Agriculture & Environment
The Third NARO-Mak Joint Scientific Conference: Participants Call for More Investment in Scientific Research
Published
3 years agoon
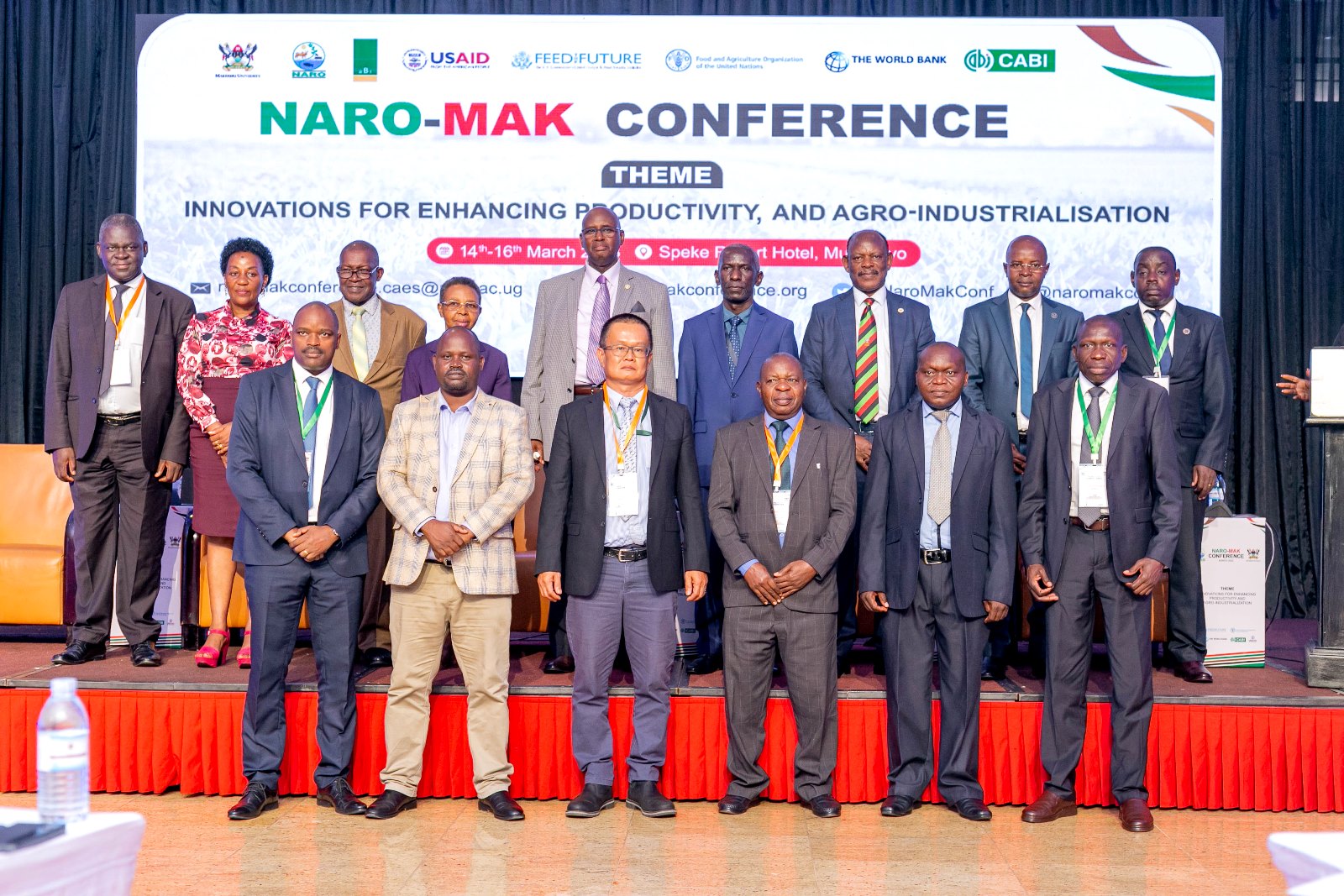

Conference theme: Innovations for enhancing productivity and agro-industrialization
Overview
Uganda’s Vision 2040, the National Agricultural Extension Policy (NAEP), the National Agricultural Policy (NAP) and the National Agricultural Extension Strategy (NAES) strategically place agriculture as a key driver to achieve socio-economic transformation in the country. The third National Development Plan (NDPIII, 2020/21-2024/25) prioritizes Agro-industrialization as a great opportunity for Uganda to embark on its long-term aspiration of increasing household incomes and improving the quality of life. Despite the fact that the economies of many African countries are still driven by agriculture, the sector remains crippled due to several challenges including climate change; inappropriate seed systems, production practices, and post-harvest management; as well as pests and diseases. The need to feed the world’s increasing population with minimal pressure on the ecosystem brings to the forefront the critical role of innovation across the entire value chain. Increased productivity is insufficient without an efficient value chain to move produce from the farm to the fork. Efficient value chains need to be supported by innovations along the pipeline.
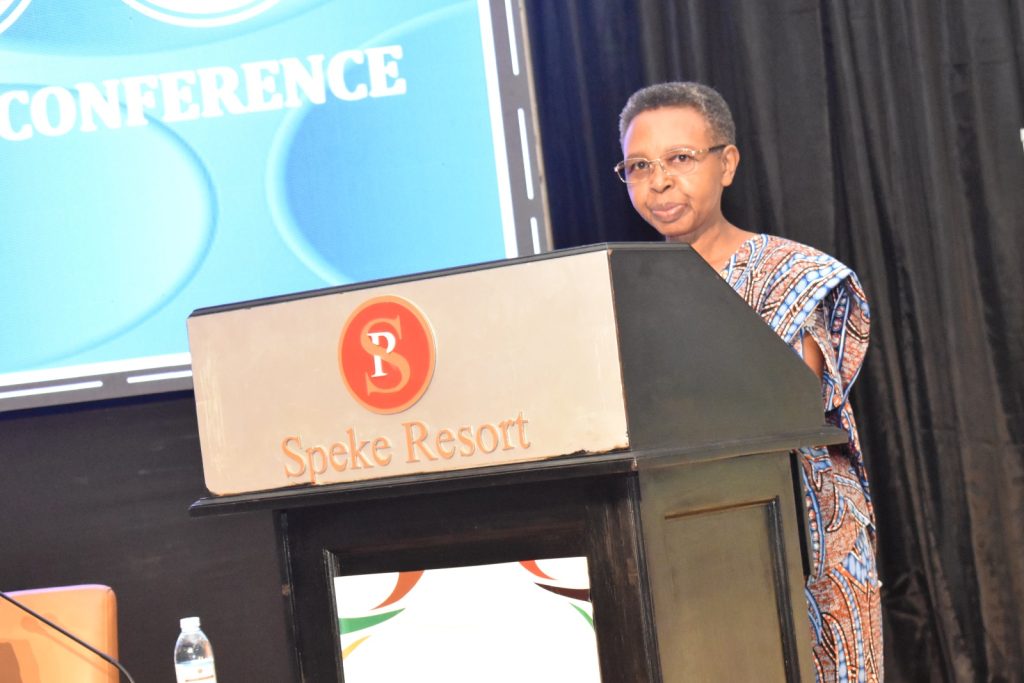

The NARO-Mak Joint Scientific Conference
As key players in the agricultural sector, the National Agricultural Research Organization (NARO) in collaboration with Makerere University in 2018 introduced the NARO-Makerere Joint Scientific Conference to serve as a platform for evidence-based dialogue on measures to transform the sector, with special focus on innovations for agro-industrialization. The conference therefore seeks to engage stakeholders including government, research and innovation systems as well as development partners to find options for accelerated agro-industrialization on the African continent. The Conference also provides opportunity for stakeholders to show-case advances in research and innovation that can contribute to the development and transformation of the agricultural sector. According to Dr Imelda N. Kashaija, Chair of the Organizing Committee of the Third NARO-Mak Joint Scientific Conference, a key gap in the development of the agricultural sector is the aspect of incomplete value chains. “Africa needs to embrace and nurture agricultural value chains that are competitive locally and at the global level. At the same time, the value chains should support the budding agro-industry. The agricultural sector must continuously innovate to compete in the changing ecosystem. Appropriate and evolving seed systems, production practices, post-harvest management and value addition to improve marketability are necessary for continuous innovation.”
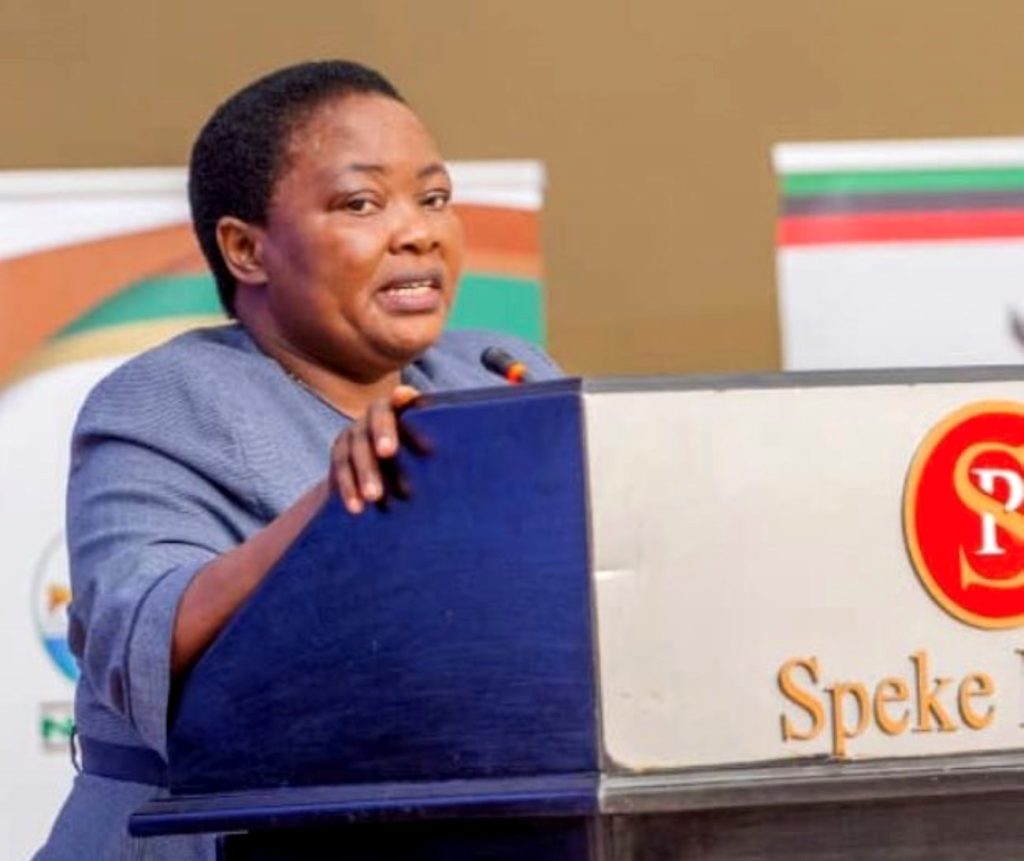

The Third Joint Scientific Conference held at Speke Resort Munyonyo
The NARO-Makerere Third Joint Scientific Conference held on 14th-16th March 2023 at Speke Resort Munyonyo sought to establish appropriate and viable strategies towards accelerated agro-industrialization, with focus on the African continent. It was officially opened by the Prime Minister of the Republic of Uganda, the Rt. Hon. Robinah Nabbanja and graced by the Minister of State for Animal Industry, Hon. Bright Rwamirama; the Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe; the Chair NARO Council, Dr William Olaho Mukani; the Director General NARO, Dr Ambrose Agona; the Chief of Party, USAID Feed the Future, Mr. Anthony Nyungu; the Principal, College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES), Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga; and the Director, Directorate of Research and Graduate Training, Makerere University, Prof. Edward Bbaale.
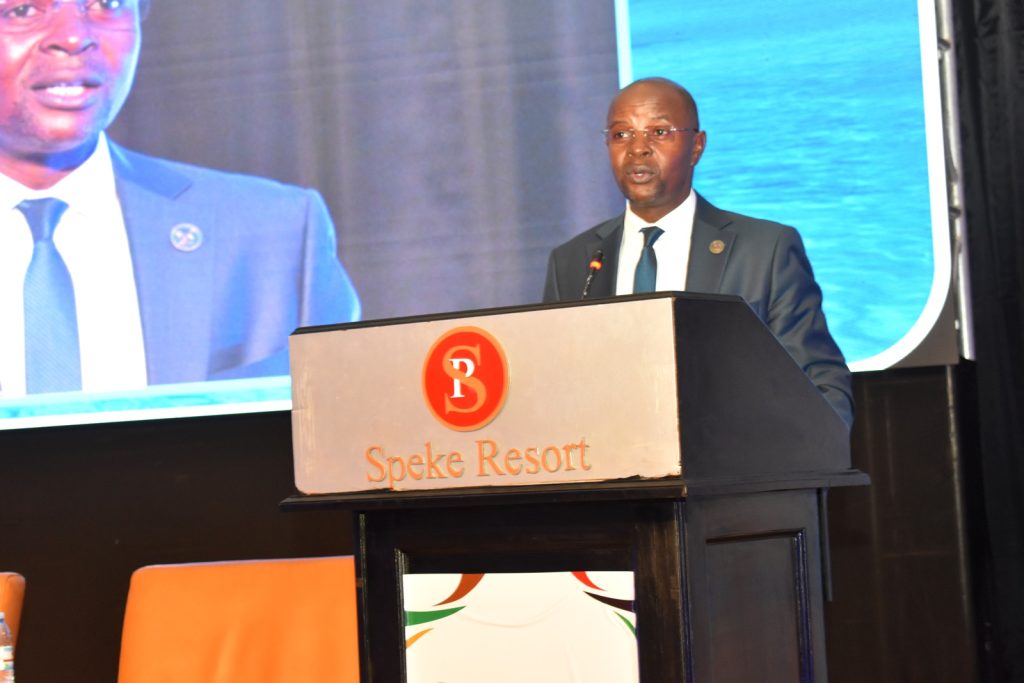

Organized under the theme; Innovations for enhancing productivity and agro-industrialization, the conference aimed to bring to the forefront, cutting edge innovations and opportunities supportive to Africa’s agro-industrialization drive, provide a platform for the establishment of viable networks and collaborations that will catalyze agro-industrialization, and to stimulate generation of new knowledge to address emerging challenges. During the three-day conference, participants including researchers from Makerere University and NARO as well as representatives from the public and private sector deliberated on a number of issues in line with challenges and opportunities in Mechanization and Agro-Industrialization; modernization of post-harvest management and food safety systems; intensification of crop productivity and seed systems; acceleration of the development of the Animal Resources-based Industry; management of interactions amongst agriculture, fragile ecosystems and the changing environment; and embracing ICT-based innovations for agricultural transformation. The conference featured keynote presentations by eminent researchers and policymakers. Mr. Ollen Wanda from Uganda Development Cooperation addressed participants on the challenges and opportunities in mechanization and agro-industrialization, whereas Prof. Robinson Mdegela from Sokoine University in Tanzania discussed the impact of COVID-19 on food systems.

Other keynote presentations included, the implications of the Russia-Ukraine War on Uganda’s Agriculture by Ms. Florence Nakazzi from the Economic Policy Research Centre; opportunities for modernizing post-harvest management for food and nutritional security by Prof. Archileo N. Kaaya from CAES, Makerere University; accelerating the development of the Livestock-based industry by Dr Sylvia B. Angubua; enhancing ICT-based innovations for agricultural transformation by Mr. Collin Babirukamu, Director E-government Services, NITA-U; intensification of crop productivity in the context of changing food systems by Prof. Patrick Okori from RUFORUM; sustainable management of agricultural production systems in a changing climate by Dr John Wasige from Busitema University; and the progress made in soybean research in Uganda by Prof. Phinehas Tukamuhabwa from CAES.

The conference also featured a panel discussion on the oil palm industry in Uganda. Panelists included Dr Gaberial Damulira, Principal Research Officer and Programme Leader, Horticulture and Oil Palm Programme at NARO; Dr Abubaker Muhammad Moki, Commissioner Policy Development and Capacity Building at Cabinet Secretariat, Office of the President, Government of Uganda; Mr. David Balironda, General Manager, KOPGT; and Mr. Chin Pit Te from AGM Oil Palm Bavuma Ltd.

Issues arising from the conference and recommendations
- The country invests only 0.3% of its GDP in research contrary to 1% recommended by the African Union. Many good ideas cannot be implemented due to lack of funding. Governments urged to invest more in research.
- Shifts in policy focus across political periods hindered agro-industrialization. To unlock the vast opportunities in agro-industry, Mr. Ollen Wanda from Uganda Development Cooperation advised that the functional/institutional based planning and budgeting approach where limited resources are allocated to broad functional areas such as extension, mechanization, irrigation, marketing without specifically targeting a particular commodity must be changed.
- Agricultural research must be broadened beyond focus on staple food commodities to other commodities of great commercial and export potential.
- Agricultural research must also be re-aligned to meet the needs of agro-industrialization.
- There is need to develop agro-industry specific integrated infrastructure and facilities such as agro-industrial parks to facilitate tertiary processing.
- Promote affordable and competitive financial products for mechanization and agro-industry for example agro-industry infrastructure and investment contingency fund.
- There is need to scale up investments in high potential commodity value chains such as cotton that have big domestic and global market value.
- In its pursuit to move the country towards middle income status, government should consider up-scaling agriculture. According to Dr John Wasige from Busitema University, subsistence farming does not create wealth. Government should therefore support farmers to engage in commercial agriculture. In his presentation on sustainable management of agricultural production systems in a changing climate, Dr Wasige noted that 90% of soil in Africa is depleted and cannot support quality agricultural production calling for interventions to improve the quality of soil. “There is need to invest in soil fertility management and irrigation. Rain-fed agriculture is not sustainable”.
- The National Fertilizer Policy (2016) should be implemented as a measure to improve the quality of soil.
- In a bid to embrace ICT-based innovations for agricultural transformation, government should consider lowering the cost of smart phones and expanding access to internet.
- Researchers called for the establishment of an E-Agriculture working group that includes Agricultural Policy and technical resources, Academia, NITA/MoICT, and development partners. They also called for the creation of a cloud-based system for Agriculture.
- There is need for vibrant seed systems focusing on crops, livestock, fisheries and forestry.
- Strengthen regional integration with a focus on context specific solutions to minimize the impact of pandemics
- Build a resilient system to serve during and after emergence of pandemic such as COVID-19.
- Put in place appropriate financing products and services.
- In a bid to modernize post-harvest management for food and nutrition security, strengthen cooperatives and credit systems for producers. It is also important to construct regional modern storage structures for grains and perishable commodities.
- Development of the Oil Palm Industry – Uganda only produces 80,000 metric tonnes of oil palm, way below the required 410,000 tonnes. There is need for research to generate appropriate technologies to support the sector.
- Government should empower young people to embrace agriculture as a viable means of employment.
- Researchers called for the elimination of fake agro-chemicals on the market
- Discussing the implications of the Russia-Ukraine war on Uganda’s Agriculture, Ms. Florence Nakazi from EPRC said Uganda should strive to have self-sufficiency to reduce its import dependency, and leverage on NDP III’s agro-industrialization strategies to develop wheat substitutes.

Remarks by the Prime Minister
In her remarks, the Prime Miniter of the Republic of Uganda, the Rt. Hon. Robinah Nabbanja appreciated NARO and Makerere University for the joint research efforts that have significantly contributed to the development of the agricultural sector, and supported government efforts aimed at moving the country to middle income status. “This conference comes slightly over one year since the President of the Republic of Uganda, H.E. Gen. Yoweri Kaguta Tibuhaburwa Museveni launched the Parish Development Model in Kibuku District. The Parish Development Model is our blueprint for organizing and delivering public and private sector interventions for wealth creation and employment generation at the parish level as the lowest economic planning unit. It therefore gives me great joy to see that the Conference theme speaks directly to some of the current efforts by Government to transition our farmers from subsistence to commercial agriculture.” Commenting on the poor state of soils, a factor greatly undermining production, the Prime Minister pledged to push for the review and implementation of the National Fertilizer Policy (2016). The Prime Minister pledged more government funding towards research and innovation. “The Government is committed to funding research aligned to the national development priorities.”

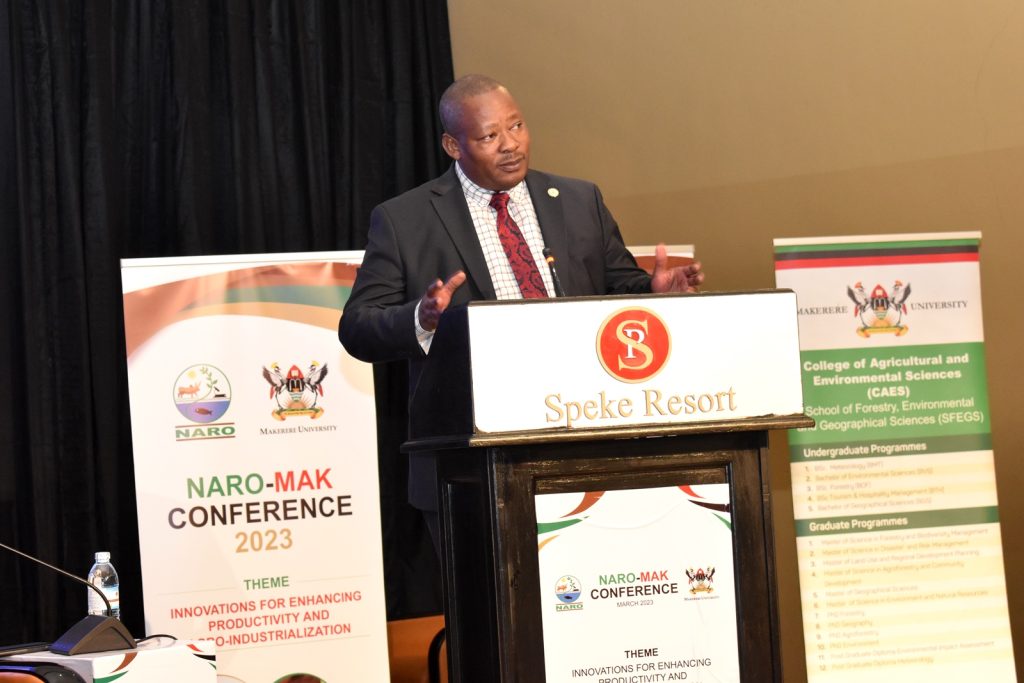
Remarks from MAAIF
On behalf of the Minister of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries (MAAIF), Hon. Bright Rwamirama, Minister of State for Animal Industry commended Makerere University and NARO for the significant research output. “Government appreciates the role of science in transforming economies and is committed to supporting scientific research and innovations,” he noted. Commenting on the poor state of soils, as one of the challenges undermining agricultural production, Hon. Rwamirama said the use of fertilizers and irrigation was no longer an option and that government was scaling up interventions towards modernization of agriculture. The Minister reiterated the need for homegrown solutions for challenges affecting the sector.

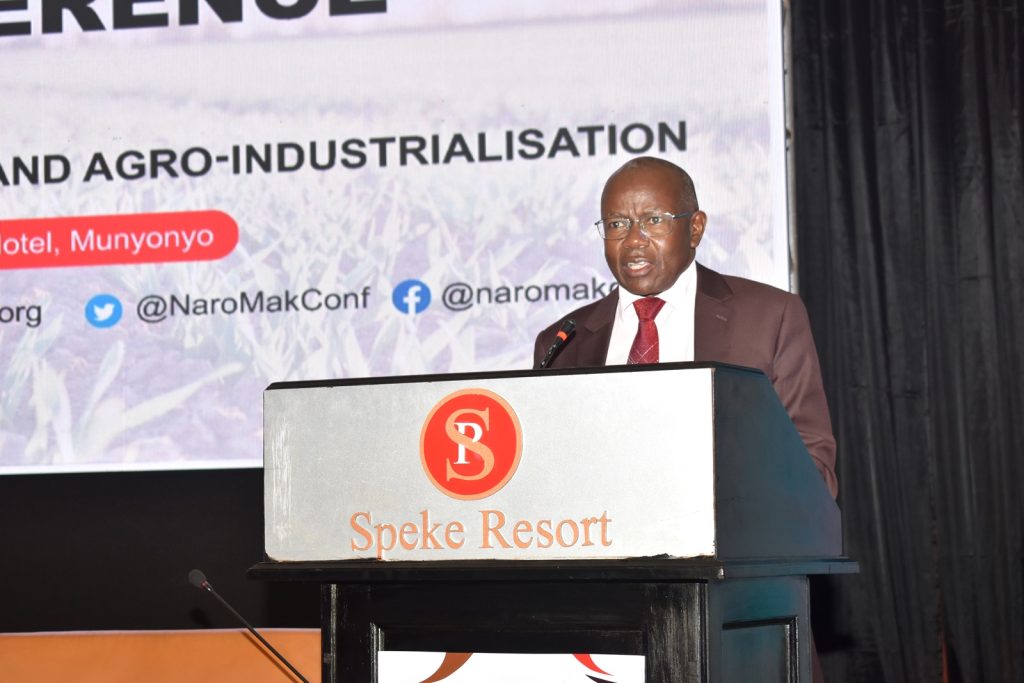
Remarks by the Vice Chancellor
The Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe acknowledged the research efforts by CAES and NARO, noting that CAES contributes 30% of research and publications at Makerere. He called for more funding towards research noting that the country spends only 0.3% of its GDP on agricultural production contrary to 1% recommended by the AU. The Vice Chancellor emphasized the importance of collaboration in research. “In modern times, research is about collaboration, the more you collaborate, the better the quality of research and output.” Highlighting the challenges crippling the agricultural sector, the Vice Chancellor explained that achieving the desired transformation calls for innovativeness. “I am happy to note that as Makerere aspires to become a research-led university as per the 2020/2030 Strategic Plan, innovativeness is one of our strategic areas of focus. It is gratifying to note that our agricultural College – CAES has adopted an ‘Innovation Intentional’ agenda enshrined in the College Transformational Pact with the aim of increasing innovativeness amongst staff and students. With this, we expect to see more innovations at the College that will greatly boost Agricultural production and agro-industrialization.” The Vice Chancellor appreciated the Government of Uganda and development partners for the support extended towards research and innovation at Makerere University.

Chair NARO Council
The Chairperson, NARO Council, Dr William Olaho Mukani reiterated the importance of innovation in the development of sustainable agriculture. “Our products do not meet international standards because of aflatoxins. “There is need for interventions to enhance the quality of our products. We appeal to the Government to set up an Agricultural Research and Innovations Fund.” Similarly, the Director General of NARO, Dr Ambrose Agona emphasized the importance of science and innovation in transforming the sector calling for more funding towards scientific research.

Remarks by the Principal CAES
The Principal of CAES, Prof. Gorettie Nabanoga briefed participants of the College’s Innovation Intentional Agenda aimed at transforming the mode of operations to increase innovations. “In line with Strategic Goal 1 that seeks to transform Makerere into research-led institution, the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES) is transforming its mode of operation in order to stimulate innovativeness and entrepreneurship within learners and faculty. In 2022, a “Pact” for Transformation Change at CAES was developed through which we shall be innovative and intentional on transforming into a College, with effective and efficient management systems, adequate supportive infrastructure and highly motivated staff to drive our Innovation Intentional agenda. Through our three schools namely; the School of Agricultural Sciences, School of Food Technology Nutrition and Bio-engineering and the School of Forestry, Environmental and Geographical Sciences and 14 research institutes, our staff shall productively engage with stakeholders and produce skilled, entrepreneurial, innovative and work-oriented graduates, able to innovatively respond to challenges, needs and aspirations in the Agricultural and Environmental sectors.”

She expressed gratitude to the Government of Uganda and all development partners for supporting research at CAES and the University in general. She acknowledged the long-time partnership between CAES and NARO that has yielded several results hence transforming the agricultural sector. She appreciated the University Council and Management for supporting CAES initiatives. She also appreciated the Conference organizing committee led by Dr Imelda N. Kashaija.

The conference was supported by FAO Uganda, the World Bank, aBi Development Ltd, USAID Feed the Future, CABI-Africa, Agriculture Search Activity, Nile Breweries Ltd, and Dr Nicholas Kiggundu from CAES.

Keynote Presentations:
- Implications of the Russia-Ukraine war on Uganda’s Agriculture – Florence Nakazi, EPRC
- Challenges and Opportunities in Mechanization and Agro-industrialization in Developing Countries – Ollen Wanda Kahurubuka, UDC
- Minimizing the Impact of COVID-19 on Food Systems – Robinson Mdegela, AFROHUN, SUAMT
- Progress in Soybean Research and Seed System in Uganda – Phinehas Tukamuhabwa et al., MAKCSID
- Intensification of Crop Productivity in the Context of Changing Food Systems – Patrick Okori, RUFORUM
- Enhancing ICT-based Innovations for Agricultural Transformation: Modernization of Agricultural Value Chains – Collin Babirukamu, NITA-U
Additional Resources:
Book of abstracts: https://naromakconference.org/schedule/
Conference pictorial: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1ZM3HMlS_sPBZPepZrt_jbT5zV6WYtQGC?usp=share_link
Conference pictorial: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1-_sp5Tki2xtSDBG0Pluia5gzUde5QJdB?usp=share_link
You may like
-


Mak News Magazine: February 2026
-


Celebrating Academic Excellence: CoBAMS Presents 975 Graduands at Mak 76th Graduation Ceremony
-


Mak 76th Graduation Ceremony: CoNAS Presents 16 PhDs & Best Performing Male Student in the Sciences
-


Medical graduates urged to uphold Ethical values
-


CAES Presents Overall Best Performing Student in the Sciences & a Record 28 PhDs at the 76th Graduation Ceremony
-


Graduation marks the next phase of accountability, graduates told
Agriculture & Environment
CAES Presents Overall Best Performing Student in the Sciences & a Record 28 PhDs at the 76th Graduation Ceremony
Published
3 days agoon
February 25, 2026
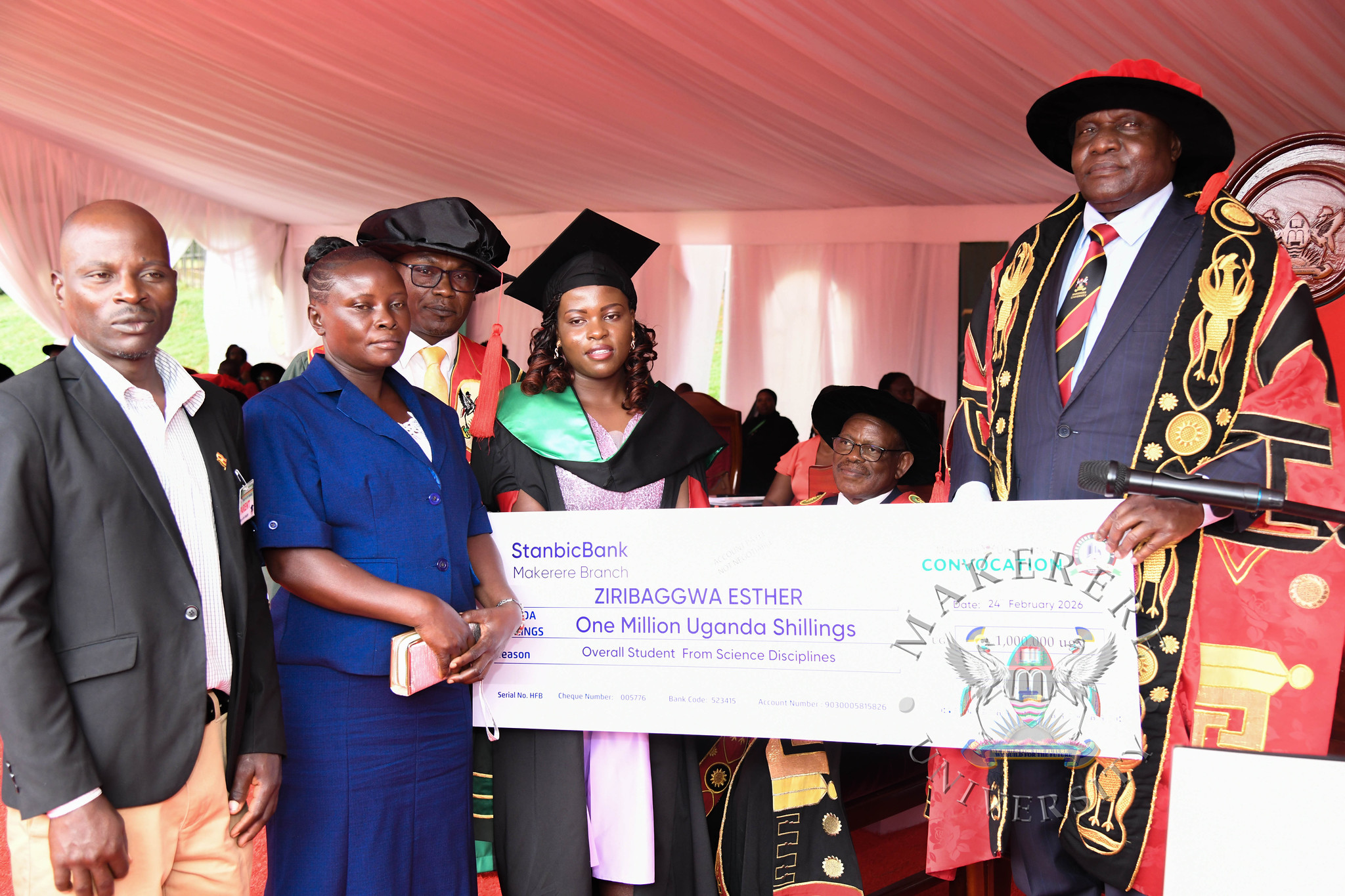
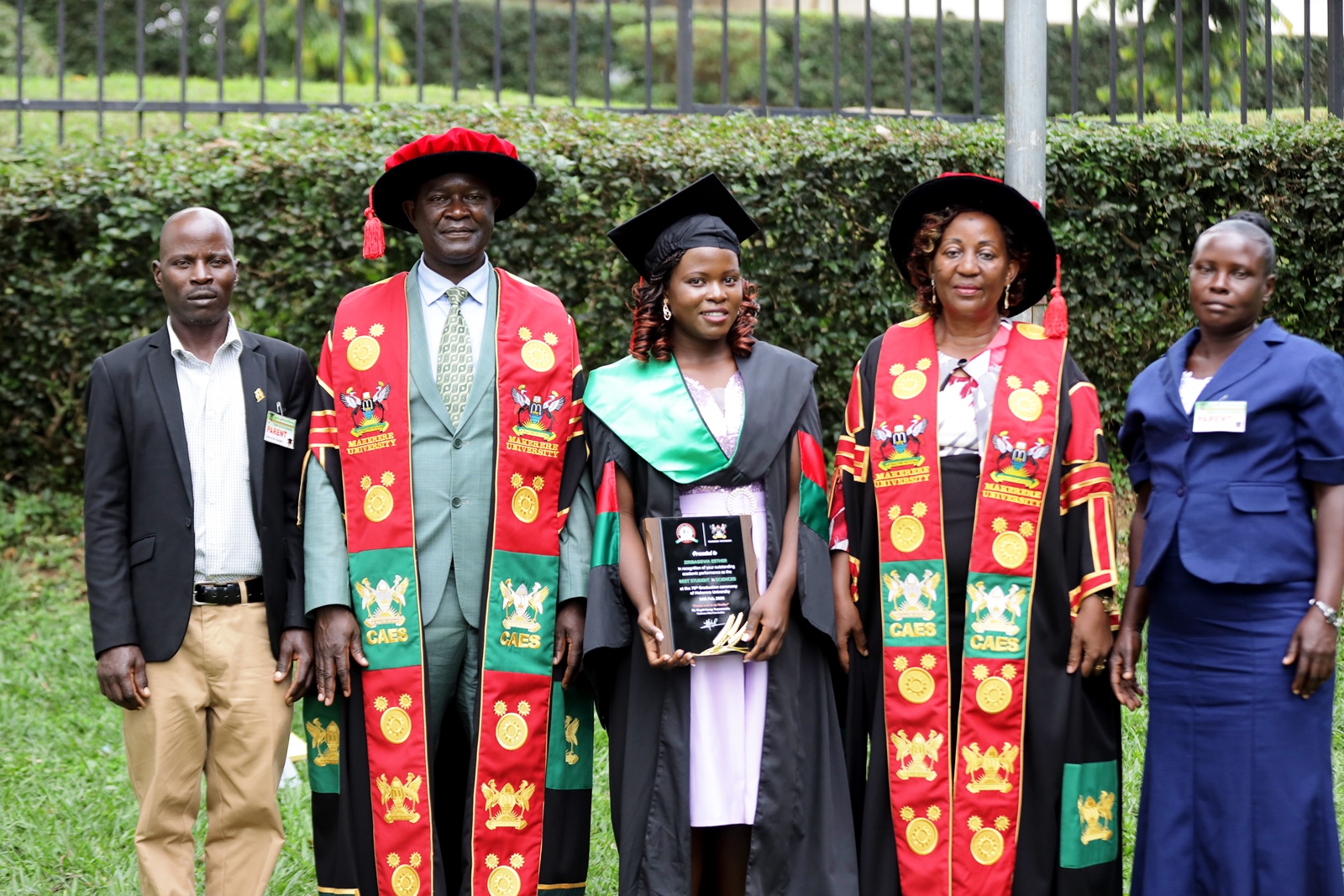
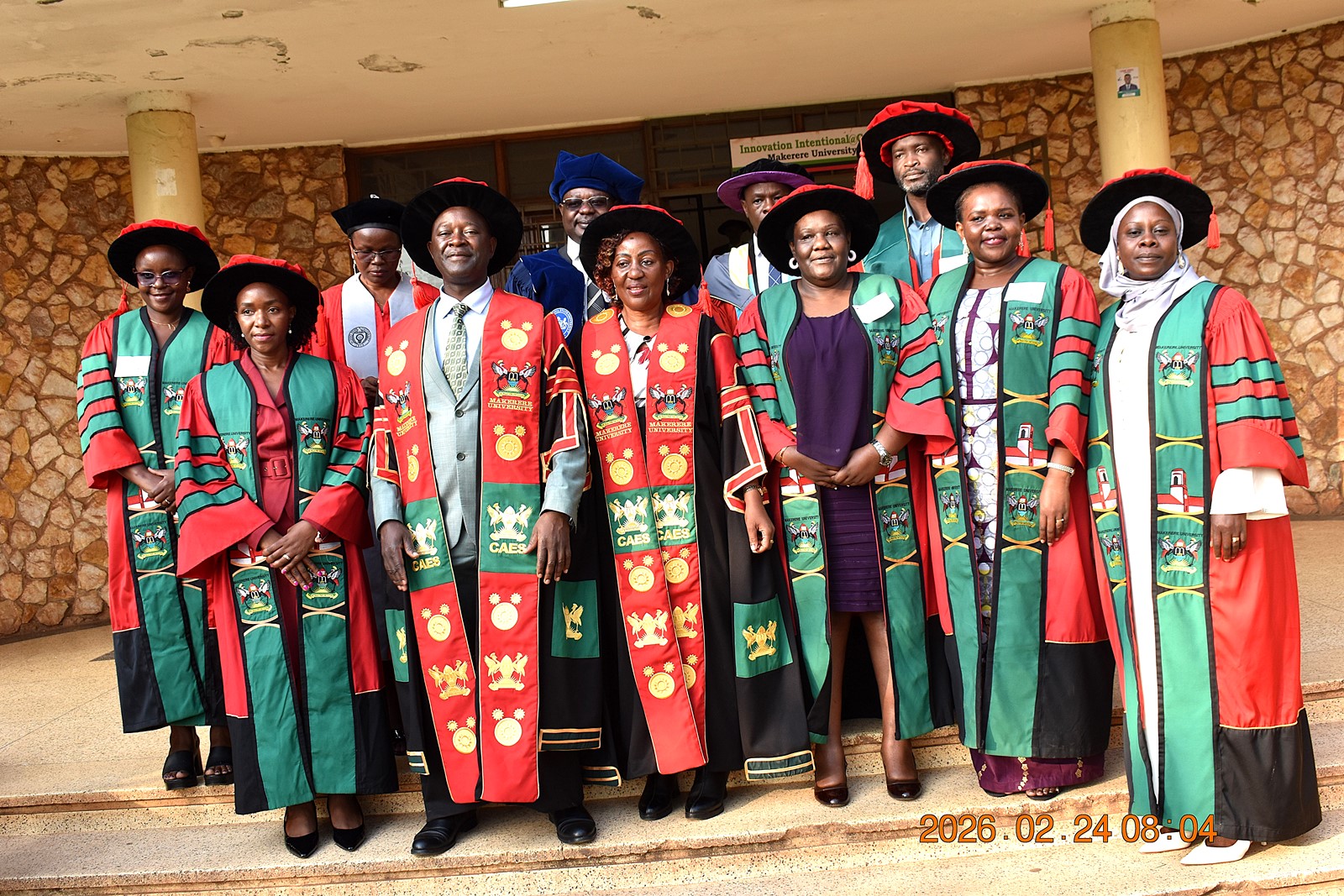
The College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES) presented the best performing student in the Sciences at the 76th Graduation Ceremony of Makerere University. Ms. Esther Ziribaggwa graduated with a CGPA of 4.77 in the Bachelor of Agricultural and Rural Innovation. She credits her success to resilience and hard work, despite the financial challenges she faced during her studies.
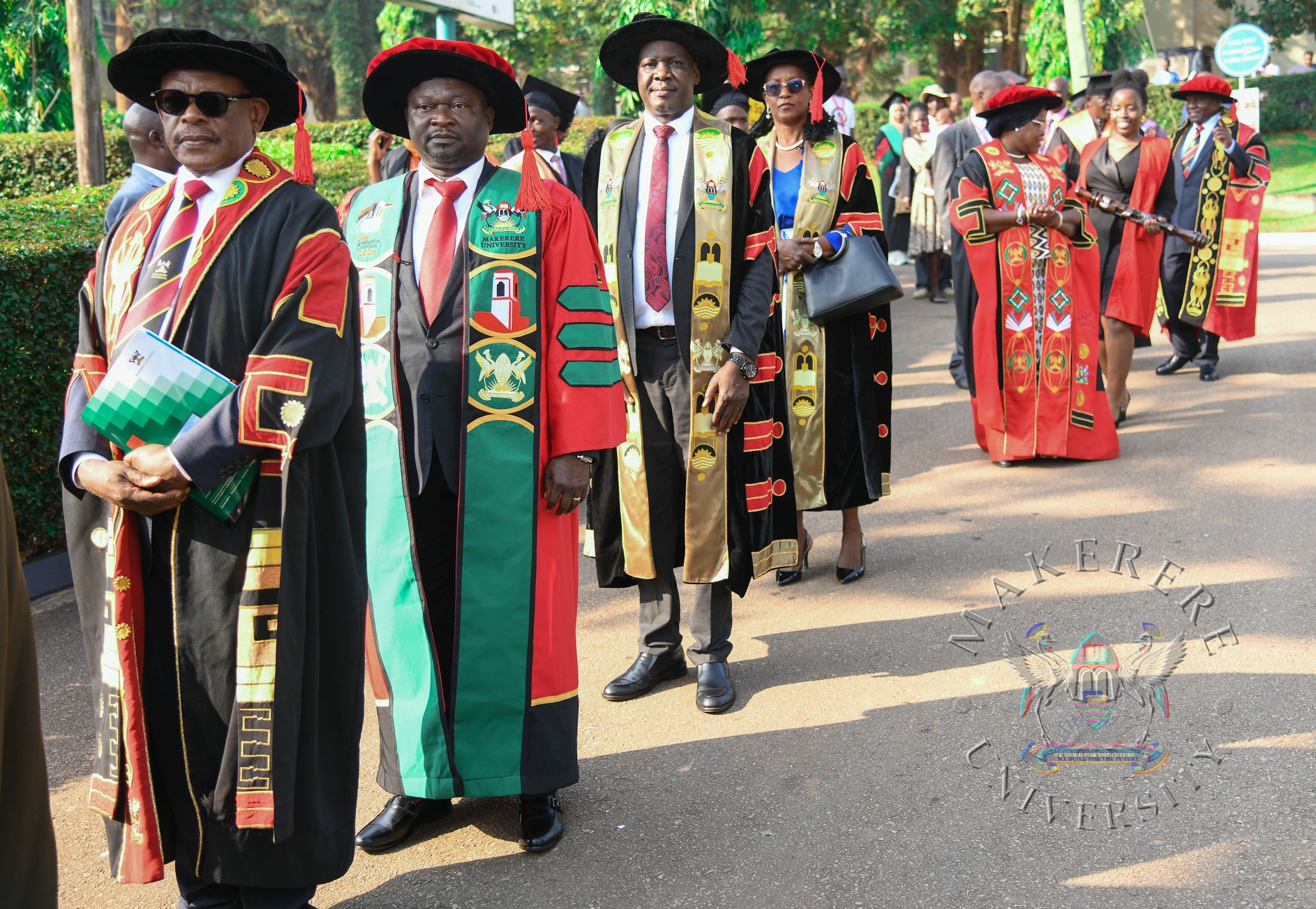
The four-day 76th graduation ceremony commenced on 24th February 2026 with the CAES, the College of Computing and Information Sciences (CoCIS), the College of Education and External Studies (CEES), and the School of Law presenting graduands for the award of degrees and diplomas of Makerere University.
CAES Graduation Statistics
CAES presented a total of 561 students (238 female and 323 male). Of these 28 (10 female and 18 male) graduated with PhD, 144 (68 female and 76 male) with Masters, 380 (157 female and 223 male) with Bachelor’s degrees, and 9 with Post graduate diplomas (3 female and 6 male). The PhD graduates included; Mr. Ainebyona Ronald Rwambuka, Ms. Amongi Winnyfred, Ms. Apil Jenifer, Mr. Asizua Denis, Mr. Astatke Dejene Kebede, Ms. Atuhairwe Privah, Ms. Ayesiga Stella Bigirwa, Mr. Biryomumaisho Dickson, Ms. Cherotich Harriet, Mr. Kalimunjaye Samuel, Ms. Kesiime Vasiter Eunice, Ms. Khakasa Elizabeth, Mr. Kimbowa George, Mr. Komi Gentle Wilson, Mr. Kusiima Kaheesi Samuel, Mr. Mathe Lukanda Musondolya, Mr. Mukama Innocent Hope Tinka, Mr. Mukengere Bagula Espoir, Mr. Nakhokho Evans Martin, Ms. Faridah Nalwanga Sendagire, Ms. Nalweyiso Amina, Ms. Nampijja Zainah, Ms. Njenga Peninah Wambui, Mr. Nkurunziza Gelase, Ms. Ojera Alal Ato Gertrude Miriam, Mr. Sebuliba Richard Mutumba, Mr. Shimali Fred, and Mr. Ssubi Allan Johnson.

Overall graduation Statistics
During the course of the 76th graduation ceremony, a total of 9,295 students will graduate with degrees and diplomas of Makerere University. Of these, 4,262 (46%) are female and 5,033 (54%) are male. A total of 213 students will graduate with PhDs, the highest number in the history of the University; 2,503 with Masters degrees; 6,343 with Bachelor’s degrees; 206 with postgraduate diplomas, and 30 with Diplomas.
Postgraduates constituted 31.4% of the total number of graduands.
Remarks by the Vice Chancellor
Addressing the congregation, the Vice Chancellor of Makerere University, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe, congratulated the graduates on reaching this significant milestone. “You graduate today from one of the finest universities in the world,” he said. “You have distinguished yourselves through discipline, integrity, and academic excellence, and we are immensely proud of you. The qualifications you carry are vital to society. We have equipped you with the knowledge and skills to secure employment or to create enterprises that will, in turn, employ others. Should you not find immediate employment, do not despair, instead, reflect on the vast opportunities around you and rise to the challenge as entrepreneurs. Do not despise humble beginnings. To our PhD graduands, you now join the global community of scholars. Africa looks to you with great expectation. Use your expertise to transform our continent.”
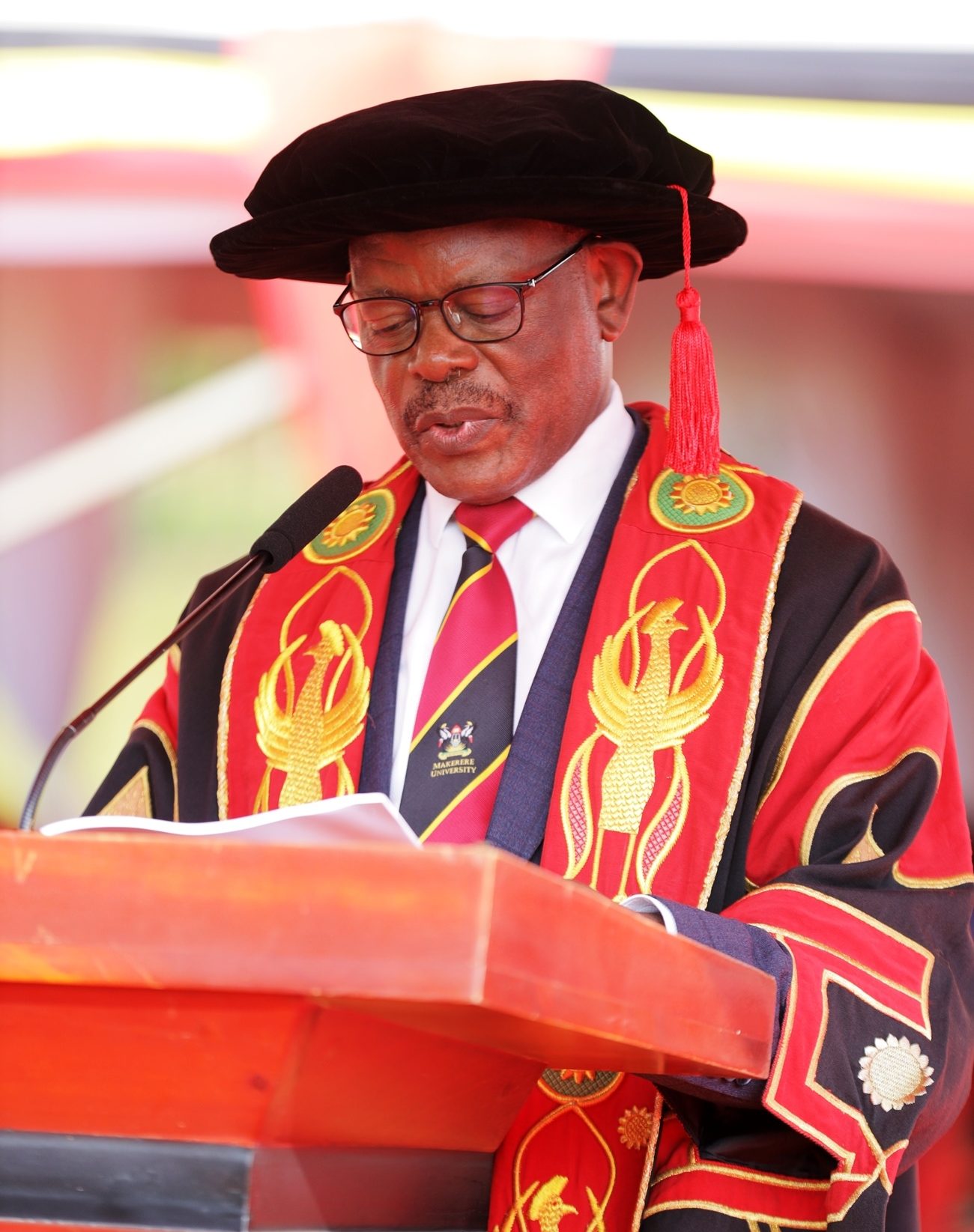

He appreciated the parents and guardians for the sacrifices they made to support their children’s education.
New Research Excellence Recognition Plans
The Vice Chancellor informed the congregation that beginning with the 76th graduation ceremony, the University will recognize outstanding PhD students who are members of staff. He congratulated those who completed their doctoral studies in record time while continuing to serve without study leave, commending their resilience and leadership. “These will receive the Makerere PhD Resilience Award”.
Similarly, the University will henceforth honour the best PhD and Master’s theses, as selected by the Higher Degrees Committee of Senate. The students with the top 10 theses at the 76th graduation are: Kawesi Paul – MA Law (School of Law), Katende Stephen – MSc Quantitative Economics (COBAMS), Najjinda Shamirah – PhD Management (COBAMS), Turyahabwe Irene – MSc Molecular Biology (COVAB), Tayebwa Dickson – PhD (COVAB), Batte Herbert – PhD Mathematics (CONAS), Ssekago Arnold – MSc Mathematics (CONAS), Namiyingo Julian – PhD Literature (CHUSS), Namata Brenda – MSCO (CHUSS), and Tayebwa Asaph Kamau – MBA (MUBS).

Recognition of the CAES Research Output
In his remarks, the Vice Chancellor commended the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences for spearheading transformative research aimed at strengthening Africa’s food systems. Among the initiatives he highlighted was the Healthy Soy Project, funded by the Danish Ministry of Foreign Affairs, which seeks to develop sustainable, affordable, and nutritious soy-based foods to combat child stunting in Uganda and other climate-affected regions. He also cited a project focused on enhancing value addition in cocoa production through the development and scaling of a single fermentation box technology, now adopted by more than 70% of farmers in major cocoa-producing districts.

Efforts to Transform Makerere into a Research-led University
The Vice Chancellor noted that Makerere University continues to advance steadily toward becoming a truly research-led institution – one that generates knowledge to empower communities, strengthen industries, and drive national transformation.
He expressed gratitude to the Government of Uganda for entrusting the University with resources to support more than 1,400 high-impact research and innovation projects under the Makerere University Research and Innovations Fund (Mak-RIF). The Fund has enabled researchers to provide practical, evidence-based solutions in sectors including agriculture, land management, energy and minerals, peace and security, and education. Through Mak-RIF, over 200 PhD students have received support to pursue their research, many of whom are graduating at the 76th graduation ceremony.

The Vice Chancellor further highlighted the pivotal role of the Makerere University Technology and Innovations Centre (MUTIC) in advancing incubation and commercialization. “The Centre offers mentorship, business development training, intellectual property support, and industry linkages to help transform research outputs into viable enterprises. To date, eleven spin-off companies have been established by students and staff, while the University’s Innovation Pod (UniPod) has incubated more than 100 projects in the past year. The short-term target is to establish 50 spin-off companies annually, with plans to double that number in the long term.”
In partnership with the Science, Technology and Innovation Secretariat in the Office of the President, the University has also introduced awards to recognize outstanding researchers and innovators. “The Innovation Commercialization Award underscores the institution’s commitment to translating research into practical products, services, and technologies that address real-world challenges and support national development,” the Vice Chancellor noted.

Prof. Nawangwe appreciated the Government of Uganda for securing a USD 162 million loan from the Korea Exim Bank to support critical infrastructure development at the University. The funding will facilitate the construction of new facilities for the School of Medicine, School of Dentistry, School of Engineering, the Science and Technology Centre, and the completion of the School of Computing and Information Sciences- an unprecedented development in the University’s history.
He also thanked development partners who provide research grants and scholarships, including the MasterCard Foundation, European Union, Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation, Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, International Development Research Centre, Korea International Cooperation Agency, German Academic Exchange Service, National Institutes of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, United States Agency for International Development, Wellcome Trust, KfW, Inter-University Council for East Africa, Regional Universities Forum for Capacity Building in Agriculture, African Research Universities Alliance, the PLUS Alliance, the Worldwide Universities Network, the Association of African Universities, the Alliance for African Partnership, the Madhvani Foundation, and the Government of Uganda through the Higher Education Students Financing Board.

He further acknowledged the Embassy of China, the Chinese Chamber of Commerce, various government ministries, State House, and private sector partners – including Stanbic, Absa, NCBA, DFCU, and Centenary Bank-for their continued support.
Remarks by the Chancellor
In his remarks, the Chancellor, Hon. Dr. Crispus Kiyonga, appreciated the parents, guardians, and sponsors whose unwavering support enabled the students to succeed.
“At the heart of the graduands’ accomplishments are the professors, lecturers, and administrators of the University, ably supported by the University Council. It is only fitting that we acknowledge and commend them for a job well done,” he noted.

He further extended profound gratitude to H.E. Yoweri Kaguta Museveni and the NRM Government for the invaluable financial and other support extended to the University.
Going forward, he encouraged the University Administration to strengthen research funding, forge stronger partnerships with the private sector to commercialize innovations, deepen structured engagement with communities, and fully leverage the abundant technological resources available to the institution.
Message from the Minister of Education and Sports
The Minister of Education and Sports, also First Lady, Hon. Janet Kataaha Museveni, represented by Hon. Dr. Joyce Moriku Kaducu – Minister of State for Primary Education, commended the Vice Chancellor and the leadership of Makerere University for upholding the standards that continue to distinguish the University across Africa and beyond.

She expressed gratitude for the spirit of constructive collaboration among management, staff, students, and development partners, noting that such cooperation is vital for institutional growth and academic excellence. She paid special tribute to the University Council, particularly the Chairperson and its members, for their dedicated oversight and stewardship. Their commitment to transparency and good governance, she observed, has strengthened public confidence in this historic institution.
A major milestone highlighted by the Minister was the establishment of the Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund (RIF), which supports high-impact research aligned with national priorities and development goals. Through this initiative, thousands of researchers and innovators have developed practical, scalable solutions that are transforming communities and key sectors across Uganda.

She reaffirmed the Ministry’s commitment to strengthening higher education through expanded research funding, digital transformation, cultural reform, and stronger collaboration between academia and industry. “The vision is clear: universities must not only produce graduates, but also solution-makers and job creators”.
Implementing the Competence-based Education and Training
Reiterating a key directive from the Ministry of Education and Sports, she emphasized that all institutions of higher learning must prepare for the full implementation of Competence-Based Education and Training by July 2027. “This reform represents more than a policy shift. It signals a fundamental transformation in how graduates are prepared, with greater emphasis on practical skills, innovation, and problem-solving.”

She urged the Vice Chancellor and his team to lead in curriculum reform, staff development, and infrastructure enhancement to ensure the successful rollout of competence-based education.
The Minister further urged university management to ensure that all satellite campuses are fully accredited and that their programmes meet the same high standards of quality and relevance as those offered at the main campus. This, she stressed, is essential to safeguarding the integrity of the University’s degrees and effectively serving students nationwide.

Addressing the graduates, she noted that Uganda and Africa need innovators to modernize agriculture, engineers to build quality infrastructure, healthcare professionals to strengthen health systems, and educators to inspire future generations. “The world you are entering is dynamic, interconnected, and technologically driven. Artificial Intelligence is reshaping industries; climate change is redefining agriculture and urban planning; and global markets are transforming employment patterns. In this rapidly evolving landscape, you must remain adaptable, creative, and committed to lifelong learning.”
Address by the Commencement Speaker, Prof. Nicholas Ozor
In his address titled Knowledge with Purpose and Service with Integrity, the Commencement Speaker, Prof. Nicholas Ozor, Executive Director of the African Technology Policy Studies Network, urged the graduates to embrace lifelong learning, prioritize purpose over comfort, build character before career, and serve something greater than themselves. He encouraged them to believe in Africa and take action, rather than waiting for solutions from elsewhere.
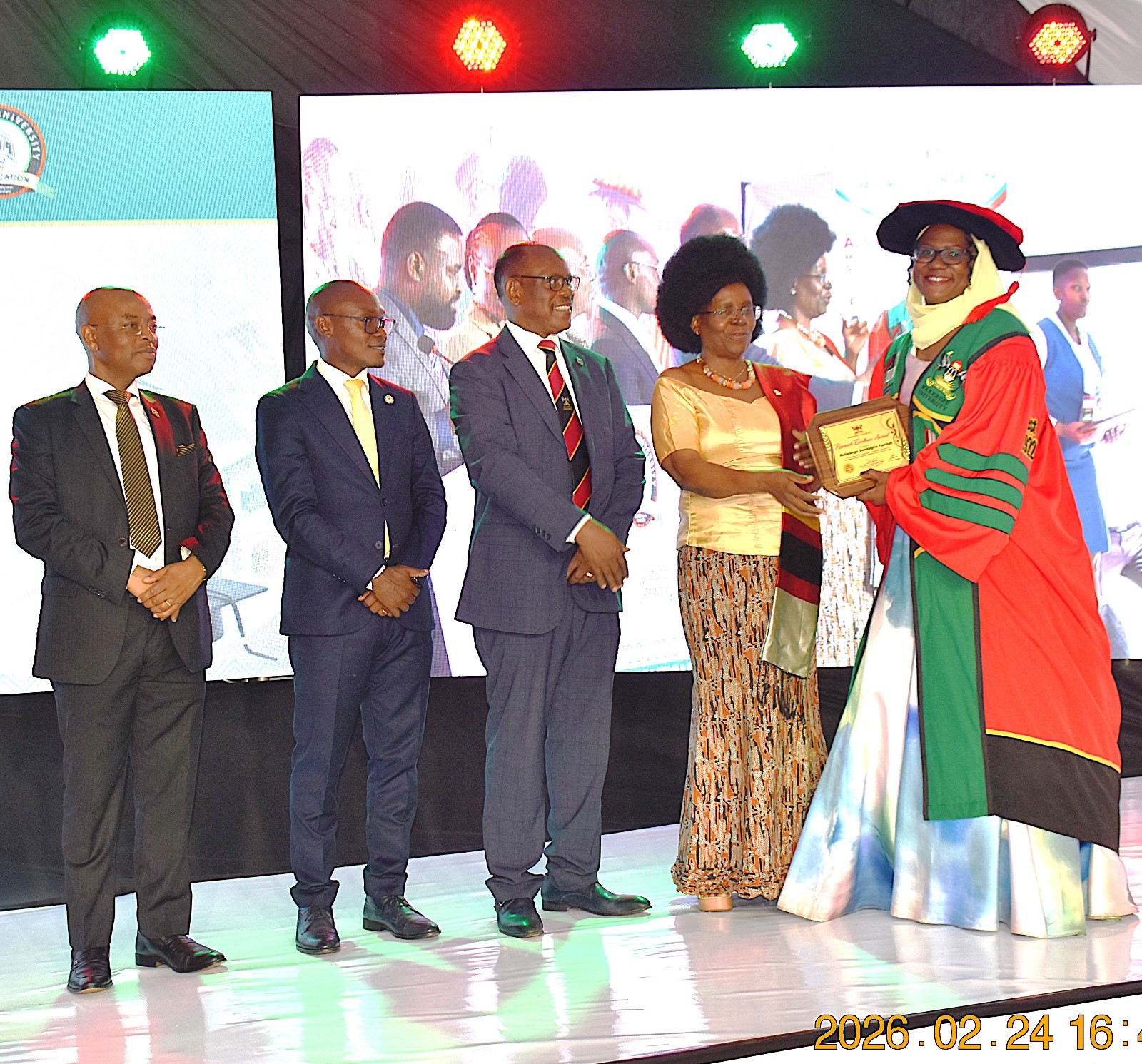

Addressing the graduates of CAES, he emphasized that they stand at the intersection of survival and sustainability. “In a world confronting climate change, food insecurity, and environmental degradation, your knowledge is vital. You will work with farmers, ecosystems, land, water, and policy. You will shape food systems and livelihoods. Respect indigenous knowledge, embrace scientific innovation, and champion sustainability. The future of Africa depends on how well we feed our people and protect our land.”
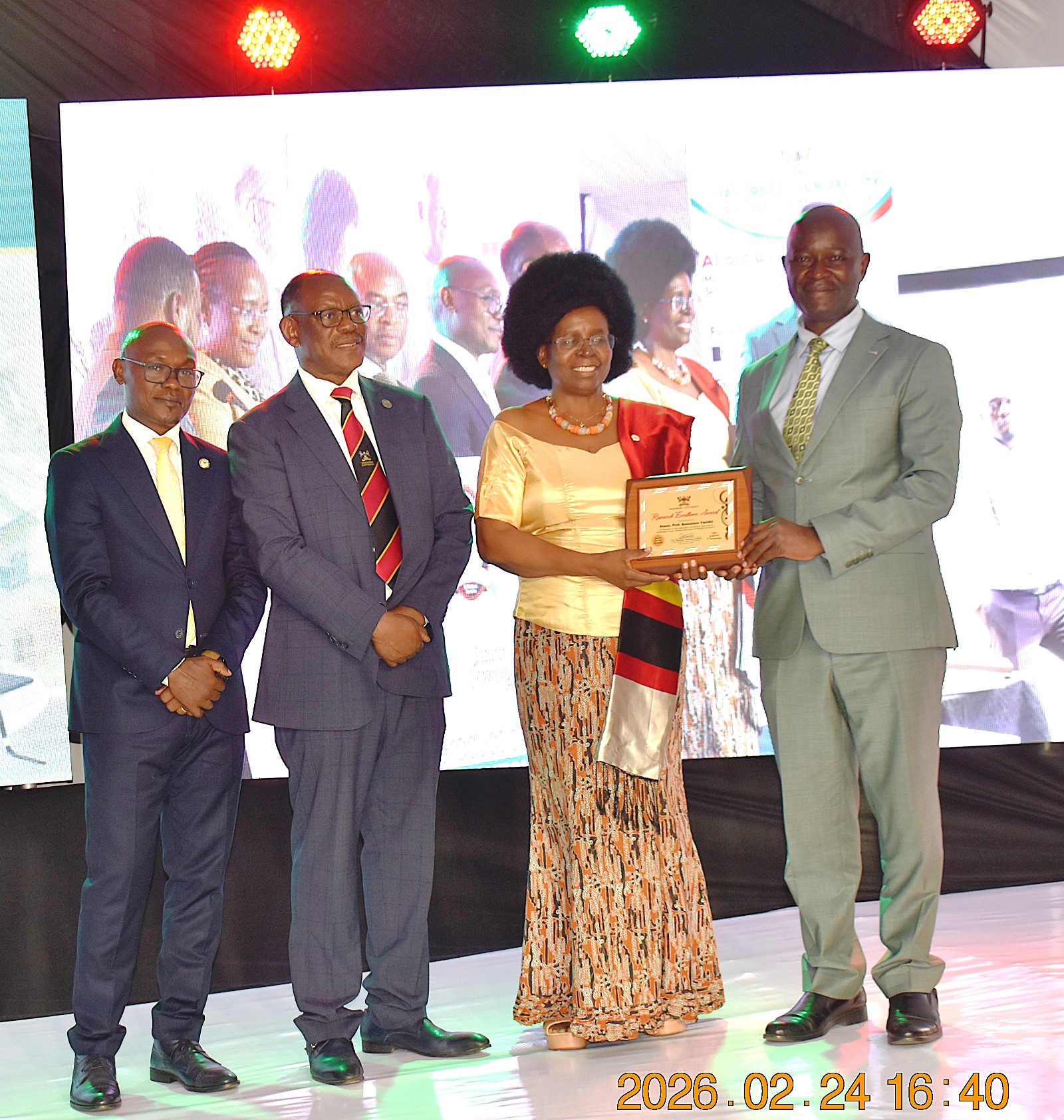

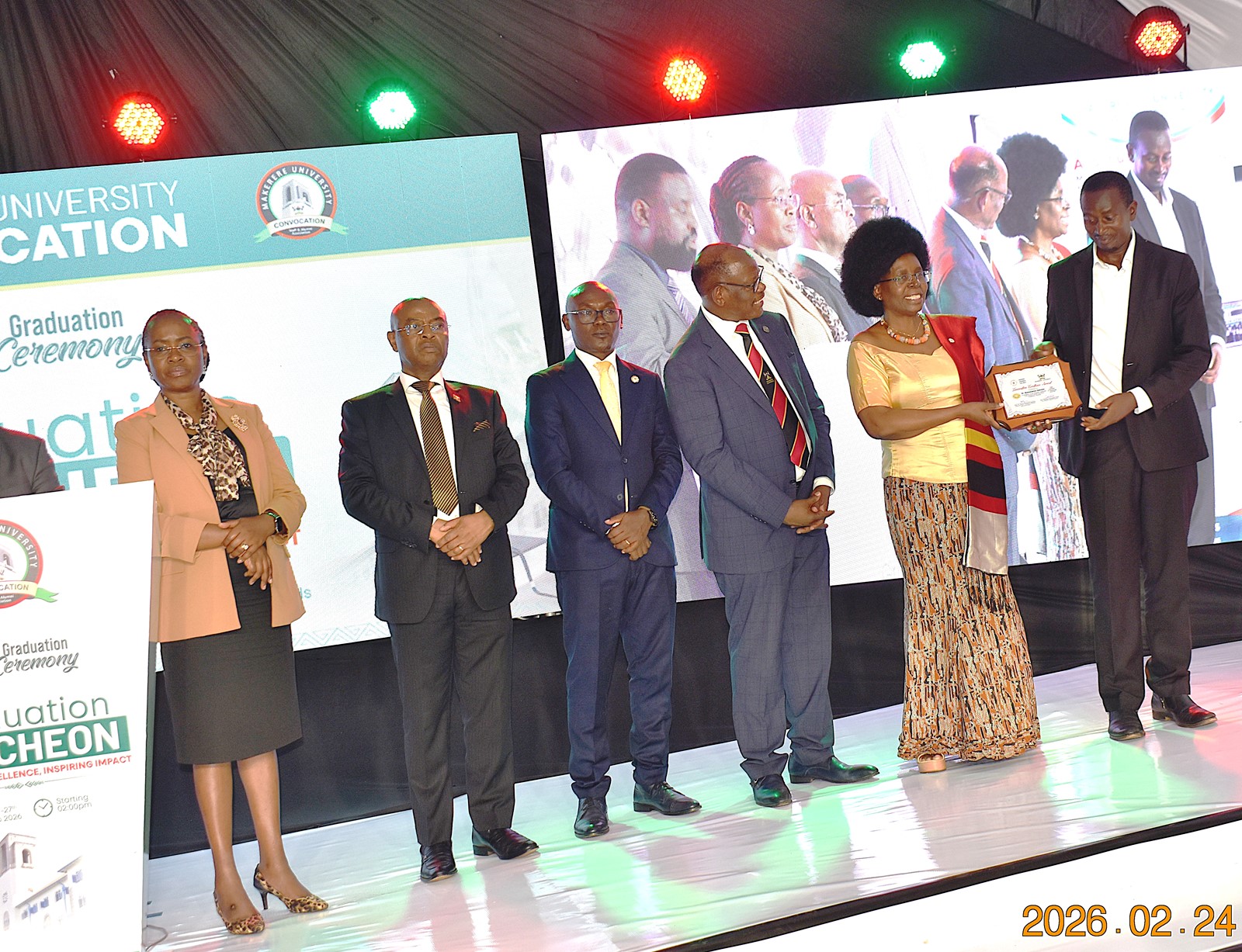
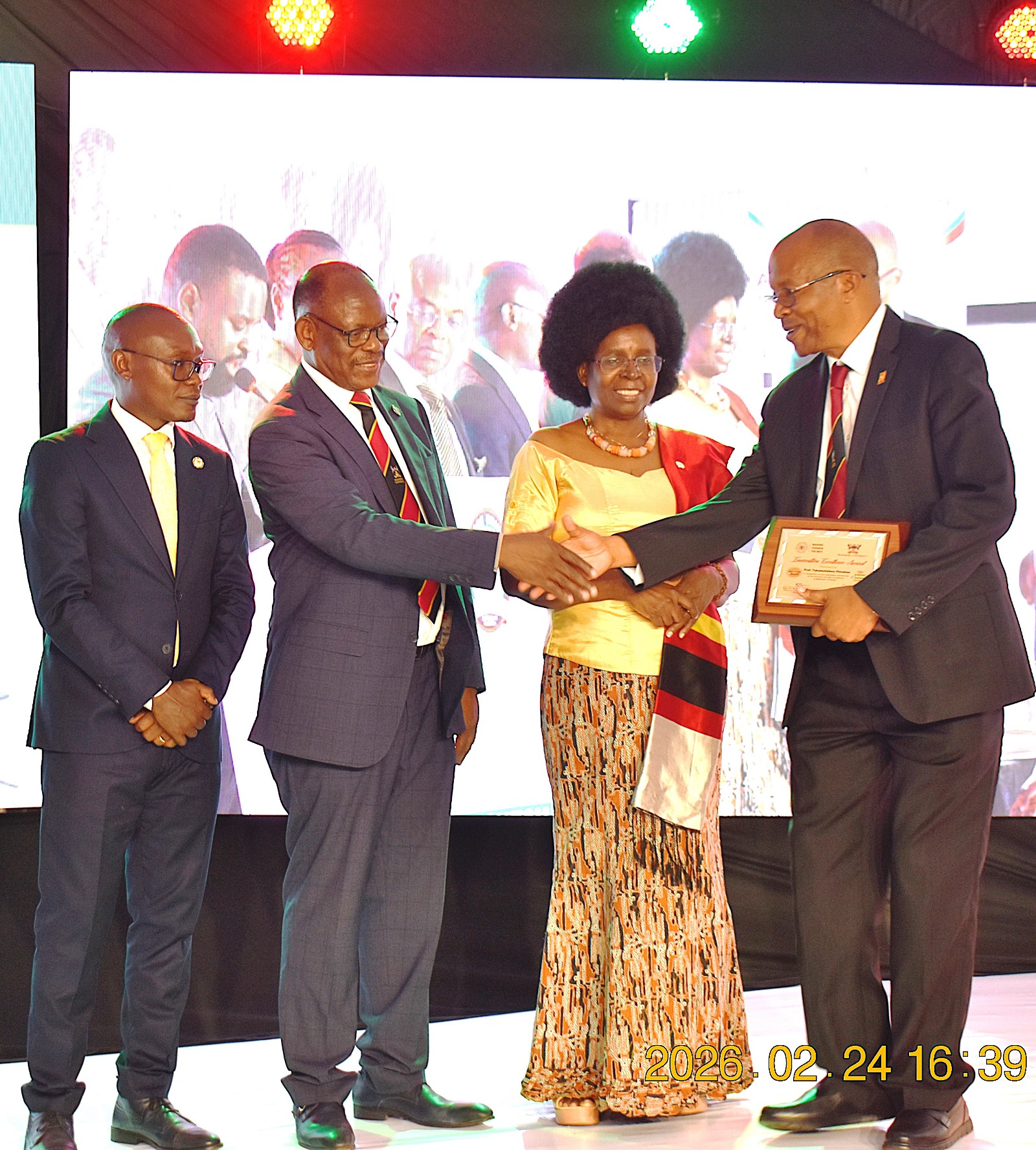
Research Excellence and Innovation Commercialization Awards
During the graduation ceremony, Makerere University recognized the top researchers and innovators from the 10 Colleges. At CAES, Dr Mugabi Robert from the School of Food Technology and Nutrition received the Overall Top Researchers Award, 2026; Dr. Nalwanga Sendagire Faridah received the Best Early Career Researcher Award, Dr Mugabi Robert scooped the Mid-Career Research Award whereas Prof. Yazidhi Bamutaze got the Senior Career Research Award. Prof. Phinehas Tukamuhabwa, Dr Ephrahim Nuwamanya, Assoc. Prof. Ahamada Zziwa, and Dr Ssempijja John Edson were recognized among the best innovators.
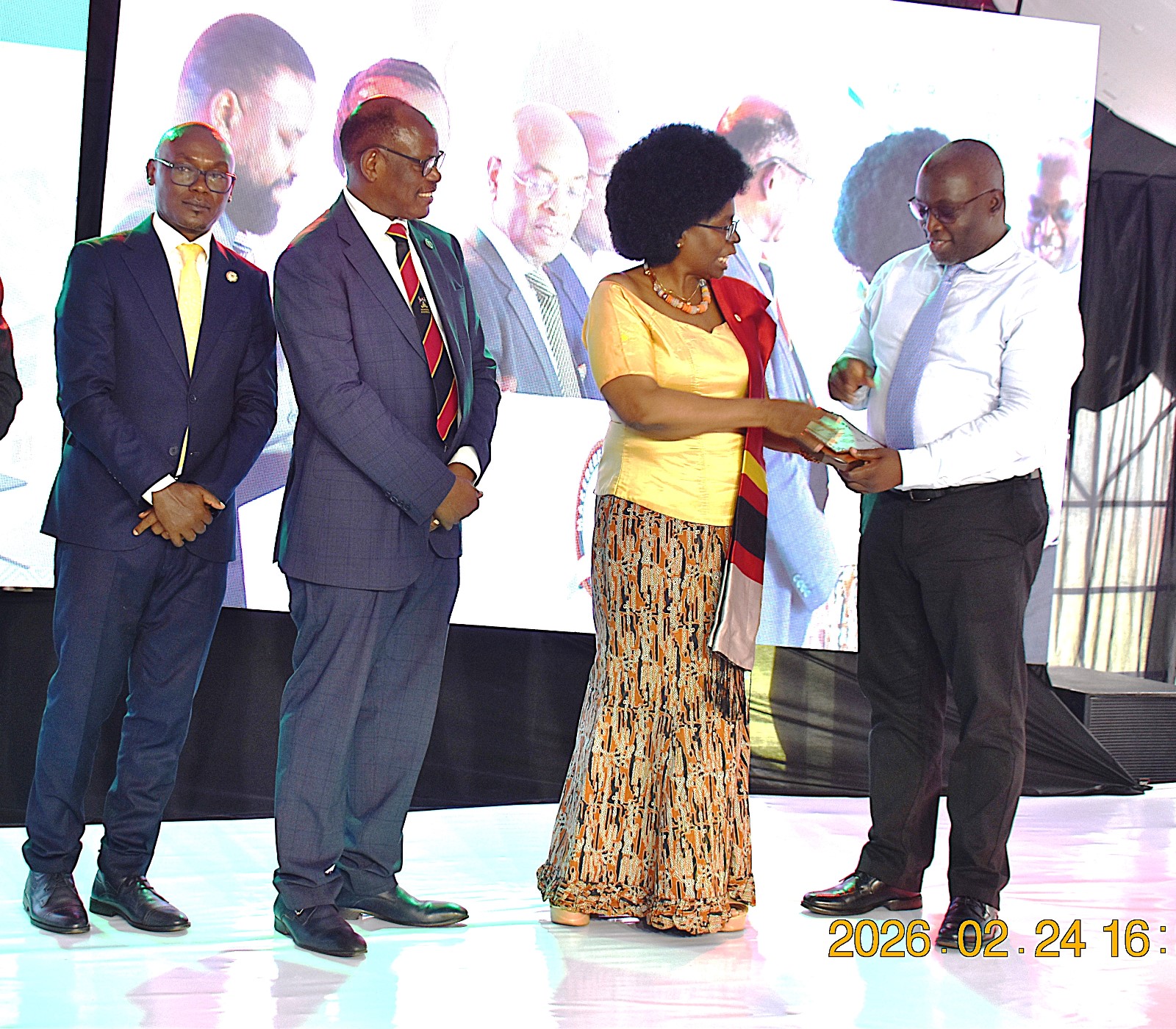

More about Esther Ziribaggwa, the overall best performing student in the sciences:
Agriculture & Environment
Mak hosts First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling
Published
1 week agoon
February 20, 2026
African economies are increasingly exposed to climate-related shocks that threaten development gains, fiscal sustainability, and macroeconomic stability. From extreme weather events and biodiversity loss to the depletion of natural capital, climate risks are reshaping economic realities across the continent. Yet many macroeconomic frameworks used in public finance and planning continue to overlook climate and nature-related risks and the long-term benefits of resilience and adaptation investments.
To address this emerging reality, over 250 participants from Africa, Europe and beyond, convened at Makerere University – Kampala, on the 12th and 13th of February 2026, to participate in the First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling.
Following the theme, “Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomics: Rethinking Growth in Africa’s Natural Resource Base, the hybrid symposium organized by Makerere University through the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling (CEACM) within the School of Economics, under the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS), the Environment for Development Initiative (EfD), and the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development (MoFPED) in Uganda, brought onboard ministers, leading economists and planners, researchers, policy makers, the academia, development partners, climate change experts and the media.
The Symposium being the first of its kind on the continent, reflected Africa’s growing determination to work collectively in confronting shared development challenges, building on recent momentum such as the formation of Pan-African Finance Ministers Forum for Climate Action (PAFMCA).
Featuring speeches and presentations from notable speakers and partners, a keynote address on Natura Capital Accounting and Climate Change Nexus in Africa and their impact on Fiscal Policy, panel discussions, expert opinions, and exhibition kiosks (World Café), the symposium presented a platform to strengthen Africa’s analytical and institutional capacity to integrate climate and natural capital considerations into macroeconomic and fiscal policy.
Vice Chancellor underscores the role of universities
Welcoming the delegates to Makerere University, the Vice Chancellor-Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe emphasized that universities must lead innovation and collaborative research efforts to support collective climate change mitigation across the continent.
In the same vein, he advocated for strong collaboration between universities in Africa and government Ministries. “Makerere’s collaboration with the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, stands as a shining example of how academia and government can strengthen economic management,” he said.
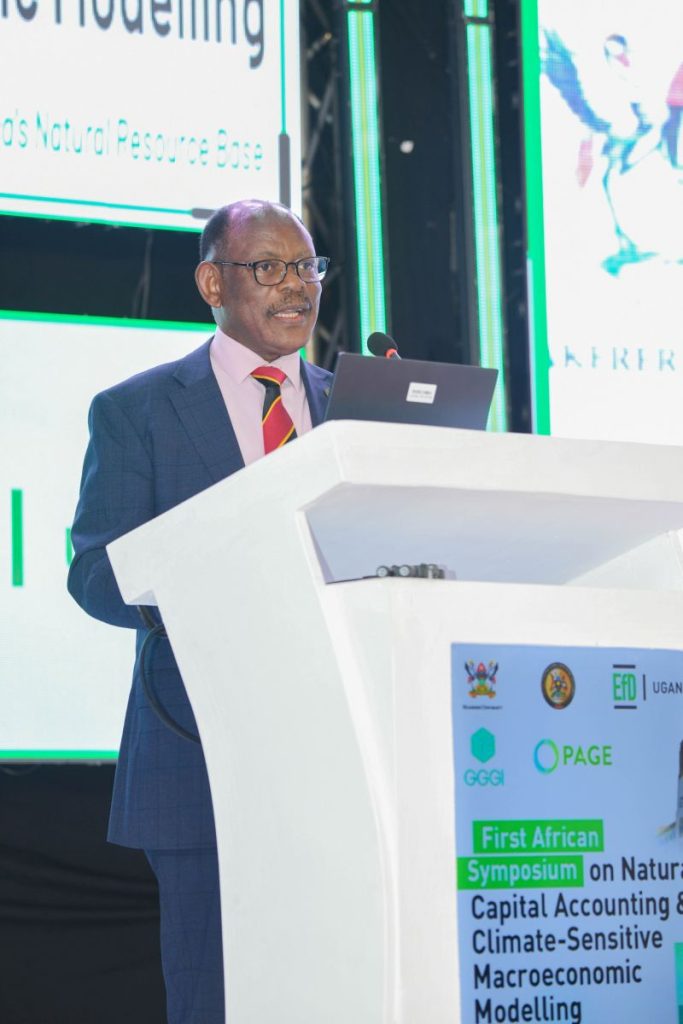

Prof. Nawangwe revealed that the collaboration between Makerere University and the Ministry, has strengthened macroeconomic modelling, fiscal policy analysis, and technical capacity within government. In addition, the partnership led to the establishment of the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling, bridging academic scholarship with real-world policy application.
“We have jointly established the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling. The Centre (established in August 2025) is anchored within the School of Economics in the Department of Policy and Development Economics, under the Master of Science in Economic Policy and Investment Modelling, a program jointly facilitated by Makerere University, the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development and the Bank of Uganda,” he mentioned.
Climate and Economic transformation are inseparable
The Vice Chancellor highlighted the critical intersection between economic transformation and environmental sustainability, noting that economies in Africa, heavily dependent on natural resources, face unprecedented pressures from climate shocks, biodiversity loss, and environmental degradation. Convinced that economic growth cannot be pursued in isolation from climate and environmental realities, he stressed the importance of integrating natural capital accounting and climate considerations into national development strategies.
Prof. Nawangwe advocated for shared responsibility of universities, research institutions, and policymakers to develop innovative analytical tools, responsive policy frameworks, and strong institutional capacities that promote sustainable growth while safeguarding environmental assets for future generations.
The Vice Chancellor commended UN PAGE and the Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI) for funding the symposium, as well as, other stakeholders namely the European Union and the Coalition of Finance Ministers for Climate Action (CoFMCA), Ministry of Water and Environment (MoWE), National Planning Authority (NPA), Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS), the National Environment Management Authority (NEMA) for being reliable partners.
Integrating Climate into Fiscal Policy
During the opening ceremony, the Minister of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, Hon. Matia Kasaija underscored the urgency of embedding climate considerations into economic planning.
“As Ministers of Finance, we are often confronted with difficult trade-offs. Our task is to balance the needs of today with sustainability for future generations,” said Hon. Kasaija, in a speech read by Hon. Henry Musasizi, the Minister of State for Finance (General Duties).

The Minister guided that traditional macroeconomic models focusing only on growth, inflation, and fiscal balance are inadequate in an era of climate shocks. He affirmed that African economies are facing interconnected challenges which directly impact economic growth. He stressed that traditional macroeconomic frameworks must evolve to systematically incorporate environmental degradation and climate shocks, whose consequences can no longer be ignored in policy analysis.
“For countries such as Uganda, whose development prospects are closely linked to natural resources and the climate-sensitive sectors, these challenges are not abstract. They affect livelihoods, public finances and long-term economic resilience,” he mentioned.
The Minister emphasized that natural capital accounting and climate-sensitive macroeconomic modelling are vital for valuing natural assets, assessing environmental costs, and guiding sound investment decisions.
Protecting Africa’s Natural Capital
Hon. Beatrice Atim Anywar, Minister of State for Environment, emphasized the urgent need to protect Africa’s ecosystems. “Africa stands at a defining crossroads. Our economies remain anchored in natural capital—forests, water resources, biodiversity, land, and ecosystems—which sustain life, generate fiscal revenue, and underpin development,” she said.
She warned that climate-related shocks are already undermining growth and public investment. “Floods, droughts, land degradation, biodiversity loss, and water stress are no longer distant risks. They are present realities, already affecting productivity and macroeconomic stability,” she said.
She emphasized the need for improved economic models that account for environmental and climate risks: “Traditional macroeconomic frameworks have not adequately captured climate risks or the long-term economic benefits of resilience and adaptation. This limits our ability to make informed policy decisions as Africa pursues economic transformation, energy security, and fiscal stability,” she stated.
Hon. Anywar highlighted collaboration with GIZ, Makerere University, and government ministries, which led to the development of the MONCAP (Model for Natural Capital Policy Assessment). “This tool is being used to assess natural capital assets for climate change, energy transition, and their linkages to the macroeconomy. It supports budgeting by estimating the cost of depleted natural capital assets,” she said.
“Water security, forest conservation, ecosystem restoration, and climate adaptation are not costs. They are investments in Uganda’s long-term economic stability, productivity, and prosperity.”
Stakeholders urged to transform climate threats into opportunities
Adam Sparre Spliid, the Deputy Head of Mission, Danish Embassy said: “Integrating climate risk and natural capital into our macroeconomics frameworks is not only academic exercise, it is a massive de-risking strategy for private investment. By bridging the gap between government policy and planning, academia and research, and the private markets, we transform climate threats into tangible opportunities.”
Sustainability includes youth, jobs and human well-being
Dr. Steven Stone, Chair of the UN PAGE Management Board, emphasized that sustainability extends beyond the environment to encompass youth, jobs, economic growth, and human well-being. “While the environment is Africa’s foundational source of wealth, sustainable development requires balancing ecological stewardship with economic progress, including income and employment for the youth which are critical priorities for countries such as Uganda.”
Dr. Stone highlighted that UN PAGE, originating from the Rio+20 Conference, supports climate-sensitive economic policy in Africa, emphasizing that dialogue, scenario-building, cross-sector collaboration, and strong partnerships are key to advancing sustainable, inclusive, and climate-resilient development.
Africa’s Wealth Declining
In the keynote address titled, Natural Capital Accounting and Climate Change Nexus in Africa and their Impact on Fiscal Policy, Paul Jonathan Martin, Manager of Environmental Operations at the World Bank for Eastern and Southern Africa, and a specialist with over 30 years in climate and natural resources, warned that Africa’s overall wealth is under threat due to declining renewable natural capital.
“Produced capital has increased by 20%, human capital by a third, but renewable capital has declined by 30%,” Martin said. “When combined, Africa’s overall wealth trajectory has been weakening since 2010.”
He stressed that natural resources must be treated as economic assets requiring systematic accounting: “Africa’s rich natural resources are fundamental for sustainable development,” he said.
Citing examples from Ethiopia and Kenya, he highlighted successful integration of natural capital into public investment and budget decisions. “In Ethiopia, there are payments for ecosystems and investment prioritization tools. In Kenya, natural capital accounting integration into budgets has strengthened public investments. Climate change has deep, cascading effects across sectors, but Africa has major potential to lead climate solutions,” he said.

Martin also highlighted the economic benefits of climate adaptation: “From 2020–2050, the cumulative effect of adaptation on Uganda’s GDP is positive. Without action, under a dry/hot climate future, GDP could significantly deviate from projected growth paths.”
Drawing on insights from over 70 country climate and development reports produced by the World Bank, the keynote speaker highlighted the profound macroeconomic impacts of climate change across Africa. He stressed the importance of integrating climate and natural capital into macroeconomic planning. He noted that Africa’s forests, water systems, and biodiversity are vital for sustainable development but face growing threats from climate change, environmental degradation, and climate-related disasters that undermine productivity, public investment, and economic stability.
He observed that traditional macroeconomic models often fail to capture the value of natural assets and regulating ecosystem services, which are critical to both economic stability and resilience but are largely excluded from GDP calculations.
Africa-Led Solutions
Prof. Edward Bbaale, Principal, College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS), stressed the importance of developing African-led solutions. “We need to champion the Africa-led model. We need approaches that fit our unique context. Africa is not here to take in other frameworks blindly,” he said.
By supporting research, training, policy dialogue and modelling innovation, the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling (CEACM) positions Makerere University as a regional hub for advancing climate-sensitive macroeconomic policy across Africa.
He highlighted CEACM’s capacity-building programs: “Our goal is to ensure African Ministries of Finance have home-grown expertise to integrate climate and natural capital considerations into fiscal and macroeconomic policy. This is critical for long-term resilience and sustainable development,” he said.
The Principal explained that establishment of independent research centres enables Makerere University to go beyond traditional academic instruction and focus deeply on societal challenges, particularly those related to climate change, environmental degradation, and biodiversity loss.

He reported that the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling is structured to advance methodological innovation, develop new data systems, and strengthen climate-sensitive macroeconomic tools that are tailored to the African context.
MONCAP Model for Policy Assessment
Dr. Peter Babyenda, a member of faculty at CoBAMS, demonstrated MONCAP (Model for Natural Capital Policy Assessment), which integrates climate and natural capital variables into fiscal and macroeconomic planning.
“MONCAP allows policymakers to estimate the economic cost of depleting natural assets such as forests, wetlands, and water resources. It helps simulate policy options and determine how investments in natural capital yield long-term benefits,” Babyenda said. “We came up with this model to aid the Ministry of Water and Environment. This model is open—you can extend it,” he added.

He highlighted capacity-building initiatives, including short courses and the Master of Science in Macroeconomic and Investment Modelling, designed to train economists to incorporate natural capital and climate into policy planning.
International Perspectives
Sweetman Liam, Ireland’s Finance Minister, highlighted the economic value of ecosystems: “There is a deeper value of landscapes in flood prevention and biodiversity. Decision-making was informed, and people started understanding economic value,” he said.
Prof. Chukwuone Nnaemeka of the University of Nigeria emphasized collaboration with national statistical agencies: “We coordinate with the National Bureau of Statistics to develop natural capital accounting metrics. Increase the use of Natural Capital Accounting in decision-making,” he stated.
Technical and Parallel Sessions
The afternoon session featured three parallel sessions focusing on Natural Capital Accounting Methodologies and Best Practices, Climate-Sensitive Fiscal and Economic Modelling, and Natural Capital Accounting and Model Uptake and Use.
Drawing on diverse expertise, the panels highlighted innovative approaches and demonstrated that natural capital is not an environmental afterthought, but a central pillar of sustainable economic and policy planning.
The first day of the African Symposium drew to a close with interactive exhibitions at the World Café, where case studies and practical demonstrations highlighted innovative approaches to integrating climate and natural capital into economic planning. Participants actively engaged in discussions and networking, forging collaborations that promise to advance climate-sensitive fiscal and development strategies across Africa, setting a strong and optimistic tone for the days ahead.
Agriculture & Environment
Uganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
Published
1 week agoon
February 20, 2026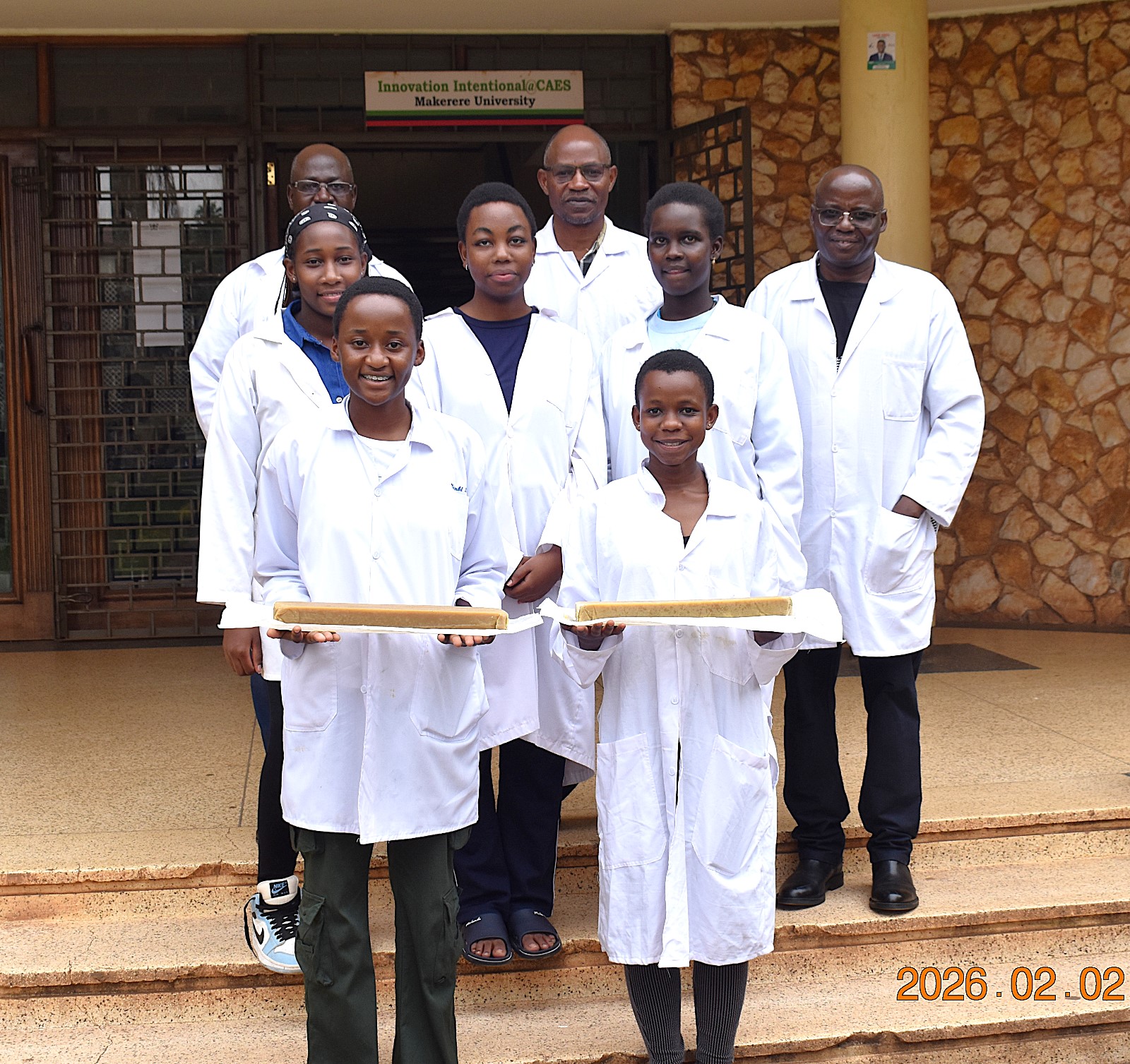
*****The students were supervised by researchers from the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES) at Makerere University, led by Prof. Fred Kabi.
The garbage challenge
With urbanization rates rising rapidly across Uganda, municipal solid garbage generation in the country’s cities is projected to increase by more than 40 percent by 2050. The growing burden of unmanaged garbage, particularly organic garbage, continues to pose environmental and public health risks, underscoring the urgent need for innovative and sustainable solutions.
It is against this backdrop that Senior Four students of Uganda Martyrs Secondary School Namugongo undertook a project to demonstrate how local market garbage challenges can be transformed into opportunities for sustainable development.
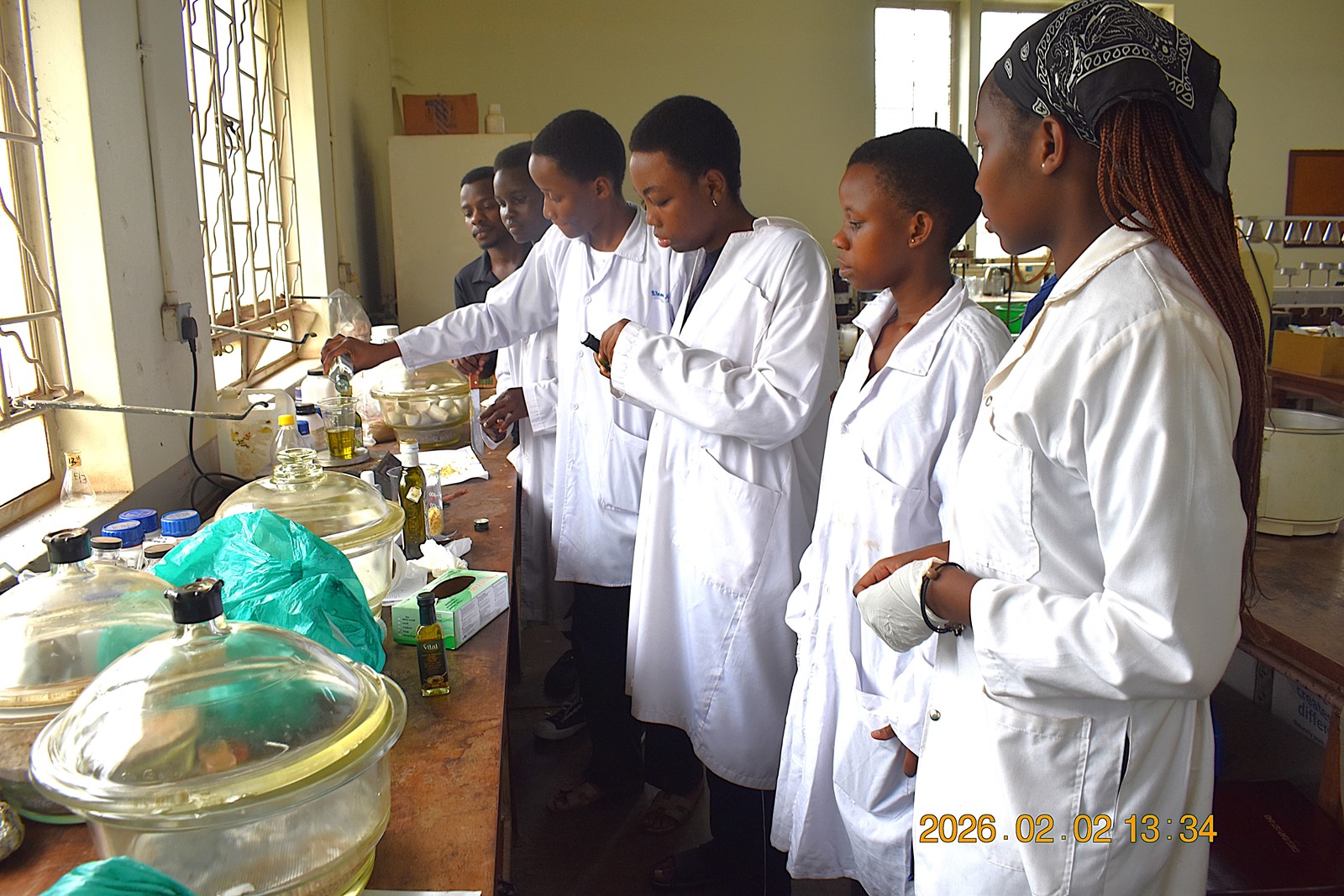

Addressing the garbage Challenge
As part of their academic project under the competence-based curriculum, the students were tasked with identifying real-world challenges within their communities and developing practical solutions using locally available resources. Through research and field observations, they identified poor garbage management, particularly the accumulation of organic waste at major dumping sites such as Kiteezi Landfill, as a critical issue.
At these sites, unsorted solid garbage often accumulates uncontrollably, sometimes leading to collapses that pose serious environmental and public health risks including water contamination by leachates, persistent foul odors, and disease outbreaks.

Rather than solely viewing solid market garbage as a problem, the students recognized its untapped potential within the biodegradable fraction of market garbage streams. Their innovative solution was to convert organic solid market waste (biodegradable garbage) into an industrial raw material for soap production by utilizing saprophagous Black Soldier Fly larvae (BSFL) to accumulate lipids and applying the scientific process of saponification.
Makerere University Support to the project
The students’ project was supervised by Prof. Fred Kabi together with technicians from the College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences (CAES) at Makerere University. Prof. Kabi and his team have been actively researching on Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) as a bio-waste management technology capable of converting biodegradable solid municipal garbage and farm waste into valuable by-products such as organic fertilizers, animal feeds, soap, and biodiesel.
Working in collaboration with Ento Organic Farm Uganda Ltd, the researchers have demonstrated how insect-based waste conversion systems can support a circular economy by transforming biodegradable waste into industrial raw materials.
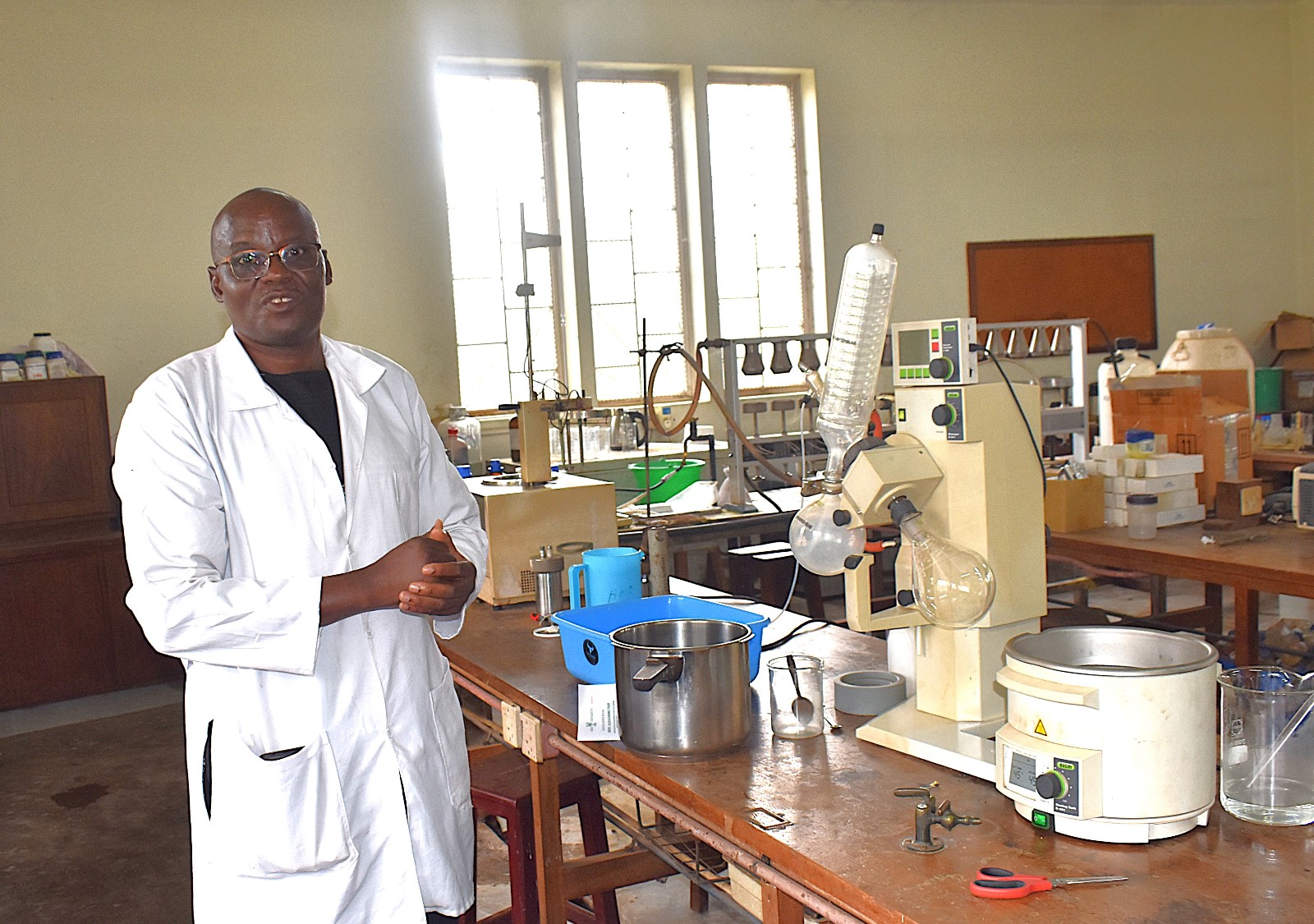

According to Prof. Kabi, the five young garbage entrepreneurs (students) began their project by collecting information on household garbage management practices. After analyzing the data, they engaged stakeholders along the garbage value chain to brainstorm all-inclusive, source-based waste management strategies.
“The students developed a solution that links efficient waste management at garbage generation source to support production of organic fertilizer, insect protein for animal feeds, and soap, which is only possible with biodegradable garbage,” Prof. Kabi explained. “This approach of the Competence Based Curriculum (CBC) for lower secondary schools supports the concept of taking Makerere University to the community of budding scientists while promoting sustainable community development through a circular economy.”
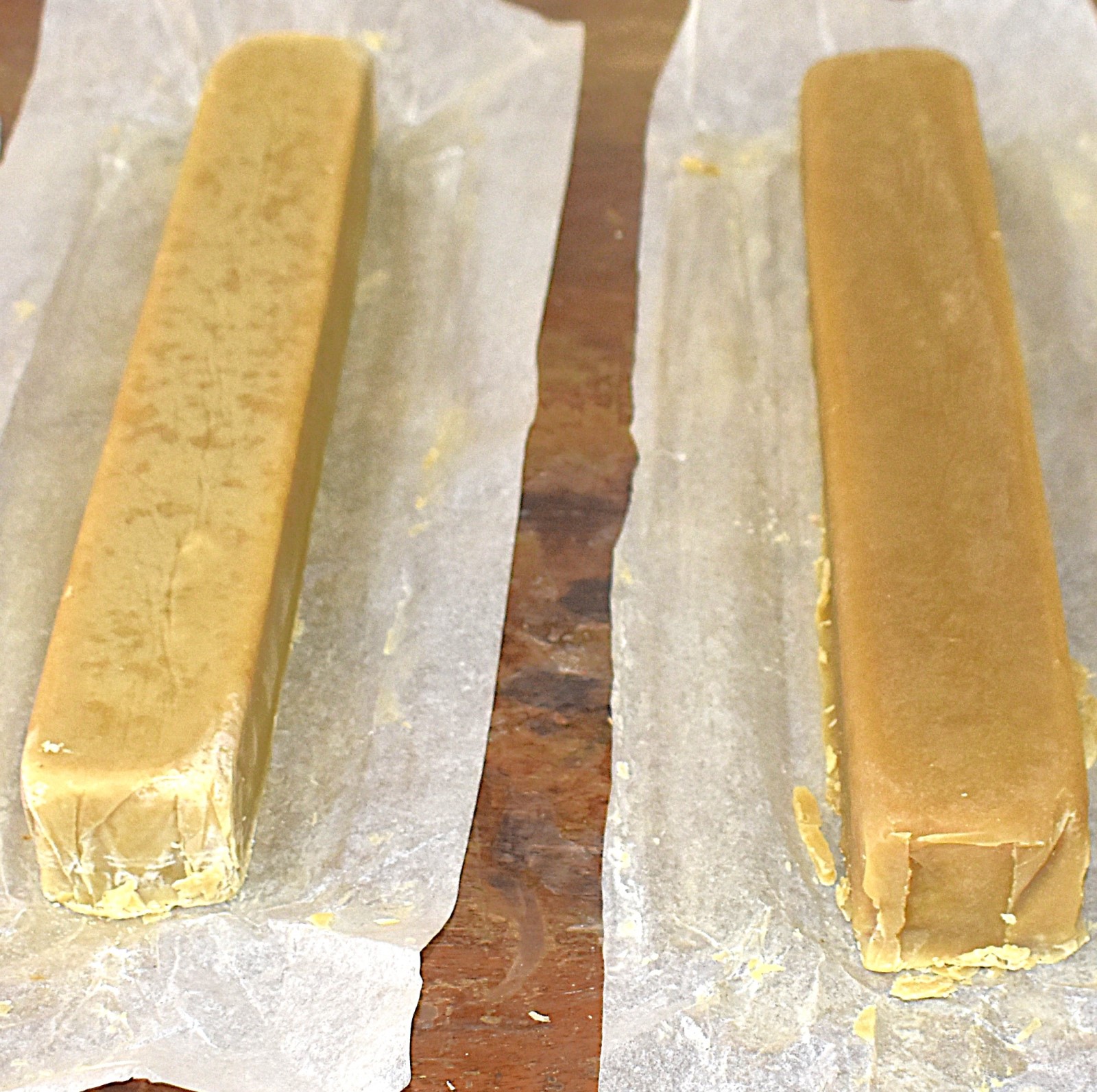
From Market Waste to Soap Bars
The Team leader, Ms. Ivy Stephanie Kitali explained the step-by-step scientific process behind the project. The students began by collecting organic waste from local markets, which was then shredded to prepare it for the larvae as a substrate. “Black Soldier Fly larvae were then introduced to the prepared waste. The larvae efficiently consumed the organic matter, greatly reducing its volume while accumulating lipids (fats) in their bodies. After maturation, we separated the larvae from the remaining waste, euthanized through blanching and dried it. Oil was then extracted from the dried larvae using ethanol as a solvent. This lipid-rich oil became the primary ingredient or raw material for soap production. To enhance the final product, the larvae oil was blended with minute quantity of sunflower oil before adding sodium hydroxide, initiating saponification, the chemical reaction that transforms fats and oils into soap,” she explained. The process ultimately yielded usable bars of soap derived entirely from what had once been discarded as unwanted market waste/garbage.
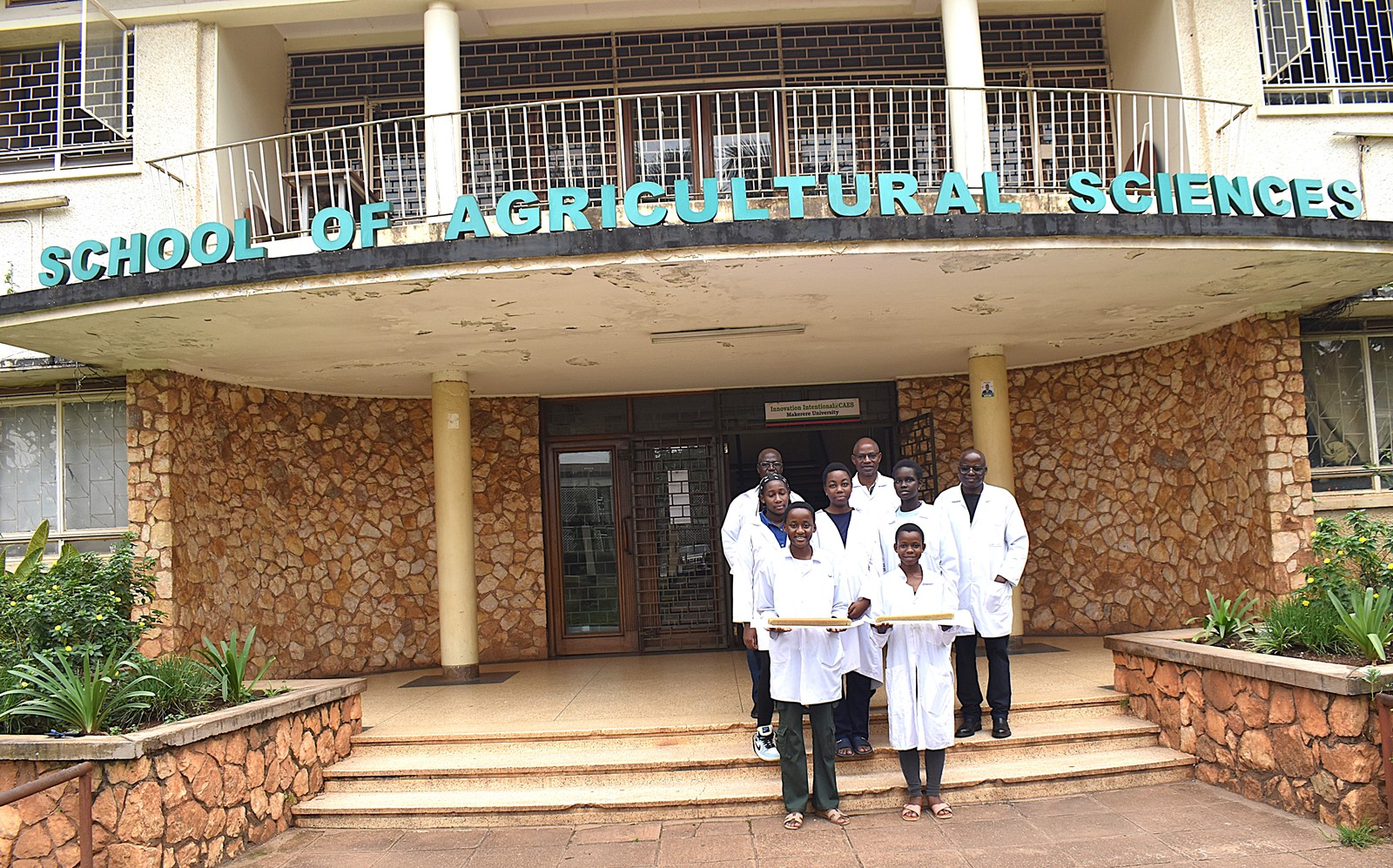

Building Skills and Sustainable Innovation
Beyond producing soap, the project provided students with hands-on training in scientific research, waste management techniques, bio-chemistry, and sustainable innovation. They gained practical exposure to insect-based biotechnology and learned how environmental challenges can be addressed through science-driven by entrepreneurship.
Trending
-

 Humanities & Social Sciences5 days ago
Humanities & Social Sciences5 days agoMeet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 Agriculture & Environment1 week ago
Agriculture & Environment1 week agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-

 General4 days ago
General4 days ago76th Graduation Highlights
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
