Computing & IS
Mak-RIF Researchers Design a Tool to Monitor the Elderly with Dementia & Cognitive Impairment for Emergency Response
Published
2 years agoon
By
Jane Anyango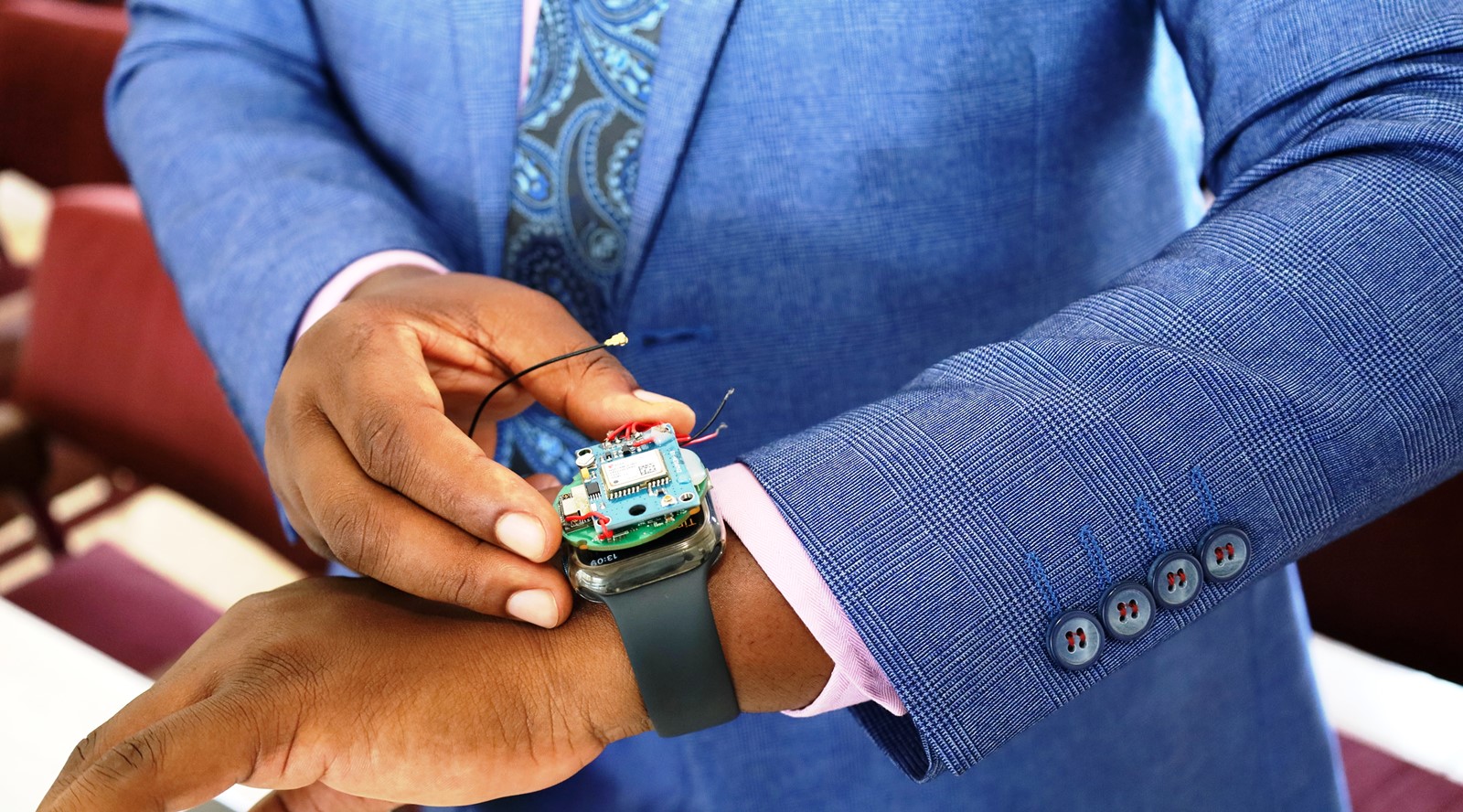
Researchers from Makerere University College of Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS), led by a second-year PhD student Paddy Junior Asiimwe have designed a device to monitor elderly people with dementia and cognitive impairment in rural Uganda.
The device, wearable by the elderly (on the hand like a wrist watch or placed in the pocket), will monitor the patients’ movement and location and then signal the caretaker and the hospital in case of emergencies.
This was disclosed during the research dissemination workshop held on 13th October, 2023 for the Makerere University Research and Innovations Fund (Mak-RIF) project titled, “Advanced Localisation Techniques on Smart Devices for Inclusive Location-based Services: A focus on healthy ageing for the elderly with dementia and mild cognitive impairment in rural communities”
This project relates to the ageing population that wants to live independent of their children or their children work in far away areas.
The Principal Investigator Mr. Paddy Junior Asiimwe noted that the biggest challenge is monitoring the elderly who are living in resource-constrained environments where access to power, internet, network and access to mobile communication is limited. The other challenge is people being not in a position to read and write.
Most available systems on the market according to Asiimwe assume that there is wireless internet everywhere, which is not the case with our local communities, more so in Uganda.
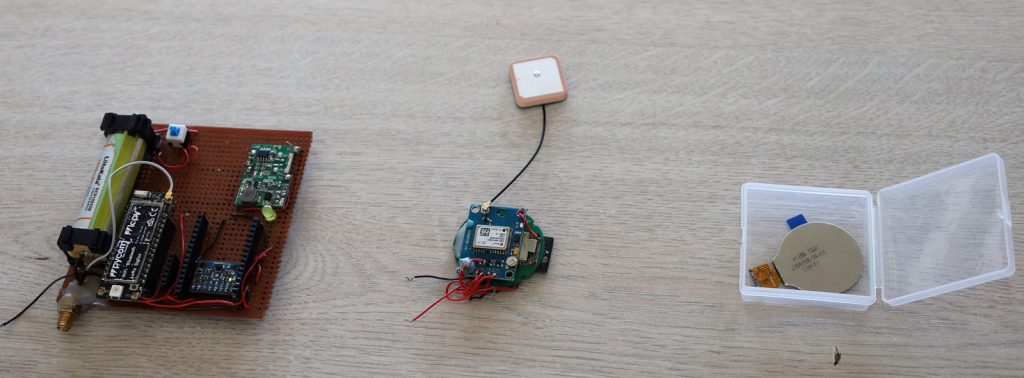
“So we are designing a system that can monitor these elderly people within their homes and still give accurate results with less power consumption, with less cost, within the limited resources that are available in those communities.
The system, Asiimwe explained, basically monitors elderly people remotely using those limited resources that are available in those rural communities.
“Our device uses GPS technology. I would say GNSS or GPS technology because the system we use now has only GPS. This system works in a way that when we first define a safe zone around a user, in technical term, what we are calling a geofence.
When the user or what we are calling an elderly person is within that safe zone, the system does not need to continue tracking him, and then sends an alert to the caretaker or to the hospital in case of emergencies.
But during that time when the user is within the safe zone, we are using what we call a PDR system. In simple terms, we are using accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer to monitor the position of the user within the safe zone.

And GPS is only turned on when the user moves out of the safe zone. In the long run, since GPS is the biggest consumer of power, we end up using less energy because most of the time the system is turned off when the user is within the safe zone.”, The PI said.
Advantages of the device
This technology according to the PI is better than the systems existing on market and would be best recommended for more resource constrained environments, which is the biggest challenge that we have in Uganda as far as accessing resources is concerned.
“One, our system is going to be cheap. Two, our system is going to operate independent of the user. The users that we have mostly in rural areas cannot read and write, and our system operates independent of them.
Three, one of the biggest challenges in these areas is power consumption, which is an assumption that most of these systems on market make, that power is everywhere. So our system can run on batteries, and these batteries, we don’t need to charge them every week, because, for example, from experiments, we tested and the battery can run for 30 days, which is enough time for someone to go and charge,” Mr. Asiimwe explained.
The technology was piloted in Apac district that formed the base for everything that was designed.
“We had a pilot study. We visited that area, met some families, also met the district administrators who took us around. We also met the administrators of the hospital, and we assessed the environment. And even after developing the system, we went back to conduct the tests. And most of the tests that we are basing on now to make results, were done in Apac district”.Asiimwe said.

Apac, according to the Principal investigator, is one of those districts in Uganda that are less developed and, with the biggest number of elderly people and more so those with dementia. In addition, the research team could easily access other projects that are already done by Makerere, like CityLab, which is already putting internet in Apac, plus some other projects that are running from Makerere that gave a foundation upon which to build the project.
After perfecting the performance of this prototype and, with more funding, the research team hopes to add more sensors to these device. For example, elderly people face the challenge of falling down. So, the team would love to add sensors that can detect when a person has fallen down, which is something very challenging, especially in our communities because people have died in bathrooms as a result of these falls.
The team also looks forward to more funding to add in more sensors to monitor more things like temperature, heartbeat, and other body functions, because the network will be in place to send the information to the caretakers.
“And then the other thing that we can also look at, for example, we had this years’ challenge of COVID. It can also be used for patients for COVID. For example, we want to know, since we were fearing to be near COVID patients, we would use this technology to monitor them within their homes. And that is one thing that we can easily integrate with this system in case there is another outbreak in the near future, God forbid, our system could be a solution “, Asiimwe said
The system can do a lot more like monitoring children in this era of child trafficking among other challenges.
Scientists must do their best beyond the minimum expectation-Prof. Oyana
Presiding over the workshop, the Principal College of Computing and Information Sciences Prof. Tonny Oyana challenged researchers and staff to go beyond certain university metrics that they are expected to meet like publishing two papers for a PhD.
Oyana cautioned scientists not to be taken up by the two papers or publishing for purpose of promotion saying, what excites a good scientist is harvesting many papers and grants.
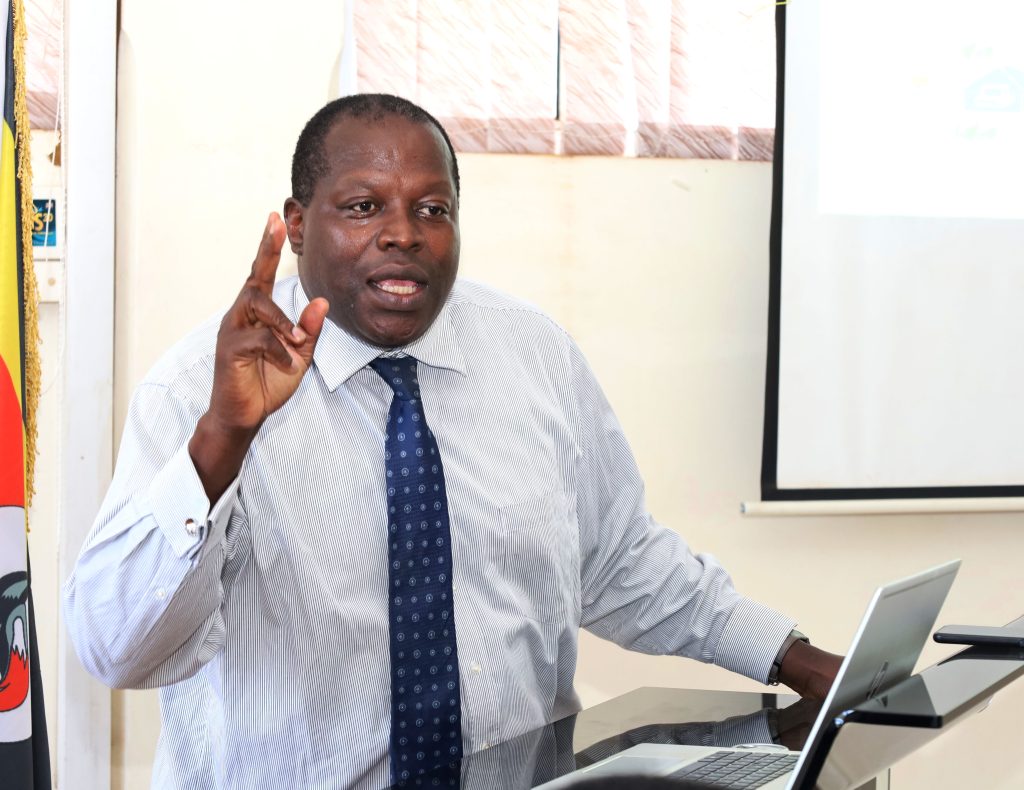

He advised Ugandans to emulate some universities around the world where scientists write five papers per year. With Uganda’s population of over 40 million people. Professor Oyana urged scientist to go beyond the standard and, the minimum if they are to remain competetive on the Ugandan and world market.
“So please, the work of a scientist is to do your best to be at your best to be optimum. Do four papers, five papers, why not? Remember that if you decide to become a scientist, you should have more. Be excited. Don’t do the minimum. If you set your standard here and you fall here, that’s good, but don’t set your standard too low.” The Principal advised.
Over 1,000 projects funded by Mak-RIF
Representing the Chair Grants Management Committee, the Mak-RIF Engagement Officer Grace Ruto-Cherotich, expressed delight and pride in the fact that the team had been able to reach the dissemination part of the project.
She said the Government of Uganda has taken keen interest in how different institutions of higher learning are contributing to national development.
“So the Mak-RIF was created with the objective of increasing generation of local research and scalable innovations that are specifically meant to impact national development. As Uganda, we have our national development plan. We are committed to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and so many other international treaties that we have signed as a nation”, she said.
Since the birth of the research and Innovation fund at Makerere, Cherotich said, so far over a thousand projects have been funded. She expressed the need for the PI to patent his product.
“We need to protect it so that by the time we introduce it to the stakeholders out there, it is already safeguarded”
She commended the research team for the multidisciplinary approach, bringing on board doctors engineers and the ICT department adding that, it is one of the Mak-RIF core values and principles.
“We want to see the multidisciplinary aspect because now this is an institution that has, or nurtures different skill sets. We have humanities, we have ICT, we have engineering, and we have medicine. So we want to see how we can leverage all those different opportunities we have, all the different colleges we have, to ensure that we build beautiful things that will cause impact to the nation.” Cherotich stressed.
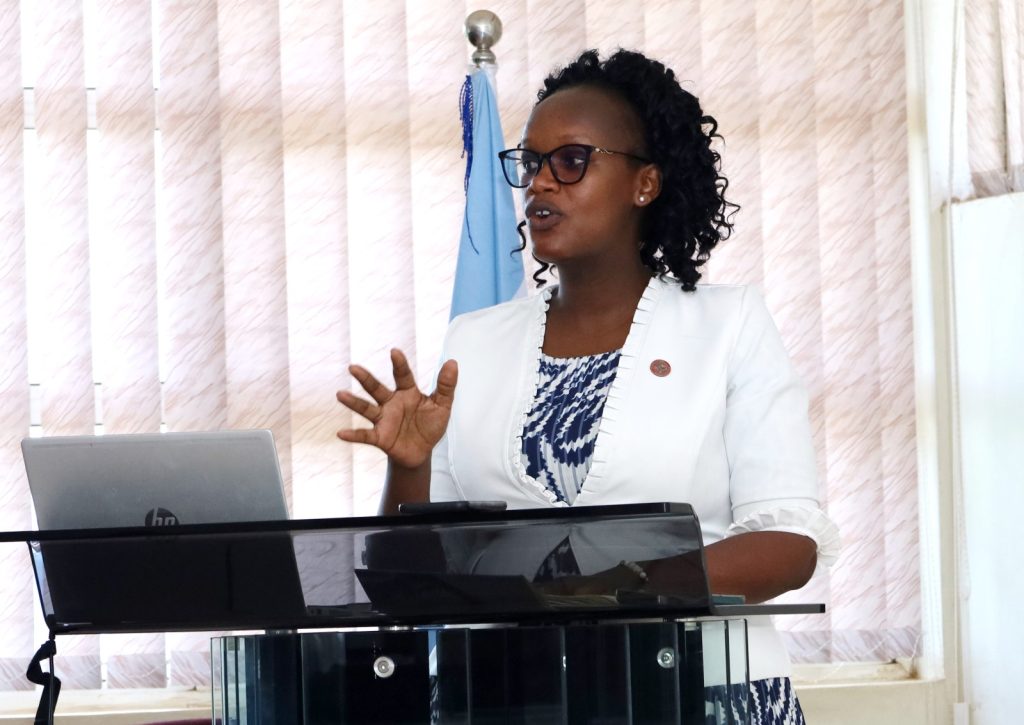

She said that the Mak RIF research agenda is derived from the national development plan and SDGs with its own internal market area strategic plan focusing on the institution being a research-led, meaning that there is need to put a lot of effort in terms of research and innovations.
In that particular research agenda, she said Mak-RIF has 14 thematic areas and recently did an analysis of which areas in those particular themes have not been focused on much.
Cherotich reported that the thematic area that focuses on public service and productivity of public servants has not really been researched, yet recent discussions with Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Public Service revealed that Government has made progress in terms of increasing or raising the salary for scientists. However, the result of that is that people are resigning, leaving their jobs to quickly get their pension and start their private business.
“So you ask yourself, where have we gone wrong in the decisions we make as a nation?
Because now that will mean that there’s going to be a very high pension budget, and then you’re going to have less productivity in the workplace. You’re even going to have reduced numbers of civil servants serving in those particular dockets of increased salaries”, she decried.
She implored researchers to do a lot of detailed research and come up with innovations to achieve what is positively impacting the nation.
The engagement officer equally commended the PI for the job well done.
“Paddy has done a lot of work in harnessing ICT to drive development and that is our theme number 11. I want to tell Paddy that we are really, really humbled and at the same time excited that we have a result, we have a product out of the work we have funded at the Research and Innovations Fund.
“And for sure, we currently have the Innovations Hub at the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS), which is also funded by Mak-RIF, and focused on commercialization and scaling up of projects that we have already, to help us realize returns on investment. So it’s a good opportunity for you”. She appreciated and said:
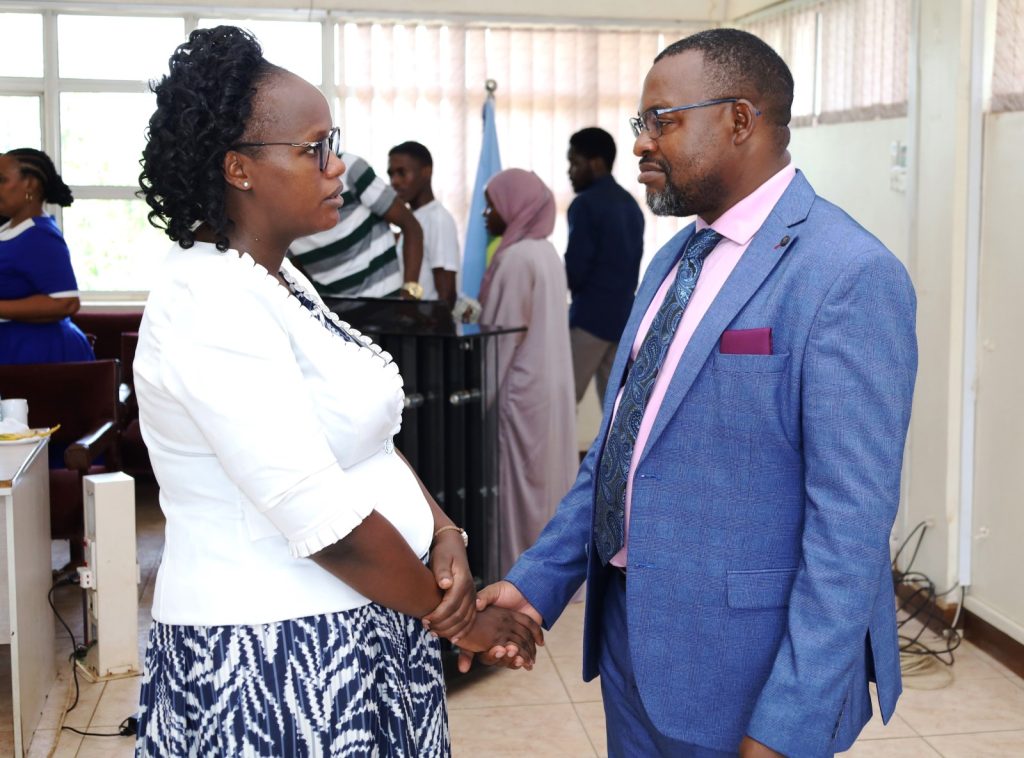

“You know, there’s RIF-5 ongoing. So depending on what you would like to do going forward, do you want to focus on IP issues? Do you want to focus on collecting more data to prove that this device actually works? We can monitor and write reports and stories. And I also want to thank you very much for the fact that you have been able to publish. So those are some of the things we can highlight on the Mak-RIF website so that everybody gets to know that there has been good work done out of certain projects.”
Cherotich also notified the team of the availability of an Intellectual Property Management Office also funded by Mak-RIF that works with the Uganda Registration Services Bureau (URSB) to ensure that IP issues are catered for, as the only way the university can protect her innovations. She urged the research team to think of how they are going to ensure that their IP is protected.
She explained that Government gives Mak-RIF UGX 30 billion every financial year. In addition she said, Mak RIF has other opportunities on offer including competitive grants, multi-year projects, needs-based track, and the PhD track that have been introduced available for Makere University staff and students.
“We have the research support office that guides you through the processes of what you need to do when you have been awarded, and what happens post-award. They take you through contract signing processes, requisitioning processes, and procurement processes.
“We also support you when it comes to issues to do with report writing. We have quarterly reports, and ultimately the final reports. We also have the station where we are right now. We also support the whole process of dissemination. How would you want your dissemination done? How would you do your slides laid out? etc”, she added.
Cherotich advised the research team on the need to involve important stakeholders that can embed their work into the policy environment of the country, or where need be, scale it up beyond the scale of what the Mak-RIF grants facilitate.
You may like
-


When Birth Becomes the Most Dangerous Moment, Wanduru & the Work of Making Labour Safer
-


Study Alert: Power in Her Hands; Why Self-Injectable Contraception May Be a Game Changer for Women’s Agency in Uganda
-


Building Skills for Better Public Investments: PIM Centre Trains Public Sector Economists
-


How Jimmy Osuret Turned Childhood Trauma into Evidence for Safer School Crossings
-


Holding the System Together During COVID-19: Steven Kabwama’s Research on Care Continuity
-


Dr. Samalie Namukose and the Quiet Work of Making Nutrition Count
Computing & IS
CoCIS CIPSD Short Courses Jan-Mar 2026
Published
3 weeks agoon
January 19, 2026By
Mak Editor
Makerere University College of Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS) is the main ICT Training, Research and Consultancy Centre in Makerere University. The College has six Academic departments comprising of the Department of Computer Science, Department of Networks, Department of Information Technology, Department of Information Systems, Department of Library and Information Sciences, and the Department of Records and Archives management.
In addition to the mainstream degree programmes, CoCIS has a specialized Center for Innovations and Professional Skills Development (CIPSD) which delivers state-of-art training in ICT e.g. the Cisco Networking Academy for Cisco related courses, the Microsoft IT Academy Program for Microsoft related courses, International Computer Driving License course, Oracle Certified Training center for Oracle, Linux and Unix Training center. CIPSD also offers Machine Learning, Big Data Analytics, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Ethical Hacking as online courses. The College is an authorized Testing center, operating under PearsonVUE and Kryterion. Listed in the table (see download below) are the courses currently offered at the Center with their next start dates, duration, and cost.
- All courses are at affordable fees catering for Students, Vacists, Professionals and
- Anyone who wants to start a career in ICT or polish his/her ICT skills.
Contact Information
E-mail: psd.cis@mak.ac.ug
Tel: +256 782 512 897 +256 752 779964
URL: https://cocis.mak.ac.ug/cipsd/
Computing & IS
Makerere University and SoonPay Sign Landmark MoU to Champion Blockchain Innovation and Financial Inclusion Across Africa
Published
2 months agoon
December 9, 2025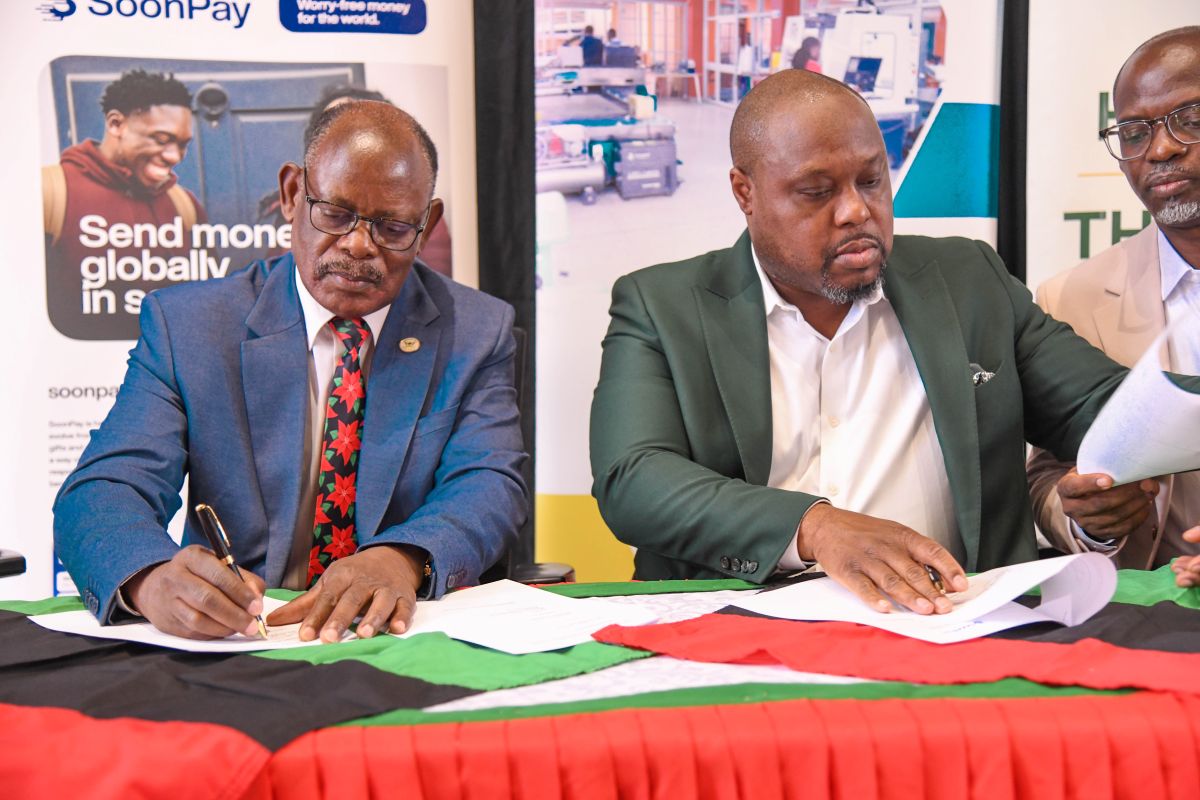
On Saturday 6th December 2025, Makerere University entered into a ground-breaking partnership with the U.S.-based fintech company SoonPay, marking a major breakthrough in Uganda’s push to integrate emerging technologies into research, innovations, higher education and national development.
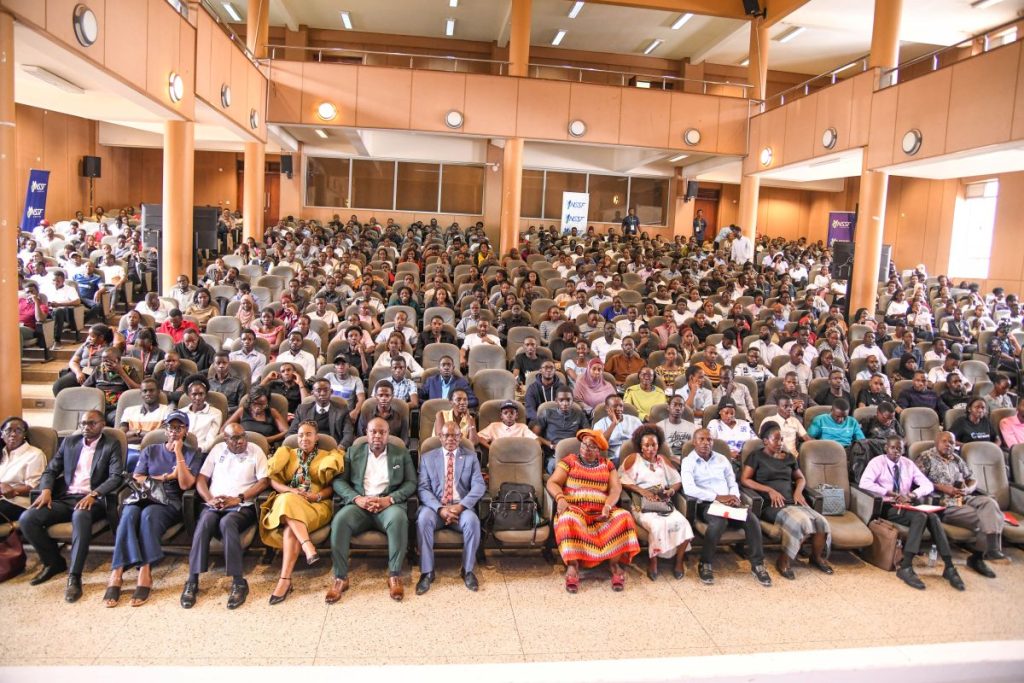
The Memorandum of Understanding was signed by the Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe and Mr. Frantz Morency, Chief Executive Officer of SoonPay L.L.C, during the Makerere University Financial Innovation Day, a high-energy event that brought together over 800 students, faculty, industry partners, and technology leaders.
The MoU institutionalizes the collaboration of Makerere University through the Makerere University Technology and Innovation Centre and SoonPay LLC. The signing ceremony was witnessed by Dr. Cathy Ikiror Mbidde-Manager of Makerere University Technology and Innovation Centre and Ms. Vuyani Jones-Blockchain Infrastructure Manager.
Organized by the Makerere University Technology and Innovation Centre (MUTIC) in partnership with SoonPay, the event ran under the theme “Innovation and Financial Inclusion for a Secure Future.” It featured keynote speeches, panel discussions, live demonstrations, and the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that will usher in a new era of blockchain training, research, and innovation at Uganda’s premier university.
The event was supported by several partners, including the National Social Security Fund (NSSF), the Uganda Blockchain Association, the National Planning Authority (NPA), Prudential Uganda, and other technology and financial sector stakeholders.
A Strategic Partnership to Transform Africa’s Digital Landscape
The newly signed MoU between Makerere University and SoonPay is expected to unlock a broad set of opportunities for students and academic staff. These include blockchain education and certification, joint research projects, internships and apprenticeships, the development of new financial inclusion tools, and the integration of emerging technologies into existing academic programs.
SoonPay’s entry into Uganda is part of a larger vision to expand blockchain-driven solutions across Africa—a continent its executives say has historically been excluded from global technological revolutions.

Impressed by the overwhelming numbers of students who filled the Yusuf Lule Central Teaching Facility Auditorium to the brim, the Vice Chancellor, said: “Dear students, by choosing to stay on campus, on a Saturday, and after completing your examinations, you have demonstrated your willingness to learn and embrace the blockchain technology as well as emerging technologies in general.”
Stating that blockchain technology is the future for Africa, the Vice Chancellor challenged the students to take charge of Africa’s digital transformation.
“You are the people to emancipate Africa from marginalization,” he declared. “What will liberate our continent is not politics—we have done too much of that. It is education, research, innovation, and technology.”
Prof. Nawangwe delivered a sweeping historical reflection, tracing Africa’s technological setbacks to the destruction of its civilization over several centuries.
“For 400 years, Africans were taken away as slaves. For another 200 years before that, our lands, knowledge systems, and technologies were disrupted,” he said. “This represents around 600 years of destruction and marginalization of African civilization.”
He urged students not to miss the opportunity that modern technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence present.

“We are lucky to be living in an era where Africa is free,” the Vice Chancellor said. “My hope is that we do not wait another 600 years to take advantage of this freedom. The most important resource we have is not minerals; it is human resources—you, the youth.”
Prof. Nawangwe reminded students that Makerere’s reputation as the “intellectual capital of Africa” places immense responsibility on their shoulders.
“You are among the very few Ugandans privileged to study at Makerere University. University graduates are not supposed to wait for jobs—you are the ones expected to create them,” he said.
Why Blockchain? Transparency, efficiency, and global competitiveness
The Vice Chancellor highlighted the transformative potential of blockchain technology, especially in improving financial systems—a sector he described as the backbone of any modern economy.
“Without efficient financial systems, nothing else works,” he said. “Blockchain offers transparency, reduces fraud, and minimizes corruption. If applied properly, it could transform how we manage finances, education, and even our natural resources, including the oil that Uganda is about to exploit.”
He added that Makerere’s students are already demonstrating global competitiveness in innovation, winning international competitions and creating products across multiple disciplines.

“The brains are here,” he said. “What we need is exposure to opportunities and technologies that will help you turn your ideas into impactful solutions.”
In a passionate keynote address, SoonPay CEO, Mr. Frantz Morency underscored why his company chose Uganda as its launchpad for blockchain adoption in Africa.
“As the Professor said, we have been excluded for more than 400 years,” he stated. “Even though we’re an American company, we know our roots. Look around the SoonPay team—you will see yourselves. We chose Uganda intentionally.”
Mr. Morency pointed to Africa’s dismal participation in the global blockchain economy. “In the U.S., blockchain generates $2.6 billion—61.7 percent of the world’s share. The rest of the world generates $1.6 billion. And Africa, just $14 million, or 0.33 percent,” he said. “That is unacceptable.”
He attributed the gap not to a lack of interest among young Africans, but to a lack of opportunity. “You want to learn—what you lacked was opportunity,” he said. “With the support of Professor Nawangwe, Dr. Cathy Ikiror Mbidde, and Dr. Margaret Nagwovuma, SoonPay wants to bridge that gap in education, technology, and economic opportunity.”
Mr. Morency also shared his personal journey, connecting his Haitian background to the aspirations of African youth.
“Many of you may see me as ‘the guy in the green suit,’ but I come from a small island—Haiti,” he said. “My mother never finished first grade; my father never finished second grade. What they gave me was integrity, work ethic, and the determination to seize opportunities when they came.”
He urged students not to seek opportunities abroad out of desperation, but to build meaningful careers in Africa. “Africa does not need to lose its talent. Why can’t you build here? Why can’t businesses, innovation, and prosperity thrive here?” he said. “Educate yourselves. Build. Create. Grow.”
A milestone for Makerere and Africa
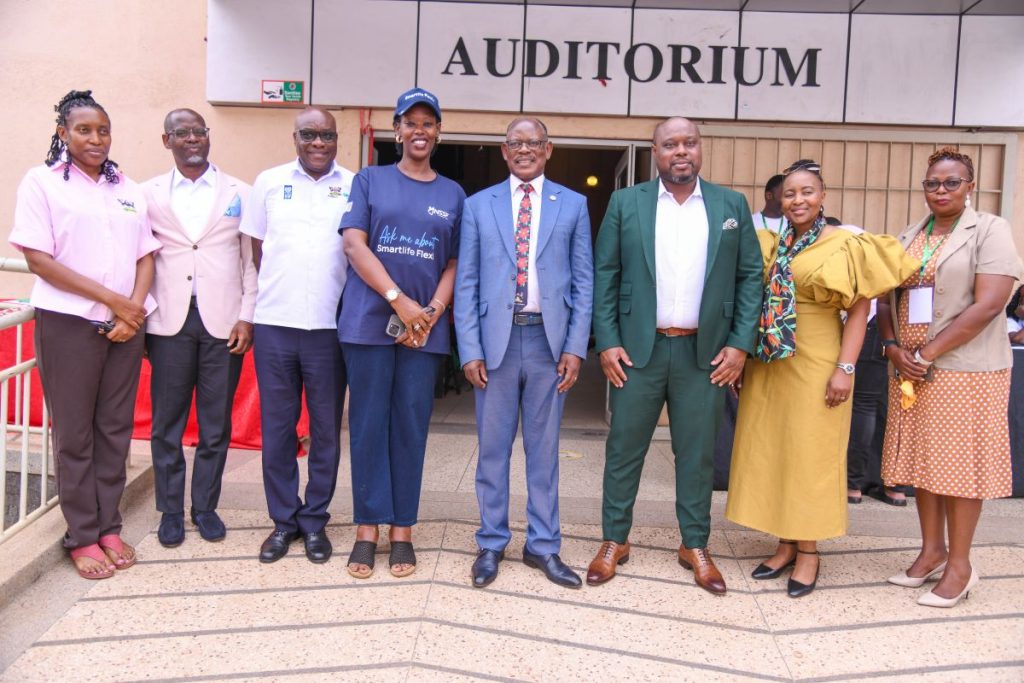
Dr. Cathy Ikiror Mbidde, Head of the Makerere University Technology and Innovation Centre (MUTIC), described the event as a “major milestone” in the institution’s evolution.
“We are here to witness one of the key emerging technologies and to reflect on how universities can embrace such milestones,” she said. “Everyone has a role to play in transforming our lives through research, ideas, and projects.”
She thanked SoonPay for choosing Makerere University, noting that students had been “instrumental” in pushing for blockchain education.
“You have been constantly asking questions, pushing us, and showing deep curiosity about blockchain. Today, we finally have answers,” she told the students.
Beyond the speeches, the event showcased SoonPay’s blockchain infrastructure, student-led innovations, and a roadmap for integrating digital finance tools into university programs. Partners such as NSSF emphasized the importance of preparing young people for a digital future.
With the MoU now in force, Makerere University is positioning itself as a regional hub for blockchain education, research, and innovation. The partnership with SoonPay aims not only to train students but to shape Uganda’s—and Africa’s—next generation of tech leaders.
Computing & IS
71 Graduate Under India–Uganda e-VBAB & Amity University Collaboration
Published
3 months agoon
November 21, 2025By
Jane Anyango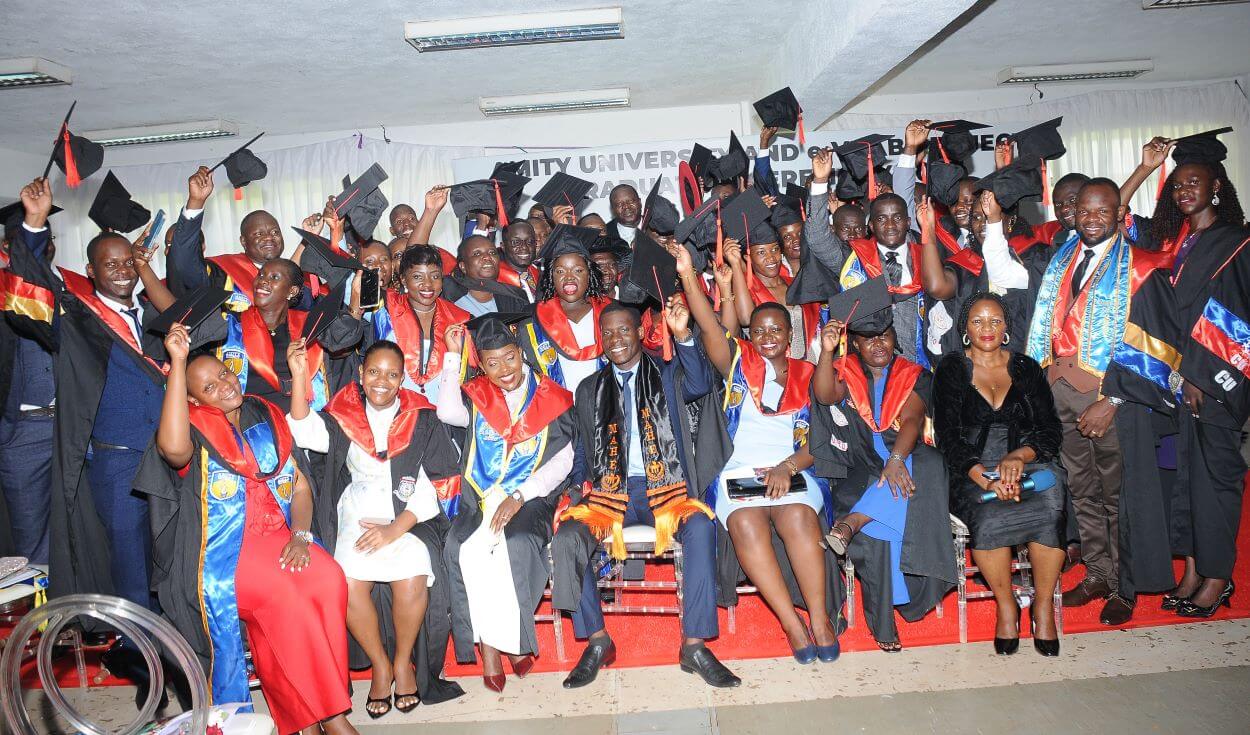
Kampala, Uganda
21st November 2025
Makerere University’s College of Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS) has graduated 71 students under Phase 2 of the e-VBAB Project, a collaboration between Amity University in India and Makerere University. The ceremony, held at Block B CoCIS, was presided over by Principal Prof. Tonny Oyana on behalf of the Vice Chancellor.
The program, funded by the Government of India, offered 100 percent scholarships to Ugandan students through the Pan-African e-Network Project, which provides tele-education and tele-medicine services across 48 African countries. Uganda signed onto the initiative in 2019, and more than 1,700 Ugandan students have benefited since its inception.
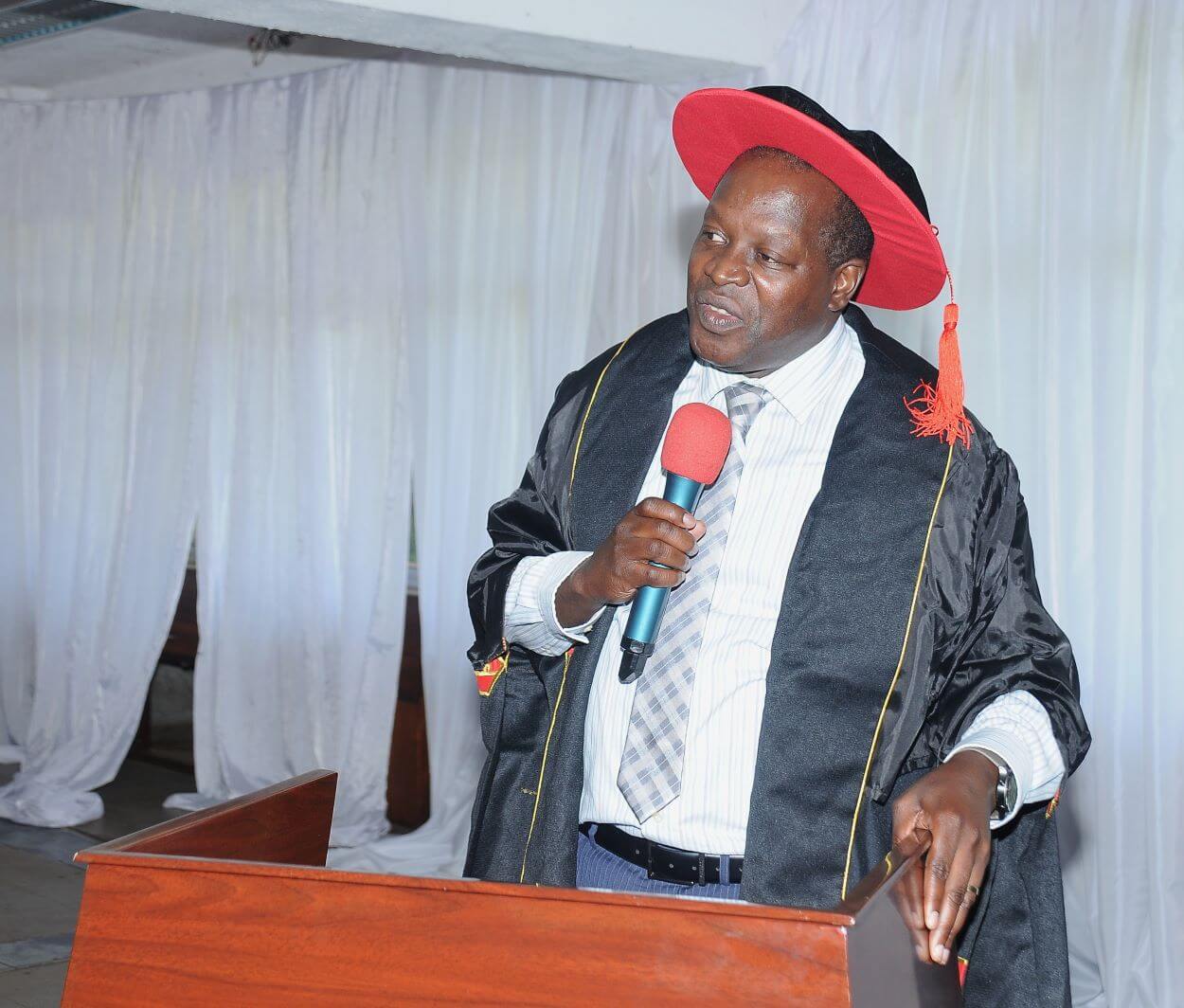

In his remarks, Prof. Oyana praised the efforts of program coordinators and support staff, singling out Madam Claire for her dedication. “Coordinating things remotely from other countries is not easy, but you have been humble enough to ensure that these graduates have seen the light,” he said. He also thanked custodians and security personnel who facilitated exams and weekend access for students.
Prof. Oyana emphasized the importance of completing studies, noting that many students remain pending. “Please encourage your friends because there’s no reason not to finish. You honor us, honor the government of India, the taxpayers, by completing,” he urged. He reminded graduates that their degrees are recognized by Uganda’s National Council for Higher Education and warned against fraudulent claims. “Only hard-earned degrees are recognized. There’s no easy way out,” he cautioned.
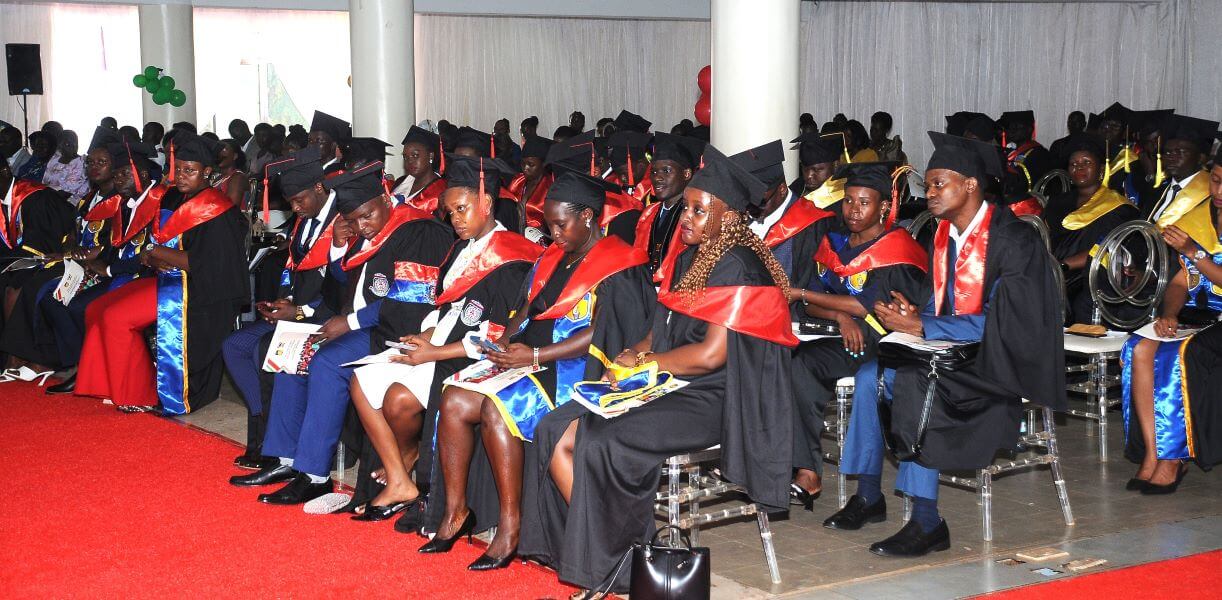

Reflecting on the program’s history, Oyana described the graduates as “COVID children” who persevered through the pandemic. He also offered career advice, stressing humility, confidence, and attitude. “Having a good attitude does not cost money. It is free. And it’s good for your heart. Happiness is not sold anywhere,” he said. He encouraged graduates to create opportunities through entrepreneurship and to value professional networks.
The graduation marked the conclusion of the e-VBAB collaboration, with Prof. Oyana reminding students of their unique place in history as the first and only cohort under the Makerere–Amity partnership. “You are the first cohort. Everybody looks upon you wondering, will you make it? History will write down that we are the only cohort,” he said.
Prof. Oyana Urges Graduates to Pursue Gifts, Confidence and Positive Attitudes
Prof. Tonny Oyana urged graduates to embrace humility, confidence, and entrepreneurship as they prepare for life beyond academia, warning that degrees alone are not a guarantee of success.
Oyana reflected on his career in academia. “But I’m still here, surviving and kicking. I have been with academia technically from 1993. I have not changed career. I grew my career through academia,” he said, noting that while psychology suggests people change careers five times, he has remained committed to one path.
He cautioned against unrealistic ambitions, particularly in politics, referencing Uganda’s crowded presidential race. “Not everybody can be president. So exercise your dreams with some caution. Don’t waste your time in an initiative that you know will not break through,” he advised, urging graduates to instead pursue areas aligned with their spiritual gifts and natural talents.

Turning to the job market, Prof. Oyana highlighted the challenges of employment. “In order to get a faculty job, you had to put in 40 applications. Now, I think it has doubled. These days, there’s no courtesy. They don’t even reply to your application,” he said. He encouraged graduates to create their own opportunities through entrepreneurship, stressing that education provides knowledge, skills, and values.
He underscored the importance of attitude, describing it as a free but powerful tool. “Having a good attitude does not cost money. It is free. And it’s good for your heart. Happiness is not sold anywhere. So, you make your attitude positive, things will be positive,” he said. He warned that arrogance and poor manners can sabotage success, urging students to practice humility both in professional and personal life.
Prof. Oyana also emphasized confidence and self-presentation. “You are your own moving advert. Don’t sabotage your own confidence. Be very clear about what you bring to the table,” he said, advising graduates to rehearse their self-introductions and prepare thoroughly for interviews.
Finally, he highlighted the value of professional networks, recalling how his PhD cohort became a lifelong support system. “It became my network for success. Please keep your network. Even if you haven’t gotten much in your life, face it,” he said.
The Principal’s remarks blended personal anecdotes with practical advice, reinforcing the message that success requires humility, preparation, resilience and strong networks beyond academic achievement.
CiPSD Director Nalubega Praises Teamwork, Urges Graduates to Believe in Themselves
The Director of the Center for Innovations and Professional Skills Development (CiPSD), Ms. Barbara Nalubega, praised graduates and staff for their teamwork and resilience .
Addressing the graduates, Nalubega said the success of the program was achieved despite challenges. “I’m very humbled that amidst all the same challenges, we have built rapport, worked as a team, and here we are. This is the day that the Lord has made,” she remarked.

She thanked graduates for their encouragement and support, noting that she had received hundreds of messages of gratitude during the course of the program. She singled out several students, including Damali, Fatuma, Josh, Sam, Paula, Sheila, and Michael, for their commitment, and extended special appreciation to Dan, who, though not part of the graduation, sent her flowers in recognition of her efforts.
Nalubega also acknowledged her colleagues and partners who played key roles in the ceremony’s success. She commended Claire, the e-learning coordinator, Annette, who managed gowns for graduates, and Brenda, the supplier, for their dedication. She revealed that she personally staked two million shillings in the Bank to ensure latecomers were accommodated. “This wouldn’t have been possible without you making payments in the bank on time,” she said.
Nalubega emphasized humility and accountability, apologizing to those who may have been hurt along the way. “Apologizing to you is not an uphill task for me. When I make a mistake, I usually apologize,” she stated.
She concluded by encouraging graduates to believe in themselves and the transformative power of education. “Through education, the son of a farm or mine worker can become the president of a great nation. Yes, believe in yourself,” she said, citing Nelson Mandela’s rise from humble beginnings to the presidency of South Africa as an example.
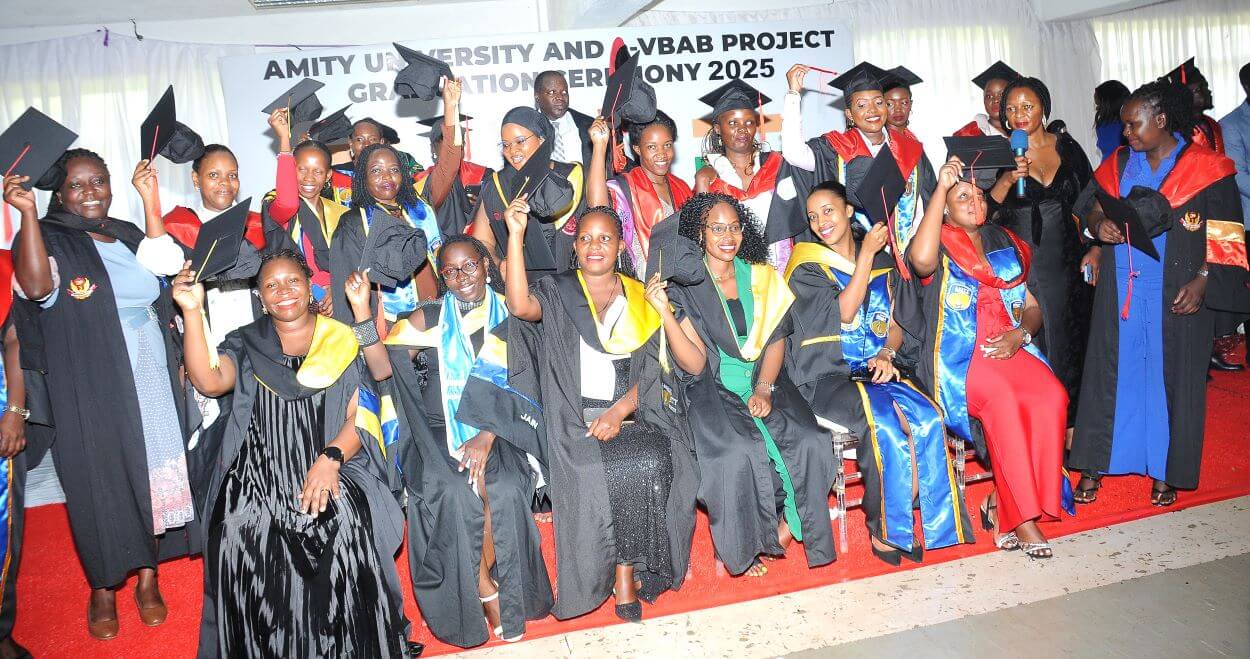

The Director’s message underscored the importance of teamwork, resilience, humility, and self-belief as graduates embark on their next chapter.
Graduates Laud Resilience, Faith and Global Support
Graduates under the e-VBAB Project and Amity University–Makerere collaboration celebrated perseverance, faith, and international partnerships as they addressed the audience during the) graduation ceremony.
Representing the e-VBAB project graduates, Isoke Gloria, a former student of Manipal Academy of Higher Education (MAHE), expressed gratitude for the milestone. “It’s not been easy, but we thank God so much for bringing us to this day. May His name be glorified,” she said. Gloria praised the scholarships provided under the project, noting, “We would never have made it here without their support. They’ve made our academic journey so easy and a success.” She also commended Makerere University and coordinator Barbara Nalubega for their encouragement and commitment.
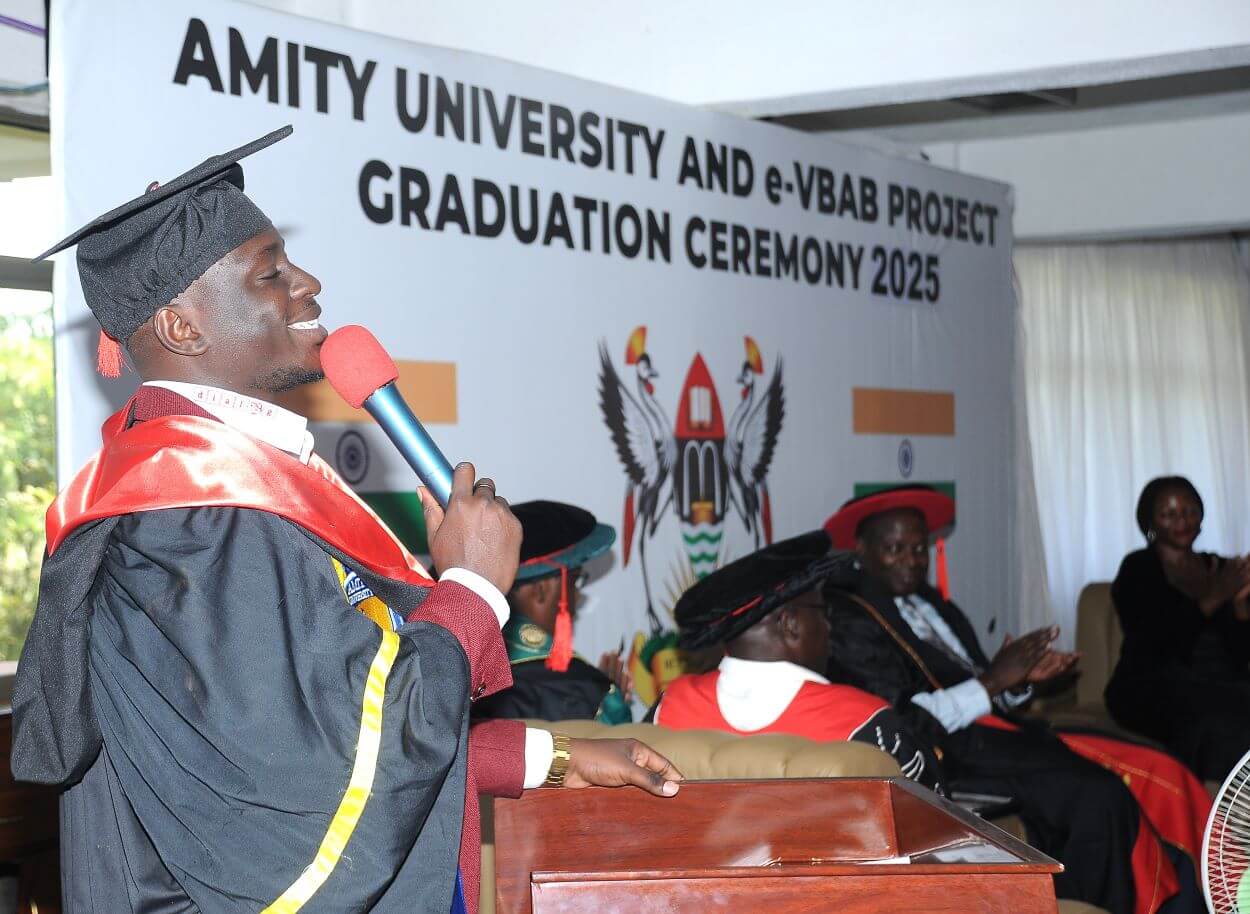
Duncan Nagenda, an Amity University master’s student, highlighted the challenges of online learning, describing it as demanding and often unpredictable. “Online education is not a joke. If you ask me, it should be added on the list of a thousand ways to die,” he said, recalling internet disruptions and strict exam protocols. He acknowledged the support of lecturers in India, parents, and Makerere staff, particularly e-learning coordinator Claire. “To my class of 2025, may your future be filled with purpose, may your opportunities be abundant, and may your journey ahead be guided by excellence and wisdom,” he concluded.

Joshua Mugabo, also from Amity University, emphasized faith and resilience. “Who would not have been here without God? It is His grace that carried us, His strength that sustained us, and His favor that opened doors we once feared were closed,” he said. Mugabo reflected on hardships such as blackouts, poor internet, and family responsibilities, but celebrated the resilience gained. “A degree might put something in our hand, but education puts something in your heart. And today’s world urgently needs what is in our hearts,” he added. He paid tribute to the Government of India, Makerere University, and mentors in Uganda and India, invoking Nelson Mandela’s words: “Education is the most powerful weapon you can use to change the world.”
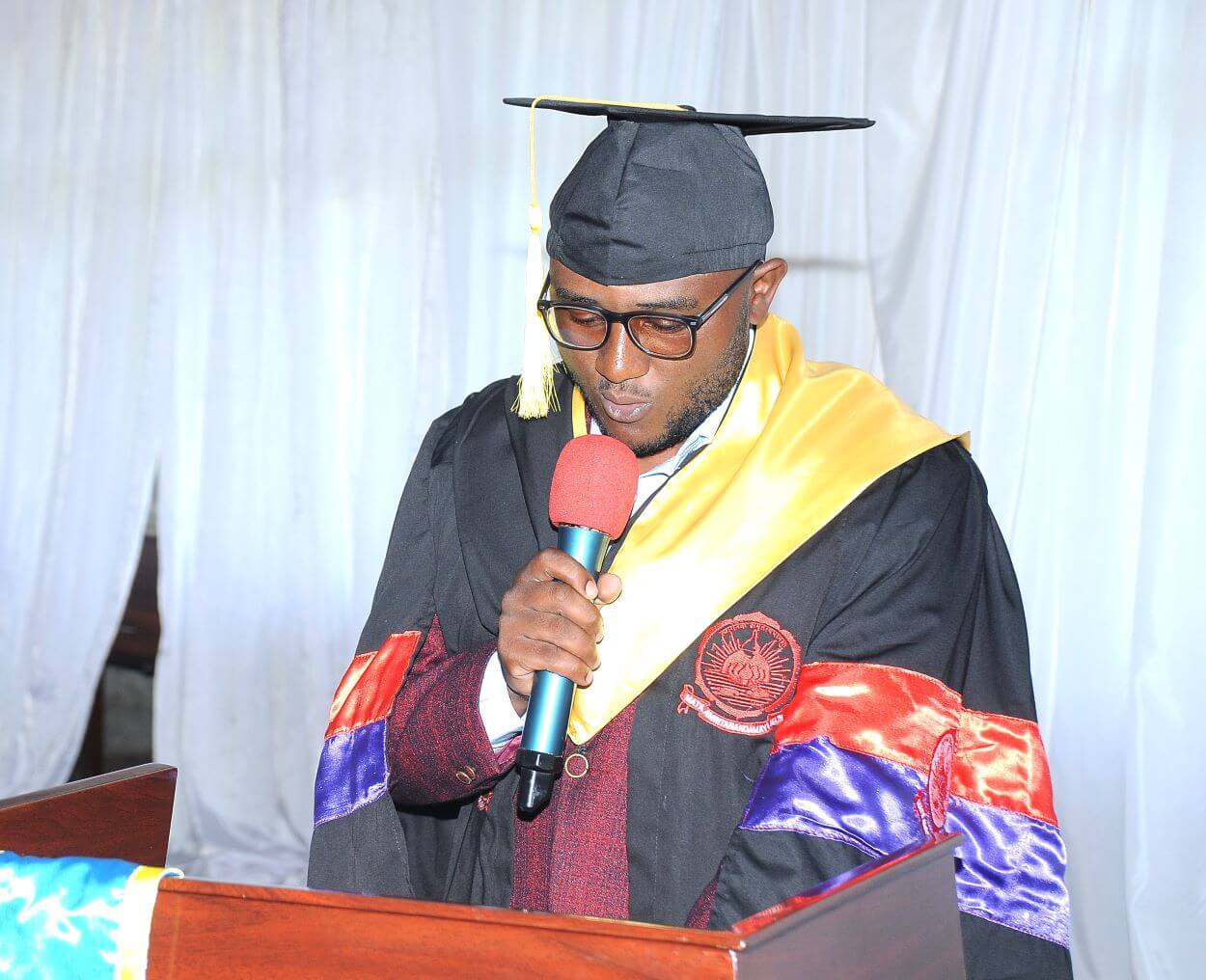

The graduates’ remarks underscored the significance of international collaboration, personal perseverance, and the transformative power of education, marking the ceremony not only as a celebration of academic achievement but also of resilience and shared vision for the future.
Find the details about this project and graduates in the booklet attached.
Trending
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoCall for Applications: Admission to Postgraduate Programmes 2026/2027
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoPress Statement: Makerere 76th Graduation Ceremony
-

 Natural Sciences1 week ago
Natural Sciences1 week agoSimon Mungudit: Mak’s Best Performing Male Science Student & Rising Star in Petroleum Geoscience
-

 Agriculture & Environment5 days ago
Agriculture & Environment5 days agoFrom Adversity to Excellence: The Inspiring Journey of Makerere’s Best Science Student, Esther Ziribaggwa
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoCall For Applications: MakNCD Masters and PhD Training Opportunities
