Education
Researchers push for innovative assessment in universities
Published
3 years agoon
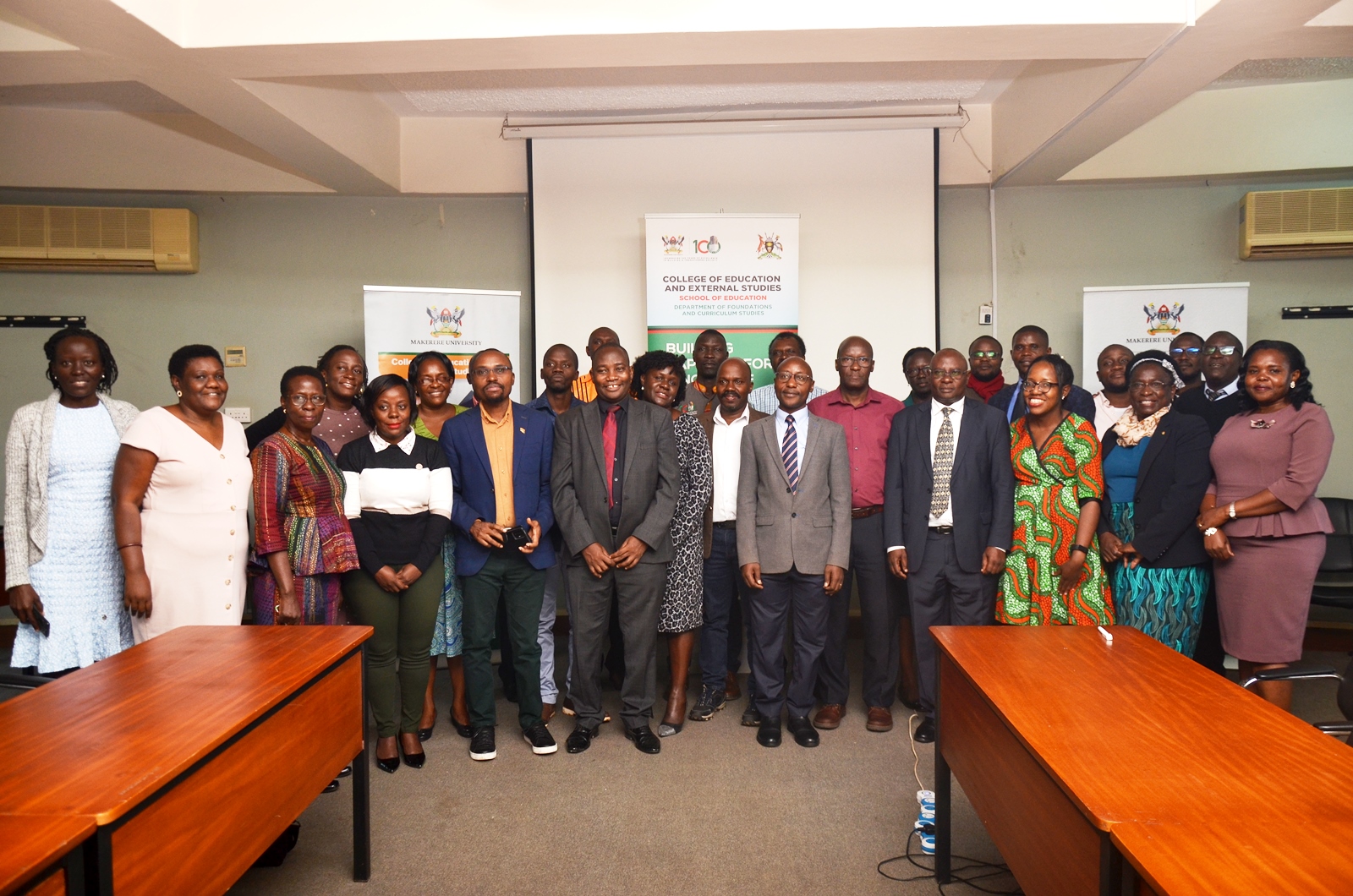

In the face of new technologies and Artificial Intelligence (AI), there is a call for universities to be more relevant to local needs while also taking into consideration the global needs. Teaching and learning has over the years evolved from being teacher centered to one that is learner centered. With the onset of COVID 19, online learning was quickly adopted across the globe, and most recently AI. These changes in the education system have called for a new mode of assessment of learning. This is what researchers from the College of Education and External Studies (CEES), led by Dr. Walimbwa Michael are advocating for.

During a training workshop on March 15, 2023 Dr. Walimbwa shared with participants the importance of innovative assessments, saying the world has evolved from the traditional methods of assessment. The researchers argue that there is need for a new mode of assessment which has a constructive alignment. Constructive alignment, according to Dr. Leah Sikoyo one of the partner trainers, demands that there is coherence between different aspects of the curriculum. “The three pillars must speak to each other; Learning outcomes; Teaching and learning experiences and assessment,” Dr. Sikoyo emphasized.
Assessment, she said should take the outcome based approach which emphasizes learning outcomes such as skills acquired, values and problem solving among others. Assessment she said should not only examine lower order thinking levels but also the middle and higher order thinking levels.

Dr. Sikoyo says that for teachers to be able to carry out innovative assessment, they too have to teach innovatively.
Prof. Betty Ezati, another trainer shared some insights on some modes of innovative assessments. She argued that Innovation – assessment should be geared at improving, solving or alleviating some perceived problem.

She said teachers need to move away from the traditional mode of assessment which is designed to identify student acquisition of content and the ability to demonstrate this acquisition.
It tends to focus on one answer, less on employable skills, it is mainly summative and written. Dr. Ezati said we need an authentic assessment which emphasizes behavioral change, design assessment to capture ‘what students can do, say and make.
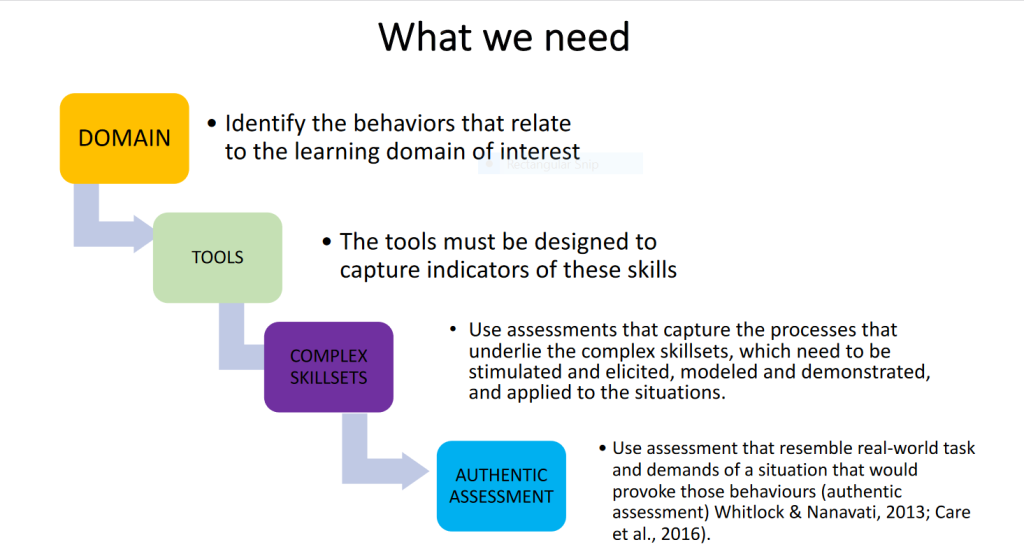
The research team shared some innovative ways of assessing students which include; Self and peer assessment which Dr. Ezati said allows students to actively participate, reduces reliance on the teacher and allows students to be independent and motivated.
Concept Map/Conceptual Diagram. This mode of assessment will require students to present a diagram that depicts known or suggested relationships between concepts and ideas on a given topic.
The other mode of assessment is portfolio, which consists of work selected by the student, reasons for the selection and self-refection on the learning process. This mode of examination may include essays, assignments, lab reports, art work, project reports, grades and test
results.

Assessing students through group work, Dr. Ezati said is a form of cooperative learning.
“Teamwork is one of the competencies that industries often require, group work helps to prepare students for their future careers,” she added.
The professor advised the use of Rubric as a tool for Authentic Assessment. Rubrics, she said establishes and sets instructional expectations and standards, offers students a vision of what the facilitator is seeking to accomplish. This she advised should be shared with the learners early enough for them to prepare. She advised that it’s important to access the 21st century skills such as critical thinking, communication skills, innovation and collaboration.

The participants were also given information on how to integrate technology in innovative assessment. The tips, given by Dr. Mayende Godfrey included the use of various online tools including Mentimeter, google jamboard, padlets, discussion forums, quizzes and the Makerere University eLearning Platform.
Speaking during the training workshop the guest of honour, Dr. Walakira Eddy from RIF, appreciated the research team, saying the topic of research is an important one for all academic staff of the university. He reiterated the RIF’s commitment support researchers in the humanities. He also thanked CEES for supporting the university with online learning during the Covid 19 outbreak.
The research team
- Dr. Micheal Walimbwa (PI)
- Dr. Shopi Mbulankende Julius
- Dr. Buluma Alfred
- Dr. Nancy Nabiryo
You may like
-


Over 9,200 to graduate at Makerere University’s 76th Graduation
-


76th Graduation Highlights
-


Strengthening Global Partnerships to Advance Research, Innovation, and Graduate Training: Makerere University Hosts Delegation from the University of Warwick
-


Olivia Nakisita and the Quiet Urgency of Adolescent Refugee Health
-


For Youth by Youth – Call for Second Cohort Applications
-


Holding the System Together During COVID-19: Steven Kabwama’s Research on Care Continuity
Education
Facilitating Access and Participation through Higher Education Access Programmes and Connected Education for Students with Refugee Backgrounds: A Global South Delphi Study
Published
2 months agoon
December 19, 2025
On 17th December 2025, a Delphi workshop was convened at Kampala Kolping Hotel, providing a collaborative platform for dialogue on standardisation and harmonisation of Higher Education Access Programmes (HEAP) across institutions, alongside strategies for portability and verification on demand through a HEAP Digital Passport. Discussions centered on accreditation, diversification of delivery and learner support, and future scenarios for HEAP and Connected Education.
Expert panelists underscored the urgent need for:
- Standardised HEAP frameworks across universities to ensure consistency in admission pathways.
- Harmonisation of HEAP curricula, duration, and procedures to eliminate barriers that hinder access and transition.
- Development of a HEAP Digital Passport enabling portability of credentials, secure digital verification, and integration with national qualification frameworks and international recognition systems.
Uganda, is one of the leading refugee-hosting countries with inclusive education policies, faces challenges in ensuring equitable access and participation for students with refugee backgrounds. While some universities offer HEAP as a bridging programme for marginalized learners, variations in programme design, delivery, and support systems still exist, which may lead to violations of accreditation. This calls for urgent standardisation and harmonisation to strengthen HEAP as a recognized transitional pathway into higher education.

Funded by Education Beyond Borders, researchers from Makerere University and the University of Edinburgh engaged stakeholders from public and private universities in Uganda through participatory workshops and expert meetings. This Delphi Workshop aimed providing a collaborative platform for dialogue on standardisation and harmonisation of Higher Education Access Programmes (HEAP) across institutions, alongside strategies for portability and verification on demand through a HEAP Digital Passport. Discussions centered on accreditation, diversification of delivery and learner support, and future scenarios for HEAP and Connected Education. The project is led by Dr. Rovincer Najjuma (Principal Investigator), with co-PIs Dr. Rebecca Nambi and Dr. Michael Gallagher.
Listening to experiences and co-creating solutions

Opening the workshop, Dr. Rebecca Nambi, a Senior Lecturer at Makerere University and Co-Investigator of the project, emphasized that the engagement was not about formal presentations, but about listening to experiences of students with refugee backgrounds that have accessed Higher Education using the HEAP programme and co-creating solutions with Expert Panelists.
Highlighting the persistent disparities in refugee participation in higher education, Dr. Nambi explained that while global and national efforts often focus on primary and secondary education, higher education remains critically under-supported. Drawing on years of research, she observed that refugee participation in higher education has historically stood at three percent (3%), later improving to about seven percent (7%), leaving the highest number of refugees excluded.
“Where do they go if they do not transition to higher education?” she asked. “Who supports them and how do institutions respond when learners arrive with disrupted educational trajectories?”
Shift from mere documentation of marginalization and adversity to practical interventions
Dr. Nambi underscored the importance of moving beyond research that merely documents marginalizationa and adversity. She advocated for practical interventions that improve systems for people with refugee backgrounds and strengthening education for host communities. “Addressing refugee education is part of a broader global agenda shaped by migration, conflict, and labour mobility in several countries.”
Dr. Nambi emphasized that HEAP provides a legitimate pathway for students with refugee backgrounds, and the ongoing adjustments aim to align the program with national standards and student needs.
Central to the discussion was the concept of connected learning, which promotes flexible, blended, and digitally supported education pathways that link learners across institutions, resources, locations, and systems.
Referencing the Makerere University E-Learning Environment (MUELE) as a key enabler of digital and interactive learning between lecturers and students at Makerere University, Dr. Nambi urged other universities to explore such a digital approach to catalyze the delivery of HEAP programmes. She noted that connected education is not solely about technology, but about harmonization, recognition, and collaboration among universities and regulators.
Comparing public and private universities, Dr. Nambi observed that private universities often have more flexible access pathways, and urged that documentation of students’ experiences of HEAP is critical to understanding gaps in provision, delivery and support
“Much of our work has involved examining how Makerere University and other universities are handling access for vulnerable students. We want to document lived experiences, analyze what is working and what is not, and generate evidence that can inform policy and institutional practice,” Dr. Nambi explained.
HEAP Emerging Challenges, lived experiences and future
Moderating one of the key sessions, Dr. Rovincer Najjuma, the Principal Investigator and a Lecturer in Digital Education and the Global South at the University of Edinburgh, guided participants through delphi workshop activities; these included engaging panelists in articulating expectations, uncertainities and risks, and developing future scenarios for HEAP accreditation, diversification of delivery and support and connected education.

Using participatory methods, participants shared insights through post-it notes and group reflections, capturing perspectives from expert panelists, HEI administrators, and students with refugee backgrounds. Dr. Najjuma encouraged an open dialogue, ensuring that student voices, particularly those with refugee backgrounds were centred in the conversation by encouraging them to share their experiences and journeys of participating in HEAP programmes.
The panelists acknowledged that while the HEAC has changed the nomenclature from HEAC to HEAP, programmatic provisions need to evolve, to address the inconsistencies that remain with respect to how institutions implement HEAP, duration, curriculum, and transfer of HEAP credit across institutions. Panelists shared about the critical gaps in awareness, mentorship, orientation, and institutional readiness to implement HEAP in ways that support refugee learners effectively.
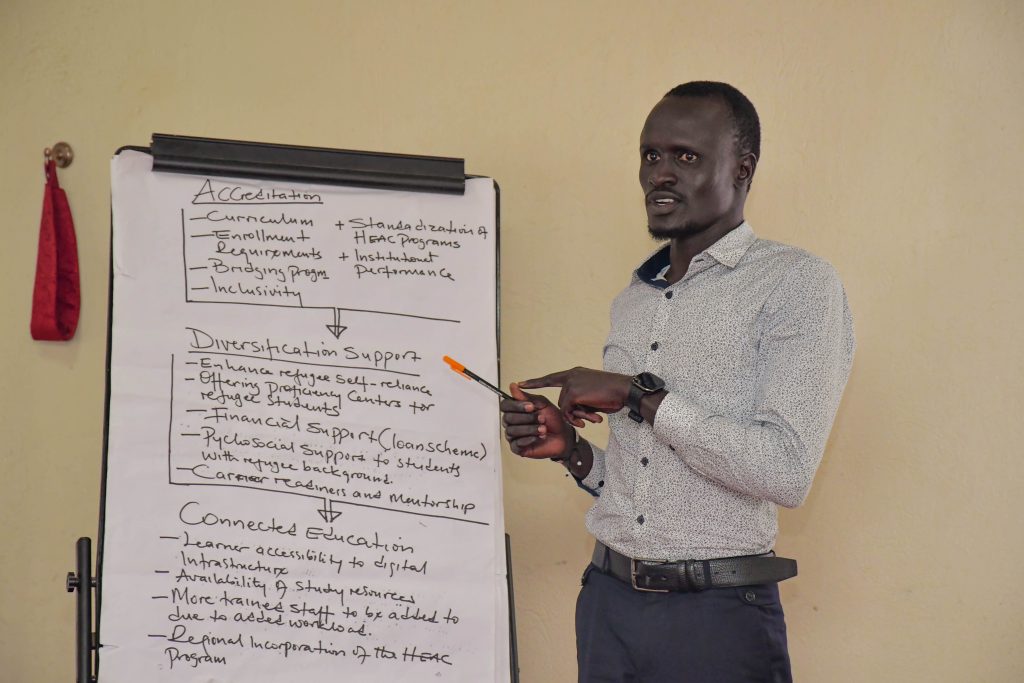

On the issues faced by students with refugee status, participants identified several recurring challenges affecting access to and participation in higher education. These included low awareness of the HEAP programmes, fragmented and uncoordinated information dissemination, and difficulties in credential recognition and transfer across institutions and country host-country education systems.
Students highlighted low self-esteem, identity struggles, and stigma, especially where access programmes are perceived as inferior to Advanced High School Certificates. They also cited financial barriers, limited digital access, mental health challenges, and lack of learner-centred teaching approaches.
Key outcomes from the workshop
Panelists outlined key expectations to strengthen access and participation, which included the development of a standardized national HEAP curriculum, with clear and uniform entry requirements, and seamless credit transfer across institutions and host countries, facilitated by the development of HEAP Digital Passport.
Mentorship emerged as a cornerstone of learner support, alongside extended orientation programmes, life skills training, and entrepreneurial education. Participants emphasized the need for blended and online learning, supported by affordable internet access and institutional investment in digital infrastructure.
Policy coherence, stakeholder engagement in policy formulation, and timely communication of reforms were identified as essential for successful implementation. Participants called for gender-sensitive curricula, student representation structures, humane and trauma-informed teaching staff, and adequate learning resources, including reference materials.
HEAP: A Structured Pathway to Higher Education
Dr. Gidraf Joseph Wanjala, Principal of the College of Education, Open and Distance Learning at Kampala International University, highlighted the evolution of access programs in Uganda.
“Historically, the higher education access framework was known as the Higher Education Access Certificate (HEAC). Last year, it was updated to the Higher Education Access Program (HEAP), reflecting a shift from a certificate to a full program, approved by the Ministry of Education and Sports,” Dr. Wanjala said.

He explained that HEAP provides structured pathways for students to progress from diploma to bachelor degree levels, from mature entry to degree programs, and from senior secondary school to higher education. “This program is inclusive of refugee students and all marginalized groups, provided there is funding and space. HEAP supports students not just academically, but also through orientation programs, mental health training, reproductive health education, and gender-responsive support,” Dr Wanjala stated.
Challenging Misconceptions
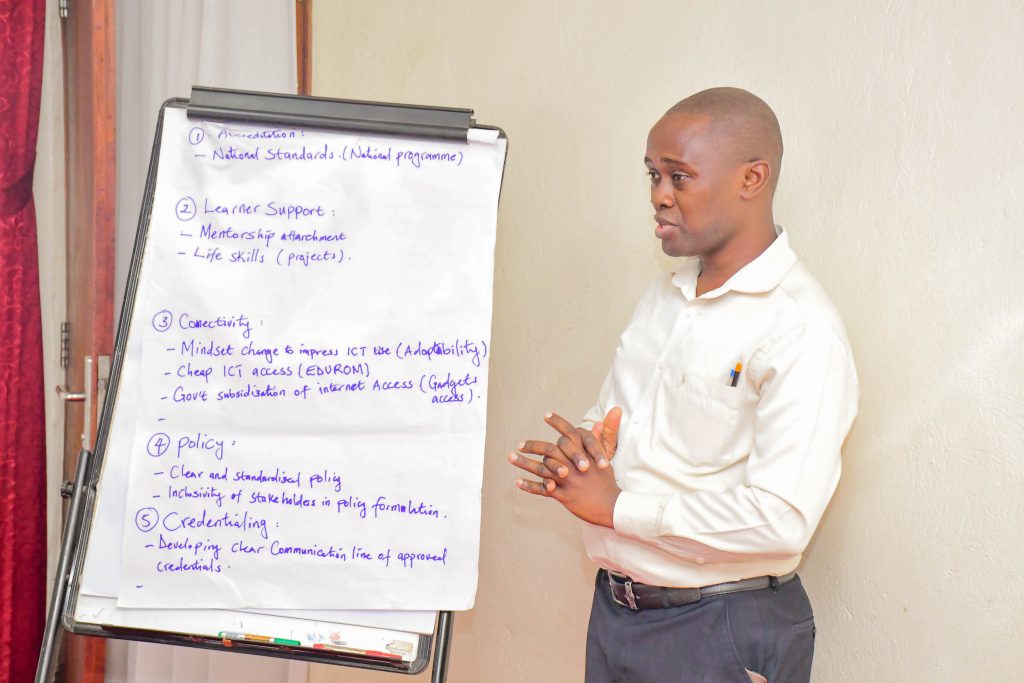

Dr. Derrick Ssekajugo, Chair of the Special Purpose Committee on Academics and Acting Principal of the College of Economics and Management at Kampala International University, addressed public misconceptions about HEAP.
“Some perceive HEAP—or previously HEAC—as only for students who could not succeed in secondary school. That is not the case. For instance, we have students who initially studied Education but through HEAP transitioned into medicine. Today, they are fully qualified professionals,” Dr. Ssekajugo said.
He also highlighted the pedagogical shift from teacher-centred to learner-centred approaches in secondary education and the need for universities to adapt. “Students entering HEAP come with diverse learning experiences, and universities must adjust to integrate them effectively into competency-based programs,” he noted.
Dr. Ssekajugo added that benchmarking with both local and international institutions is critical to identify gaps and best practices, which inform ongoing program improvements and policy reforms.
HEAP and standardization, accessibility and inclusivity
Sharing their vision for HEAP, panelists recommended standardization, accessibility, inclusivity and foundational nature of HEAP. They advocated for a competence-based HEAP, with a standardized curriculum, offline and online access to resource books and materials, diversification of delivery and support through blended learning and a HEAP Digital Passport for portability and verification on demand.
Education
Real life project: Makerere University Vice Chancellor hands over constructed Wall Fence to Makerere College School
Published
3 months agoon
November 13, 2025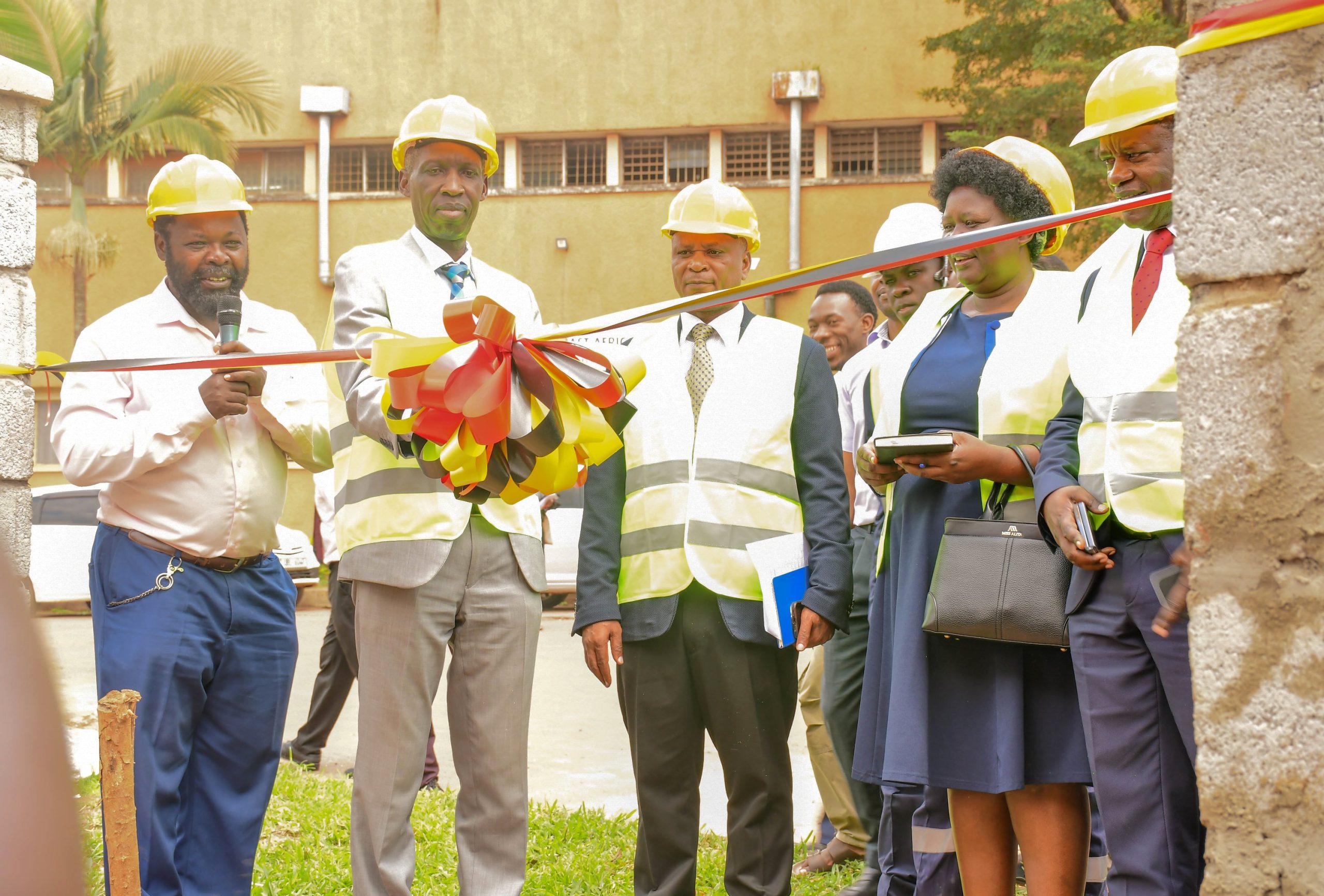
By Ritah Namisango and Harriet Musinguzi
On 12th November 2025, Makerere University officially handed over a newly constructed wall fence to Makerere College School. The real-life project was executed by technical students pursuing higher diploma courses in Civil Engineering and Architecture under the Uganda Vocational and Technical Assessment Board (UVTAB). The students are enrolled at the Centre for Lifelong Learning and Teaching, which operates within the College of Education and External Studies (CEES) at Makerere University.
The Centre for Lifelong Learning, in partnership with UVTAB, is involved in implementing real life projects within the communities-a practical approach that ensures that students identify problems within the community, hold collaborative discussions, and come up with projects to solve the problems.
The handover ceremony of the newly constructed Wall Fence was witnessed by key stakeholders that included officials from UVTAB, the College of Education and External Studies (CEES), the College of Engineering, Design, Art and Technology (CEDAT), the leadership of Makerere College School, UVTAB Deputy Executive Secretary and the technical students pursuing the higher diploma in Architecture and Civil Engineering.

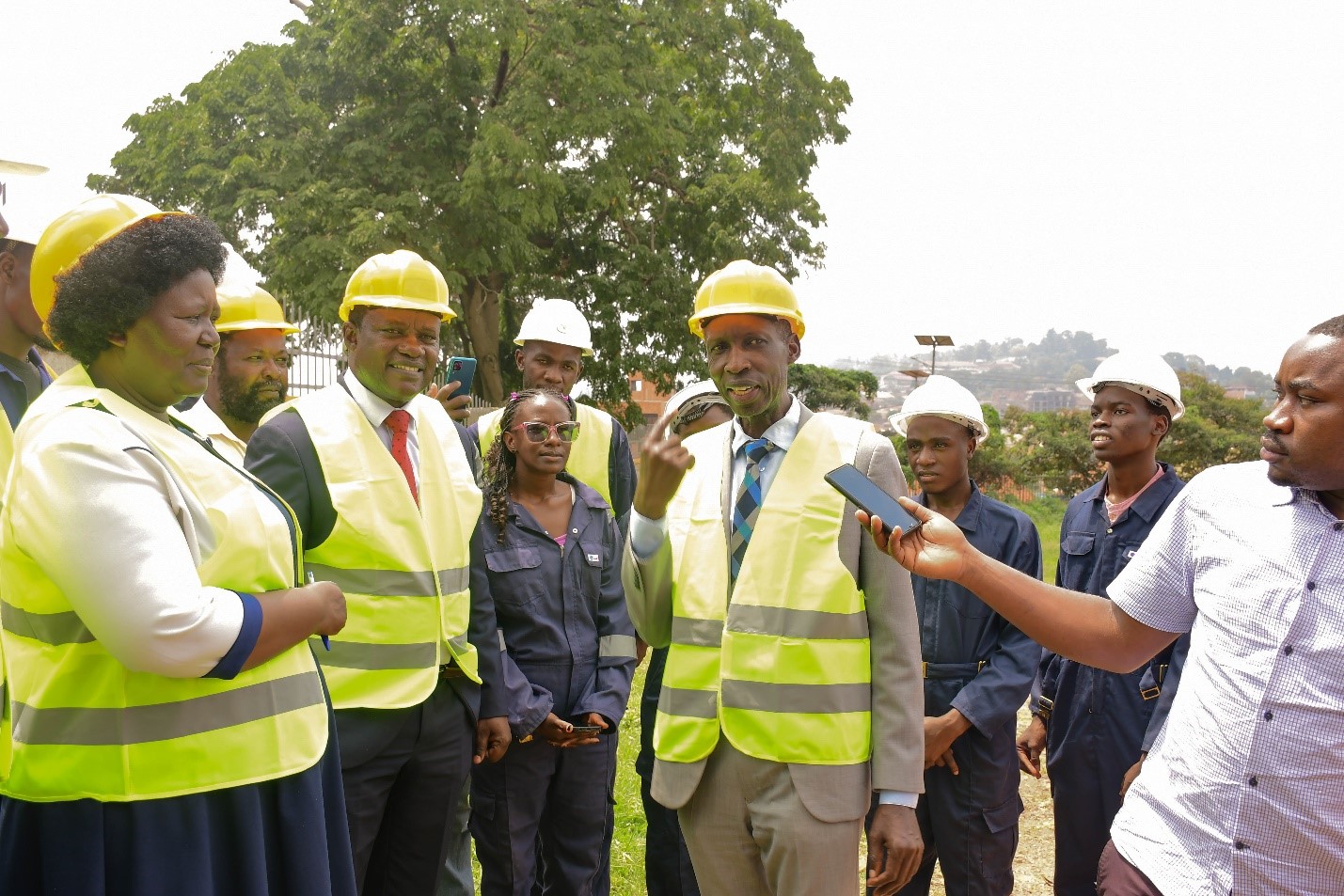
The Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe, represented by the Principal of the College of Education and External Studies, Prof. Anthony M. Mugagga, expressed heartfelt gratitude to Dr. Martin Muyingo, Head Teacher of Makerere College School, for providing a valuable learning space to students under the lifelong learning and teaching program. He acknowledged Prof. Dorothy Okello-Chairperson of the Uganda Vocational and Technical Assessment Board (UVTAB), Prof. Moses Musinguzi-Principal of CEDAT, course instructors, and students for their commendable contributions. He noted that the newly constructed wall stands as a testament to the power of lifelong learning and practical teaching.
The Vice Chancellor commended the management and staff of the College of Education and External Studies (CEES) for implementing programmes through the Centre of Lifelong learning, which are aligned to the Makerere University’s Strategic Plan. He observed that the partnership with UVTAB increases the number of students accessing quality education services, enhances lifelong learning, promotes practical education, and contributes to community transformation.

Congratulating the technical students upon this milestone, and in solidarity, the Vice Chancellor wrote: “I am an architect and courses in my profession go deep to my heart. Congratulations to the students, the engineers, and course instructors.”
Prof. Nawangwe emphasized the importance of architecture-related courses and praised Makerere’s longstanding commitment to student-centered learning, innovation, and thought leadership principles that have guided the university for over two decades. He highlighted that Makerere’s strategic direction aligns with Uganda’s National Development Plan IV and Vision 2040, which advocates for inclusive, equitable, and lifelong education. This vision, he said, reflects the aspirations of His Excellency President Yoweri Kaguta Museveni and the Government of Uganda’s education agenda.
He explained that the Centre for Lifelong Learning (CLL) at CEES, serves as a bridge between the university and the community. It offers opportunities to Ugandan youth and individuals who lack the financial means or academic qualifications to access Makerere’s mainstream programs, to join UVTAB technical education programmes, with instructors at Makerere University Centre for Lifelong Learning. Students enrolled in the program typically come from A-level backgrounds or hold certificates from technical institutions.
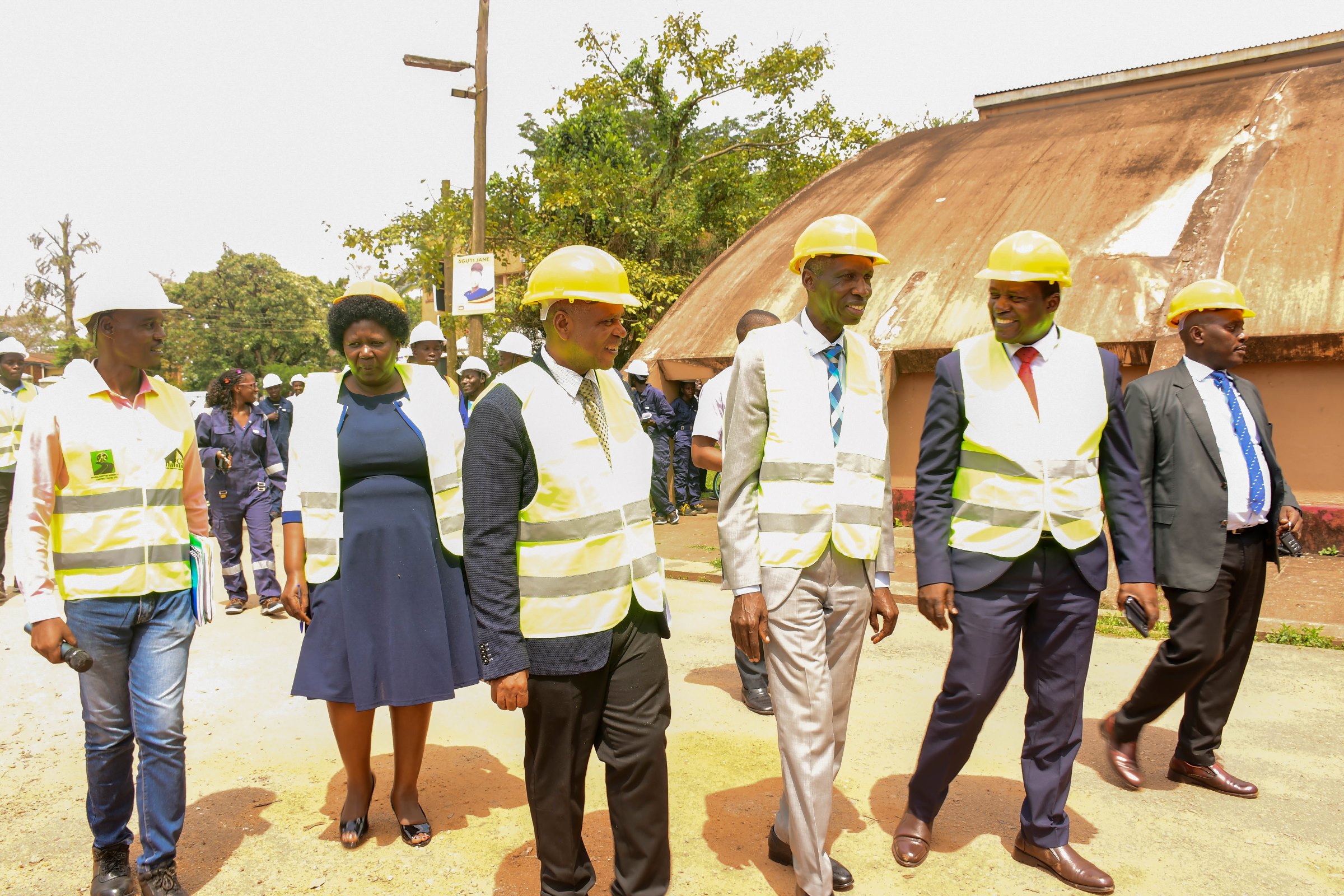

He highlighted that long before the Government of Uganda, through the Ministry of Education and Sports, restructured the secondary school curriculum to embrace competence-based teaching and learning, Makerere University had already been championing student-centered education. For over two decades, the university has promoted innovation, experiential learning, and thought leadership.
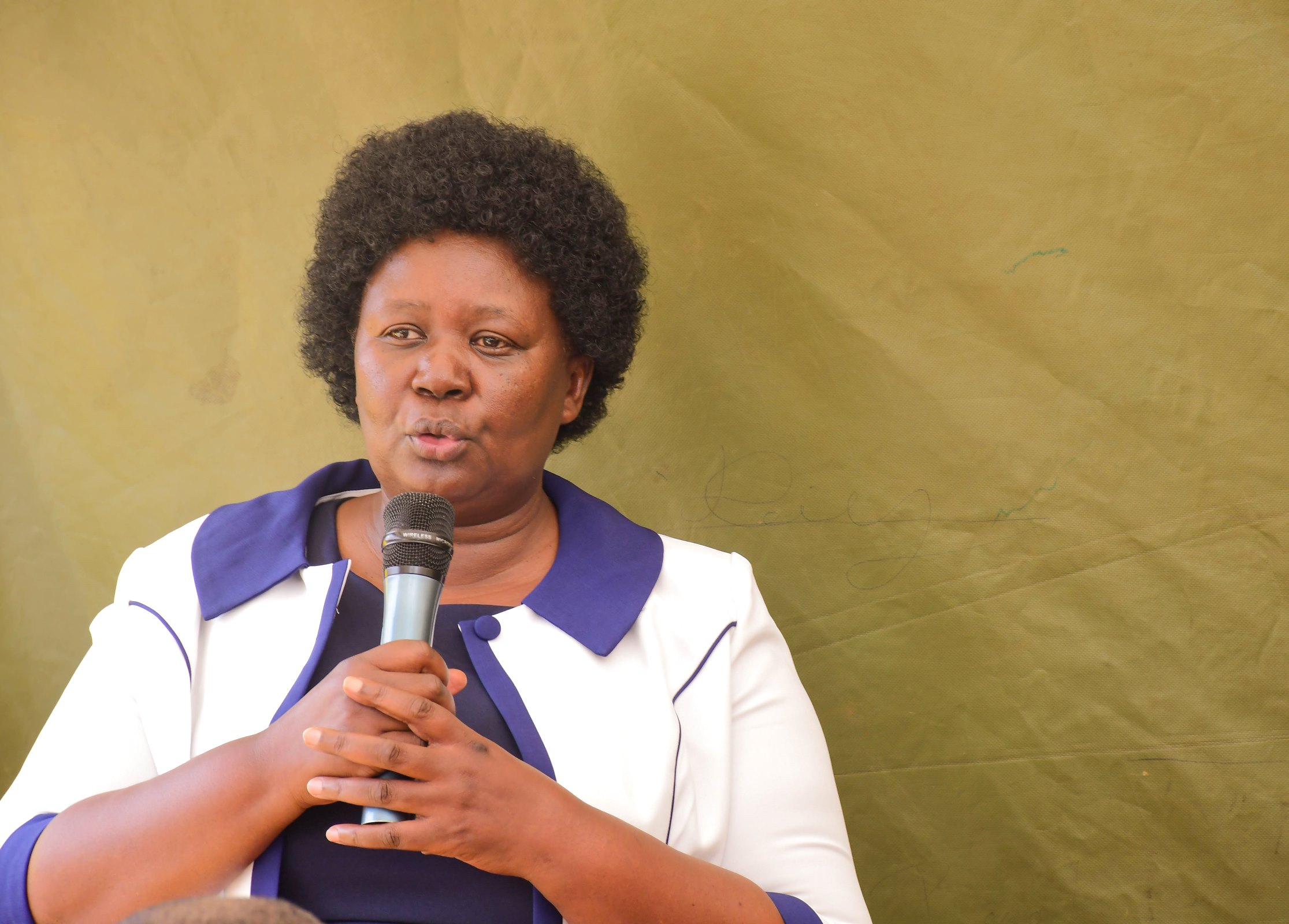

Ms. Jalia Nassaza, the Acting Deputy Executive Secretary of the Uganda Vocational and Technical Assessment Board (UVTAB), emphasized the importance of real-life projects within the Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) curriculum. She explained that these projects enable students to identify community challenges, engage in collaborative discussions, and develop practical solutions ultimately shaping them into holistic professionals. Through this approach, learners gain essential skills in planning, teamwork, and applying theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios. Ms. Nassaza emphasized the need for an education system in Uganda that equips students to solve local problems and improve their surroundings. “We want to make our education realistic by translating knowledge into solving problems,” she affirmed.
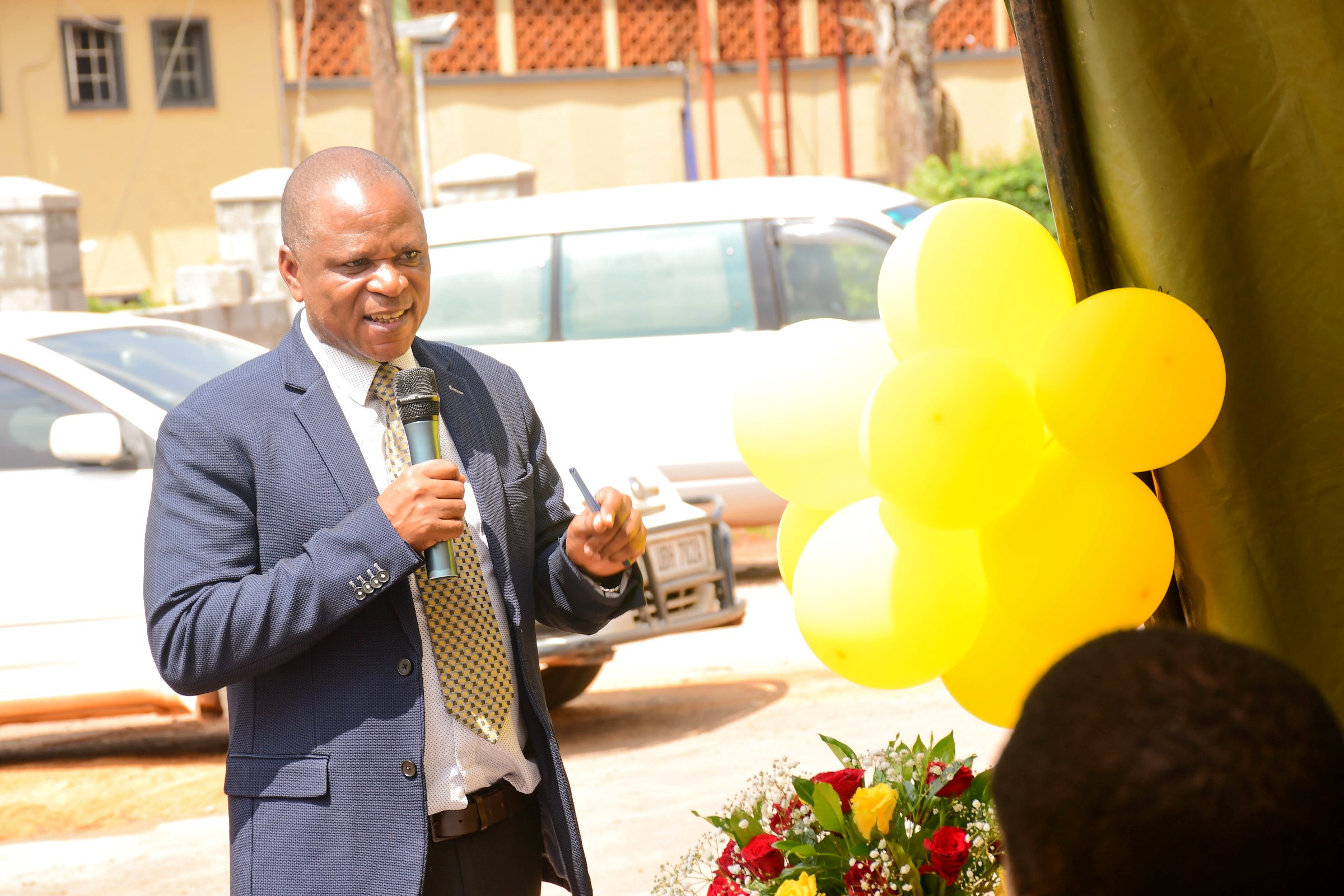

The Principal of the College of Engineering, Design, Art and Technology, Prof. Moses Musinguzi while congratulating the students upon the completed wall fence structure and other projects, noted that as professionals, scientists get a lot of public criticism because they are the core of providing solutions to societal problems. He said the commissioning of the fence was testimony that the university in partnership with UVTAB, was teaching students ways of solving problems around them. He said that as a college, CEDAT provides access to the required infrastructure in the labs, workshops, and studios, as well as technicians who support the teaching.
Prof. Musinguzi said Makerere University was considering a revision of the assessment, making continuous assessment total to 60%, while classwork is rated at 40%. He also mentioned the CEDAT model, whereby the university was considering utilizing students in technical subjects to support the Estates and Works Department in infrastructural maintenance and service works instead of hiring externally, and that students on both Diploma and Degree programs would be engaged. ‘We need to see scientists directly engaged in the development of the country,’ he emphasized.
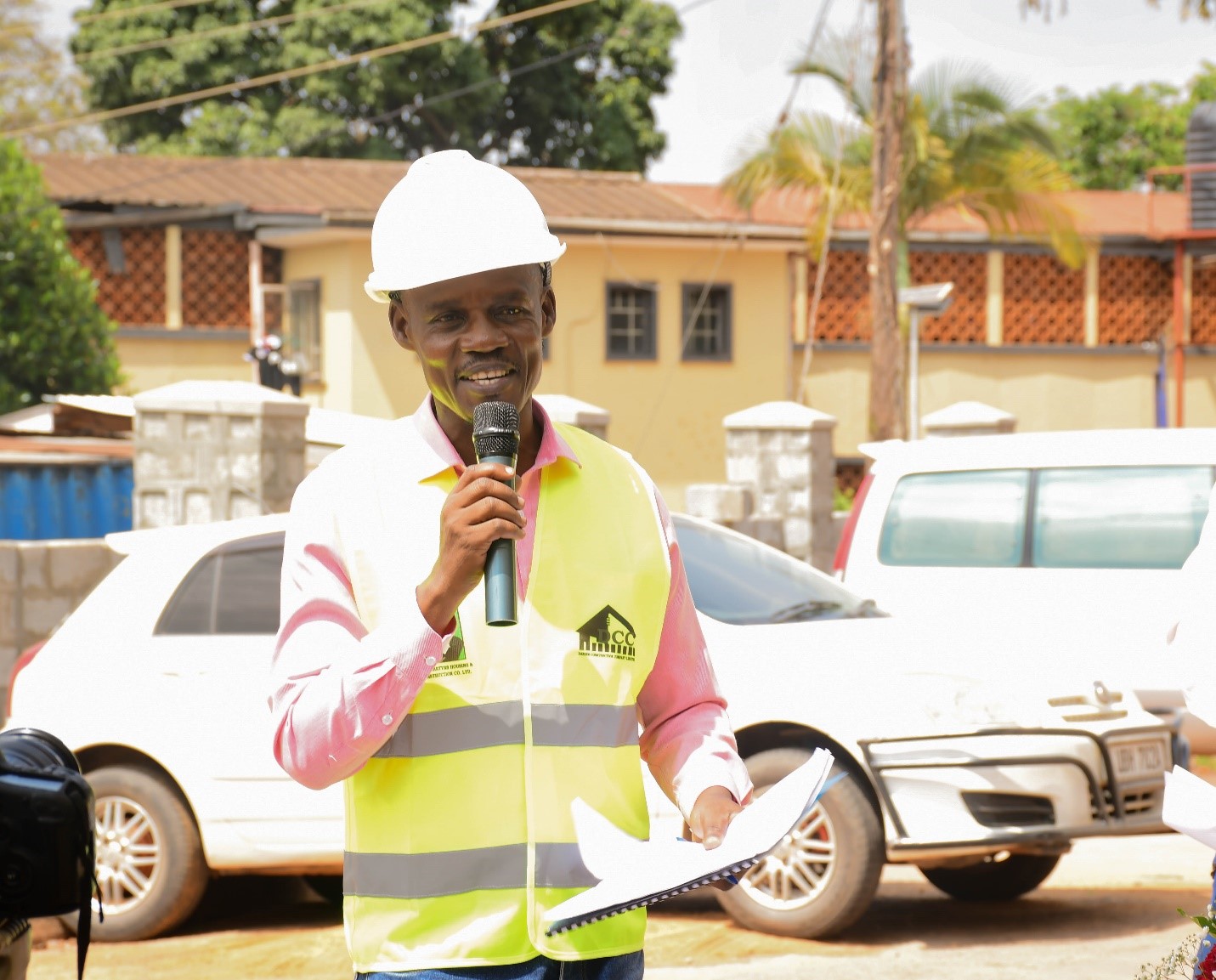

Speaking on behalf of the instructors, Mr. Barnabas Mabonga highlighted some of the students’ requirements that included the need for basic tools, providing opportunities for their academic progression to degree programs, and strengthening the safety measures. Some of the actual projects that the AVTAB technical students under CEES and CEDAT have worked on at Makerere College School include: a yard constructed at the boys’ hostel, the wall fence, and a drainage system. He said 173 students out of whom 28 are girls, were enrolled in the Civil Engineering and Architecture higher diploma program. He informed the Vice Chancellor and other guests present that the students in the real-life learning and teaching programs were excelling in performance, with a pass rate of 99%.
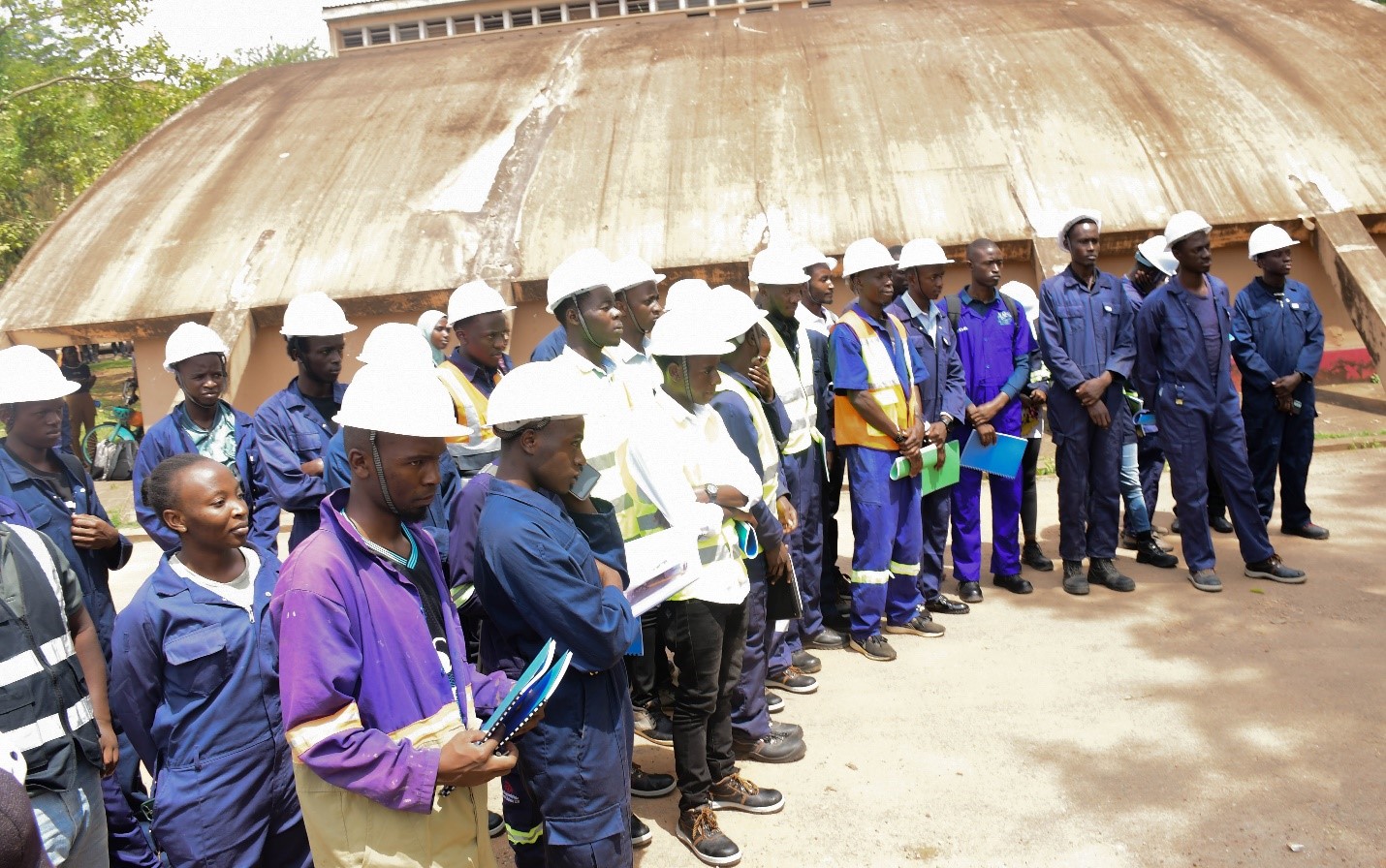

Dr. Oscar Mugula, Coordinator of the Centre for Lifelong Learning, emphasized the value of community engagement in their academic programs. He noted that the partnership with Makerere College School began two years ago, when students from the center undertook repair works on the school’s infrastructure. The collaboration has proven mutually beneficial, with the beneficiary school experiencing reduced development costs, while students, particularly those studying technical drawing, gained hands-on experience through the perimeter wall project, which contributed to their coursework and project assessments for the year.
In partnership with UVTAB, the Centre for Lifelong Learning offers diploma courses in Civil Engineering, Architecture, and Electrical Engineering. The students pursuing these courses are examined and accredited by UVTAB. Students benefit from experiential learning at CEDAT, where they are encouraged to innovate using affordable, locally sourced materials. They are also placed in real-world workstations and garages to observe best practices and avoid unethical conduct. Graduates of the program either join the workforce or continue their academic journey at the university.

The Center for Lifelong Learning at CEES is charged with the duty to take the university to the community, providing opportunities to Uganda’s youth and persons interested in technical education, who may not have the requisite funds or grades to join the university’s degree programmes. The students on the program are either directly from A-level or other technical institutions.
Education
Digital Education: CEES holds stakeholders’ workshop to inform curricula for Postgraduate Diploma in Education (Online Track)
Published
4 months agoon
November 7, 2025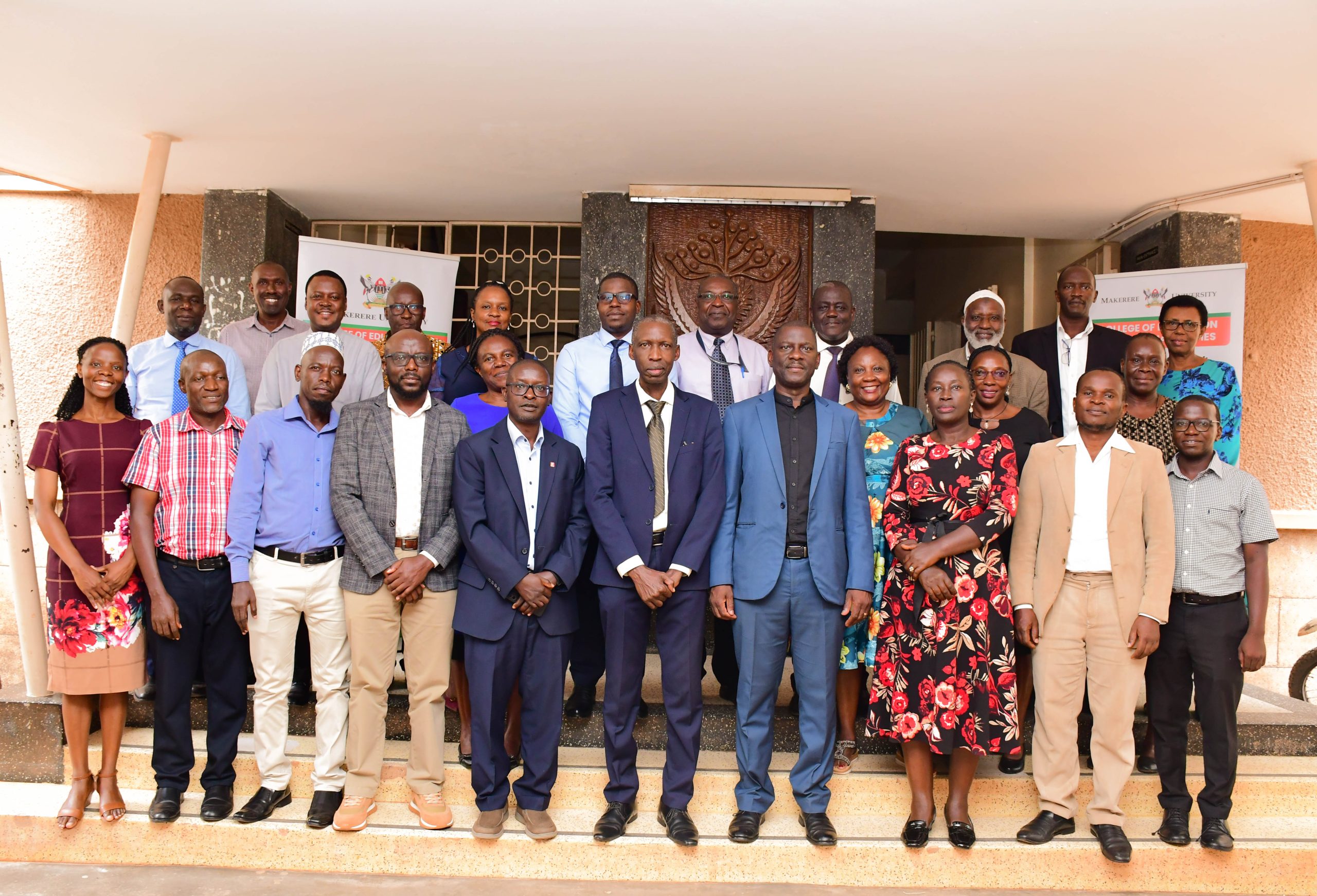
November, 4th 2025: Makerere University through the College of Education and External Studies, has been offering the Postgraduate Diploma in Education (PGDE) following the face-to-face delivery model.
In addition, to the physically taught Postgraduate Diploma in Education, the College of Education and External Studies, embarked on a process of curriculum development, for the online delivery model (PGDE-online).
This strategic option presents learners with a choice to either enroll for the physically taught (face to face) or the online Postgraduate Diploma in Education.
The introduction of the online mode of delivery for the Postgraduate Diploma in Education was informed by wide consultations, which revealed that many working adults including teachers, and distant learners, who wished to study the programme, were unable to attend. Engagements with such prospective applicants, called for the online delivery option.
To address this challenge, in March 2024, the College of Education and External Studies, embarked on developing the curriculum for the online option. The PGDE (online track) will be delivered on the Makerere University eLearning Environment (MUELE).
According to staff at the College of Education and External Studies, the online delivery model will enable learners to study remotely while acquiring modern pedagogical and digital skills essential for the 21st century education.
College hosts Stakeholders’ workshop to enrich curricula for the online delivery option:
On 4th November 2025, the College of Education and External Studies hosted a stakeholders’ workshop to enrich the curriculum document.
The workshop brought on board various stakeholders, including representatives from the Ministry of Education and Sports (MoES), the National Curriculum Development Centre (NCDC), the Department of the Academic Registrar, Directorate of Graduate Training, former students of the College who studied the Postgraduate Diploma in Education (face-to-face), staff from other units within Makerere University, and representatives from other education institutions including Ndejje University, Uganda Christian University-Mukono, and Uganda Martyrs’ University-Nkozi.
Remarks by the Head of Department:
Welcoming the participants, Dr. Genza Gyaviira Musoke, the Head of the Department of Foundations and Curriculum Studies thanked the stakeholders for accepting to dedicate time, to participate in the workshop. He called upon the stakeholders to suggest strategies aimed at ensuring that the PGDE delivered though the face-to-face model blends and complements the proposed online track.
College Principal emphasizes digital pedagogies:
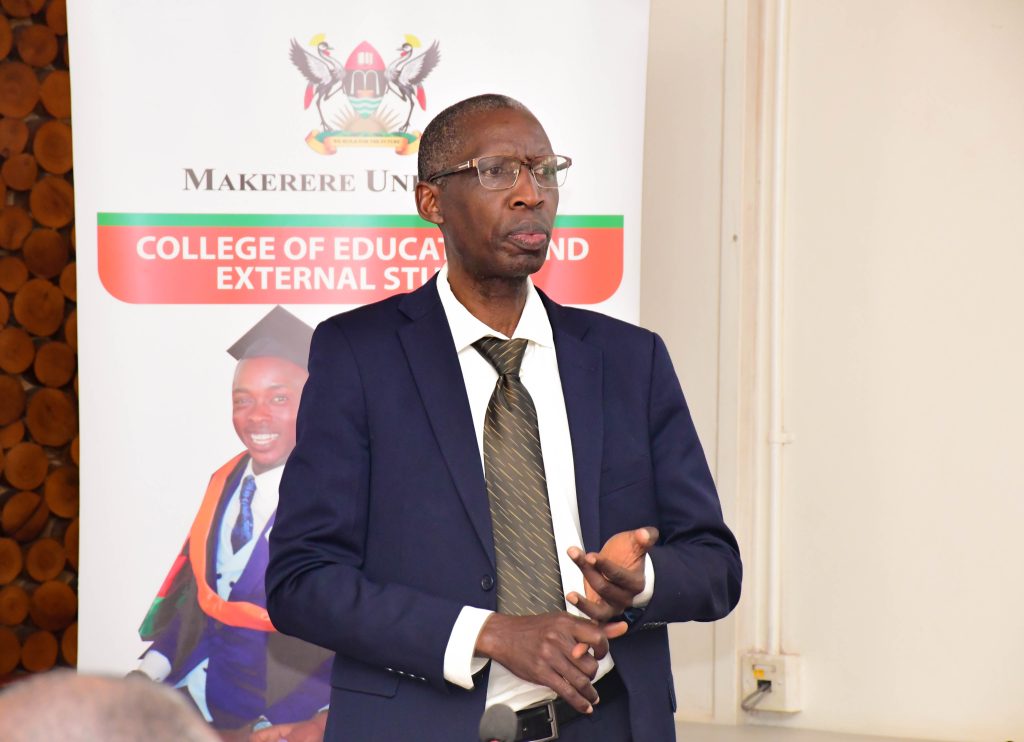

The Principal, notified the stakeholders, that the College of Education and External Studies through the Institute of Open, Distance and e-Learning (IODeL), is credited for the operationalization of the Makerere University e-Learning platform (MUELE), which enabled online teaching and learning during the CoVID-19 pandemic.
Impressed by this milestone, the Vice Chancellor-Professor Barnabas Nawangwe, tasked the College of Education and External Studies, to come up with innovative teaching and learning pedagogies.
On this note, Professor Mugagga applauded the Department of Foundation and Curriculum Studies and the School of Education, for responding to the call from the Vice Chancellor, which has led to the development of the curriculum for the online delivery of the Postgraduate Diploma in Education (PGDE-online).
Emphasizing the trends in the education sector, he highlighted the technological demands presented by the Competence based curriculum (CBC), the National Teacher Policy of 2019, the Ministry of Education and Sports requirements for all teachers to be degree holders, and the need to embrace artificial intelligence (AI). He stressed that these reforms require teachers who are grounded in digital/online pedagogies, to nurture, teach and mentor, the next generation of students and teachers.
Presentation from the Director of Open, Distance and e-Learning:

Professor Paul Birevu Muyinda, underscored that the development of the online delivery of programs fits within the digital strategy for Uganda, launched by the Ministry of Education and Sports (MoES) in August 2024.
In line with the Ministry’s vision of increasing access to education, through the online delivery of the Postgraduate Diploma in Education, Makerere University is extending access to quality education services.
Professor Muyinda noted that the online delivery option, is aligned to the digital transformation agenda of the University, which is stipulated in the University’s Strategic Plan.
He acknowledged the Chairperson of the Committee, Dr. Harriet Najjemba, and her team for the valuable work, which has led to the draft curriculum, that the stakeholders had convened to discuss.
Opening the Stakeholders’ Workshop:

The Deputy Vice Chancellor (Academic Affairs), Professor Sarah Ssali, represented by Dr. Julius Kikooma, the Director of Graduate Training, commended the College of Education and External Studies, for the timely intervention, that will enable students to access quality education online. Noting that the evolution of academic programmes is within her mandate, Professor Ssali thanked the College for bringing on board various stakeholders, to provide valuable ideas.
Presentation of the proposed curriculum for the PGDE (online):

Presenting the proposed curriculum, Dr. Alfred Buluma from the School of Education highlighted the comprehensive design, online teaching and learning infrastructure for programme delivery, programme objectives and outcomes, core course units and electives, employment prospects, as well as, the availability of competent and technologically grounded staff to deliver the programme.
Dr. Buluma explained that the Postgraduate Diploma in Education (online) shall be a blended programme, heavily online, and with limited face-to-face interactions. He emphasized that Makerere University possesses adequate resources and infrastructure to support the program.
He acknowledged the involvement of staff from multiple departments: Humanities and Higher Education, Science and Technical Education, and Foundations and Curriculum Studies, alongside e-learning support staff.
Input from internal stakeholders:
Principal of the College:
Professor Anthony Muwagga Mugagga submitted that the proposed curriculum should embrace the ethical use of artificial intelligence (AI) in teaching and learning. He urged the participants to critically think about the delivery of experiments and practical classes online.
Reflecting on the remote areas in Uganda, where citizens do not have access to electricity and Internet, Professor Mugagga challenged the stakeholders, to bear in mind, the issue of inclusive education, and the possibility of delivery of online education, to teachers and students in such areas.
Directorate of Graduate Training:
Associate Professor Julius Kikooma, guided that the programme should strengthen the research capabilities of students/learners. He explained that the programme should provide a linkage to the research priorities stated in the Makerere University research agenda, as well as, the National Development Plan (NDPIV). As the team designs the curriculum, he encouraged them to study the University Senate guidelines document. He advised the team to include the knowledge areas, and learning outcomes. Citing the Graduate Students Handbook, Associate Professor Kikooma stressed the section on quality assurance that highlights the following competence areas: disciplinary knowledge, transferable skills, professional, and research competences.
Department of the Academic Registrar:
Stating its responsibility, the Senior Assistant Academic Registrar-Ms. Enid Kemari, who represented the Academic Registrar-Professor Buyinza Mukadasi, explained that the Department ensures that the proposed curriculum meets the standards set by the University and the National Council for Higher Education.
She referenced the Makerere University Policy on Open, Distance, and E-Learning, highlighting its main objective of increasing access to higher education through flexible learning modes. Ms. emphasized several key policy areas critical to the new online teacher education programme.
She commended the School of Education for aligning its program with national and institutional policies, noting that it will enable teachers, especially those already employed, to upgrade their qualifications without leaving their jobs. “It will contribute significantly to improving education quality in Uganda,” she said.
Plenary Session involving external stakeholders:

The plenary session provided the following recommendations.
- The online delivery should encompass the 21st century education expectations and demands of a learner and teacher.
- In addition, to increasing access to quality education, the curriculum document under the section “justification of the programme” should state the new areas in the education field, and the changed context under which teachers are operating.
- It should emphasize using the Makerere University e-Learning Environment (MUELE) in both teaching and learning.
- The curriculum should focus on developing the skills of learners (not only as those being taught), but also being empowered as learners to teach using the online delivery.
- There is need for retooling courses for both the teachers and learners as well as engagements on using artificial intelligence (AI) ethically.
Way forward:
Dr. Genza Gyaviira Musoke, highlighted that the input from stakeholders would be incorporated into the proposed curriculum. He briefed the participants that the proposed curriculum would be presented to the School of Education Academic Board, the College of Education and External Studies Academic Board, the University Senate and Council, and to the National Council for Higher Education.
Trending
-

 Humanities & Social Sciences2 days ago
Humanities & Social Sciences2 days agoMeet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-

 Health6 days ago
Health6 days agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 Agriculture & Environment5 days ago
Agriculture & Environment5 days agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoCall for Applications: Short Course in Molecular Diagnostics March 2026
