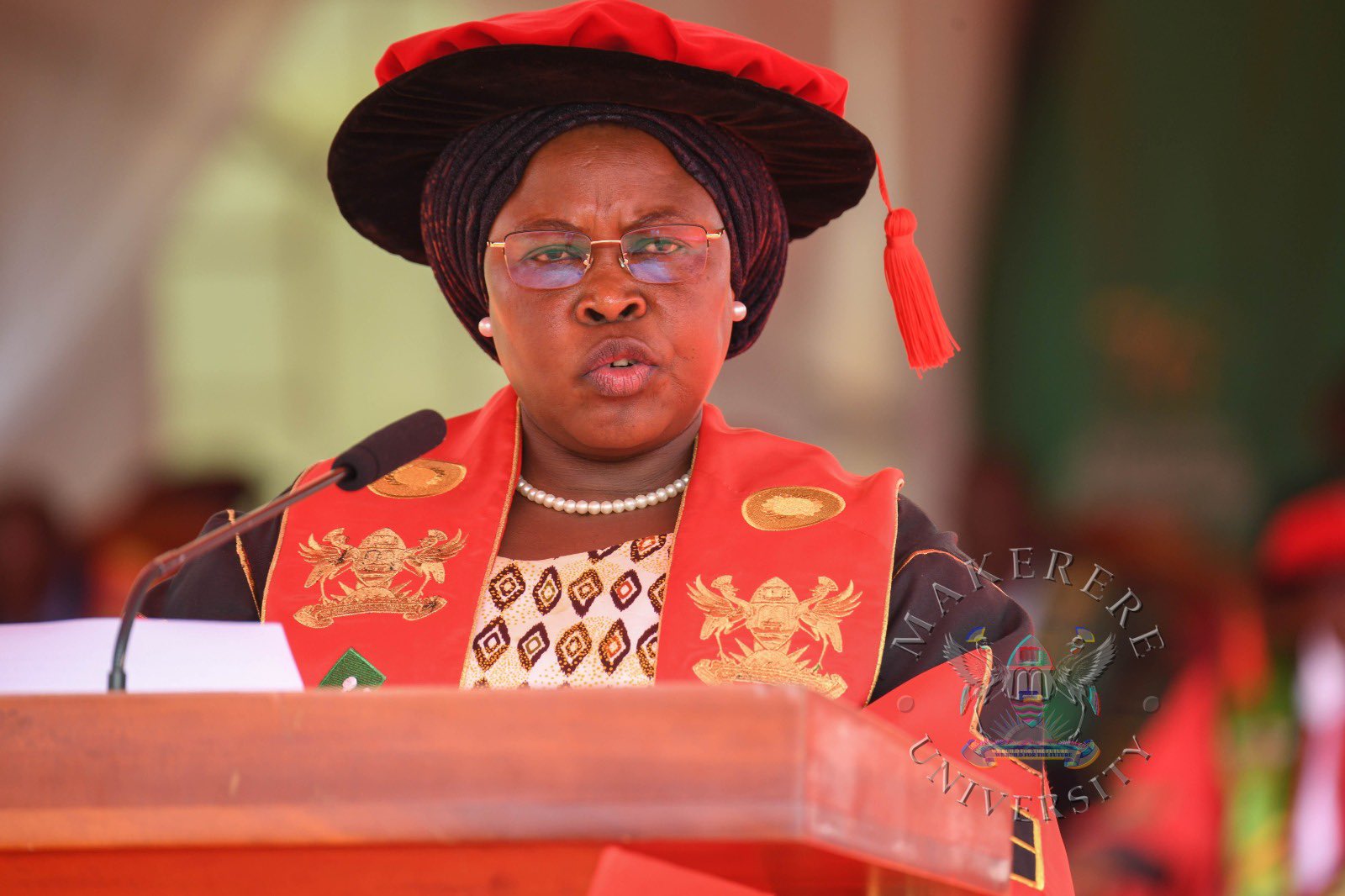

Turning to the graduands, the Minister encouraged them to see themselves not merely as job seekers, but as job creators and solution-makers.
Uganda and Africa need innovators who will modernize agriculture; engineers who will build quality infrastructure; healthcare professionals who will strengthen health systems; and educators who will inspire the next generation,” the Honourable Minister said.
She reminded graduates that they are entering a rapidly changing world shaped by Artificial Intelligence, climate change, and shifting global markets. To thrive, she advised them to remain adaptable, creative, and committed to lifelong learning.
She also encouraged graduates interested in entrepreneurship to tap into the Government’s Parish Development Model, which provides community-based financing and production support.
Quoting Proverbs 3:5–6, the Minister urged the graduates to trust in God as they embark on their next chapter.
She extended special appreciation to the Mastercard Foundation for its 13-year partnership with Makerere University in expanding access to education and empowering young people in Uganda and beyond.
In his speech, the Chancellor of Makerere University, Dr Crispus Kiyonga, urged graduands to harness research, innovation and technology to drive Uganda’s transformation.
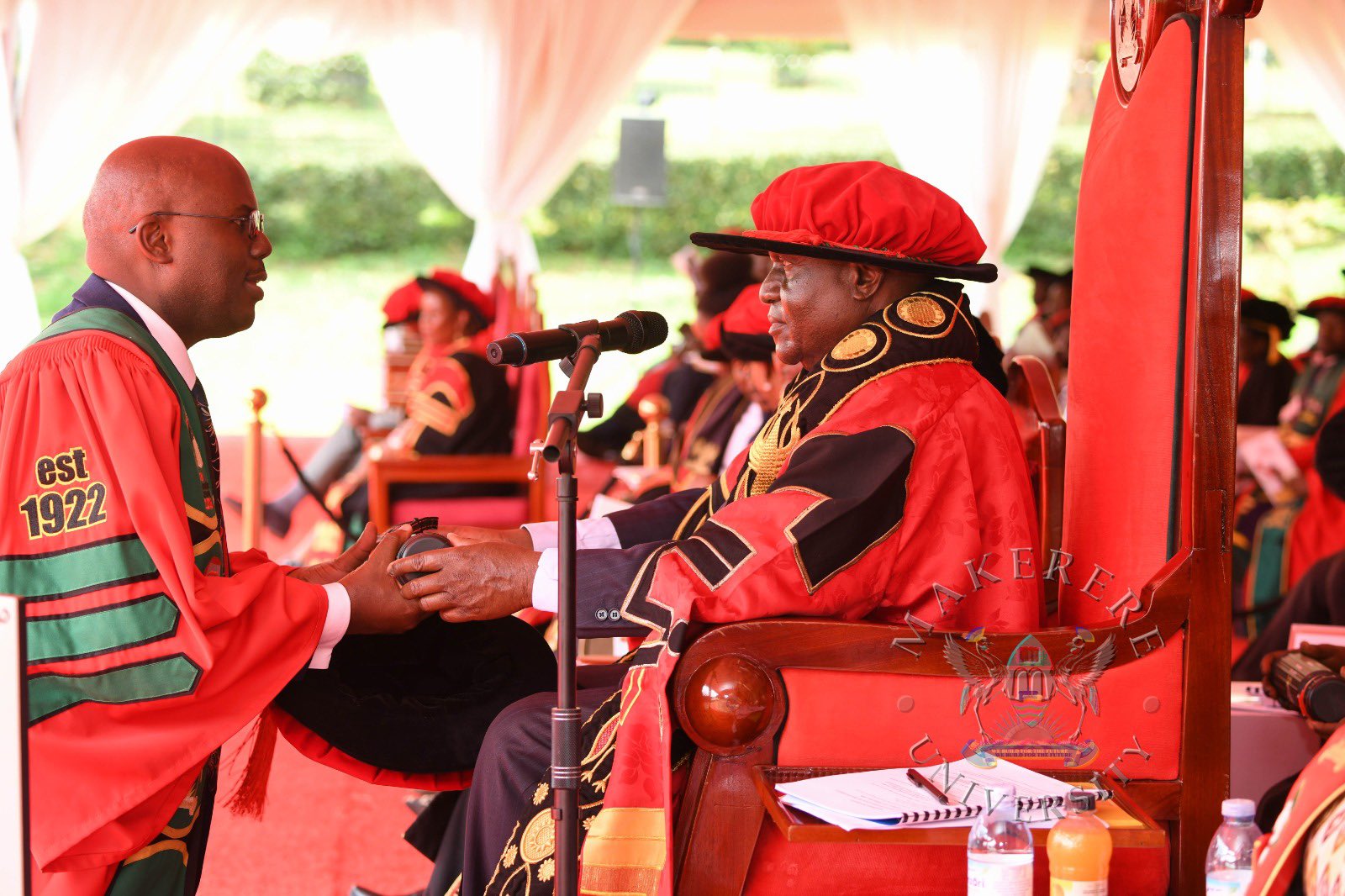

“This is a milestone in your lives. You have invested time, discipline and hard work to attain these qualifications. It is important that you derive value from this achievement, not only for yourselves, but for your families and for society.” Dr Kiyonga, said.
Dr. Kiyonga expressed gratitude to the Government of Uganda for its continued financial support to the University, particularly the funding allocated under MakRIF, which he described as critical in strengthening the institution’s research capacity.
“Research plays a very vital role in the development of any community. Makerere as the oldest University in the country is doing a significant amount of research, However, more work is required to mobilize additional resources to further strengthen research at the University.” Dr Kiyonga, noted.
Acknowledging the challenges of a competitive job market, Dr. Kiyonga encouraged graduates to think beyond traditional employment pathways.
“It is true that the job market may not absorb all of you immediately. But the knowledge you have acquired is empowering. You can create work for yourselves, individually or in teams.” Dr Kiyonga, said.
He advised the graduands to embrace discipline, integrity and adaptability in the workplace, and to take advantage of technology and digital platforms to innovate and respond to societal challenges.
“Every development challenge presents an opportunity. Believe that you can apply your knowledge to create solutions with impact.” He said.
Addressing the congregation, the Vice Chancellor, Prof Barnabas Nawangwe, congratulated the graduands, particularly staff and societal leaders on their respective achievements.
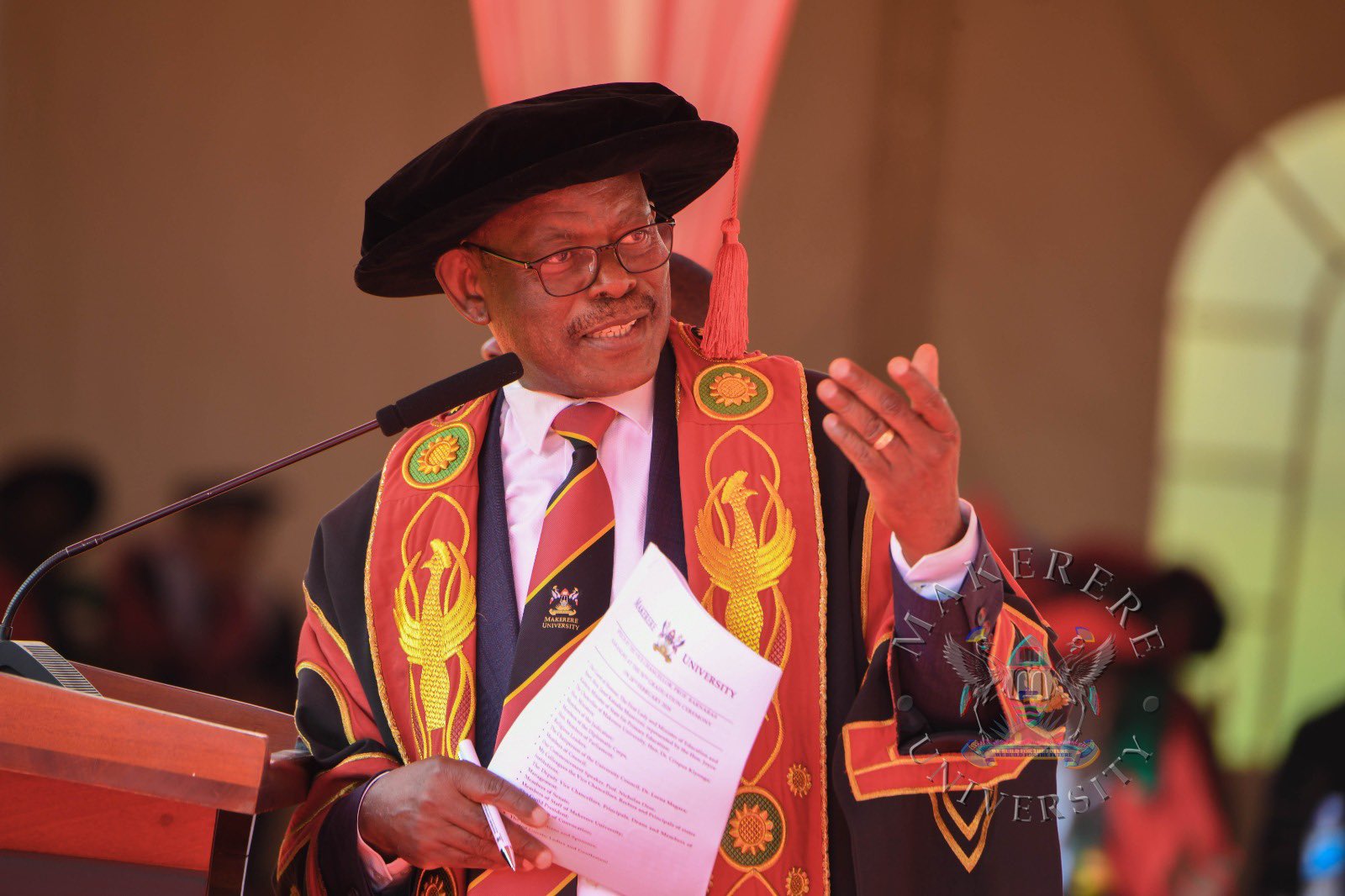

“I congratulate all our graduands upon reaching this milestone. In a special way I congratulate the members of staff, Ministers, and Members of Parliament that are graduating today as well as children and spouses of members of staff,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
In his speech, Prof Nawangwe, recognized outstanding PhD students, particularly members of staff. who completed their PhDs in record time without even taking leave from their duties.
He called upon graduates not to despise humble beginnings but rather reflect on the immense opportunities around them and rise to the occasion as entrepreneurs.
“You are all graduating with disciplines that are needed by society. We have equipped you with the knowledge and skills that will make you employable or create your own businesses and employ others. Do not despair if you cannot find employment. Instead, reflect on the immense opportunities around you and rise to the occasion as an entrepreneur,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
Prof Nawangwe called upon the graduands of PhDs to use their degrees to transform the African continent.
“As you leave the gates of Makerere I urge you to put to good use the knowledge you have received from one of the best universities in the World to improve yourselves, your families, your communities, your Country and humanity. Let people see you and know that you are a Makerere alumnus because of the way you carry yourself in society with dignity and integrity. Put your trust in God and honour your parents and opportunities will be opened for you,” Prof Nawangwe, said.
Delivering a key note address, Prof. Nicholas Ozor, the Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network Nairobi, Kenya ((ATPS). Reminded the graduates that a degree is not a finish line but the beginning of accountability. “The world is a complex, fast changing and deeply unequal. Degrees make you responsible for others not better than them,” Prof Ozor, said.

The 76th Graduation Ceremony of Makerere University will be held from Tuesday 24th to Friday 27th February, 2026. A total of 213 PhDs (87 female, 126 male), 2,503 Masters (1,087 female, 1,416 male), 206 Postgraduate Diplomas (80 female, 126 male), 6,343 Undergraduate Degrees (2,999 female, 3,344 male), and 30 Undergraduate Diplomas (9 female, 21 male) will be graduating from all the Colleges.
Ms. Sarah Aloyo and Ms. Nakato Dorothy both students of the Bachelor of Procurement and Supply Chain Management emerged as the best in the Humanities and Best Overall students with a CGPA of 4.93. Mr. Ssewalu Abdul, a Bachelor of Leisure and Hospitality Management student emerged second best in the Humanities with a CGPA 4.90. Ms. Esther Ziribaggwa emerged as the best student in the Sciences with a CGPA of 4.77 in the Bachelor of Agricultural and Rural Innovation, while Mr. Simon Mungudit emerged second best in the Sciences with a CGPA of 4.76 in the Bachelor of Science in Petroleum Geoscience and Production.
Commencement Speakers
- Day 1 – Prof. Nicholas Ozor, the Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network, Nairobi, Kenya
- Day 2 – Prof. Dr. Maggie Kigozi, Chairperson Makerere University Endowment Fund Board
- Day 3 – Dr. Patricia Adongo Ojangole, Managing Director, Uganda Development Bank Limited
- Day 4 – Ms. Reeta Roy, Former President & Chief Executive Officer, Mastercard Foundation
The 76th Graduation Ceremony will be held at the Freedom Square following the schedule below:
Tuesday, 24th February, 2026
College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES)
College of Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS)
College of Education and External Studies (CEES)
School of Law (SoL)
Livestream Link for Day 1: https://youtube.com/live/wVGPA0FJ9pU
Wednesday, 25th February, 2026
College of Health Sciences (CHS)
College of Natural Sciences (CoNAS)
College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Bio-security (CoVAB)
School of Public Health (SPH)
Thursday, 26th February, 2026
Makerere University Business School (MUBS)
College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS)
Friday, 27th February, 2026
College of Engineering, Design, Art and Technology (CEDAT)
College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHUSS)
Institute of Gender and Development Studies (IGDS)
Makerere Institute of Social Research (MISR)
General
Mak Selected to Host Alliance for African Partnership Africa Office
Published
1 day agoon
February 23, 2026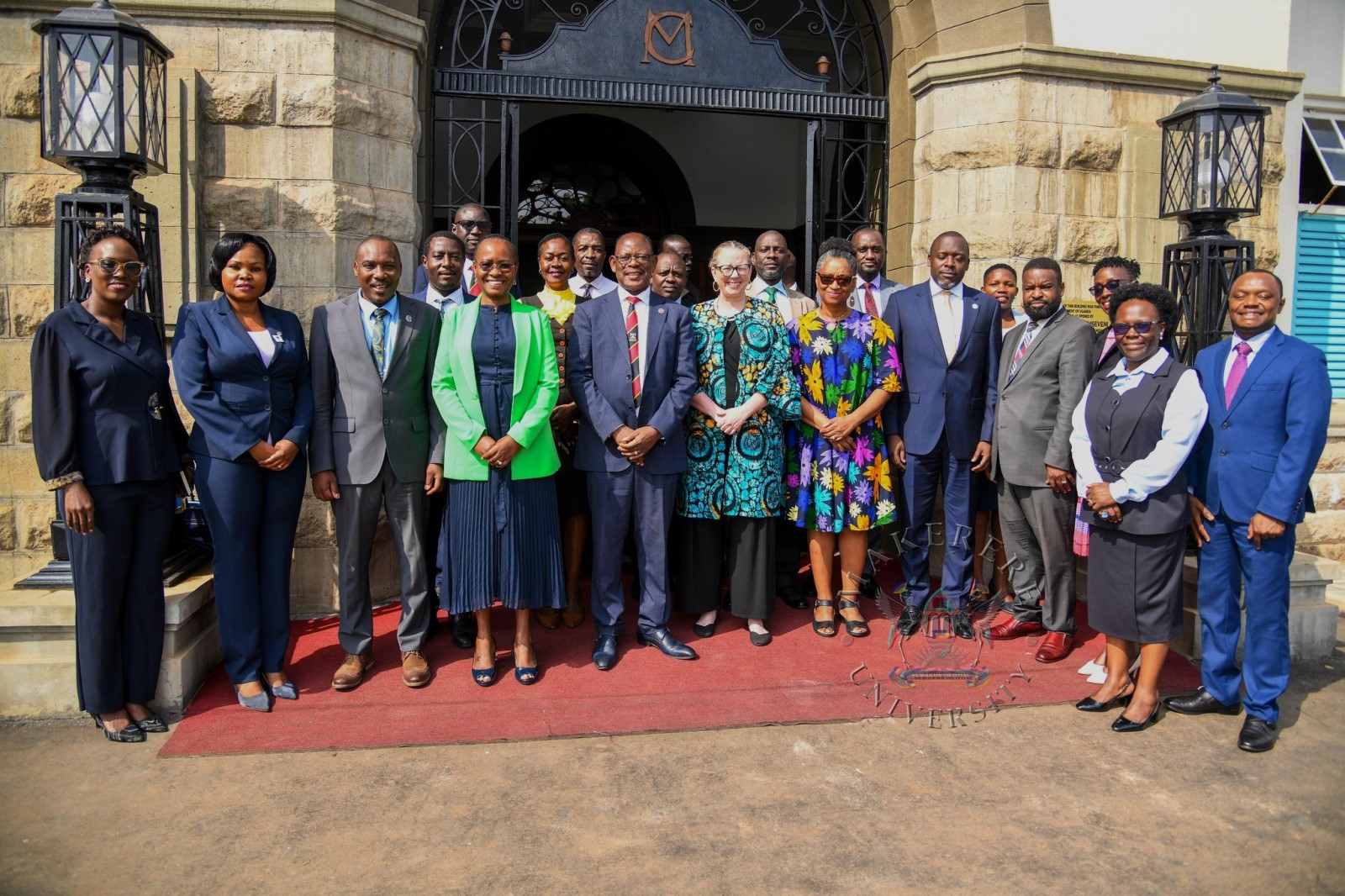
Makerere University has been selected to host the Africa Office of the Alliance for African Partnership (AAP). The significant milestone that underscores Makerere’s role in fostering research, innovation, and global collaborations across the continent was announced at a meeting of the University’s Central Management with an AAP delegation on 23rd February 2026.
Makerere’s selection was based on the University’s robust commitment, alignment with the AAP’s Strategic Plan, and proven ability to manage consortium activities. The AAP, which was initiated by Michigan State University (MSU) in collaboration with Ten African Universities and agricultural policy research networks in 2016, targets critical challenges in education, youth empowerment, health and nutrition, agri-food systems, science and technology, water, energy, environment, and culture and society.
Addressing the delegation consisting of AAP Co-Directors from MSU, Dr. Jose Jackson-Malete and Dr. Amy Jamison, accompanied by newly-appointed Director of the AAP Africa Office, Dr. Racheal Ddungu Mugabi and Ms. Clare Cheromoi, the Vice Chancellor, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe who appreciated the choice of Makerere to host the Africa Office said:
“One of the greatest challenges facing African universities is PhD training, particularly supervisory capacity. Through partnerships such as the Alliance for African Partnership we can leverage international expertise to strengthen supervision—whether through training supervisors or through joint supervision arrangements.”
Prof. Nawangwe equally applauded joint initiatives such as the Grant Writing and Publication project, which gave rise to the establishment of a Writing Centre that he said can be used to build capacity in AAP member universities with Makerere as the hub. Officially launched on 21st March 2023, the project is living up to its expectation of becoming a springboard for strong postdoctoral collaborative research for both institutions and other US universities.
Dr. Titus Awokuse, Vice Provost and Dean for International Studies and Programs at Michigan State University (MSU) who attended virtually, reiterated that Makerere’s selection reflects its long-standing commitment to advancing African higher education, research excellence, and meaningful global collaboration.
Reflecting on the origins of the Alliance for African Partnerships (AAP), Dr. Awokuse explained that nearly a decade ago, MSU initiated a transformative conversation in Atlanta centered on the question: How should we partner differently? From this dialogue emerged AAP—an Africa-centered consortium that now brings together 12 institutions across Africa and the United States.
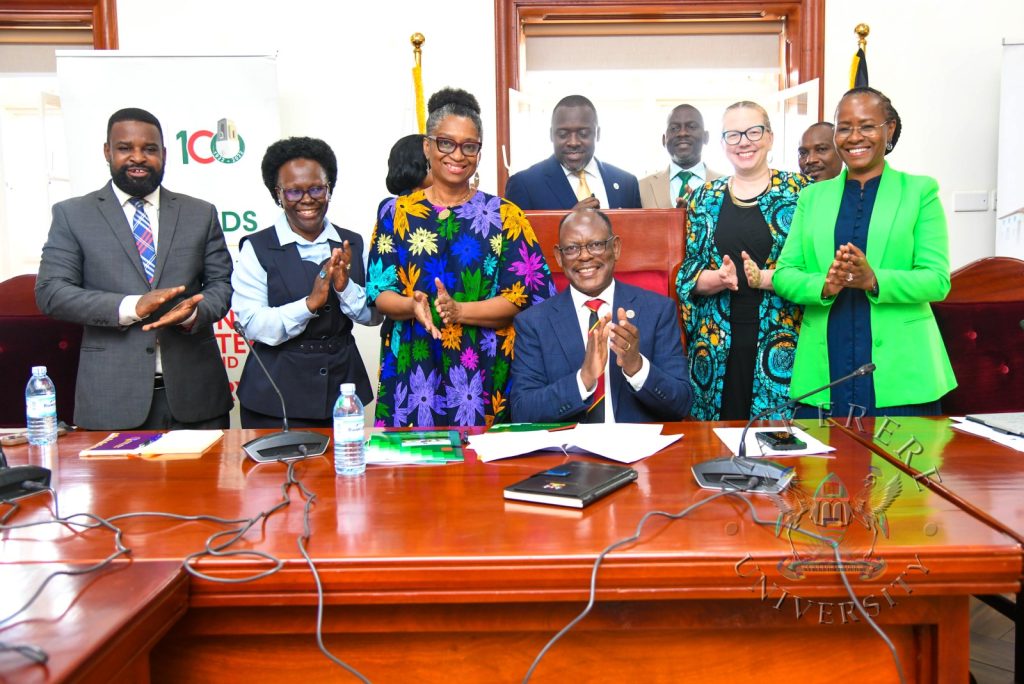

He emphasized that AAP is grounded in equity, mutual benefit, shared leadership, and deep respect for African priorities and expertise. Since its founding, MSU has served as convener and key supporter, working with member institutions to strengthen research collaboration, promote faculty and student engagement, and address shared development priorities.
Dr. Awokuse underscored that AAP’s success is the result of collective vision and commitment, not the efforts of a single institution. He paid tribute to Lilongwe University of Agriculture and Natural Resources for hosting the Africa Office in its early years and acknowledged the foundational leadership of the inaugural Africa Office Director.
He described the launch of the Africa Office at Makerere University as a significant milestone that reinforces Africa-led leadership, strengthens regional collaboration, and enhances responsiveness to emerging opportunities. MSU, he affirmed, remains fully committed to AAP and to working closely with Makerere and all consortium partners to expand collaborative research, nurture the next generation of scholars, and advance Africa-led solutions to global challenges.
The newly-appointed AAP Africa Office Director, Dr. Racheal Ddungu Mugabi is a member of faculty in the Department of Development Studies, Institute of Gender and Development Studies. Her work on intersectional inequalities in Uganda and other Global South regions uniquely positions her to drive collaborative research and partnerships at the Africa Office.
Initially founded by ten African Universities and MSU, AAP now comprises eleven African members including; the African Network of Agricultural Policy Institutes (ANAPRI)-Zambia, Egerton University-Kenya, Lilongwe University of Agriculture and Natural Resources (LUANAR)-Malawi, Makerere University-Uganda, United States International University-Africa-Kenya, Universite Cheikh Anta Diop-Senegal, Universite Yambo Ouologuem de Bamako-Mali, University of Botswana-Botswana, University of Dar es Salaam-Tanzania, University of Nigeria, Nsukka-Nigeria, and the latest, University of Pretoria-South Africa.
These Universites collaborate under Focal Points to advance policy-relevant research and sustainable development. Makerere University’s Focal Point is Prof. Robert Wamala, Director of Research, Innovations and Partnerships (DRIP).
Addressing the University Management, Dr. Jackson-Malete outlined the African Futures Research Leadership Program, which nurtures early career scholars through mentorship and skill-building as one of AAP’s flagship programs. She noted that the Program that prioritizes female participants or men committed to promoting women in higher education has for the first time during its fifth cohort admitted the first male, Dr. Alfadaniels Mabingo from the Department of Performing Arts and Film, Makerere University.
The AAP Africa Office at Makerere will coordinate activities, boost research collaboration, mobilize resources, and enhance global engagements for socio-economic transformation. This aligns with Makerere‘s broader goals of leveraging international expertise to build resilient institutions.
View more photos from the event: https://flic.kr/s/aHBqjCLjoA
Trending
-

 Humanities & Social Sciences2 days ago
Humanities & Social Sciences2 days agoMeet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-

 Health6 days ago
Health6 days agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 Agriculture & Environment5 days ago
Agriculture & Environment5 days agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoCall for Applications: Short Course in Molecular Diagnostics March 2026
