Agriculture & Environment
Soybean Breeders Deliberate Strategies for Improving Productivity
Published
2 years agoon
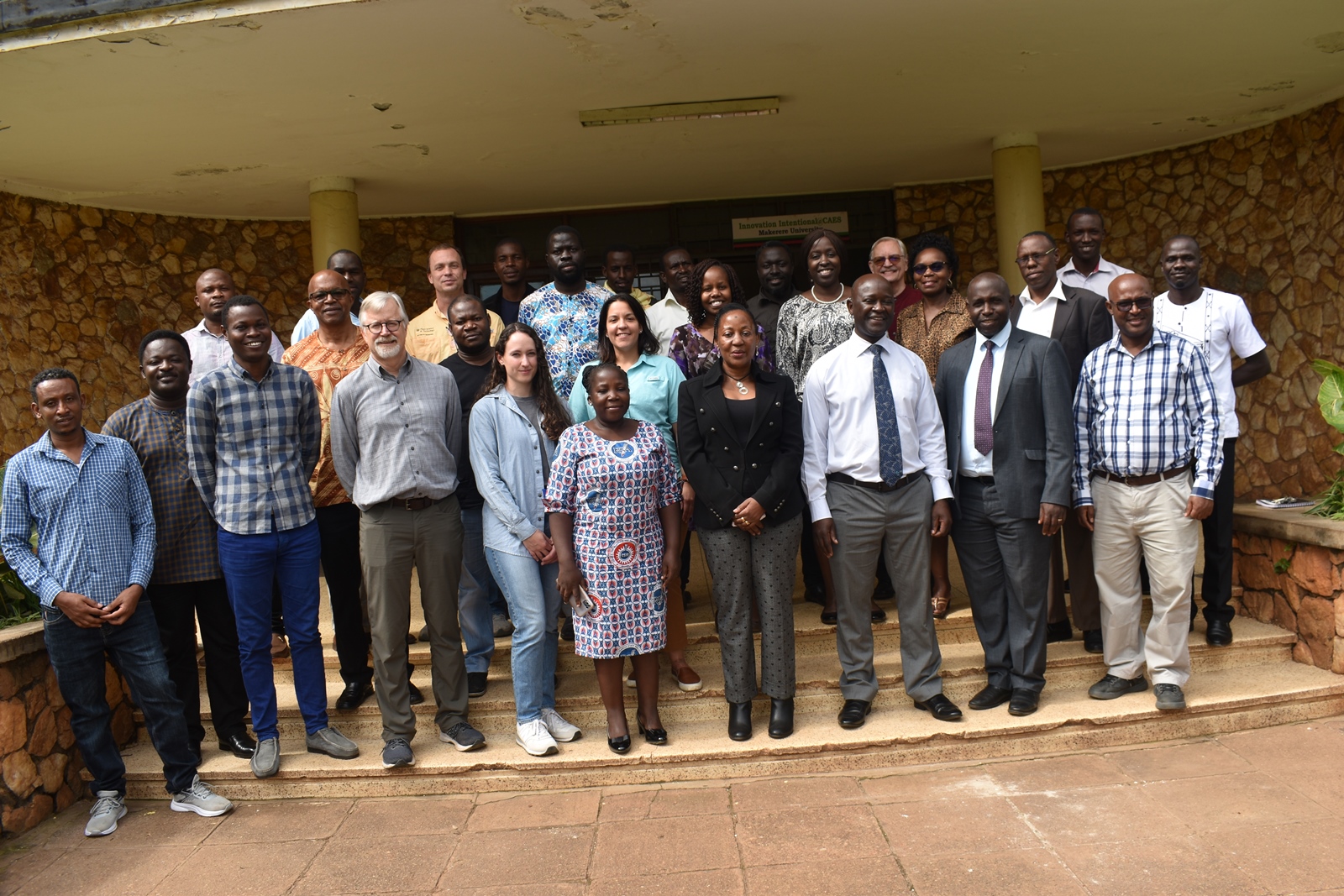

The breeders from USA, Brazil and across Africa, including scientists from CGIAR met at Makerere University on 28th November-1st December 2023 to share experiences, best practices and ideas on collaboration, and to brainstorm on ways of improving productivity.
Overview
Soybean (Glycine max) serves as one of the most valuable crops in the world, not only as an oil seed crop and feed for livestock and aquaculture, but also as a good and cheap source of protein for human diet and as a biofuel feedstock. The protein content of soybean is the highest among legume crops, averaging 40% on a dry matter basis. Soy-foods are generally considered to be nutritious and healthy based on their nutrient composition which includes protein, fat, carbohydrates, dietary fibres as well as minerals and phytoestrogens (or isoflavones). Due to its nutritional superiority, soybean-based foods are highly recommended for children under 5 years, expectant mothers, and HIV/AIDS patients. Impact studies have shown that regular soy food consumption can reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering serum cholesterol by about 33%. It can also reduce the risk of rectal cancer by 80%, mammary tumour by 40%, and breast cancer by 50%.

Economic viability
Production of soybean stands at 264 million MT worldwide, with United States of America (USA), Brazil and Argentina being the largest producers. In Africa, Nigeria, South Africa, Zambia and Uganda are the largest producers, with annual volumes estimated at 1.5 million metric tonnes (FAO, 2017). The Soybean Market size is estimated to reach $259 billion by 2030 (IndustryARC – Soybean Market Forecast 2023-2028).

The economic viability of soy production is determined by the commercial utilization of both its sub-products, meal and oil, which, respectively, account for about two thirds and one third of the crop’s economic value. Soymeal accounts for over 60% of world output of vegetable and animal meals and occupies a prominent position among protein feedstuffs used in the production of feed concentrates, while soybean oil is the single most important vegetable oil, accounting for 20% of global vegetable oil production. The widespread use of soybean oil in particular as edible oil is mainly due to (i) its plentiful and dependable supplies, (ii) its competitive price, (iii) its neutral flavour, and its stability in both unhydrogenated and partially hydrogenated form. Indirectly, the rapid rise in the demand for compound feed has contributed considerably to the rise in soybean and soyoil production. Soybean contributes significantly to the total value added by the agricultural sector in the major producing countries and particularly so in Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and the USA. In these countries, soybean and its two main sub-products also occupy an important position in export earnings from agriculture as well as in terms of total merchandise exports (FAO). In Uganda, soybean is number one income earner crop in Northern and Eastern Uganda. Farmers in the region earn at least UGX1,200,000 per hectare per season.

Challenges undermining productivity
Despite the significant strides registered by soybean growing countries, and the health and economic benefits that the crop presents, a number of challenges still undermine productivity. These include; pests and diseases, prolonged droughts and prolonged rains, poor agronomic practices, inaccessibility to good seed by farmers, drudgery in the production chain (Planting and harvesting) and market price fluctuations, as well as mismatches in supply and demand. Surging input costs, supply disruptions of fertilizers and alternative crops caused by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and lingering COVID-19 effects have added more uncertainty and volatility to the soybeans market, driving up the prices. Home grown technologies, local seed business approach, and addressing the whole value chain, are envisaged as some of the strategies to overcome the challenges. Adapting crop management, conserving and improving soil conditions by minimizing tilling, increasing crop diversification, protecting soil from erosion, as well as the development of drought-tolerant varieties, will be key to withstand the emerging climate challenges.
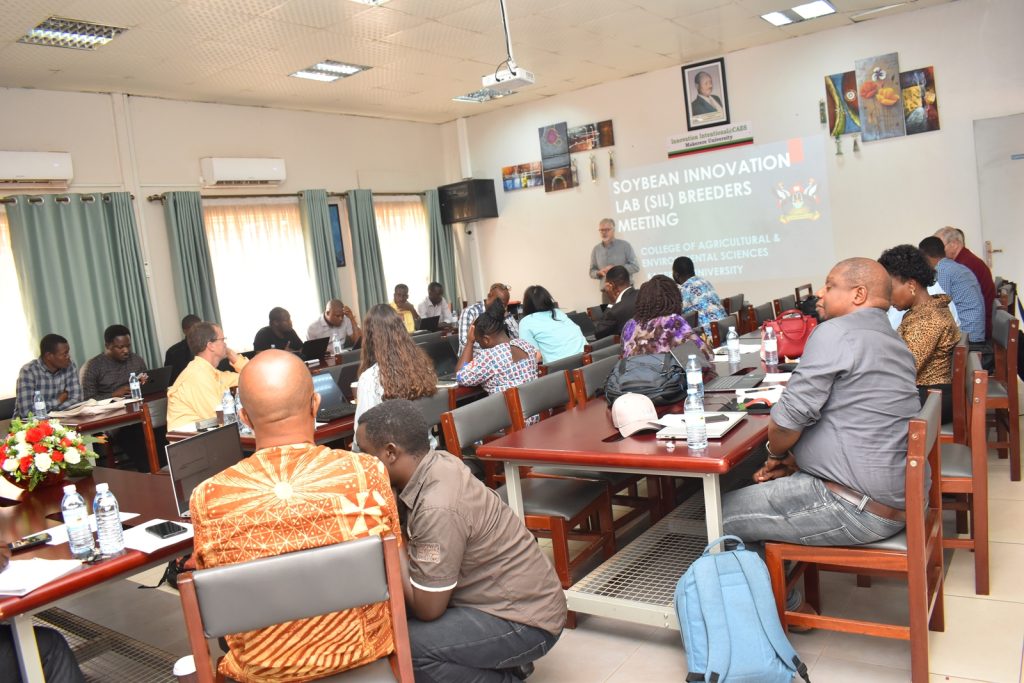

Soybean Breeders meeting at Makerere
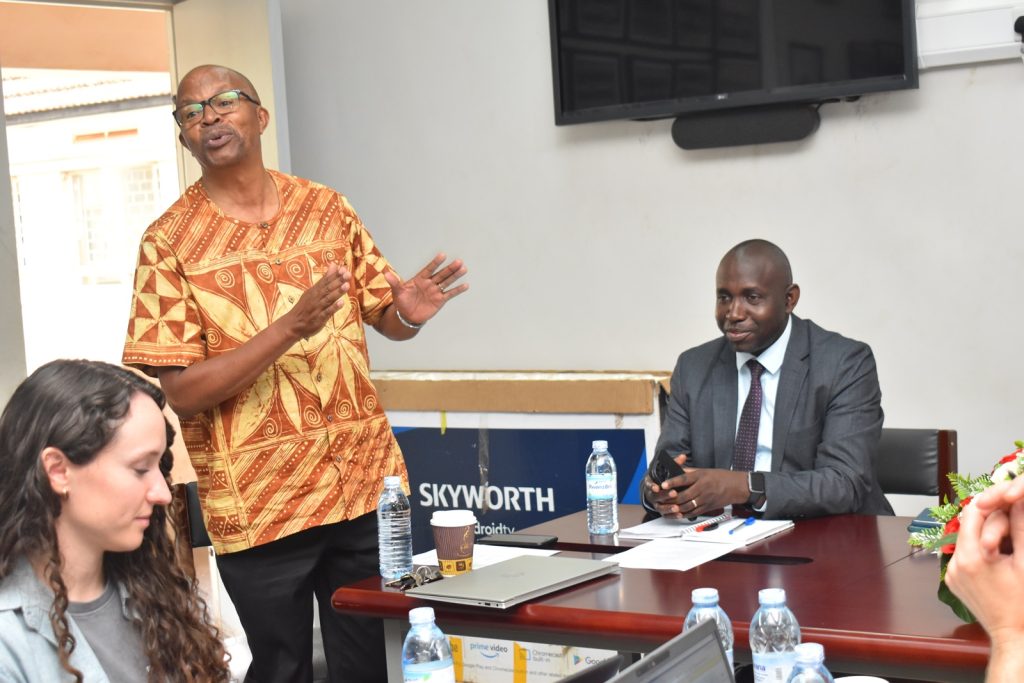
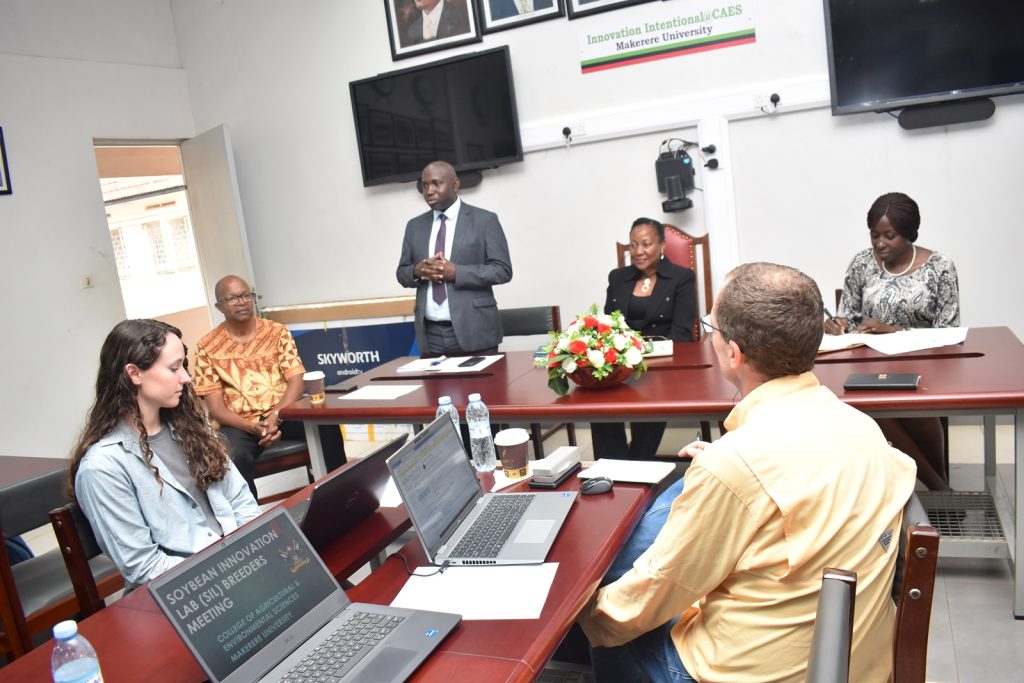
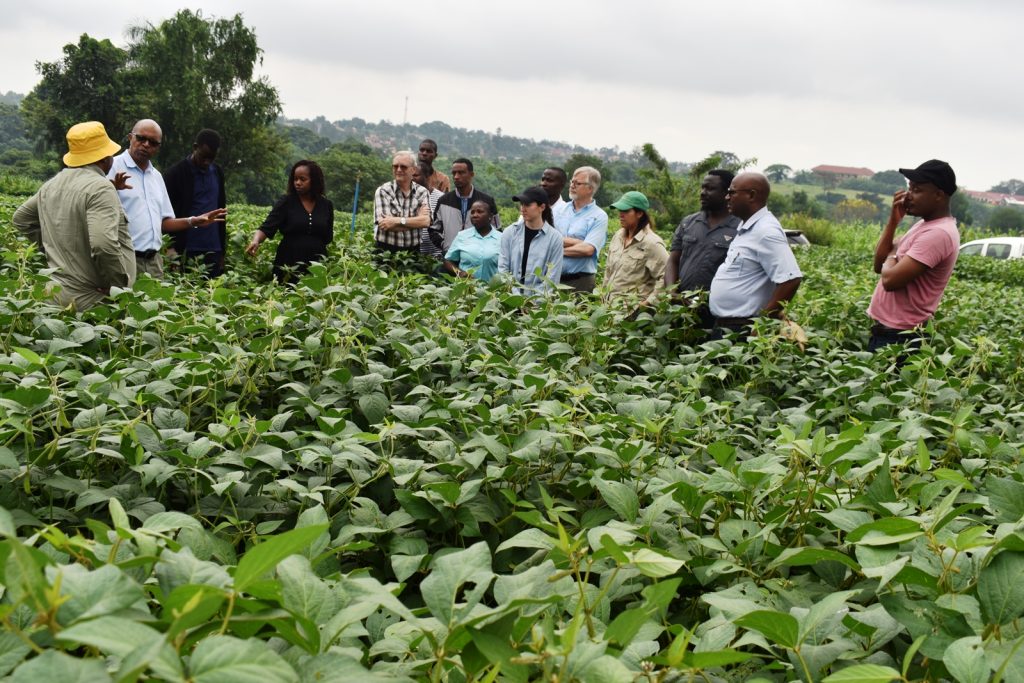
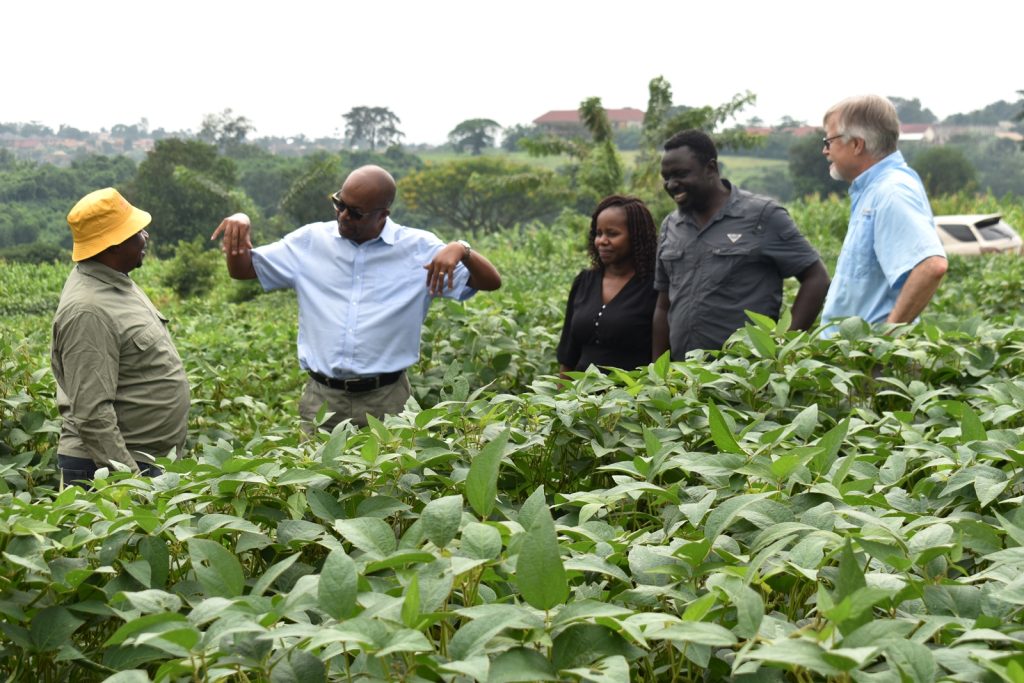
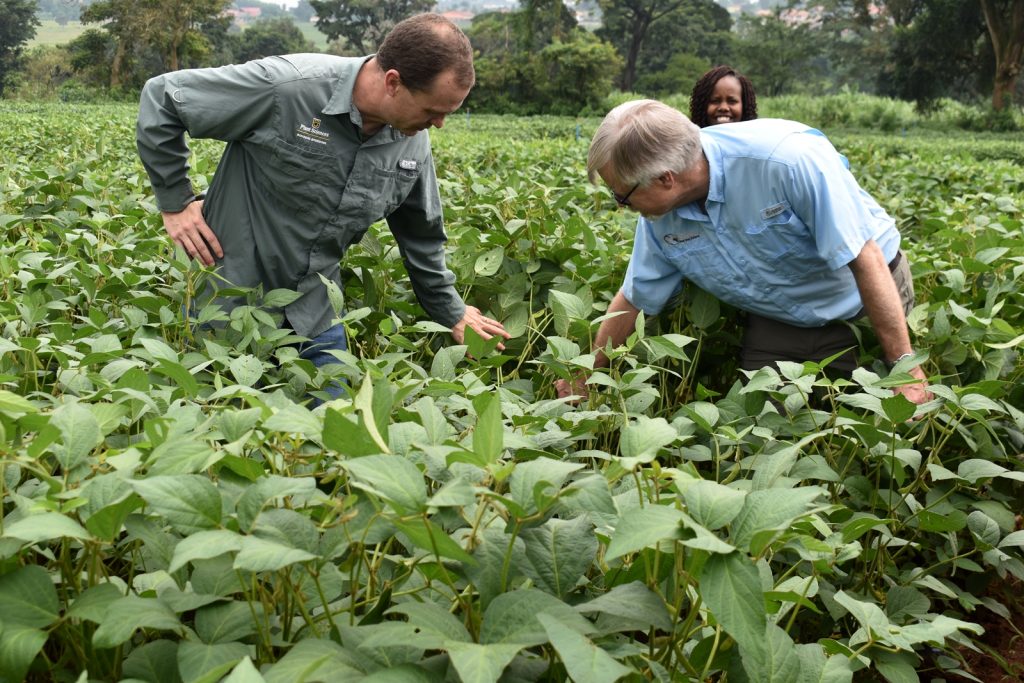
Soybean breeders from USA, Brazil, and across Africa including scientists from CGIAR on 28th November 2023 met at Makerere University to share experiences, best practices, and ideas on collaboration, and to brainstorm on ways of improving soybean productivity. The meeting held at the School of Agricultural Sciences (SAS), College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES) was organized by the Makerere University Centre for Soybean Improvement and Development (MAKCSID) and the Soybean Innovation Lab (SIL) of the University of Illinois with support from USAID. It was coordinated by Prof. Phinehas Tukamuhabwa, Principal Investigator for the Soybean Breeding and Seed Systems at Makerere, and Prof. Brian Diers from SIL, University of Illinois. It was graced by the Principal of CAES, Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga, the Deputy Principal, Prof. Yazidhi Bamutaze, and the Dean, SAS, Dr John Baptist Tumuhairwe. During the meeting, participants shared progress reports of their respective institutions, highlighting the achievements registered in soybean breeding and seed systems, best practices, challenges undermining productivity, and strategies for improvement. In his presentation, Prof. Diers briefed participants on SIL breeding efforts, indicating that 20 varieties had been developed between 2019-2022 up from the 7 developed between 2013-2018. He also shared updates on the renewed funding from USAID, and the support extended towards new breeding programmes at IITA in Nigeria, IITA in Zambia, EIAR in Ethiopia, Makerere University, and SARI in Ghana.

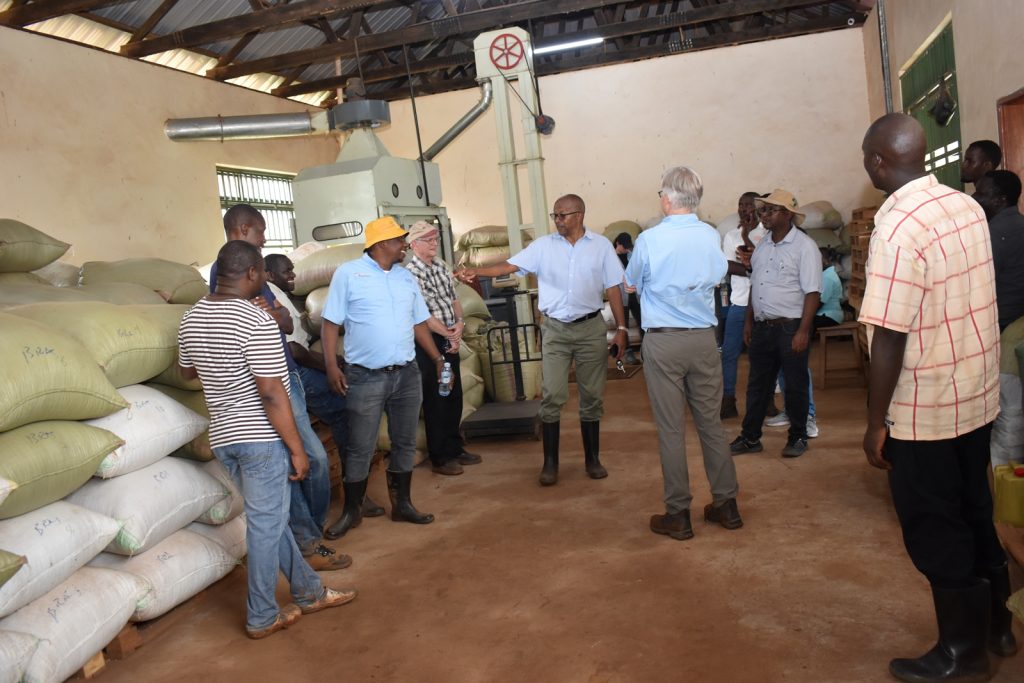
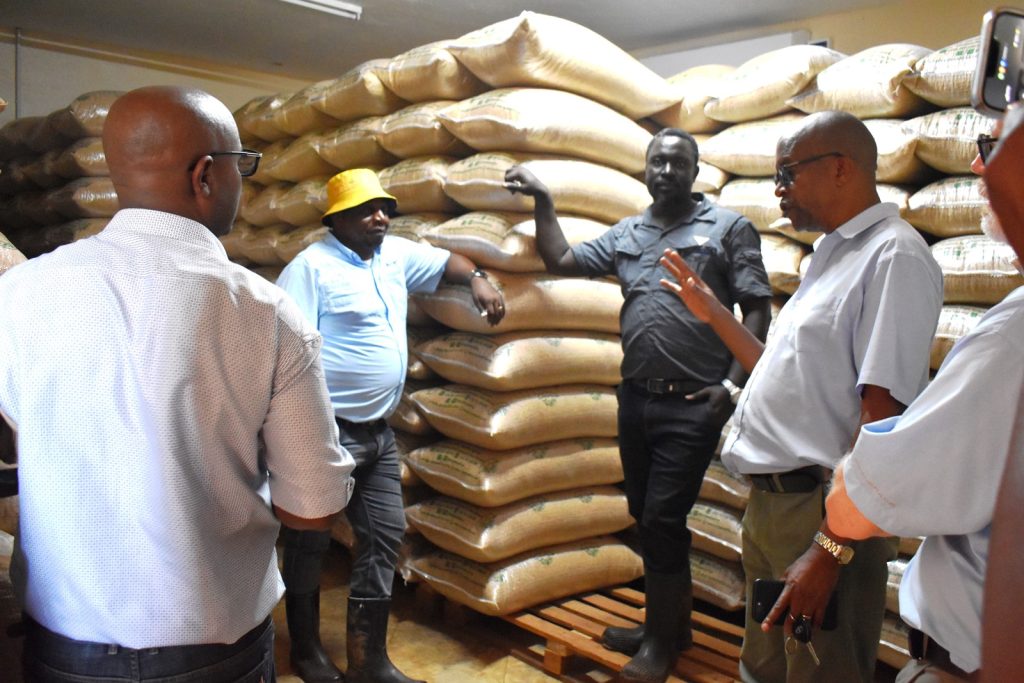
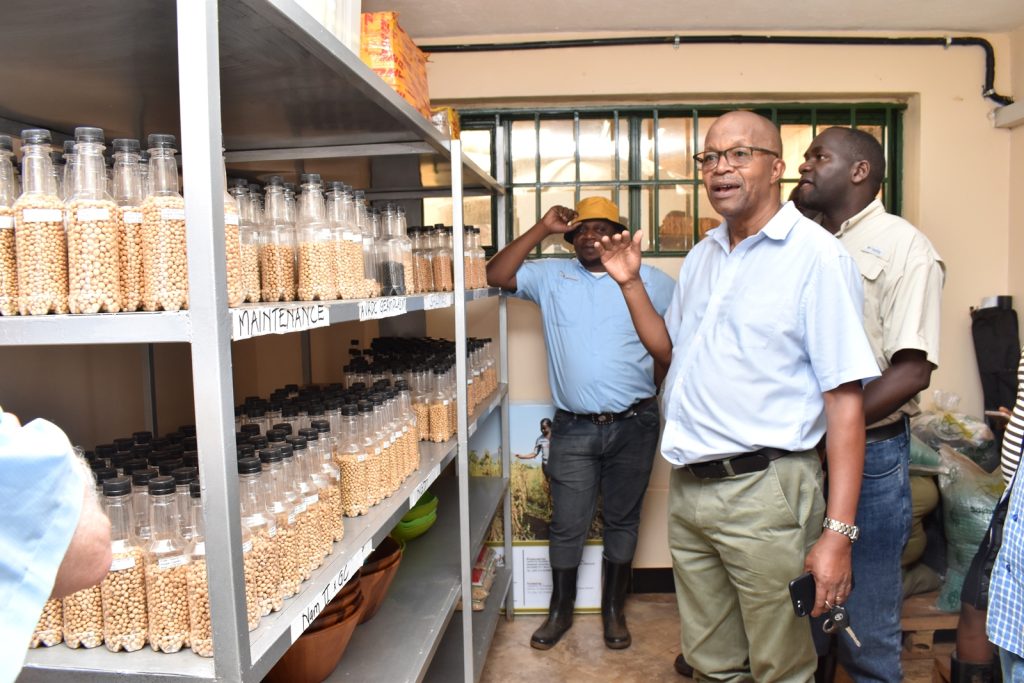
Delivering a presentation on soybean research in Uganda, Prof. Tukamuhabwa noted that the country had registered significant strides with the production of six high yielding varieties namely; Maksoy IN, Maksoy 2N, Maksoy 3N, Maksoy 4N; Maksoy 5N, Maksoy 6N. Recent impact studies indicated that the new varieties developed by MAKCSID were the most planted and accounted for 93% of the soybean varieties grown by Ugandan farmers. Currently, Maksoy 1N is the most widely adopted variety by farmers, while Maksoy 3N has the largest quantities of foundation seed disseminated by the Centre. According to Prof. Tukamuhabwa, the Centre also established a state-of-the-art seed storage facility for early generation seed (Breeders and Foundation seed) and soybean germplasm used for breeding other varieties. Other facilities are soybean processing equipment (soycow) and Soybean roaster that are used to add value to soybeans. The growth of the soybean sub-sector in Uganda is mainly attributed to the availability of a wide range of improved varieties, government investment in soybean research, and increased private sector investment along the soybean value chain. Despite the achievements, Prof. Tukamuhabwa outlined a number of factors undermining soybean seed systems in Uganda including; the presumed high cost of seed by farmers, counterfeit seed in the market, limited interest in self-pollinating crops by most private seed companies, weak seed policy enforcement, limited access to seed, and unpredictable weather conditions. He expressed gratitude to all development partners that have supported the growth of the MAKCSID programme including; USAID through SIL, the Government of Uganda through the Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries (MAAIF VODP), NARO, NAcRRI, RUFORUM, AATF, AGRA, Soybean Africa Limited, NAADS, Smart Foods, ISSD Uganda, IITA, and all local soybean stakeholders.
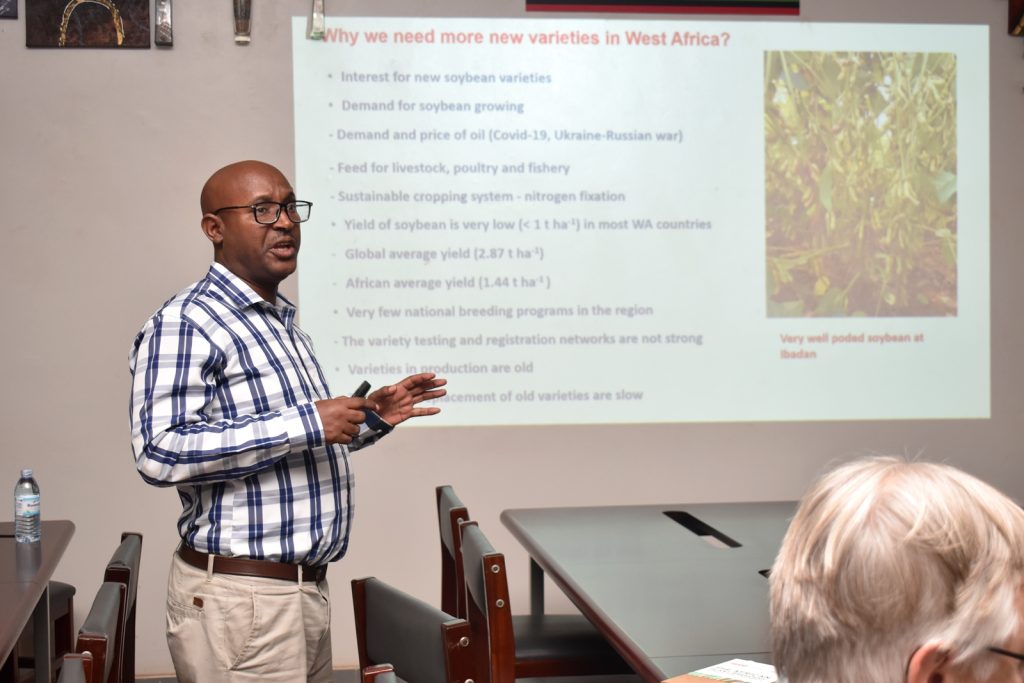

At the meeting, participants including Godfree Chigeza from IITA, Zambia; Abush Tesfaye (IITA, Nigeria), Masresha Yirga (EIAR, Ethiopia), Harun Murithi (SIL), Andrew Scaboo (University of Missouri), Elizabeth De Meyer (University of Missouri), and Carrie Miranda (North Dakota State University) delivered presentations on the progress of their breeding and research programmes.

A major concern arising from the meeting was the increasing threat of rust. Through efforts of the Centre for Soybean Improvement and Development (MAKCSID), the soybean rust pandemic was brought under control, through breeding and dissemination of superior varieties to the farming communities.

Going forward, participants emphasized the need to set up a rust reference centre, early warning systems, and disease nurseries – potential lines for monitoring virulence. They also called for an increase in germplasm acquisition, capacity building for germplasm storage and utilization, introduction of bruchid tolerant genotypes, introduction of soybean genotypes suitable for mechanical harvest, mechanization of production processes, leveraging the scarce research infrastructure, and the development of necessary skills amongst scientists and staff.
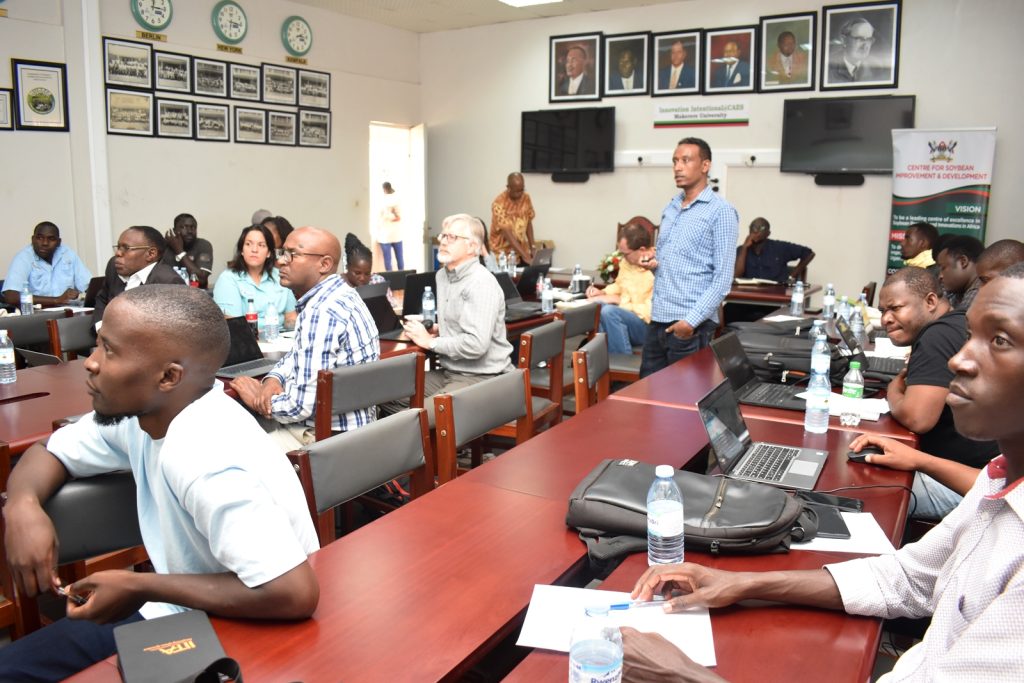

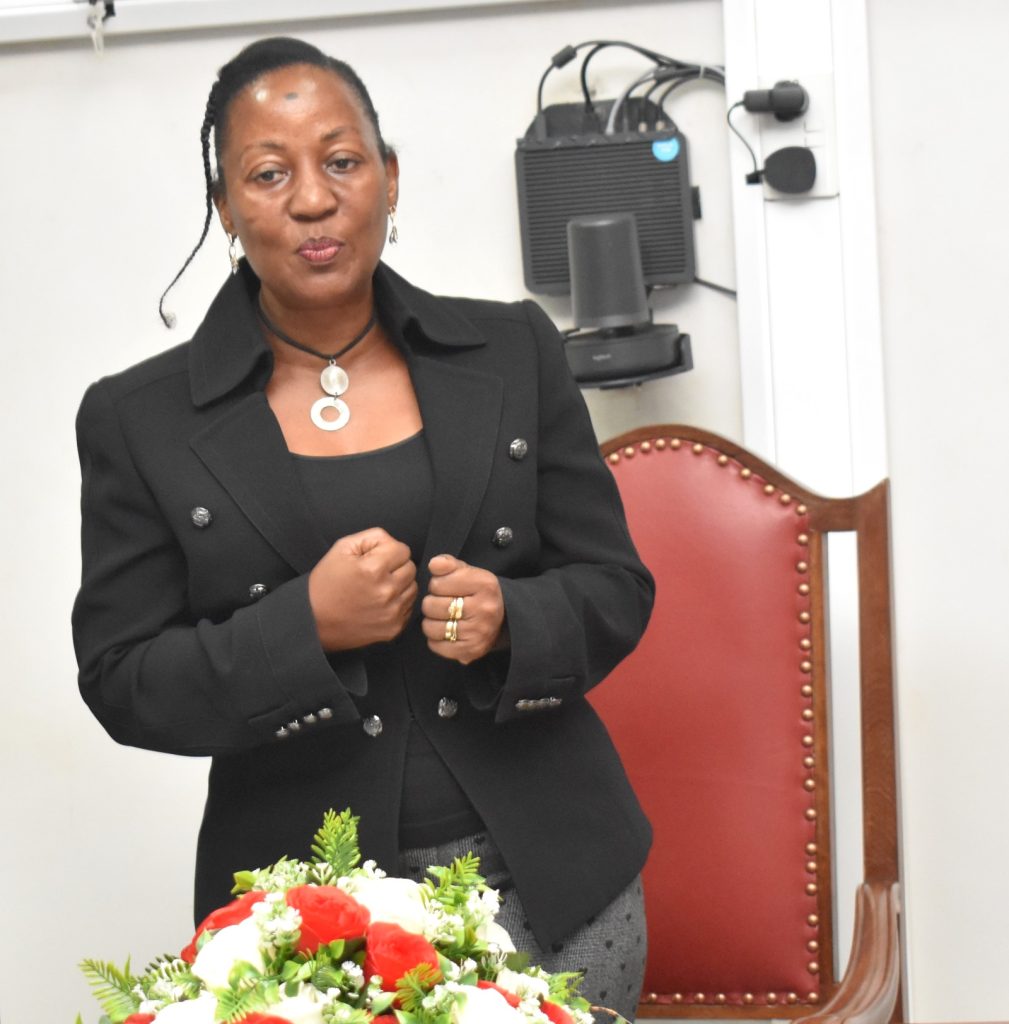
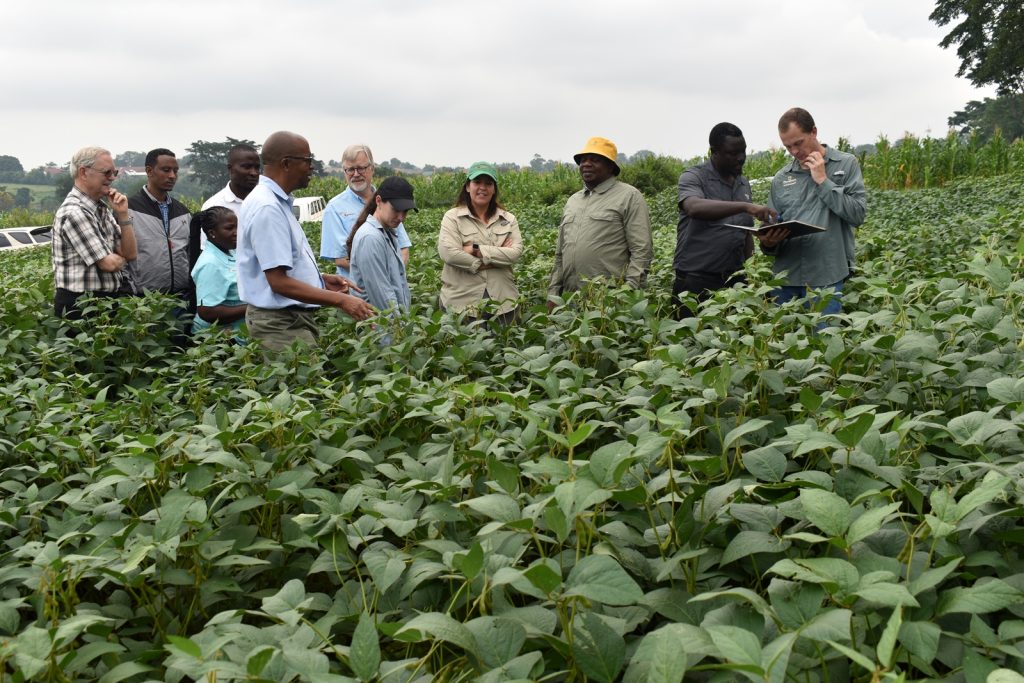
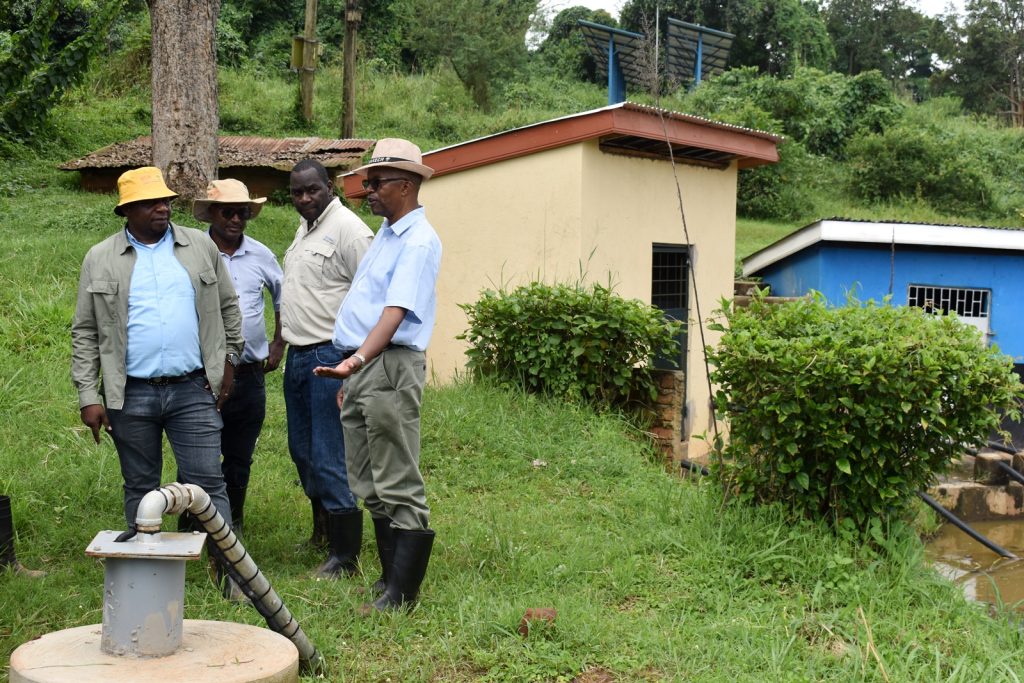
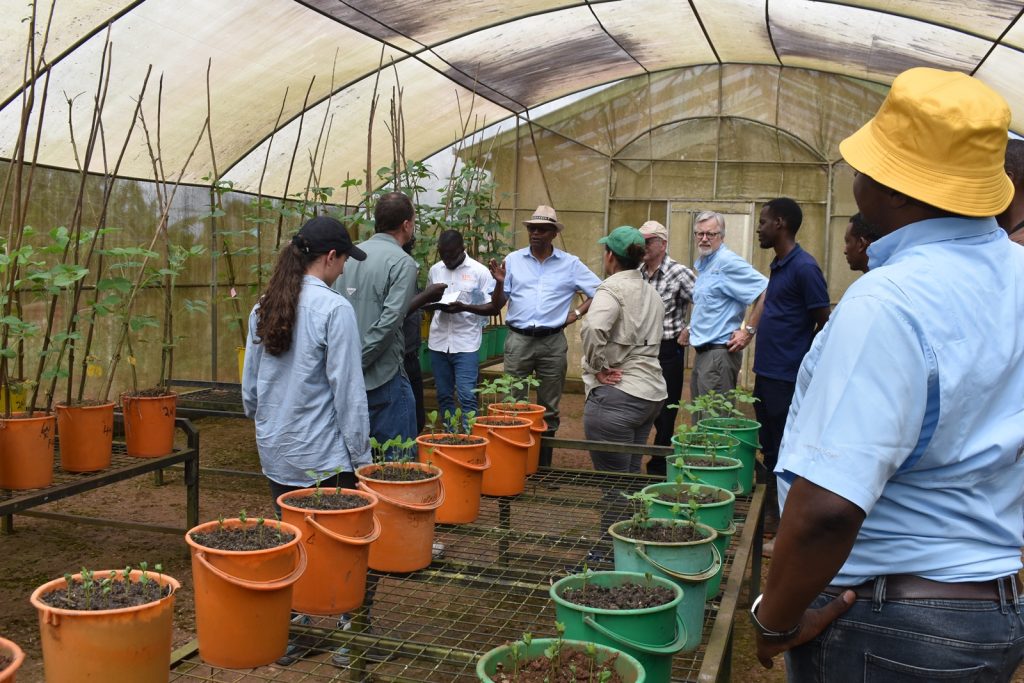
In her remarks, the Principal of CAES, Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga expressed gratitude to participants for leading soybean development initiatives. She also appreciated the development partners for supporting the programme. Commenting on the significance of the crop, she said under NDPIII, soybean had been identified as a game changer and one of the crops to improve the country’s food systems. “The crop has been targeted for its oils and nutritional benefits. It is therefore important that we move it to the next level in terms of resistance to diseases, adaption to climate change, and development of fast growing varieties.” She specifically thanked the breeding team led by Prof. Tukamuhabwa for making Makerere the leading Centre in quality soybean seed production and distribution in the country. During their four-day visit, the soybean breeders visited the screen houses, soybean fields, and the Early Generation Seed Unit at MUARIK where they provided enriching insights for improvement. The team also toured Nakabango/Jinja trials as well as the Bugi ZARDI highland soybean trials.
More photos from the meeting
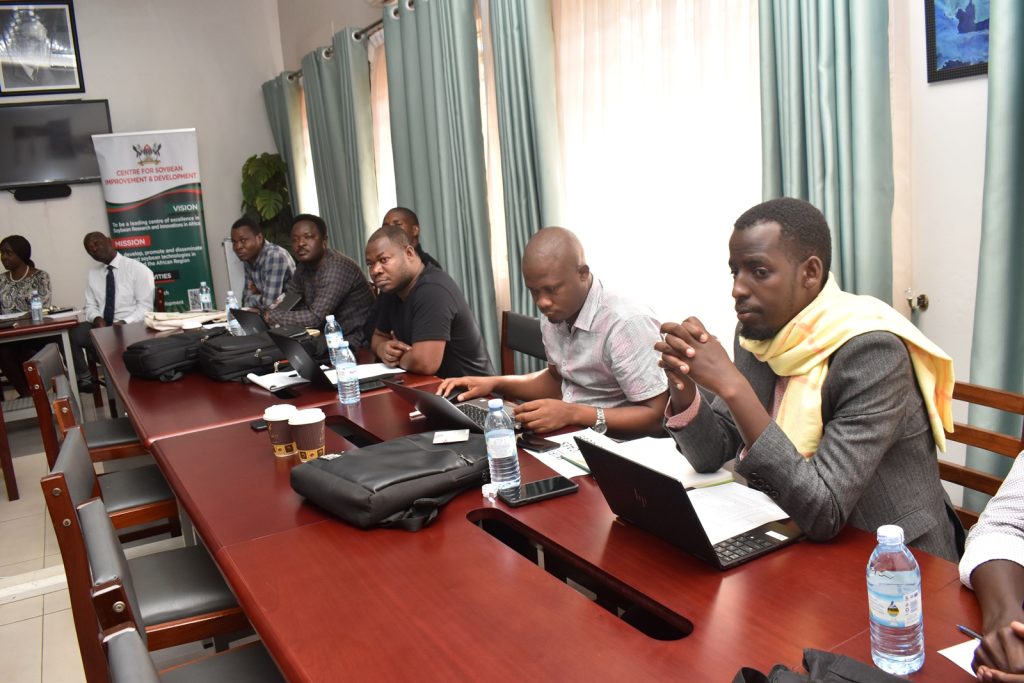
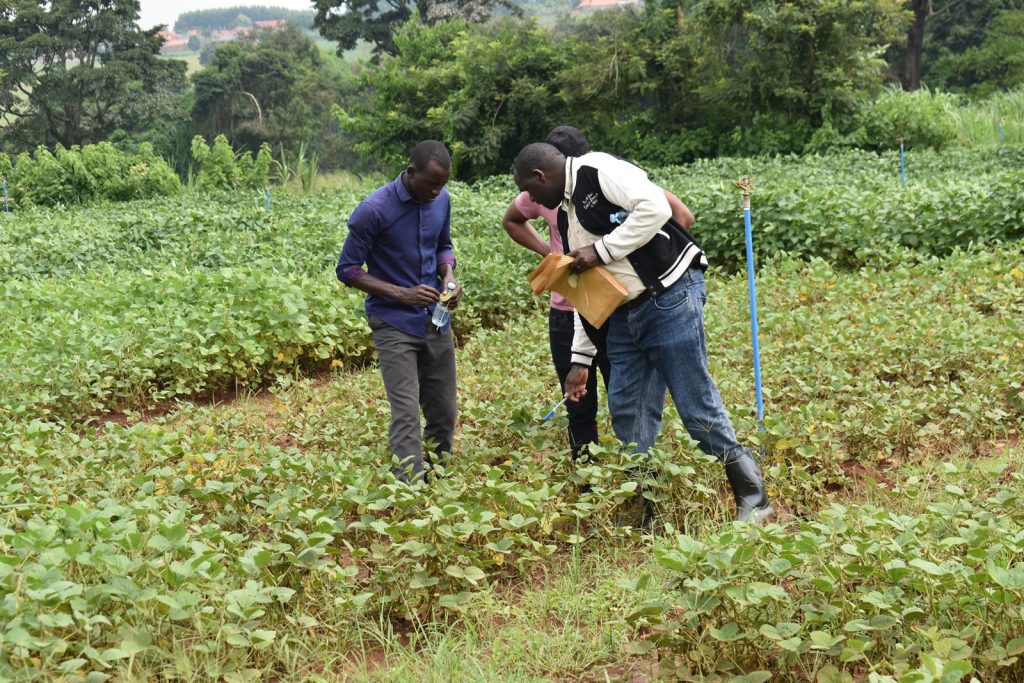
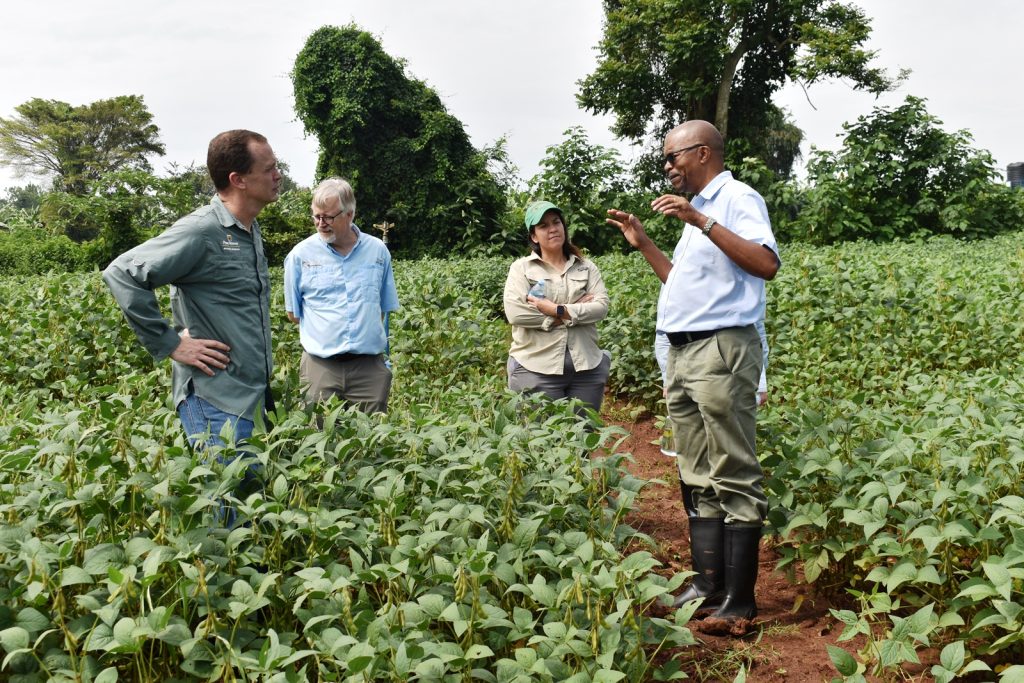
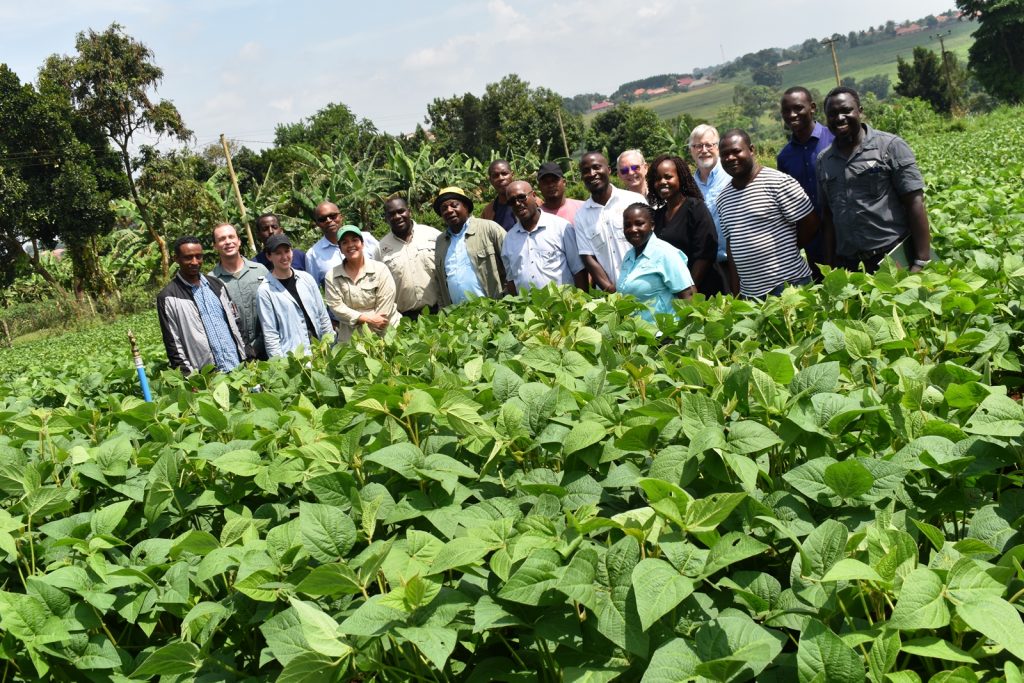
















You may like
-


Call for Abstracts: Digital Health Africa 2025
-


Undergraduate Admission Lists for International Applicants 2025/2026
-

Admission Lists -Disability and District Quota Schemes 2025/26
-


Emorimor Calls for Makerere to Upgrade Parenting Course
-


Uganda Deepens Economic Governance with Training on Regulatory Cost-Benefit Analysis
-


NbS4Tea Project Team Makes Great Progress, Deploys Drones for Data Collection
Agriculture & Environment
NbS4Tea Project Team Makes Great Progress, Deploys Drones for Data Collection
Published
1 week agoon
June 24, 2025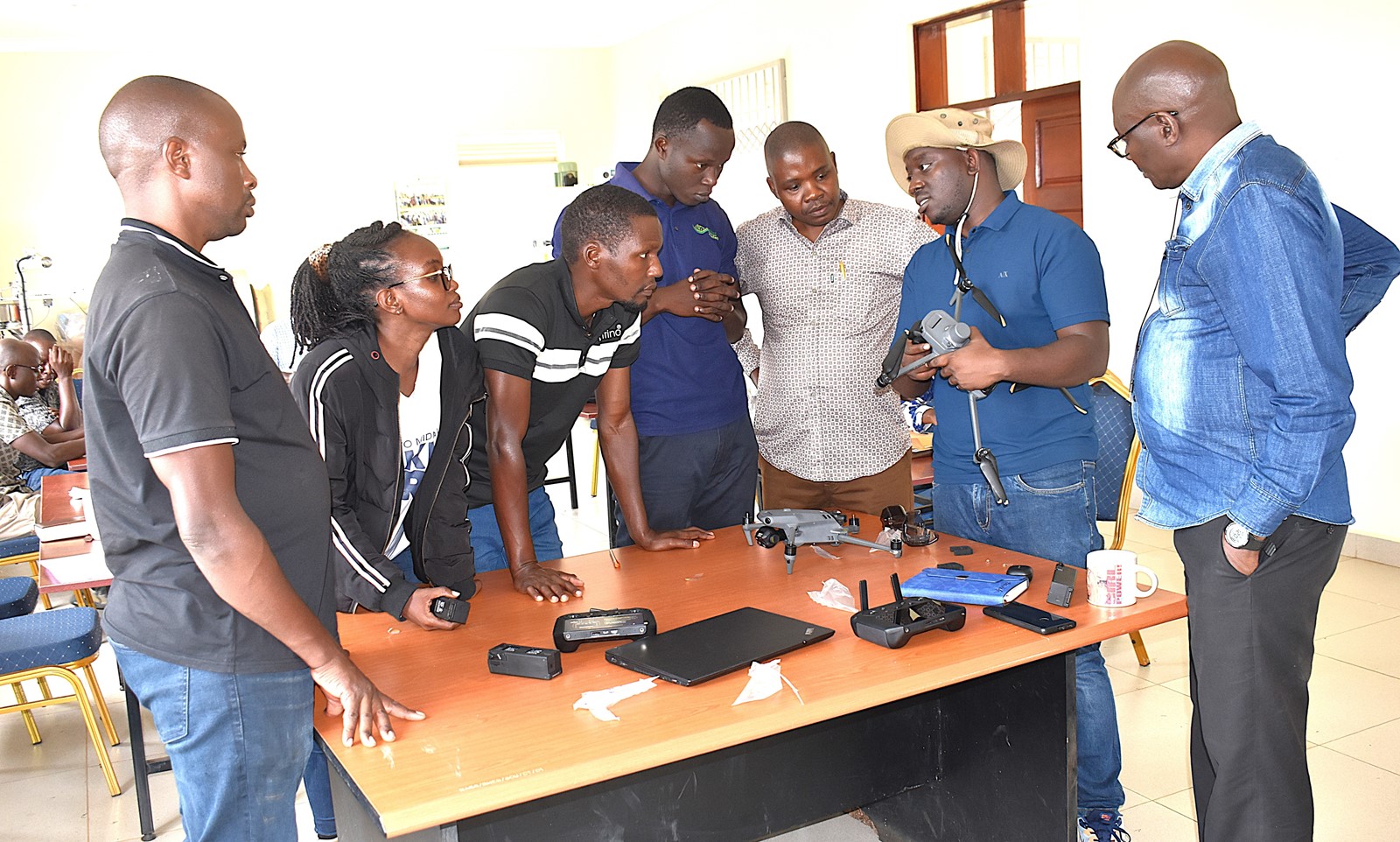
****Funded by the Danish Fellowship Centre under Denmark’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs, NbS4Tea is a five-year initiative aimed at enhancing climate resilience and tea productivity in Uganda.
Launch of drones for data collection
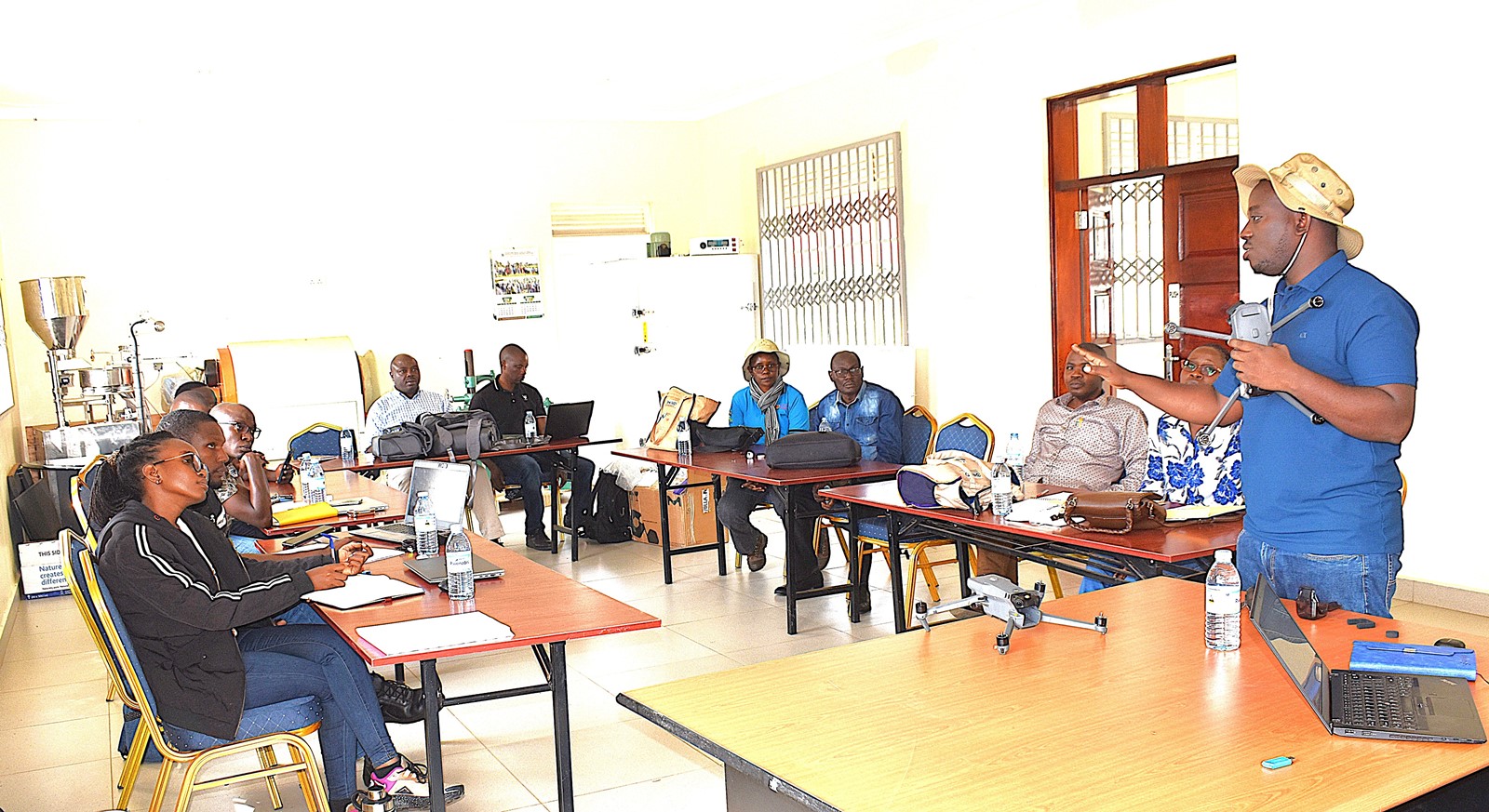
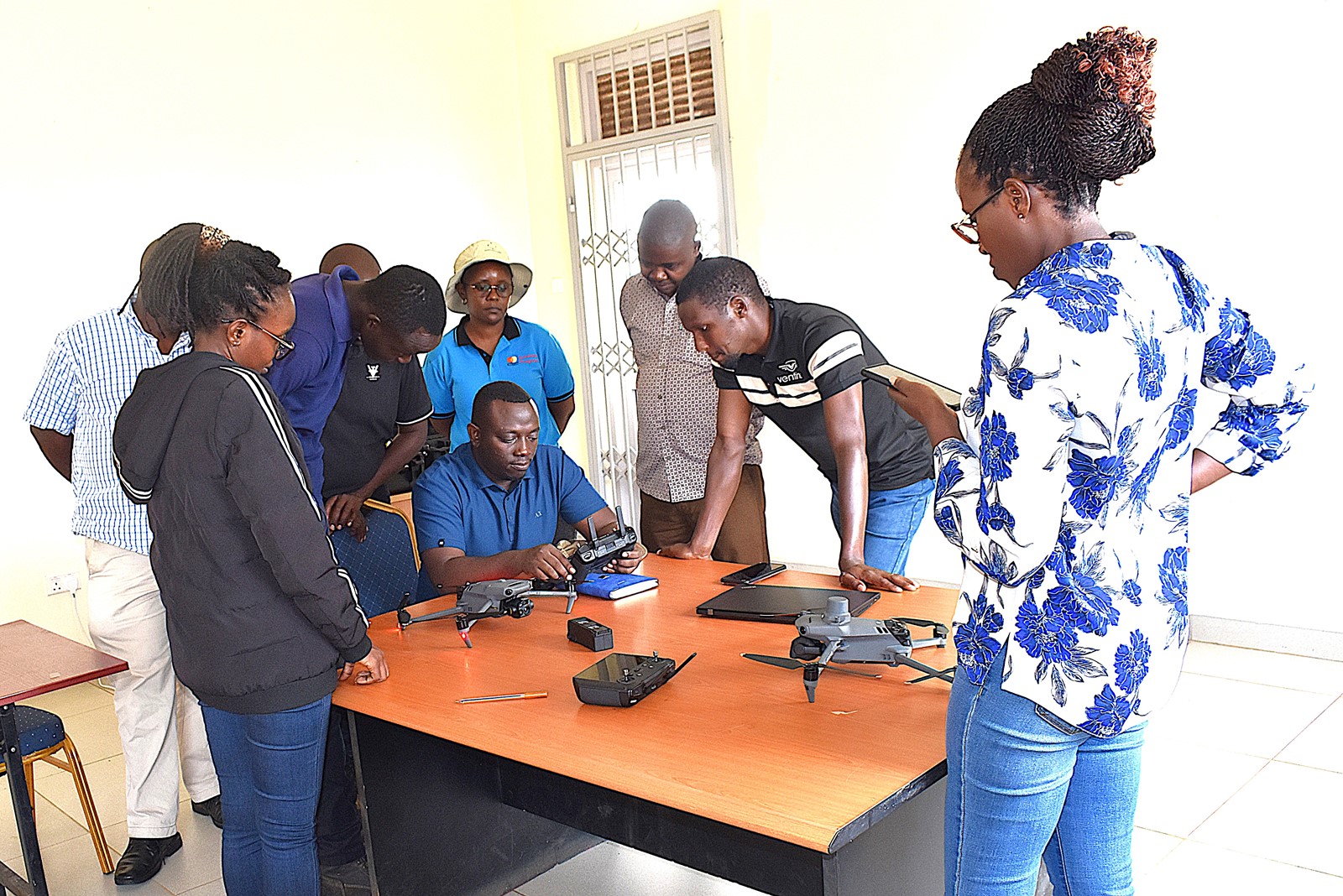
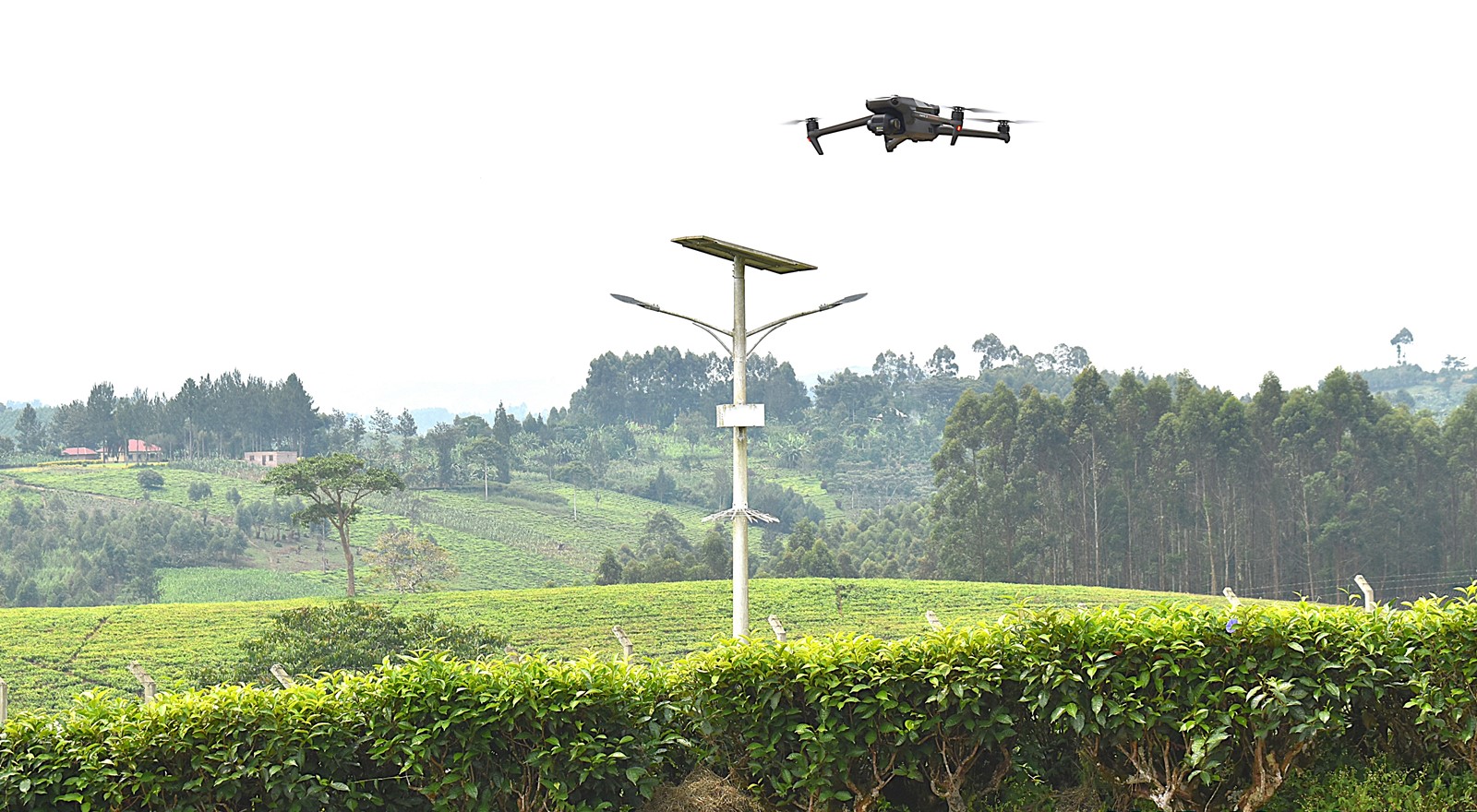
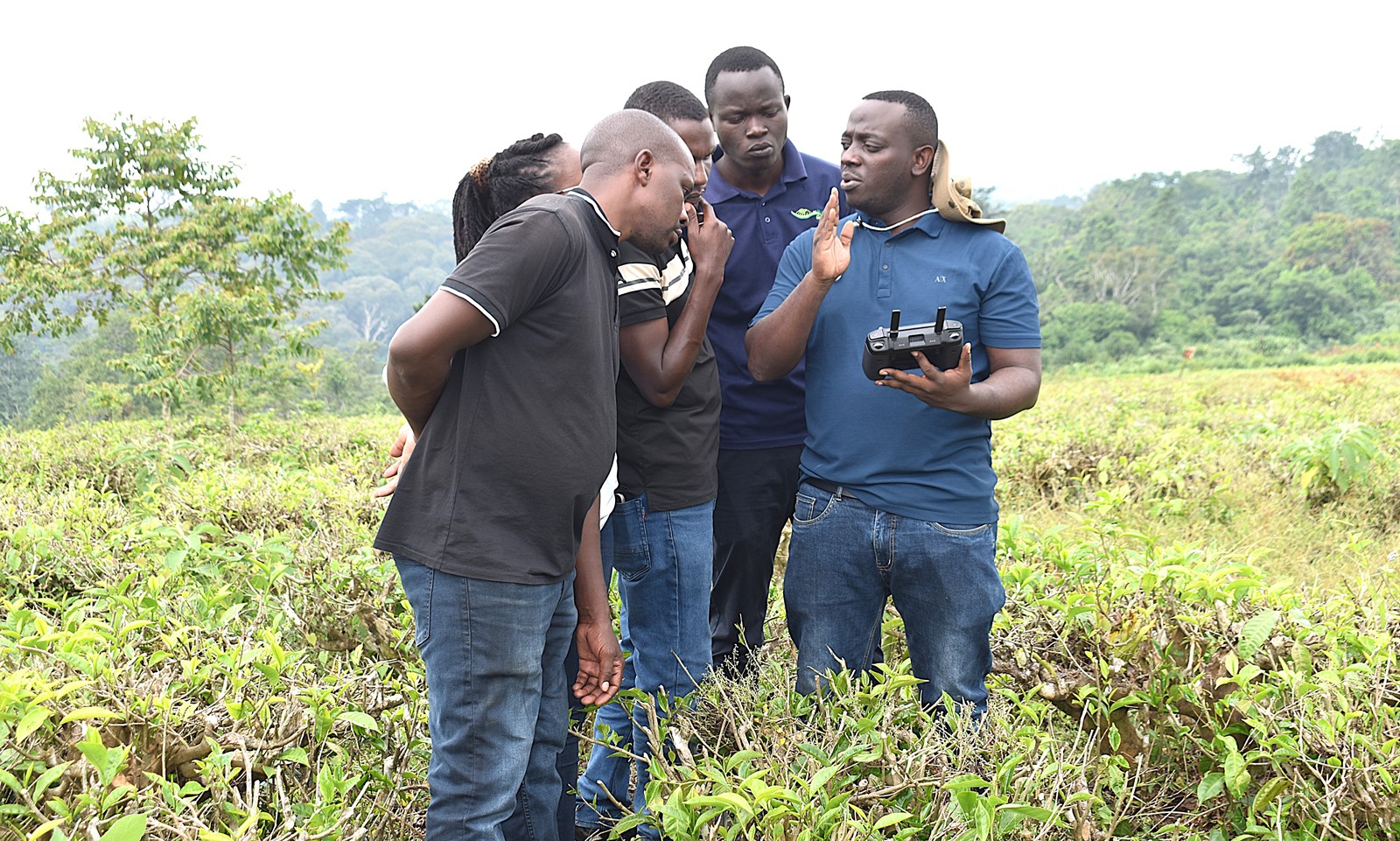
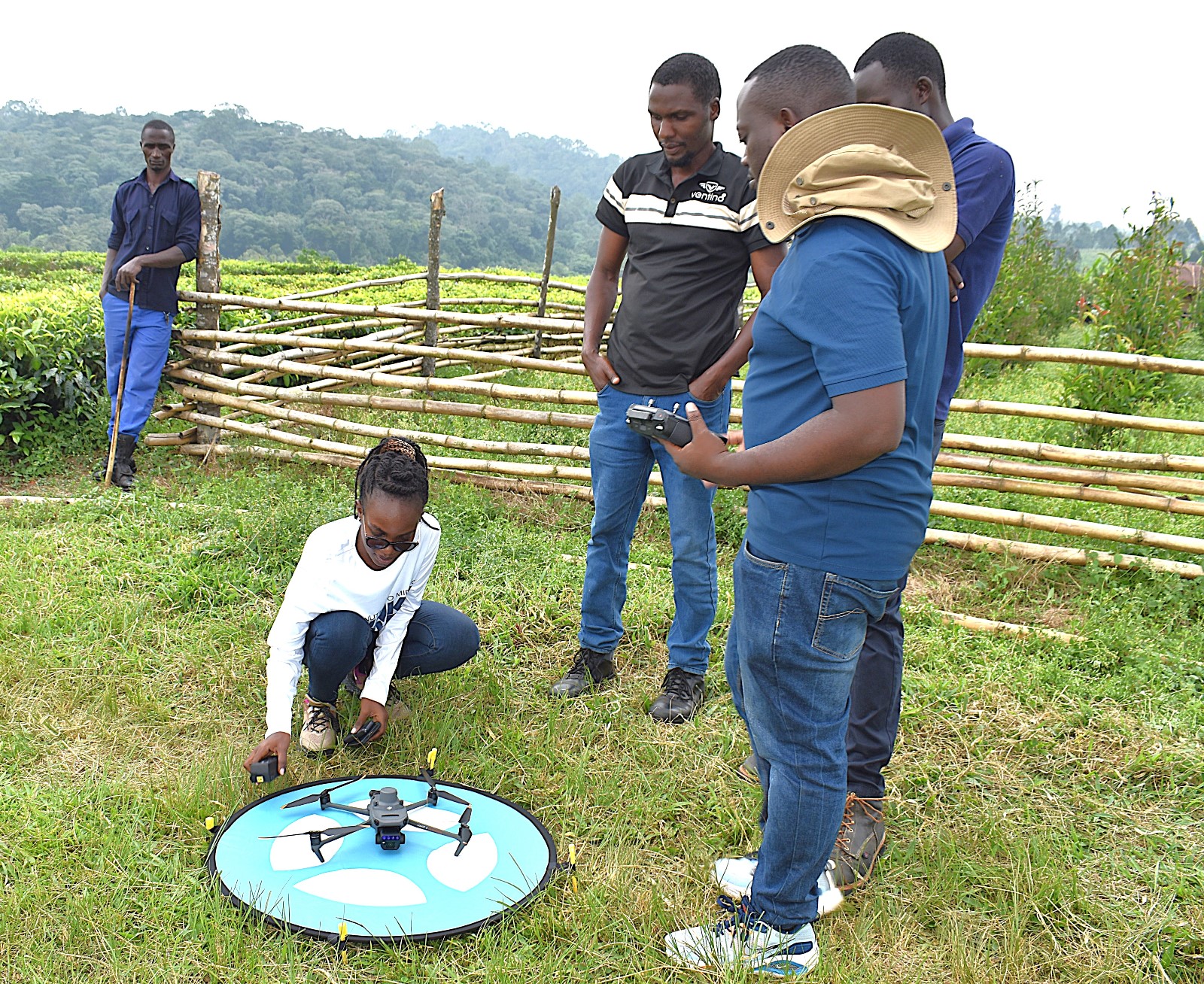
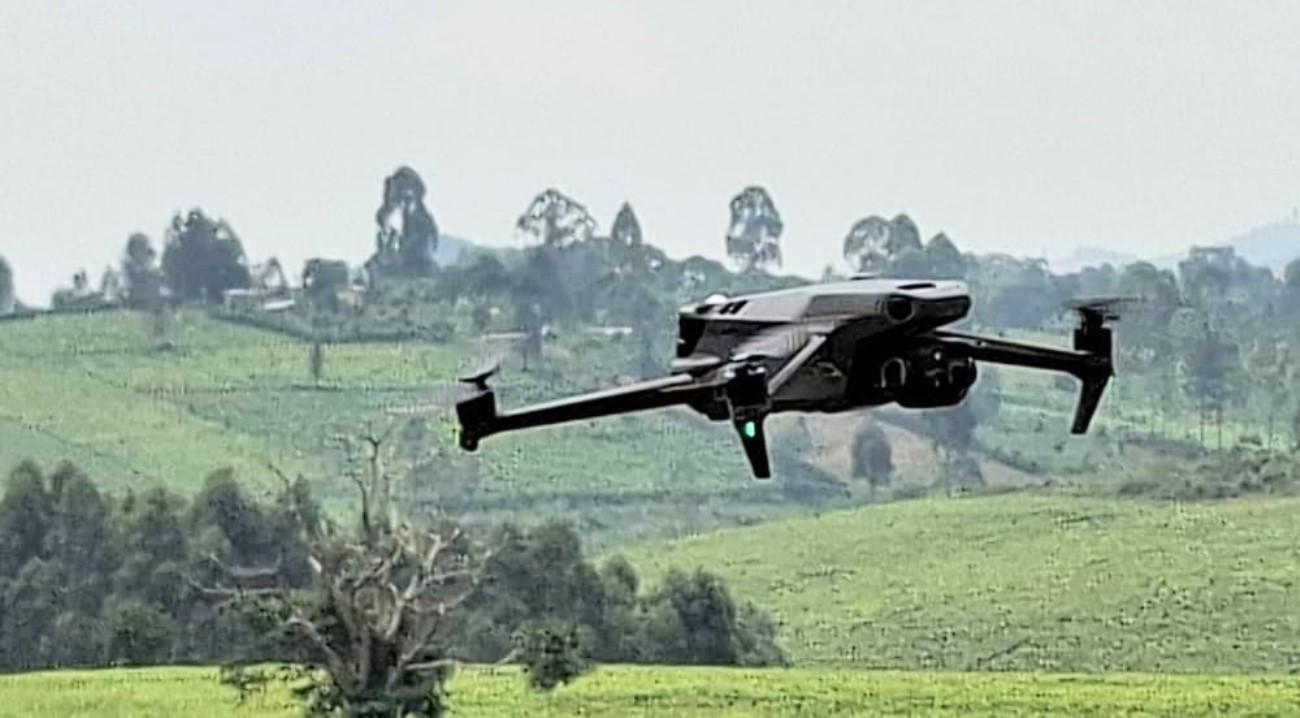
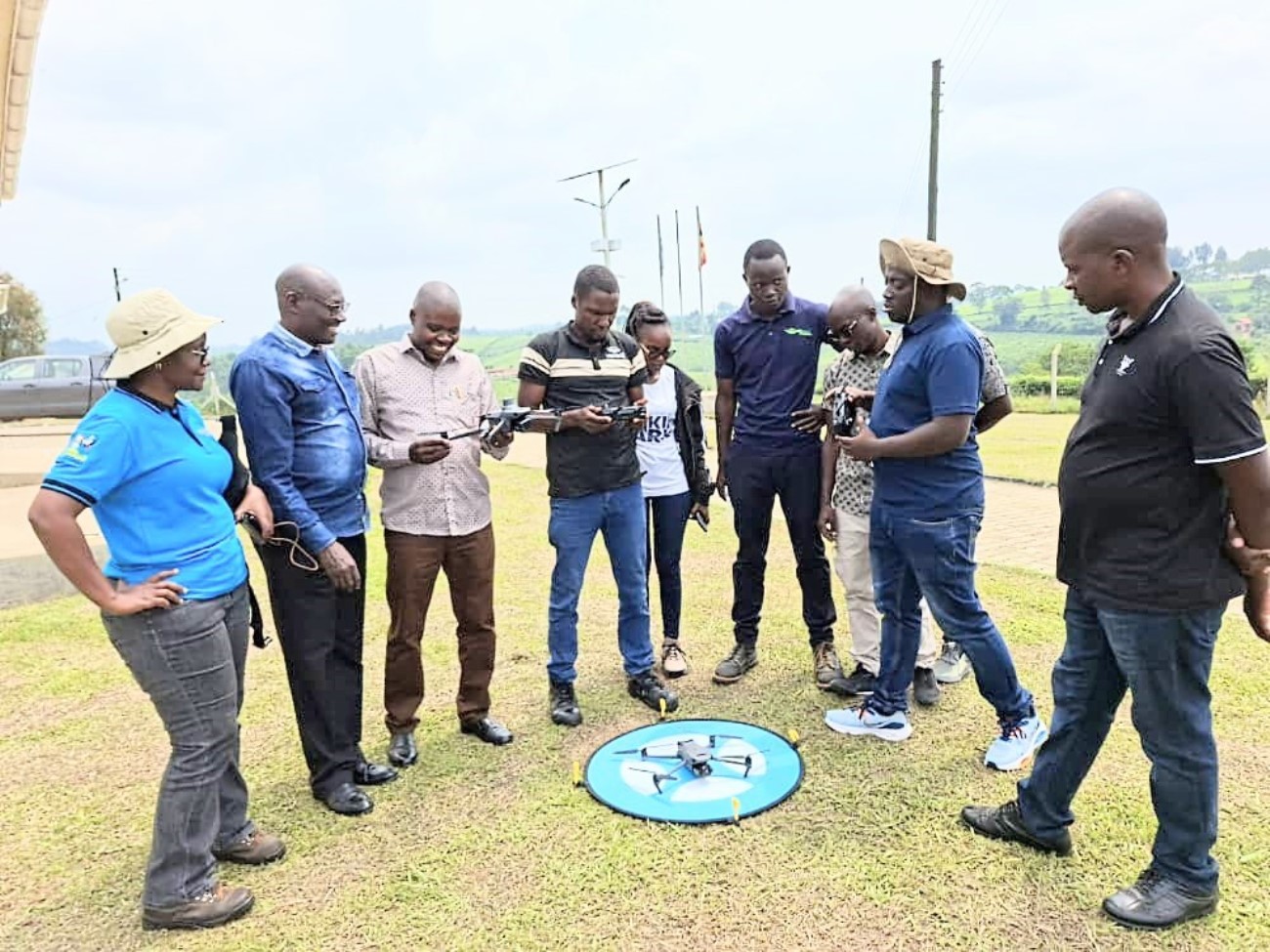
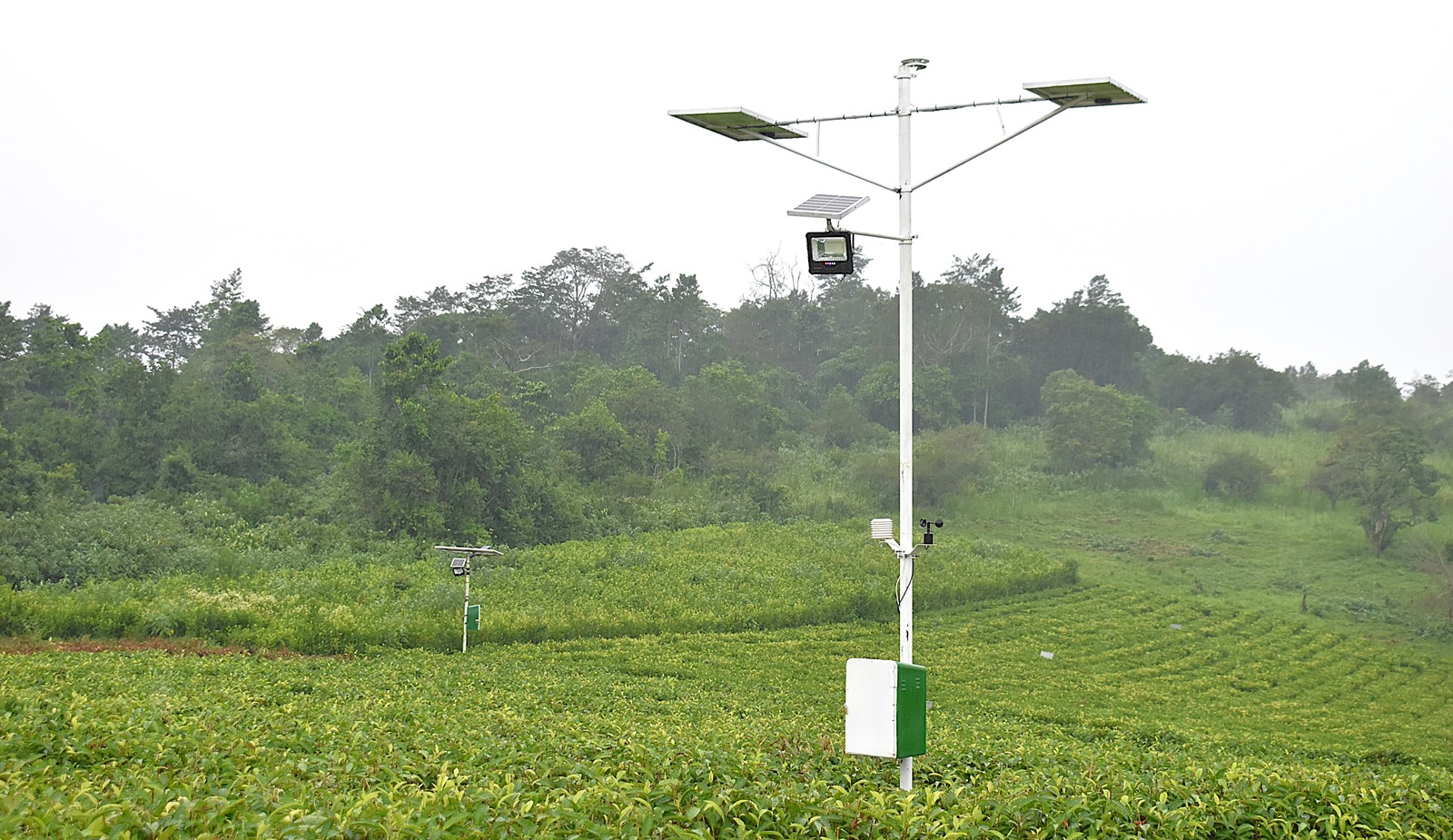
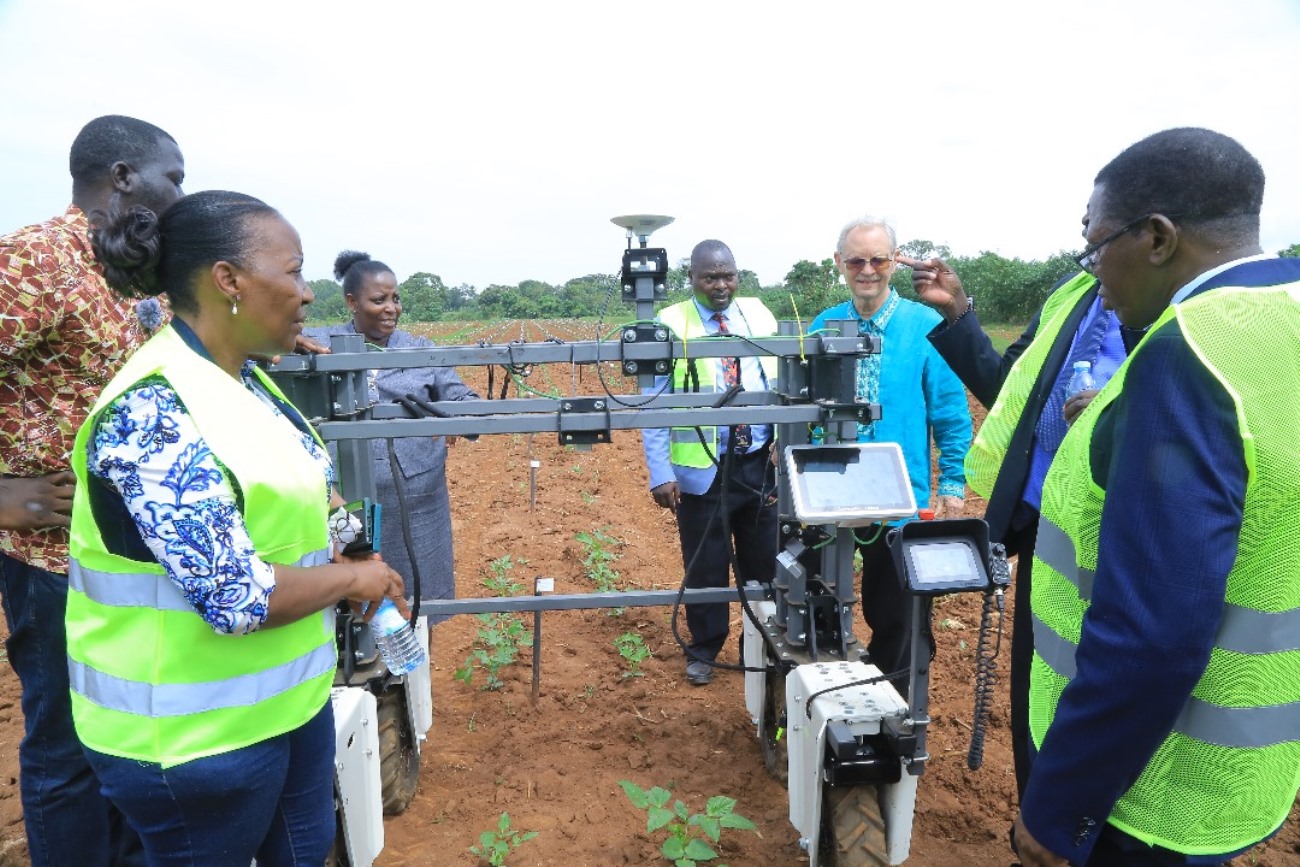
The Nature-based Solutions for Tea (NbS4Tea) project has registered a significant milestone with the successful deployment of drones to improve environmental and agricultural data collection.
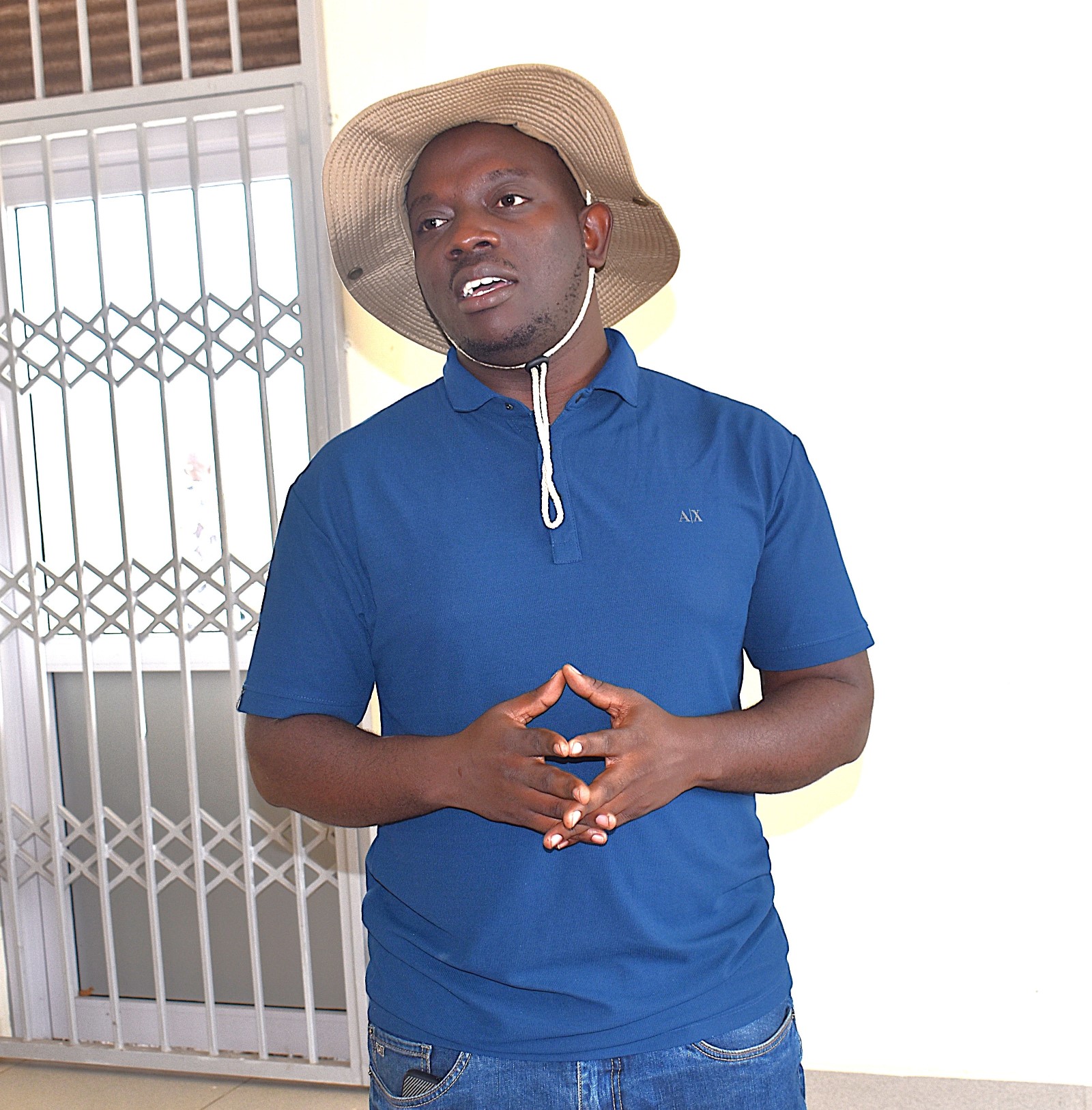
On 19th June 2025, the project team officially launched the drones at the Rwebitaba Tea Research Centre in Kyenjojo District, the project’s main research hub. The launch event included hands-on training sessions by Mr. Timothy Mutungi, a certified Remote Sensing Drone Pilot. Mr. Mutungi provided detailed instruction on drone operation, safety procedures, and data acquisition techniques specifically tailored to the project’s goals. The training was attended the core NbS4Tea researchers as well as students supported by the project.

By utilizing drone technology, the team will be able to capture high-resolution imagery and gather critical environmental data across vast tea-growing areas. This will enable more precise assessments of biodiversity, soil health, water use, and overall ecosystem services. The valuable insights generated will guide the development of sustainable, nature-based agricultural practices with the potential for widespread adoption throughout the tea industry.
About the NbS4Tea Project
NbS4Tea is a five-year initiative aimed at enhancing climate resilience and tea productivity in Uganda. Funded by the Danish Fellowship Centre under Denmark’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs and led by Dr Emmanuel Arthur from Aarhus University, the project is being implemented through a consortium of Ugandan and Danish institutions namely: Makerere University, the National Agricultural Research Organization (NARO), Uganda, Uganda Tea Association, Aarhus University, Denmark, and Kick-start International.

The primary objective of the project is to sustainably close the tea yield gap in Uganda by developing research-driven, nature-based solutions that enhance the climate resilience of tea production systems. This involves identifying climate-resilient tea varieties, integrating tea prunings and banana by-products, utilizing nitrogen-fixing agroforestry trees, and improving irrigation management. The approach emphasizes socio-economic feasibility, capacity building in research, and a market-oriented, multi-stakeholder collaboration to ensure both environmental and economic sustainability.
At Makerere University, the project is coordinated by Dr Alex Nimusiima from the Department of Geography, Geo-Informatics and Climatic Sciences at CAES. Other Project members are; Dr Grace Nakabonge from the Department of Forestry, Biodiversity and Tourism; Dr Prossy Nakawuka from the Department of Agricultural and Bio-systems Engineering; Dr Twaha Ali Basamba from the Department of Agricultural Production; and Dr Alice Turinawe from the Department of Agribusiness and Natural Resource Economics.

Specific objectives
- Identify and quantify climate change impacts on tea yield and quality based on historical and newly obtained data and novel data mining methods.
- Screen, select and recommend tea varieties adapted to abiotic (drought and heat) and biotic stresses (diseases and pests).
- Develop new knowledge on the potential of local waste biomass (tea prunings, banana pseudostems and peels) as soil amendments- mulch, compost, biochar, to recycle nutrients, improve soil fertility, increase carbon sequestration and alleviate drought.
- Reveal NbS through agroforestry combined with organic mulch, irrigation and resilient tea varieties that increase biodiversity and tea yield.
- Innovate new methods to enhance tea production under climate change through rainwater harvest and climate-smart irrigation infrastructure.
- Empower vulnerable groups (women, youth, and people with disabilities) in tea production and processing to ensure multi-actor involvement and socio-economic benefit outreach of the proposed NbS in tea cultivation and production.
- Identify export market strategies for NbS tea products, aligned with consumer preferences.

Progress thus far
Launched in January 2024, the project, organized in five work packages, has registered significant progress. Each of the work packages listed below supports one PhD student and one Masters’ student. The PhD students are: i) Mr. Adiga Hassan from the Department of Geography, Geo-Informatics and Climatic Sciences at CAES conducting research under work package 1; ii) Ms. Sarah Namayengo from the Department of Forestry, Biodiversity and Tourism conducting research under work package 2; Ms. Vivian Namutebi from the Department of Soil Science and Land Use Management undertaking research on work package 3; Mr. Keneth Chelimo from the Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering conducting his research under work package 4; and Ms. Moreen Asasira from the Department of Agribusiness and Natural Resource Economics focusing on work package 5. The Masters students are: i) Ms. Evelyn Katasi from the Department of Environmental Management at CAES (work package 1), Mr. Vereriano Turyahebwa from Department of Forestry, Biodiversity and Tourism (work package 2); Mr. Ben Okurut from the Department of Soil Science and Land Use Management (work package 3); Mr. Augustine Okot from the Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (work package 4); and Mr. Augustine Kigozi from the Department of Agribusiness and Natural Resource Economics (work package 5)

Work packages and achievements registered
Work Package 1: Climate change impacts on tea yield and quality – Headed by Dr. Alex Nimusiima
This work package centres on the analysis of historical and projected climate conditions in the study area. It examines how current climate patterns influence tea production, as well as the potential effects of future climate change on tea yield and quality.
Progress
i) A household survey assessing the socio-economic status of tea farmers and the effects of climate variability on their livelihoods has been completed.
ii) The collected data has been cleaned, and the Masters student supported under this work package is currently writing her thesis based on the survey findings.
iii) A historical climate analysis of the study area has been conducted by the PhD student, who is now preparing a manuscript.

Work Package 2: Screening & selecting tea genotypes for resilience to abiotic and biotic stresses – Headed by Assoc. Prof. Grace Nakabonge
This work package focuses on evaluating existing tea genotypes for their resistance to pests and diseases, using chlorophyll fluorescence imaging as a diagnostic tool.
Progress
i) A screen house has been constructed to serve as the experimental site.
ii) Germplasm from two tea varieties is currently being cultivated in the screen house in preparation for the upcoming experiments.
iii) A drone has been acquired to assist in data collection for this work package.

Work Package 3: Evaluation of NbS for climate resilience, higher yield and biodiversity- Headed by Assoc. Prof. Twaha Ali Basamba
This focuses on the characterization of mulch and biochar derived from tea prunings to improve soil health. It also aims to quantify the added value of Nature-based Solutions (NbS) in enhancing tea productivity, promoting climate resilience, and supporting biodiversity.
Progress
- So far, Biochar has been produced from tea prunings and characterized.
- The Masters student supported under this work package is writing his thesis on the results of biochar characterization.

Work Package 4: Innovating smart and scalable irrigation technology for improved tea production- Headed by Dr. Prossie Nakawuka
This work package aims to develop and evaluate smart, scalable irrigation solutions to boost tea production. It focuses on assessing how irrigation impacts tea yield and quality, measuring water use efficiency, and analyzing the economic returns of irrigation practices. Additionally, it explores deficit irrigation and climate-resilient strategies to ensure sustainable tea farming in changing environmental conditions.
Progress
- The irrigation infrastructure is now in place and fully operational at Rwebitaba Tea Research Centre in Kyenjojo District.
- The experimental plots for irrigation experiments are already in place with water pipes.

Work package 5: Socio-economic assessment of tea-agroforestry and selected tea varieties – Headed by Dr. Alice Turinawe
This work package emphasizes co-creation within multi-stakeholder innovation networks to evaluate the economic feasibility and market access of tea agroforestry systems. It also focuses on promoting gender balance and understanding consumer valuation of Nature-based Solutions (NbS) tea from Uganda.
Progress
To date, two co-creation workshops have been successfully conducted and the Masters student under this work package is currently analyzing the workshop results as part of their research.

Expected outputs and outcomes
- Increased tea production, productivity, and biodiversity through the adoption of NbS.
- Increased research and technical capacity of Makerere and R-ZARDI.
- Holistic stakeholder insight on economic feasibility, consumer acceptance and market access strategies, especially for vulnerable groups in the tea value chain.
- Increased job prospects for youth and women in tea production sub-sectors.
- Improved social status and increased incomes of tea farmers, traders, and exporters.
- Improved economic and environmental quality by recycling biomass waste into value-added products dedicated to soil enhancement.
- 4+ high-yielding tea genotypes adapted to drought and heat, diseases and pests.
- 15+ scientific articles, conference presentations.
- Five PhDs and Five MSc degrees.
- Market access assessment and empowerment.

Details on the project: https://news.mak.ac.ug/2024/01/new-caes-project-to-improve-tea-production-in-uganda/
More photos from the event



Agriculture & Environment
New Mak-CAES Project to Spur Green Growth in East Africa
Published
3 weeks agoon
June 13, 2025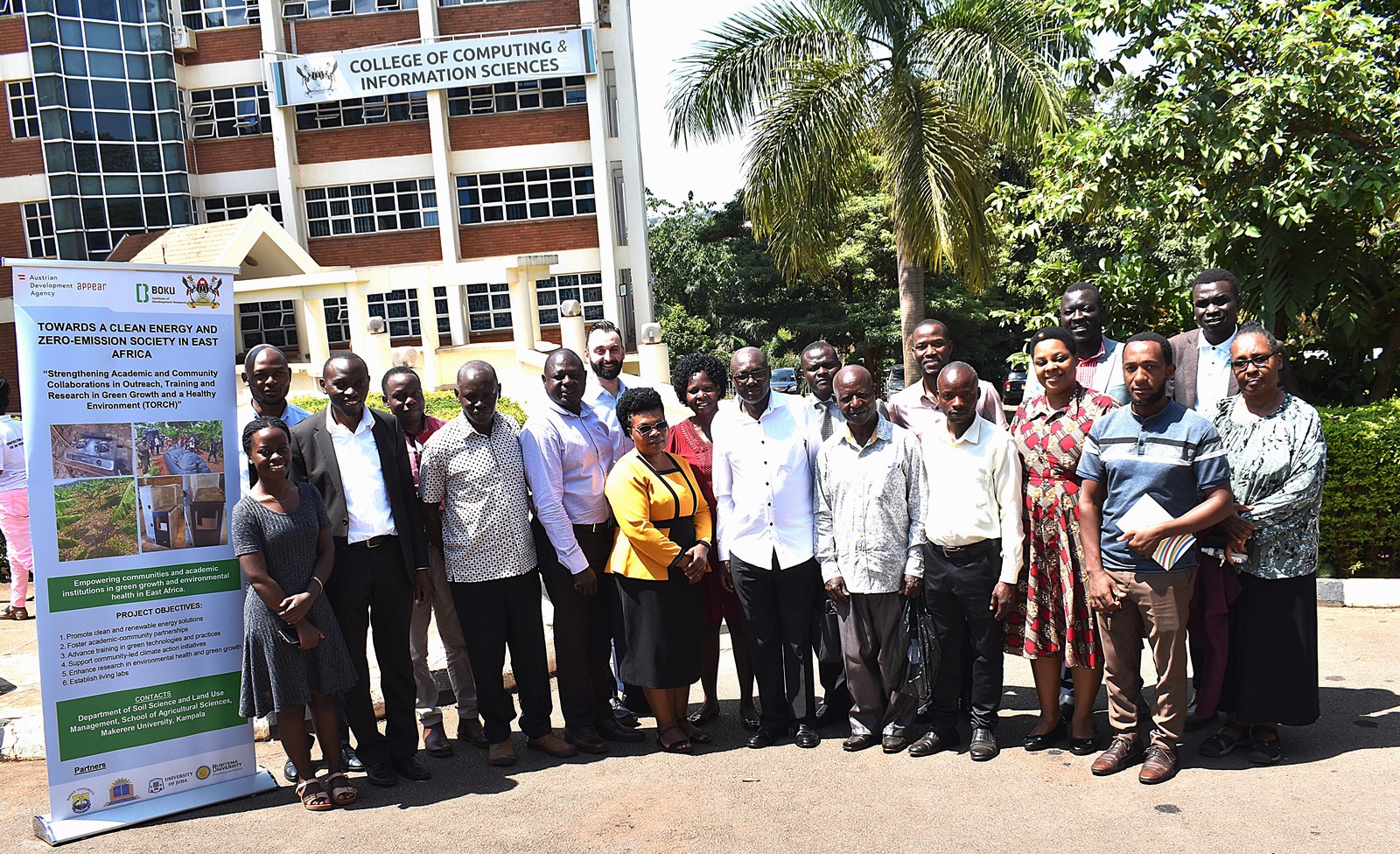
Makerere University, through its Department of Soil Science and Land Use Management at the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES), has launched a new project aimed at fostering green growth and promoting sustainable development across East Africa. This initiative aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and create eco-friendly, low-carbon communities through collaborative research, education, and technology.

Introducing the TORCH Project: Towards a Clean Energy and Zero-Emission Society
The two-year project, code-named TORCH (Towards a Clean Energy and Zero-emission Society in East Africa), seeks to strengthen cooperation between academia and local communities to promote green growth and environmental sustainability. Funded by the OeAD-GmbH under the Austrian Partnership Programme in Higher Education Research for Development (APPEAR), TORCH focuses on clean energy solutions, carbon emission reduction, and community empowerment through training, research, and co-creation of green technologies.

Officially launched by the Principal of CAES, represented by Dr. Paul Mukwaya, Head of the Department of Geography, Geo-Informatics and Climatic Sciences at Makerere University, TORCH builds upon existing East African government policies. The project will implement the innovative concept of living labs, where universities, communities, and stakeholders co-design, co-create, and co-produce affordable, reliable green technologies tailored to local needs.

Key Objectives and Activities
TORCH aims to:
- Enhance teaching on green growth by integrating principles into selected academic curricula.
- Establish three living laboratories in Central, South Western, and Eastern Uganda to boost co-creation on energy efficiency and low-carbon emissions.
- Increase human capacity through short courses, field research, and training.
- Empower women in science and technology.
- Promote novel green technologies and support policy transformation.
- Strengthen partnerships among universities in East Africa.
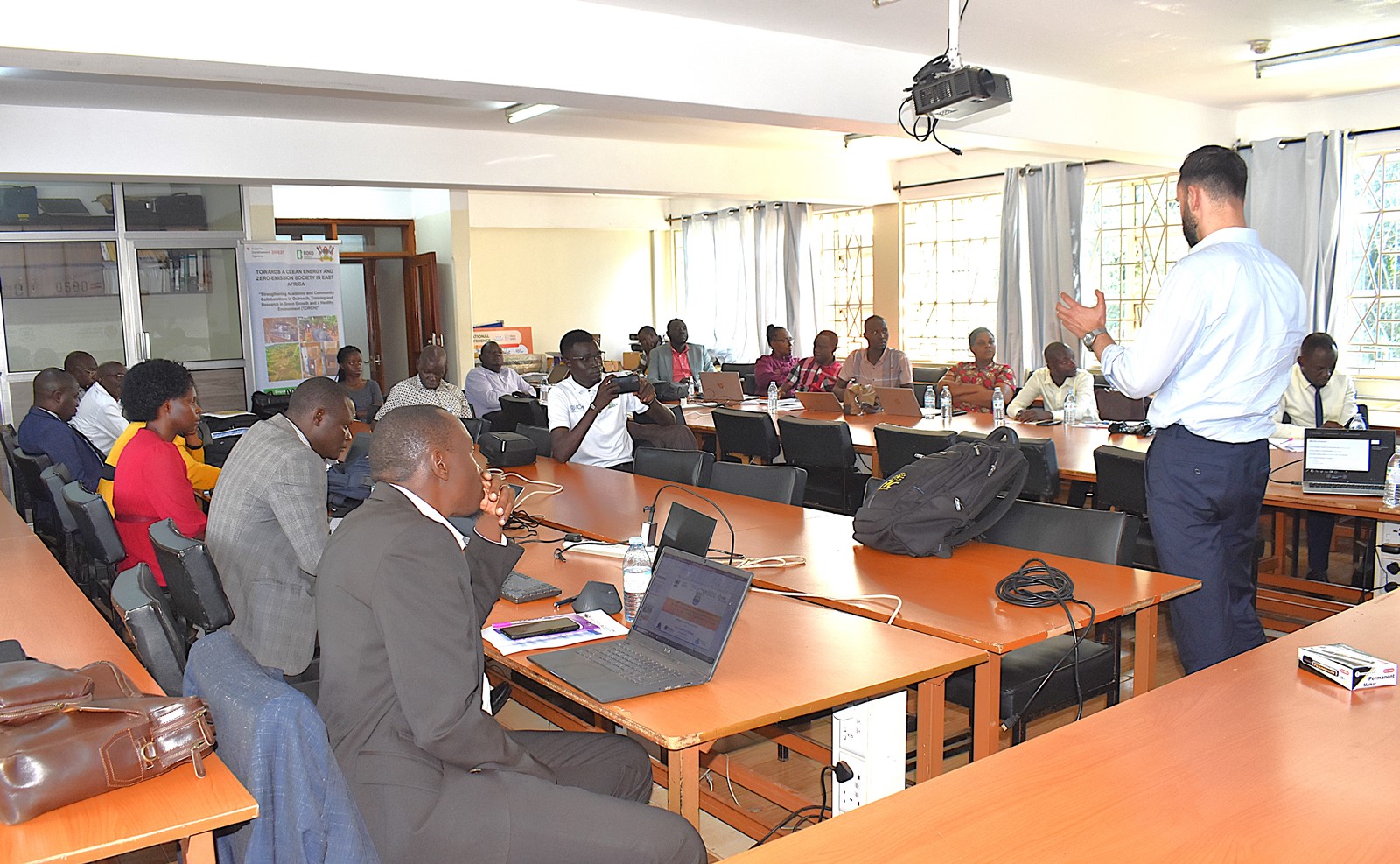

These activities directly contribute to achieving several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including SDGs 4 (Quality Education), 5 (Gender Equality), 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and 13 (Climate Action), while also reducing health risks and conserving the environment.

Leadership and Partner Institutions
The overall project coordinator is Dr. Patrick Musinguzi, Lecturer in the Department of Soil Science and Land Use Management at Makerere University. TORCH involves several partner institutions, including: Makerere University (Uganda), University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna (Austria), Kabale University (Uganda), Busitema University (Uganda), Kyambogo University (Uganda), and the University of Juba (South Sudan).

Highlights of the Launch Ceremony
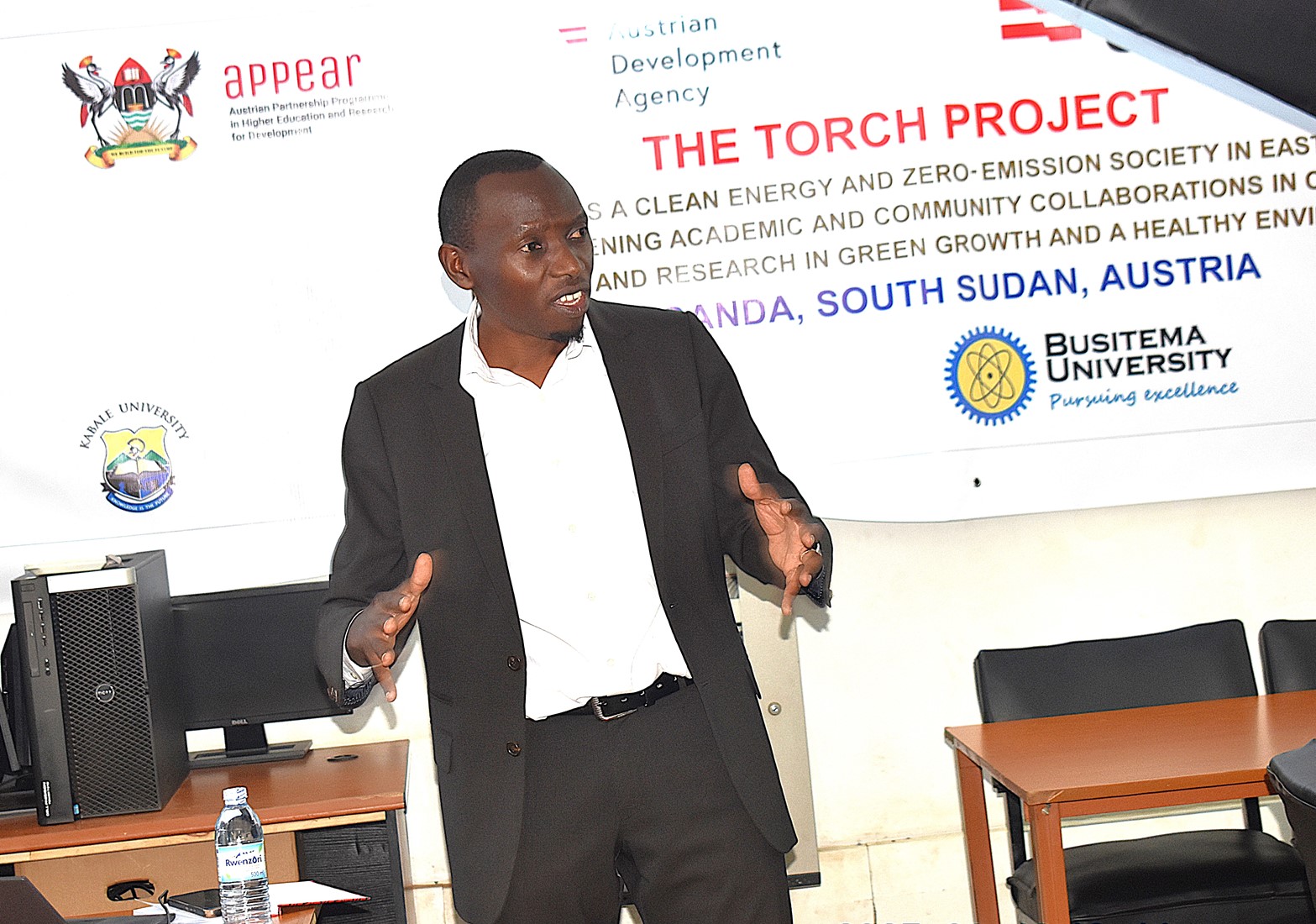
During the launch ceremony held in the GIS Lab at Makerere University, and attended by representatives from the partner institutions, Dr. Musinguzi presented an overview of TORCH, outlining key strategies for implementation and expected outcomes. Central to the project’s strategy is the integration of green growth principles into Makerere University’s academic curriculum. This will be formally proposed to the University Management for adoption. Additionally, the project aims to strengthen the university’s research agenda in this critical area. This will involve supporting faculty and student-led research projects and generation of evidence-based insights on green growth to influence policy at both local and national levels. There are also plans to establish three living labs in Central, South Western, and Eastern Uganda to serve as practical hubs for advancing green growth.

Expert Insights on Community Engagement
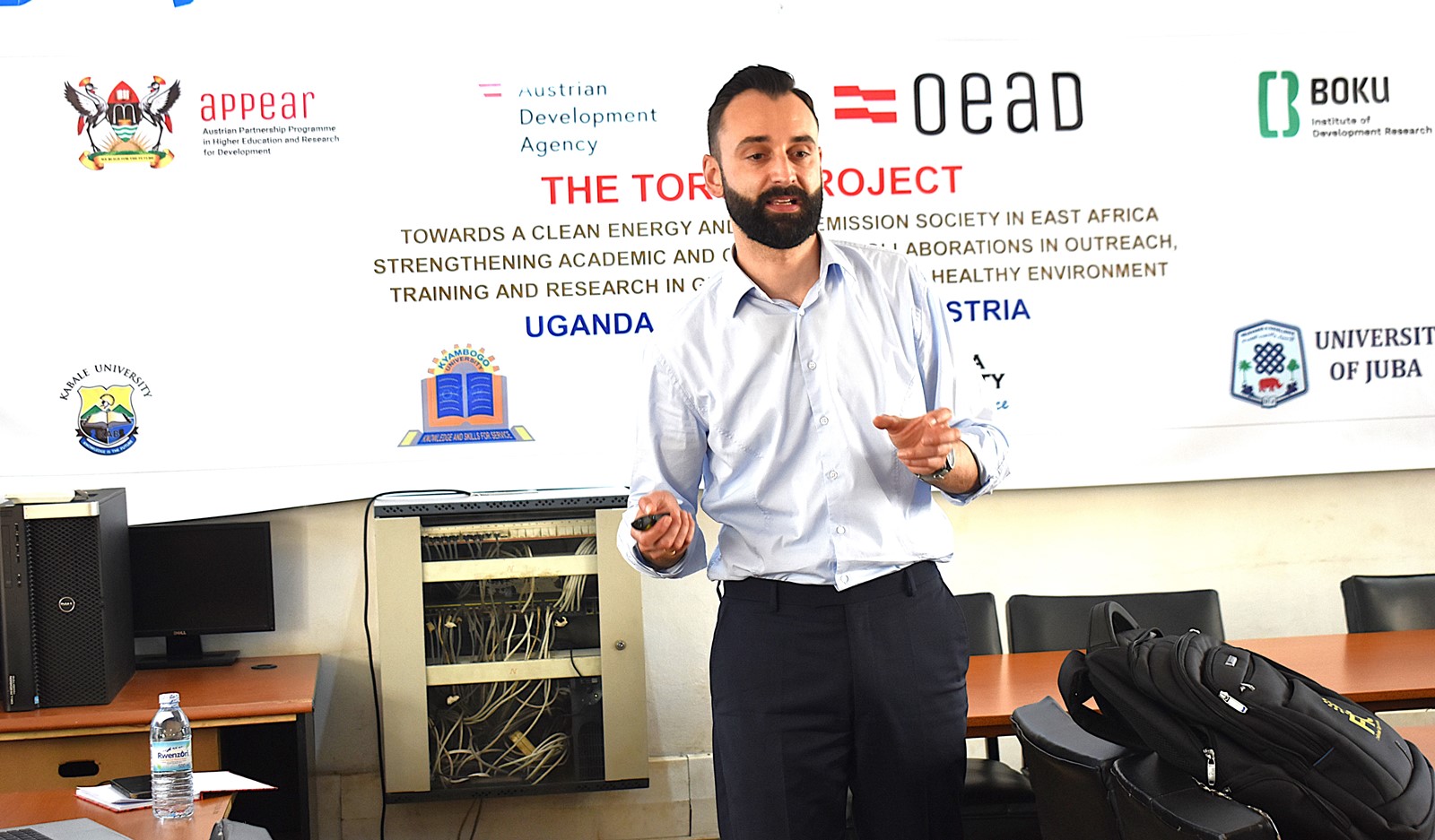
In his presentation, Mr. Andreas Bauer from the University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna provided valuable insights into the critical role that living labs play in promoting sustainable, green growth. Highlighting practical examples and innovative approaches, Mr. Andreas Bauer emphasized how living labs serve as dynamic platforms for collaboration between researchers, industry stakeholders, and local communities, enabling real-world experimentation and the development of eco-friendly solutions that drive environmental and economic progress.

To emphasize the importance of collaboration between local communities and the academia, Mr. Kayanja Susane, a farmer from Kawumu Village in Luweero District, explained that, with guidance and support from the project team, he learned to produce biogas from animal waste -a reliable source of energy that reduces dependence on traditional fuels, subsequently minimizing environmental degradation.

Research Focus
As part of the strategy to guide implementation, the project team brainstormed potential ecological and social indicators of low emissions in homesteads, and proposed several research areas to support green growth. Proposed research areas include:
- Life cycle analysis
- Circular economy practices within homesteads
- Gender integration and the intersection of gender with green growth
- The role of livestock in promoting green growth
- Evaluating the impact of interventions on total emissions
- Barriers to adopting green innovations
- The use of indigenous knowledge in promoting green growth
Addressing the participants, the Principal of the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES), represented by Dr. Paul Mukwaya, Head of the Department of Geography, Geo-Informatics, and Climatic Sciences at Makerere University, commended the project as a timely initiative aligned with the University’s research agenda. He underscored the importance of collaborating with other stakeholders, noting that similar projects have been conducted within and outside Makerere. Dr. Mukwaya called for the adoption of the theory of change framework to ensure the project delivers measurable, sustainable impacts that extend beyond policy briefs and gender mainstreaming, ultimately contributing to lasting green transformation in the region. He expressed appreciation to the project funders for their unwavering support to Makerere University.

Refurbished gate to boost the institute’s aesthetics, security, accessibility, and sustainability
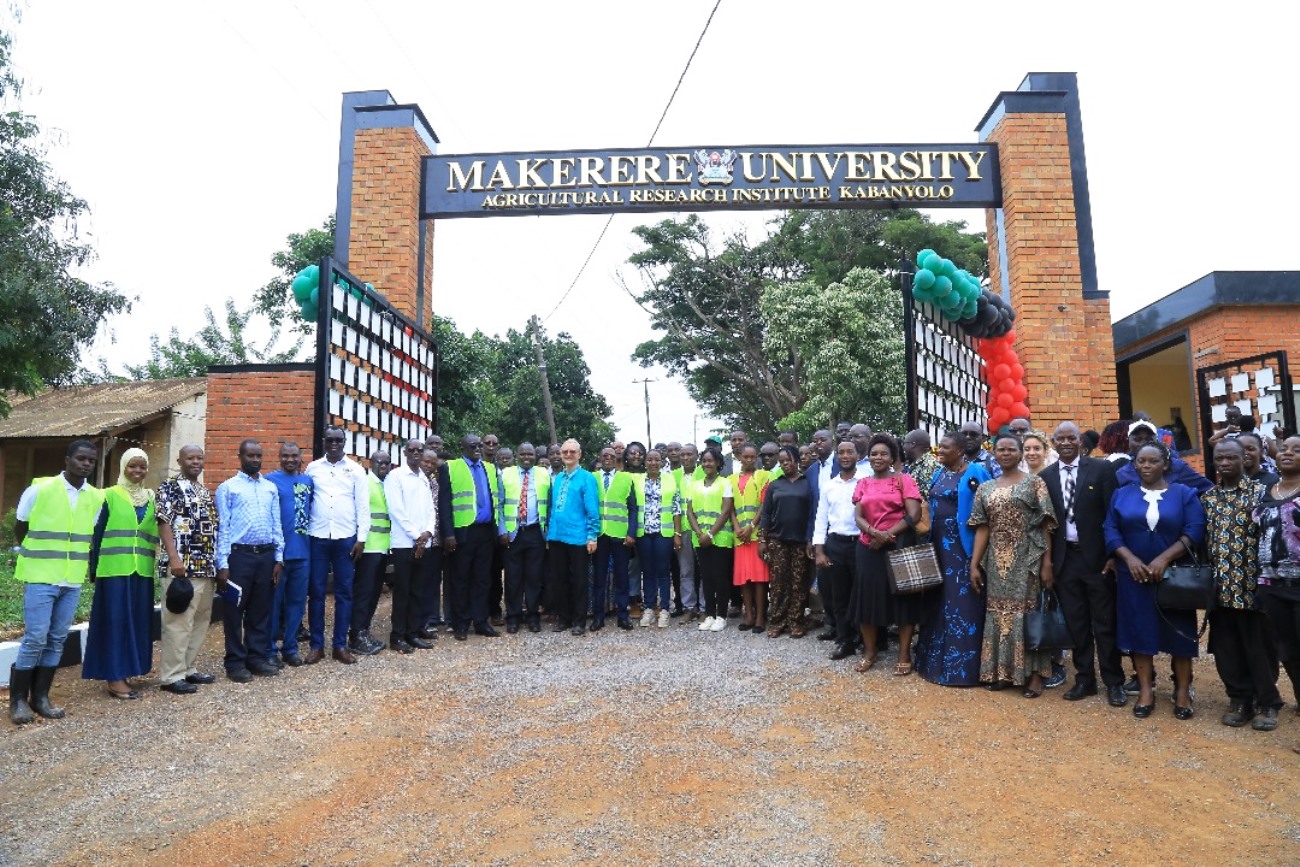
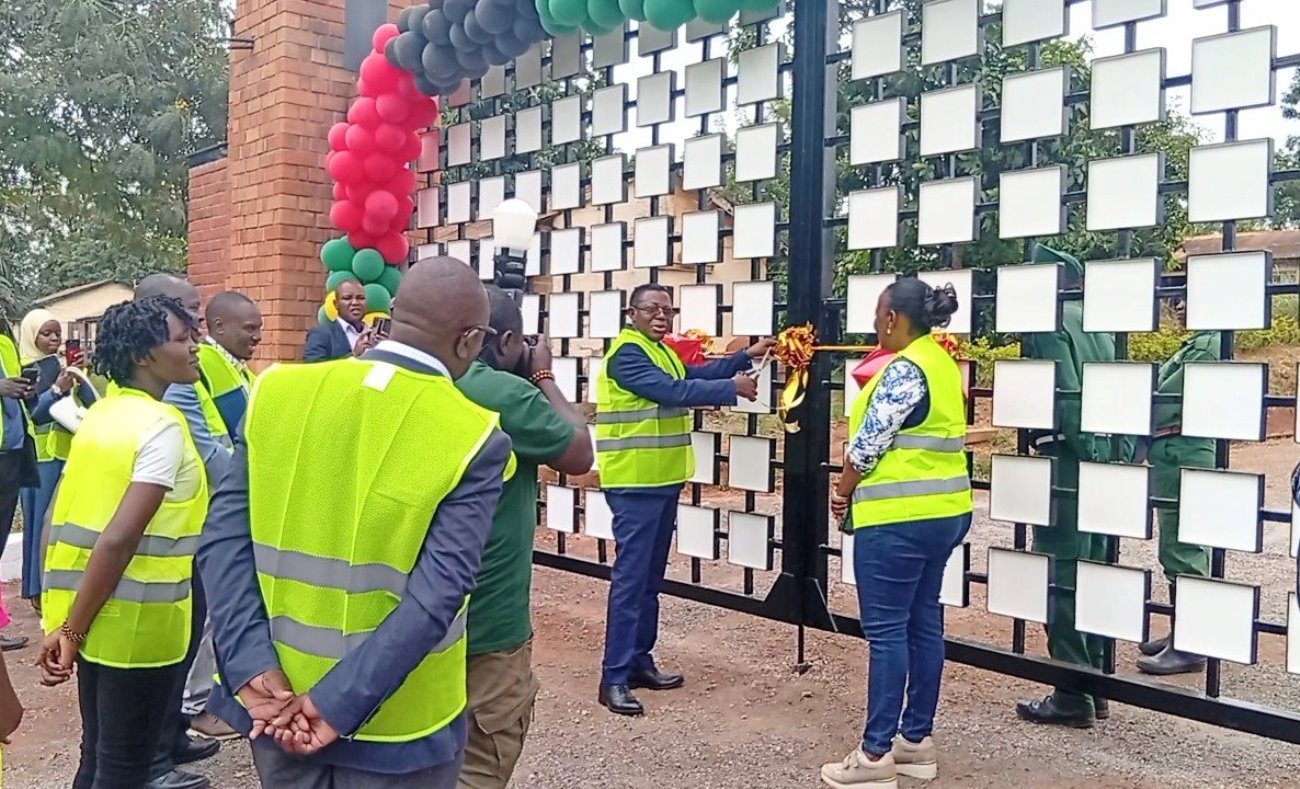
Makerere University College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES) has completed the refurbishment of the main gate at the Makerere University Agricultural Research Institute Kabanyolo (MUARIK). The renovation was carried out by students from both CAES and the College of Engineering, Design, Art, and Technology (CEDAT), under the supervision of their academic mentors.
According to the Principal of CAES, Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga, the revamped gate now truly reflects the spirit of Makerere University and will significantly enhance the institute’s visual appeal, security, accessibility, and sustainability. The refurbished gate was officially commissioned by the Vice Chancellor, represented by the First Deputy Vice Chancellor in charge of Academic Affairs, Prof. Buyinza Mukadasi. The ceremony was attended by the Deputy Vice Chancellor in charge of Finance and Administration, Prof. Winston Tumps Ireeta, alongside CAES staff, students, and partners.

About MUARIK
Established in 1953, MUARIK serves as a hub for numerous research projects and facilities within CAES. It houses centres such as the Makerere University Regional Centre for Crop Improvement (MaRCCI), the Makerere University Centre for Soybean Improvement and Development (MakCSID), the Continuing Agricultural Education Centre (CAEC), the Centre of Excellence in Waste Management, and the Consortium for Enhancing University Responsiveness to Agribusiness Development (CURAD).
Additionally, MUARIK hosts KOICA-funded projects, including a modern layers production unit and a climate-controlled greenhouse for vegetable production. These units operate independently but collectively contribute to MUARIK’s dynamic research environment.

MUARIK also houses research units for the School of Agricultural Sciences (SAS) such as the Biotechnology and Tissue Culture Laboratories, experimental fields, Horticulture and Livestock Units, and the black soldier fly project. It accommodates training and research facilities for the Schools of Food Technology, Nutrition, Bioengineering, and the School of Forestry, Environmental, and Geographical Sciences. It also hosts hostels for both local and international students who stay at the Institute to gain practical experience in production and research under typical farming conditions.
Enterprises and Research at MUARIK
Enterprises at MUARIK include approximately 100 acres of pastures, a dairy farm, feed mill, silage production, poultry unit, piggery unit, banana and coffee plantations, maize and soybean crops, horticulture, goat farming, and the recently revived rabbit unit featuring four breeds: New Zealand White, Chinchilla, California White, and Flemish Giant.

Current research initiatives focus on edible insects and worms as alternative livestock feeds, agroforestry, horticulture, and value addition in food processing. MUARIK maintains a strong partnership with the Uganda Flowers Exporters Association (UFEA), collaborating on the commercial testing of new flower species to diversify Uganda’s flower exports beyond traditional rose bouquets. Collaborative efforts also include identifying native natural enemies to control Chrysanthemum pests, working with UFEA, Wageningen University, breeders, and the National Agricultural Research Organization.
As part of Uganda’s National Agricultural Research System (NARS), MUARIK prioritizes research in biotechnology, tissue culture, plant breeding, improved farming methods, agro-processing, value addition, and marketing.

Tour to Assess the Capacity and Condition of Facilities at MUARIK
As part of the commissioning ceremony, the Principal of CAES, Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga, led visitors on a comprehensive tour of the Makerere University Agricultural Research Institute, Kabanyolo (MUARIK). The purpose of the tour was to provide first-hand insight into the institute’s current infrastructure, operational capacity, and ongoing challenges.
During the visit, Prof. Nabanoga highlighted both the strengths and limitations of the institute. While the tour showcased MUARIK’s potential as a hub for agricultural research and innovation, it also brought to light a number of critical issues affecting its functionality. Chief among these is the persistent challenge of land encroachment, which continues to threaten the integrity and sustainability of the institute’s operations.

In her remarks, Prof. Nabanoga commended Dr. Cyrus Ongom, the outgoing Director of MUARIK, for his unwavering dedication to safeguarding the institution’s land. She acknowledged his resolute efforts in the face of persistent threats and numerous challenges, emphasizing the vital role he played in preserving MUARIK’s integrity. “This year, we aim to further reposition MUARIK as a leading centre for agricultural innovation and production in the region,”said Prof. Nabanoga. “Our focus will be on strengthening research, fostering partnerships with stakeholders, and enhancing the capacity of our infrastructure to support sustainable and impactful agricultural practices.”
The Principal expressed gratitude to all who have supported the transformation journey of CAES. “As we celebrate our achievements today, we take this moment to recognize and honour everyone who has been part of our transformation journey,” the Principal said. “We are especially grateful to the Vice Chancellor, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe for his unwavering support, which has been instrumental in driving the College forward.”
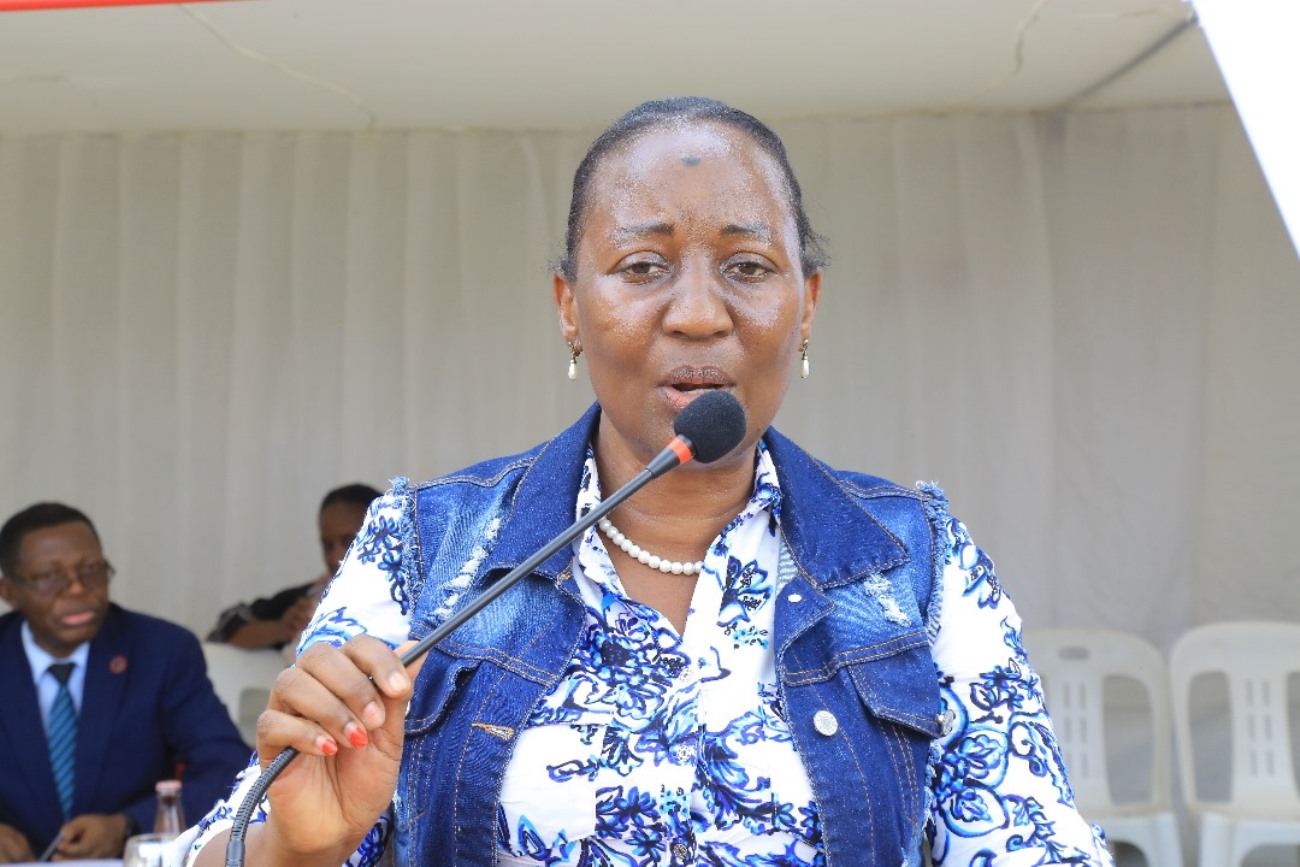

Delivering his remarks, the Deputy Vice Chancellor in charge of Academic Affairs (DVCAA), Prof. Buyinza Mukadasi, commended the CAES for its remarkable achievements in training and research.
“From my assessment, CAES has consistently excelled across its core mandates – training, research, production, and community outreach. The College has played a crucial role in advancing the agricultural sector through innovative research, high-quality academic programmes, and meaningful community engagement. These efforts have made a significant contribution to Uganda’s national development goals and the transformation of its agricultural landscape. Given its demonstrated success and strategic relevance, CAES is highly deserving of enhanced investment and funding to further expand its impact,” he stated.

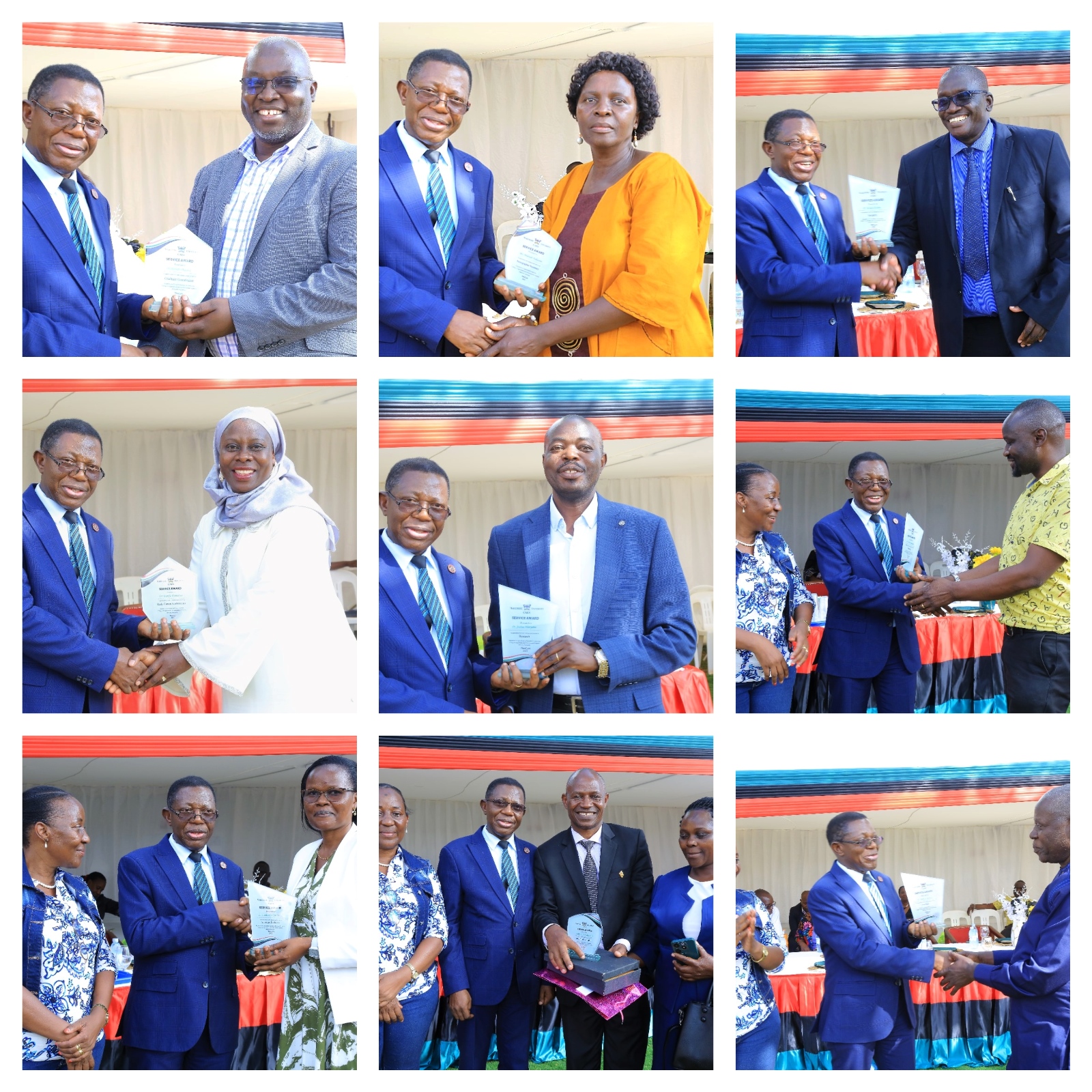
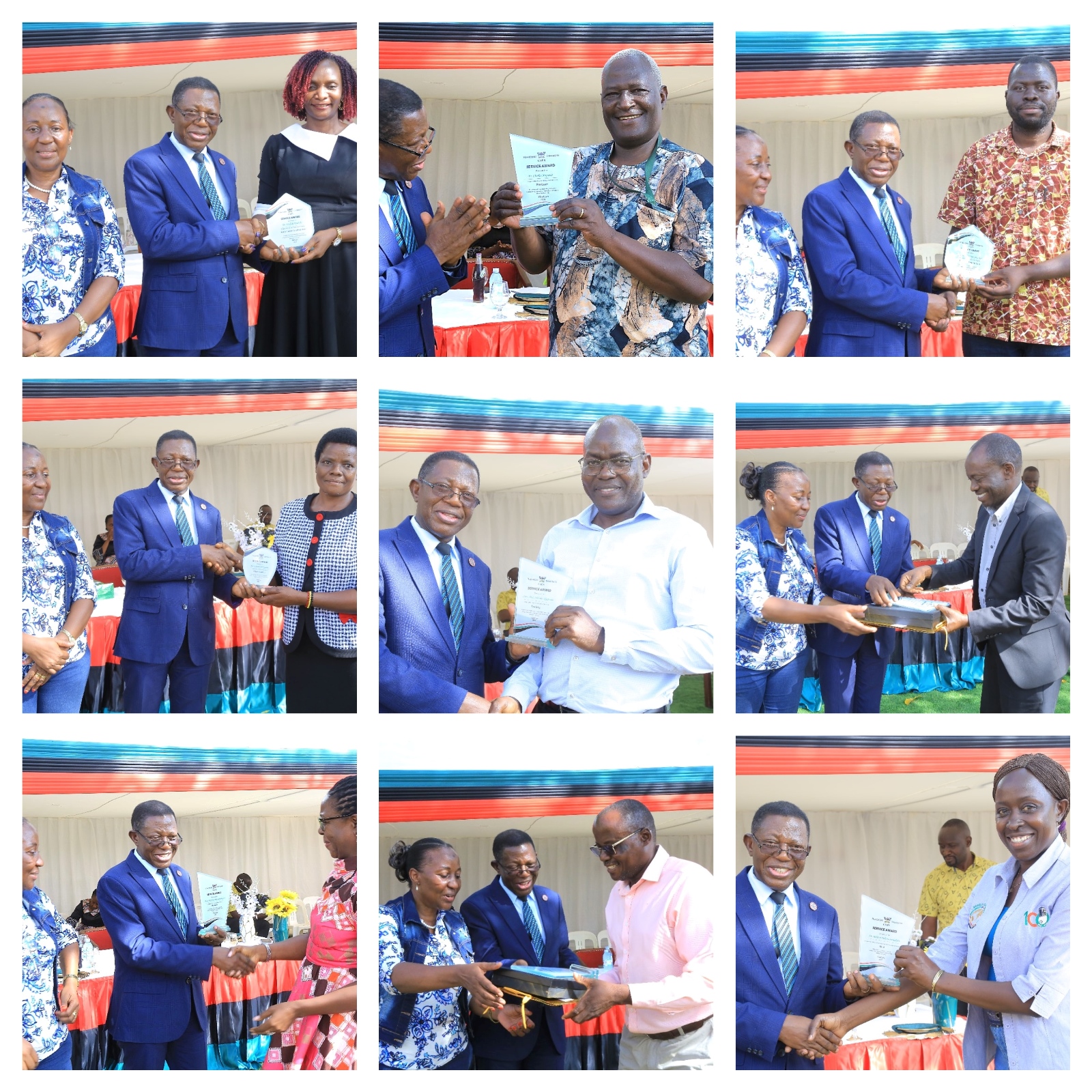
CAES Annual Awards and Staff Recognition Ceremony
The CAES Annual Awards and Staff Recognition Ceremony celebrated the outstanding achievements of dedicated teaching, administrative, and support staff. During this special event, several members of staff were acknowledged and honoured for their exceptional performance, commitment, and contributions to the College’s success.
Commenting on the significance of the awards, Prof. Buyinza praised the initiative, emphasizing that such recognition serves as a powerful motivator. He highlighted how acknowledging excellence not only boosts morale but also inspires continued dedication and fosters a culture of high performance.

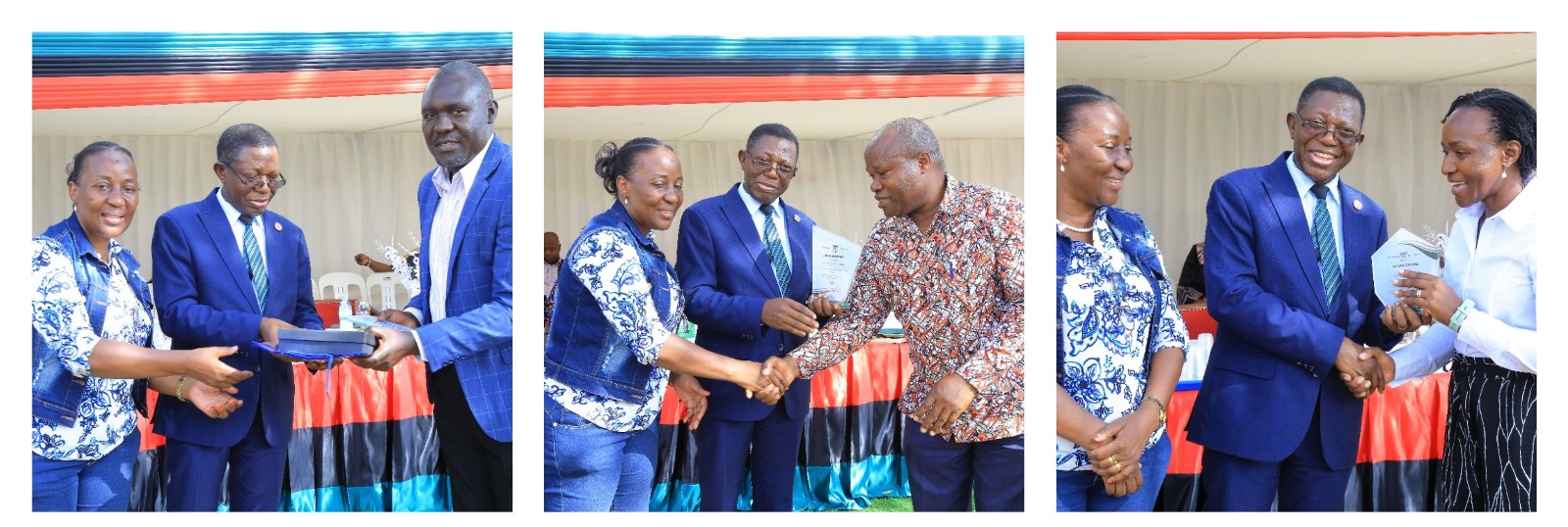
Click on the link below to access the list of staff recognized for exceptional performance.
More pictures from the event





Trending
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoMature Age Scheme Exam Results for 2025/2026
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoFreshers’ Joining Instructions 2025/2026
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMastercard Foundation Board pays its inaugural visit to Makerere University
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoUVCF Makes Case for HEAC Programme
-

 General1 day ago
General1 day agoUndergraduate Admission List Self Sponsorship Scheme 2025/2026
