Health
Research Links Social Support to Improved Contraceptive Decision-Making for Women
Published
2 years agoon

Researchers at Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) are urging the Ugandan government to boost healthcare funding to enhance reproductive health services. Dr. Dinah Amongin, an obstetrics and gynecology expert at MakSPH, has expressed concern about the lack of access to family planning methods, which forces women to use less preferred options due to unavailability.
Dr. Amongin notes that within just six months to a year of using contraception, some women encountered issues and switched methods. This highlights the need for the Ministry of Health to improve the availability of various contraceptive options. A rights-based approach to contraception ensures that women have access to a range of methods, preventing situations where desired options are unavailable at health facilities.
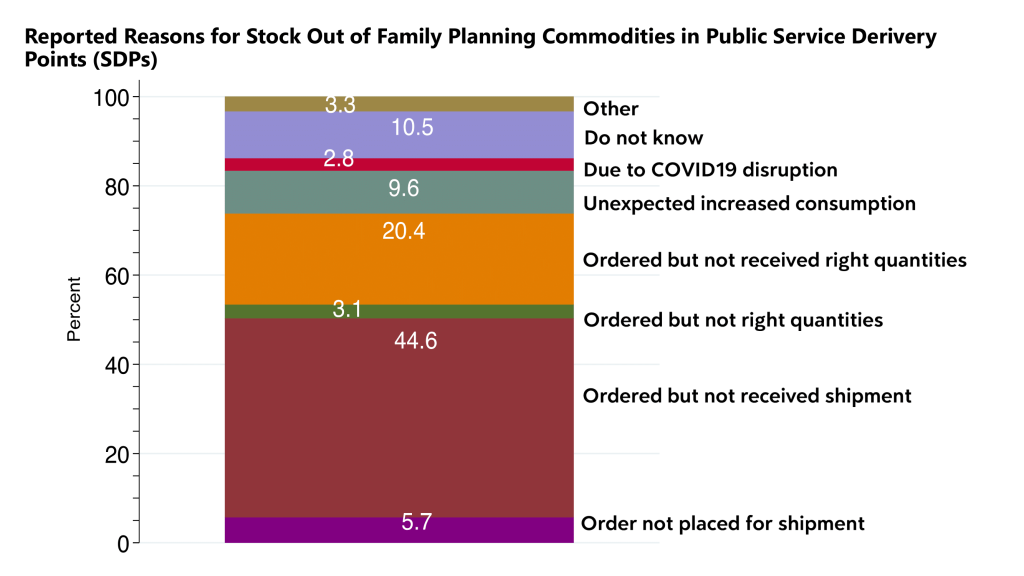
“Stockouts are a significant issue, and this extends to parliamentary discussions on health sector budgets. As we focus on human capital development and improving maternal and newborn health outcomes, we must consider crucial components like preventing unwanted pregnancies through family planning. The budget allocation for the health sector directly impacts this issue. When women cannot access their preferred contraceptive methods due to stockouts, it reflects a failure in our legislative and budgeting processes. This situation forces women to switch to fewer desirable methods, which is not acceptable,” says Dr. Amongin.
Adding that; “These are things we need to continue discussing as a country but we must invest into family planning. We can talk about human capital development but until we step up and actually support women to prevent unwanted pregnancies, support them in their decisions of whether she wants to use a method for contraception or not. That is her choice. We must make sure access to the methods of her choice is actually addressed.”

Dr. Amongin’s comments follow a recent study on the I-CAN/Nsobola/An atwero social support intervention, piloted in Mayuge and Oyam districts in 2023. The study highlights that social support significantly improves women’s ability to make informed contraceptive choices, potentially leading to better reproductive health outcomes.
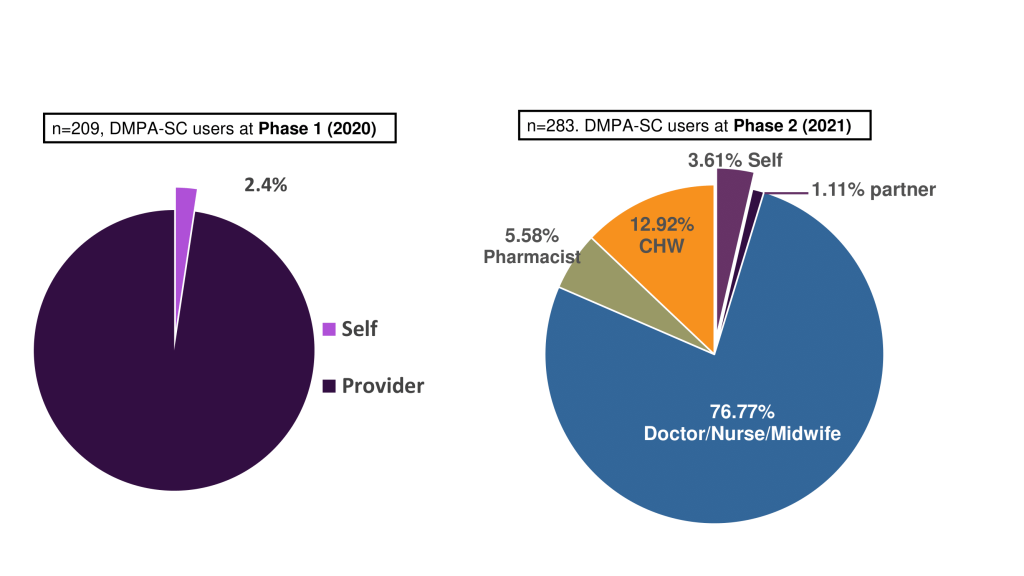
Part of the Innovations for Choice and Autonomy (ICAN) project, the study shows that self-injection with DMPA-SC (Sayana Press) could increase contraceptive use, especially among women with limited access to healthcare. Despite the rollout of this method in 2017, its use remains low in Uganda. Sayana Press as popularly known is a subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA-SC). It is a hormonal birth control shot, administered under the skin and is an all-in-one contraceptive that puts women in charge of their reproductive health.
Social support boosts self-efficacy, enhances privacy, and reduces access barriers, making self-management easier. Family planning helps manage the number and timing of children, lowering maternal and infant mortality rates and reducing complications from pregnancy. Conversely, unmet contraceptive needs can lead to unintended pregnancies and their associated risks.

In Uganda, 52% of pregnancies are unwanted or mistimed, with over 43% due to unmet family planning needs. The country’s youthful population complicates the issue, with 50% under 17 years old, at least according to the recent National Population Census. Notably, 10% of girls, one in every 10 girls you encounter, has already had sex before she turns 15 years, and 20% of boys, two in 10 boys have engaged in sexual intercourse by the same age.
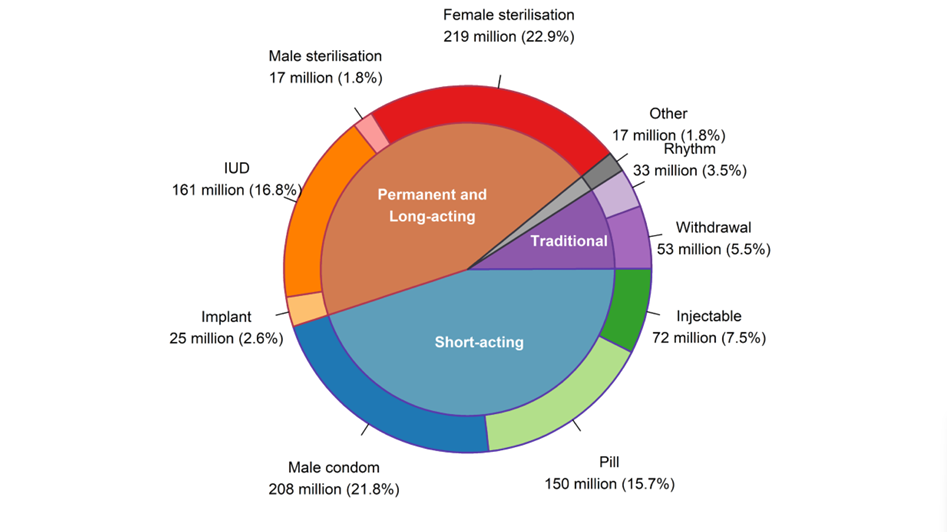
Methods of contraception include oral contraceptive pills, implants, injectables, patches, vaginal rings, intra uterine devices, condoms, male and female sterilization, lactational amenorrhea methods, withdrawal and fertility awareness-based methods.
Global statistics show that 77.5% of women aged 15–49 had their family planning needs met with modern methods in 2022, up from 67% in 1990. In sub-Saharan Africa, the proportion of women who have their need for family planning satisfied with modern methods (SDG indicator 3.7.1) continues to be among the lowest in the world at 56 per cent. Nevertheless, it also increased faster than in any other region of the world, having more than doubled since 1990, when this proportion was only 24 per cent.
Among 1.9 billion women of reproductive age (15-49 years), an estimated 874 million women use a modern contraceptive method and 92 million, a traditional contraceptive method. The number of modern contraceptive users has nearly doubled worldwide since 1990 (from 467 million). Yet, there are still 164 million women who want to delay or avoid pregnancy and are not using any contraceptive method, and thus are considered to have an unmet need for family planning.
Slow progress is due to factors like limited method choices, restricted access, fear of side effects, cultural opposition, and gender-based barriers.
Between 2015 and 2019, there were 121 million unintended pregnancies annually worldwide – 48 per cent of all pregnancies. Despite decreases in the rate of unintended pregnancy in all regions over the past three decades, nearly one in 10 women in sub-Saharan Africa, Western Asia and Northern Africa, and Oceania (excluding Australia and New Zealand) continue to experience an unintended pregnancy every year

In Uganda, where healthcare services are stretched thin and women juggle numerous responsibilities, accessing contraceptives can be challenging.
Dr. Amongin emphasizes that self-injection methods like DMPA-SC, also known as Sayana Press could ease the burden on women facing long queues and logistical challenges at health facilities. “This method allows for discretion and reduces the need for frequent visits, which is crucial for women with busy lives,” she says.
Researchers argue that the health sector’s budget should include substantial funding for family planning. The high cost of inaction is evident: neglecting family planning leads to unplanned pregnancies, which ultimately burdens families and the nation. Addressing this issue early in the life cycle is crucial to prevent these long-term consequences.
“This is the gist of the matter behind all our research, that a woman’s preference needs to be respected. The health facilities must stock commodities so that when a woman is in need, she actually gets it,” noted Dr. Amongin.
Dr. Peter Waiswa, an Associate Professor at MakSPH, stresses the importance of informed choice in family planning. ICAN studies across Kenya, Malawi, Nigeria, and Uganda show that self-injection benefits all women, including young adolescents. “Supporting young people to make informed choices helps prevent unintended pregnancies,” says Prof. Waiswa.
“We spent four years trying to understand which women benefit from injecting themselves. And we found that all women benefit from it, including younger children. Because younger children in Uganda, whether we hide our heads in the sand or not, especially those 12 years and above are having sex and some of them using contraceptives,” Professor Waiswa says.

What is factually true is that by age 18, 60% of Ugandans have reported having sexual intercourse. Despite the benefits, dropout rates from family planning methods remain high due to side effects and lack of support. Dr. Waiswa also, a Public Health specialist, critique and dreamer for better health systems for mothers, newborns and children in Africa calls for better education and support to address these issues.
“As a way of being supported in a safe space whereby people are not asking questions, they are not fearing parents, they are not fearing other people, then they can use the methods. What we did in Mayuge and Oyam, we trained women who are users of family planning. To identify people who need to use family planning but are not currently using and then they go and see whether they can use or not. And we found that when people are supported, those groups which are currently not being reached can be reached by family planning,” argues Prof. Waiswa.
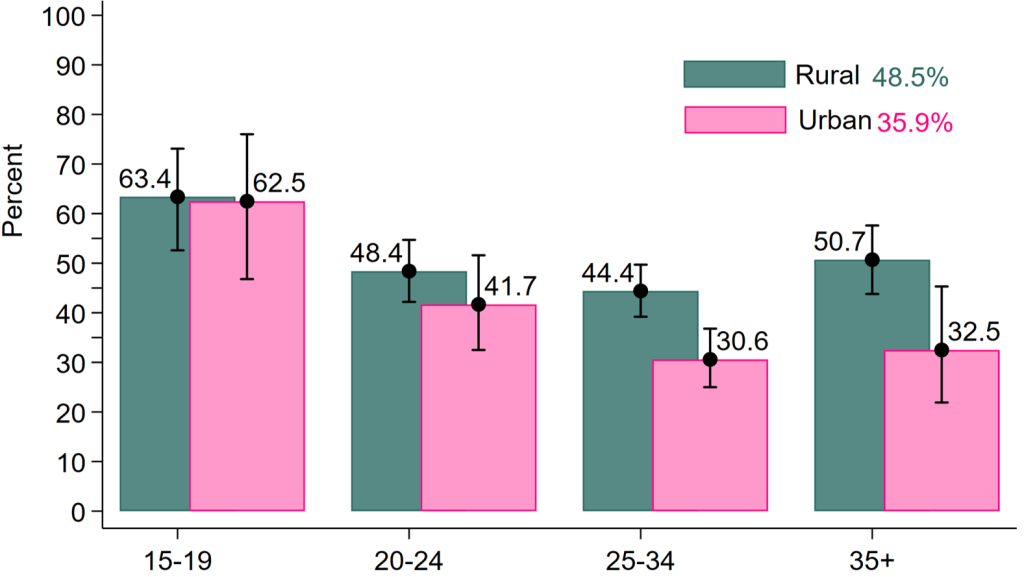
A 2021 study found that contraceptive discontinuation significantly impacts the effectiveness of family planning services, leading to higher fertility rates, unwanted pregnancies, and induced abortions.
Analysis of data from PMA 2020 show that 6.8% of women discontinued contraceptive use, with discontinuation linked to factors such as age, marital status, method type, and health concerns. The study suggests prioritizing interventions to encourage contraceptive use among young people and promoting partner involvement and awareness, as many contraceptive methods are not discreet.
Prof. Waiswa is concerned of the high dropout rate from family planning methods, where many women discontinue use due to side effects, a need for better education and support.
“We need to see how to educate women so that they are informed when they are choosing a method to use. They need to have enough information because when they discontinue, the method can be ineffective, can cause side effects, but also these methods are expensive, so they waste money. There are a lot of those who change to other methods. We are learning a lot on the use of family planning why we still have a large unmet need,” says Prof. Waiswa.
Ms. Roseline Achola, Technical Specialist for Sexual and Reproductive Health and Self-Care at the Ministry of Health, hailed the MakSPH study on self-injection contraception. She noted that the findings will help her enhance support for self-care initiatives. However, she expressed that only 29% of women willing to self-inject as indicated in the study is still low, highlighting a need to address barriers to increase acceptance as well as managing sexually active adolecents. “We must discuss how to handle minors seeking contraception to prevent unintended pregnancies,” she says.
On Friday August 23, 2024, the Daily Monitor reported, an increase in young girls adopting family planning to combat teenage pregnancies and school dropouts. Quoting data from the Uganda Health Information System, statistics show that between March 2023 and March 2024, 2,476 girls under 15 had their first antenatal care visit, and 1,755 gave birth. The highest number of pregnancies among this age group was in Oyam district.
In this period, Lango subregion saw 52 pregnancies among this age group, with Oyam district recording the highest at 10 cases. The 2021 UNFPA fact sheet indicates that Busoga region, particularly Kamuli and Mayuge districts, has the highest rates of teenage pregnancies, with 6,535 and 6,205 cases respectively.
“As the country, it’s clear that adolescents are limited to access to contraception because of so many reasons. For us as a Ministry, any woman between the age of 15 to 49 is a woman of reproductive age and that tells you that she is capable of getting pregnant and when such a girl of probably 15 years goes to a facility to seek for contraception, it rings a message that actually she is sexually active. So how do we handle her? So that is a matter of discussion for the country.
It is a matter that the nation needs to decide on, because we all know the girls are getting pregnant, the girls want to use contraception, but they have no access because of the fact that they are children,” wondered Achola.

Unintended pregnancies and Uganda’s abortion paradox
Abortion in Uganda, is largely illegal except in specific circumstances. It contributes to maternal death due to unsafe practices. Between 2010 and 2014, WHO reported that 30.6million abortions conducted were safe and 25.1million were unsafe. 97% of these occurred in developing countries. In East Africa, the total number of abortions per year according to the Lancet are around 2.65million.
The Ministry of Health’s HMIS data show a rise in abortion cases, with 96,620 reported between July 2020 and June 2021in both government and private health facilities.
Another recent study on the quality of post-abortion care by MakSPH researchers Assoc. Prof. Lynn Atuyambe, Dr. Justine Bukenya, Dr. Arthur Bagonza and Mr. Sam Etajak highlights the need for accurate post-abortion care data to improve healthcare planning and policymaking.
Dr. Arthur Bagonza, a Public Health Consultant and Research fellow with specialization in health systems at MakSPH and one of the uality of post-abortion care has called for accurate abortion data to improve healthcare planning and policymaking. He notes that health workers often avoid documenting abortion data due to legal fears and calls for reforms to restrictive laws to ensure accurate reporting without legal repercussions.
“All assessed health facilities reviewed in our study achieved a 100% timeliness rate for report submissions. However, significant disparities were observed in data accuracy between different levels of health facilities, with lower-level facilities (HC IIs and HC IIIs) showing higher rates of data discrepancies,” says Dr. Bagonza.

According to Dr. Amongin, the high incidence of early sexual activity among Uganda’s youth is a pressing public health issue.
“We know as a country many women continue to die following unsafe abortions; abortions for pregnancies that they did not want. And these abortions are highest among adolescents and also other women categories.
We would want to ensure that we actually enhance access to contraceptives, but making it easier for them to have it and putting the power in the hands of a woman to as much extent as we can. So that a woman can practice what we call self-care, but of course she also will need the support of the healthcare system. But we want this power in women’s hands because of all the challenges that the women actually can encounter in accessing these methods,” she said.
On her part, Achola insists that abortion should not be a last resort for women and urges them to abstain or use protective means in order to avoid unwanted pregnancies. She notes that as long as abortion remains illegal in Uganda, many health workers will avoid addressing it, leading people to unsafe alternatives.
“I can’t be happy because abortion means we have failed to give people a method of their choice to prevent that pregnancy. Or the people are not able to access contraception to prevent unintended pregnancies. Abortion is not the last resort, it’s not a solution because it has its own complications as well,” says Achola.

Despite this, Achola, notes most of the women who walk in health facilities with post-abortion complications must be attended to. “Whereas we don’t encourage people to do abortions, as Ministry of Health we are mandated to handle all complications for anyone who walks in our facilities because our priority is to save life. We want to urge women to avoid certain things. Why should you wait for unintended pregnancy to occur and then abort?”
Dr. Charles Olaro, a Senior Consultant Surgeon and the Director Health services – Curative in the Ministry of Health highlights the financial burden on individuals seeking health services and suggests exploring private sector opportunities and community-based approaches to improve access. “We need to balance values and rights while addressing access barriers,” he notes.
According to Dr. Olaro, the autonomy and agency of women in sexual and reproductive health, particularly in African cultures remain a challenge where social norms may require women to defer decisions to their partners.

He notes that there is a high burden of abortion and self-harm, with a significant portion of maternal mortality attributed to sepsis, which is often a result of unsafe abortions in Uganda.
“We still need evidence to ensure that access barriers are addressed. And this is a question I keep on asking Makerere University, yes, we have a young population but how are these people accessing contraceptives. Other issue we have to deal with is complex. I know we have to do a balance between values and rights, but we will be able to look at that when they gain the success to do it.”
Dr. Olaro points out that individuals often face a financial burden in health services, spending more on prescriptions than on the medications themselves. He suggests exploring private sector opportunities and a community-based approach to improve access to healthcare.
NB: The PMA surveys are spearheaded by Associate Professor Fredrick Makumbi and Dr. Simon Kibira of MakSPH, with support from the Uganda Bureau of Statistics and the Ministry of Health. The initiative also receives funding from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, The Children’s Investment Fund Foundation (CIFF), and is supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Institute for Population and Reproductive Health at Johns Hopkins University and Jhpiego.
You may like
-


Makerere University Students Triumph in National Conservation Competition
-


Mak Cooperative Society holds AGM: Growth, Transparency and Member Welfare Take Centre Stage
-


From Campus to Community: Universities Lead Teso in Fight Against Greenhouse Gas Emissions
-


Makerere University Launches Short Course to Strengthen Climate Change Reporting
-


Makerere University and World Bank Sign Partnership to Strengthen Environmental and Social Sustainability Capacity
-


Makerere University Explores Expanded Partnership with Stanbic Bank to Advance Innovation and Investment
Health
Makerere Graduation Underscores Investment in Africa’s Public Health Capacity
Published
7 days agoon
March 4, 2026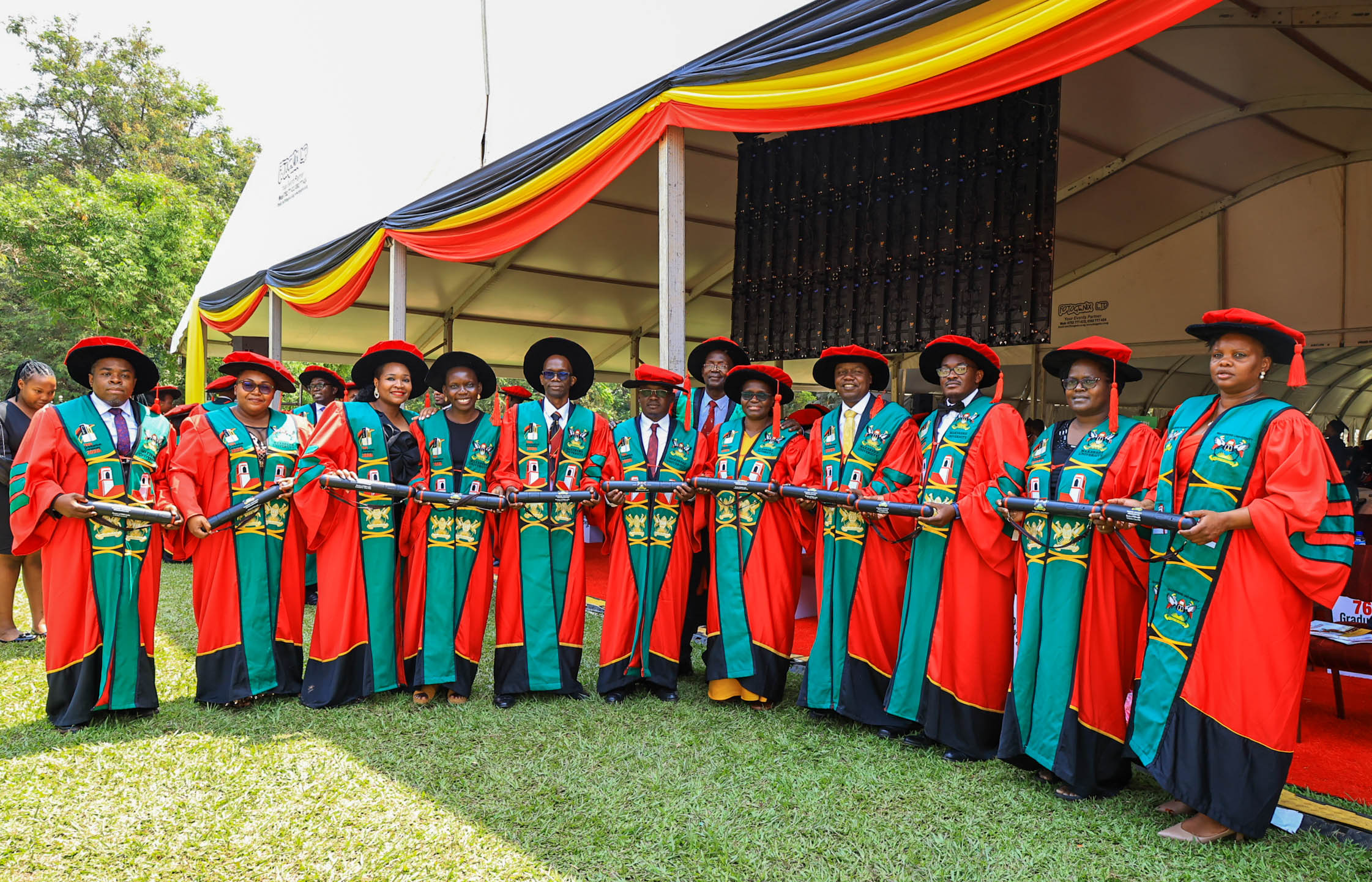
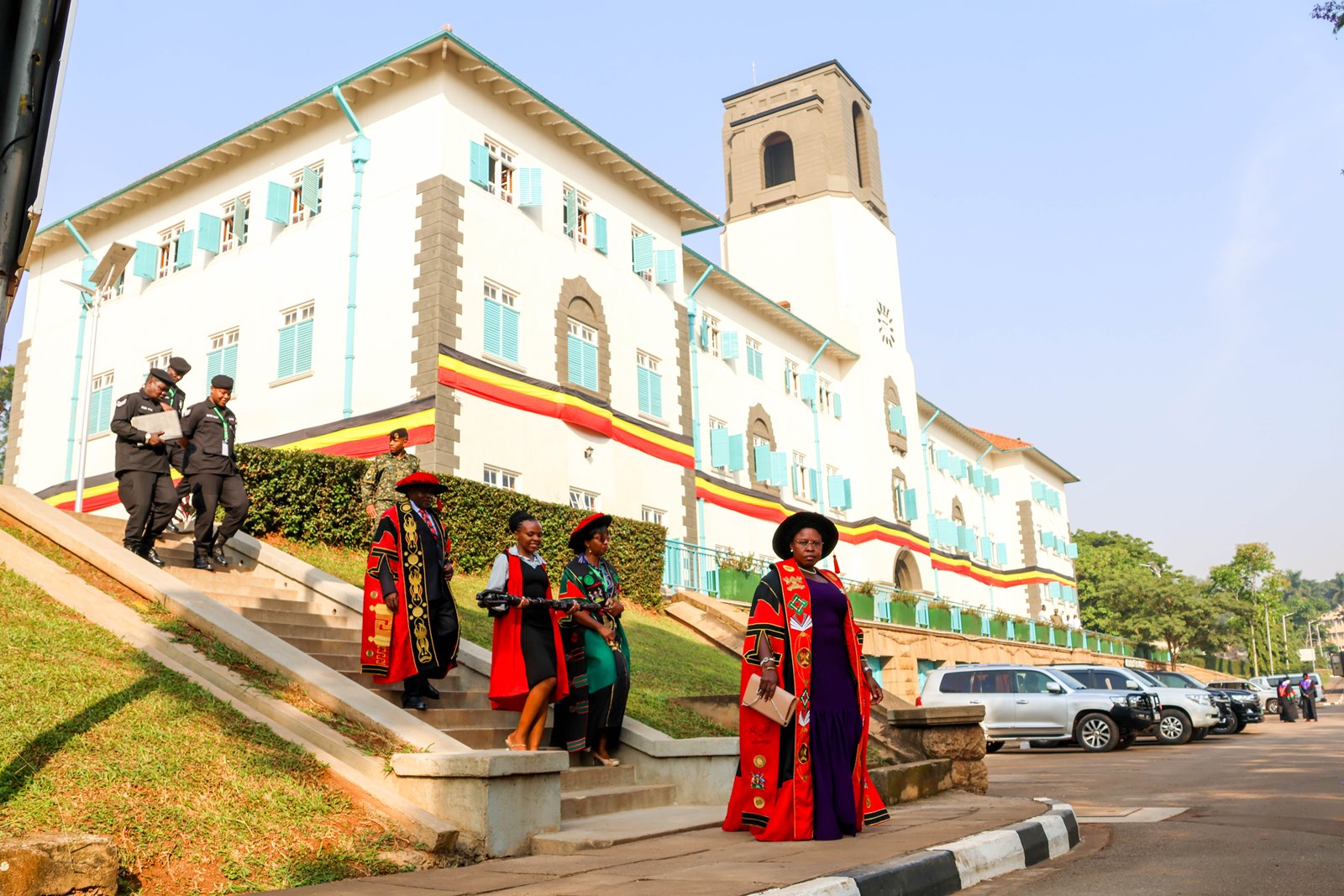
KAMPALA, 25 February 2026 — Higher education must move beyond awarding degrees to producing solutions for national and global crises, speakers said on Wednesday as Makerere University continued its 76th Graduation Ceremony, positioning universities as central actors in strengthening Africa’s public health capacity.
Addressing graduands on Wednesday, February 25, 2026, at Freedom Square, national leaders and university officials framed graduation not as a ceremonial endpoint but as an investment in workforce readiness, research leadership, and evidence-driven governance, particularly at a time when health systems across the continent face growing pressure from pandemics, demographic change, and climate-related risks.
The message resonated strongly through presentations from Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) and Makerere University College of Health Sciences (MakCHS), whose graduates enter professional service amid renewed global attention to health system resilience, scientific leadership, and locally generated research.
Delivering the commencement address on Day Two of Makerere University’s 76th Graduation Ceremony, Dr. Margaret Blick Kigozi, Board Chairperson of the Makerere University Endowment Fund, reflected on her graduation in 1976 during a period of national uncertainty under then-Chancellor President Idi Amin. She recalled leaving Uganda soon after with her young family, carrying “little more than education, values, and hope,” an experience she used to frame lessons on resilience, purpose, and responsibility in uncertain times.
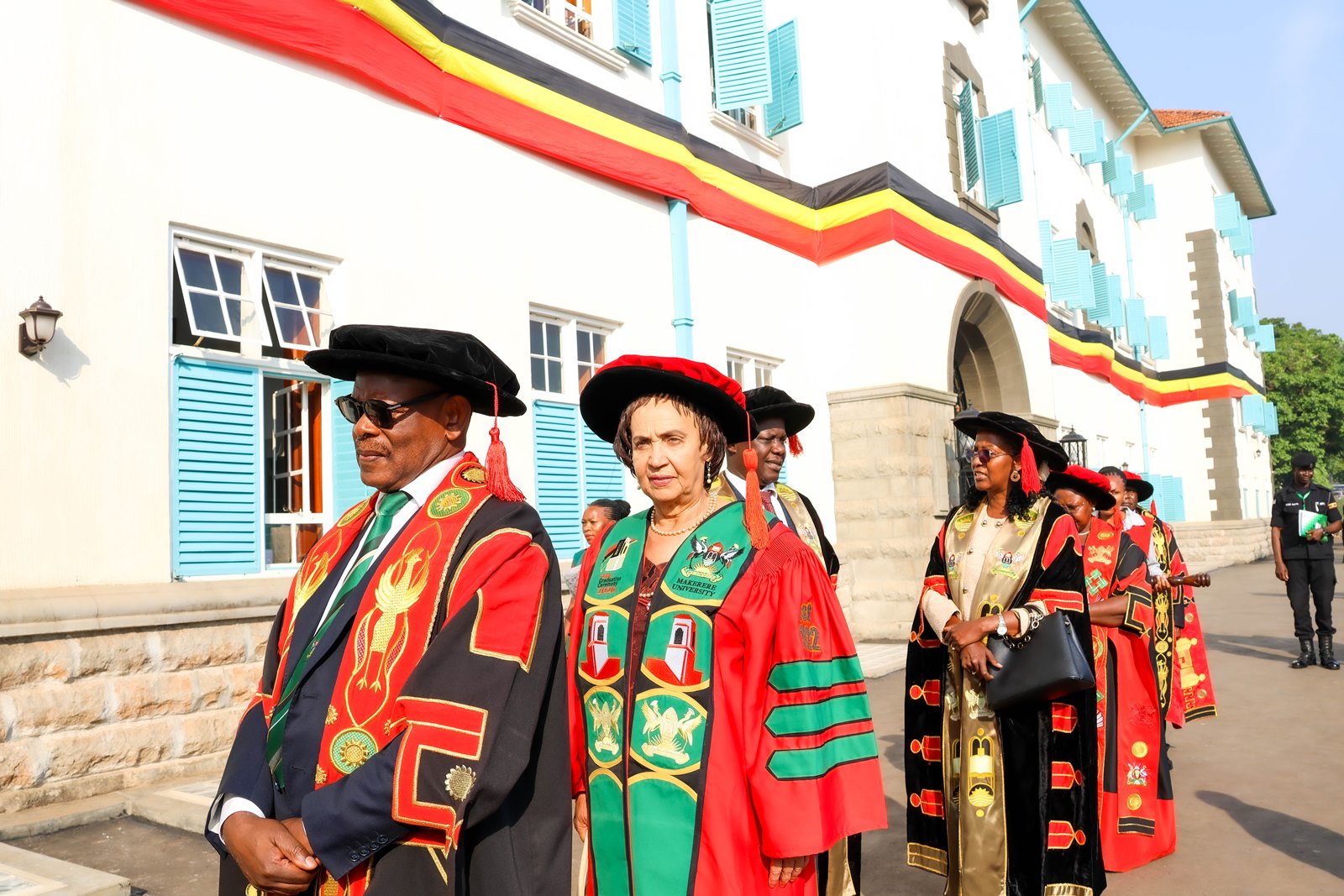

Challenging graduates to rethink professional success, she reminded those entering health and life sciences that their training carries extraordinary influence.
“Power does not make you important; it makes you responsible,” she said. “You will decide who is listened to and who is dismissed, who waits and who is rushed through, who feels safe and who feels small. Your education has trained you to ask better questions, but your humanity must guide the answers. Behind every chart, every case, every experiment, there is life, and life deserves care, patience, and dignity.”
Throughout the ceremony, speakers returned to a common refrain: societies increasingly depend on evidence, and universities must produce professionals capable of translating knowledge into policy, practice, and community impact.
Across the four-day congregation, the University will award 9,295 degrees and diplomas, including 2,503 Master’s degrees, 6,343 Bachelor’s degrees, 206 Postgraduate Diplomas, and 30 Diplomas. But beyond the numbers, speakers repeatedly returned to a central question on how higher education can translate academic growth into national development and health security.
On day two, graduands were presented from the College of Natural Sciences, the College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Biosecurity, the College of Health Sciences, and the MakSPH, the latter positioned squarely within Africa’s ongoing struggle to expand its pool of trained epidemiologists, health systems researchers, and policy leaders.
Vice Chancellor Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe noted that Africa averages just 80 researchers per million people, compared to a global average of 1,081, warning that the human resource gap remains substantial.
“Today the School of Public Health presents graduands joining the field at a time when Africa faces a critical shortage of highly trained public health leaders,” he said.
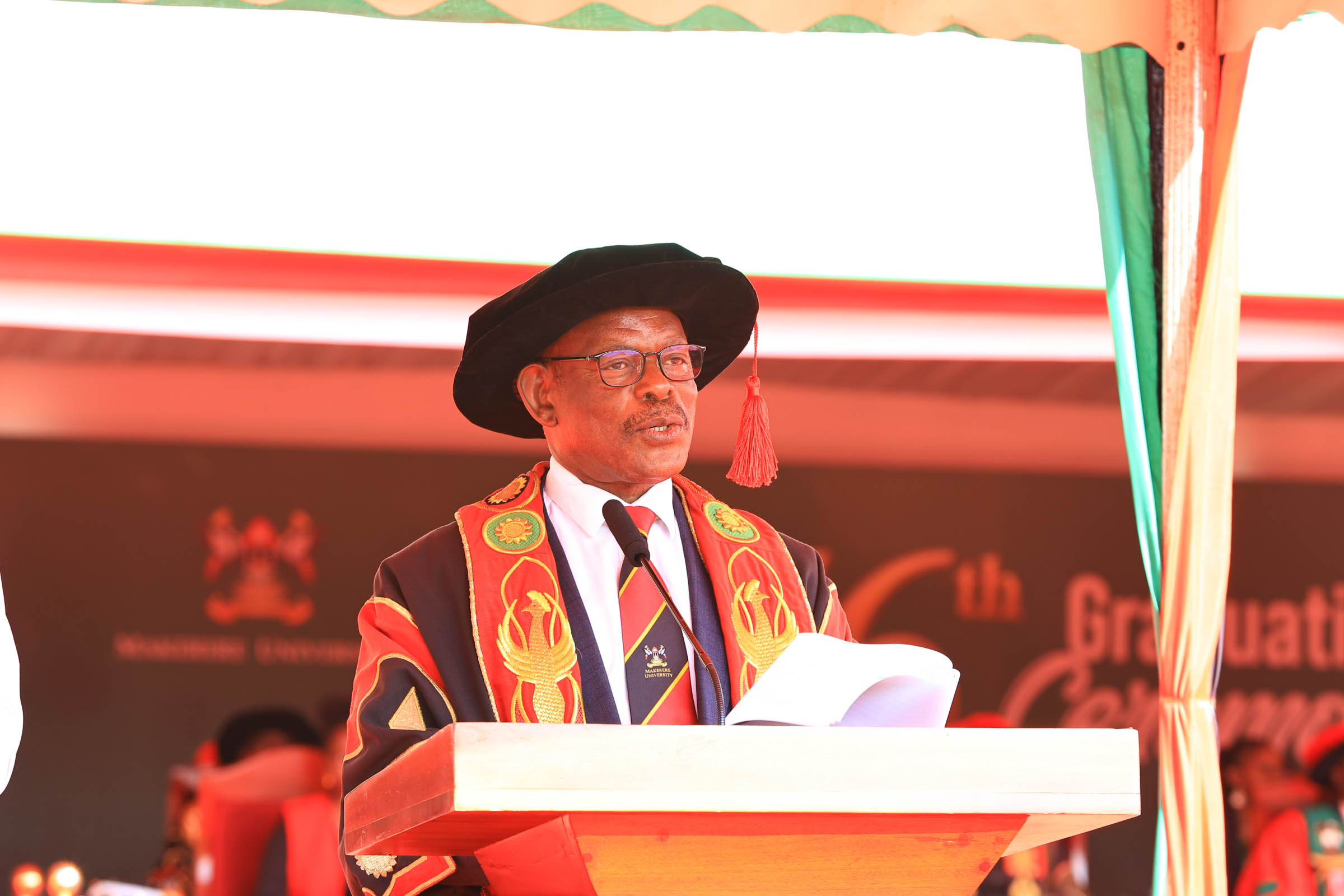

The School of Public Health presented seven PhD candidates: Aber Harriet Odonga, Komakech Henry, Lubogo David, Nakisita Olivia, Namukose Samalie, Ntaro Moses, and Osuret Jimmy. It also graduated 195 Master’s students and 29 Bachelor of Environmental Health Science graduates, including four first-class honours recipients led by Phillip Acaye with a CGPA of 4.63.
Their research spans maternal and child health, epidemic preparedness, sanitation behaviour change, nutrition systems integration, and injury prevention, areas increasingly recognised as foundational to national development rather than peripheral health concerns.
University Chancellor Dr. Crispus Kiyonga emphasized that research must move beyond academic publication into policy and implementation.
“Research plays a very vital role in the development of any community,” he said, linking university scholarship directly to Uganda’s national development agenda.
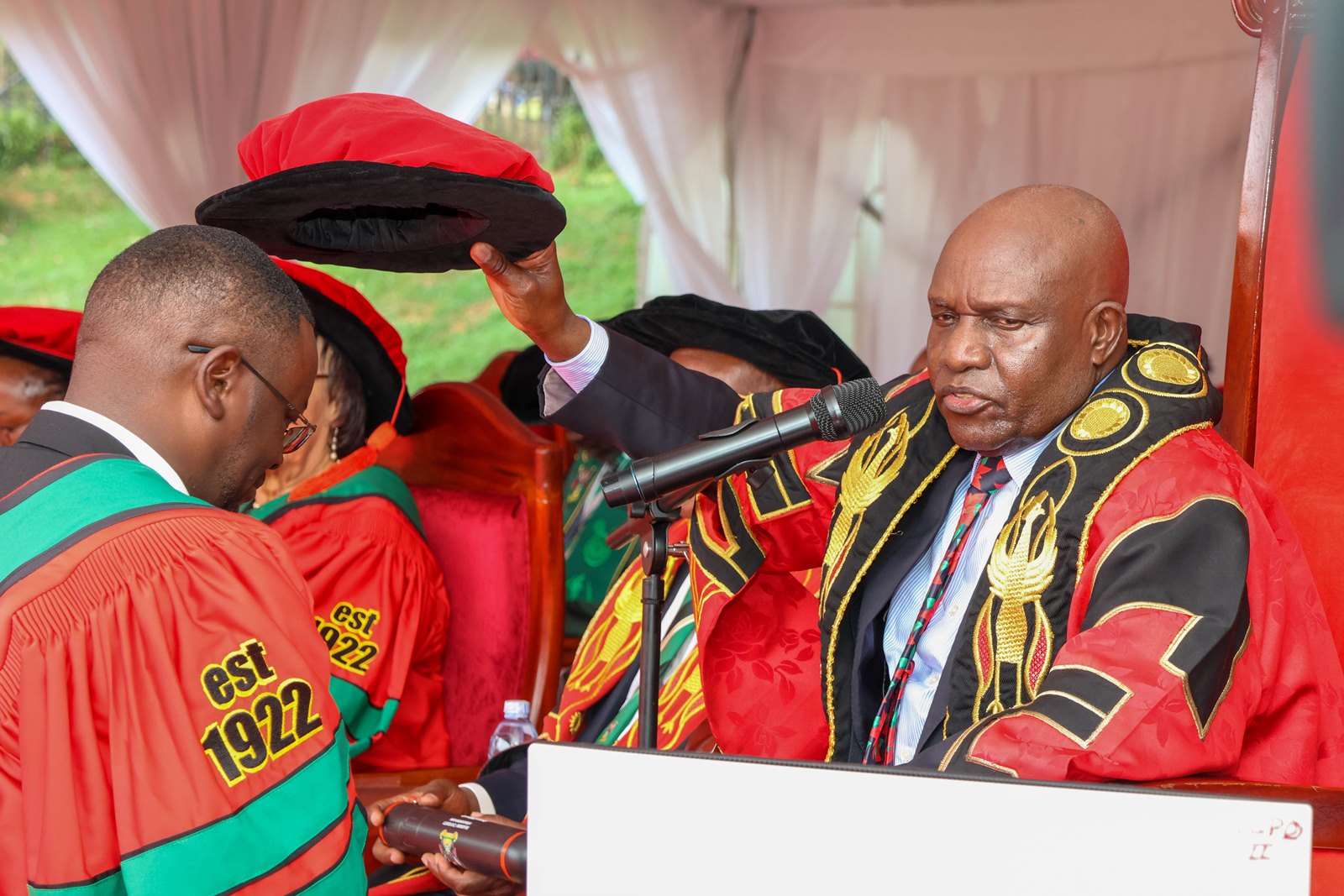

For public health education, that responsibility carries particular urgency. The COVID-19 pandemic, recurring disease outbreaks, and climate-linked health risks have exposed how deeply national stability depends on scientific capacity.
The chancellor hailed the Government of Uganda for committing UGX 30 billion through the Makerere University Research and Innovations Fund (MakRIF).
Mak Urged on More PhDs
Representing the First Lady and Minister of Education and Sports, State Minister Dr. Joyce Kaducu Moriku described doctoral training as central to Uganda’s research ambitions, noting government efforts to expand funding and modernize higher education systems.

“Universities must produce more PhDs to strengthen the national research agenda,” she said, adding that competence-based reforms aim to align training more closely with societal needs.
“More PhDs also mean the university is growing in academic leadership and an increase in research. So, keep the numbers growing, especially in Science, Technology, and Engineering,” she added.
The 213 PhDs conferred this year, a record, signal more than institutional expansion but a response to structural deficits.
Africa bears approximately 25% of the global disease burden but produces a disproportionately small share of global health research. The continent’s research density remains far below global averages. In this context, each doctoral graduate becomes not merely an academic achievement but a strategic asset.
A University Responding to Its Moment
For the School of Public Health, the graduation reflects a broader evolution in how public health training is conceived. Rather than focusing solely on the treatment of disease, the field increasingly addresses systems, sanitation, nutrition, behavioural change, surveillance, prevention, and climate change, areas where research directly shapes everyday life.
Recent MakSPH-led initiatives, including national HIV impact surveys and digital health system expansion, demonstrate how academic institutions increasingly function as implementation partners to the government rather than observers.
Over the past five years, MakSPH has supported the national scale-up of electronic medical records through the CDC-funded Monitoring and Evaluation Technical Support (MakSPH-METs) programme, and led the Third Uganda Population-Based HIV Impact Assessment (UPHIA 2024–2025), the first fully Ugandan-implemented national survey of its kind.
Launched in 2020, the METs program has supported the nationwide scale-up of UgandaEMR+, transitioning thousands of facilities to secure electronic medical records and deploying critical ICT infrastructure. In March 2026, these systems will be formally transitioned to the Ministry of Health, reflecting sustainable national ownership.
Health
Three MakSPH Faculty Honoured with Makerere University Research Excellence Awards 2026
Published
1 week agoon
March 2, 2026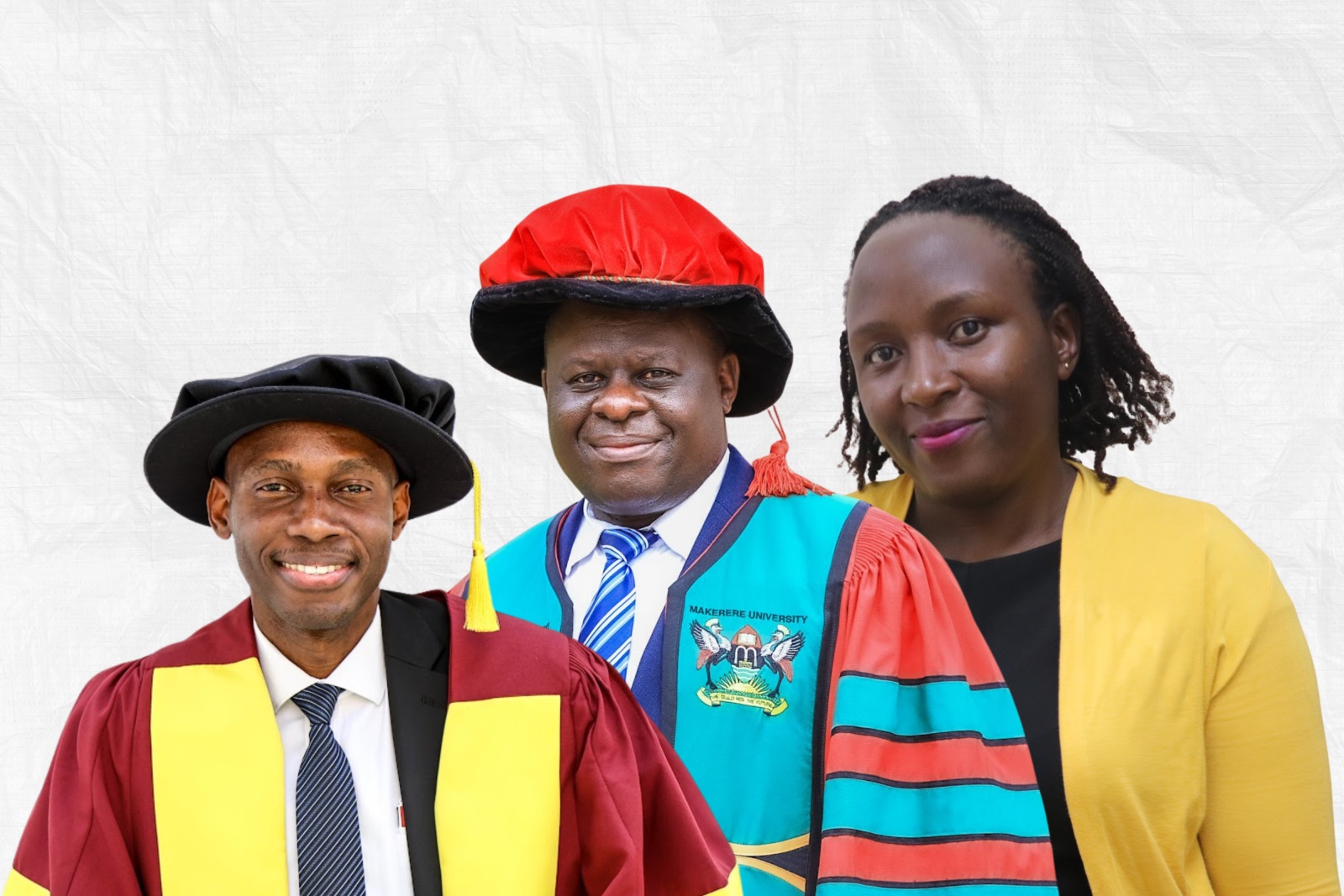
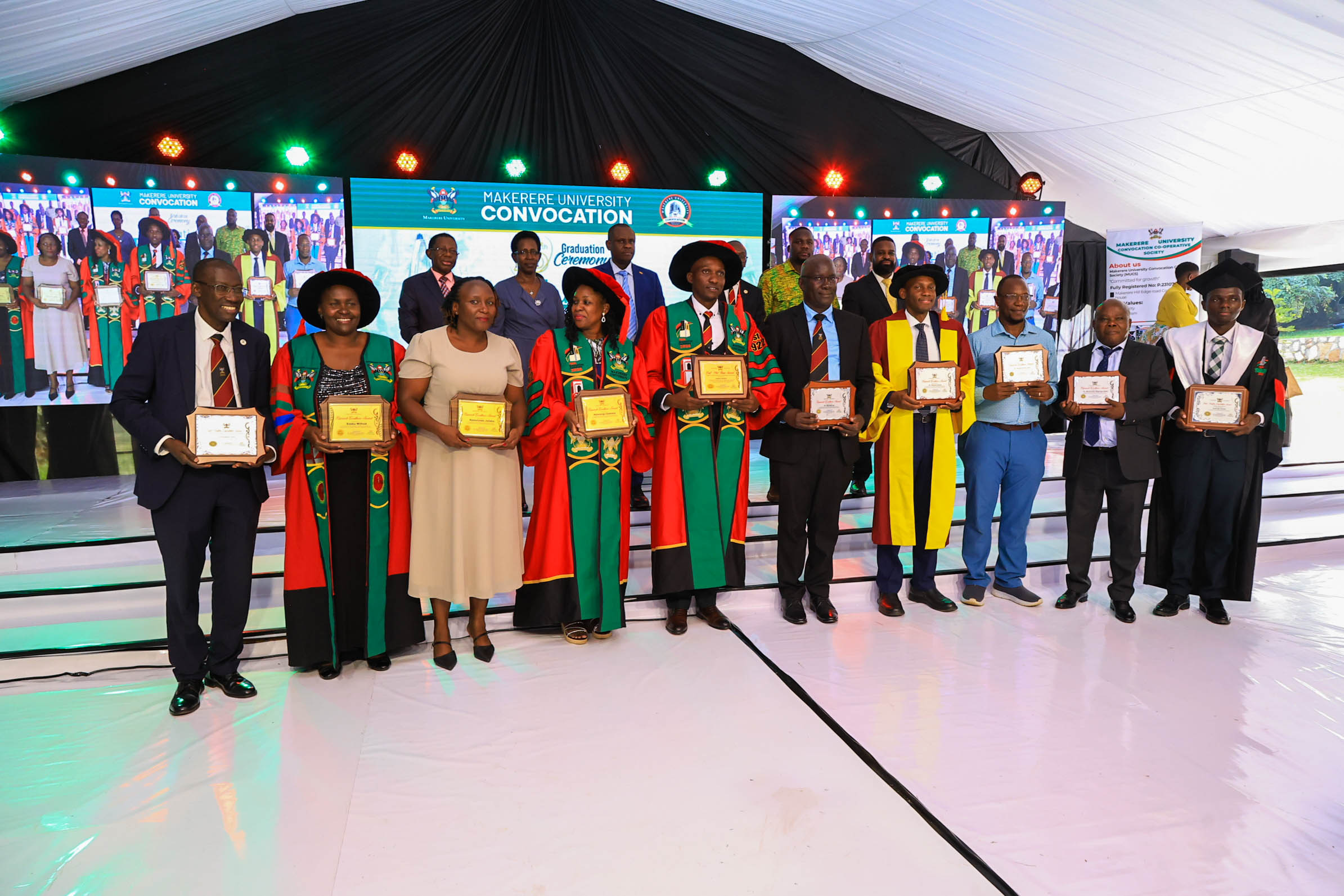
KAMPALA—Three faculty members from Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) have been recognised at the Makerere University Vice-Chancellor’s Research Excellence Awards 2026, highlighting the School’s expanding contribution to research leadership, scientific productivity, and policy-relevant scholarship across Africa.
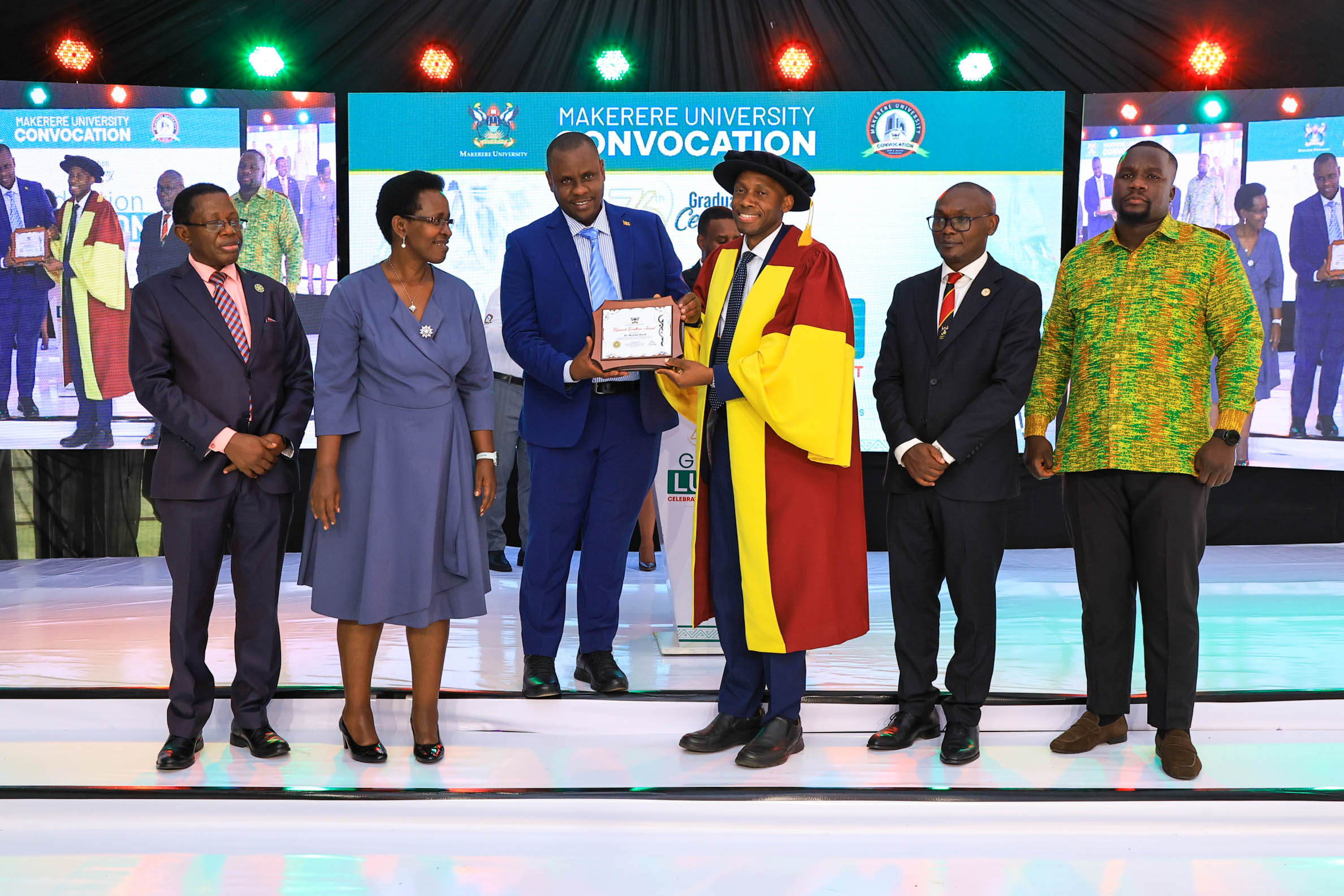
Associate Professor Peter Kyobe Waiswa, Associate Professor David Musoke, and Juliana Namutundu received honours during the University’s 76th Graduation Ceremony at Freedom Square, where Makerere celebrated scholars whose work has demonstrated exceptional research achievement and impact beyond academia.

The annual awards, coordinated by the Directorate of Research, Innovation and Partnerships (DRIP), recognise faculty and staff whose scholarly output and leadership advance Makerere University’s ambition to become a research-led institution.
“This recognition celebrates sustained excellence in research productivity and contributions to knowledge that advance both national and global discourse,” Vice-Chancellor Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe said. “We are strengthening a culture where research does not remain confined to journals but translates into solutions for society.”
Among the university’s top researchers was Assoc. Prof. Peter Kyobe Waiswa, a health systems scientist whose work focuses on maternal, newborn, and child health. Waiswa ranked among Makerere’s overall top researchers after publishing 43 peer-reviewed papers in 2025, tying with three-time award winner Prof. Moses Kamya of the School of Medicine in the College of Health Sciences.
His research examines how health systems function at their most fragile moments, including childbirth, early life, and community-level care, addressing questions of equity, service delivery, and health system performance across Africa.
Also recognised was Dr. David Musoke, an Associate Professor of Disease Control, whose 25 publications earned distinction among senior career researchers. His work spans environmental health, community health systems, and implementation research, areas increasingly viewed as critical to preventing disease before it reaches hospitals.

In the early-career category, Juliana Namutundu received recognition for emerging research leadership, reflecting Makerere’s effort to nurture the next generation of African scholars.
Together, the awards underscored MakSPH’s growing influence within Makerere’s research ecosystem, particularly in fields linking science directly to population wellbeing.

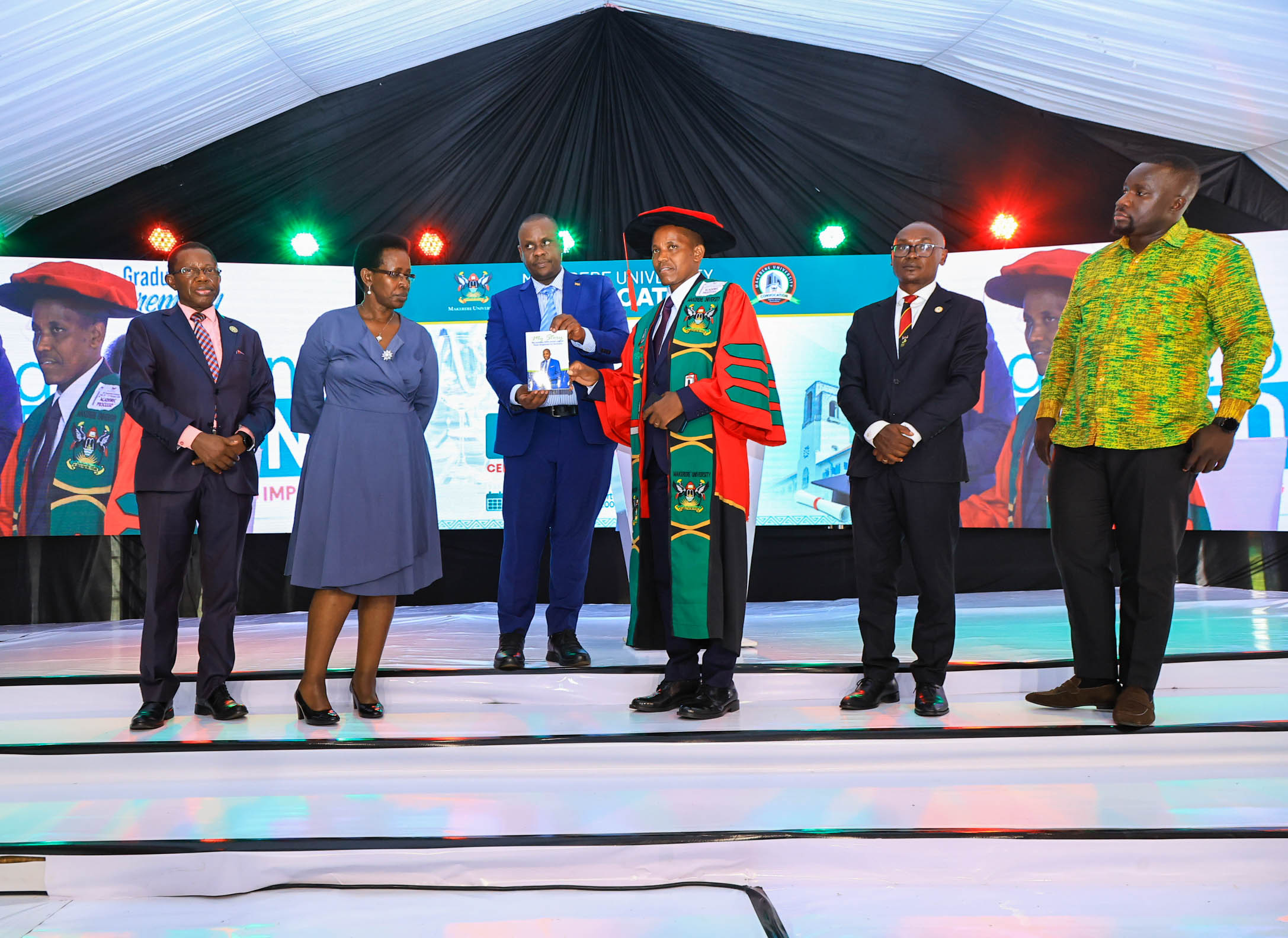
The Research Excellence Awards were established to encourage publication in high-impact journals while reinforcing Makerere’s ambition to become a globally competitive research university. Nominations are reviewed by the Board of Research and Graduate Training, chaired by Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Academic Affairs) Prof. Sarah Ssali.
Awardees were honoured during a graduation luncheon organised by the Makerere University Convocation, the institution’s alumni and staff association, which described the event as a celebration of “excellence and inspiring impact.”
The ceremony also recognised forms of scholarship extending beyond traditional academic publishing.
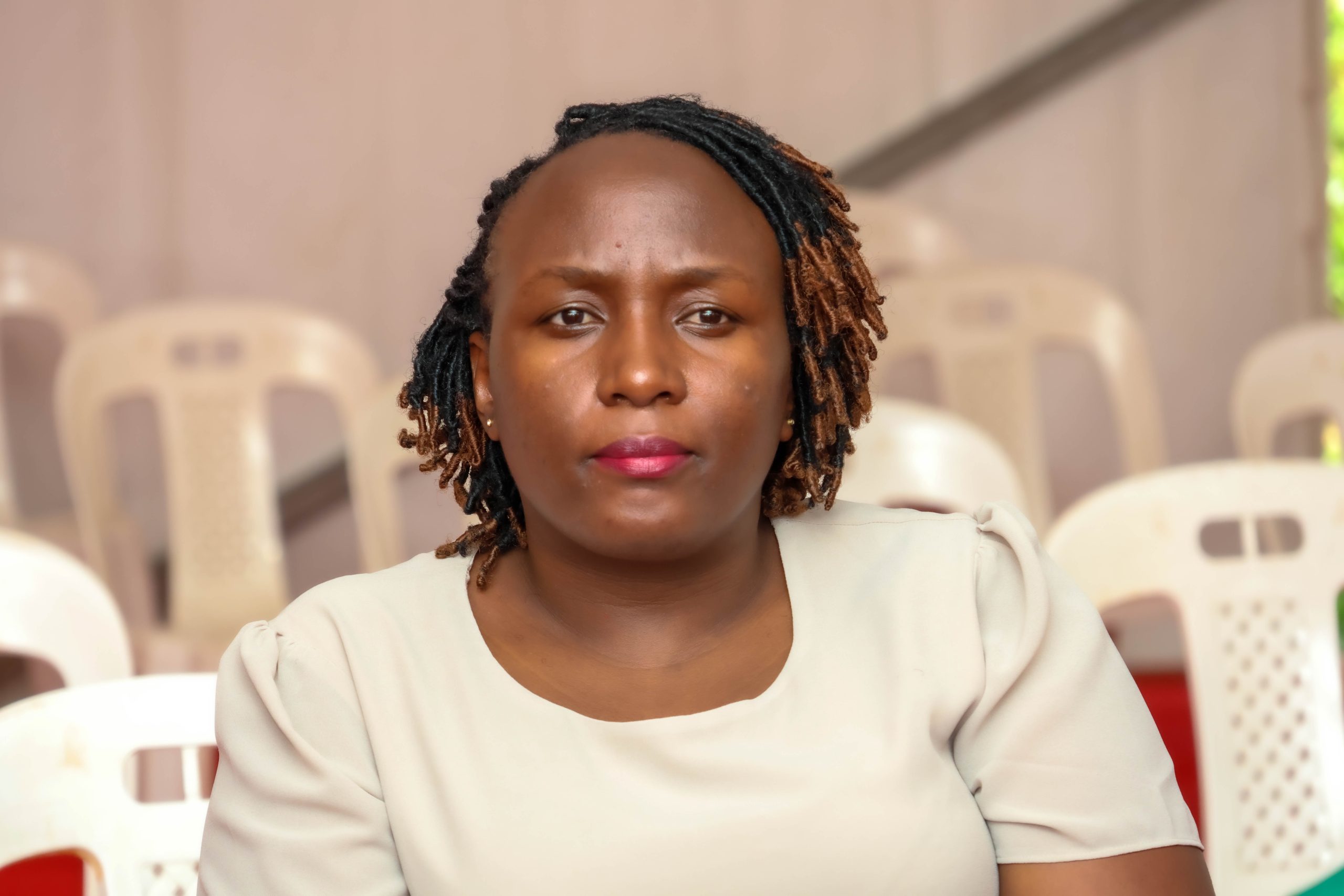
Dr. Geofrey Musinguzi, a research associate at the School of Public Health, was honoured for his book My Journey with Rectal Cancer, an account of diagnosis, treatment, and recovery that blends personal testimony with public health advocacy.
Diagnosed at age 44 while a visiting scholar at the University of Antwerp in Belgium, Musinguzi sought medical care after experiencing persistent symptoms, including rectal bleeding and back pain. His treatment involved surgeries, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and a year living with a colostomy bag.

Rather than keeping the experience private, he documented it publicly to challenge cancer stigma and encourage early screening. The book, launched at the School of Public Health in August 2024, highlights how lived experience can shape public health awareness alongside scientific research.
The recognition reflects a broader understanding of research impact, one that includes scholarship capable of influencing behaviour as well as policy.

Makerere’s emphasis on research excellence comes as African universities face increasing pressure to produce locally grounded evidence while competing globally for visibility and funding. For MakSPH, whose work spans disease surveillance, environmental health, and health systems research, publication output increasingly serves as both academic currency and development infrastructure.
“These awards are part of our broader effort to position Makerere as a truly research-led institution,” Nawangwe said, adding that scholarship must remain aligned with national and regional priorities.
Health
Makerere’s 76th Graduation Ceremony: CHS showcases research strength with 26 PhD Graduates
Published
2 weeks agoon
February 26, 2026By
Zaam Ssali
The second day of the Makerere University 76th Graduation Ceremony, held on Wednesday 25th February, marked another proud moment as the institution continues its tradition of academic excellence and national service. Graduands were presented for conferment of degrees and award of diplomas from the College of Health Sciences (CHS), College of Natural Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Biosecurity and School of Public Health.
The College of Health Sciences presented a total of 746 graduands for conferment of degrees including 26 PhD, 293 Masters, 425 Bachelors and 2 Diplomas. This is a testament to CHS and Makerere University’s contribution in training skilled health professionals and strengthening Uganda’s health systems through education, innovation and research.
Speaking to the congregation, Professor Barnabas Nawangwe – Vice Chancellor, Makerere University welcomed everyone to Day 2 of Makerere University’s 76th Graduation. He congratulated the 9,295 graduands comprising 4,262 (46%) female graduates and 5,033 (54%) male graduands who will be awarded degrees and diplomas through the graduation week; 213 graduands are PhD recipients. He commended the efforts of staff, parents, and sponsors in supporting the students’ journeys.
He reminded the congregation that outstanding researchers were honored on Day 1 of the graduation for excellence in scholarly work and impactful publications, reaffirming the University’ commitment to research productivity and academic distinction. In addition, the Innovation Commercialization Award was also presented, highlighting Makerere’s focus on turning research into practical solutions that address real-world challenges and drive national development.
The Vice Chancellor highlighted the history of the College established in 1924 cognizant of its impact on Uganda’s Health sector and beyond. He said, ‘As the College enters its second century, it is strengthening specialist training to address increasingly complex health challenges’. CHS has introduced fellowship programmes to equip physicians with advanced expertise which are useful in transforming health systems across Uganda and the region. In 2025 alone, 16 fellows graduated in Pediatric Hematology and Oncology, with additional fellowships underway in Newborn Health, Interventional Radiology, Emergency Care Medicine, and Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine.
Professor Nawangwe also noted the progression of one of the centres of excellence at CHS, the Makerere University Lung Institute (MLI) established a decade ago to address the growing burden of lung disease in Uganda. He said, ‘today, the MLI serves 6,000 patients annually, shapes national policy and has embarked on construction of a new building, signalling a renewed commitment to advancing respiratory health in Uganda and beyond’.
He also reminded the congregation that CHS continues its centennial celebrations, including the upcoming Alumni Dinner Gala on March 6th 2026 to raise funds for refurbishing the iconic Davis Lecture Theatre, culminating in the unveiling of a Centennial Monument later this year.
Professor Nawangwe applauded the steady advancement of Makerere University into a research-led institution, generating knowledge that drives communities, strengthens industries, and advances national transformation.
Professor Maggie Kigozi was the commencement speaker for Day 2. Professor Kigozi, a distinguished alumna reflected on how her time at Makerere University shaped her life, career, and values, recalling her graduation in 1976 during a period of national uncertainty. Forced to leave Uganda soon after with little more than her education and determination, she noted that her Makerere training opened doors across the region, enabling her to serve in leading health institutions in Zambia, Kenya, and Uganda. Addressing the graduands, she emphasized that their Makerere education remains a powerful passport to opportunity and carries with it the responsibility to uphold excellence and integrity wherever they serve.
She urged graduates in the health and life sciences to handle the power of their profession with humility, compassion, and responsibility, reminding them that behind every patient, case, or experiment lies a life deserving dignity. Beyond clinical expertise, she encouraged them to develop business and financial skills to build sustainable health services and create opportunities for others. She also reassured them that failure is part of growth, noting that resilience, continuous learning, and balance in life are essential to meaningful success as they step forward as ambassadors of the Makerere legacy.
Delivering a speech on behalf of the First Lady and Minister of Education and Sports, Janet Kataha Museveni, the State Minister for Primary Education, Hon. Dr. Joyce Moriku Kaducu, said the Government had deliberately deepened investment in higher education to position universities as drivers of national development.
Hon. Kaducu described the establishment of the Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund (RIF) as a major milestone, noting that it supports high-impact research aligned to national priorities and has enabled thousands of researchers to deliver practical solutions benefiting communities across Uganda. She also highlighted Parliament’s approval of a 162 million US dollar concessional loan from the Korea EXIM Bank to upgrade science, technology and innovation infrastructure at Makerere University, including modern laboratories, smart classrooms and advanced facilities for engineering and health sciences, to better prepare students for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The Minister announced plans to construct a national stadium at Makerere and other higher education institutions to promote sports development and talent identification. She reiterated the directive for all universities to fully implement Competence-Based Education and Training by July 2027, urging Makerere to lead curriculum reform, staff training and infrastructure development while ensuring satellite campuses meet full accreditation and uphold academic standards, transparency and accountability.
Addressing graduates, Hon. Kaducu encouraged them to become job creators in sectors such as agriculture, infrastructure, healthcare and education, and to leverage opportunities like the Parish Development Model for entrepreneurship. She commended Makerere’s leadership and partners and congratulated the Class of 2026 on their achievement.
In his address to the congregation, Dr. Crispus Kiyonga – Chancellor, Makerere University congratulated graduands upon making it to the 76th Graduation Ceremony of Makerere University. He described their achievement as a milestone in both personal growth and national development, urging them to apply their knowledge creatively to benefit society. He acknowledged the contribution of academic staff, administrators, the University Council, and expressed gratitude to the Government of Uganda and President Yoweri Kaguta Museveni for continued support.
Dr. Kiyonga called on the university community to strengthen research, expand private sector partnerships, and leverage technology to address Uganda’s development challenges. Emphasising research as central to national progress, Dr. Kiyonga noted the Government’s UGX 30 billion investment annually in the Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund (MakRIF) and praised the Science, Technology and Innovation Secretariat, Office of the President for supporting initiatives at the University advancing homegrown solutions to national challenges. He also highlighted a strengthened partnership with the Korean government, securing a USD 162 million loan from the Korea Exim Bank to boost infrastructure and staff capacity.
While acknowledging limited formal employment opportunities, he encouraged graduates to innovate and create jobs. He further commended the university’s digitalization efforts and outlined four priorities: increased research funding, private sector collaboration, community engagement, and effective use of technology.
During the 76th graduation ceremony running from the 24th -27th February, 2026, a total of 9,295 graduands will be awarded degrees and diplomas in various disciplines. Of these, 213 will receive PhDs, 2,503 Masters Degrees, 206 postgraduate Diplomas, 6343 Bachelor’s Degrees and 30 Diplomas. 46% of the graduands are female and 54% are male.
Trending
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 Agriculture & Environment2 weeks ago
Agriculture & Environment2 weeks agoCAES Presents Overall Best Performing Student in the Sciences & a Record 28 PhDs at the 76th Graduation Ceremony
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
-

 Natural Sciences2 weeks ago
Natural Sciences2 weeks agoMak 76th Graduation Ceremony: CoNAS Presents 16 PhDs & Best Performing Male Student in the Sciences
