Agriculture & Environment
New Project to Improve Relevance of CAES PhD Graduates
Published
12 months agoon
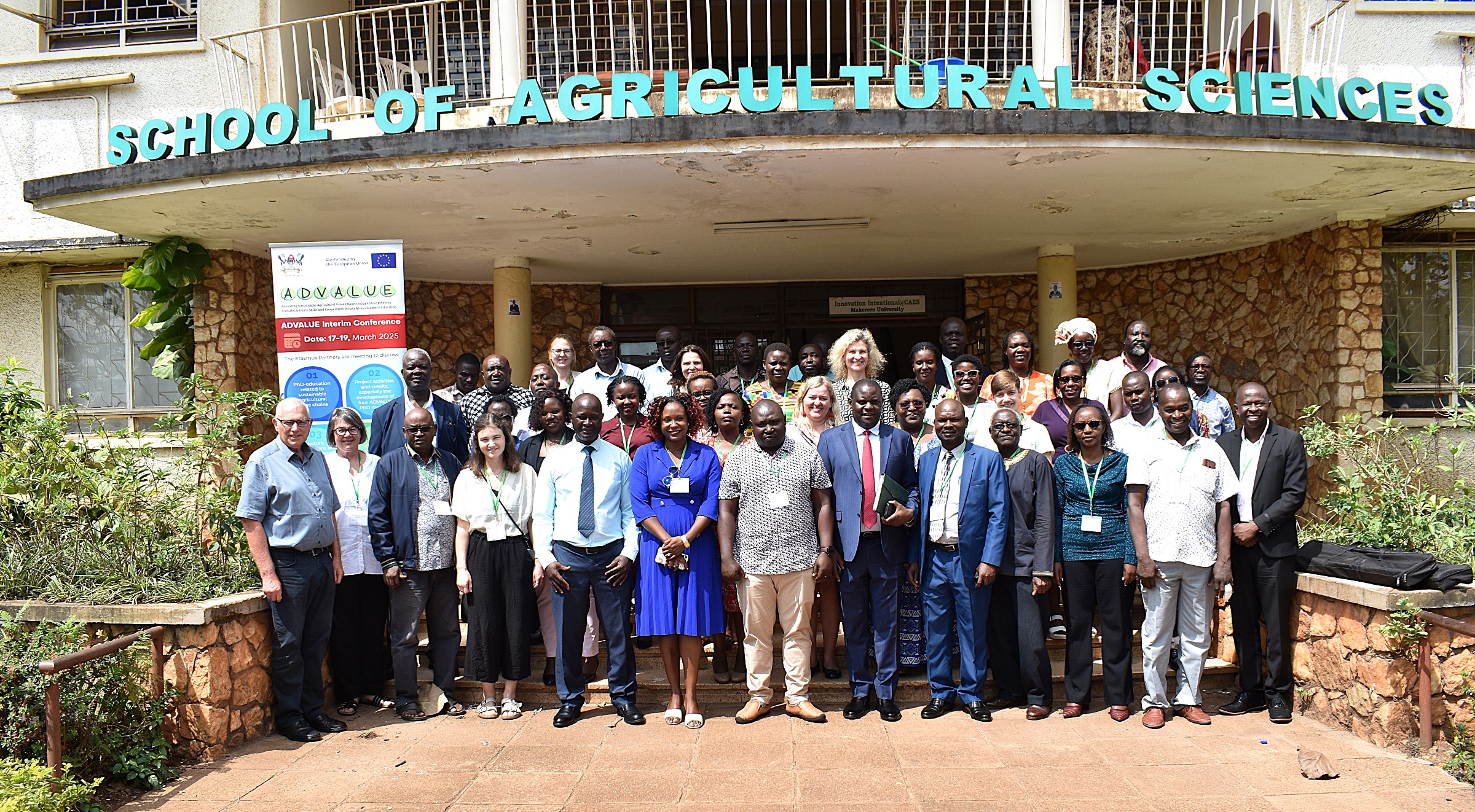

Working with potential future employers of PhD students in Kenya and Uganda, Advancing Sustainable Agricultural Value Chains through Strengthening Trans-disciplinary Skills and Cooperation in East African Doctoral Education (ADVALUE) Project aims to develop curricula that best prepare academic specialists in agricultural sciences for their careers.
Overview
The lack of skills-oriented training significantly undermines the relevance of doctoral graduates in today’s rapidly evolving job market, particularly within industries such as agriculture, where practical expertise and adaptability are essential. While doctoral programmes traditionally emphasize research and theoretical knowledge, they often fail to equip graduates with the hands-on, industry-specific skills needed to address real-world challenges. In agricultural value chains, for instance, the ability to apply advanced research to optimize production, supply chain management, sustainability practices, and technological advancements is crucial. Without a strong foundation in these practical areas, doctoral graduates may struggle to effectively contribute to innovation and efficiency in agricultural systems. From improving crop yields through data analysis to enhancing logistics and distribution methods, agricultural value chains require professionals who can seamlessly integrate research with practical application.

What the ADVALUE Project targets to address
Co-funded by the European Union, the ADVALUE Project—Advancing Sustainable Agricultural Value Chains through Strengthening Trans-disciplinary Skills and Cooperation in East African Doctoral Education—seeks to modernize doctoral education in agricultural and agro-environmental sciences at universities in Uganda and Kenya. This initiative aims to enhance trans-disciplinary skills to promote the development of sustainable agricultural value chains, addressing pressing challenges such as food insecurity, unemployment, and climate change.
Project partners include; Nuertingen-Geislingen University, Germany (NGU); German Institute for Tropical and Subtropical Agriculture (DITSL); Czech University of Life Sciences Prague (CZU); Swedish University of Agricultural Science (SLU); Makerere University, Uganda; Uganda Christian University (UCU); University of Nairobi, Kenya (UoN); Pwani University Kenya (PU); Regional Universities Forum for Capacity Building in Agriculture, Uganda (RUFORUM). Associated Partners: European Alliance in Agricultural Knowledge for Development, Belgium (AGRINATURA); National Agricultural Research Organization, Uganda (NARO); National Council of Higher Education, Uganda (NCHE); Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organisation (KALRO); Ministry of Education Science and Technology Kenya (MoEST). The project PI is Prof. Dr. Heinrich Schüle. In Uganda, the project is coordinated by Prof. John Tabuti.

Project objectives
- Develop innovative courses on trans-disciplinary research methodologies and value chain analysis within doctoral programmes.
- Strengthen collaboration with key stakeholders to ensure research is demand-driven and fosters innovation.
- Enhance the expertise of both academic staff and doctoral students.
- Improve quality assurance frameworks and development processes in doctoral education.
To achieve these goals, ADVALUE is developing four modules for PhD students that will be integrated into the curricula of the partner universities in Kenya and Uganda, taking into account the experiences and expectations of local stakeholders and potential future employers. The modules will include topics on scientific work, trans-disciplinary research, rangeland management, and agricultural value chains. The collaboration and exchange between the universities and representatives from the working environment, government organisations and international partners aims to strengthen the career prospects of postgraduate students in East Africa and promote their expertise with regard to the local requirements for achieving the SDGs.

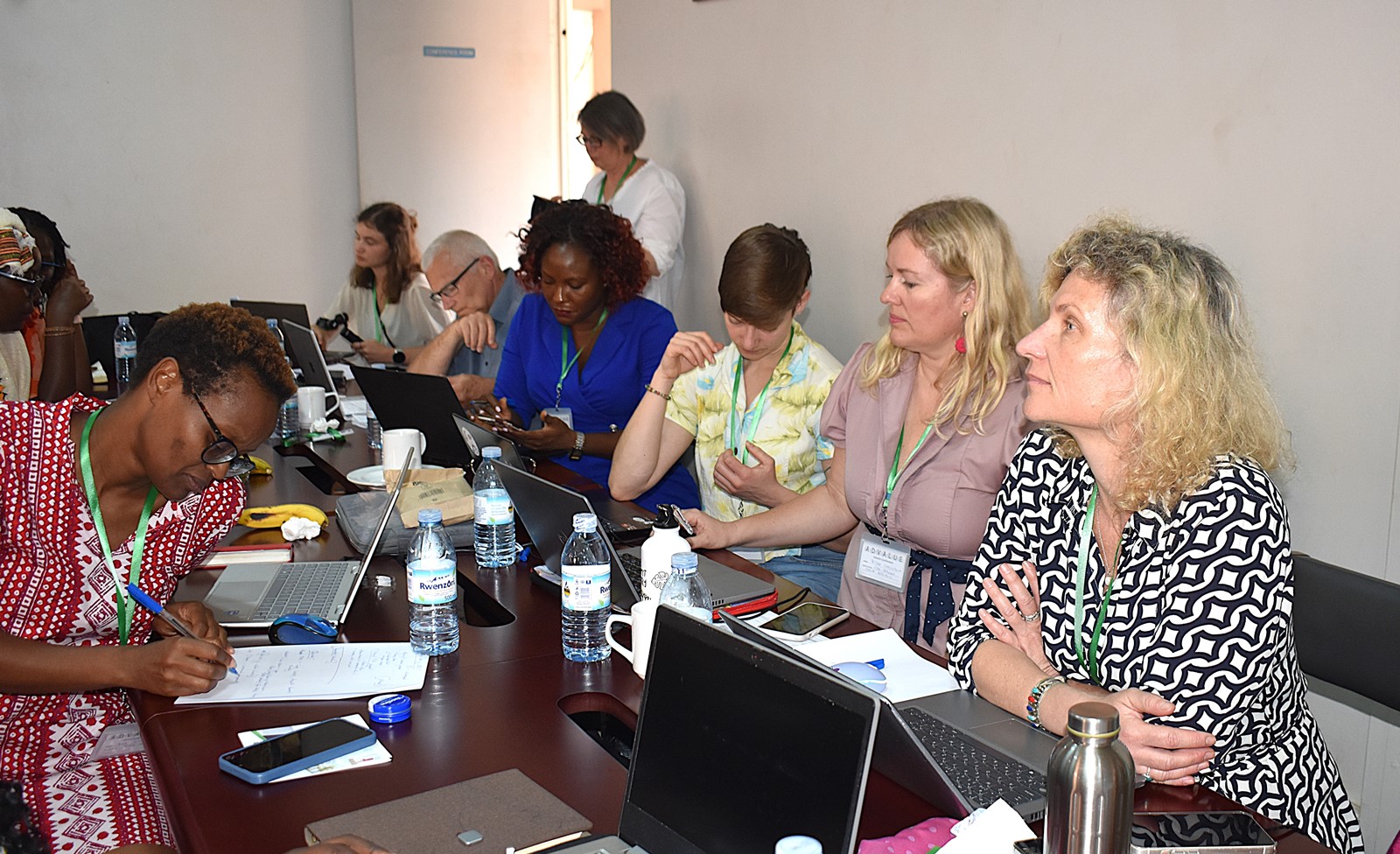
The ADVALUE interim conference
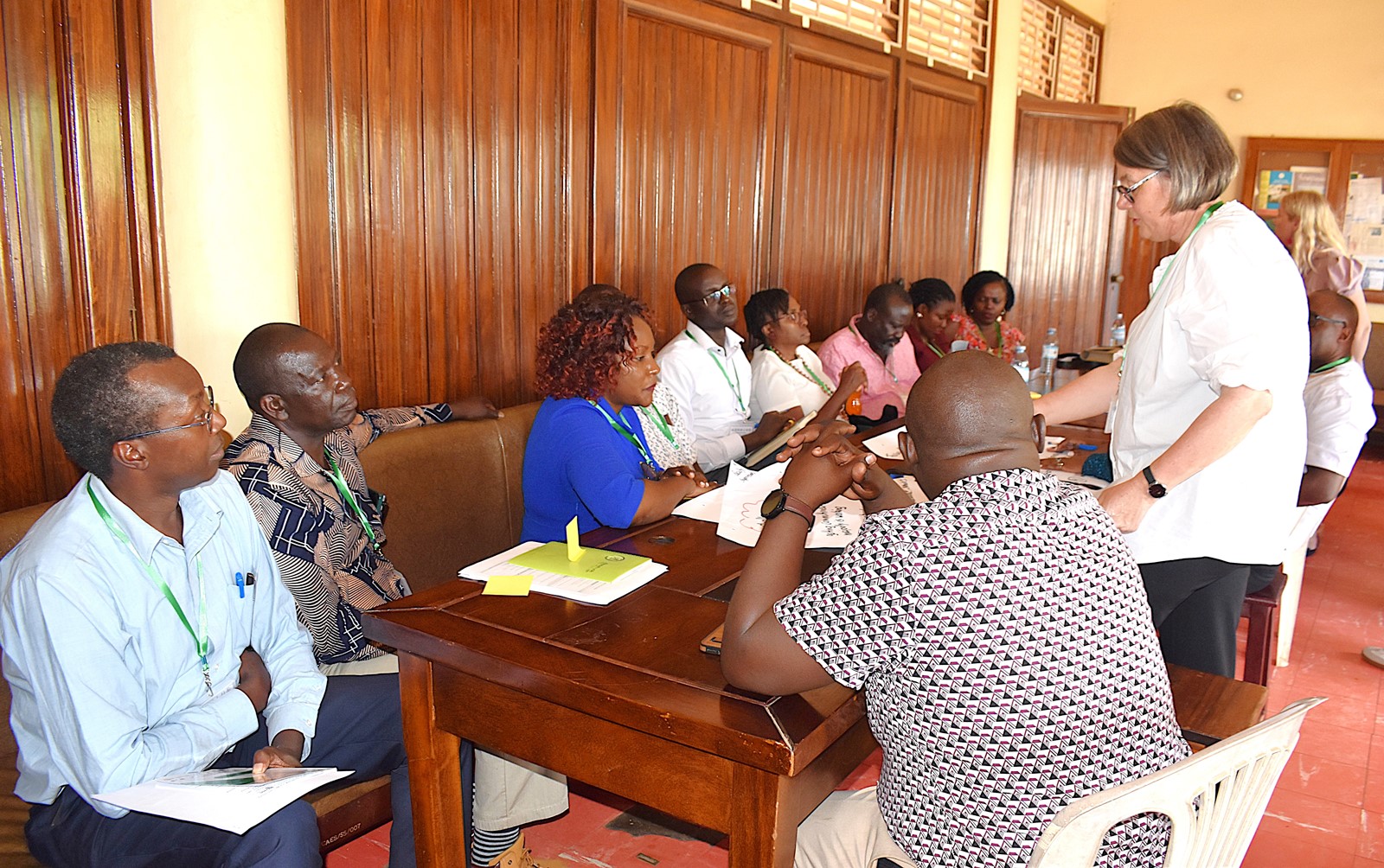
The project team held an interim conference at Makerere University on 17th-19th March 2025 to evaluate the state of PhD education in agriculture, incorporating diverse insights from both European and East African perspectives. The conference brought together academic staff, students, and leaders from partner institutions, associated organizations, and key stakeholders in the Agricultural sector.
The conference aimed to highlight the progress and findings of the project, offering a platform for discussing PhD research on agricultural value chains within higher education institutions (HEIs). A key focus was on trans-disciplinary approaches, as well as fostering dialogue on quality criteria for PhD programs. Additionally, the event served as a formal meeting for the project’s Steering Committee and provided an opportunity for partners to refine their assessments of doctoral education in line with established quality standards and institutional contexts.
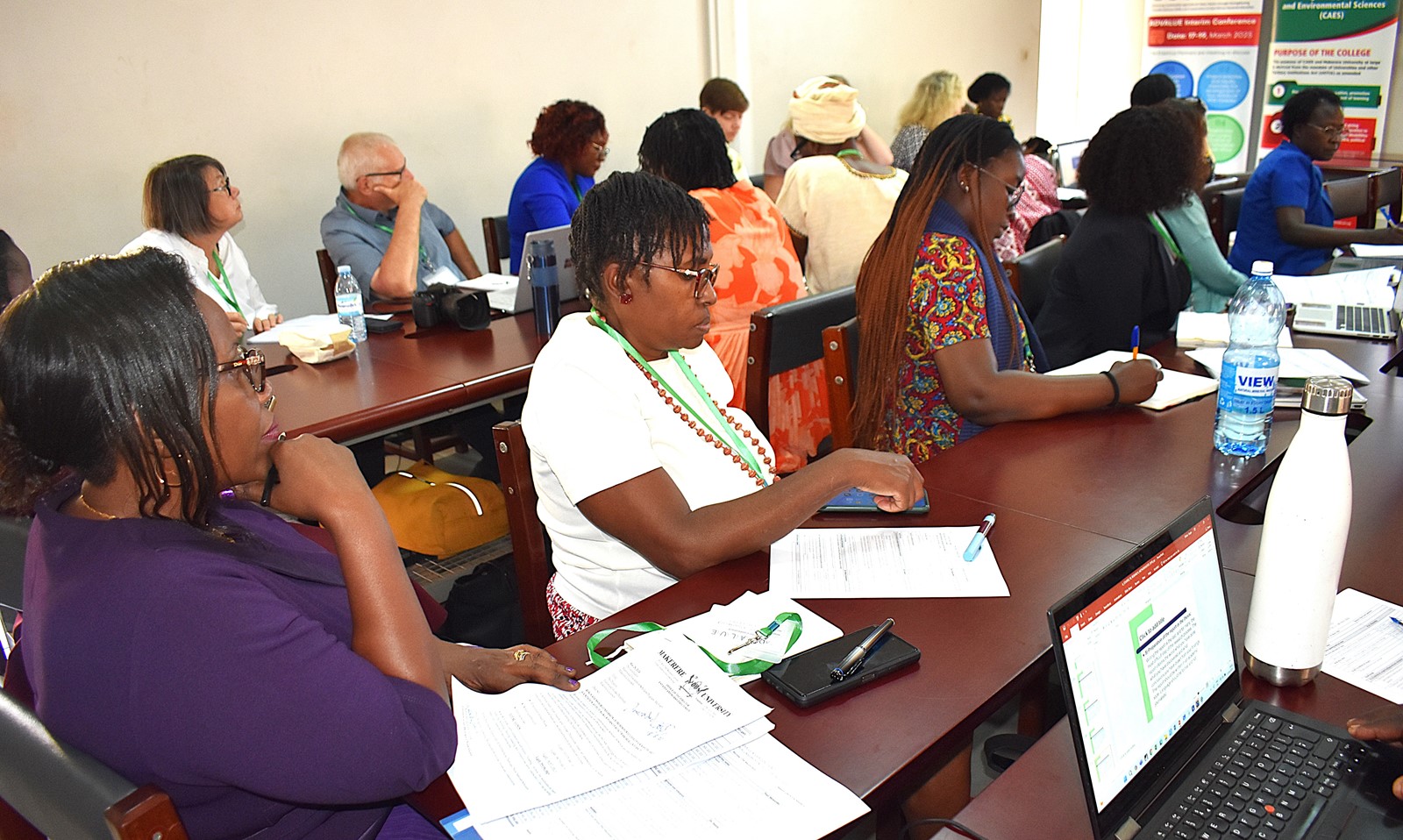

Presentation by Mr. Joseph Nkandu on the Agricultural Value Chains in E.A
In his address on the sustainability of agricultural value chains in East Africa, Mr. Joseph Nkandu, Executive Director of NUCAFE (Uganda’s national umbrella organization for coffee farmers), emphasized the vital role that higher education plays in strengthening and advancing agricultural value chains. He stressed the importance of aligning education with the region’s broader development goals to ensure that future generations of agricultural professionals are equipped with the necessary skills for sustainable growth. “Education must become more practical and closely integrated with the region’s development objectives,” he noted. He praised the initiative, noting that the project would greatly enhance doctoral training at partner institutions, empowering students with advanced knowledge and skills to support and sustain agricultural value chains across East Africa. “The sustainability of Africa’s value chains is essential if we are to meet the demands of the growing population,” he added.
Uganda’s agricultural value chains are a cornerstone of its economy. However, several challenges threaten their sustainability, including climate change, which affects crop yields and water availability; inadequate infrastructure, which hinders market access; limited access to finance for smallholder farmers; land degradation; and insufficient technology adoption. Moreover, pest outbreaks and post-harvest losses further undermine the efficiency and profitability of agricultural systems. Tackling these challenges is essential to improving the sustainability and resilience of Uganda’s agricultural sector.
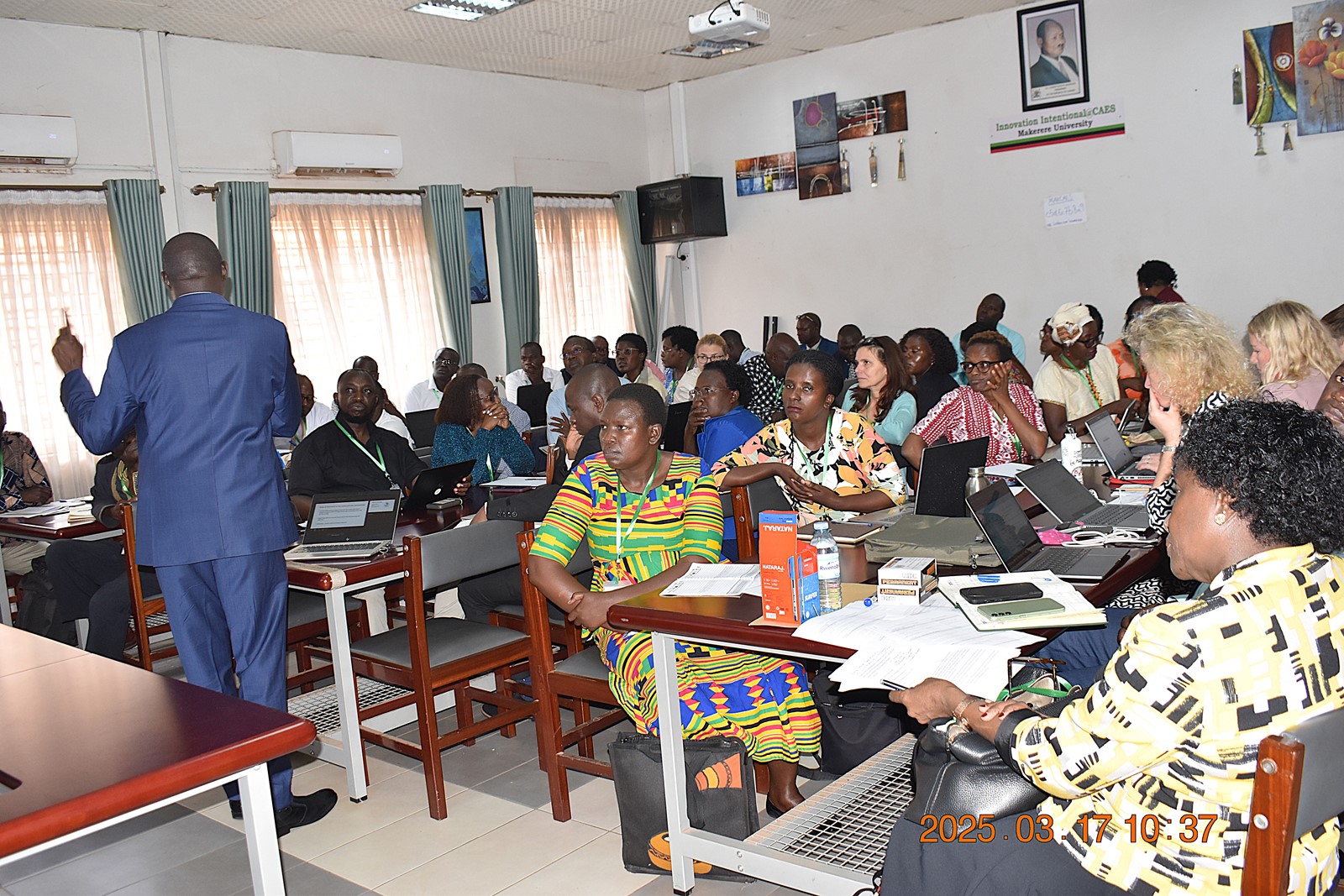

Remarks from NCHE
In her remarks, Prof. Mary Okwakol, the Executive Director of the National Council for Higher Education, emphasized the critical role of doctoral training in driving societal progress. She explained that advanced research and innovation resulting from doctoral programmes not only contribute to academic advancement but also pave the way for ground-breaking discoveries. “These discoveries, in turn, play a pivotal role in shaping and transforming nation-states by addressing pressing challenges, fostering economic growth, and improving the quality of life for communities.” Prof. Okwakol called for continued investment in doctoral education to harness its potential for national development and global competitiveness.

Highlighting the challenges related to Doctoral training, the Deputy Principal of CAES, Prof. Yazidhi Bamutaze, noted that the project was timely and would greatly strengthen the research capabilities of doctoral students, ensuring that their skills are more aligned with current academic and industry needs, ultimately improving the overall relevance and impact of their research outputs. “As Makerere University strives to become a research-intensive institution, the importance of collaboration cannot be overstated. This project will make a substantial contribution to this goal.”

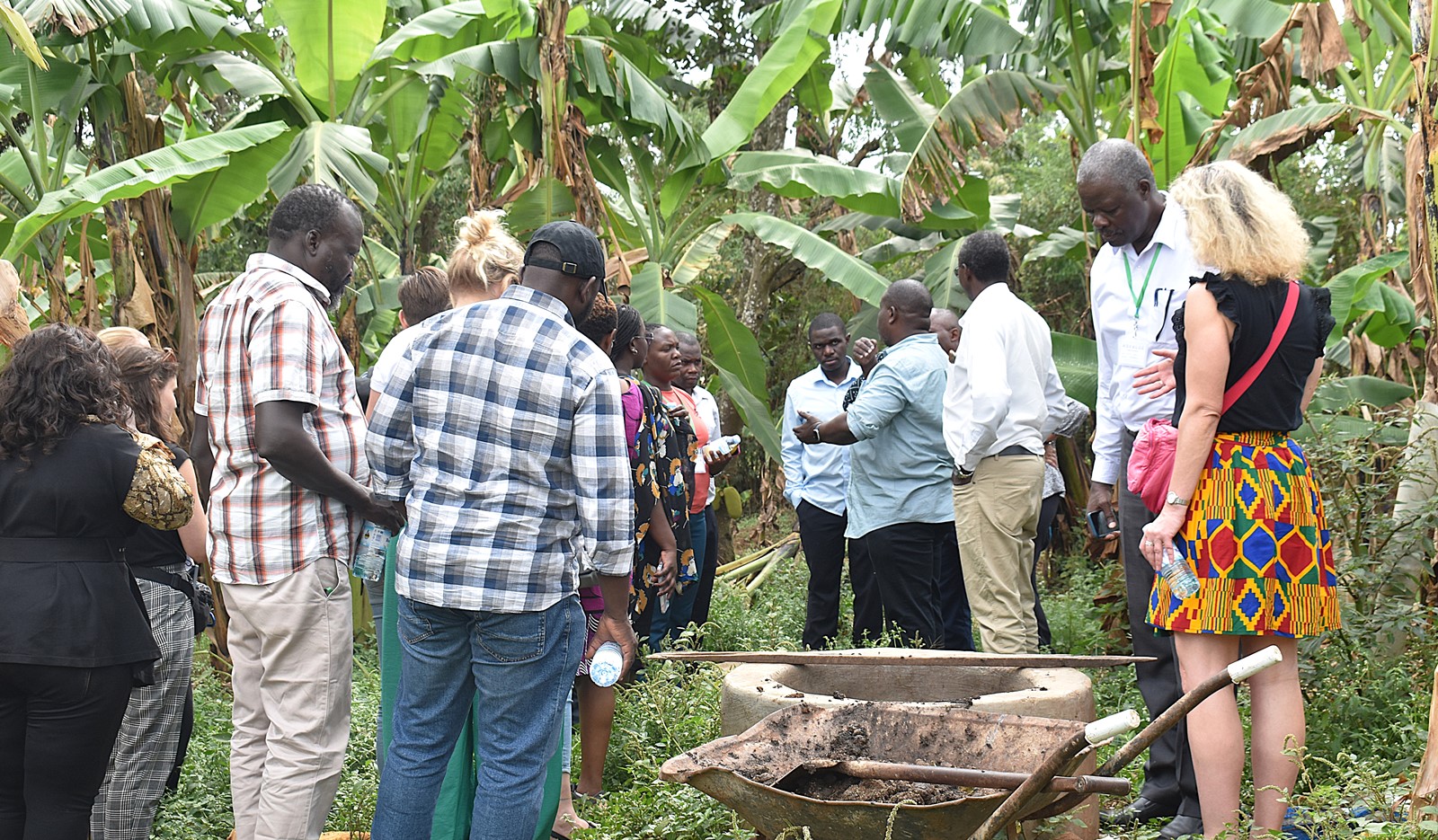
Engagement with smallholder farmer in Matugga
During the conference, the project team had the opportunity to visit the farm of Mr. Sam Mpiira, a dedicated smallholder farmer located in Matugga, within Nansana Municipality. The visit allowed the team to gain first-hand insight into Mr. Mpiira’s farming practices, observe the challenges he faces, and better understand the impact of various agricultural initiatives in the region. This experience was an important part of the conference, as it provided a real-world context to the discussions on smallholder farming and rural development.

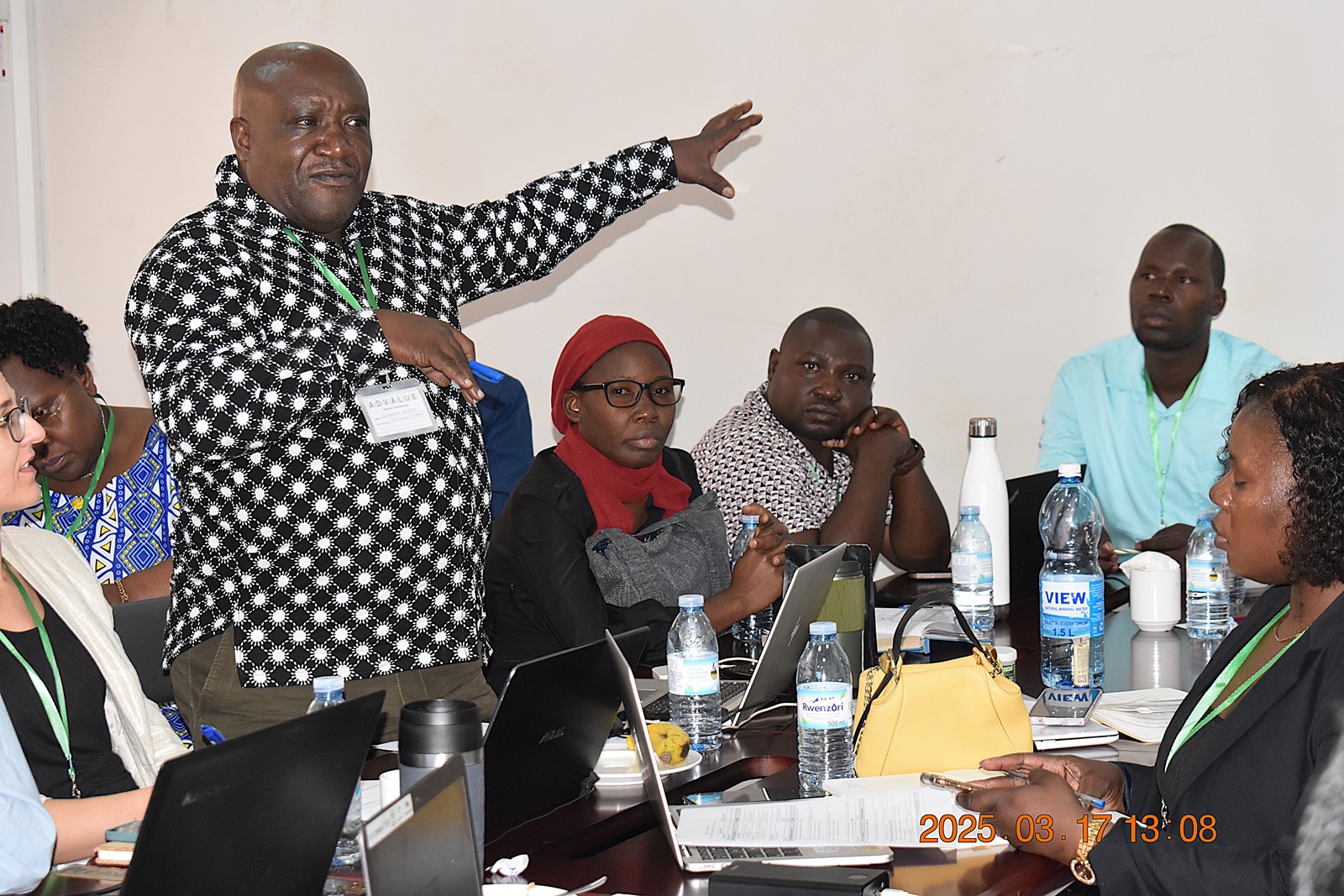
Key Issues Arising from the Workshop
- Overemphasis on theoretical science: While science is extensively studied, its practical application remains problematic.
- Outdated supervision: Many PhD supervisors are not up-to-date with current research trends. There is a need for educational frameworks that align with the latest development agendas.
- Technician mentality among graduates: A significant number of PhD graduates tend to think like technicians rather than innovators. Many struggle to apply the knowledge they’ve acquired and lack the ability to think creatively.
- Lack of innovation: There is a notable absence of innovation among doctoral graduates, which hinders progress.
- Evolving skillsets in value chains: There is an urgent need to address the changing skillsets required across different value chains.
- Unrealistic PhD programme durations: The prescribed durations for PhD programmes are often unrealistic and fail to reflect the complexity of the research process.
- Competing priorities: The multiple demands on students’ time hinder their ability to complete doctoral studies in time.
- Financial barriers: Limited funding continues to undermine the success and sustainability of doctoral training programmes.
- Lack of student commitment: Some doctoral students exhibit a lack of commitment and dedication to their studies, impacting their success.
- Negative student attitudes: Students often display an underestimation of the role and guidance of their supervisors, which affects their academic progress.
- Inadequate research facilities: Limited access to essential research facilities hampers the quality of doctoral research.
- Weak analytical skills: Many doctoral students lack the necessary analytical skills to perform at the required level of their academic discipline.
- Gender-based challenges: Gender roles negatively impact the performance and progression of female doctoral students, limiting their academic potential.
- Supervisory workload: Excessive workload on supervisors affects the quality and effectiveness of their mentorship.
- Need for relearning in value chains: Achieving sustainability in value chains demands continuous relearning and adaptation.
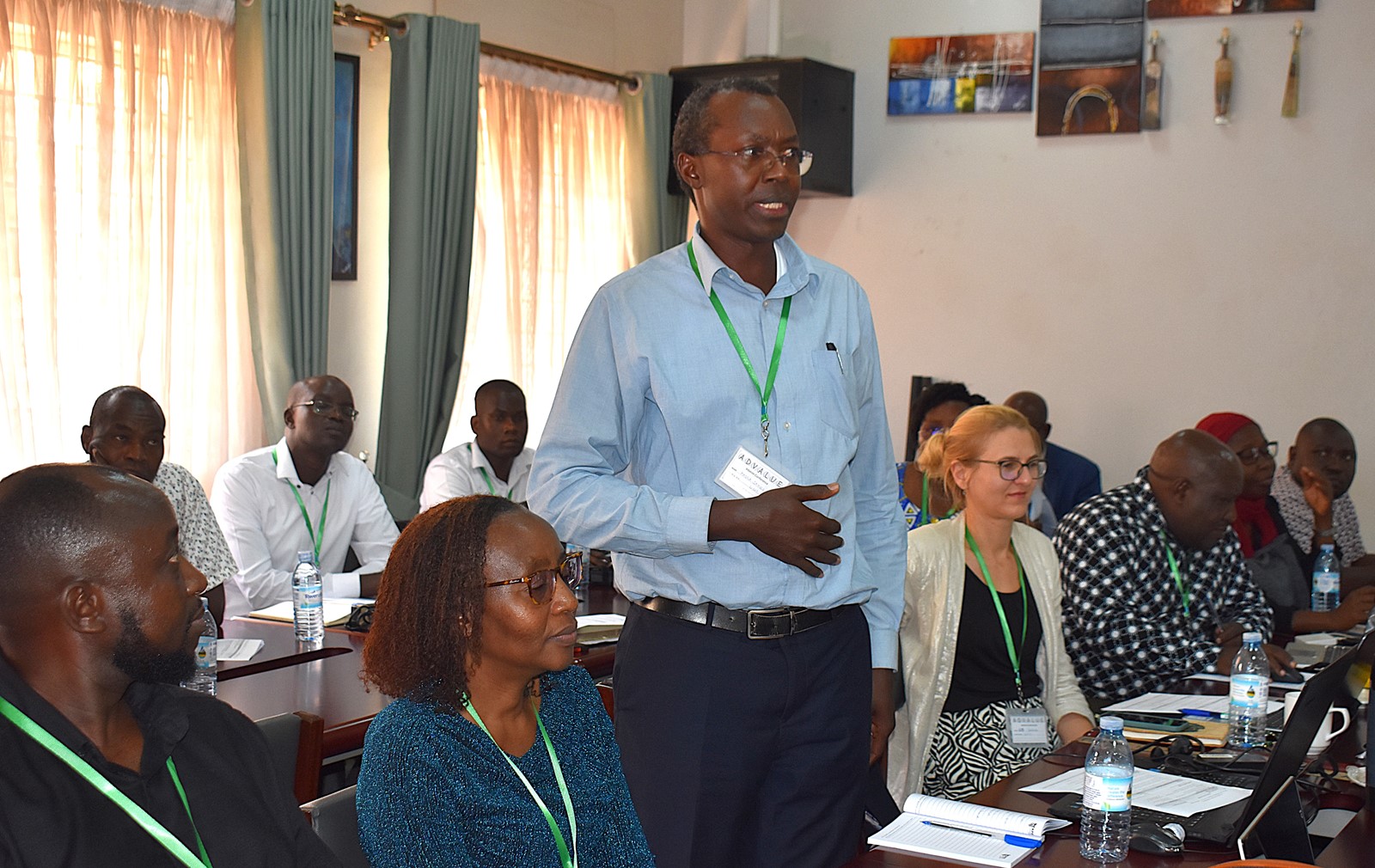

Recommendations
- Dedicated study leave: Doctoral students should be granted leave from other responsibilities to focus fully on their research.
- Creating research spaces: Institutions must create dedicated, conducive workspaces for doctoral students to foster collaboration and focus.
- Increase funding opportunities: More scholarships and financial support should be made available to PhD students to ease financial barriers.
- Research-oriented supervision: Supervisors must establish and maintain active research agendas to ensure they remain relevant and effective in guiding students.
- Strengthen institutional collaboration: Encouraging greater collaboration between Higher Education Institutions can foster exchange of ideas and resources to enhance doctoral research outcomes.
Photos from conference activities
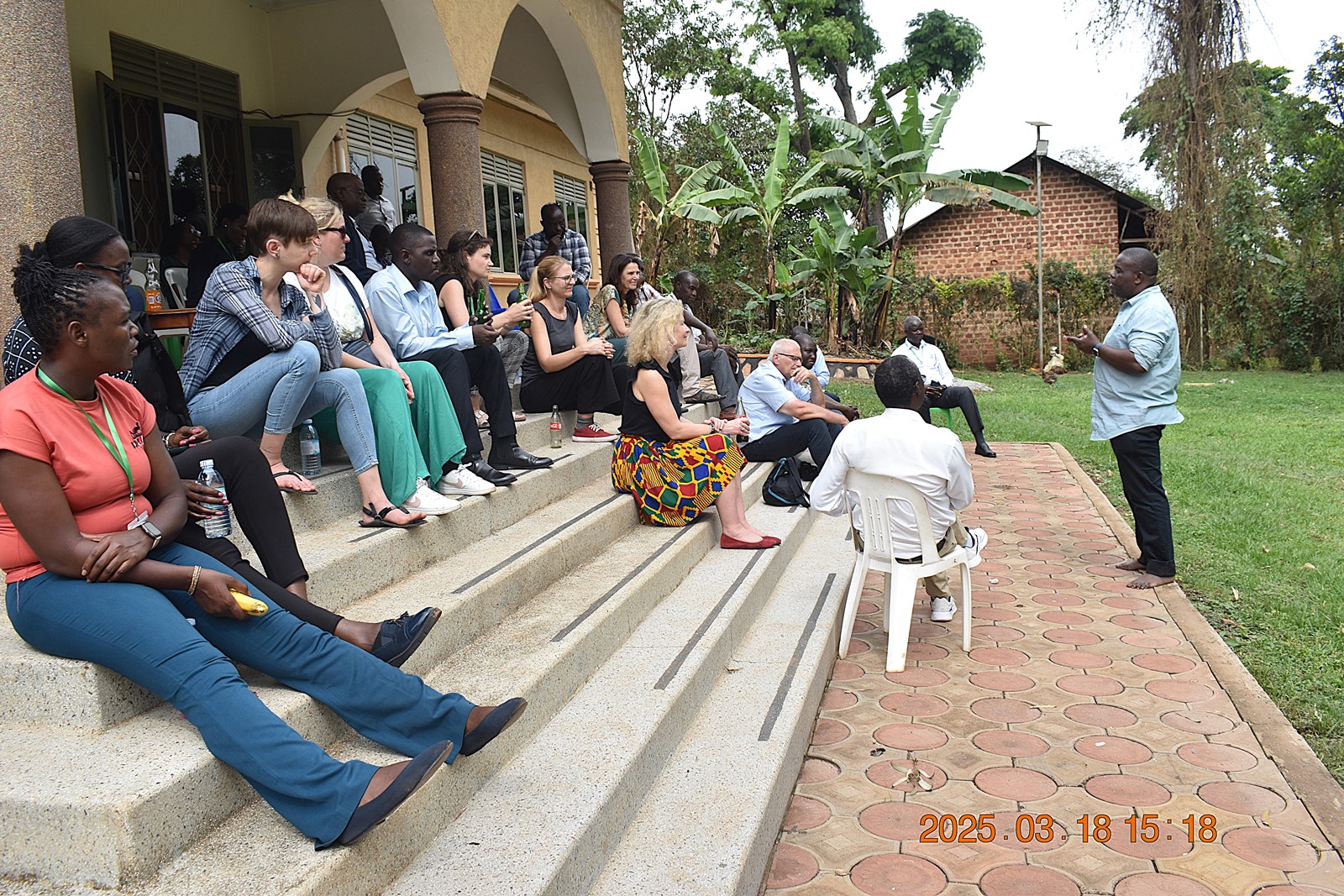
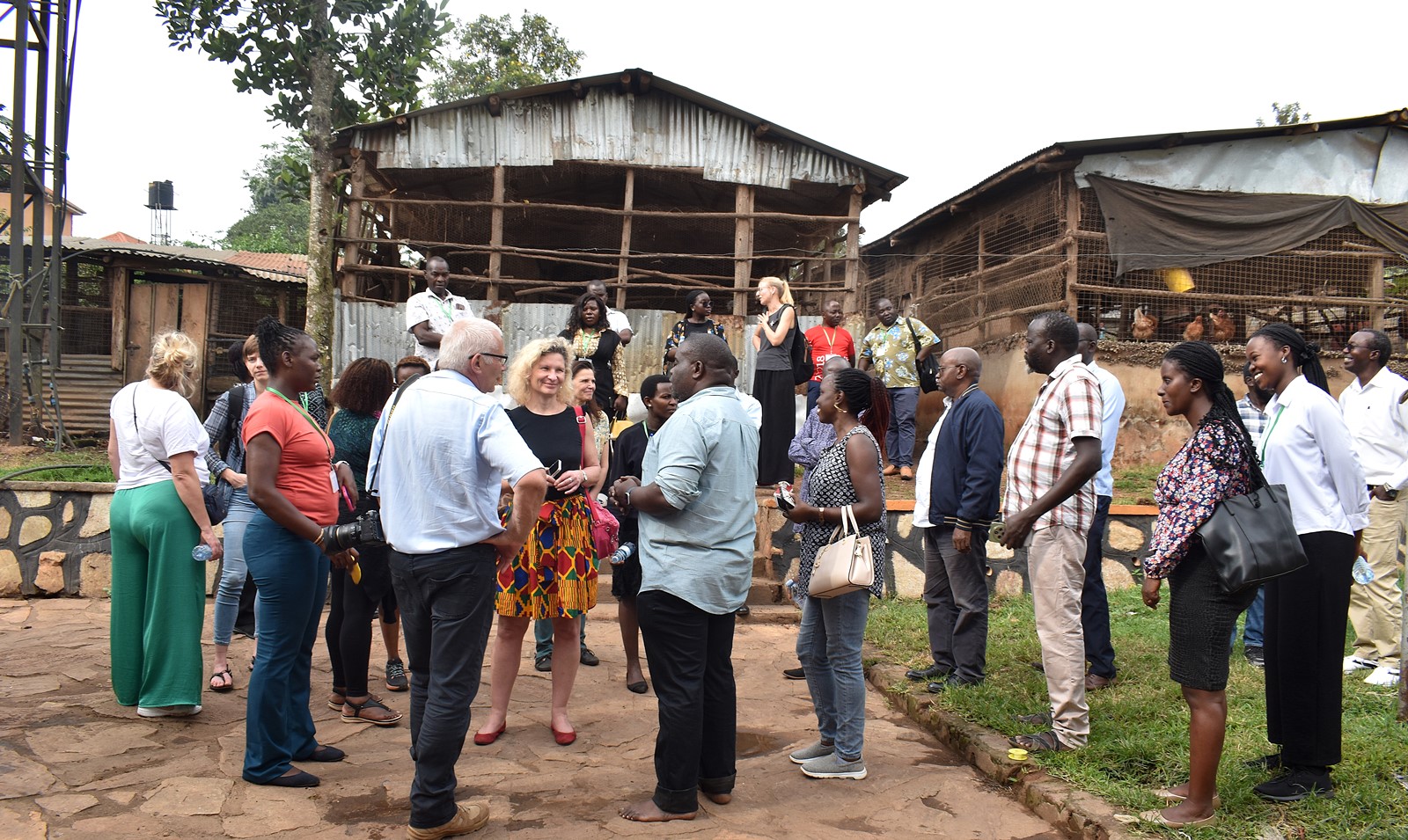
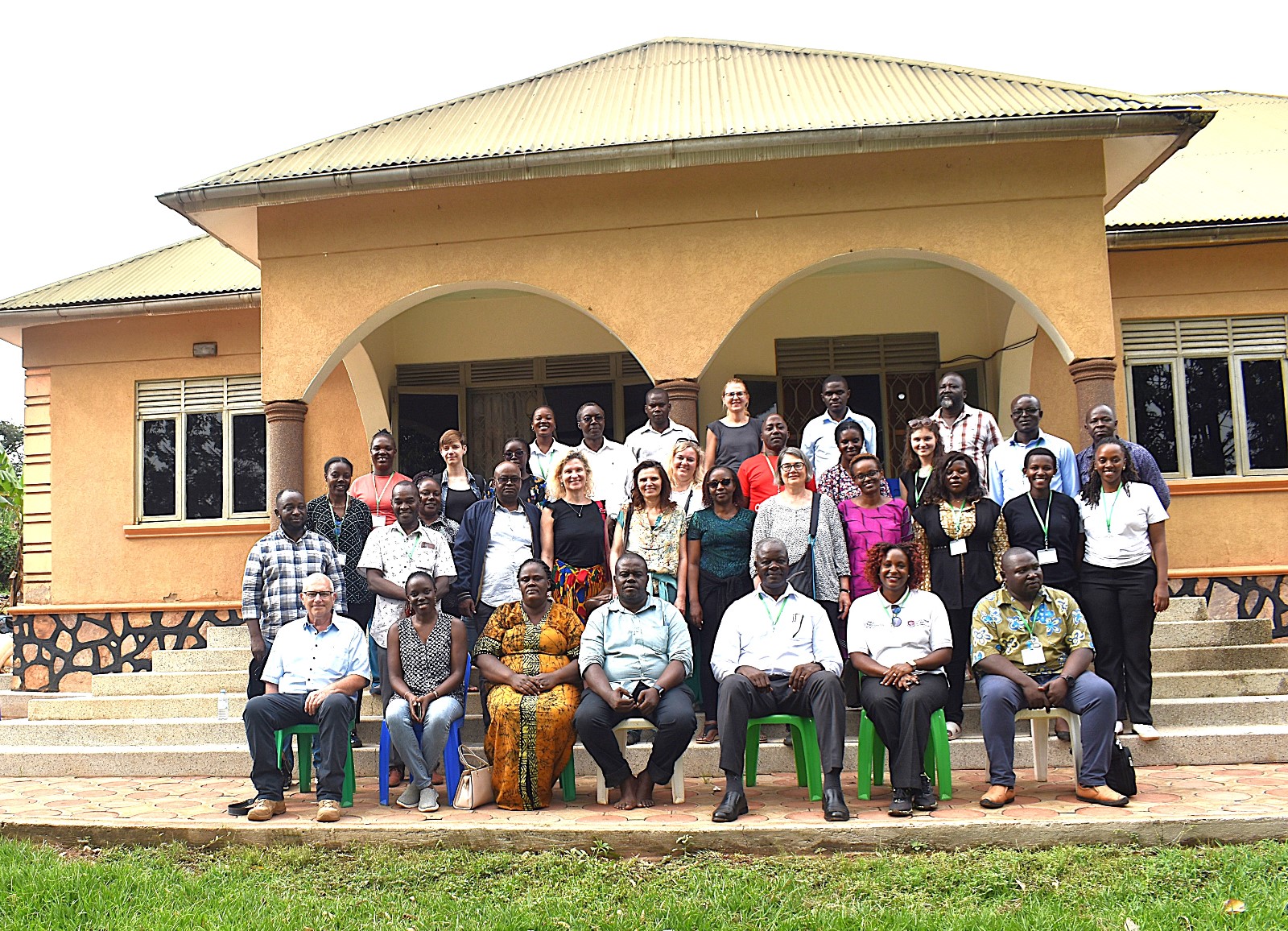
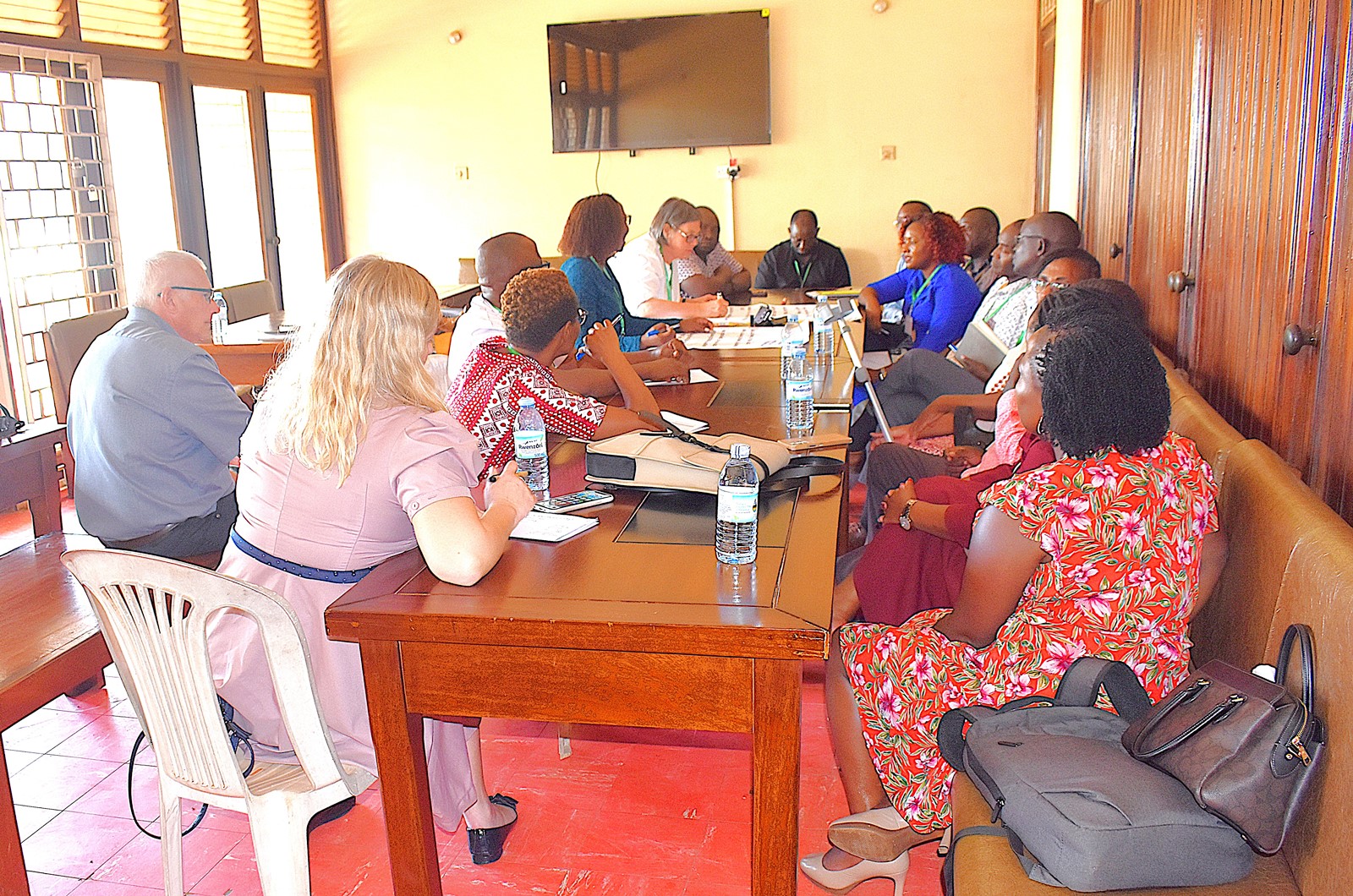






More photos at:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1cZwlLXt5YBWoeMfO0wVbdva0NLIQ5sHr
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/107GJR6nCZJwKjmfrwveGXw7As2AhAQWt
You may like
-


82% Stressed: Uncovering the Hidden Mental Health Burden Among Kampala’s Taxi Drivers
-


Makerere University and International Partners Sign MoU for the 9th Kampala Geopolitics Conference
-


Farmers’ Preferences Drive Success in Tree-Planting, Duke Scholar Finds
-


AI SHOWDOWN: Careers Fair 2026 Kicks Off at Makerere
-


Makerere University Students Triumph in National Conservation Competition
-


Mak Cooperative Society holds AGM: Growth, Transparency and Member Welfare Take Centre Stage
Agriculture & Environment
Makerere University Students Triumph in National Conservation Competition
Published
4 days agoon
March 10, 2026By
Mak Editor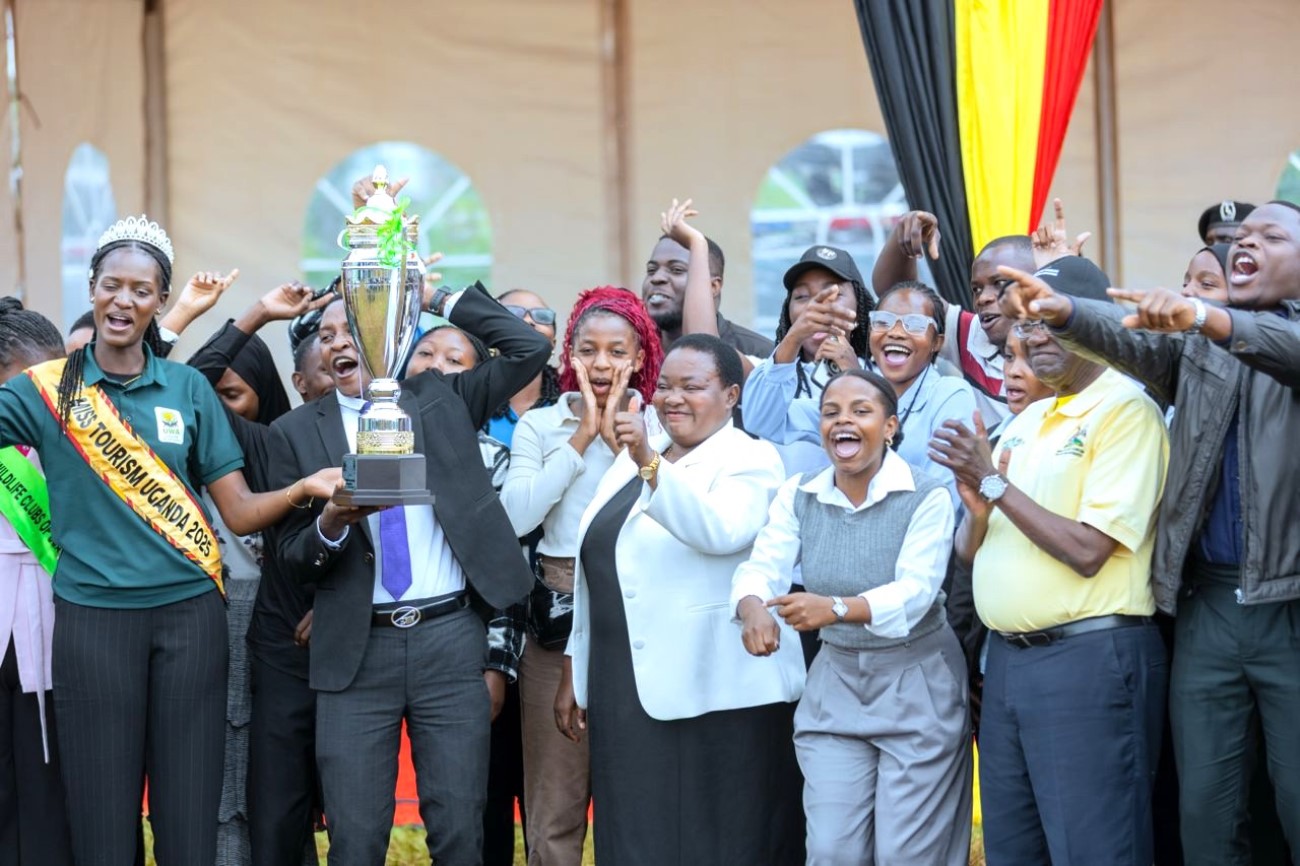
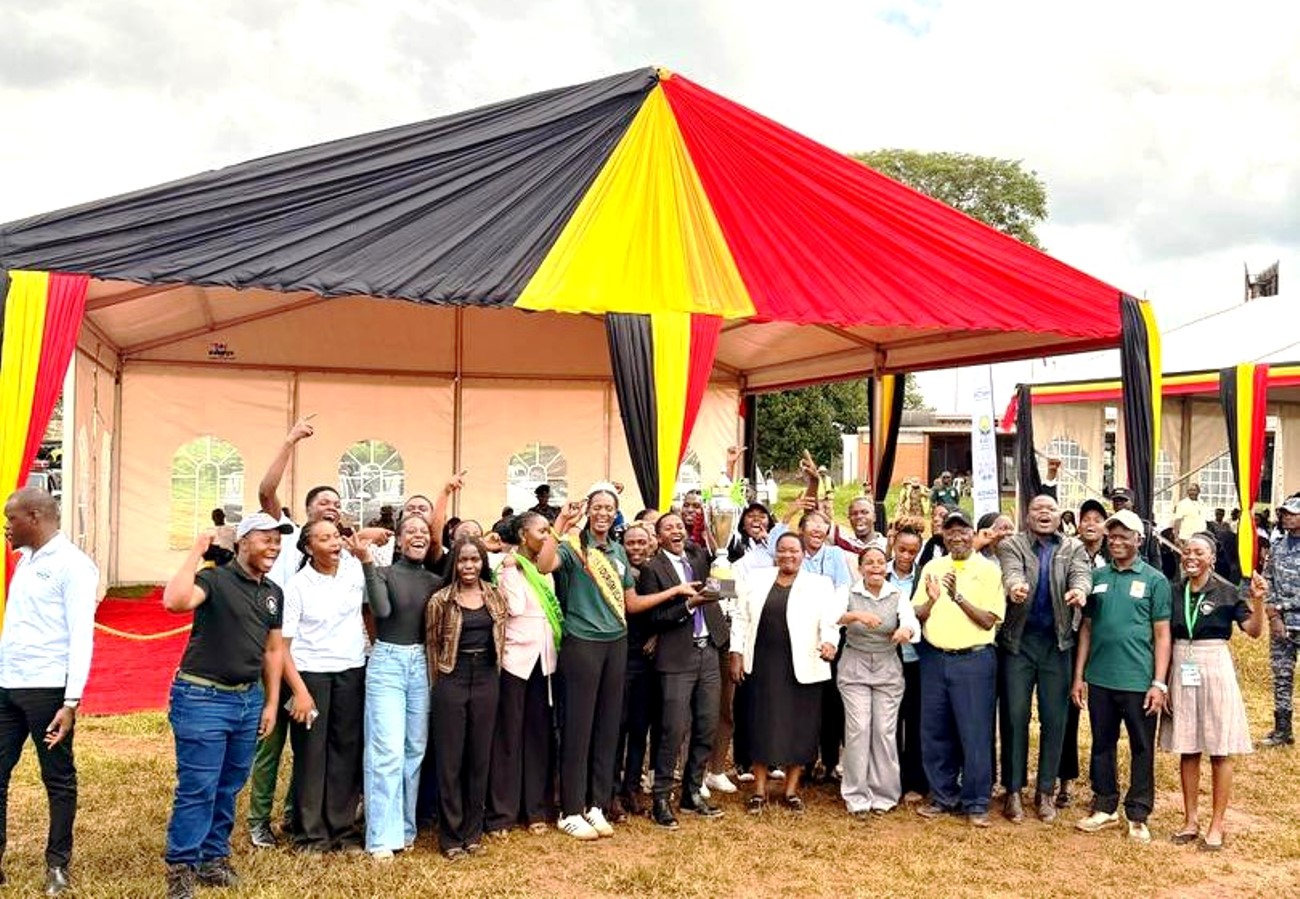
Makerere University students have once again demonstrated academic excellence and commitment to environmental conservation after emerging as the overall winners in the Uganda Wildlife Authority Tertiary Institutions Conservation Competitions held during the national celebrations to mark the World Wildlife Day.
On 25th February, a team of eight students, including members of the Makerere University Tourism Association (MUTA), proudly represented the university at the competitions organized by the Uganda Wildlife Authority. The event took place at the Uganda Wildlife Education Centre in Entebbe and brought together students from various tertiary institutions across the country to showcase knowledge and innovation in wildlife conservation.

The competitions formed part of the activities marking World Wildlife Day and were held under the theme “Medicinal and Aromatic Plants: Conservation, Health, Heritage and Livelihoods.” The theme highlighted the importance of protecting plant biodiversity, particularly species that support traditional medicine, cultural heritage, and sustainable livelihoods.
After a highly competitive contest that tested participants’ knowledge of conservation, biodiversity, and environmental sustainability, Makerere University emerged as the overall winner. The Uganda Wildlife Research and Training College finished as the first runner-up, while Nkumba University secured the second runner-up position.
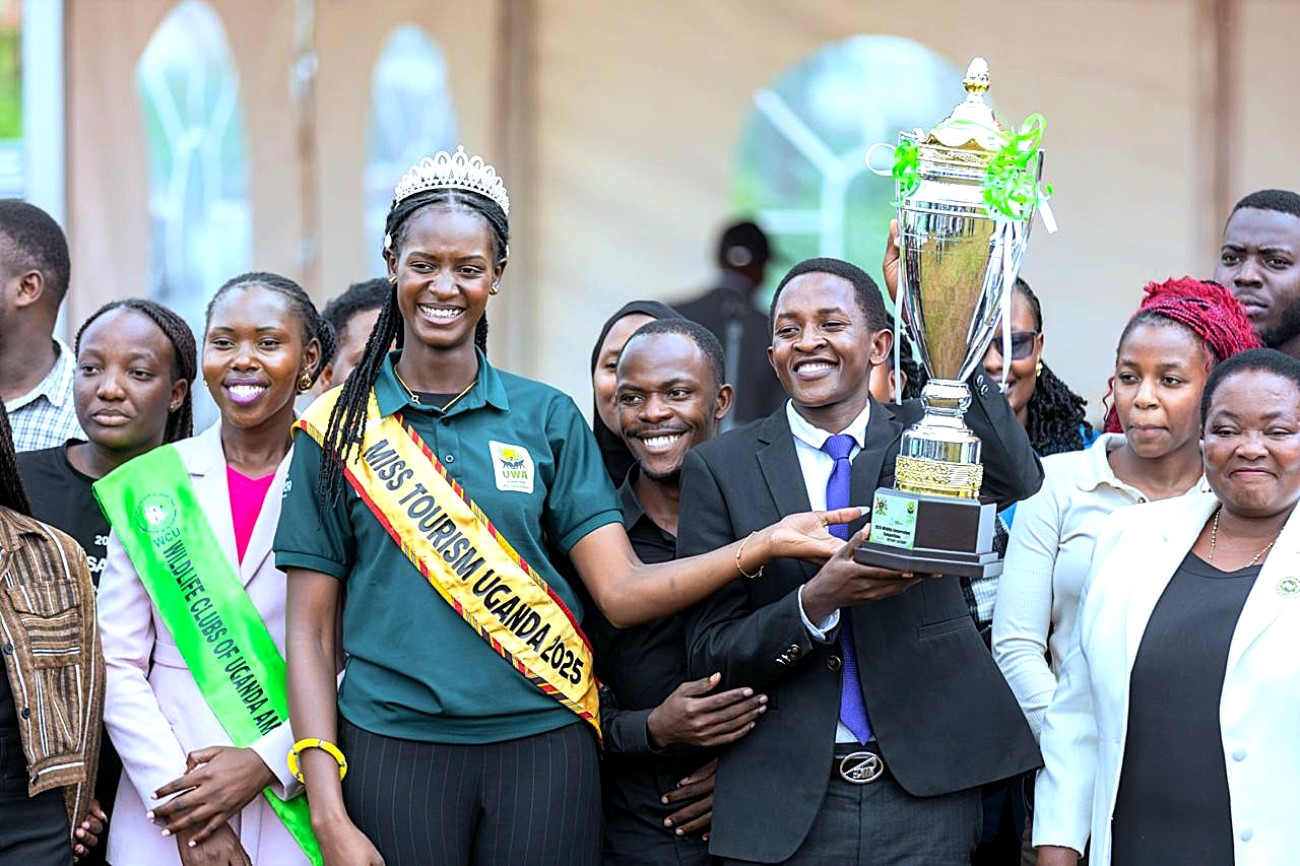

The team’s achievement was officially recognized during the national World Wildlife Day celebrations held on 3rd March at the Entebbe Works Grounds. During the ceremony, the students were awarded a trophy in recognition of their outstanding performance.
The award was presented by Uganda’s Prime Minister, the Rt. Hon. Robinah Nabbanja, alongside the Minister of Tourism, Wildlife and Antiquities, Hon. Tom Butime, and the State Minister for Tourism, Wildlife and Antiquities, Martin Mugarra. The leaders commended the students for their remarkable achievement and emphasized the critical role young people play in promoting conservation and protecting Uganda’s natural heritage.
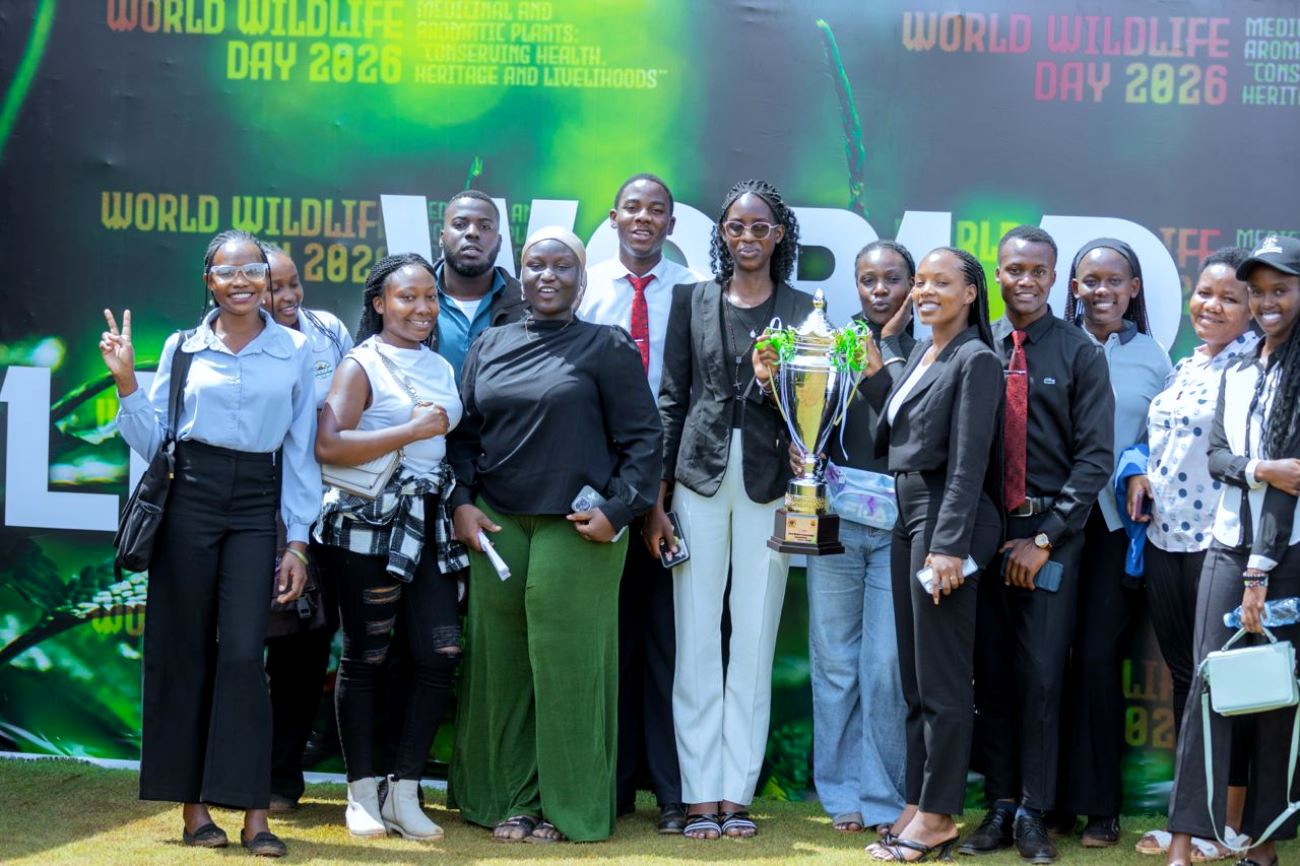

The winning team comprised students from diverse academic disciplines as follows:
- Iradikunda Jemimah – Bachelor of Biomedical Laboratory Technology
- Nankabirwa Edith Mirembe – Bachelor of Science in Tourism and Hospitality Management
- Agenrwoth Brenda – Bachelor of Science in Tourism and Hospitality Management
- Joel Kibirango – Bachelor of Science in Tourism and Hospitality Management
- Elvis Mujuni Kamara – Bachelor of Science in Biological Sciences (Botany/Zoology)
- Kamyuka Ben – Bachelor of Science in Biological Sciences (Botany/Zoology)
- Karisa Geofrey – Bachelor of Science in Forestry
- Nyangoma Caroline – Bachelor of Science in Forestry
According to Prof. Jim Ayorekire, Head, Department of Tourism at Makerere University, the win not only highlights Makerere University’s continued leadership in conservation education but also underscores the importance of empowering young people to take an active role in protecting biodiversity and promoting sustainable use of natural resources.
Agriculture & Environment
From Campus to Community: Universities Lead Teso in Fight Against Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Published
5 days agoon
March 9, 2026By
Mak Editor
By John Omoding
When Immaculate Acom inhaled smoke from traditional firewood stoves, it was a daily struggle. Her eyes watered, her lungs ached, and cooking became a source of illness rather than nourishment.
Today, Acom’s home in Aten Village, Odudui Parish, Arapai Sub-county, Soroti District, has transformed into a living laboratory for green energy solutions, a hub where university researchers, students, and local farmers collaborate on practical strategies to combat climate change.
“I used to cough every time I cooked. Now, with a biogas digester built by my husband, I can cook and light our home safely,” she says, pointing to the small green dome beside her house. “This is a relief for all the mothers in the community.”

Bringing Academia to the Grassroots
Acom’s story is part of the TORCH Project, a multi-university initiative involving Makerere University, Busitema University, Kabale University, and the University of Juba. The project seeks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices at the community level.
Unlike conventional environmental campaigns, the TORCH Project emphasizes direct engagement with local communities. Role models within villages are identified and trained in modern agricultural practices, clean energy use, and environmentally friendly living standards.
Dr. Jolly Akullo Oder, TORCH Project Coordinator at Busitema University, explains:
“Our mandate is to go to the community, share knowledge, listen to their challenges, and co-create solutions. This is not about lecturing – it’s about learning together.”

The project’s operational area spans a ten-square-kilometer zone around Busitema University’s Arapai campus, where researchers, students, and community members meet regularly to exchange ideas and implement practical solutions.
A Living Lab for Green Growth
The initiative, branded as a living lab, aims to achieve green growth, rural carbon credits, and the adoption of affordable green technologies.
Dr. Patrick Musinguzi, Principal Investigator from Makerere University, emphasizes the community-centric approach: “We are here to sit at the table with the community, discuss the challenges of global warming and greenhouse gas emissions, and chart a path forward together. Awareness is the first step to action.”
The project focuses on tangible interventions, including biogas digesters, sustainable tree planting, and energy-efficient farming methods, to reduce carbon emissions at the household and community level.

Community Voices: From Awareness to Action
For local farmers like John Michael Elebu, the university outreach is both eye-opening and practical. “I’ve never seen academics come to the community and engage with us so openly. I hope they can provide free improved tree seedlings to support our farming and fight climate change,” Elebu said.
Acom urges men in the community to take an active role in adopting clean energy technologies. Her husband, David Okwi, is among those championing the integration of green technologies into everyday agricultural practices.
“Promoting renewable energy and sustainable farming isn’t just about protecting the environment,” Okwi says. “It also improves health, saves money, and strengthens the resilience of our families.”
Universities as Catalysts for Environmental Change
The TORCH Project represents a unique model of academic-community collaboration, where research and practical application intersect.

Universities provide expertise, training, and access to modern technologies.
Community members contribute local knowledge, labor, and willingness to adopt change.
Together, they tackle climate change, energy poverty, and environmental degradation at the grassroots.
Dr. Akullo notes that the initiative will expand its activities continuously, monitoring outcomes, adapting approaches, and scaling up best practices across Teso and neighboring regions.
Way forward
By turning households into living laboratories, the TORCH Project aims to bridge the gap between knowledge and action.
For residents like Acom and Okwi, the benefits are immediate: cleaner air, reduced health risks, and practical solutions for everyday life. For Teso, the project could serve as a blueprint for climate-smart rural development across East Africa.
“Change begins at home,” Dr. Musinguzi says. “When communities understand the challenges of green gas emissions and know how to respond, the impact spreads far beyond one village or household.” In Aten Village, the hum of a biogas stove and the sight of thriving tree seedlings offer a glimpse of what is possible when universities partner with communities, creating hope for a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future.
Agriculture & Environment
Makerere University Launches Short Course to Strengthen Climate Change Reporting
Published
5 days agoon
March 9, 2026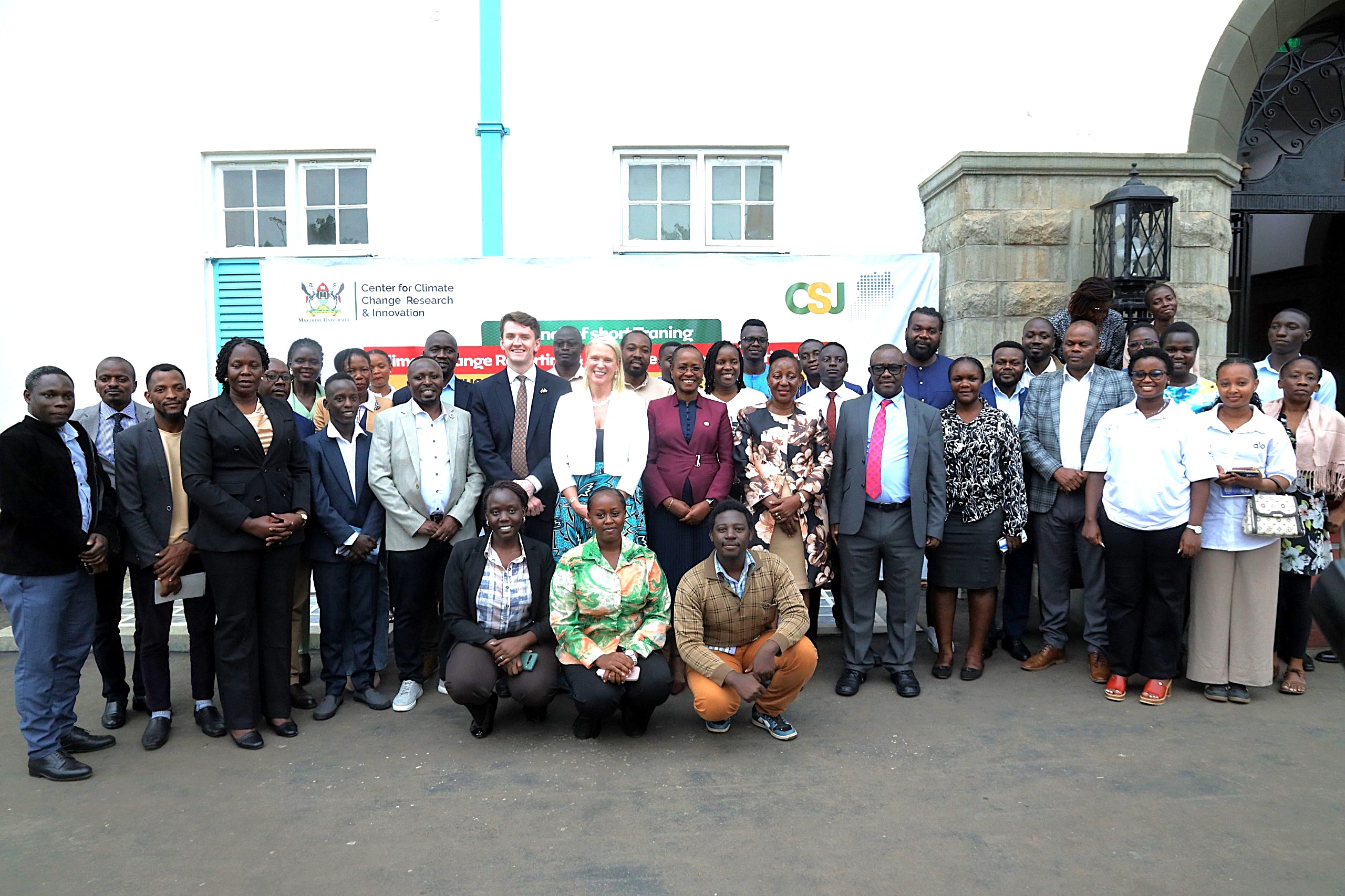
By Hasifa Kabejja & Ritah Namisango
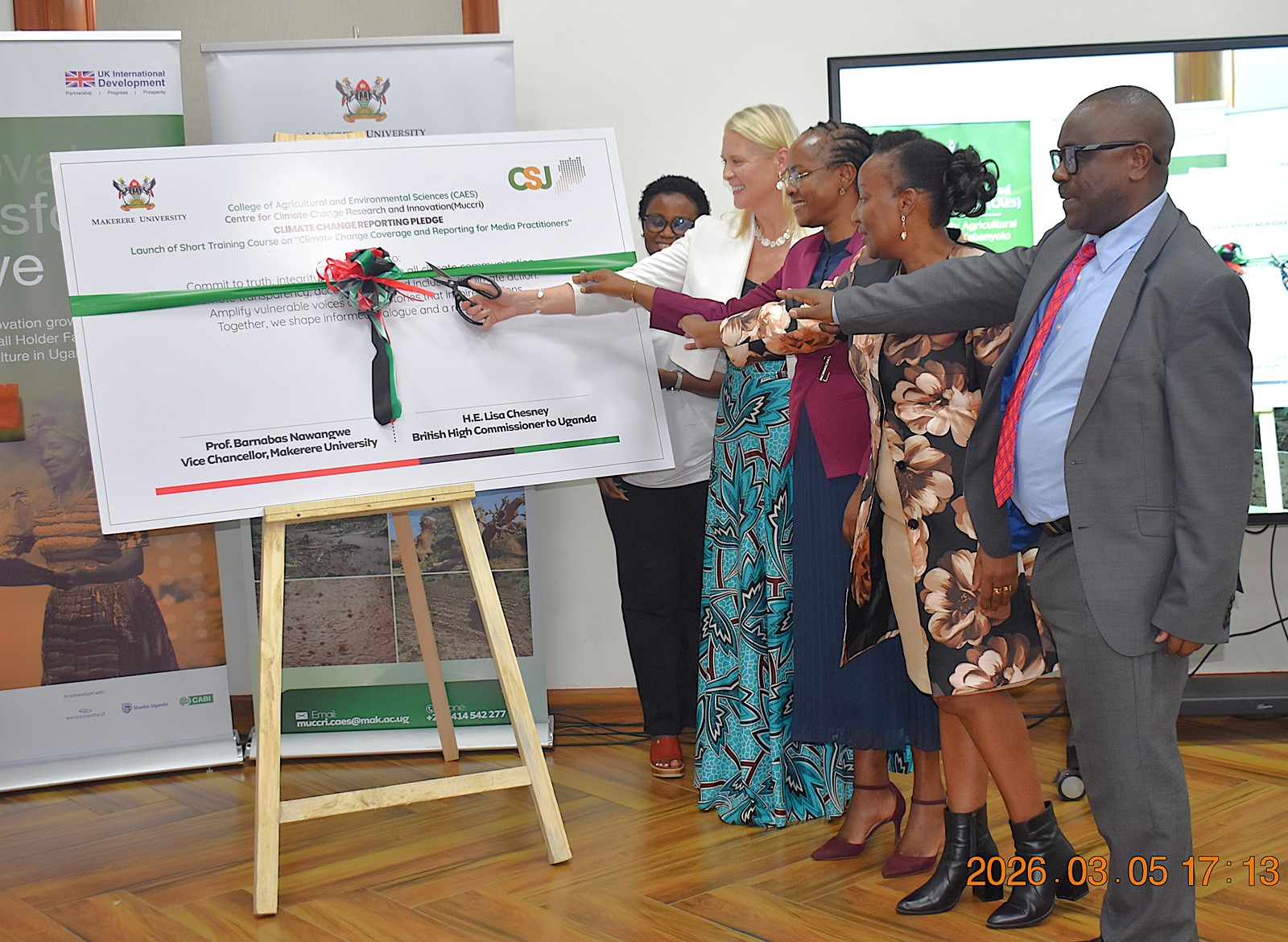
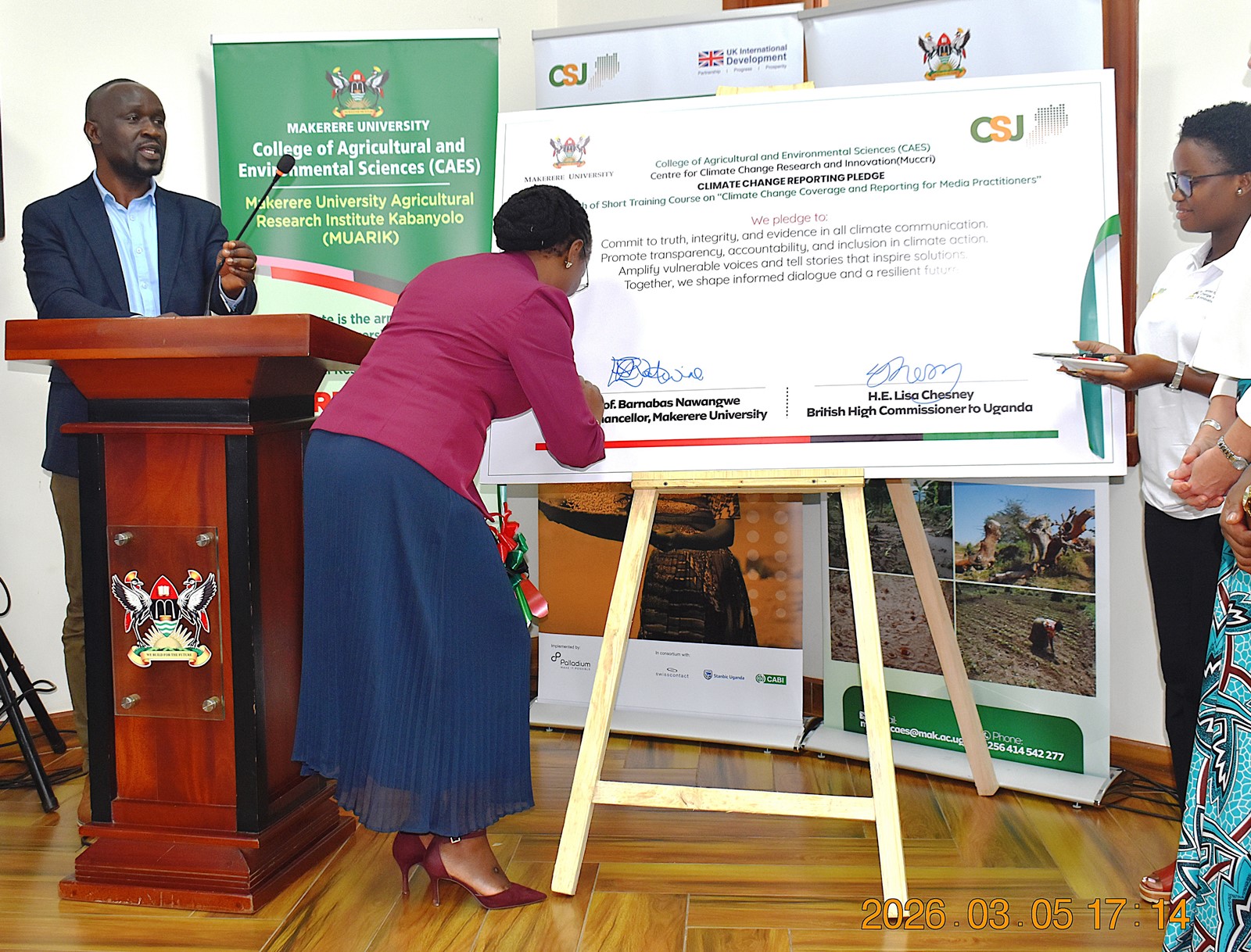
Makerere University, in partnership with the British High Commission in Uganda, has launched a specialized short training course aimed at equipping media practitioners and digital content creators with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively report on climate change and related environmental issues.
The course was officially launched on 5th March 2026 by the British High Commissioner to Uganda, Her Excellency Lisa Chesney. The ceremony was graced by the First Deputy Vice Chancellor in charge of Academic Affairs (DVCAA), Prof. Sarah Ssali, who represented the Vice Chancellor, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe. It was attended by the Principal of the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES), Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga, and representatives from Climate Smart Jobs (CSJ), the Editors Guild, and media practitioners and content creators focused on climate-related issues.

About the short course on climate change reporting
Developed by the Makerere University Centre for Climate Change Research and Innovation (MUCCRI) under the leadership of Prof. Revocatus Twinomuhangi, the course was designed to improve climate science reporting. Through the training, media practitioners will gain a deeper understanding of climate science, climate finance mechanisms, policy frameworks, and local climate solutions and innovations. The programme also aims to empower journalists to tell impactful and meaningful climate stories.
“As the coordinating team at MUCCRI, we worked with climate scientists, policy experts, and media practitioners to develop a programme that is accessible, practical, and engaging,” Prof. Twinomuhangi explained.

According to Prof. Twinomuhangi, the training will be delivered entirely online, making it accessible to participants across Uganda and beyond. It is self-paced, allowing participants to learn at their convenience while continuing with their professional responsibilities. At the same time, it has been designed to remain interactive and engaging through multimedia lectures, real-world case studies, and practical exercises.
The course consists of eight modules that together provide a comprehensive introduction to climate change reporting. These modules cover climate science, climate governance and policy, climate finance, nature-based solutions, inclusive climate reporting, and solutions-oriented journalism. Participants will also gain practical skills in interpreting data, asking critical questions, and crafting compelling climate stories.

“Our goal is not only to build knowledge but also to empower media professionals to report on climate change with confidence, depth, and accuracy,” Prof. Twinomuhangi explained.
He expressed gratitude to the UK Government, through the Climate Smart Jobs Programme, for supporting climate resilience initiatives in Uganda. He also thanked the Palladium Group, the implementer of the CSJ programme, for selecting MUCCRI to design and deliver this training under the Media Training and Mentorship initiative.

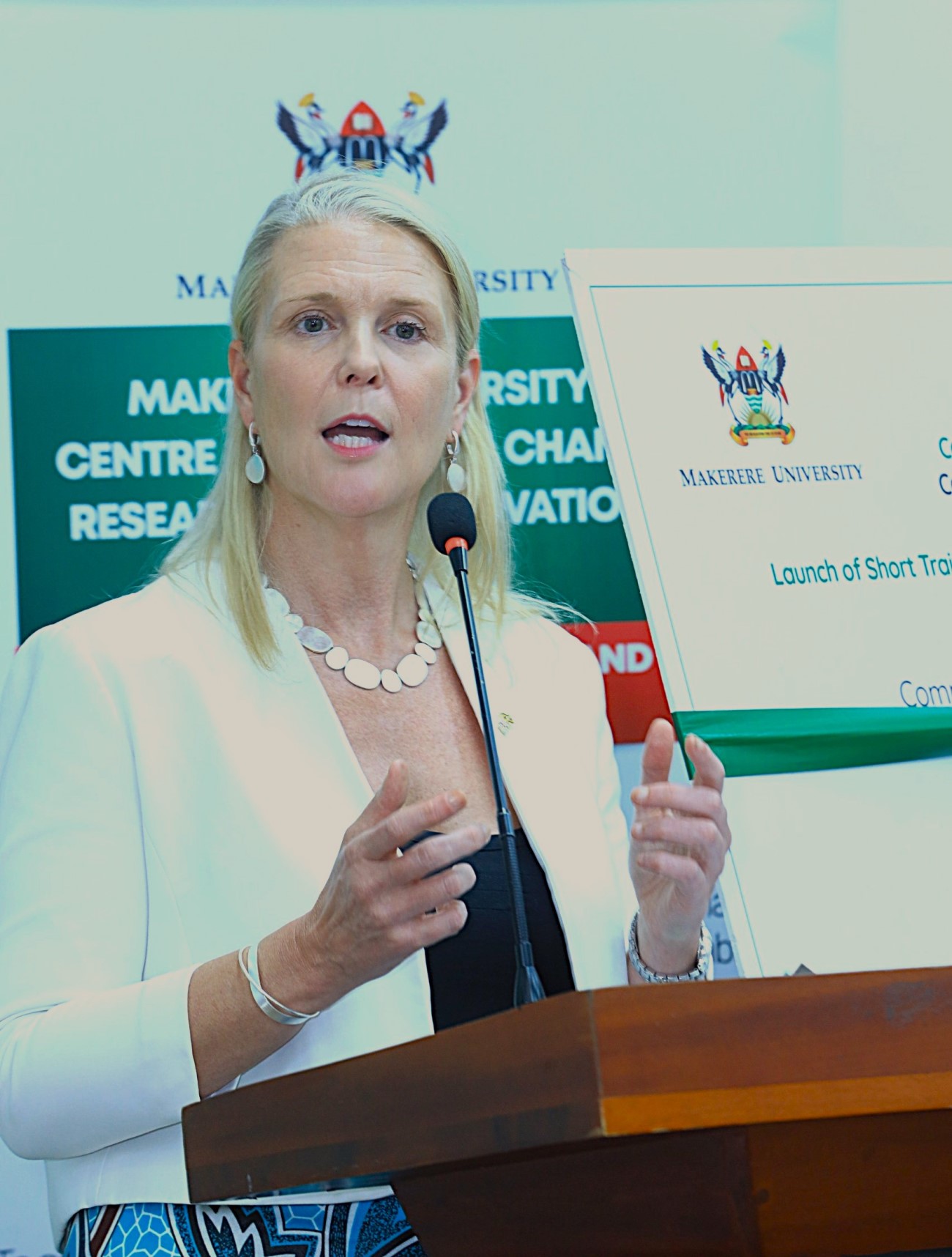
Remarks by H.E the British High Commissioner to Uganda
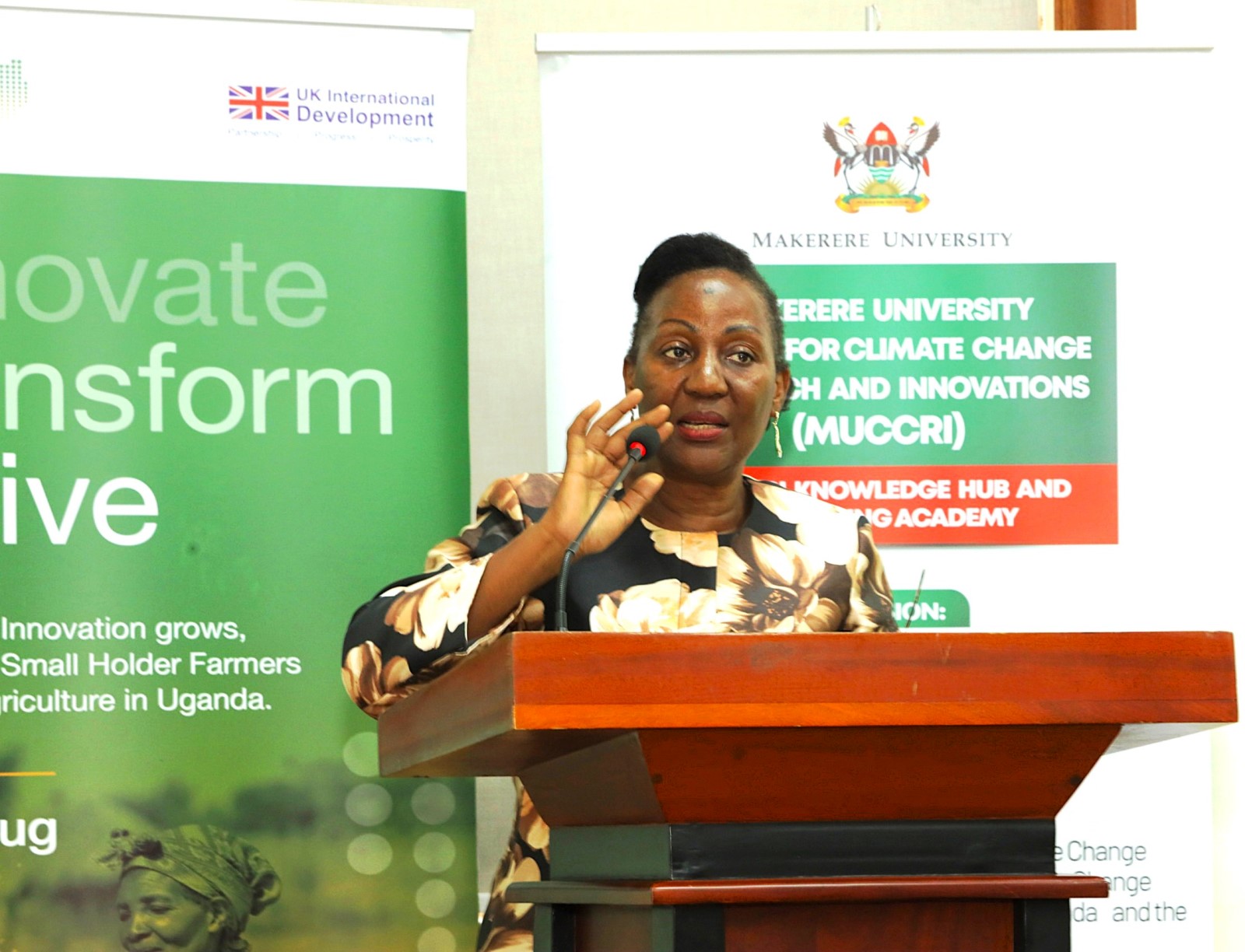
In her remarks, Her Excellency, the British High Commissioner to Uganda Lisa Chesney, described the initiative as both timely and essential, emphasizing the critical role the media plays in shaping public understanding of climate change.
She noted that climate change impacts communities differently, with women often bearing the greatest burden because they are heavily involved in agricultural production and ensuring food security for their families.

“Clear and accurate reporting on climate change is crucial in helping communities understand the risks and the solutions,” she said.
Relevance of the course to Makerere University
On behalf of the Vice Chancellor, Prof. Sarah Ssali, DVCAA, praised the programme as a reflection of Makerere University’s multidisciplinary, research-led approach to addressing national and global challenges. She highlighted the vital role of the media in translating complex scientific knowledge and policy into accessible information for the public.
“The short course we launch today is both timely and important. It draws on Makerere University’s research expertise and translates that knowledge into practical skills for media practitioners. It provides journalists with tools to better understand climate science, climate finance, carbon markets, adaptation strategies, and issues of equity and inclusion in climate action. By doing so, it strengthens the media’s ability to inform public dialogue and support evidence-based decision-making.”
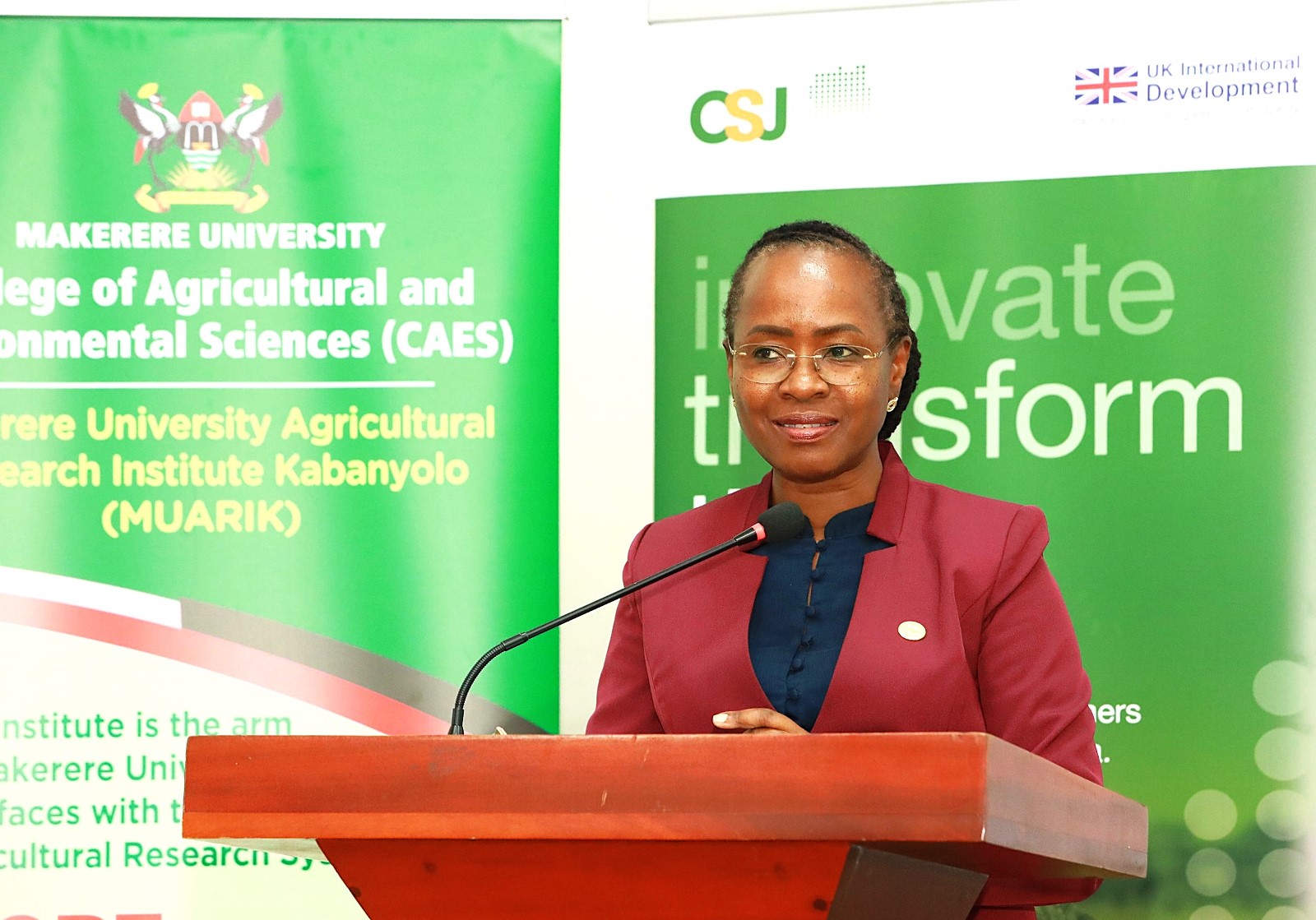

She equally appreciated the UK Government for supporting the initiative. “We are grateful for the confidence placed in the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences and in particular, the Makerere University Centre for Climate Change Research and Innovations to design and deliver this training. Such partnerships enable universities to translate research into real-world impact.”
Remarks by the Principal of CAES
Highlighting the challenges posed by climate change and the complexities in reporting climate-related issues, the Principal of CAES, Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga, reiterated the critical role of journalists in raising public awareness, translating scientific findings, and fostering informed dialogue that can drive effective climate action.

“The short course was therefore designed with a clear purpose: to equip media practitioners with the knowledge, tools, and confidence needed to report on climate change accurately and responsibly,” Prof. Nabanoga said, emphasizing CAES’s commitment to advancing climate solutions through research in sustainable agriculture, environmental governance, forest restoration, and nature-based interventions.
Appreciation from the Editors Guild
On behalf of the Editors Guild, Mr. Alex Atuhaire applauded the funders for supporting quality journalism, noting that the course will strengthen storytelling skills and improve climate reporting across Uganda’s media landscape.
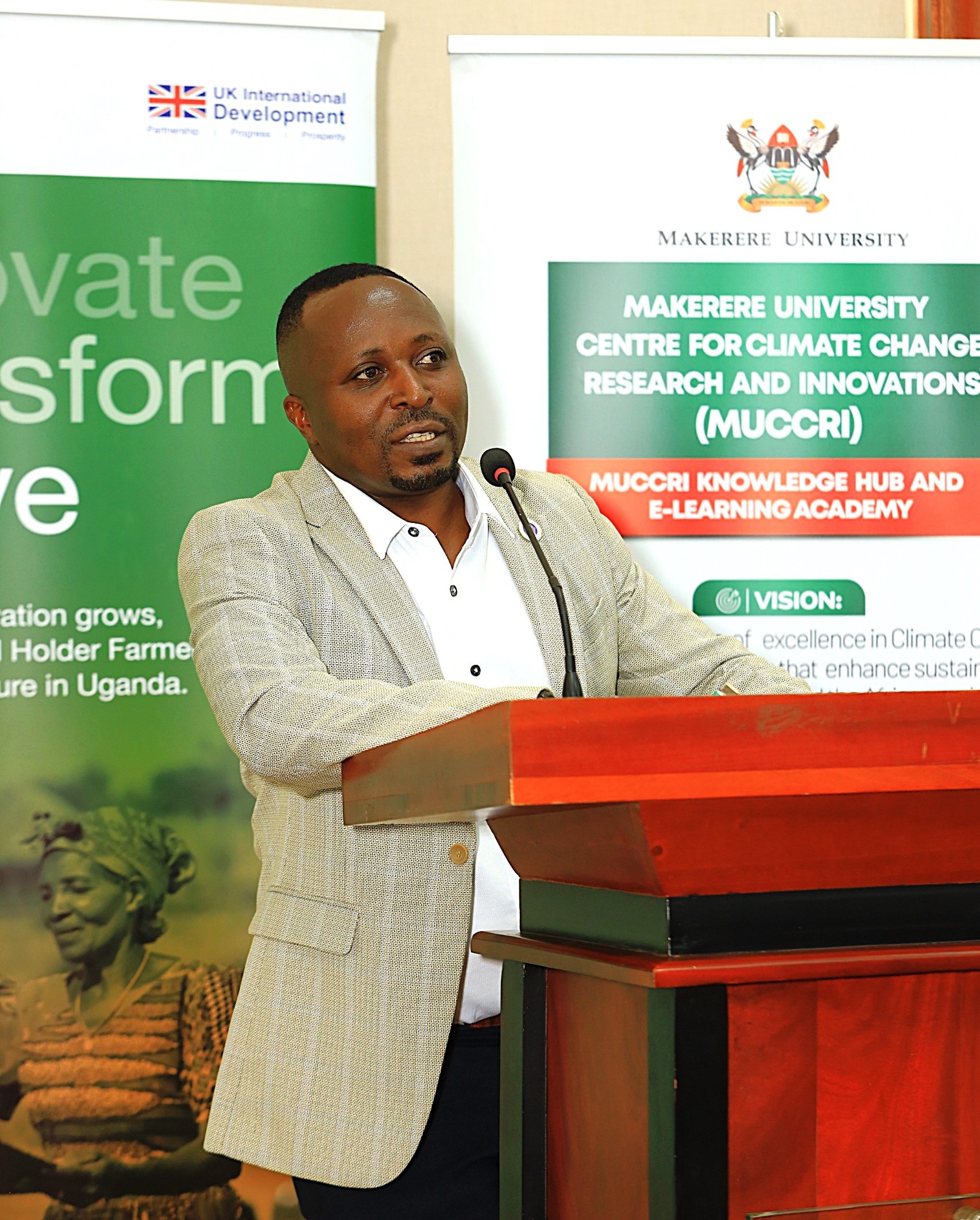

“The launch comes at a pivotal moment as the media navigates the opportunities and challenges of an increasingly digital landscape. The retooling course will breathe life into impactful, skilled, and authentic storytelling on climate change in our newsrooms,” Mr Atuhaire said. The Editors Guild pledged continued support in improving the quality of climate reporting across media platforms in the country.
Relevance of the programme to media practitioners
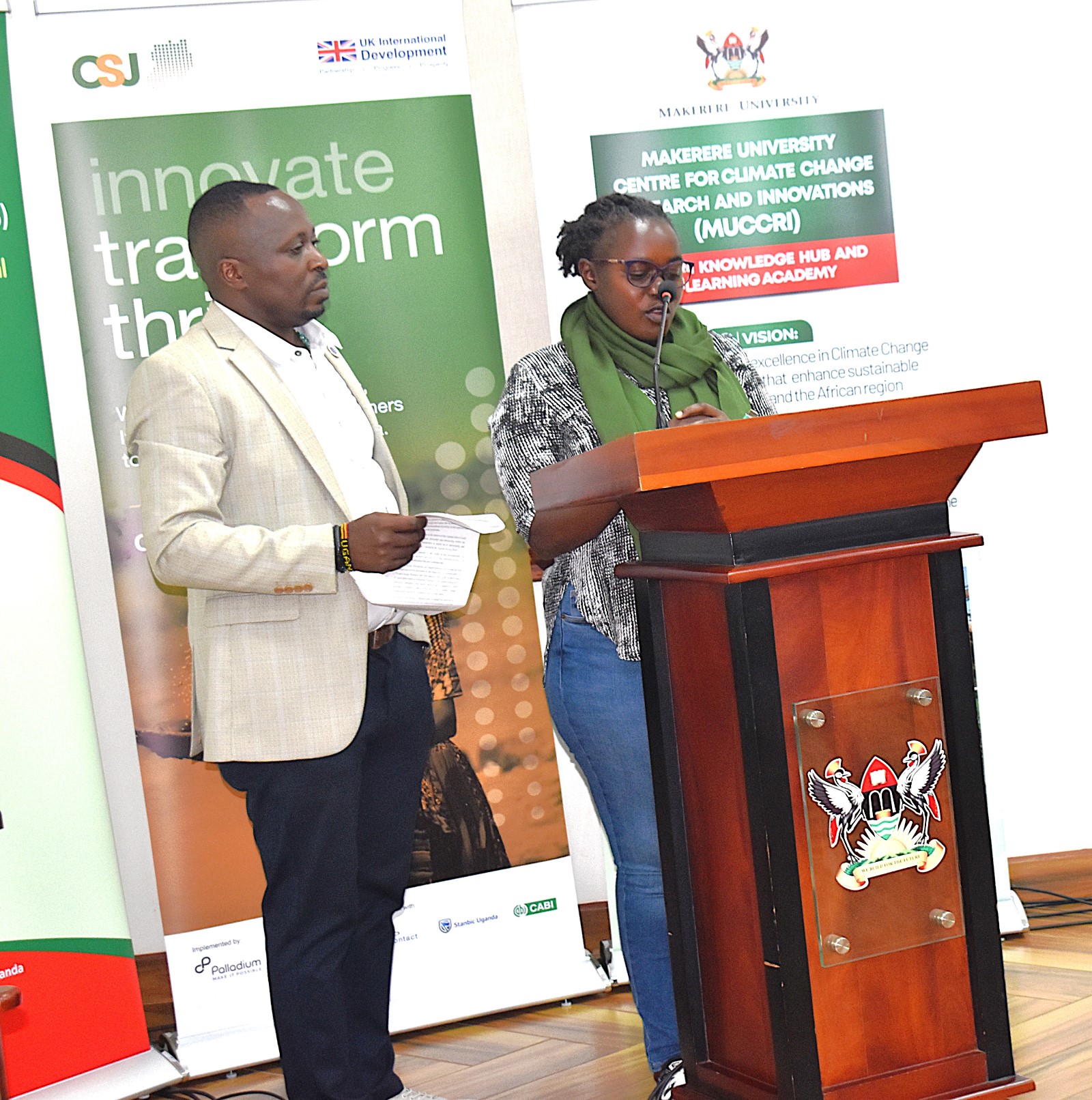
Sharing her experience, media practitioner Leonard Namukasa highlighted the complexities of reporting on climate change, describing it as scientific, investigative, and inherently challenging. She explained that limited access to reliable scientific data complicates coverage, noting that many people mistakenly equate climate change reporting with general environmental journalism. She welcomed the course, saying it will greatly address some of these challenges.

About MUCCRI
The Makerere University Centre for Climate Research and Innovation (MUCCRI) was established in 2014 within the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences to strengthen climate knowledge generation, knowledge management, and policy engagement. Over the years, MUCCRI has contributed to a wide range of initiatives, including climate knowledge management platforms such as the Climate Adaptation Knowledge Base (CCKB), the SDSN Uganda Chapter, research on climate-induced migration, and programmes that promote sustainable agriculture, nature-based solutions, climate-smart cities, climate finance, locally led adaptation, and community resilience.

MUCCRI is a member of the Least Developed Countries Universities Consortium on Climate Change (LUCCC), a global network of universities working together to advance climate research, knowledge exchange, and capacity building in least developed countries. Through these efforts, the Centre aims to bridge the gap between climate science, policy, and society.
More photos from the launch



Trending
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMakerere University commemorates 13 transformative years of partnership with Mastercard Foundation
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMakerere University and World Bank Sign Partnership to Strengthen Environmental and Social Sustainability Capacity
