Health
Study to Address the Social drivers of Mental Illness Launched in Uganda by Kennesaw State University & Makerere University
Published
3 years agoon
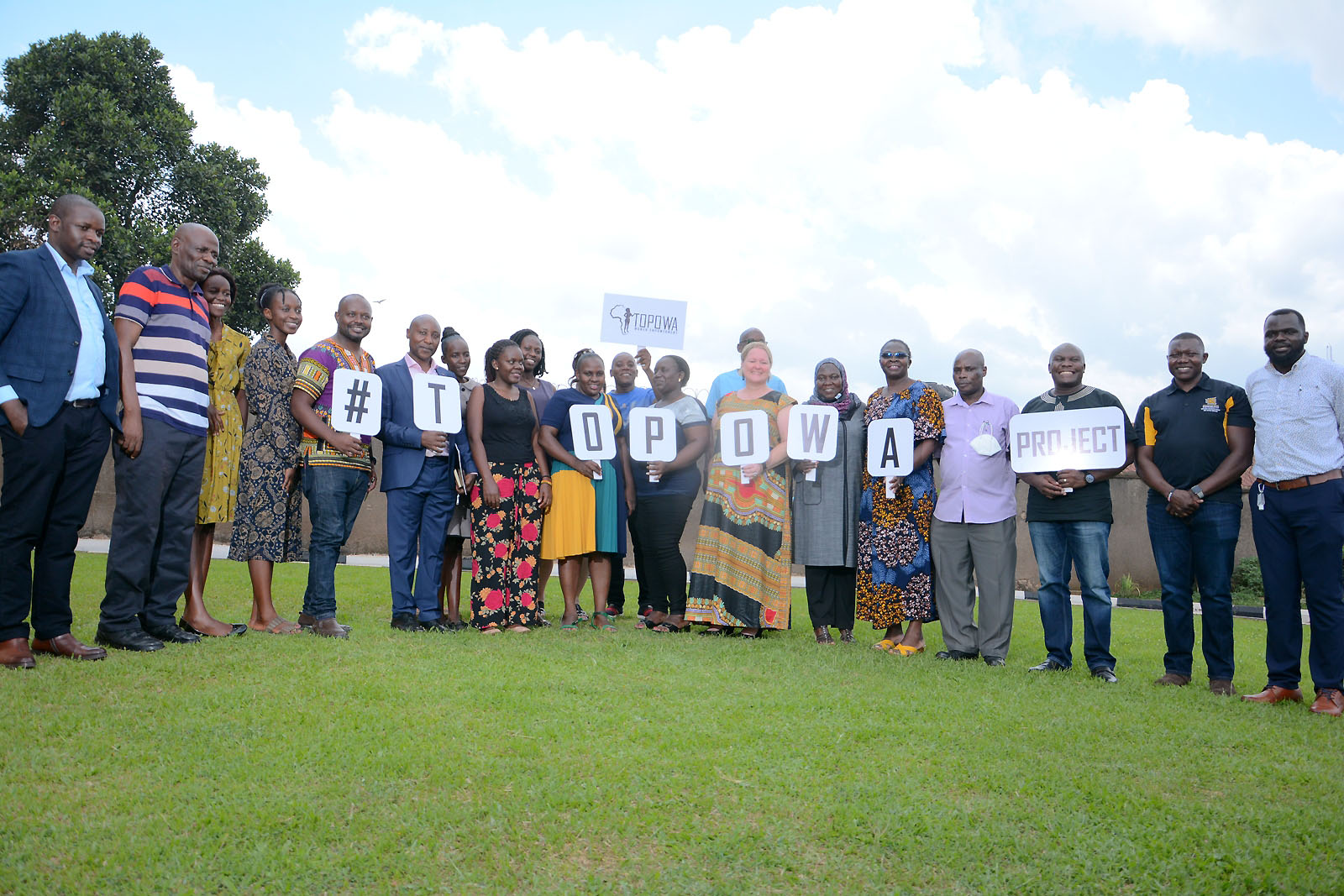
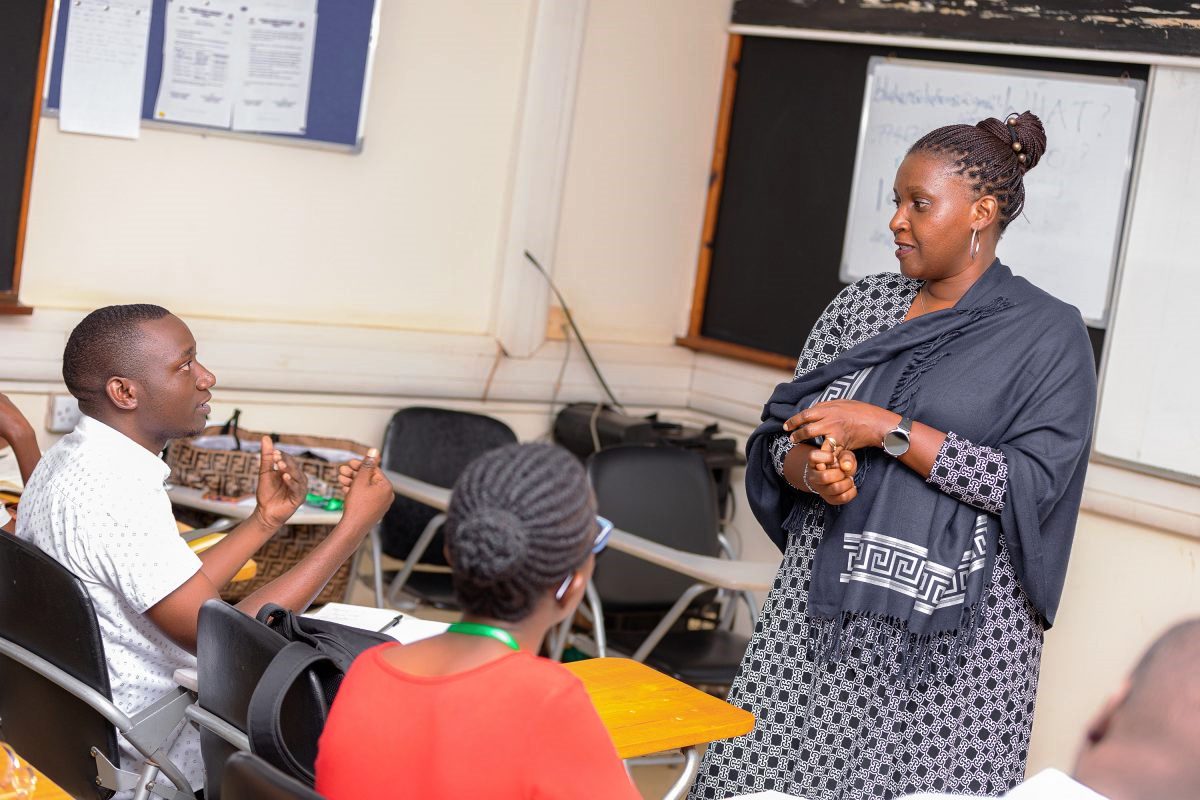
A new 5-year study has been announced to determine the link between social drivers and mental health among young women who live in the slums of Kampala in Uganda. Kennesaw State University (KSU) received the five-year $3.3 million award from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and has partnered with Makerere University to conduct this interdisciplinary project.
Mental illnesses are understudied, and scarce services lack evaluations, particularly in low-resource settings such as slums. In response to the vulnerable state of adolescent girls and young women in the urban slums, the team of researchers are implementing this five-year project named “TOPOWA” (The Onward Project On Well-being and Adversity), which means to “keep pushing forward and never giving up”, in the Luganda language.
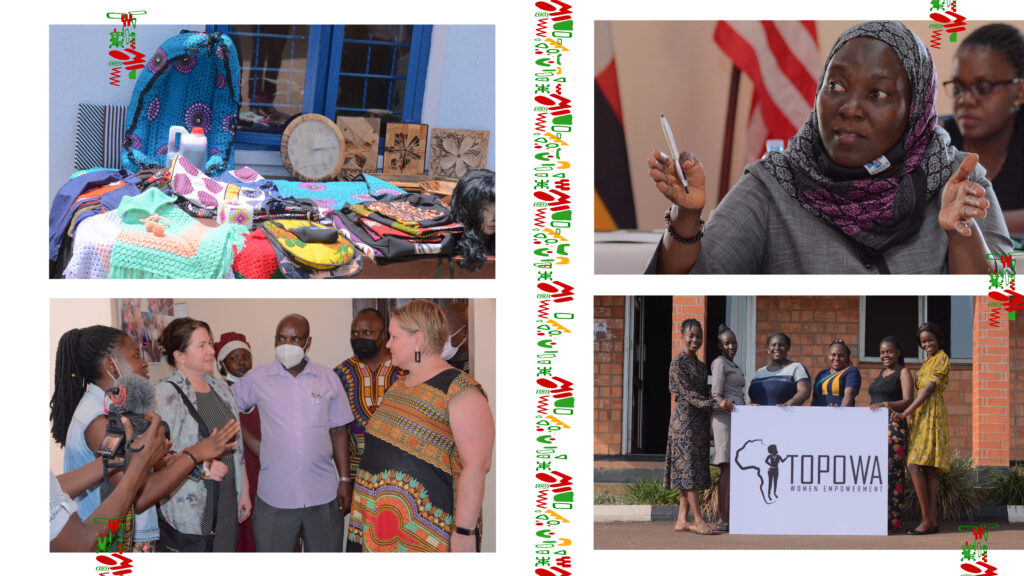
Makerere University through the School of Public Health is teaming up with two U.S universities, Kennesaw State University (KSU) and Georgia State University (GSU) in the U.S. to implement the research component of the study. The Uganda Youth Development Link (UYDEL), a community-based organization in Kampala will lead the intervention components.
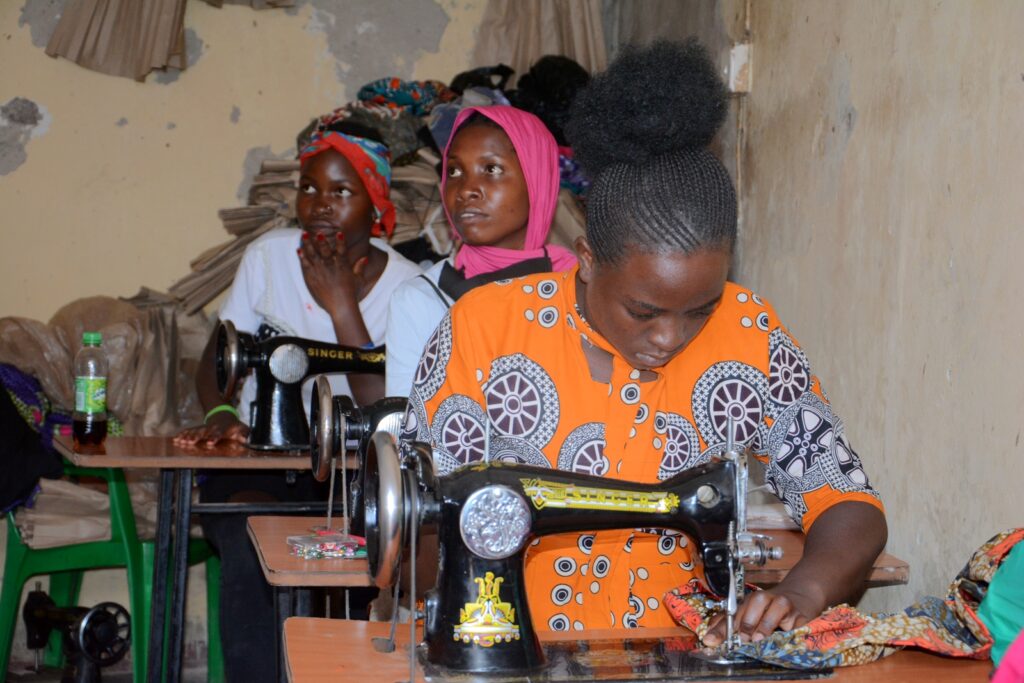

First of its kind, “the TOPOWA project will examine if a community-based intervention program comprised of vocational training, entrepreneurship and economic empowerment, team building through sports, and psychosocial support (“Socioeconomic Strengthening Targeted Training: “SeSTT”). leads to better mental health outcomes among disadvantaged women living in slums” said Dr. Monica Swahn, the Principal Investigator of the study.
The TOPOWA research project will focus on young women ages 18-24 years, the age period when most mental health symptoms are manifested and expressed. If the study shows that the intervention makes a difference in mental health outcomes (i.e., anxiety, depression, suicidality and substance use symptoms and disorders) for young women, it can address the tremendous unmet mental health needs in Uganda. The study will also increase the understanding of the community and neighborhood characteristics of the urban slums where the young women reside.
It was launched on Tuesday March 8, 2022, on International Women’s Day, a global holiday celebrating the social, economic, cultural, and political achievements of women. Speaking at the launch, Dr. Swahn, the Principal Investigator, and also Professor and Dean of the Wellstar College of Health and Human Services at KSU said “TOPOWA was in support of global action to advance gender equality and the empowerment of women and girls”
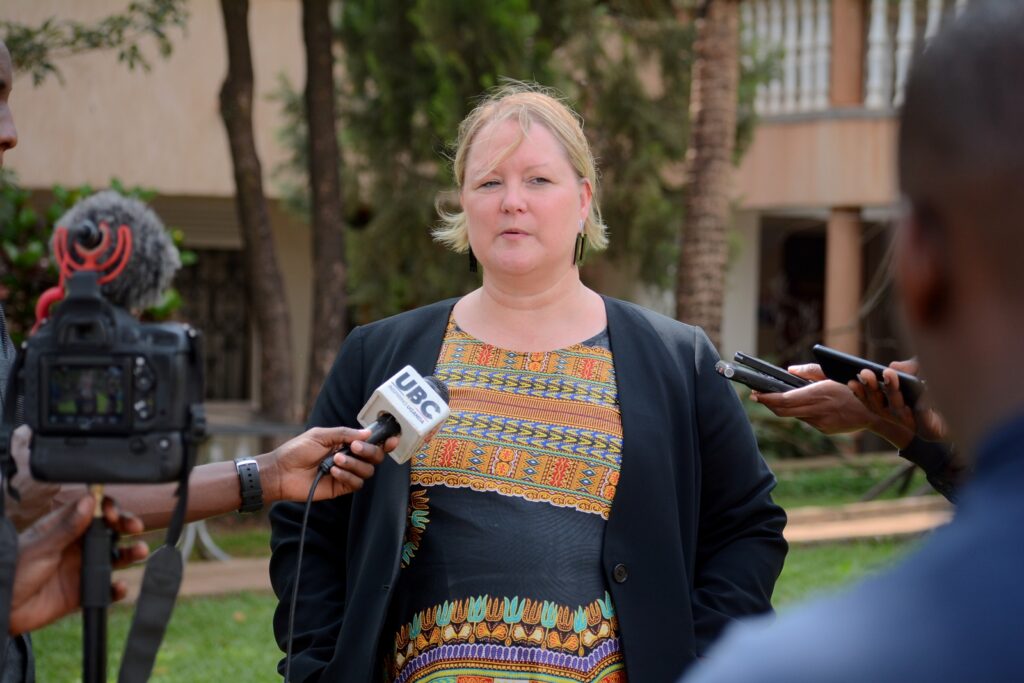

She also noted that this was a ground-breaking study, with investigators representing diverse expertise from three universities.
“Our TOPOWA project is ground-breaking because we look at the social drivers of mental illness and how to mitigate them. We conceived this project before the pandemic, but now with the pandemic, we know more than ever how mental health has been understudied and the growing scope of unmet need in the community,” she said. Dr. Swahn also added that, “We don’t have enough interventions for mental health in particularly among vulnerable populations in low-resource settings. So, what we have learnt post-COVID is that we need to find scalable interventions to better support mental health for women who live in poverty, particularly women who live in slums.”
Using a multicomponent 27-month, parallel prospective cohort design of young women, the study team will recruit 300 participants from three selected UYDEL study sites in Banda, Bwaise and Makindye to determine the pathways and mechanisms of mental health outcomes. The study will involve focus groups, a Photovoice project, community mapping, surveys, use of sleep wearables, saliva and stress reactivity to detect and determine stress levels of the young women.
The investigators will measure stress though threat reactivity in fear conditioning tests, ratio of salivary cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and α-amylase, and sleep quality by deploying Fitbit wearable sensors for each study participant as well measuring environmental stressors through geotrackers.
“We will ask these young women to wear these Fitbits. These will pick up on the measure of sleep. We know that when people are stressed, they have poor mental health, but also, they have poor sleep,” said Prof. Swahn. She adds that these Fitbit devices are worn just like a wrist watch. “They will give us a lot of insight to what happens at night when people are sleeping. The women may or may not be sleeping as well as they should. So again, it’s another marker of stress, their well-being and physical health. It really adds another important innovative component of the study. We looked for other studies across the sub-Saharan Africa and have not found any studies that use this technology in this type of setting so these gadgets will give us a lot of insight.”

Dr. Catherine Abbo, an Associate Professor of Psychiatry at Makerere University College of Health Sciences, and Co-Investigator of the TOPOWA study, says depression and other mental health issues are on the rise in Uganda, though they continue to go unrecognized.
“These women actually don’t even reach the clinic but people just suffer while they are in the communities. There are different anxiety disorders. So, the current estimates from the previous research shows about 1 in every 4 people have mental health issues,” Dr. Abbo says.
Asked about what could be the drivers of mental health in young adults, Dr. Abbo contends some of the drivers are psychosocial arising from the environment we live in while others maybe genetically predisposed.
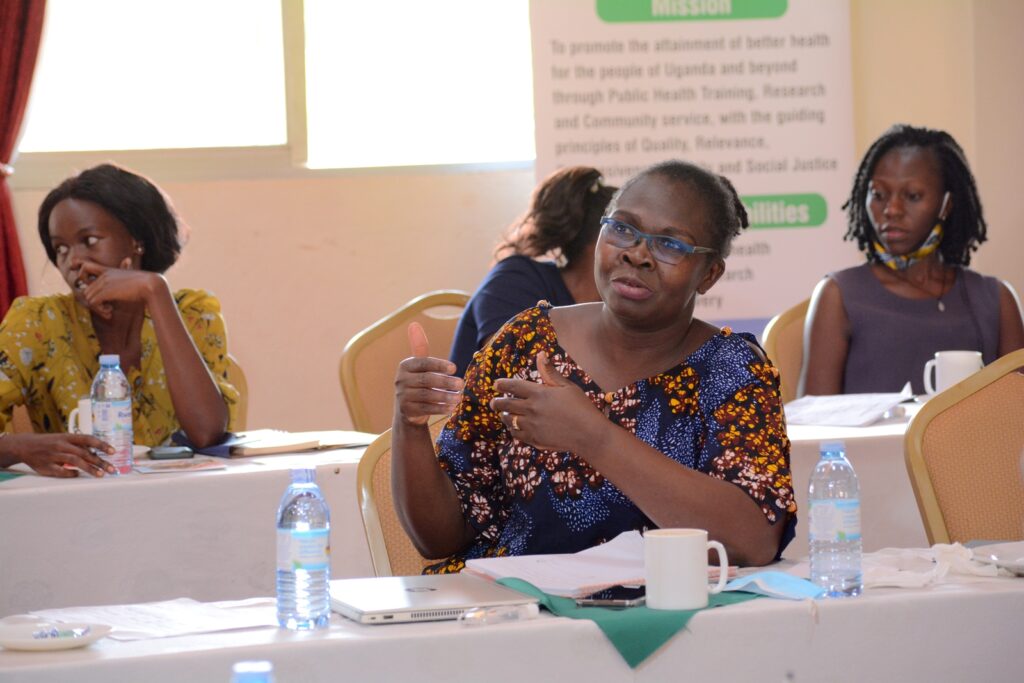

“If you are going to live in an environment that is poverty stricken, you are going to live in an environment where you are not going to access education, you are not going to have support that you need to be mentally healthy, you become vulnerable to getting mental illness and that is the environmental aspect. And then we have individuals, who, because of their genetic makeup, may develop cause mental illness,” she said.
According to Dr. Abbo, the wearables are new technologies and that this is the first of its kind to be used in research in Uganda. “You know sometimes people go jogging and have phones that take the number of their steps, heart rate, so in the general population we have gadgets that can measure some aspects of body reactions but particularly in this case, it’s going to measure sleep patterns, that signify stress levels.”
Mr. Rogers Kasirye, UYDEL’s Executive Director, argues that many a time, intervention projects have been implemented among youth but they fail because of the inability to tackle underlying issues affecting the young people. He says this study to investigate the mental health status of the young women will go a long way in impacting the way such initiatives can be implemented to achieve greater success.
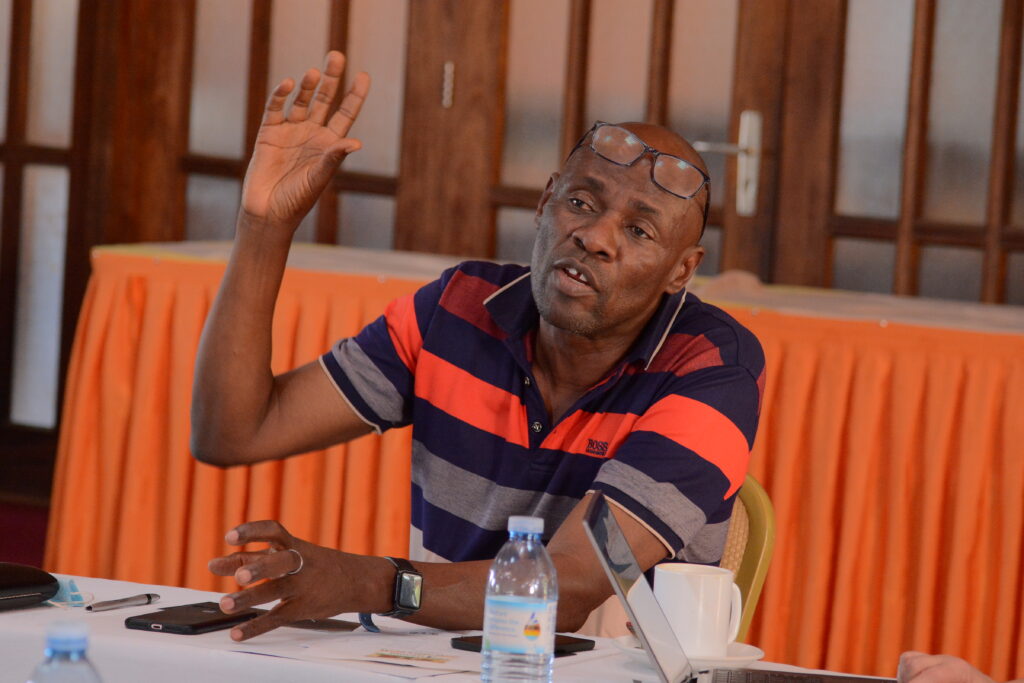

According to Mr. Kasirye, for over 25 years, UYDEL has worked with young people in the in the slums of Kampala and impacted many young people through their skilling and rehabilitation programs. He pointed out that that a majority of the young people in slums face a lot of challenges including poverty, lack of shelter while others have long lost contact with their families.
“But we don’t go beyond to investigate and support their psychosocial needs. From experience, some people who come to our facilities have alcohol and other problems. Many times, they are even failing to sleep. Some even come to the Centre and tell you that they have not had a meal. You know what it means to sleep on an empty stomach. Others say they lost contact with their families while others say they have been sexually abused and others raped. In other words, they have a mountain of psychosocial needs that must be addressed. With this project, we hope to track girls for several years to match the research findings with empowerment interventions,” said Mr. Kasirye.

Ms. Anna Kavuma, the Deputy Executive Director, UYDEL says the COVID-19 pandemic has had a toll on mental health issues among young women by increasing their vulnerability.
She notes that whereas the boys have equally been affected by the pandemic and could have pushed them to high stress levels, girls have a high level of vulnerability with responsibilities such as bringing up the children, dealing with pregnancies, accessing medical supplies as well as shelter.
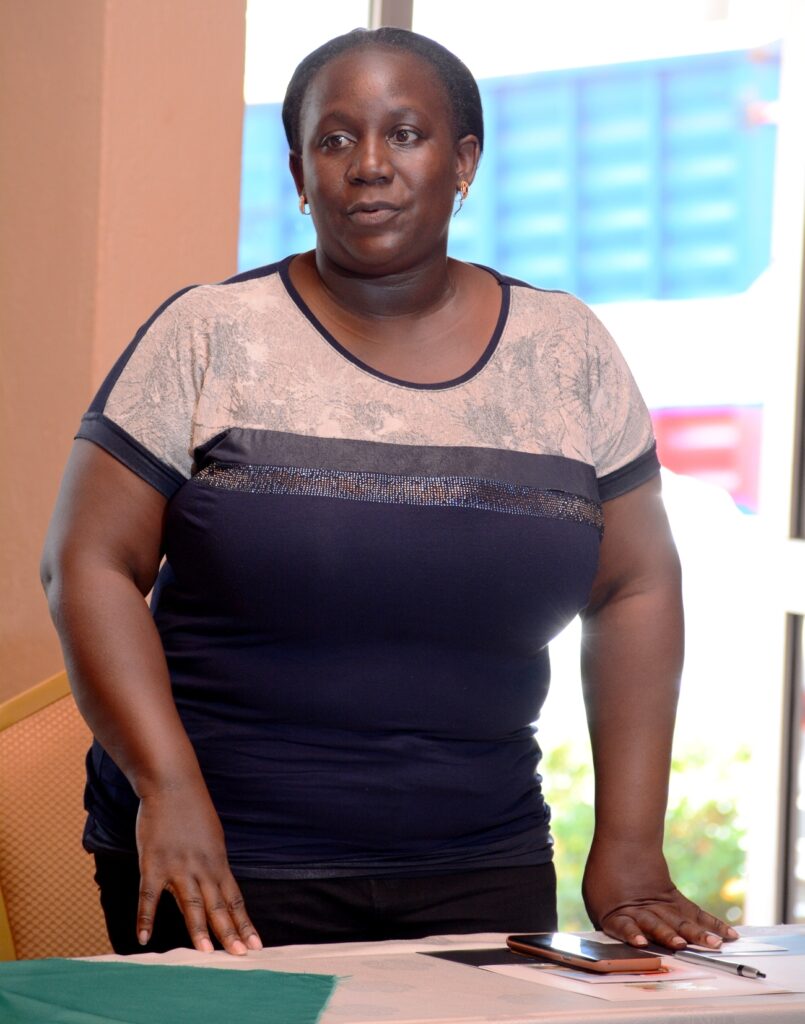

“It’s quite difficult for the girls. It’s an understatement for me to say that they are not highly affected by mental issues in Uganda, that is why this project is coming in to understand that. For instance, if we gave young girls vocational skills and training in beauty and cosmetics, or any other vocational skilling, will it help reduce on these stresses that they have? Will it help address the underlying factors that they are facing? Will it help to improve the way they sleep? Will it help improve the stress levels? These are areas we are trying to study and we are hopeful that the results of the study will inform not only programming and practice but also inform policy environment as well,” said Nabulya.
The project’s intervention arm will look at skilling the adolescent girls and young women with the cost-effective beauty training, which the researchers say is also very easy to implement. Dr. Swahn, the PI noted, “We are hoping that if it’s shown to be effective, that is something that can be implemented in other communities and we know that many are offering vocational training but they have not been evaluated the way we are doing it with a very vigorous scientific protocol.

Dr. Rhoda Wanyenze, Professor and Dean, Makerere University School of Public Health thanked Prof. Swahn and UYDEL for partnering with MakSPH to implement this important project citing that the School was ready to work with the team.
“Mental health for young people is such an important area and very timely coming after the challenges and stress from the Coronavirus pandemic! We are excited to partner with you on this project,” said Prof. Wanyenze.
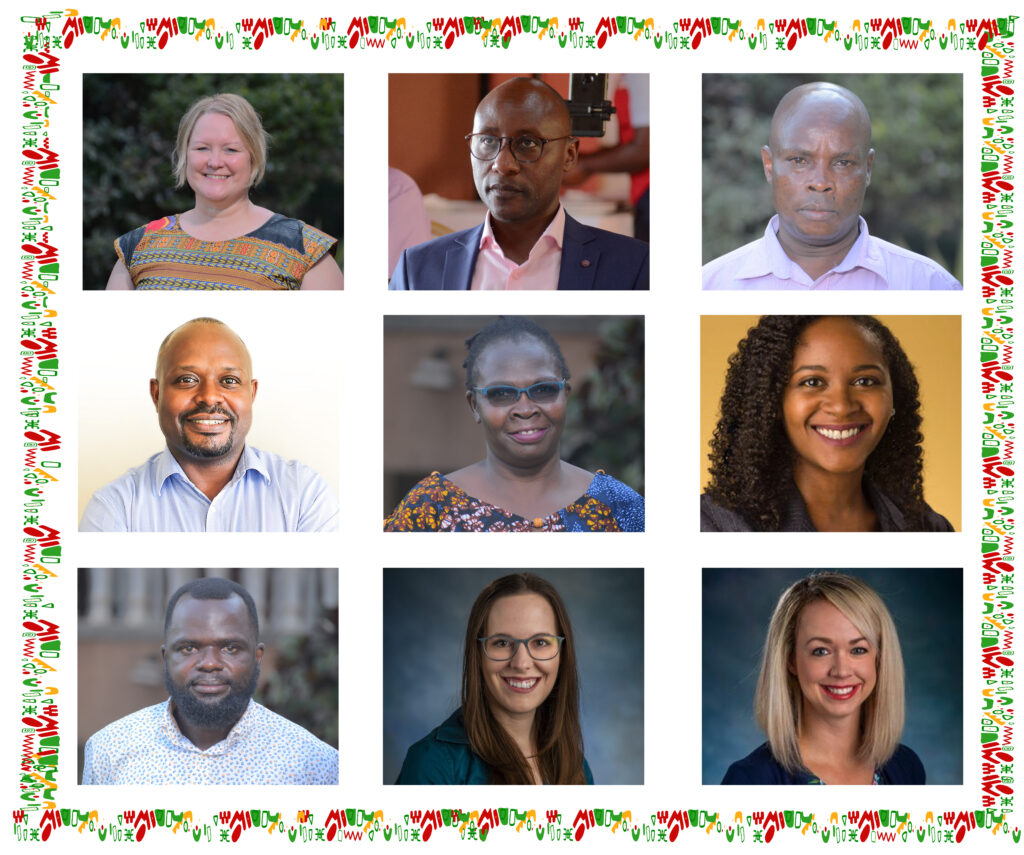
The TOPOWA Research Team is composed of nine investigators spanning two continents and three universities. The Project’s Principal Investigator (PI) is Dean and Professor Monica Swahn of Kennesaw State University. The Co-Investigators of the project include Dr. Cathy Abbo, Dr. Godfrey Bbosa, Dr. John Bosco Isunju, Charles Ssemugabo and Dr. Eddy Walakira from Makerere University, Dr. Ebony Glover from KSU and Dr. Rachel Culbreth and Dr. Karen Nielsen from GSU.

The Executive Director of UYDEL, Rogers Kasirye, leads the implementing partner whose mission is “to enhance socioeconomic transformation of disadvantaged young people through advocacy and skills development for self-reliance”.
The TOPOWA Project Advisory Board is composed of members from the Kampala City Government, the Ministry of Health, the Ministry of Gender Labour and Social Development as well as the Dean for the Makerere University School of Public Health.
Davidson Ndyabahika is the Communications Officer, MakSPH/TOPOWA Project
Article originally posted on MakSPH website
You may like
-


Emorimor Calls for Makerere to Upgrade Parenting Course
-


Uganda Deepens Economic Governance with Training on Regulatory Cost-Benefit Analysis
-


UVCF Makes Case for HEAC Programme
-


Mastercard Foundation Board pays its inaugural visit to Makerere University
-


Mak CEES discusses partnership with King Salman Global Academy for the Arabic Language
-


Meet Safali Libia, a Mastercard Foundation Scholar-alumnus who rebuilt his life as a refugee in Uganda
Health
Emorimor Calls for Makerere to Upgrade Parenting Course
Published
8 hours agoon
June 30, 2025By
Zaam Ssali
The Iteso Cultural Leader, His Highness Emorimor Papa Paul Sande Emolot, has called on Makerere University to elevate the Science of Designing, Adaptation, and Implementation of Evidence-Based Parenting Interventions course into a fully-fledged programme. This, he argued, would strengthen the capacity of practitioners implementing parenting interventions across Uganda.
Speaking at a graduation ceremony held on 11th June 2025 at Makerere University where 35 practitioners completed the 12-week course, Emorimor Papa Emolot emphasized the transformative power of effective parenting. He urged aspiring parents and advocates of the Parenting for Respectability model to enroll in the course.

Citing the impact in his own sub-county and village, the cultural leader revealed that over 800 families had already benefited from the programme.
“We now see peace and love in homes where there was once conflict. Without good parenting, you risk raising animals instead of children,” he passionately stated.
He praised the course for equipping practitioners, policymakers, and researchers with the skills needed to design culturally sensitive, evidence-based parenting interventions tailored to Uganda’s context. Among the notable graduates was Her Royal Majesty Juliet Among Emolot Atomeileng Akaliat Toto, who reaffirmed her commitment to advancing family-strengthening initiatives using the skills and knowledge acquired.
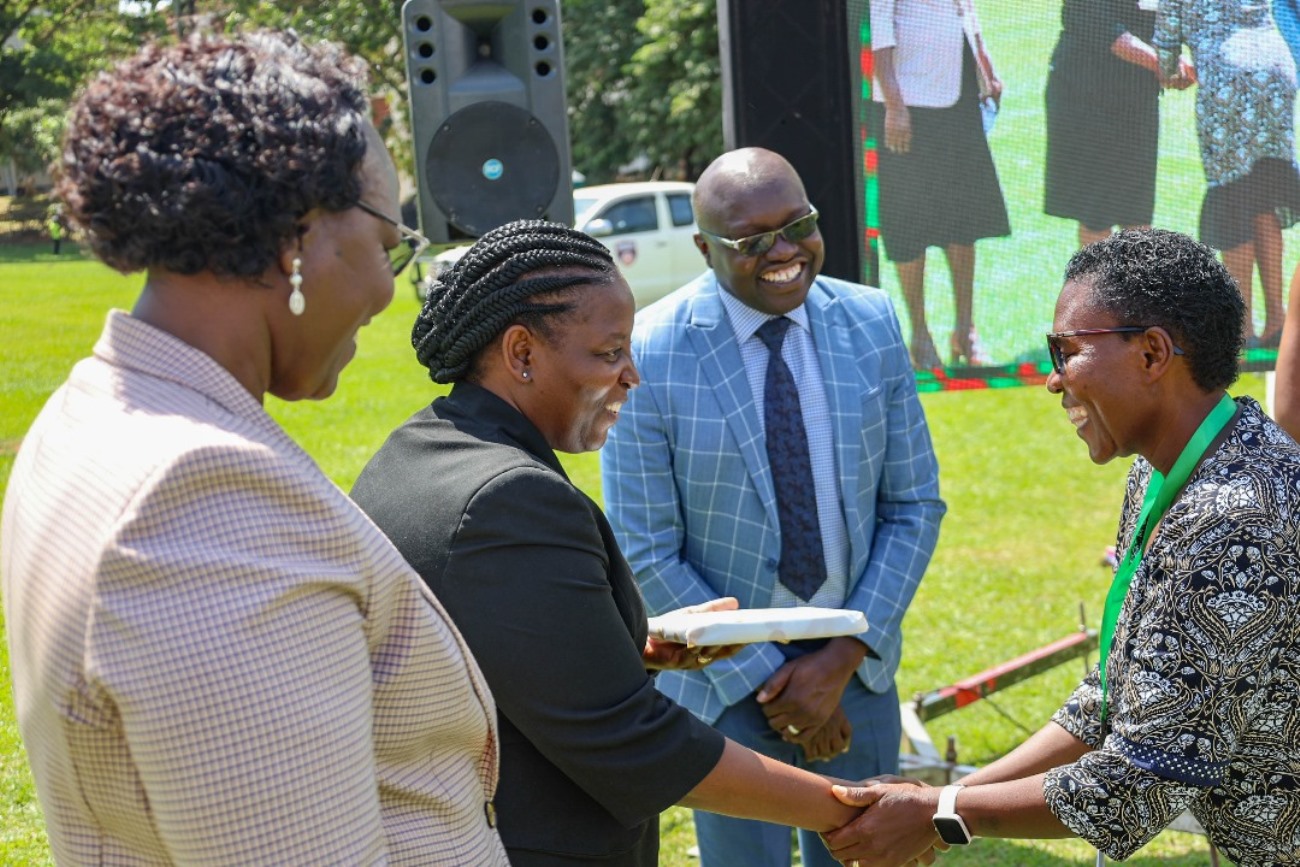

Dr. Godfrey Siu, Senior Lecturer and Course Leader at Makerere University, described the course as a timely intervention. During this remarks, Dr. Siu described the event as a significant milestone in advancing the field of evidence based parenting intervention and family strengthening in Uganda.
“This course is meant to empower you as practitioners, policy makers and all those involved in development and implementation of parenting work. It provides both theoretical knowledge and practical tools essential for developing high quality interventions”, Dr. Siu noted. He urged the pioneer group to carry forward the expertise as champions of designing, adaptation and implementation of evidence parenting interventions.
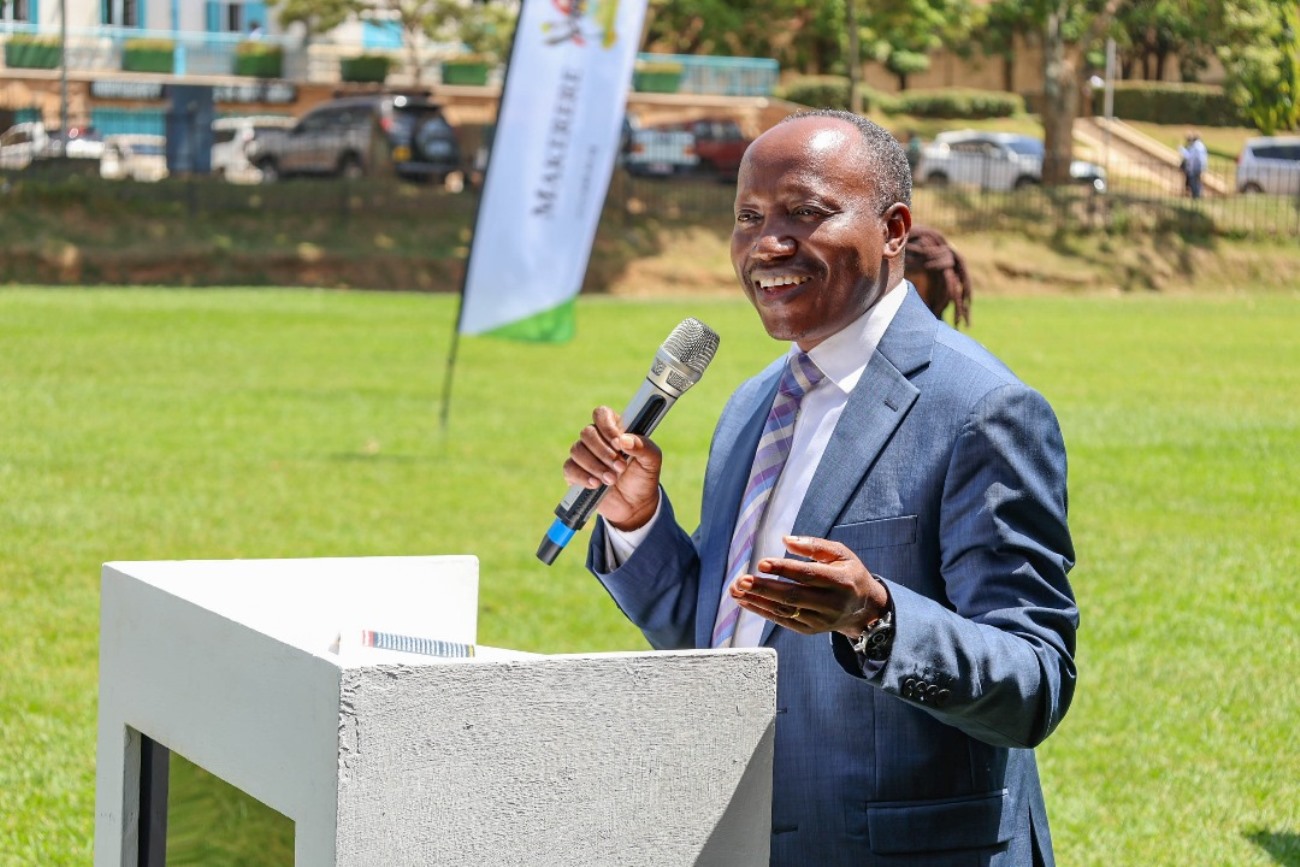

Representing the Permanent Secretary of the Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development, Dr. Aggrey David Kibenge, Juliana Naumo, Commissioner for Culture and Family Affairs, said the course supports the government’s agenda to address negative social outcomes affecting families.
“By grounding parenting in research, harmonizing policy with practice, and advocating for equity, we will ensure no family is left behind,” she said. “Cross-sectoral collaboration is key to unlocking transformative change.”
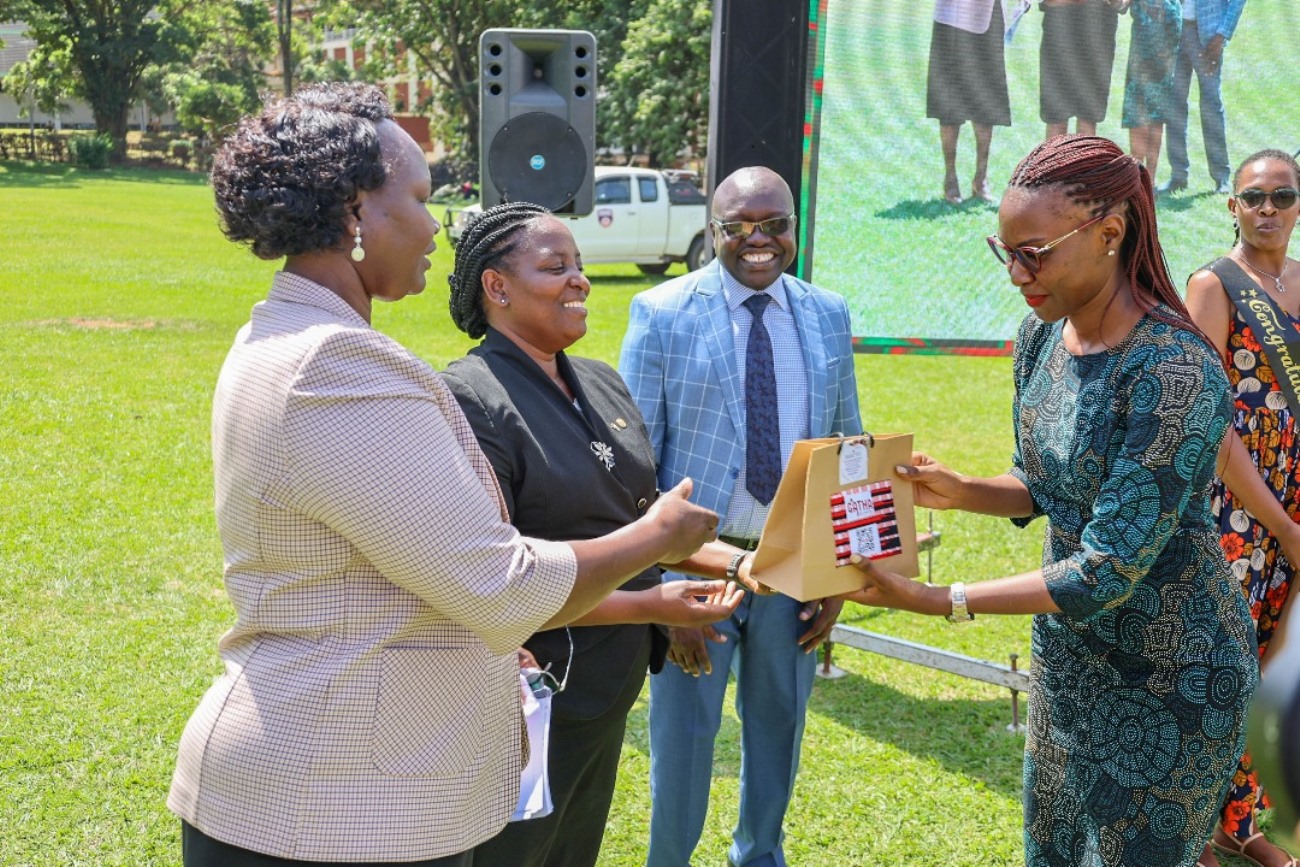

Ms. Naumo highlighted the government’s commitment—both technical and financial—to support outstanding student projects from the course. She stressed the importance of equipping professionals with the skills to bridge gaps between research and practice for consistent, high-quality parenting support across Uganda. While delivering the Vice chancellors speech by Dr. Helen Nambalirwa, Principal of the CHUSS, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe commended the graduates as a beacon of hope.
“At a time when parenting faces challenges like digital distractions, changing societal norms, and a rising mental health crisis, Makerere reaffirms its support for interventions that drive the societal transformation we desire,” Nawangwe stated.
Prof. Richard Idro, Deputy Principal of the College of Health Sciences, acknowledged the growing parenting challenges in Uganda and the region, adding that the course was a major step towards standardizing parenting interventions nationwide.

He applauded the Child Health and Development Centre (CHDC) for leading this paramount and critical initiative.
Mr. Hosea Katende, Course Administrator at CHDC, emphasized the importance of integrating systematic methods, ethical principles, robust evidence, and collaboration to create lasting impact in parenting.
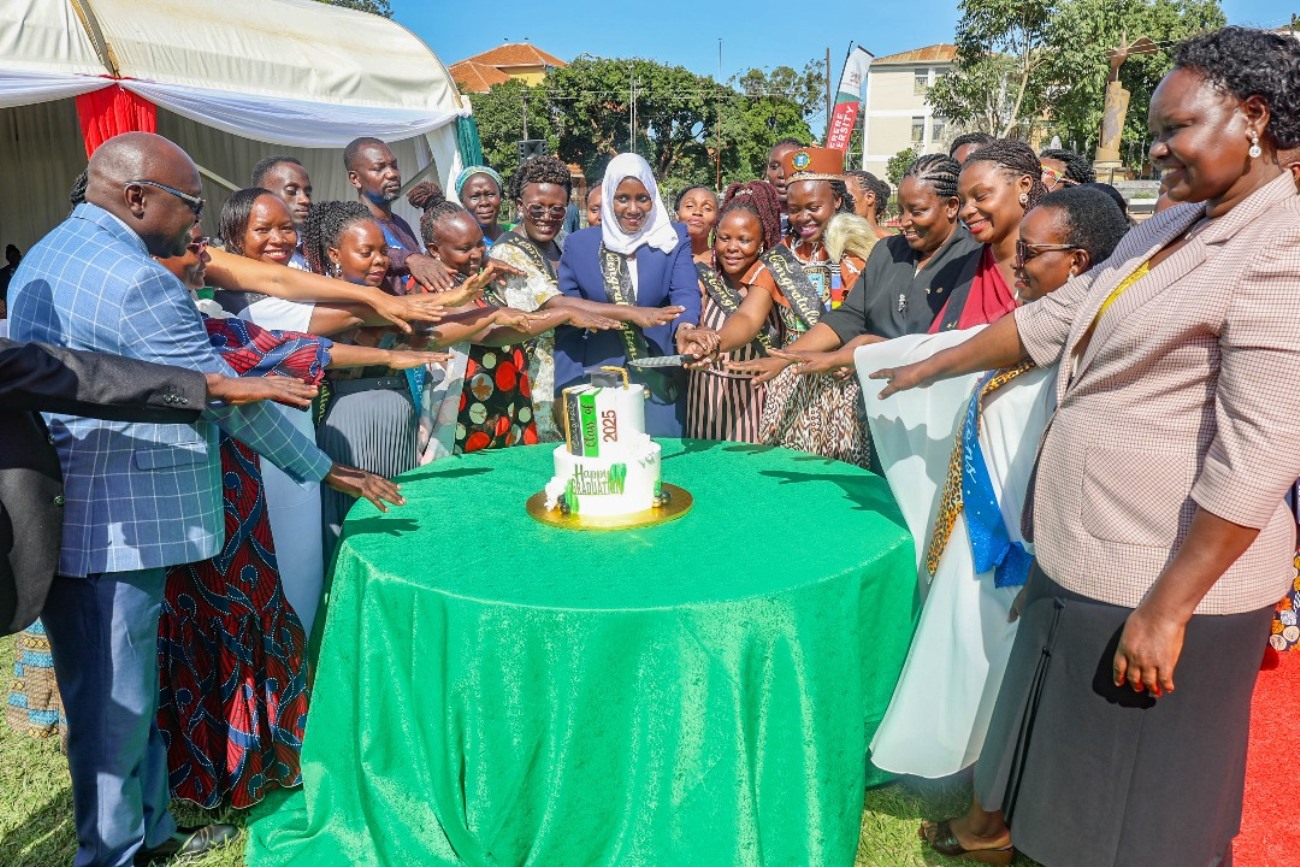

Dr. Aggrey Dhabangi, Lecturer at CHDC, representing Dr. Herbert Muyinda, Director of CHDC, acknowledged the contributions of partners such as the ELMA Foundation and Echidna Giving for their financial and capacity-building support. He also appreciated the Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development, among other stakeholders, for their technical guidance in the programme’s successful implementation.
Dr. Dhabangi extended gratitude to cultural institutions, especially the Kingdom of Teso, and acknowledged growing collaborations with other cultural institutions such as the Kingdom of Acholi, in the shared mission of building strong families as the foundation of Uganda’s future.
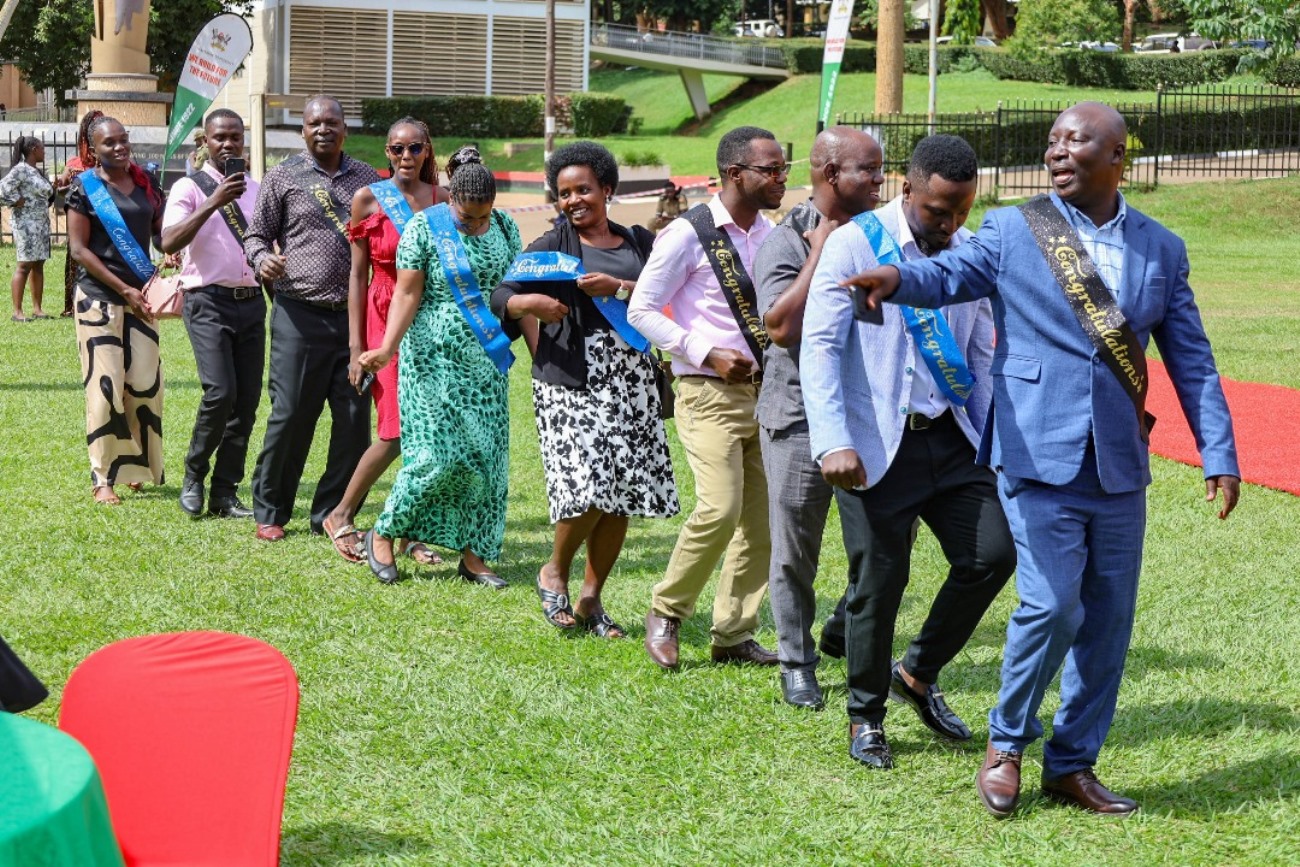

He extended his heartfelt gratitude to cultural institutions, especially the Kingdom of Teso, and others kingdoms such as the Kingdom of Acholi, in building Uganda’s future through creating strong families. Nuruh Mbalyowere, a Rehabilitation and Reintegration Officer with the Uganda Prisons Service, was honored for developing the best parenting intervention titled “Parenting Behind Prison Bars.” She expressed her intention to apply the knowledge gained both at home and in her workplace.
Health
MakSPH, DJC Launch Short Course on Health Communication
Published
1 week agoon
June 20, 2025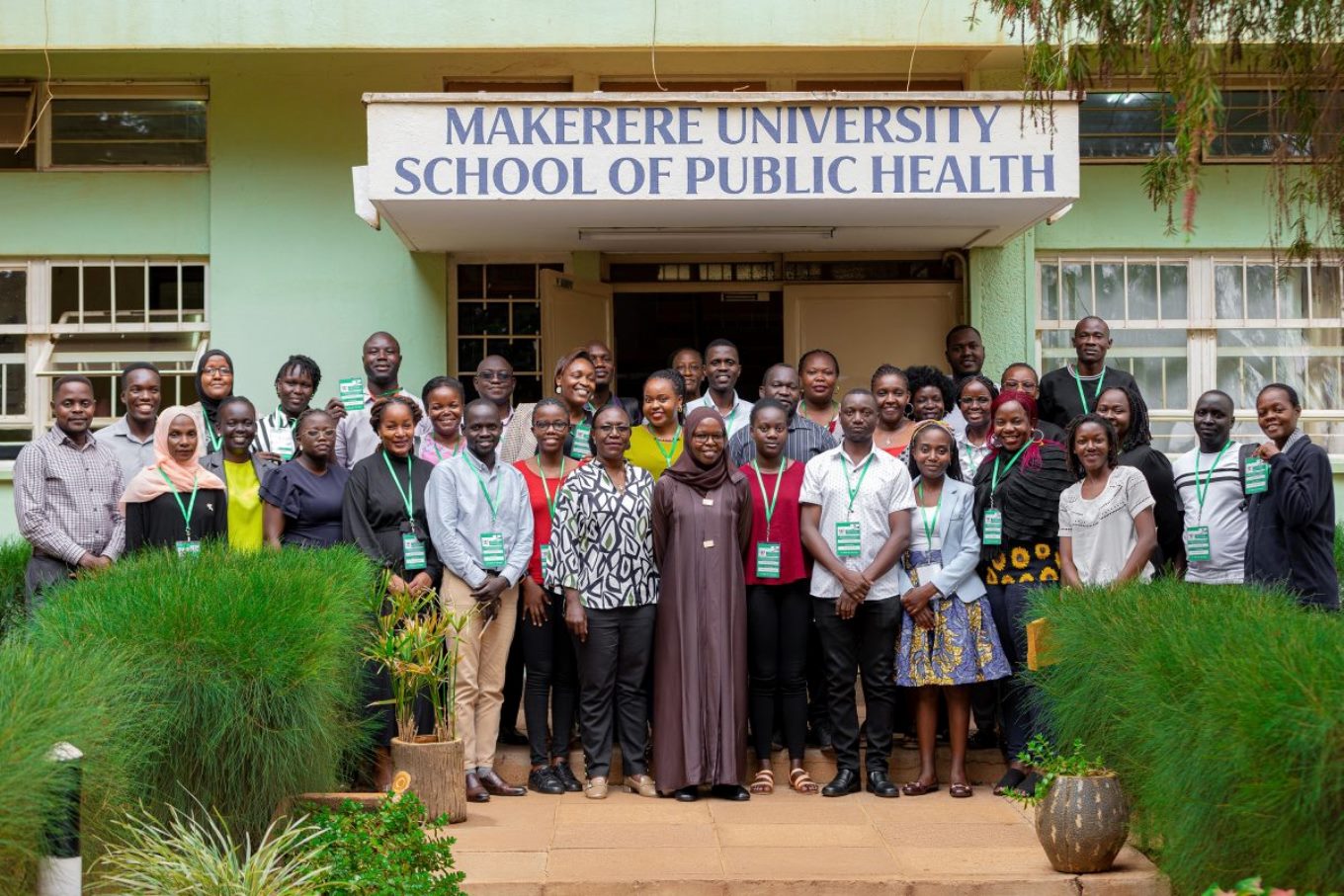
By Okeya John and Primrose Nabankema
The intensive one-month course, running for the first time from June 5 to July 24, 2025, is jointly offered by Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH)’s Department of Community Health and Behavioural Sciences (CHBS) and the Department of Journalism and Communication (DJC) at the School of Languages, Literature, and Communication (SLLC), co-designed in 2024 with support from the Rockefeller Foundation through Amref Health Africa.
It seeks to equip healthcare providers at the community level, public health and environmental health practitioners, communication specialists, health educators, community development officers, social scientists, and policy makers, among others, with strategic communication skills to improve public health messaging, strengthen community engagement, and support evidence-based interventions, ultimately empowering participants to effectively engage communities and improve population health outcomes across Uganda and the region.
Launching the course, the heads of the Department of Journalism and Communication and the Department of Community Health and Behavioural Sciences noted that participants who complete the short course will gain practical tools to influence behaviour change, build trust, and deliver timely, accurate, and relevant health information to the communities they serve. The first cohort attracted more than 60 applicants, with 36 reporting for the opening in-person session on June 5, 2025, at MakSPH in Mulago. Between now and July, participants will undergo a hands-on, multidisciplinary learning experience within the Certificate in Health Communication and Community Engagement program, which combines theory and practice.
Among the participants in the first cohort of the certificate course, designed as a pilot for the anticipated Master of Health Promotion and Communication to be jointly offered by the two departments at Makerere University, is Ms. Maureen Kisaakye, a medical laboratory technologist specialising in microbiology and antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and currently pursuing a Master’s in Immunology and Clinical Microbiology at Makerere. She is driven by a passion to help reverse the rising tide of AMR, a growing global health threat where drugs that once worked are no longer effective. Kisaakye is particularly concerned about common infections, like urinary tract infections, becoming increasingly resistant and harder to treat.
“I enrolled in this course because I’m an advocate against antimicrobial resistance, and it came at a time when I needed to deepen my knowledge on how to implement our projects more effectively and engage with communities. The experience has broadened my understanding of AMR and its impact on society, and strengthened my passion for community-driven health initiatives and advocacy,” Kisaakye said, explaining why she enrolled for the short course.

Kisaakye’s work in antimicrobial resistance extends beyond the lab. Having earned her degree in medical laboratory science from Mbarara University of Science and Technology, she founded Impala Tech Research in 2024 to drive impact and save lives. She has led grassroots AMR campaigns that integrate antimicrobial stewardship with water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) education in underserved urban communities, including the informal settlements in Kampala. She also has since designed peer-led initiatives that empower university students as AMR Champions, building a network of informed youth advocates. Kisaakye believes the health communication course will sharpen her ability to design and deliver impactful, community-centred interventions in response to the growing threat of drug resistance.
“The department collaborates with many partners within and beyond the University, including the School of Public Health, where we are working to develop the subfield of health communication and promotion. Our goal is to train specialists in this area and build a community of practice, something we have each been doing in our own spaces. There’s a lot of work ahead, and COVID-19 showed us just how urgently we need a generation trained to do this kind of work, and to do it very well,” said Dr. Aisha Nakiwala, Head of the Department of Journalism and Communication, during the opening of the short course on June 5.
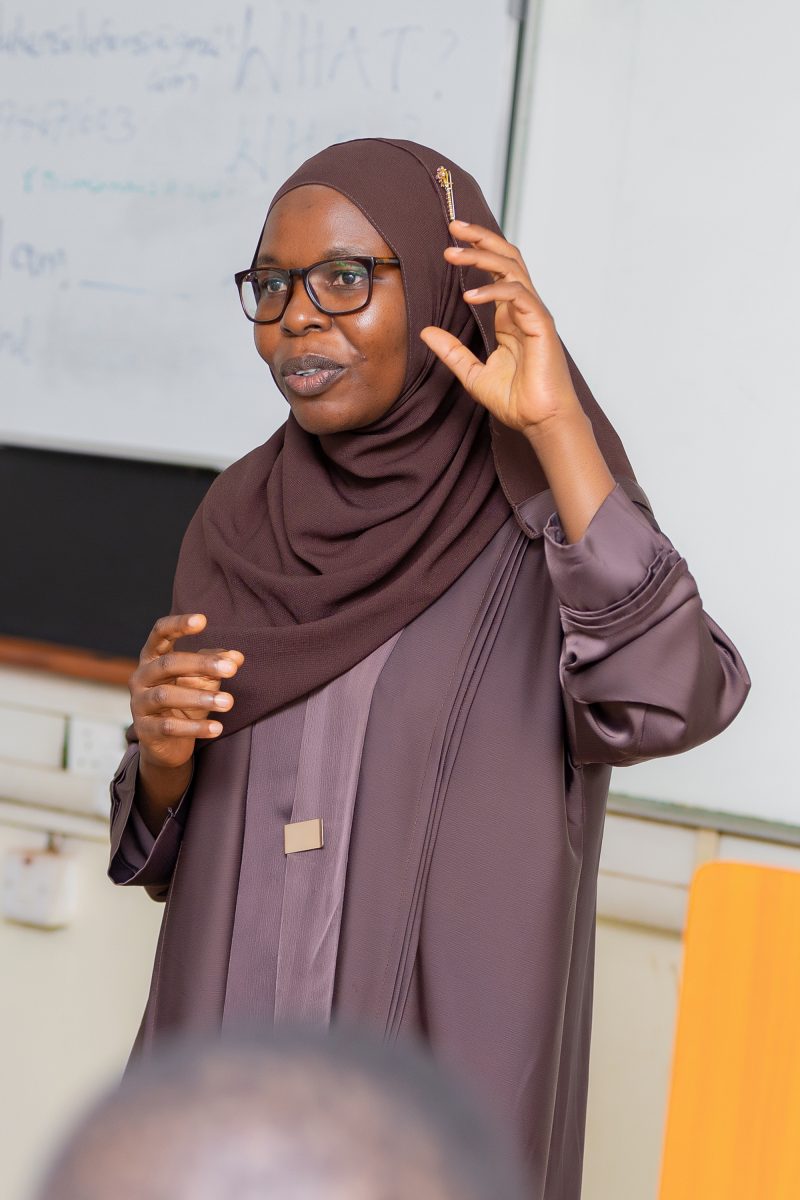

She assured participants they were in good hands and underscored the importance of the partnership between the Department of Journalism and Communication and the School of Public Health, describing it as a vital collaboration that brings together strategic communication and public health expertise. This dynamic, multidisciplinary approach, she noted, is essential to developing practical solutions that empower communities, strengthen health systems, and ultimately improve livelihoods.
The course offers a hands-on, multidisciplinary learning experience, with participants intended to explore key modules including Health Communication and Promotion, Risk Communication, Smart Advocacy, Community Mapping, Community Mobilisation and Empowerment, and Strategies for Community Engagement. The course combines theory with real-world application, and its assessment includes a field-based project and a final exam.
“You are our first cohort. We are seeing the fruits of our efforts in bringing this short course to life. It was born out of a joint initiative to develop a Master’s programme in Health Promotion and Communication,” said Dr. Christine Nalwadda, Head of the Department of Community Health and Behavioural Sciences. “We carried out extensive consultations with our different key stakeholders during the process and discovered a real need for such a course. It was the stakeholders who even named it; this course name didn’t come from us.”
For Kisaakye, by the end of the course in July, she hopes to have sharpened her skills in health promotion and strategic communication, particularly in crafting targeted messages that help individuals and communities effectively respond to threats such as antimicrobial resistance. She also aims to gain practical experience in designing, implementing, and evaluating community health initiatives that can strengthen her advocacy and drive lasting impact.

Health
Call for Abstracts: 2nd East African Symposium and Expo on Trauma, Injuries, and Emergency Care – 2025
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 19, 2025By
Mak Editor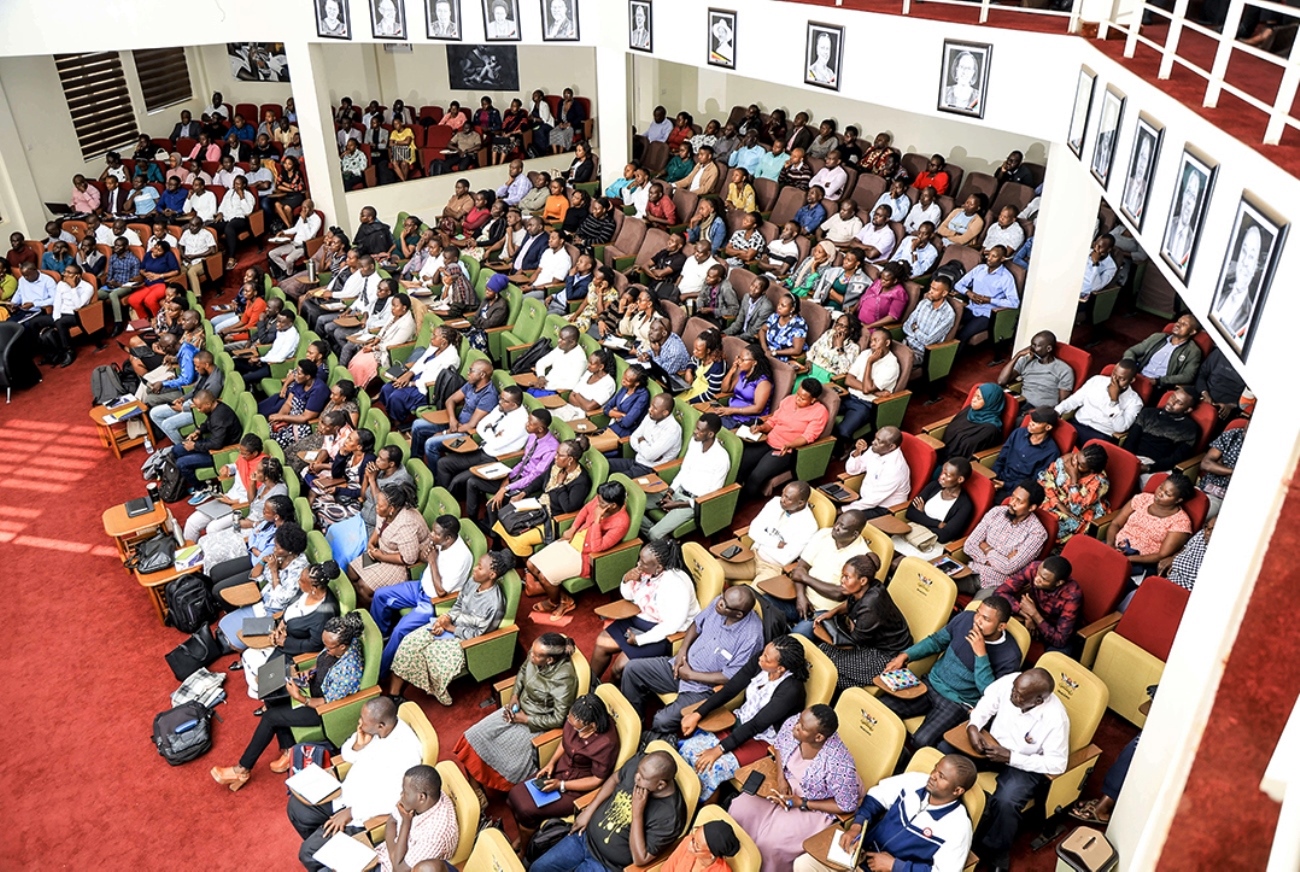
The Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH) is excited to invite researchers, professionals, and students to be part of an inspiring and impactful event!
Venue: School of Public Health Auditorium, Makerere University Main Campus
Dates: August 7–8, 2025
Theme: “Understanding the burden and impact of injuries in East Africa to improve Emergency Care preparedness, mitigation, and response.”
Submit Your Abstracts Now!
Join the conversation that drives change in trauma and emergency care across East Africa. Share your research, innovations, and insights that can shape the future of healthcare response in our region.
Submission Deadline: July 10, 2025
Submit here: triadcommunications@musph.ac.ug
Register to Attend: https://aapug.org/east-african-symposium-and-expo-on-trauma-injury-disability-and-emergency-care-2025/
Together, let’s drive change and improve lives through research and collaboration. Don’t miss this opportunity to make a difference!
Trending
-

 General3 days ago
General3 days agoMature Age Scheme Exam Results for 2025/2026
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoFreshers’ Joining Instructions 2025/2026
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMastercard Foundation Board pays its inaugural visit to Makerere University
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoUVCF Makes Case for HEAC Programme
-

 Natural Sciences2 weeks ago
Natural Sciences2 weeks agoCoNAS Participates in the 2025 National Science Week Exhibition
