Agriculture & Environment
Mak Launches IGE in Practice Programme
Published
5 years agoon

By Hilda Makune for EfD-Mak
Makerere University has launched a new program dubbed “Inclusive Green Economy (IGE) in Practice”. IGE in Practice, is a collaborative programme between Makerere University’s Environment for Development Initiative (EfD-Mak) Center and the University of Gothenburg, Sweden fully funded by Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida). Other participating countries are Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania and Rwanda.
The program is aimed at strengthening Uganda’s capacity for transformation towards an Inclusive Green Economy largely under the United Nations SDG 8 that focuses on promoting sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all.
IGE in Practice will focus on the use of environmental policy instruments, and specifically economic instruments such as environmental taxes, pollution fees, subsidies or subsidy reduction and other types of fiscal incentives for societal development in line with the Global Agenda 2030.
The program is an advanced in-service training with direct applicability in the participants’ daily work involving theoretical training within IGE, practical exercises, project development and support for implementing own change work.
The official program launch and training was held at at Makerere University’s Central Teaching Facility 2 (CTF2) on 4th June, 2021 with six (6) selected senior public servants competitively selected among the 19 participants nominated through the Permanent Secretary, Minsitry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development and relayed via zoom to other participants.
The selected senior public servants were from the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, Ministry of Water and Environment, the National Planning Authority (NPA) and the National Environment Management Authority (NEMA).
These selected public servants will undergo a one year course (running from June 2021 to June 2022) and upon successful completion, given a title of IGE fellows and are expected to become IGE change agents and IGE trainers in their different Ministries, Departments and Agencies.
The function was also attended by the Principal, Makerere University College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS) Assoc. Prof. Eria Hisali, the Director EfD-Mak Centre who is also, Dean, School of Economics Assoc Prof. Edward Bbaale and Makerere University IGE program support team – Dr. John Sseruyange, Lecturer in School of Economics and Mr. Peter Babyenda the Policy Engagement Specialist in charge of coordinating the training program. These were joined by Prof. Anders Ekbom, the IGE program head at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
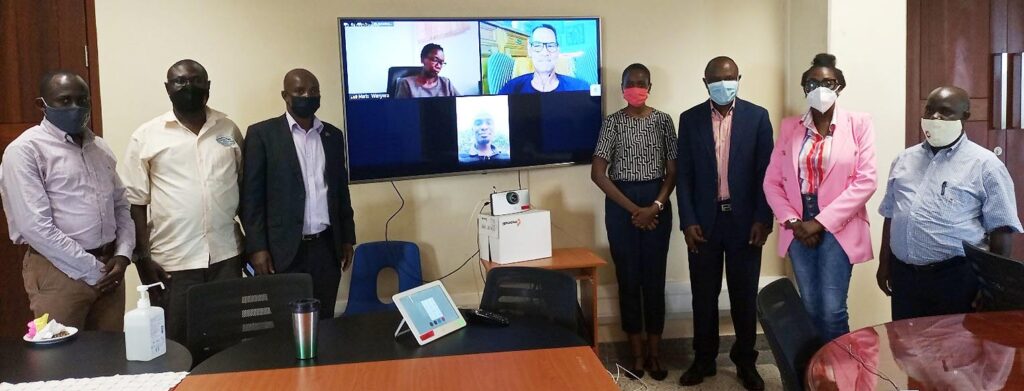
In his opening remarks, the Principal CoBAMS Assoc. Prof. Eria Hisali said the future for sustainable growth across the global is in Inclusive Green Economy, a new phenomenon, yet to be fully tapped into. He thanked the donors for putting trust in the university assuring them that they shall rise to the task that they are taking up.
He underscored the importance of IGE as extremely important in the case of Uganda and across the developing world presenting a number of opportunities and areas of interest to harness such as Water, Agriculture Energy that have been adequately taken care of in the planning frame work under the National Development Plan of Uganda.
“There is vast potential in the area of Renewable Energy; we have a potential to produce up to around 6,000mega watts of renewable energy, and yet what has been exploited as of now is under 500mega watts so, there is quite a big potential in the renewable energy in Uganda.
The good will we still have with the donor community, Inclusive Green Economy naturally includes among others tapping into the appropriate technology, good technology and value addition”, the Principal said.

Assoc. Prof. Hisali noted that although there are a number of opportunities and initiatives available in the Inclusive Green Economy, the concept is still new across the private and public arena. He implored the university IGE team to ponder on the issues such as stakeholder coordination, engagement, and involvement.
“Even when you sample across the public and the private sector, not everyone would appreciate the concept in the same way. The coverage is still limited. How do we get the different stake holders on board? How do we exploit now the untapped potential in terms of an Inclusive Green Economy?
The development philosophy of Uganda is largely the private Sector, will naturally play a very big role in driving the development process. Therefore, the question here is how do we incentivize the private sector to take up these different aspects of Inclusive Green Economy investments.
There are a number of initiatives under Inclusive Green Economy investments which are across the country both in the private and public sector. There are different sectors in different locations. How do we plan to coordinate these sectors?” Assoc. Prof. Hisali questioned.
The Director, EfD-Mak Center who is also part of the support team of Inclusive IGE Assoc. Prof. Edward Bbaale introduced EfD as a global network of Environmental Research Centers comprising fifteen centers across the world coordinated in the EfD Secretariat, a special unit in the School of Business, Economics and Law at the University of Gothenburg Sweden.
He said the EfD impact modal values a lot academic training which feeds into the Applied Research and also, institutional development which ultimately leads to Research Policy interaction and then the realization of an impact.
The Director said the meeting was about Inclusive Green Economy in practice, a capacity building program where the trainees will be equipped with information about the IGE Program, what it is about, why IGE, what the training will cover and the role of the centre and the trainees.
Prof. Bbaale expressed the need to ensure commitment by the participants on the program tasks and also connect with each other and understand each other’s roles.

He reported that the first round of this program will run until March 2022 and targets the senior civil servants mainly the economists. In Uganda. Prof. Bbaale said 19 participants were recommended but 6 were selected but the program too has a regional focus with 5 participants from Kenya, Rwanda with 6, then, Tanzania and Ethiopia each with 6.
“The main objective is to strengthen East African countries capacity to transform into an Inclusive Green Economy through; Increased knowledge and Application of Economic and Environmental policy instruments; Organizational change, how do we change the organizations where we work to make sure that we are well aligned in the inclusive Green Economy agenda and; Strengthen National systems for Inclusive and sustainable Economic development”, Bbaale said.
In the program out line, Prof. Bbaale said, phase 1 in March –April 2021was a call for applications and phase 2 is the startup meetings which was being done and running according to plan. In phase 3 there will be trainings on the Inclusive Green Economy aspects, theories and practices.
Prof. Bbaale reported that Phase 4 shall have the Golden thread called the Inclusive Green Economy Project where each participant will have to design a project in their different organizations intended to show how they can change their organizations and how well they can align themselves in a Green Economy.
In the same phase 4, the Director said, there will be support workshops, high level policy workshops, support meetings from the mentors and the peer running reviews followed by regional course between October and March 2022 and then national workshops.
“This program is an advanced in-service training with direct applicability, where participants will get great understanding, knowledge and ability to critically review and analyze the current economic policies and conditions while at the same time find opportunities for transformation towards a Greener Economy. Therefore, this means you are a change agent in your organization, the training will strengthen the role of the participant as a change champion.
The program is organized by the UGOT, the center for sustainable development in collaboration with several expert organizations and Makerere University being part of that under the EfD- Mak Center. A team of experts and Lecturers include; those from Sweden but also other international experts with extensive experience.
The program is fully funded by the Swedish International Development operational Agency (SIDA). All costs are covered by the UGOT. Therefore, the participants will only contribute their time.” Assoc. Prof. Bbaale added.
He highlighted some of the benefits from the program at individual level, organizational and at the system level that combines the entire country.
At individual level he said, there is peer to peer learning, understanding the inclusive green economy, its usefulness, risks and opportunities of applying these economic instruments, and increased knowledge of organizational change, how does one start up the change at organization level and how to build network efforts at international level.
At organizational level; he explained that one will benefit by building capacity on behalf of the organization in the area of Inclusive Green Economy; Application of economic instruments and increased priority on Inclusive Green Economy and the Introduction of Inclusive Green Economy or economic instrument projects and support of the ongoing IGE projects.
At national level, he said the benefits range from Strengthened National systems for green economic transformation; Improved cooperation between government agencies and across countries of collaboration and; Enhanced application of green economy analysis and economic instruments for IGE transformation
Program Training Methodologies
In terms of training Methodologies, the Director said, these shall include; advanced professional capacity building program, which will have action learning methodologies online; under that shall have online meeting place for professionals in planning and policy development strategic and resource green economy.

Since it is going to be an action learning experience, part of it shall be exchange of knowledge and sharing of experiences. There shall be interaction in terms of group work, discussions, joint learning i.e. on line and then develop the Golden Thread – the Inclusive Green Economic Project which will be developed from the different organizations.
The Program Tasks according to Prof. Bbaale include participation in the training, developing and implementing the Inclusive Green Economy Project and conducting and participating in National policy review workshops for peer learning.
As part of the tasks; one will be a trainer and as a participant, one will be given a title of Inclusive Green Economy Fellow (IGE-Fellow) which will distinguish one from those that have not undergone this program.
As a Fellow, one will be required to actively involve the workmates/colleagues where one will form a team at their place of work with in their organization. One will work on experiences and work projects and actively contribute on their own expertise and experiences.
One will in addition manage development and implementation of a number of tasks through the 10months of the program duration and upon graduation and successful achievement of all tasks, one will be awarded a certificate and become part of the IGE-Fellow networks or program alumni.
All IGE-Fellows are assigned a support team which includes; Country Academic partners and expert advisors on Inclusive Green Economy.
Prof. Bbaale said, the role of the support team is to; Provide feedback on ones assignments and tasks, offer advice on critical questions, support and encourage one to keep moving on the program. This support team understands the Inclusive Green Economy processes, changes process and organization capacity program and they will challenge, coach , encourage and also critically review the written tasks and helps fellows with the information sharing and IGE networking.
Program Guide for the Trainings
- 10th-11 June as the first training
- 17th -18 June second training
- 9th -10th September third training
- 16th -17th September fourth training
These trainings will be conducted virtually.
Giving his remarks via zoom, the IGE program head at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden. Prof. Anders Ekbom said, Inclusive Green Economy (IGE) is one of the Agenda of 2030 of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 8).
He said the rich and poor countries cannot do things the same way for various reasons and that is why development is not sustainable.
“And therefore we cannot go on the way we do. The Rich countries consume too much while the poor countries cannot invest in technologies that are sustainable. Investments are not environmentally or socially and economically sustainable. Our horizons are too short.
Therefore, the agenda is to guide development and this program focuses on SDG 8 which really deals with jobs, decent work but also sustainable economic development,” Prof. Anders Ekbom said.

He said IGE is a practical approach to address and work with SDG8 and that it is broader than just Green Economy because one can go for policies that promote green growth but at the expense of the poor or the marginalized people.
He clarified that, one has to emphasize on inclusion or social acceptance as one designs the green economy policies.
He explained that the SDGs are made up of 5Ps, i.e. Prosperity, People, Planet, Peace and Partnerships where the first three Ps represent Inclusive Green Economy.
In the case of IGE Prof. Anders said there is need to ensure that the economy and the environment are brought together in a large extent.
“The concept of IGE is to bring the social, economic and environmental issues together for integration, inclusion of people in planning, decision making and the outcomes. Environmental sustainability, social sustainability and economic sustainability, the three need to come together so as to have a comprehensive sustainable development”, Prof. Anders Ekbom said.
IGE according to Prof. Anders is made up of several concepts; resource efficiency, system mitigation, system resilience, strong communities and habitats, sustainable economic growth, Inclusive economic growth, equity, poverty reduction, strengthening of rights and social inclusion.
He said the Green economy wants to reduce pollution, reduce inefficiency, reduce waste, economize the natural resources and go for extensive use of natural resources while IGE has to make use of internal policy plans, and other departments as well.
“This does not mean taking over their jobs but rather working together through campaigns and other means.
IGE needs to promote green jobs and sustainable employment. Need to move from the Ministry of Environment and NEMA, and involve the Ministry of Finance because these organizations sit on very powerful tools to manage the environment through economic empowerment.
IGE needs to move away from the victims being paid for polluting the environment but rather have the polluters pay for polluting the environment. That way the environment will be preserved.
Need to move from environmental conservation and protection to sustainable management”. Prof. Anders Ekbom stressed.
You may like
-


Makerere University Affirms E-Mobility Push with Fast-Charging Station Launch
-


Farmers’ Preferences Drive Success in Tree-Planting, Duke Scholar Finds
-


Makerere University Launches Short Course to Strengthen Climate Change Reporting
-


Advert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-


Call for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-


Makerere University Researchers Awarded UCIF Grant to Tackle Maize Contamination with Innovative Plant-Based Fungicide
Agriculture & Environment
Makerere University Students Triumph in National Conservation Competition
Published
4 days agoon
March 10, 2026By
Mak Editor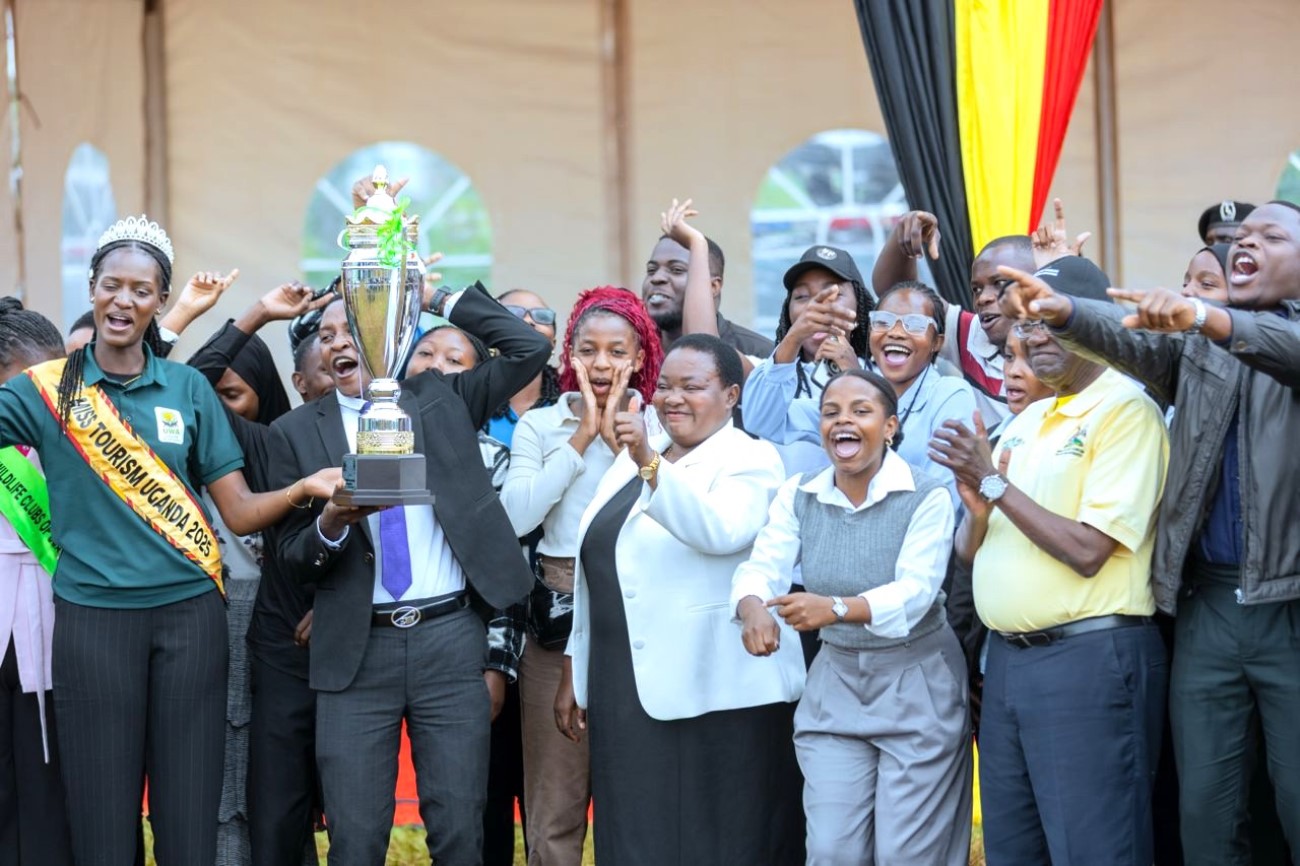
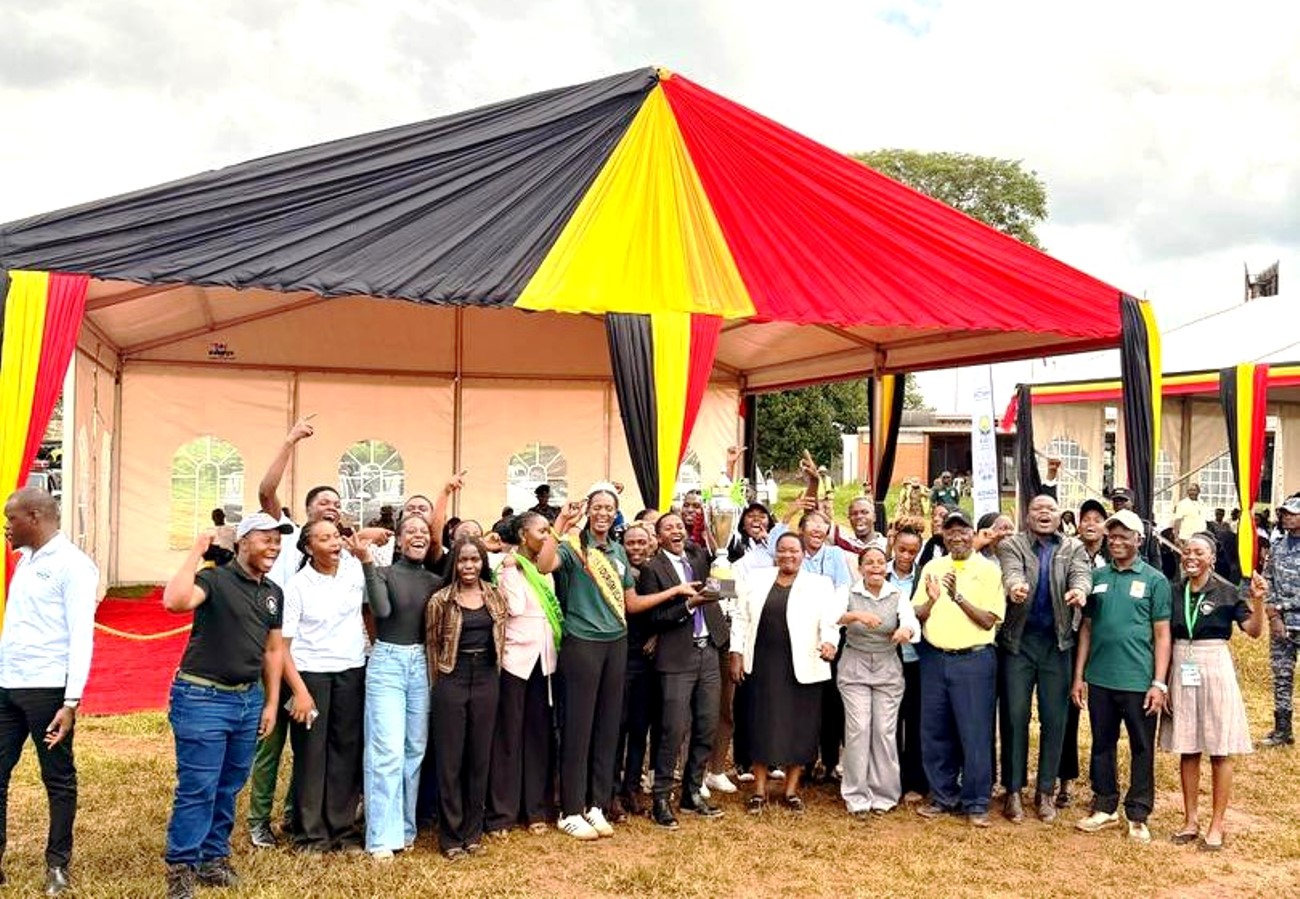
Makerere University students have once again demonstrated academic excellence and commitment to environmental conservation after emerging as the overall winners in the Uganda Wildlife Authority Tertiary Institutions Conservation Competitions held during the national celebrations to mark the World Wildlife Day.
On 25th February, a team of eight students, including members of the Makerere University Tourism Association (MUTA), proudly represented the university at the competitions organized by the Uganda Wildlife Authority. The event took place at the Uganda Wildlife Education Centre in Entebbe and brought together students from various tertiary institutions across the country to showcase knowledge and innovation in wildlife conservation.

The competitions formed part of the activities marking World Wildlife Day and were held under the theme “Medicinal and Aromatic Plants: Conservation, Health, Heritage and Livelihoods.” The theme highlighted the importance of protecting plant biodiversity, particularly species that support traditional medicine, cultural heritage, and sustainable livelihoods.
After a highly competitive contest that tested participants’ knowledge of conservation, biodiversity, and environmental sustainability, Makerere University emerged as the overall winner. The Uganda Wildlife Research and Training College finished as the first runner-up, while Nkumba University secured the second runner-up position.
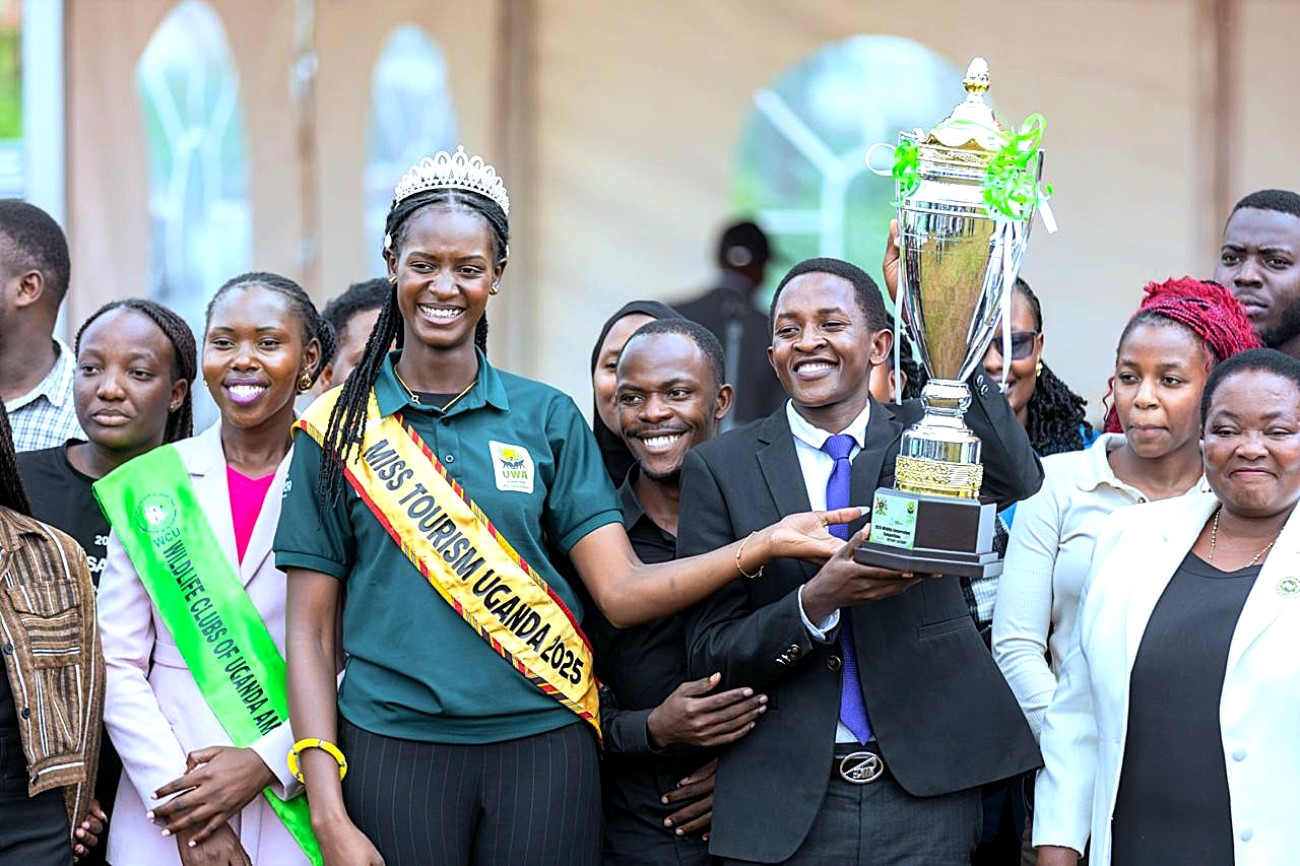

The team’s achievement was officially recognized during the national World Wildlife Day celebrations held on 3rd March at the Entebbe Works Grounds. During the ceremony, the students were awarded a trophy in recognition of their outstanding performance.
The award was presented by Uganda’s Prime Minister, the Rt. Hon. Robinah Nabbanja, alongside the Minister of Tourism, Wildlife and Antiquities, Hon. Tom Butime, and the State Minister for Tourism, Wildlife and Antiquities, Martin Mugarra. The leaders commended the students for their remarkable achievement and emphasized the critical role young people play in promoting conservation and protecting Uganda’s natural heritage.
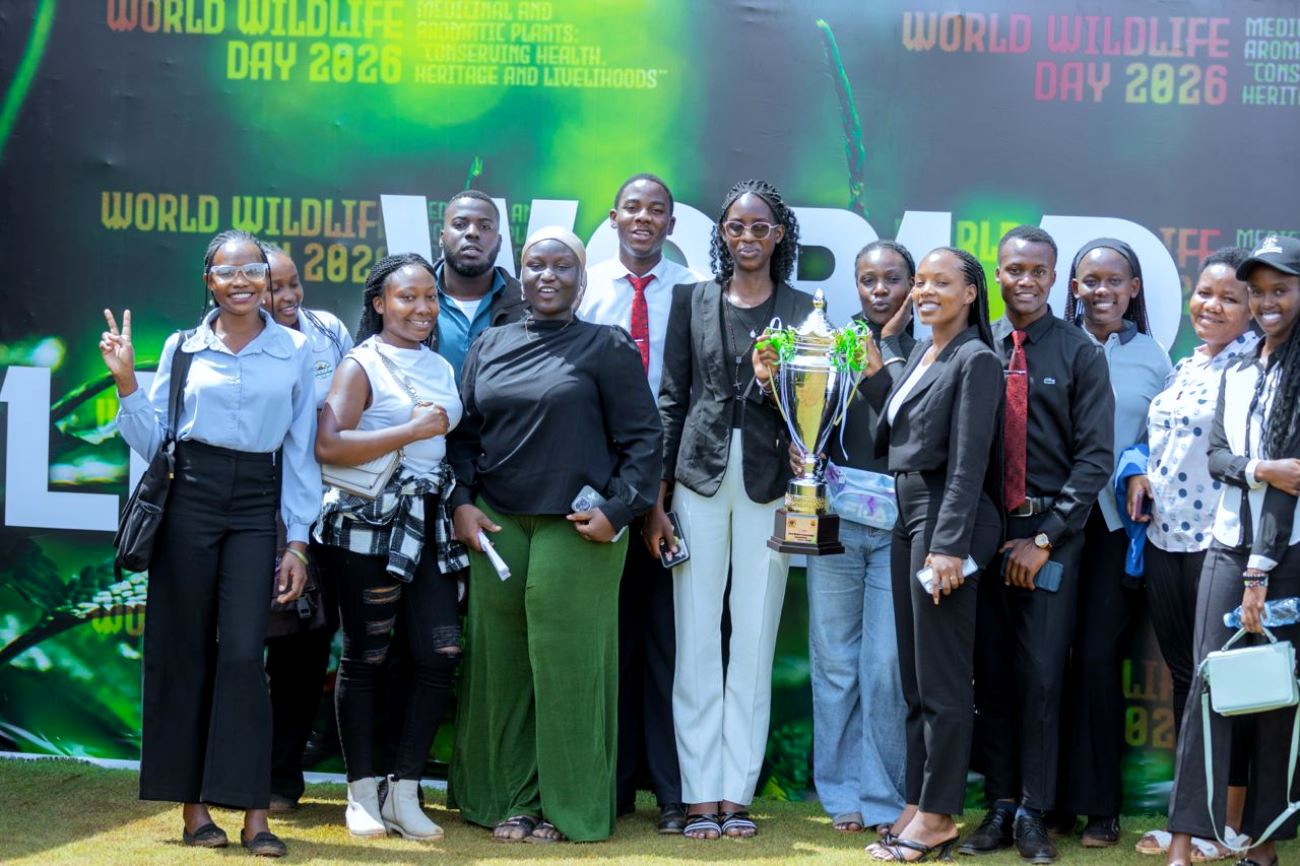

The winning team comprised students from diverse academic disciplines as follows:
- Iradikunda Jemimah – Bachelor of Biomedical Laboratory Technology
- Nankabirwa Edith Mirembe – Bachelor of Science in Tourism and Hospitality Management
- Agenrwoth Brenda – Bachelor of Science in Tourism and Hospitality Management
- Joel Kibirango – Bachelor of Science in Tourism and Hospitality Management
- Elvis Mujuni Kamara – Bachelor of Science in Biological Sciences (Botany/Zoology)
- Kamyuka Ben – Bachelor of Science in Biological Sciences (Botany/Zoology)
- Karisa Geofrey – Bachelor of Science in Forestry
- Nyangoma Caroline – Bachelor of Science in Forestry
According to Prof. Jim Ayorekire, Head, Department of Tourism at Makerere University, the win not only highlights Makerere University’s continued leadership in conservation education but also underscores the importance of empowering young people to take an active role in protecting biodiversity and promoting sustainable use of natural resources.
Agriculture & Environment
From Campus to Community: Universities Lead Teso in Fight Against Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Published
5 days agoon
March 9, 2026By
Mak Editor
By John Omoding
When Immaculate Acom inhaled smoke from traditional firewood stoves, it was a daily struggle. Her eyes watered, her lungs ached, and cooking became a source of illness rather than nourishment.
Today, Acom’s home in Aten Village, Odudui Parish, Arapai Sub-county, Soroti District, has transformed into a living laboratory for green energy solutions, a hub where university researchers, students, and local farmers collaborate on practical strategies to combat climate change.
“I used to cough every time I cooked. Now, with a biogas digester built by my husband, I can cook and light our home safely,” she says, pointing to the small green dome beside her house. “This is a relief for all the mothers in the community.”

Bringing Academia to the Grassroots
Acom’s story is part of the TORCH Project, a multi-university initiative involving Makerere University, Busitema University, Kabale University, and the University of Juba. The project seeks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices at the community level.
Unlike conventional environmental campaigns, the TORCH Project emphasizes direct engagement with local communities. Role models within villages are identified and trained in modern agricultural practices, clean energy use, and environmentally friendly living standards.
Dr. Jolly Akullo Oder, TORCH Project Coordinator at Busitema University, explains:
“Our mandate is to go to the community, share knowledge, listen to their challenges, and co-create solutions. This is not about lecturing – it’s about learning together.”

The project’s operational area spans a ten-square-kilometer zone around Busitema University’s Arapai campus, where researchers, students, and community members meet regularly to exchange ideas and implement practical solutions.
A Living Lab for Green Growth
The initiative, branded as a living lab, aims to achieve green growth, rural carbon credits, and the adoption of affordable green technologies.
Dr. Patrick Musinguzi, Principal Investigator from Makerere University, emphasizes the community-centric approach: “We are here to sit at the table with the community, discuss the challenges of global warming and greenhouse gas emissions, and chart a path forward together. Awareness is the first step to action.”
The project focuses on tangible interventions, including biogas digesters, sustainable tree planting, and energy-efficient farming methods, to reduce carbon emissions at the household and community level.

Community Voices: From Awareness to Action
For local farmers like John Michael Elebu, the university outreach is both eye-opening and practical. “I’ve never seen academics come to the community and engage with us so openly. I hope they can provide free improved tree seedlings to support our farming and fight climate change,” Elebu said.
Acom urges men in the community to take an active role in adopting clean energy technologies. Her husband, David Okwi, is among those championing the integration of green technologies into everyday agricultural practices.
“Promoting renewable energy and sustainable farming isn’t just about protecting the environment,” Okwi says. “It also improves health, saves money, and strengthens the resilience of our families.”
Universities as Catalysts for Environmental Change
The TORCH Project represents a unique model of academic-community collaboration, where research and practical application intersect.

Universities provide expertise, training, and access to modern technologies.
Community members contribute local knowledge, labor, and willingness to adopt change.
Together, they tackle climate change, energy poverty, and environmental degradation at the grassroots.
Dr. Akullo notes that the initiative will expand its activities continuously, monitoring outcomes, adapting approaches, and scaling up best practices across Teso and neighboring regions.
Way forward
By turning households into living laboratories, the TORCH Project aims to bridge the gap between knowledge and action.
For residents like Acom and Okwi, the benefits are immediate: cleaner air, reduced health risks, and practical solutions for everyday life. For Teso, the project could serve as a blueprint for climate-smart rural development across East Africa.
“Change begins at home,” Dr. Musinguzi says. “When communities understand the challenges of green gas emissions and know how to respond, the impact spreads far beyond one village or household.” In Aten Village, the hum of a biogas stove and the sight of thriving tree seedlings offer a glimpse of what is possible when universities partner with communities, creating hope for a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future.
Agriculture & Environment
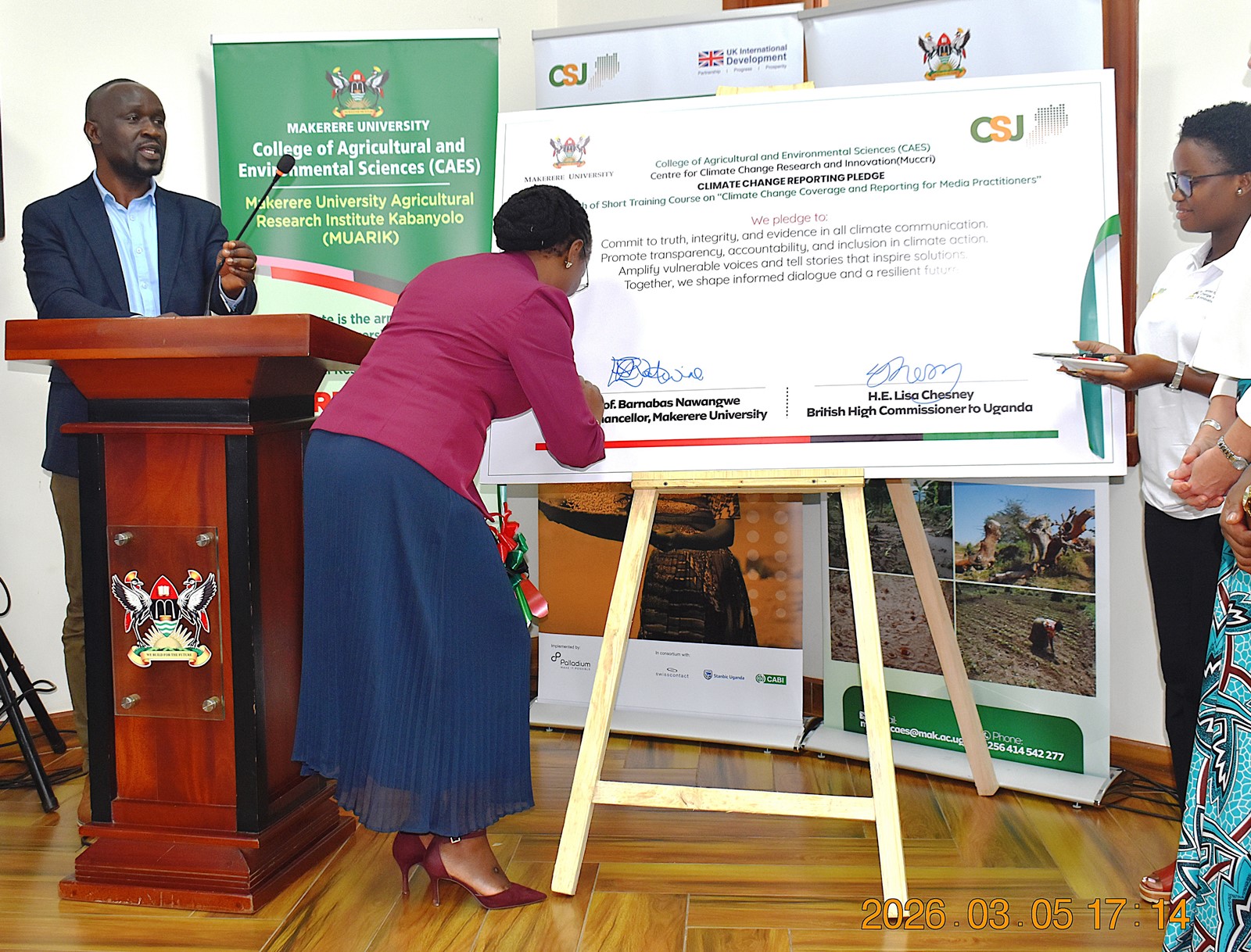
Makerere University Launches Short Course to Strengthen Climate Change Reporting
Published
5 days agoon
March 9, 2026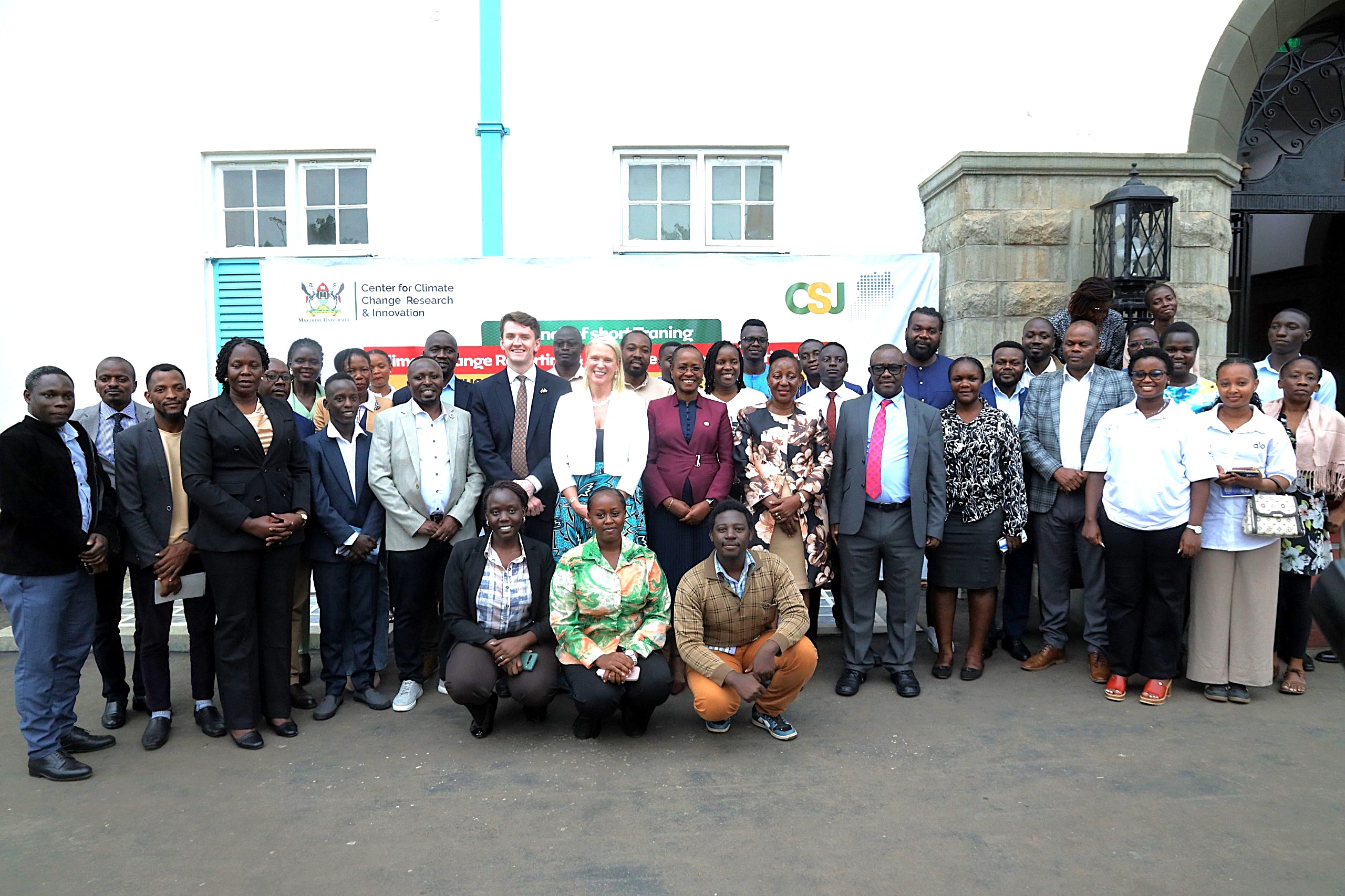
By Hasifa Kabejja & Ritah Namisango
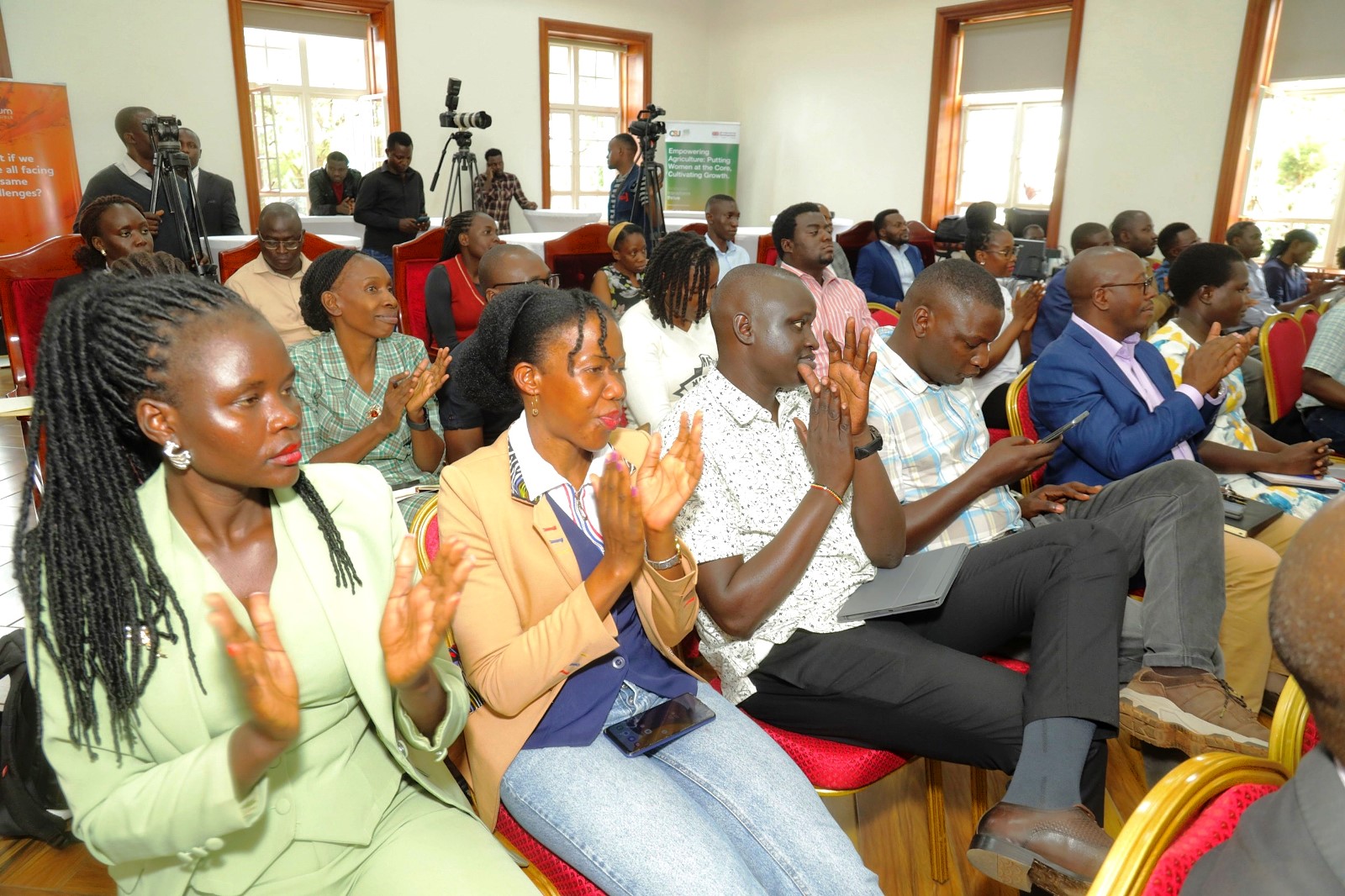
Makerere University, in partnership with the British High Commission in Uganda, has launched a specialized short training course aimed at equipping media practitioners and digital content creators with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively report on climate change and related environmental issues.
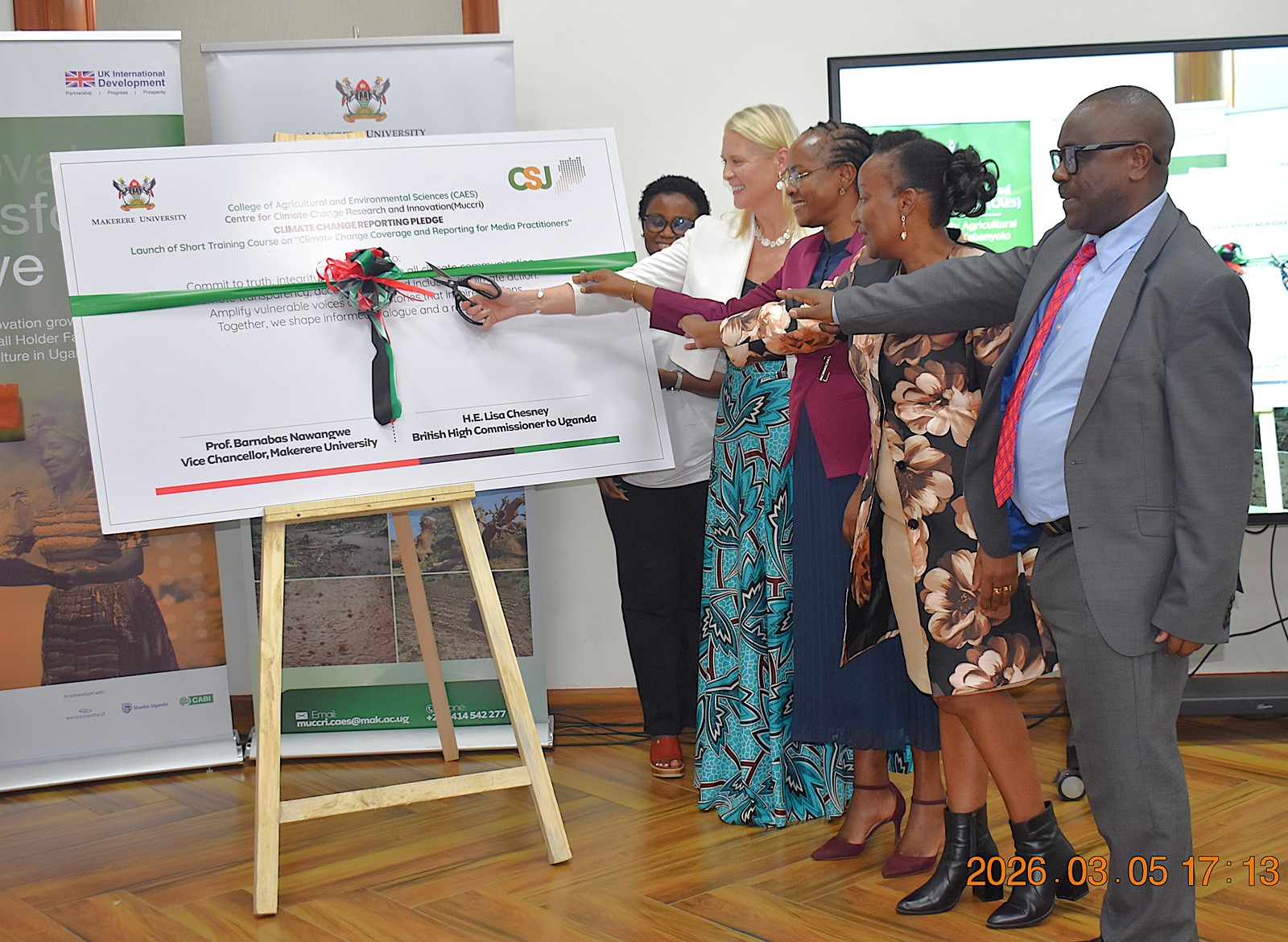
The course was officially launched on 5th March 2026 by the British High Commissioner to Uganda, Her Excellency Lisa Chesney. The ceremony was graced by the First Deputy Vice Chancellor in charge of Academic Affairs (DVCAA), Prof. Sarah Ssali, who represented the Vice Chancellor, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe. It was attended by the Principal of the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES), Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga, and representatives from Climate Smart Jobs (CSJ), the Editors Guild, and media practitioners and content creators focused on climate-related issues.

About the short course on climate change reporting
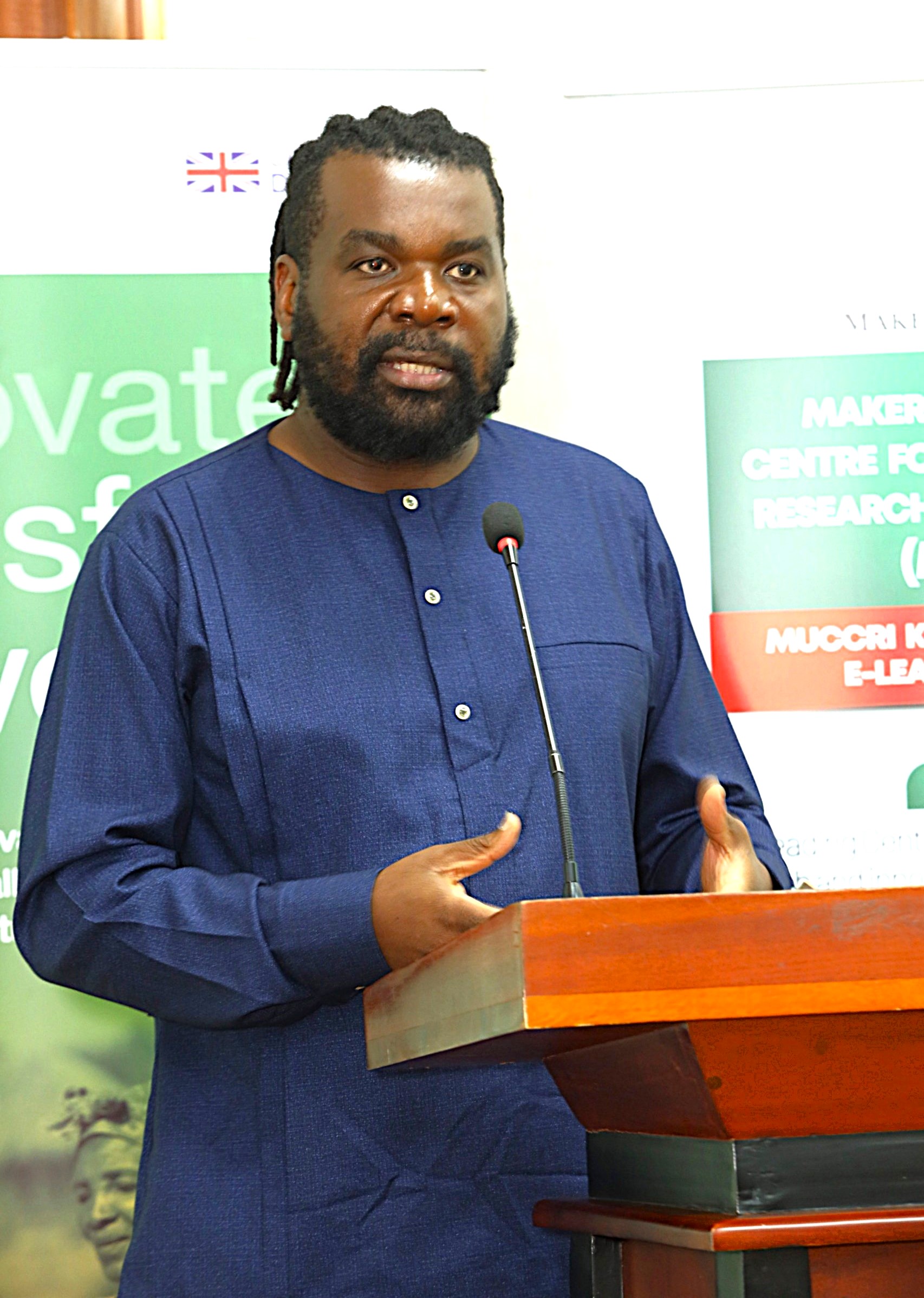
Developed by the Makerere University Centre for Climate Change Research and Innovation (MUCCRI) under the leadership of Prof. Revocatus Twinomuhangi, the course was designed to improve climate science reporting. Through the training, media practitioners will gain a deeper understanding of climate science, climate finance mechanisms, policy frameworks, and local climate solutions and innovations. The programme also aims to empower journalists to tell impactful and meaningful climate stories.
“As the coordinating team at MUCCRI, we worked with climate scientists, policy experts, and media practitioners to develop a programme that is accessible, practical, and engaging,” Prof. Twinomuhangi explained.

According to Prof. Twinomuhangi, the training will be delivered entirely online, making it accessible to participants across Uganda and beyond. It is self-paced, allowing participants to learn at their convenience while continuing with their professional responsibilities. At the same time, it has been designed to remain interactive and engaging through multimedia lectures, real-world case studies, and practical exercises.
The course consists of eight modules that together provide a comprehensive introduction to climate change reporting. These modules cover climate science, climate governance and policy, climate finance, nature-based solutions, inclusive climate reporting, and solutions-oriented journalism. Participants will also gain practical skills in interpreting data, asking critical questions, and crafting compelling climate stories.

“Our goal is not only to build knowledge but also to empower media professionals to report on climate change with confidence, depth, and accuracy,” Prof. Twinomuhangi explained.
He expressed gratitude to the UK Government, through the Climate Smart Jobs Programme, for supporting climate resilience initiatives in Uganda. He also thanked the Palladium Group, the implementer of the CSJ programme, for selecting MUCCRI to design and deliver this training under the Media Training and Mentorship initiative.

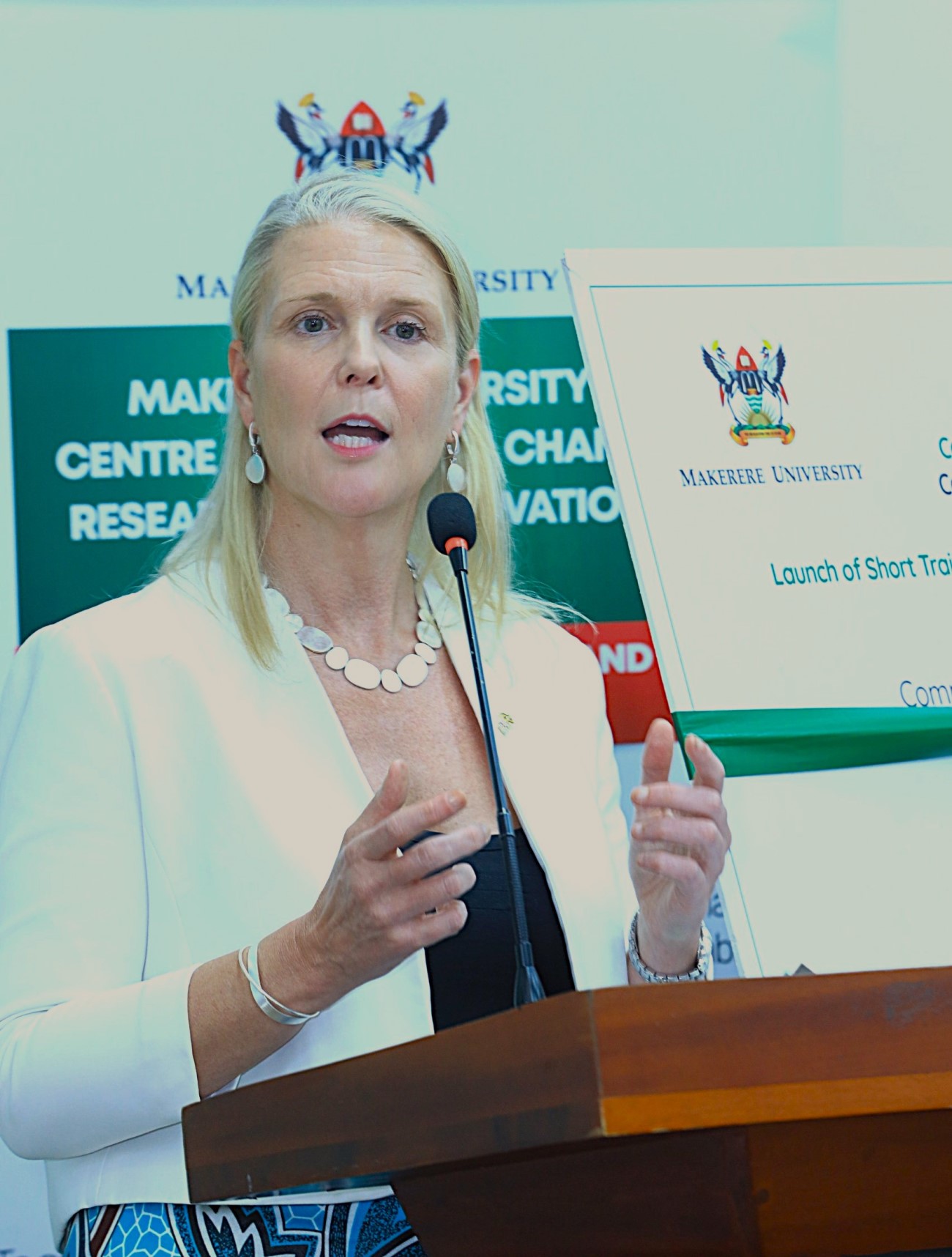
Remarks by H.E the British High Commissioner to Uganda
In her remarks, Her Excellency, the British High Commissioner to Uganda Lisa Chesney, described the initiative as both timely and essential, emphasizing the critical role the media plays in shaping public understanding of climate change.
She noted that climate change impacts communities differently, with women often bearing the greatest burden because they are heavily involved in agricultural production and ensuring food security for their families.

“Clear and accurate reporting on climate change is crucial in helping communities understand the risks and the solutions,” she said.
Relevance of the course to Makerere University
On behalf of the Vice Chancellor, Prof. Sarah Ssali, DVCAA, praised the programme as a reflection of Makerere University’s multidisciplinary, research-led approach to addressing national and global challenges. She highlighted the vital role of the media in translating complex scientific knowledge and policy into accessible information for the public.
“The short course we launch today is both timely and important. It draws on Makerere University’s research expertise and translates that knowledge into practical skills for media practitioners. It provides journalists with tools to better understand climate science, climate finance, carbon markets, adaptation strategies, and issues of equity and inclusion in climate action. By doing so, it strengthens the media’s ability to inform public dialogue and support evidence-based decision-making.”

She equally appreciated the UK Government for supporting the initiative. “We are grateful for the confidence placed in the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences and in particular, the Makerere University Centre for Climate Change Research and Innovations to design and deliver this training. Such partnerships enable universities to translate research into real-world impact.”
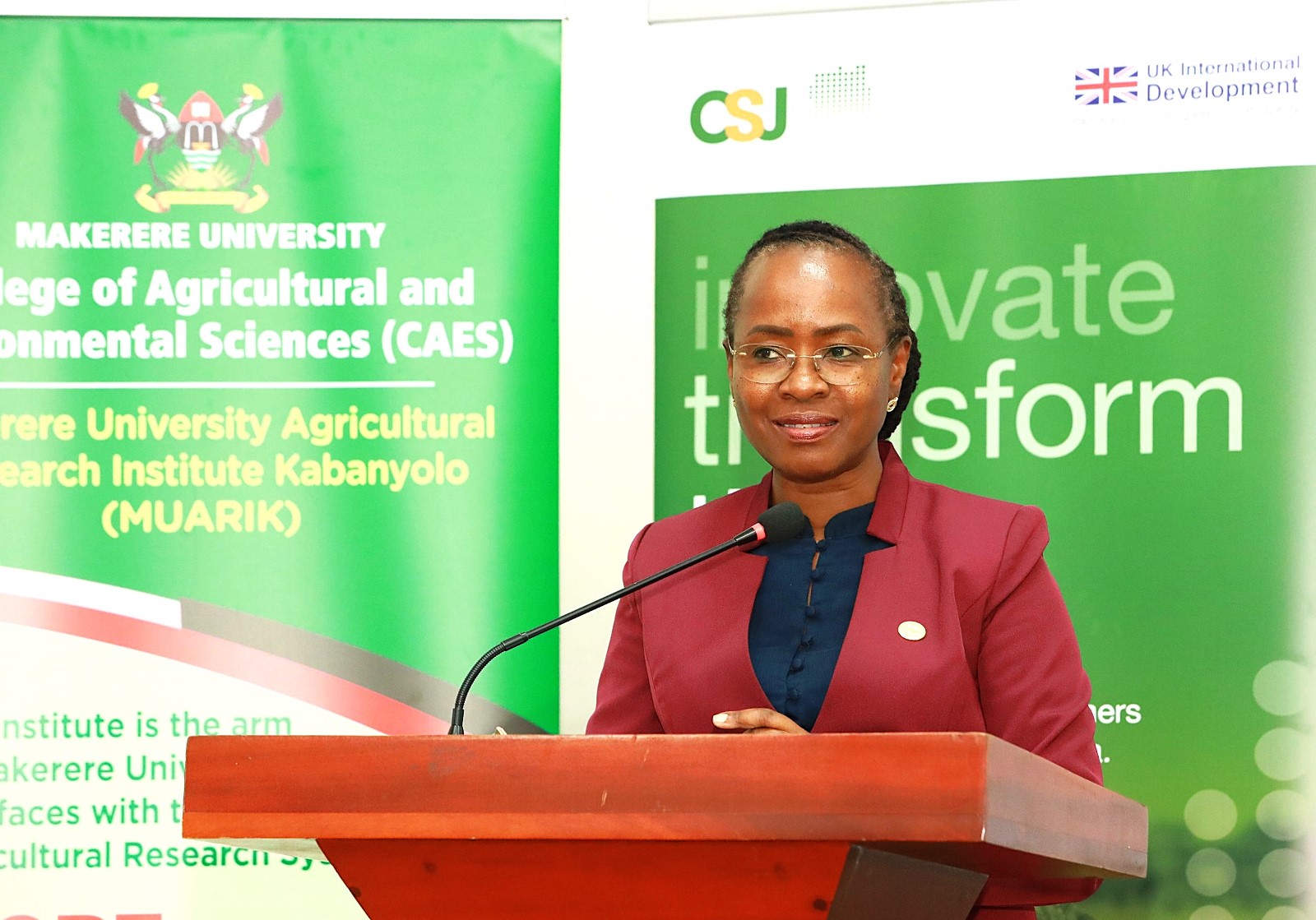
Remarks by the Principal of CAES
Highlighting the challenges posed by climate change and the complexities in reporting climate-related issues, the Principal of CAES, Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga, reiterated the critical role of journalists in raising public awareness, translating scientific findings, and fostering informed dialogue that can drive effective climate action.
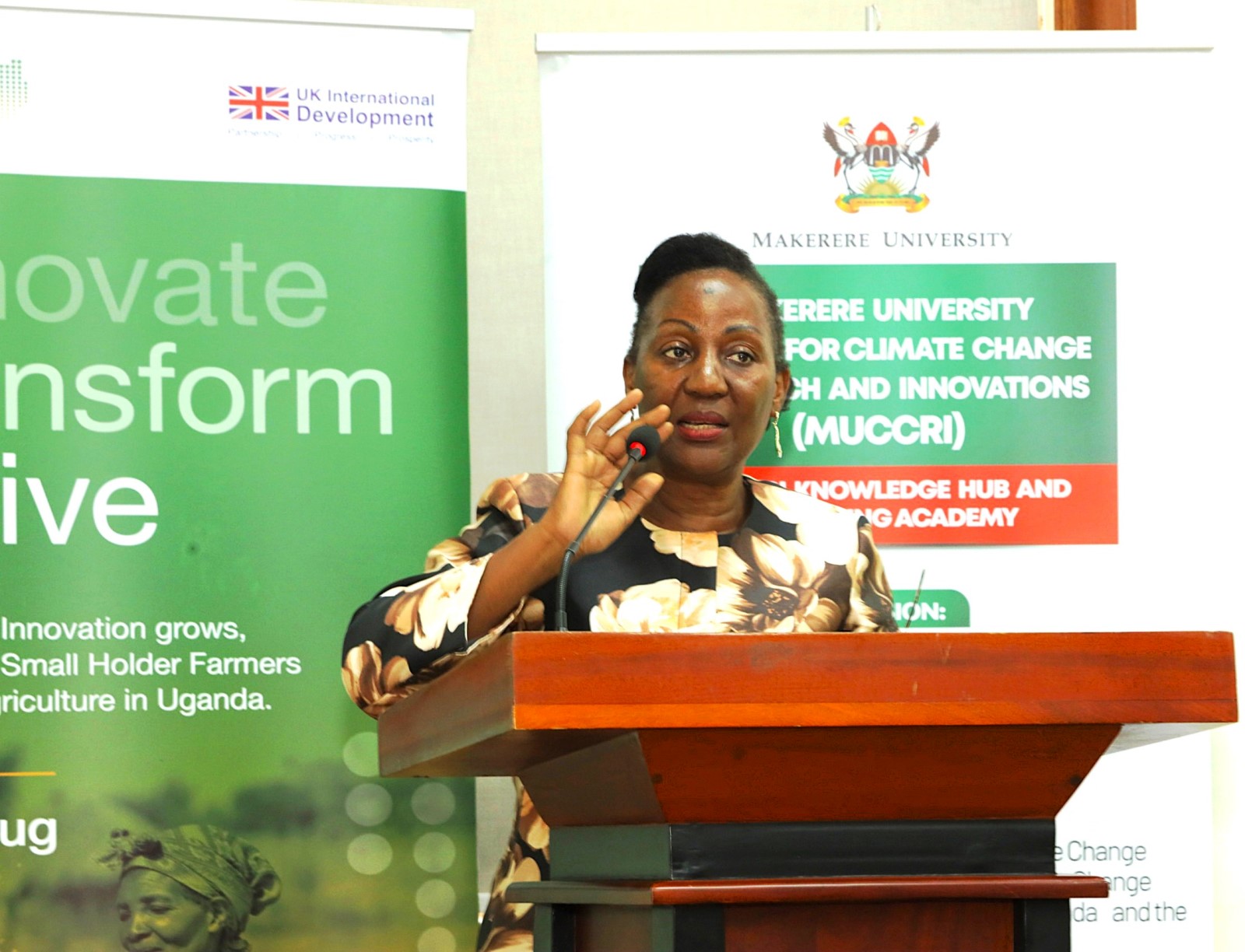

“The short course was therefore designed with a clear purpose: to equip media practitioners with the knowledge, tools, and confidence needed to report on climate change accurately and responsibly,” Prof. Nabanoga said, emphasizing CAES’s commitment to advancing climate solutions through research in sustainable agriculture, environmental governance, forest restoration, and nature-based interventions.
Appreciation from the Editors Guild
On behalf of the Editors Guild, Mr. Alex Atuhaire applauded the funders for supporting quality journalism, noting that the course will strengthen storytelling skills and improve climate reporting across Uganda’s media landscape.
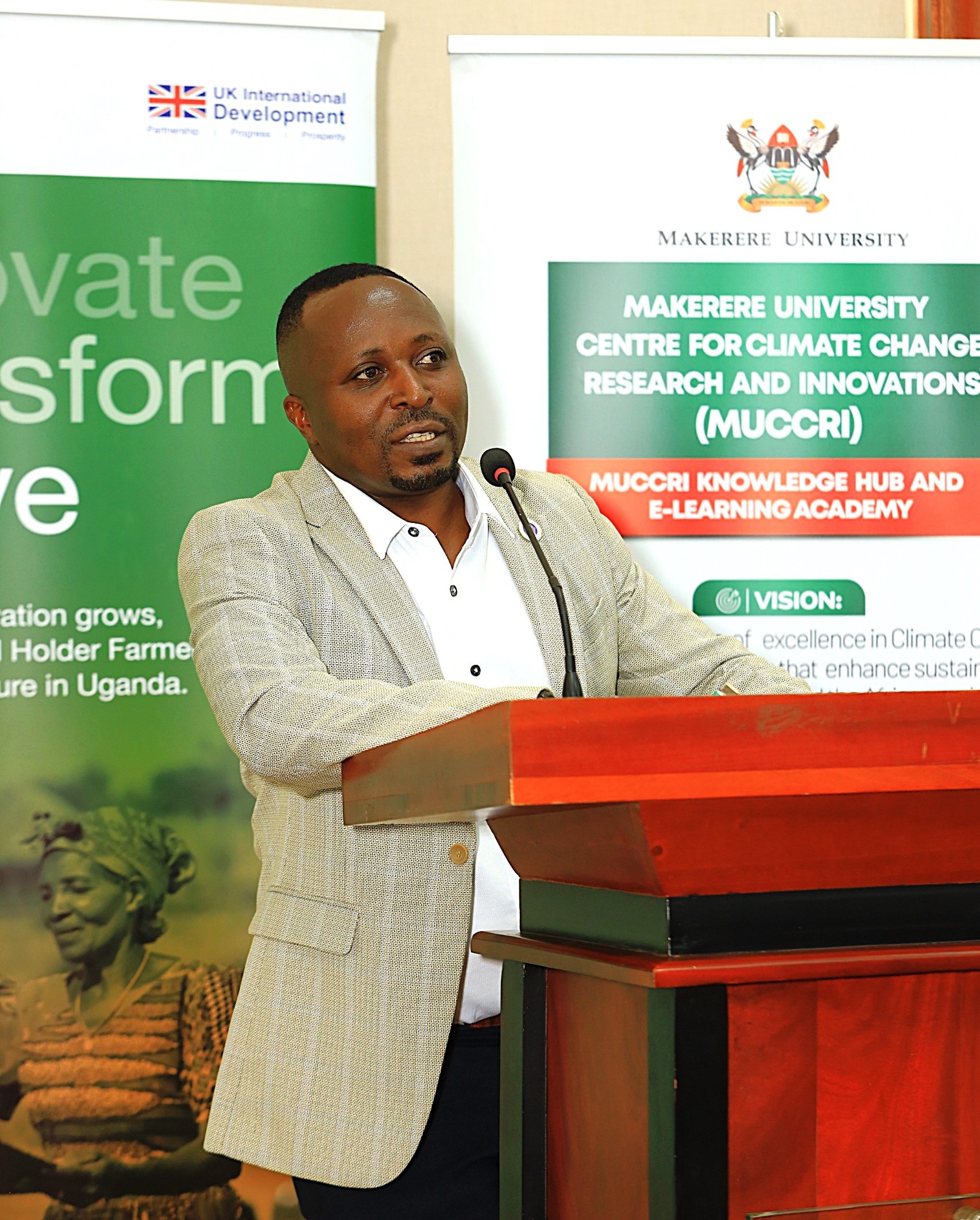

“The launch comes at a pivotal moment as the media navigates the opportunities and challenges of an increasingly digital landscape. The retooling course will breathe life into impactful, skilled, and authentic storytelling on climate change in our newsrooms,” Mr Atuhaire said. The Editors Guild pledged continued support in improving the quality of climate reporting across media platforms in the country.
Relevance of the programme to media practitioners
Sharing her experience, media practitioner Leonard Namukasa highlighted the complexities of reporting on climate change, describing it as scientific, investigative, and inherently challenging. She explained that limited access to reliable scientific data complicates coverage, noting that many people mistakenly equate climate change reporting with general environmental journalism. She welcomed the course, saying it will greatly address some of these challenges.

About MUCCRI
The Makerere University Centre for Climate Research and Innovation (MUCCRI) was established in 2014 within the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences to strengthen climate knowledge generation, knowledge management, and policy engagement. Over the years, MUCCRI has contributed to a wide range of initiatives, including climate knowledge management platforms such as the Climate Adaptation Knowledge Base (CCKB), the SDSN Uganda Chapter, research on climate-induced migration, and programmes that promote sustainable agriculture, nature-based solutions, climate-smart cities, climate finance, locally led adaptation, and community resilience.

MUCCRI is a member of the Least Developed Countries Universities Consortium on Climate Change (LUCCC), a global network of universities working together to advance climate research, knowledge exchange, and capacity building in least developed countries. Through these efforts, the Centre aims to bridge the gap between climate science, policy, and society.
More photos from the launch



Trending
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMakerere University commemorates 13 transformative years of partnership with Mastercard Foundation
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMakerere University and World Bank Sign Partnership to Strengthen Environmental and Social Sustainability Capacity
