Health
Makerere & Johns Hopkins Universities Release Report on Speed and Helmet Use in Kampala
Published
2 years agoon
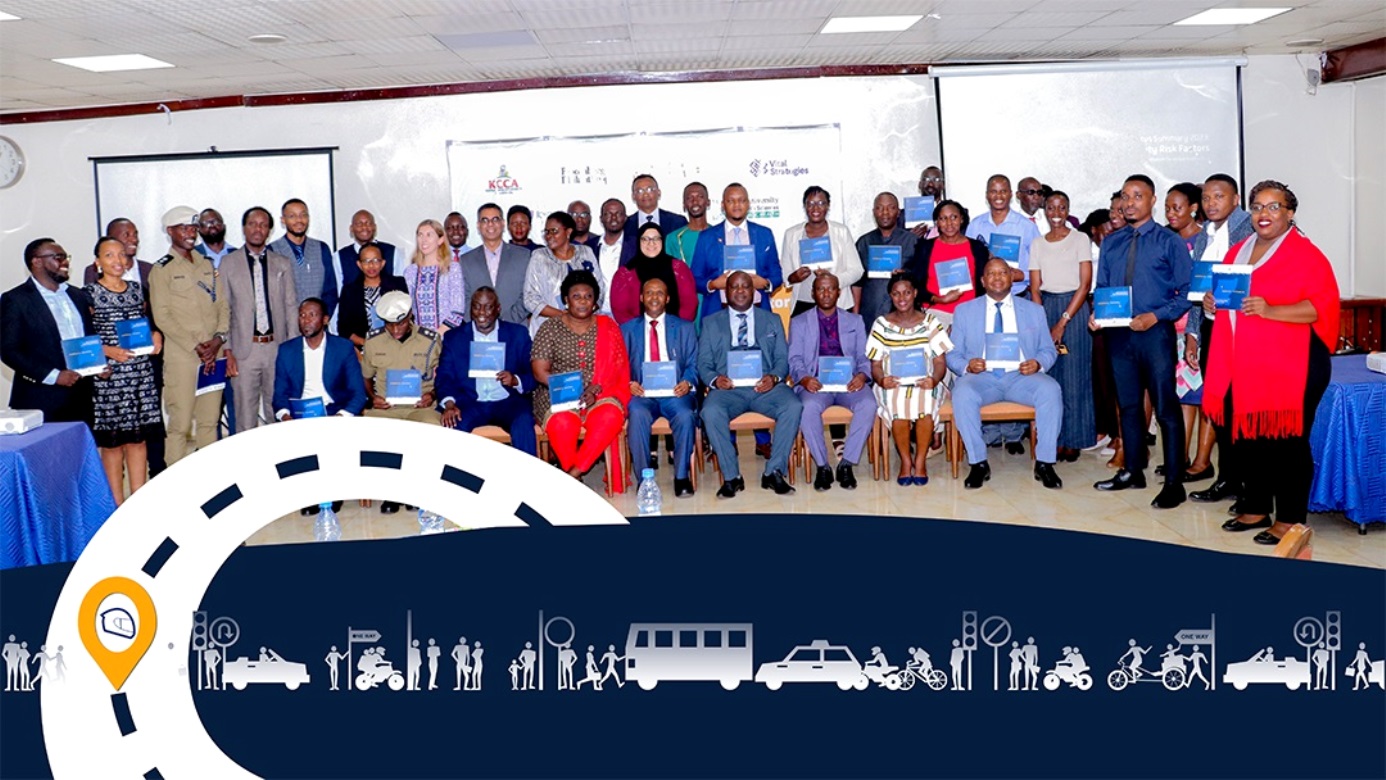

Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) and the Johns Hopkins International Injury Research Unit (JH-IIRU) have launched the status summary report 2023; Road Risk Factors for Kampala, Uganda, in partnership with Kampala Capital City Authority (KCCA) and Vital Strategies.
The report was launched at Hotel Africana in Kampala on January 16, 2024. It delineates key findings, including the average speed of speeding vehicles at a high average of 57km/hr, higher speeds on roads partially accessible to pedestrians compared to roads freely accessible to pedestrians. Also, helmet usage remains low among motorcyclists and is almost non-existent among passengers, contributing to a rise in accidents and fatalities since 2020.
There has been a variable trend in the reported numbers of deaths and serious injuries since 2018. Specifically, in 2022, there was a 1% increase in reported deaths compared to 2021, while serious injuries witnessed a 4% decrease during the same period.
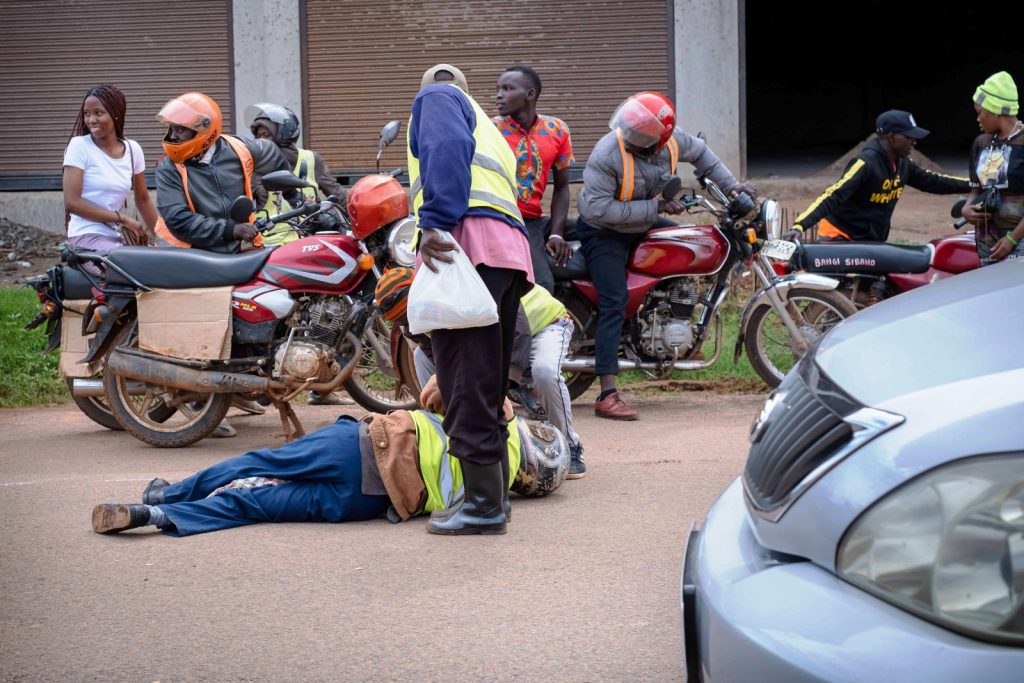
In 2018, a total of 294 death were recorded, 315 recorded in 2019 while 236 were recorded in 2020. In 2021, there were 419 road traffic death and 425 recorded in 2022. Motorcyclists accounted for nearly half (49%) of the reported deaths followed by pedestrians made up 44% of deaths. In a bid to improve road safety by providing quality data, the research the Bloomberg Philanthropies Initiative for Global Road Safety (BIGRS) made roadside observations on speed and helmet use in Kampala City.
The researchers made six observation rounds citing 500,000 for speed and 600,000 cyclists to determine helmet use. The results, based on data collected between February 2021 and October 2023 indicate that the mean speed among speeding vehicles was high mostly among sport utility vehicles (SUVs) at 10%, sedans/saloons at 9%, minibuses/minivans at 8), and pickup/light trucks at 7%. Five percent of the observed vehicles were exceeding the posted speed limit.

Speeding in Kampala
Presenting findings, Mr. Bonny Balugaba, a Researcher based at the Trauma, Injuries and Trauma Unit of MakSPH noted that the international best practices for speed management recommend a safe speed of 30 km/h on roads where conflicts between cars and unprotected users are possible. Also, 50 km/h speed is recommended at intersections where side-on conflicts between cars may occur. This is particularly applicable in urban areas.
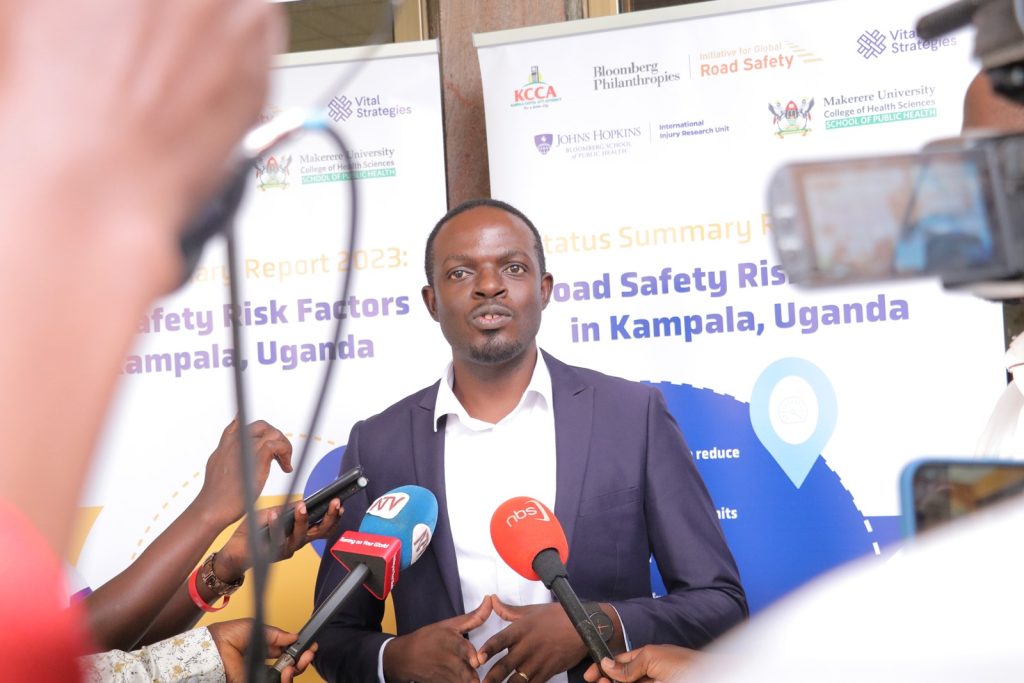

“If in Kampala we are seeing 57km/h speed, it means that we are way above the recommended speed limits and we know that beyond 40km/h, the chances of survival of someone that has been knocked are very minimal,” says Balugaba.
The researchers recommend enforcing a 50 km/h speed limit in metropolitan areas and a 30 km/h limit in places where motorized traffic interacts with bikes and pedestrians. In order to safeguard vulnerable road users, particularly the Ministry of Works and Transport and the Kampala Capital City Authority, it suggests implementing speed-calming techniques including bumps and signage as well as designating low-speed areas.
Investigators further advise the Kampala Metropolitan Traffic Police to increase enforcement, especially on local roads and on vehicles such as SUVs, sedans, pickup trucks, minibuses on routes with limited pedestrian access. It is recommended that public awareness campaigns and enforcement measures regarding the dangers of speeding be regularly monitored and evaluated to ensure continued efficacy.
Balugaba noted; “Mass media is good but if you are telling me the dangers of speed but am not apprehended on speed then it tends to entertainment. You come, entertain me with your campaign and adverts and go away but you are not enforcing.”

Helmet Use in Kampala
Helmet use compliance among motorcyclists was notably low at 39%, and even lower for passengers at 2%. This trend persisted on both local and collector roads (39%) and arterial roads (40%). During weekends, helmet use dropped by 20%. Ride-share motorcycle drivers, particularly Safe Boda, exhibited the highest compliance at 84%, surpassing commercial motorcycle drivers (50%), taxi drivers (55%), and private/government motorcycle users (55%).
From 2020 to 2022, 210 motorcycle occupants and 185 pedestrians lost their lives. Notably, 40% of pedestrian fatalities resulted from collisions with cars, SUVs, or pickups, whereas 36% of motorcycle deaths were attributed to accidents involving other motorcycles.
“We saw that only 2% of the motorcycles are using helmets. This really means that the situation is still bad. We need to put in place measures knowing that helmets save those that are wearing them,” says Balugaba.
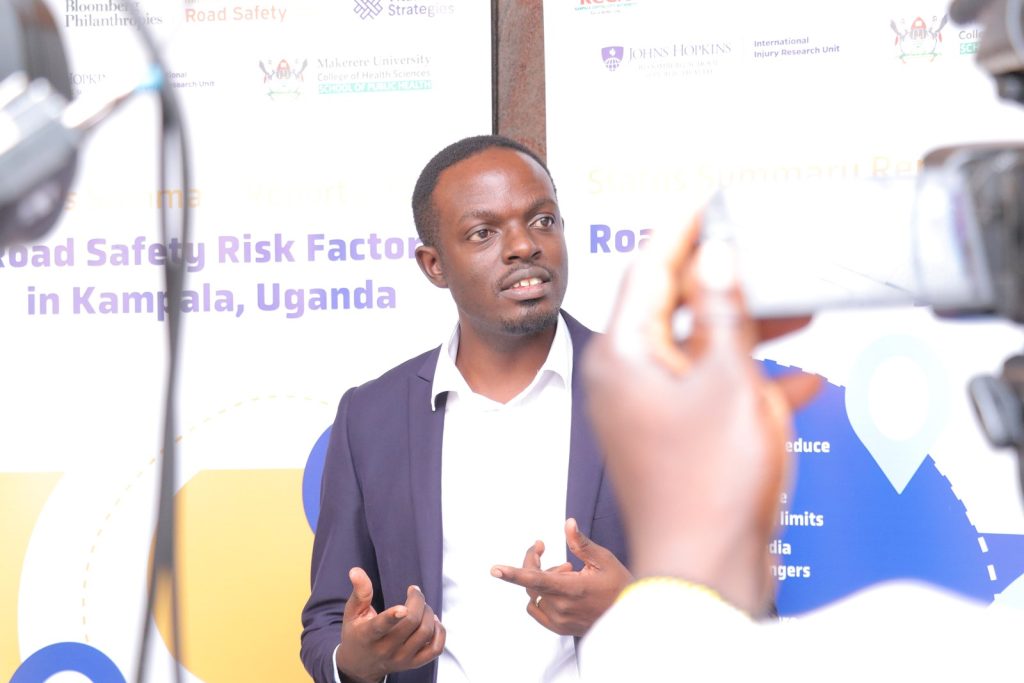

Adding that while four of every 10 riders are wearing a helmet but less than one in every 10 passengers has a helmet. “is it that passengers have harder heads than riders? That in case they are involved in a crash, they don’t get affected? These are issues we need to work on.”
While sharing the data outcomes, Dr Raphael Awuah, the African Regional Advisor on Data and Surveillance for Vital Strategies notes that while many of the cities in Africa, pedestrians constitute the majority fatalities, this is different for Kampala. “For most parts of Africa, we see that pedestrians account for most fatalities. However, in Kampala, this is not the case. We see that majority of the deaths are among the motorcyclists and this trend has been observed since 2018. So clearly this emphasizes the need to prioritize the vulnerable road users in Kampala particularly motorcyclists and pedestrians.”

The top five locations for pedestrian fatalities and serious injuries from 2019 to 2022 are high-capacity roads: Kampala Road, Jinja Road, Bombo Road, Entebbe Road, and Masaka Road.
The distribution of motorcycle fatal crash locations does not exhibit any clear pattern, but there is a noticeable concentration on high-capacity highways. Kampala Road, Masaka Road, Bombo Road, Kisaasi Road, and the Northern Bypass are the top five places.
“While it is true that these are high capacity roads, speeding is probably one of the causes of fatalities. I hope we will use this data to inform the discussions, actions, plans, strategies to reduce the outcomes that I have just shared,” observed Dr Raphael Awuah.
The Kampala Metropolitan Traffic Police has been urged to increase the enforcement of proper helmet use, with a focus on passengers, taxis, and commercial motorbikes on arterial, local, and collector roads all week round. Also, KCCA and the Ministry of Works and Transport may want to start public awareness programs promoting the appropriate use of helmets and advocate for sanctions and fines for improper helmet wear in conjunction with coordinated increased enforcement.

“This is about behavioral change. It is extremely difficult. We are all humans. All of us know that speeding is bad for us but when we get behind the wheel, we will still try to speed. All of us know that wearing a helmet will protect our heads, but only 2% of us wear helmets when we are riding on a motorcycle. So what else is needed? Yes, knowledge is important, it is important to tell people why they should be putting on these helmets and the consequences they will face if they don’t wear them but it is also important to have reinforcing mechanism. Yes, mass media campaigns are important but equally important is visible and widespread enforcement,” explained Dr. Abdulgafoor Bachani, Director of JH-IIRU.

On his part, Dr. Fredrick Oporia said “Road safety is an issue of concern to everyone. To improve this safety, we must have high-quality data on the risk factors and share it with our stakeholders. Most importantly, we need local stakeholders who are charged with making laws and policies for the country because this is a systems issue that calls for systems thinking. We must involve the local to get the attention of the international.”
SP. Michael Kananura, spokesperson, Traffic and Road Safety Directorate, Uganda Police Force says there is a regulation on helmet use targeting not only riders but also passengers, although he acknowledges challenges with enforcement. He calls on the public support these public health and road safety measures.
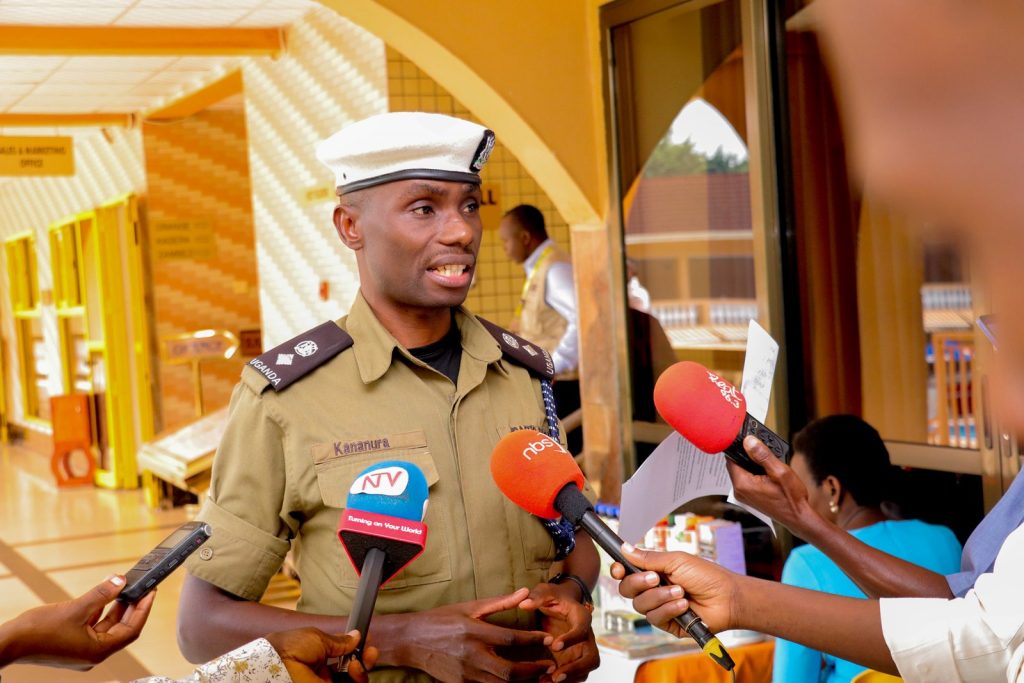

“We really appreciate our colleagues from MakSPH and the rest for this work and the academia generally for the work you are doing in as far as research is concerned and also being able to share with us this data. We also use this data to improve in our enforcements. It guides us on areas of improvement and prioritization. The data really is so helpful to us and we also continue to work to see how we can improve in that area. We have a unit in traffic directorate that is for enforcement basically,” SP Kananura.
Comments from KCCA leadership
Hon. Kizza Hakim Sawula, the lord councilor from Lubaga and Executive Secretary and a Minister for Works and Physical Planning –KCCA noted that one of the causes of this these accidents in the capital city is the poor-quality roads that wear out easily with numerous potholes and the meagre maintenance budget appropriated by parliament to the city authority.

“Can you imagine that each kilometer of the road within Kampala is constructed at an average cost of 14 billion shillings. For the last three budgets, we were getting 78bn but but in the current budget, we received only 43 billion shillings for the entire capital, for the entire financial year for roads, drainages and traffic lights. How many kilometers are we looking at? 3 kilometers for a financial year, 43 billion shillings?
We used to get Shs26 billion from the national road fund, for road maintenance every financial year. You can confirm from the mayors and load counselors here. This time around, we received only 11 billion for all the maintenance. Now, what do we expect out of that money? So, the task is upon the members of the Parliament to improve on the budget. We have 2,110 kilometers of roads within Kampala. Only 654 kilometers are paved, when shall we complete the entire balance? So, we need a budget, enough budget from the members of parliament. When we talk to MPs they only talk about loans we get from development partners which is usually for new roads,” explained Hon. Sawula.
Concerned, Nakawa Division Mayor, Paul Mugambe said it was disheartening that many people continue to lose their lives prematurely. He cited that not every death is predetermined by the Lord. “Driving at excessively high speeds, and resulting in a crash is not the Lord’s decision. Many individuals lose their lives prematurely due to reckless behavior, and it’s truly regrettable.”

Mr. Mugambe urged Police to use the evidence provided to improve on the enforcement of road traffic laws and regulations.
Prof. Elizeus Rutebemberwa, the Deputy Dean, MakSPH thanked the Bloomberg Philanthilopies “for supporting us to help ourselves” and the JH-IIRU for the technical support to the TRIAD unit, the university and many partners. He also noted that the urban population in Uganda is steadily increasing and called for proactive and inclusive urban planning.

“From 2012, the urban population was 20%. In 2022, which is one year and a half ago, it was 26%. So, one in four people in Uganda were in urban areas. Now in 2040 it is estimated that 33 million would be living in urban areas and that would be 46%. So, it’s not getting better, it’s getting worse. So, we need to manage our urban areas so that people don’t shift from the rural areas to come to die in urban areas,” said Prof. Rutebemberwa.
He called on government and the city authority to fast-track mass transport systems to reduce congestion on the roads. “Look at the traffic that come to Kampala. They are in private cars and each one is carrying one person. In very few cases, two people. Now, if you have all those cars for one kilometre stretch, you could actually park all those people in one bus. And you have all space and you reduce the pollution, why should this be difficult for people to know that. For you to have an organized urban area, you need mass transport. You don’t need to research to know that. So why don’t we have them? Some of these things, some of them we talked about in the national drive, dedicated walk lanes.
According to Becky Bavinger, from the public health area of Bloomberg Philanthropies, road traffic injuries are the leading cause of death for people aged 5 to 29. She mentioned that the fatalities from road traffic are at a crisis level in Uganda.

“I want to say this again. This is the leading cause of death. It’s not HIV. It’s not tuberculosis. It’s real traffic injuries for people aged 5 to 29. Those are the young people. We had the mayor talking about the economic impact as well. These are young people going to school, getting trained, coming back into your workforce, starting out in the workforce, and you’re losing their lives. There’s a forthcoming research from the Road Safety Coalition Uganda looking at the loss of GDP from road traffic injuries. In 2017, your government reported 3,500 deaths. The WHO estimated it was double that at about 6,000. It has gone up. In 2021, your government reported 4,159 deaths. Again, the WHO estimated it was about double that at 7,300. This is not good. This is a crisis and we need everyone working together on it,” Ms. Bavinger said.
She noted that Bloomberg Philanthropies will be working over these next two years with KCCA and with the government of Uganda to institutionalize data collection and the surveillance of road traffic injuries and deaths to improve its accuracy.

“These data are critical to forming your decision making. I just want to conclude by saying congratulations to Makerere University, to Johns Hopkins University, but ultimately to KCCA for launching this report, for conducting this research and this is not easy research to conduct. To the stakeholders, use these data. Please, please do not go home and put this report on your shelf. Look through it. Talk to the journalist. Get the media to write stories about this, let everyone know what is happening,” said Bavinger.
You may like
-


Makerere University School of Public Health Graduates First Cohort of Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Short Course
-


Climate variability found to shape malaria trends in Yumbe District
-


Mak hosts First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling
-


Uganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-


Uganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-


Olivia Nakisita and the Quiet Urgency of Adolescent Refugee Health
Health
Makerere University School of Public Health Graduates First Cohort of Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Short Course
Published
2 days agoon
February 20, 2026By
Mak Editor
Kampala, Uganda – The Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) has marked a significant milestone with the graduation of the first-ever cohort of its Cost-Effectiveness Analysis (CEA) Short Course. The pioneering programme is designed to strengthen capacity in economic evaluation in Uganda and beyond.
The virtual graduation ceremony honored eleven (11) participants who completed the course. The cohort included professionals from academia, research institutions, government agencies, and non-state actors, reflecting the increasing demand for skills in economic evaluation across sectors.
The short course was developed and implemented by the Department of Health Policy, Planning, and Management (HPPM) in response to the increasing need for evidence-informed decision-making in a context of limited resources.
In her remarks during the ceremony, Assoc. Prof. Suzanne Kiwanuka, Head of the Department of Health Policy, Planning and Management (HPPM) at MakSPH, congratulated the inaugural cohort for completing what she described as a “critical and timely” course.
“With decreasing resources and rising demand for services driven by population growth and the emergence of high-cost technologies, decision-makers must make difficult choices,” she noted. “Cost-effectiveness analysis is no longer optional. It is central to conversations in the corridors of power.”
The CEA short course was designed to equip policymakers, researchers, and practitioners with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills in economic evaluation. Participants were introduced to key principles of health economics, costing methodologies, decision-analytic modelling, Markov modelling, sensitivity analysis, and interpretation of incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs).
According to Prof. Elizabeth Ekirapa, the course lead at MakSPH, this inaugural offering had been “a long time coming,” following years of discussions within the department about building local expertise in economic evaluation.
Delivered over 10 days through interactive online sessions, the course combined lectures, case studies, and hands-on modelling exercises using contextually relevant datasets. Participants were required to develop and present applied cost-effectiveness projects as part of their assessment, allowing them to translate theory into practice.

During the feedback session at the graduation ceremony, faculty emphasized the importance of clarity in defining study perspectives, selecting appropriate outcomes, and aligning research questions with modelling approaches.
Dr. Chrispus Mayora, one of the facilitators, highlighted the need to carefully select outcomes that directly reflect the intervention being evaluated. “When thinking about outcomes, ask yourself: Is this aligned with what I want to study? Interesting outcomes are not always the most appropriate ones,” he advised.
Participants were also encouraged to select modelling techniques such as decision trees or Markov models based on the research question and the nature of the disease or intervention under study.
Prof. Ekirapa described the graduates as “trailblazers,” noting that their feedback would shape future iterations of the course. “When you are the first cohort, you are like pioneers,” she remarked. “We are committed to improving this course to ensure it becomes a world-class programme.”
For many attendees, the graduation ceremony was a new experience, as certificates were awarded virtually an approach that participants welcomed as innovative and inclusive.
“Cost-effectiveness analysis enables us to maximise value for money,” noted Dr. Crispus Mayora of MakSPH. “It allows decision-makers to compare interventions systematically and ensure that limited resources achieve the greatest possible benefit.”
The programme aligns with Makerere University’s broader mandate to provide high-quality training that responds to national and regional development priorities. Participants who successfully complete the course receive a certificate signed by the Dean of the School of Public Health.
As the ceremony concluded, faculty encouraged continued engagement beyond the classroom. Graduates were urged to refine their project ideas and collaborate with the department in advancing research and policy discussions.
The successful completion of the first CEA short course marks an important step in building a cadre of professionals equipped to conduct rigorous economic evaluations. With plans to expand and refine the programme based on participant feedback, the HPPM department under MakSPH is positioning itself as a regional leader in health economics and policy analysis training.
Health
Uganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
Published
4 days agoon
February 18, 2026
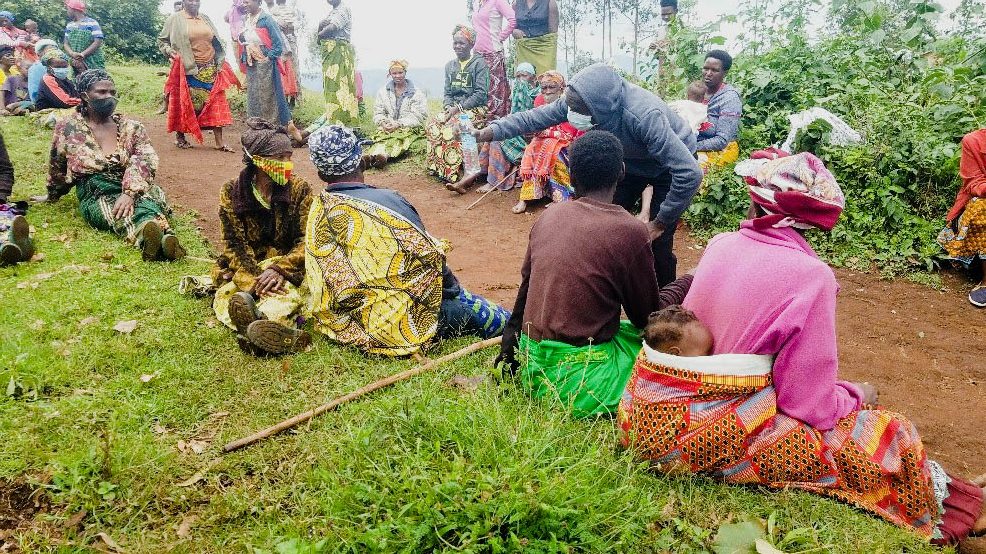
Silhouettes slip along narrow paths, farmers heading to their gardens, women balancing yellow jerrycans on their hips, children in oversized sweaters hurrying to school, and herders steering cattle toward open pasture, each movement part of a choreography older than memory. This is a quiet ritual in Kabale’s terraced hills, moments before the sun lifts.
The quiet procession to ahakashaka, or omukishaka, often sees figures moving quickly along familiar footpaths in the half-light, as children and adults walk with the urgency of habit. It is not a stroll but often a small, hurried run before daylight exposes what should be private.
It is February 2026, and the century-old Makerere University is celebrating its 76th Graduation Ceremony. The world paces and races toward artificial intelligence and digital revolutions. But some families still begin their day by rushing to the bushes for relief and concealment, while others engaged in economic activities such as gardening and grazing have no sanitation option other than using their surroundings to respond to the nature call!
The deadline to end open defecation is 2030. The science is settled, and the commitments are written into Sustainable Development Goal 6. Yet in parts of Kabale, only a small fraction of households is truly open defecation free.
In his PhD research, Dr. Moses Ntaro did not start with global targets or conference declarations. He began where the morning run ends, at the edge of the compounds, behind banana stems, along worn paths leading to Omukishaka. He asked whether students, equipped not with bricks but with conversation, follow-up, and persistence, could help communities replace that dash with something quieter: a door that closes.
What he found is both hopeful and unsettling. Change is possible. But dignity, like sunrise, should not require a run. And with 2030 approaching, time is no longer generous.

The Question That Would Not Let Him Go
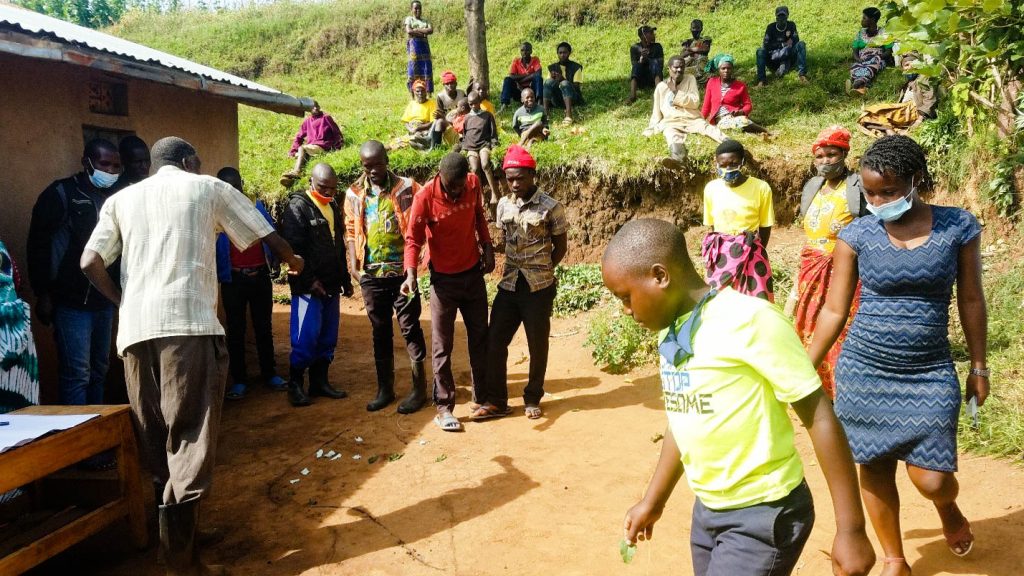
Ntaro did not encounter open defecation as a statistic. While on foot and serving as Assistant Coordinator of Community-Based Education at Mbarara University of Science and Technology (MUST), he learned while supervising students placed in rural communities across southwestern Uganda. They walked villages together, conducted transect walks… and they observed.
“In my role as academic coordinator,” he explains, “students always took me on transect walks within the villages to show me how high open defecation practice was. The effect was evident in the high prevalence of intestinal infections we saw in health facility records.”
The link between sanitation and disease was not theoretical but visible in clinic registers. Diarrhea, intestinal worms, recurring infections among children, and more were all visible in the clinic registers.
Nineteen years ago, in 2007, Uganda adopted Community-Led Total Sanitation (CLTS), a strategy designed to trigger collective behavior change and eliminate open defecation. Progress, however, remained uneven. That same year, Ntaro was working as an Environmental Health Officer with the Water and Sanitation Development Facility under the Ministry of Water and Environment. He was three years away from completing his Environmental Health degree at Makerere University School of Public Health.
And so, the question emerged, to Ntaro, that, ‘If students are already embedded in these communities through COBERS placements, why are we not intentionally harnessing them to accelerate sanitation change?’
That question became his PhD.

This is a Crisis That Should No Longer Exist
Globally, more than 350 million people still practice open defecation. Sub-Saharan Africa carries a disproportionate share. SDG 6, specifically Target 6.2, commits the world to ending open defecation and ensuring universal access to safe sanitation and hygiene by 2030. It prioritizes women, girls, and vulnerable populations. It speaks of dignity, of safely managed services, and of disease prevention.
We are four years away from that deadline. And in rural Kabale District, somewhere in southwestern Uganda, Ntaro’s research found that only 3 percent of households were truly open defecation-free.
Yes, three percent. His 2025 BMC Public Health study examined 492 residents. The average age was 49. Nearly 30 percent had no formal education. Most were women, the custodians of household hygiene and child health.
The determinants of Open Defecation Free (ODF) status were deeply behavioral.
Male-headed households had higher odds of being ODF. Households with clean compounds, clean latrine holes, and consistent handwashing practices were significantly more likely to sustain sanitation improvements.
Sanitation, Ntaro realized, is not only infrastructure but also power, memory, habit, and social expectation.
“Factors associated with ODF status were not just economic,” he notes. “They were behavioral and contextual.”

Why It Feels So Wrong to Still Discuss This
Talking about open defecation in 2026 feels unsettling for three reasons. First, it feels like a failure of basic dignity.
Think of an era of global connectivity and rapid technological advancement, and hundreds of millions still lack privacy. For women and girls, this exposes them to harassment, exploitation, and fear. Sanitation is not just about disease but safety.
Second, it feels like an avoidable health crisis. One gram of feces can contain millions of viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Open defecation directly fuels cholera, typhoid, diarrhea, and environmental enteropathy, a silent contributor to child malnutrition and stunting. The science is settled, and yet the practice persists.
Third, it feels like a poverty trap. Illness leads to lost productivity; lost productivity deepens poverty, and poverty limits investment in sanitation. The cycle continues.
“Open defecation is not simply a sanitation issue,” Ntaro says. “It is linked to poverty, nutrition, and broader development.”

Testing a Different Approach
Ntaro’s doctoral thesis, “Effect of Student Community Engagement on Open Defecation-Free Status,” tested whether health profession students could effectively facilitate Community-Led Total Sanitation.
In some villages, traditional Health Extension Workers led the sanitation process. In others, trained students facilitated it under the COBERS (Community-Based Education, Research, and Service) model, which places medical trainees in community health facilities to learn through real-world practice, bridging classroom theory with primary care and public health work in rural settings.
Through this model, students led triggering, follow-ups, and community engagement. Open defecation declined. More households achieved Open Defecation Free status. And the cost per household was lower than in traditional approaches.
“Students were more effective,” Ntaro explains. “More households became open defecation-free compared to the traditional approach. And they were a cheaper human resource.”
But cost was not the real breakthrough. Presence was. Students stayed for weeks. They returned to check on latrines. They built trust. They kept coming back. Because sustainability, Ntaro argues, is not built in a single visit. It is built in repetition.
“There is a need for continued follow-ups and continued student engagement if long-term impact is to be realized.”
Change cannot be declared once and forgotten.

Behavior… and Not Just Bricks
Using the RANAS framework, Ntaro found that households that remembered to wash hands and kept latrines clean were far more likely to sustain Open Defecation Free status. In sanitation, behavior leaves evidence.
“Behavioral change interventions that empower communities,” he recommends, “such as CLTSH, should be strengthened to increase households with ODF status.”
In other words, building latrines is not enough, but communities must believe in them.

The Defense and the Countdown
On December 11, 2025, Ntaro defended his PhD. Examiners pressed him on scale and sustainability. Could student engagement be institutionalized? Could universities be embedded in district sanitation planning?
His answer was pragmatic: “Yes, but community-based education must be included in planning and budgeting.”
Four years remain to meet SDG 6.2. Four years to end open defecation and turn dignity from promise into practice. In 2026, this conversation should feel outdated. Instead, it remains urgent.

The Slow Work of Restoration
In Kabale, progress does not look dramatic. It looks like a latrine door closing firmly behind someone, a handwashing station with water and soap, a compound swept clean. It looks like a child who does not fall ill this month. Public health victories are often quiet.
As Makerere University approaches its 76th Graduation Ceremony, Dr. Ntaro Moses stands among its PhD graduands not with theory alone, but with evidence that change can be accelerated by reimagining who leads it. Students, he shows, are not only learners. They are the workforce, facilitators, and bridges between policy and path.
The hills of Kabale still wake under mist. But in more compounds now, privacy exists where bushes once stood open. Dignity is not restored in headlines, but one household at a time.
And with 2030 approaching, Ntaro’s work leaves a final, unavoidable question: if we already know how to end open defecation, if we already have the tools, the evidence, and the people, what, exactly, are we waiting for?

— Makerere University School of Public Health Communications Office, Graduation Profiles Series, 76th Graduation Ceremony
Health
Olivia Nakisita and the Quiet Urgency of Adolescent Refugee Health
Published
4 days agoon
February 18, 2026
Kampala wakes early, but for some girls, the day begins already heavy. In Uganda, nearly three-quarters of the population is under 30, growing up happens fast, and often without protection. One in four Ugandan girls aged 15–19 has already begun childbearing, giving Uganda the highest teenage pregnancy rate in East Africa.
Layered onto this is displacement. The country hosts about 1.7 million refugees, many living in cities like Kampala, where survival depends on navigating systems not designed with them in mind. Also, nationally, 1.4 million people live with HIV, and 70 per cent of new infections among young people occur in adolescent girls, a reminder that vulnerability is rarely singular. When COVID-19 shut the country down, the consequences were immediate, with pregnancies among girls aged 15–19 rising by 25.5 per cent, while pregnancies among girls aged 10–14 surged by 366 per cent.
The numbers tell a story of youth, risk, and quiet urgency. But they do not tell it all. For years, Olivia Nakisita, a public health researcher,has followed how adolescent girls, many of them refugees, navigate pregnancy in Kampala: how far they must travel for care, how early they arrive or delay, and how often services that exist fail to meet them where they are. Her work lives at the uneasy intersection of policy and lived reality, where access does not always translate into care.
February 25th 2026, is the day that her work on whether urban health systems are truly ready for the youngest mothers they now serve will bring her to Freedom Square at Makerere University, where she will graduate with a PhD in Public Health.

Her doctoral journey, focused on maternal health services for adolescent refugees in urban Uganda, has unfolded at the intersection of scholarship, community service, and the daily realities of young girls navigating pregnancy far from home.
The Work That Came Before the Question
Long before she began writing a PhD proposal, Olivia Nakisita was already immersed in adolescent health. As a Research Associate in the Department of Community Health and Behavioral Sciences at Makerere University’s School of Public Health, she taught graduate and undergraduate students, supervised Master’s research, and worked closely with communities. Beyond the university, she led New Life Adolescent and Youth Organization (NAYO), a women-led organisation she founded in 2021 to strengthen access to sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) information and services for adolescents and young people.
It was through this community work that a troubling pattern began to surface.
“During our community service,” she explains, “we noted increasing teenage pregnancies, and we also noted challenges with access to maternal health services by teenage pregnant girls.”
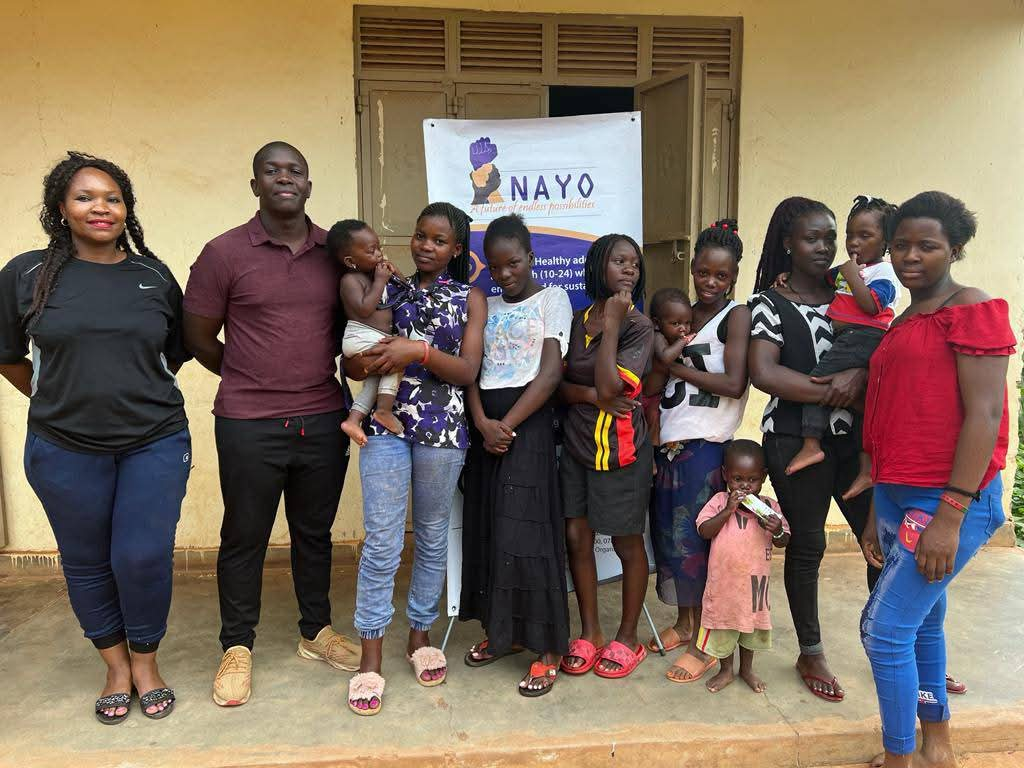

Among those girls were adolescents living as urban refugees in Kampala, young, displaced, often poor, and navigating pregnancy in a city not designed with them in mind.
For Nakisita, the concern deepened through her academic training in Public Health Disaster Management, one such programme that prepares multidisciplinary professionals with the technical expertise and leadership competencies required to plan for, mitigate, respond to, and recover from complex disasters through a public health lens. This programme sharpened Nakisita’s interest in how displaced populations survive within complex urban systems. Uganda’s integrated health model, where refugees and host communities are expected to use the same facilities, appears equitable on paper. In practice, it can be unforgiving.
“I got interested in understanding how these refugees who get pregnant manage to navigate the complexities of integration in host societies like Kampala,” she says. “This was driven by the desire to address their needs and to inform and evaluate existing refugee health policies.”

That desire became the foundation of her PhD.
Asking Hard Questions in a Crowded City
Her doctoral research, “Maternal Health Services for Adolescent Refugees in Urban Settings in Uganda: Access, Utilisation, and Health Facility Readiness,” was conducted in Kampala between November 2023 and August 2024. It combined quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews, engaging 637 adolescent refugees aged 10–19 years, alongside health workers and facility assessments.
Her findings showed high perceived access to maternal health services. Clinics existed. Services were available. Yet utilisation, particularly of antenatal care (ANC), lagged. “About three-quarters of the girls attended at least one antenatal visit,” she explains, “but only about four in ten attended in the first trimester.”
And that gap matters. Public health research shows that early and regular antenatal care allows health workers to detect high-risk pregnancies, initiate supplements such as iron and folic acid, monitor fetal development, and provide psychosocial support. Without it, risks compound silently.
By contrast, her study found that facility-based deliveries were remarkably high, with nearly all adolescent refugees (98.3%) giving birth in health facilities, suggesting that the system was reachable, but uneven.

Where the System Falls Short
Her research went beyond utilisation to examine whether health facilities were actually ready to serve adolescent refugees.
Findings show that lower-level health centres in Kampala were moderately prepared to offer adolescent-friendly maternal health services. Some staff were trained. Some spaces existed. Despite this, critical gaps remained. For instance, facilities lacked essential equipment and supplies. Non-provider staff were often untrained. Separate, private spaces for adolescents were limited. Language barriers complicated care. Overcrowding strained already stretched health workers.
In her qualitative interviews, health workers expressed empathy and willingness to help. Many relied on peer educators and community health workers to reach adolescent refugees. But good intentions were not enough.
“They recommended training of healthcare workers, translators for refugees, and improvement in the availability of essential drugs, supplies, and equipment,” Nakisita notes.
She notes that readiness is not just about infrastructure but about the people, preparation, and priorities.
Research with an Emotional Cost
For Nakisita, working with adolescent refugees required care, not only methodologically, but emotionally.
Finding participants in Kampala was itself a challenge. Unlike settlement settings, urban refugees are dispersed, often invisible. Ethical considerations were constant. Adolescents who had given birth were legally considered emancipated minors, but their vulnerability remained.
Though the thesis focused on systems rather than personal narratives, Nakisita’s earlier work with adolescents informed every decision she made. It shaped how she framed questions, interpreted data, and weighed policy implications. This was not detached research, but careful, deliberate, and grounded.
The Scholar Formed by Continuity
Nakisita’s PhD sits atop more than 18 years of experience in training, research, and community service. She is an alumna of Makerere College School (UCE), 1996 and Greenhill Academy Secondary School (UACE), 1998, a long journey through Uganda’s education system before her Diploma in Project Planning and Management at Makerere University completed in early 2000s.
She would later return eight years later to Makerere University for her Bachelor’s degree in Social Sciences and a Master’s in Public Health Disaster Management, and now a PhD in Public Health.
Her academic rigor is reflected in extensive training across SRHR, impact evaluation, research methods, ethics, disaster resilience, and humanitarian health. She has presented at regional and international conferences and published in peer-reviewed journals on adolescent health, refugee maternal care, gender-based violence, and health systems readiness.
As a PhD student, she supervised three Master’s students to completion, with another currently progressing, quietly extending her influence through mentorship.



When Evidence Demands Action
If policymakers were to act on one lesson from her research, Nakisita says; “Emphasis should be given to maternal health services for adolescents.” “They are high-risk mothers,” she adds.
Her findings call for targeted community-based interventions, outreaches, home visits, and financial support for adolescents who cannot afford prescribed drugs, delivery requirements, or critical tests like ultrasound scans.
They also call for health systems to move beyond one-size-fits-all models, recognising that age, displacement, and poverty intersect to shape how care is accessed and experienced.
Now that her PhD is complete, Nakisita plans to translate research into action. Several papers from her study have already been published. A policy brief is planned to influence decision-making in urban and humanitarian health settings.
When asked what she would say directly to adolescent refugee girls navigating pregnancy in unfamiliar cities, her response is simple and direct.
“If it happens,” she says, “as soon as you find out, go to the nearest health facility and seek care. Always return for the visits as asked by the health worker. Ensure that you deliver in a health facility with a skilled health worker.”
Arrival, Without Illusion
When Dr. Olivia Nakisita steps onto the graduation stage at Freedom Square, applause will follow. But the true significance of that moment lies in health facilities still struggling to adapt; in adolescent refugees whose pregnancies unfold quietly in rented rooms and crowded neighborhoods; in policies waiting to be sharpened by evidence.
Her scholarship does not promise quick fixes but offers clarity.
Among the PhDs conferred at Makerere University’s 76th graduation, her work reminds us that some research does not begin in libraries and does not end with theses. It lives on in the slow, necessary work of making health systems see those they have long overlooked.
— Makerere University School of Public Health Communications Office, Graduation Profiles Series, 76th Graduation Ceremony
Trending
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoAptitude Exam (Paper 1) Results for the Mature Age Entry Scheme 2026/2027
-

 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoHow Jimmy Osuret Turned Childhood Trauma into Evidence for Safer School Crossings
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoFor Youth by Youth – Call for Second Cohort Applications
-

 General5 days ago
General5 days agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
