Health
Poorly implemented COVID-19 incentives eroded health workers’ motivation in Africa – Study
Published
2 years agoon
By Okeya John & Davidson Ndyabahika
As the COVID-19 pandemic swept across Africa, it brought with it a wave of unprecedented challenges, impacting economies, social dynamics, and political structures. National healthcare systems were particularly strained, prompting governments to implement various strategies to combat the virus and its repercussions. Among these measures were the introduction of incentives, both financial and non-financial, aimed at boosting the morale of health workers and bolstering the capacity of healthcare systems to respond to health emergencies.
Due to COVID-19’s increased risks and demand on healthcare workers working in already overburdened health systems, incentive packages must be strengthened. Researchers conducted a multi-country qualitative study in DRC, Nigeria, Senegal, and Uganda with funding from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Gates Ventures/Exemplars in Global Health. The study examined pandemic-related workplace incentives. In 60 virtual interviews via phone and Zoom, ministry officials, policymakers, and health care providers provided important viewpoints.
Entitled “Health Workforce Incentives and Dis-Incentives During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Experiences from Democratic Republic of Congo, Nigeria, Senegal, and Uganda,” the research conducted by healthcare experts delved into the realm of incentive mechanisms, their allocation, and the inadvertent dis-incentives experienced by the health workforce amidst the pandemic response efforts.
The researchers were from Makerere University School of Public Health (Uganda), University of Kinshasa (DRC), University of Ibadan (Nigeria) and University of Dakar (Senegal). The research team comprised Suzanne Kiwanuka, Ziyada Babirye, Steven Kabwama, Andrew Tusubira, Susan Kizito, Rawlance Ndejjo, Marc Bosonkie, Landry Egbende, Berthold Bondo, Mala Ali Mapatano, Ibrahima Seck, Oumar Bassoum, Mamadou Leye, Issakha Diallo, Olufunmilayo Fawole, Segun Bello, Mobolaji Salawu, Eniola Bamgboye, Magbagbeola David Dairo, Ayo Steven Adebowale, Rotimi Afolabi, and Rhoda Wanyenze,
In their work, the scientists authoritatively note that: “Health worker incentives during the COVID-19 response were mostly unplanned, predominantly non-financial, and invariably implemented. Across these countries, there were neither guiding frameworks nor standard pre-determined packages of financial and non-financial incentives for health workers during emergencies.”
Before the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in December 2019, “Africa already had weak health systems,” they note, citing that the pandemic exposed this challenge, increasing work overload for health workers, mental stress, infections and deaths, who in turn, needed incentives to adequately work to respond and deliver good health outcomes during the emergency.
However, due to the dire working conditions, the Word Health Organization (WHO) had warned that frontline healthcare workers were most at risk of acquiring the deadly COVID-19 virus. In their report, WHO highlighted that between January 2020 and May 2021 alone, over 80,000 to 180,000 health and care workers respectively, had died of COVID-19 globally, calling for urgent need to reverse the tide.
From this study, Senegal faces a doctor and nurse shortage with only 0.38 healthcare workers per 1,000 people, well below the WHO recommendation. By December 2021, Senegal had recorded 75,055 COVID-19 cases and 1,890 deaths, including five health workers. Similarly, Uganda, with approximately 2.58 healthcare workers per 1,000 people, reported 146,030 COVID-19 cases and 3,306 deaths, including 37 health workers.
The researchers also noted that the DRC had 1.05 healthcare workers per 1,000 people, with 79,632 cases and 1,225 deaths, including 35 health workers. Nigeria faced a similar challenge, with 2.0 healthcare workers per 1,000 people, 243,450 cases, and 3,031 deaths by December 2021, including seven health workers. These findings stressed the strain on Africa’s fragile healthcare systems in responding to the COVID-19 pandemic.
“These challenges and consequences resulted in health workers either absconding from duty or in extreme circumstances, resigning from the health profession and opting for alternative professions,” the researchers note in their review of the COVID-19 response in Africa. They state that elsewhere by this time, measures had already been mounted to motivate health workers, necessitating a similar response in the continent.
In the countries where the study was conducted, the strategies adopted by governments and development partners to counter declining health worker motivation included offering financial rewards like allowances and salary increments, and non-financial incentives like adequate provision of medicines and supplies, on the job trainings, medical care for health workers, social welfare including meals, transportation and housing, recognition, health insurance, psychosocial support and increased supervision.
The researchers found that the financial rewards were a big motivating factor for the health workers in these countries in sustaining the health systems and COVID-19 efforts, while the non-financial incentives also contributed to improved health worker determination.
The incentives, although a success, however in their strength lied the weaknesses. The multi-country study reveals that the incentives had the double effect of creating disincentives and demotivating healthcare workers. This was occasioned by the lack of personal protective equipment, transportation to health facilities during lockdown, long working hours, harassment by security forces and perceived unfairness in access and adequacy of the rewards.
The study got its findings from virtual key informant interviews with the staff at ministries of health, policy makers, and health workers. In the study report, health managers and workers in DRC, Nigeria, Senegal, and Uganda confirmed that health workers received monetary benefits as a means of motivation for their effort towards the continuity of health services.
In Senegal, incentives were reported to mostly be financial. However, in DRC, although the salaries of the health workers involved in COVID-19 testing were reported to be similar to all other staff in response committees like epidemiological surveillance, case management, and communication, the government moved to temporarily waiver taxes to bait the COVID-19 health workers during the pandemic.
“Since financial incentives were mostly administered in an ad-hoc manner, some health workers felt they were unfairly distributed and complained about the lack of transparency in the allocation of these incentives. In Nigeria, it was reported that payments did not meet the health worker expectations, while in Uganda, it was reported that allowances were given selectively to some health workers such as those involved in contact tracing, COVID 19 testing, and COVID 19 isolation units but not to others.” The study report reads in part.
Respondents also revealed that although allowances were availed, there was dissatisfaction caused by delays and non-payment. In Uganda for example, the recruitment of additional 700 staff on contract although initially perceived positively, their irregular dismissal following budget shortfalls created discontentment and immense pressure for the government.
Accordingly, the authors observe that the incentive packages in the four African countries were inconsistent, lacked transparency, adequacy, and equity. “Therefore, there is a need to develop guiding frameworks within which governments and partners can deliver incentives and reduce dis-incentives for the health workforce during emergencies.”
The study suggests that during health emergencies like COVID-19, increased risks and workloads should mandate the provision of safety gear and adequate supplies. However, the researchers caution that both financial and non-financial incentives can have unintended consequences if perceived as unfair in their implementation.
They also call for incentives to be pre-determined, equitable and transparently provided during health emergencies ‘because arbitrarily applied financial and non-financial incentives become dis-incentives’, while still holding that the financial incentives are only useful in as far as they are administered together with non-financial incentives such as supportive and well-resourced work environments.
“Governments need to develop guidelines on incentives during health emergencies with careful consideration of mitigating potential dis-incentives. The harmonization of roles across state and non-state sector players in incentivizing the health personnel during health emergencies is paramount.” The study affirms.
Find the detailed scientific study here.
You may like
-


Celebrating Academic Excellence: CoBAMS Presents 975 Graduands at Mak 76th Graduation Ceremony
-


Mak 76th Graduation Ceremony: CoNAS Presents 16 PhDs & Best Performing Male Student in the Sciences
-


Medical graduates urged to uphold Ethical values
-


CAES Presents Overall Best Performing Student in the Sciences & a Record 28 PhDs at the 76th Graduation Ceremony
-


Over 9,200 to graduate at Makerere University’s 76th Graduation
-


MakSPH Environmental Health Graduates Trained to Prevent Disease at Its Source
Health
MakSPH Environmental Health Graduates Trained to Prevent Disease at Its Source
Published
5 days agoon
February 24, 2026
In most health systems, attention turns to illness after it appears in clinics and hospitals. Environmental Health works earlier, often invisibly, by preventing disease before treatment becomes necessary. At Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH), this preventive philosophy shapes the training of students learning to manage health risks at their source, through sanitation systems, safer environments, community engagement, and evidence-based public health action.
This year, as MakSPH presents 29 graduands approved by the Makerere University Senate for the award of the Bachelor of Environmental Health Science (BEHS) degree, four outstanding students graduate with first-class honours. Their journeys, shaped by different personal histories and professional ambitions, provide a clear view of how the School prepares practitioners whose work begins long before patients reach health facilities. Through academic training, field practice, research exposure, and leadership experience, the programme equips graduates to address the environmental and social conditions that determine health outcomes across communities.

Environmental health occupies a distinctive position within public health practice. Rather than focusing primarily on diagnosis or treatment, practitioners work at the intersection of science, policy, and society, addressing risks linked to water and sanitation, food safety, occupational health, climate change, and urbanisation. The discipline demands technical competence alongside communication, systems thinking, and community engagement, capabilities that increasingly define modern public health leadership.
The journeys of Nakulima Bushirah, graduating with a CGPA of 4.58 on February 25, 2026, Mujurani Alphersiiru with 4.44, and Cherop Eric with 4.41, alongside Phillip Acaye, the cohort’s overall best student with a CGPA of 4.63, demonstrate how MakSPH shapes students from varied beginnings into professionals grounded in prevention. Their paths reveal a shared formation that links classroom learning with real-world health challenges and prepares graduates to prevent disease before it occurs.
Bushirah Nakulima’s Turn Toward Prevention
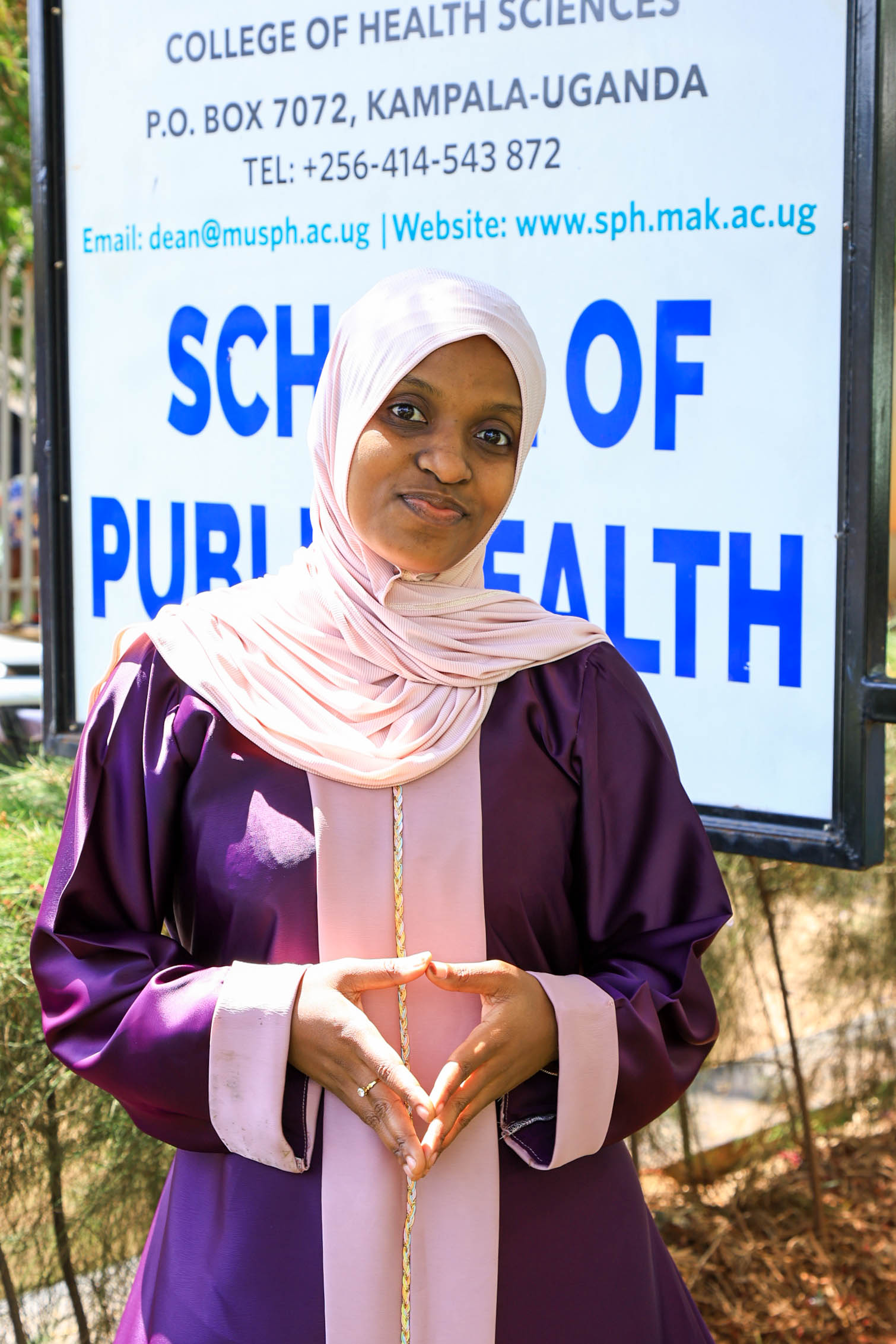

For Bushirah Nakulima, environmental health began during a period of uncertainty. The COVID-19 pandemic repeatedly disrupted her Bachelor of Pharmacy studies at Kampala International University, prompting reflection about the kind of health professional she wanted to become. A conversation with a family friend working in preventive health introduced an alternative path, one focused not on treating illness after onset but on preventing it altogether.
“When I applied to Makerere University in 2022, I was considering two career paths,” she recalled. “I prayed to Allah to guide me toward the best one. When I was admitted to the Bachelor of Environmental Health Science, I accepted it wholeheartedly, and I came to appreciate it even more as I studied.”
Her academic foundation had already demonstrated consistency. She progressed from Melody Junior School in Nansana, where she obtained aggregate eight in 2010, to Shuhada’e Islamic School in Nyamitanga, completing O-Level with 25 aggregates in 2016 and A-Level with 10 points in 2018. Pharmacy initially appeared the logical continuation, yet environmental health offered something broader in scale and impact.
“Environmental Health offered an opportunity to prevent illness and suffering before it occurs,” she explained. “It allows a single intervention, such as WASH or health education, to protect many people at once, and it provides flexibility to work across diverse environments. It offered freedom to operate in various settings, which truly connects with my personality since I love exploration.”
At MakSPH, classroom concepts quickly translated into practice. During her internship at Mukono Municipal Council, she conducted school health education sessions, participated in inspections of markets and abattoirs, and engaged communities facing sanitation challenges. Field exposure deepened her understanding of how environmental conditions directly shape disease patterns, reinforcing prevention as both a scientific and social responsibility.
Leadership further expanded her training. Serving as the 90th Female Guild Representative Councillor (GRC), she represented the School of Public Health in the Student Guild structure, facilitating engagement between students and School leadership on academic and welfare matters. The role strengthened her capacity for representation, negotiation, and collaborative problem-solving, skills central to public health practice, where advocacy and systems engagement are inseparable from technical expertise.
Graduating with a CGPA of 4.58, Bushirah’s research examined roadside vendors’ exposure to air pollution in Kampala, reflecting growing concern about occupational and urban environmental risks. She now plans to pursue advanced training in public health, building on MakSPH’s emphasis on evidence-driven and community-centred practice.
Cherop Eric’s Return to the Classroom
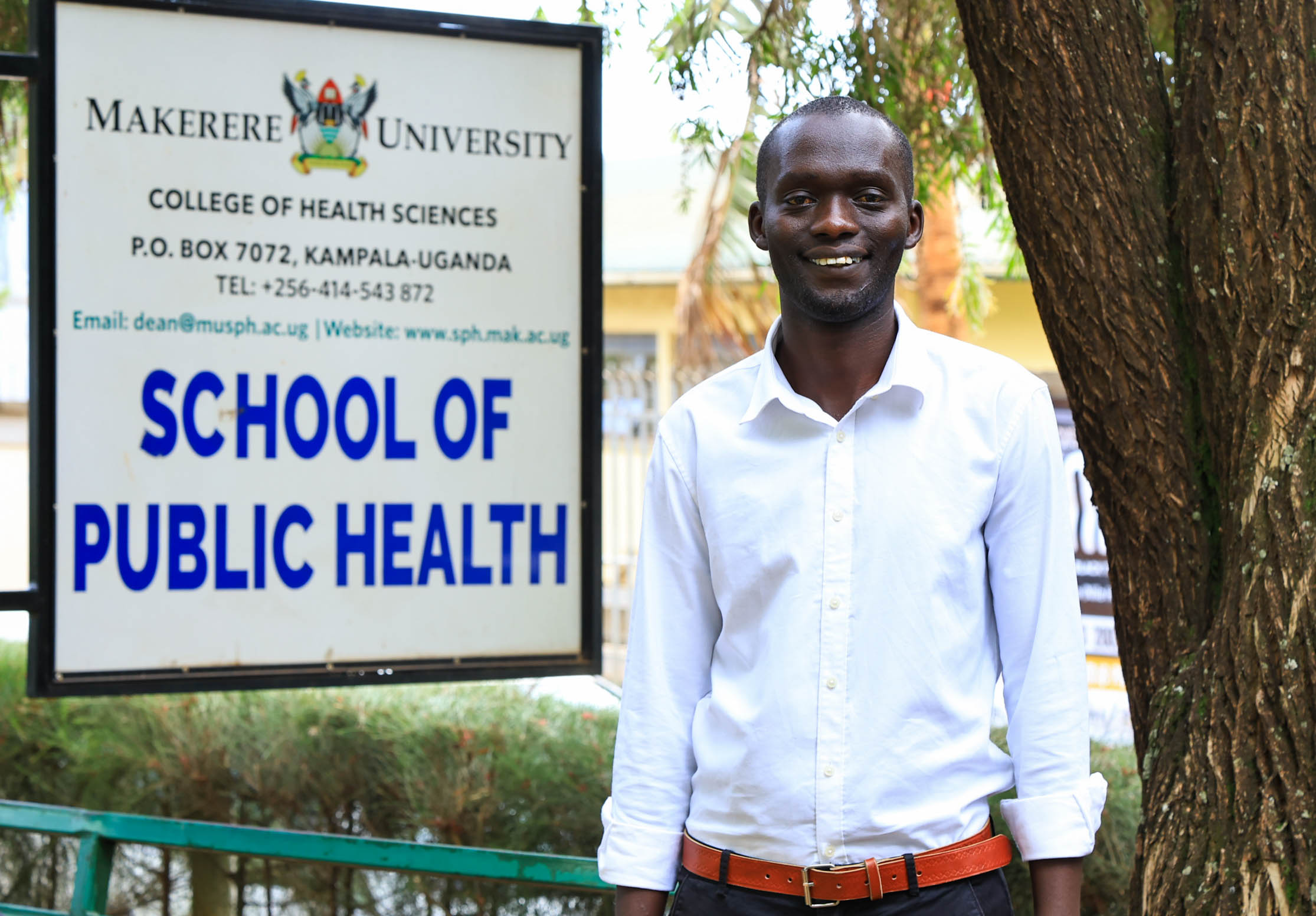

Eric Cherop’s journey into environmental health began not in lecture halls but in community service. Raised in Kapchorwa District, he was shaped by economic hardship and resilience, experiences that informed his commitment to community well-being.
He completed his Primary Leaving Examinations at Chema Primary School, a Universal Primary Education institution, attaining 24 aggregates in 2008. He later joined Sipi Secondary School, where he obtained 37 aggregates at Uganda Certificate of Education in 2012 and continued at the same school for A-Level, earning 8 points at Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education in 2014.
After earning a Diploma in environmental health sciences from Mbale School of Hygiene between 2015 and 2017, he entered public service as an Environmental Health Officer and Community Field Facilitator with Kapchorwa District Local Government. His work included sanitation campaigns, climate resilience initiatives, nutrition education, and household behaviour change programmes. Over time, field experience revealed the limits of practice without deeper theoretical grounding.
“I wanted to understand not only what works in communities, but why it works,” he explains. Enrolling in the BEHS programme at MakSPH in 2022 allowed him to connect practical experience with analytical training. Coursework strengthened competencies in environmental risk assessment, participatory engagement, and data-driven planning. Mentorship reshaped how he interpreted evidence.
“My lecturers helped me move beyond seeing data as numbers,” he said. “I learned to see it as evidence that guides decisions and improves accountability.” Graduating with a CGPA of 4.41, Eric now aims to advance evidence-driven leadership at the intersection of climate change, nutrition, and environmental health, ensuring interventions remain grounded in community realities.
Mujurani Alphersiiru’s Path into Environmental Health
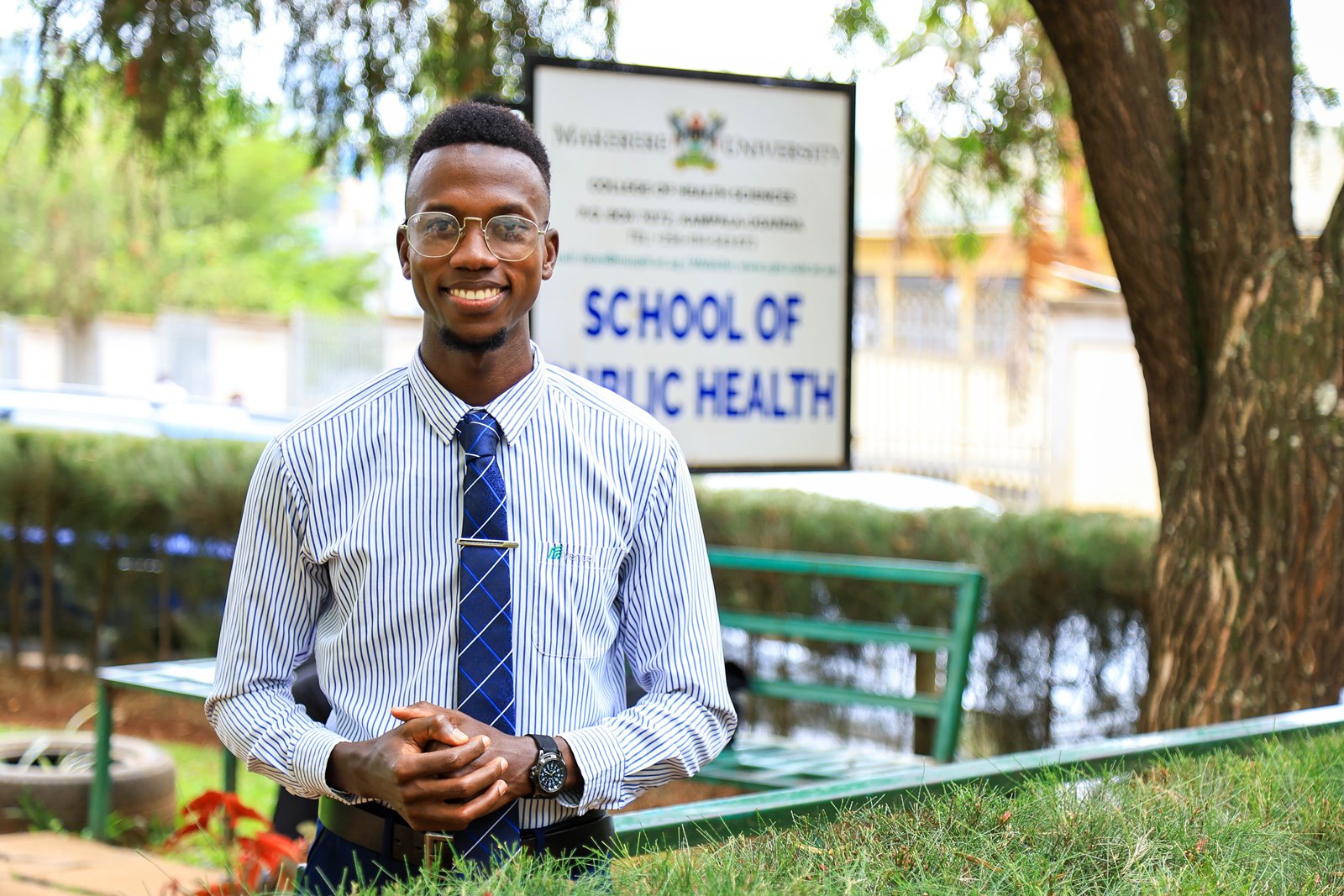

For Mujurani Alphersiiru, Environmental Health arrived at an unexpected moment, when his academic future appeared uncertain. Financial pressures had begun to threaten the continuation of his Bachelor of Nursing Science studies at Kampala International University Western Campus, raising the real possibility that his university education might end prematurely. The turning point came when the government district quota admission list was released, offering him placement at Makerere University under Bunyangabu District and opening an alternative academic pathway he had not previously considered.
At the time, environmental health was unfamiliar to him. “I didn’t know what environmental health was,” he recalls. “But I celebrated because I had reached my dream university.” Orientation sessions and early coursework gradually reframed that uncertainty, revealing a discipline grounded in prevention, systems thinking, and public health policy. What began as an unexpected opportunity soon developed into a clear professional direction.
Serving as class president and 90th Male GRC for the School with Nakulima Bushirah, Mujurani organised student activities, mobilised community outreach initiatives, and advocated for improved learning environments. Balancing leadership responsibilities with academic performance required deliberate discipline and time management.
His educational foundation began at St. Augustine Butiiti Demonstration Primary School in Kyenjojo, where he scored 12 aggregates in 2014. He later attended Pride Secondary School in Mityana, attaining 25 aggregates at O-Level in 2018, before proceeding to Kibiito Secondary School in Bunyangabu, where he obtained 13 points at A-Level in 2021, performance that earned him government sponsorship for university education. At MakSPH, faculty mentorship further strengthened both his academic rigour and commitment to public service.
“Government sponsorship meant responsibility,” Mujurani said. “I had to plan my time carefully while remaining active in school programmes.” Graduating with a CGPA of 4.44, his interests now centre on governance and accountability within health systems, particularly strengthening the implementation of public health policies.
Training Prevention Professionals
Taken together, the three journeys demonstrate how MakSPH’s Environmental Health training converts diverse personal backgrounds into a shared professional orientation centred on prevention. Through interdisciplinary coursework, field placements, research mentorship, and leadership opportunities, students develop competencies that extend beyond technical knowledge to include systems thinking and public engagement.
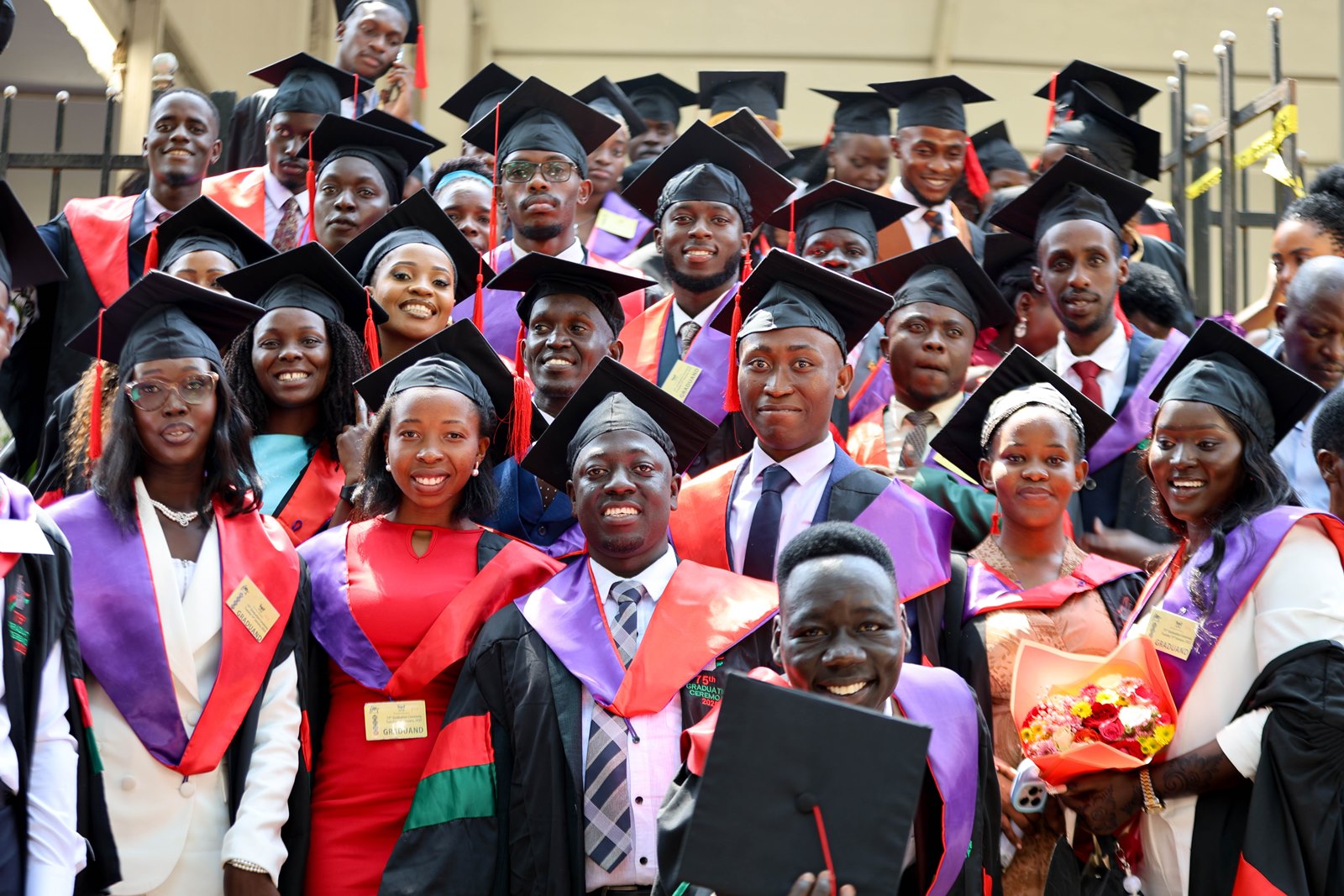

The BEHS programme, established in 2000 within MakSPH’s Department of Disease Control and Environmental Health, remains the School’s only undergraduate degree and has trained more than 1,000 graduates who now serve across government institutions, non-governmental organisations, academia, and international health programmes. Its continued evolution reflects growing recognition that strengthening health systems requires professionals capable of addressing environmental risks before illness occurs.
The achievements of this year’s graduates, therefore, represent more than academic distinction. They reflect a model of training designed to prepare professionals whose work reduces the need for treatment by preventing disease at its source, reinforcing MakSPH’s role in shaping Uganda’s environmental health workforce.
Health
Philliph Acaye and the Making of Uganda’s Environmental Health Workforce
Published
5 days agoon
February 24, 2026
As Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) presents 29 graduands on February 25, 2026, at Makerere University’s 76th Graduation Ceremony, for the conferment of the Bachelor of Environmental Health Science (BEHS) degree, the journey of the cohort’s best student provides a compelling window into both individual resilience and institutional impact. Philliph Acaye, graduating with a CGPA of 4.63, represents more than academic distinction. His story reflects the lived realities that shape many public health professionals in Uganda and shows how rigorous training can transform experience into leadership within health systems.

Education Shaped by Conflict
Acaye was born on October 2, 1993, in Wangduku Village, Palenga Parish, Pajule Sub-County, Pader District in northern Uganda, a region deeply affected by the Lord’s Resistance Army (LRA) insurgency in the early 2000s, where education and security often existed in constant tension. As a child, schooling unfolded alongside displacement and uncertainty, conditions that shaped an entire generation growing up during the conflict.
“Around 2002, before we had fully moved into the IDP camps, we often ran with our parents whenever there were LRA attacks,” he recalls. “But on several occasions, they caught us unaware. During one of the attacks, they abducted me and moved with me for close to seven kilometres, from Wangduku to Pajule Trading Centre in Pader. At first, they said I was too young to be moved with. I was around nine or ten years old. Later, I understood that someone among them personally knew my father and did not want me taken, so he used my age as the reason, and they left me behind.”

He narrates that several relatives and neighbours, including some of his childhood friends, were not spared, among them an uncle whose whereabouts remain unknown to this day. “If they had gone with me,” Acaye reflects quietly, “I could be dead, or I might not have studied.” The remark sits deep and places his graduation in context, not simply as personal success, but as the outcome of persistence through years when conflict repeatedly disrupted education across northern Uganda.
Between 2002 and 2006, his schooling continued inside Pajule Internally Displaced Persons (IDP) Camp, where families lived in overcrowded settlements and depended largely on relief food. Learning environments were unstable, teachers travelled under risk, and lessons were frequently interrupted by insecurity. Even within the camps, attacks remained possible. Education progressed slowly, but it continued, sustained by families and teachers who insisted that schooling remained essential despite uncertainty.
When communities gradually returned home, Acaye rebuilt his academic track record step by step. He completed Primary Leaving Examinations in 2007 with an aggregate of 19 and was the best pupil at Wangduku Primary School, at a time when enrolment remained low because many families feared returning to villages. He proceeded to Pajule Senior Secondary School, completing O-Level in 2011 with 31 aggregates, and later obtained 10 points at A-Level in 2013 from Kitgum High School.
However, his progression was shaped by consistent recovery after disruption, supported by relatives, teachers, community mentors, and educational assistance from Invisible Children, a post-LRA conflict recovery NGO led locally by Ms. Laker Jolly Okot, which supported his A-Level education.
Professional direction emerged during his training at the Mbale School of Hygiene, where he pursued a Diploma in Environmental Health Science from 2014 to 2016 and graduated with a strong CGPA of 4.4. The diploma opened immediate employment opportunities in community and humanitarian health settings back home, followed by service in local government. Today, he works as a Health Inspector in Kitgum District Local Government, implementing sanitation monitoring, infection prevention activities, and community health interventions. Practical experience strengthened his understanding of public health challenges but also revealed limits in technical depth that he felt required further training.
Training the Public Health Professional
His admission to MakSPH in 2022 through the government diploma-entry sponsorship scheme represented a deliberate academic decision rather than a career reset. He sought broader analytical skills and a stronger grounding in environmental health systems, particularly in areas of surveillance, planning, and evidence-based decision-making.
“I realised some technical aspects were not fully covered at the diploma level. I wanted to understand public health beyond implementation and learn how decisions are justified scientifically,” Acaye explained.

The sponsorship, he observed, transformed that ambition into possibility and remains central to how he understands his academic journey at Makerere University. “I am grateful to the Makerere University selection committee, the MakSPH selection committee, and the Government of Uganda for this opportunity. Opportunities like this are not guaranteed, and I recognise the trust placed in me to undertake and complete the three-year BEHS programme.”
The transition into university study was not seamless, though. His admission had come earlier than planned, and he began coursework without formal study leave while still tied to workplace obligations in Kitgum. Sustained support from district leadership, particularly Dr. Okello Henry Otto, the District Health Officer, eventually enabled him to secure study leave and concentrate fully on academic work. Now with stability came rapid academic improvement, supported by peer learning, faculty mentorship, and a strong curriculum that emphasised analytical reasoning alongside applied practice.
Acaye attributes his transformation to the programme’s academic culture rather than individual brilliance. “The programme helped me realise that what I was doing before was only a surface understanding,” he argued. “I learned to approach public health more deeply.” Exposure to research methods, he revealed, reshaped how he interpreted field experience and encouraged him to submit an abstract to an international academic conference, marking his transition from practitioner to emerging researcher.
For Mr. Abdallah Ali Halage, the MakSPH Coordinator of the BEHS programme, such outcomes reflect intentional design rather than coincidence. He noted that student success is rooted in a training philosophy that combines technical instruction with professional discipline from the moment students enter the programme. According to him, orientation focuses not only on coursework but also on expectations of conduct, independence, and responsibility. “When students join, we brief them on how seriously they must approach their academic journey,” he said. “That grounding helps shape their performance over time.”

Mr. Halage argued that while some high-performing students enter through diploma schemes, achievement ultimately depends on commitment and effort rather than background. He cited Acaye’s consistent curiosity and self-motivation as defining traits, noting that strong academic results tend to follow students who actively engage with the learning process.
“I congratulate Philliph and his colleagues upon attaining first-class honours and performing very well academically. Philliph has been hardworking and self-motivated. He has consistently shown a strong interest in his studies, and that commitment has helped him achieve this result. He has been a very good student,” Mr. Halage attested.
He added that the achievement reflects a broader culture within the programme. “Our students are disciplined and independent. Their commitment, together with support from the School management, the College and University leadership, has contributed greatly to their success.”

From Individual Achievement to Institutional Impact
The broader significance of Acaye’s achievement becomes clearer when placed within the evolution of the BEHS programme itself. Established in 2000 within MakSPH’s Department of Disease Control and Environmental Health (DCEH), the programme remains the School’s sole undergraduate degree and was among the earliest environmental health bachelor’s programmes in East Africa. In more than two decades, it has produced over 1,000 graduates, expanding professional capacity beyond diploma-level training and strengthening Uganda and the region’s environmental health workforce across government, non-governmental organisations, educational institutions, and points of entry such as airports and border services.
Mr. Halage explained that the programme helped redefine career pathways within the government of Uganda’s public service structures by introducing degree-level expertise into environmental health roles. Graduates now serve as Environmental Health Officers, Senior Environmental Health Officers, and technical specialists contributing to policy implementation and service delivery across multiple sectors. The academic pathway has also expanded vertically, with postgraduate training opportunities at MakSPH currently enabling graduates to progress into research, teaching, and doctoral-level specialisation, ensuring continuity within the discipline.

A Programme Shaping Regional Practice
The reputation of Makerere University’s Bachelor of Environmental Health Science programme is also increasingly influencing regional institutions. During a strategic benchmarking visit to MakSPH on July 30, 2025, Dr. Ratib Dricile, Dean of the Faculty of Health Sciences at Muni University, described the School of Public Health as a reference point for universities seeking to strengthen environmental health training in the region.
The main reason the delegation visited Makerere University School of Public Health was that Muni University remains a young and growing institution located in north-western Uganda along the borders with the Democratic Republic of Congo and South Sudan, where porous borders contribute to frequent cross-border diseases, many of which are preventable through strong environmental health approaches, Dr. Dricile explained.

“Makerere University, with over 100 years of institutional experience and 25 years running the Environmental Health programme, was the right place for us to benchmark, particularly in curriculum design, course content, programme structure, and implementation,” he said. “We were impressed by the work being implemented and gained more than we initially expected. By integrating these experiences, we believe the Muni University curriculum can become even stronger. The collaboration will allow us to adopt innovations built on Makerere’s long experience, and we believe that working together with Makerere University will strengthen Muni University institutionally and contribute positively to our university’s growth and ranking.”
It is within this institutional tradition, built over decades of training environmental health professionals across Uganda and the region, that Philliph Acaye’s achievement takes meaning. For him, graduating top of the class remains grounded in practical purpose rather than prestige. He views a first-class degree as an opportunity rather than an endpoint. Recalling guidance from his lecturers, he said strong academic results can open doors but must be followed by demonstrated competence. “A first class helps you get shortlisted,” he said. “After that, you must prove yourself.”

His immediate plans reflect that perspective. He is currently pursuing additional training in Health Services Management at Gulu College of Health Sciences while preparing for postgraduate study in either public health or environmental and occupational health. At the same time, he continues supporting pupils in his community and plans to mobilise resources to provide sanitary pads for girls at his former primary school, an initiative he believes will help reduce school dropout rates in rural areas.
Acaye’s journey, from disrupted schooling in an IDP camp to graduating top of MakSPH’s BEHS programme for the 2022 cohort, reflects the deeper purpose of public health education. As MakSPH presents its newest cohort for graduation this week, his story demonstrates how the programme turns lived experience into professional capacity, strengthening communities and health systems across Uganda and the region, one graduate at a time.
Health
Makerere University School of Public Health Graduates First Cohort of Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Short Course
Published
1 week agoon
February 20, 2026By
Mak Editor
Kampala, Uganda – The Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) has marked a significant milestone with the graduation of the first-ever cohort of its Cost-Effectiveness Analysis (CEA) Short Course. The pioneering programme is designed to strengthen capacity in economic evaluation in Uganda and beyond.
The virtual graduation ceremony honored eleven (11) participants who completed the course. The cohort included professionals from academia, research institutions, government agencies, and non-state actors, reflecting the increasing demand for skills in economic evaluation across sectors.
The short course was developed and implemented by the Department of Health Policy, Planning, and Management (HPPM) in response to the increasing need for evidence-informed decision-making in a context of limited resources.
In her remarks during the ceremony, Assoc. Prof. Suzanne Kiwanuka, Head of the Department of Health Policy, Planning and Management (HPPM) at MakSPH, congratulated the inaugural cohort for completing what she described as a “critical and timely” course.
“With decreasing resources and rising demand for services driven by population growth and the emergence of high-cost technologies, decision-makers must make difficult choices,” she noted. “Cost-effectiveness analysis is no longer optional. It is central to conversations in the corridors of power.”
The CEA short course was designed to equip policymakers, researchers, and practitioners with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills in economic evaluation. Participants were introduced to key principles of health economics, costing methodologies, decision-analytic modelling, Markov modelling, sensitivity analysis, and interpretation of incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs).
According to Prof. Elizabeth Ekirapa, the course lead at MakSPH, this inaugural offering had been “a long time coming,” following years of discussions within the department about building local expertise in economic evaluation.
Delivered over 10 days through interactive online sessions, the course combined lectures, case studies, and hands-on modelling exercises using contextually relevant datasets. Participants were required to develop and present applied cost-effectiveness projects as part of their assessment, allowing them to translate theory into practice.

During the feedback session at the graduation ceremony, faculty emphasized the importance of clarity in defining study perspectives, selecting appropriate outcomes, and aligning research questions with modelling approaches.
Dr. Chrispus Mayora, one of the facilitators, highlighted the need to carefully select outcomes that directly reflect the intervention being evaluated. “When thinking about outcomes, ask yourself: Is this aligned with what I want to study? Interesting outcomes are not always the most appropriate ones,” he advised.
Participants were also encouraged to select modelling techniques such as decision trees or Markov models based on the research question and the nature of the disease or intervention under study.
Prof. Ekirapa described the graduates as “trailblazers,” noting that their feedback would shape future iterations of the course. “When you are the first cohort, you are like pioneers,” she remarked. “We are committed to improving this course to ensure it becomes a world-class programme.”
For many attendees, the graduation ceremony was a new experience, as certificates were awarded virtually an approach that participants welcomed as innovative and inclusive.
“Cost-effectiveness analysis enables us to maximise value for money,” noted Dr. Crispus Mayora of MakSPH. “It allows decision-makers to compare interventions systematically and ensure that limited resources achieve the greatest possible benefit.”
The programme aligns with Makerere University’s broader mandate to provide high-quality training that responds to national and regional development priorities. Participants who successfully complete the course receive a certificate signed by the Dean of the School of Public Health.
As the ceremony concluded, faculty encouraged continued engagement beyond the classroom. Graduates were urged to refine their project ideas and collaborate with the department in advancing research and policy discussions.
The successful completion of the first CEA short course marks an important step in building a cadre of professionals equipped to conduct rigorous economic evaluations. With plans to expand and refine the programme based on participant feedback, the HPPM department under MakSPH is positioning itself as a regional leader in health economics and policy analysis training.
Trending
-

 Humanities & Social Sciences6 days ago
Humanities & Social Sciences6 days agoMeet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 General5 days ago
General5 days ago76th Graduation Highlights
-

 Agriculture & Environment1 week ago
Agriculture & Environment1 week agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
