Health
Rising to the Top: Carol Nabbanja’s Journey to Becoming the Best Graduating Student from MakSPH
Published
2 years agoon
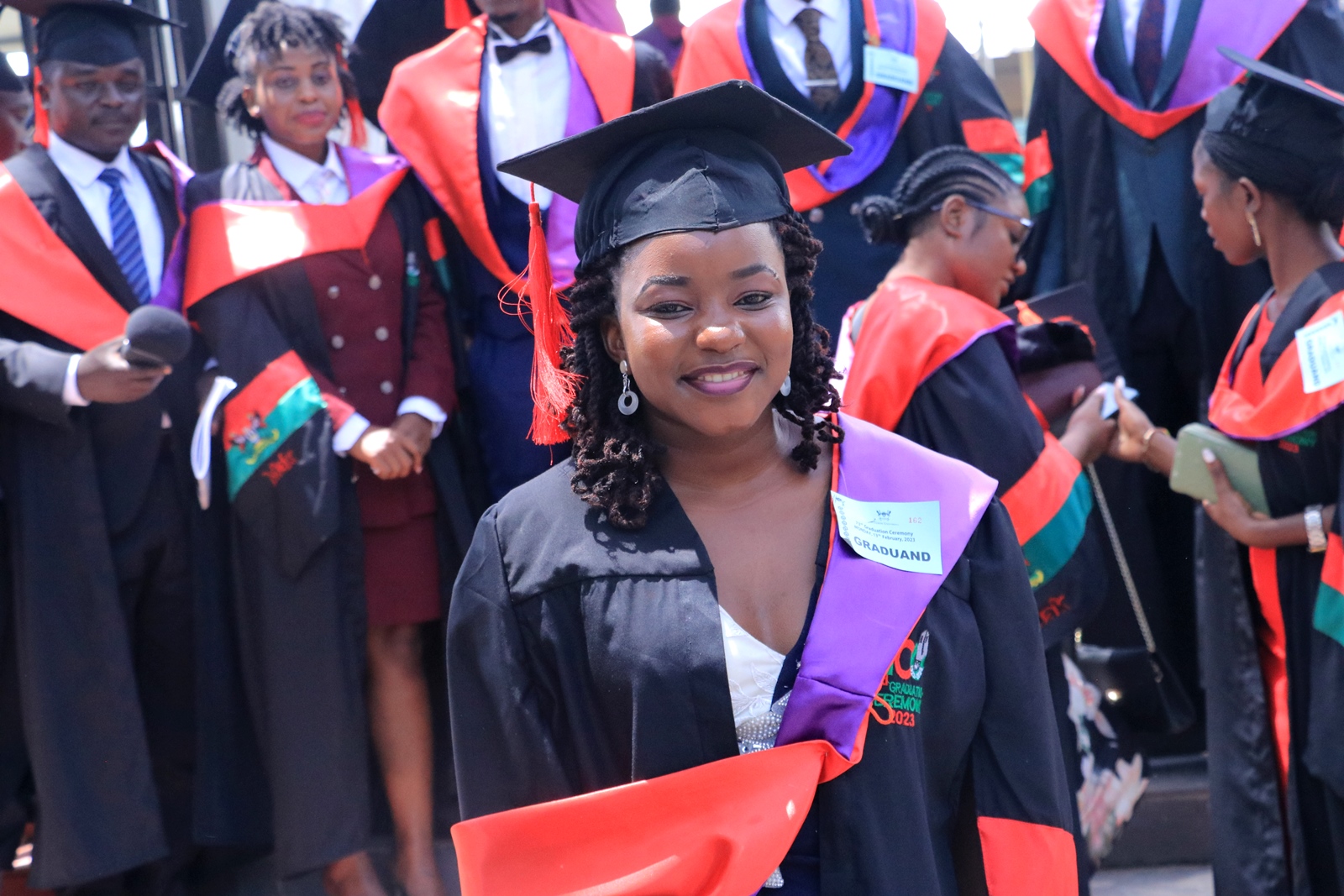

Carol Esther Nabbanja, 22, is set to graduate with First Class Honours in Bachelor of Environmental Health Science (BEHS) from the Makerere School of Public Health as the best-graduating student in the school this year. She graduates in Makerere University‘s 73rd Graduation ceremony today.
With a CGPA of 4.61, she has emerged as the best-graduating student in the MakSPH this year. She graduates alongside her other 43 classmates who made it to the graduation list this year.
Born in Kitemu village, Nsangi Parish, Wakiso District, to Samuel Mawejje, and Alice Naggawa, Nabbanja is the third born of four siblings and first to come to Makerere University, the very first to be on a government scholarship, and the very first to go through Kings College Budo.
Right from her childhood, Nabbanja has always been passionate about health and clean environments, which started from her early years as a head monitor at a government-aided St. Charles Primary School, where she did her nursery to primary five and the sanitation prefect at Clevers Origin Junior School.

While at St. Charles, Naggawa, Nabbanja’s mother was not convinced that she would make a foundation for a great future. She wanted better for her daughter. Nestled in the bustling streets of Kitintale, lies Clevers Origin Junior School, a beacon of hope for many students in the area. For Naggawa, her daughter’s joining the school would mark the beginning of a new chapter in her life.
She approached the owner of the school, Christopher Mugwanya, who happened to be her brother. Despite being a private school, Mugwanya, a kind-hearted and supportive uncle, offered the Nabbanja a half-bursary based on academic merit and family relationship. “I was overjoyed and couldn’t wait to start his new journey at Clevers Origin,” says Nabbanja.
Settling into her new school, Nabbanja encountered some challenges in mathematics, but her uncle was there to help. “I had some challenges in math, but he ably supported me, he gave me food, visited me when my mother couldn’t make it, and sometimes I would stay at his place over the holidays. He was really supportive. I was able to overcome my difficulties in math and excel in my studies. In fact, my grades improved and I found a newfound passion for learning. I am grateful for the support from my uncle and I feel proud of my academic achievements so far.”

Because of her unwavering determination and hard work, the School was convinced that she would sit her Primary Leaving Examinations (PLE) in Primary Six.
“I did PLE in P.6. The centre I registered at was in Nateete and I was the only first grade there but I didn’t want those results. I decided to wait for my actual time, and when it came, I excelled. I got aggregate 5,” says Nabbanja.
She was the best-performing female academician in her cohort. This was a significant achievement, as her cohort had the best grades since the school was founded. “I was also awarded the best female academician during my time at the school. I, in fact still have the certificate. I have also always been pertinent about health, and so I took up positions like the Sanitation Prefect,” says Nabbanja.
Nabbanja also had a passion for cleanliness and health. As the Sanitation Prefect, she made sure that the school environment was clean and hygienic at all times, something that was important to her from a young age. “I always loved a clean environment and to have everything in its place, so my interest developed that early.”

Joining Kings College Budo
Given her outstanding performance, Nabbanja was offered several scholarships to join Secondary School. “I was the very first from that Clevers Origin Junior School to ever go to Kings College Budo—we were two students that performed well, a boy who got 4 and me who got 5 and joined Budo on merit. My parents were offered other offers of schools giving me scholarships but Budo was exceptional. We had to make a decision that would set for me a good standard.”
Her journey to Makerere School of Public Health was paved at Budo. She was initially worried about School fees and how her father, a taxi driver would raise money to support her education.
“On joining my S.1, my parents were worried about the high fees, and the fact that I had studied on bursaries up to this point, they were not financially ready. We were paying about Shs1.4M. My mother talked to the Deputy Head Teacher, Rebecca Kiwanuka, who told her to let me join and that things would work out in the long run. Fortunately, my parents paid fees for S. 1,” says Nabbanja.
Unsure of how the second term would go, by sheer luck, Ligomarc Advocates, a financial and corporate law firm located at Social Security House in Kampala was celebrating 10 years and the partners decided to go back to their high schools and support students who were having financial issues
“By God’s grace, after the meeting between the School administration and the law firm, Mrs. Kiwanuka, our deputy head teacher informed me that I had gotten a sponsor,” Nabbanja says.
Ligomarc Advocates did not only sponsor her education but also provided opportunities for her to work with them during school breaks.
“Ligomarc took me for the 6 years I was at Budo. They were not just sponsors but also supporters, they supported me financially, came for V.Ds [Visitation Days], and also gave me an opportunity to work with them as an office attendant during my vacations. I also assisted the administration, delivering letters here and there. They supported me beyond just academics,” she says.
Budo was a turning point in Nabbanja’s life. It exposed her to new experiences and taught her valuable life lessons that have stayed with her to this day. She thrived in her studies, maintaining an average of 94 and earning 10 out of 8 aggregates in S.4 and 16 out of 20 in S.6.
Nabbanja never lost sight of her goals and was motivated by quotes from her late headmaster, Mr. Patrick Bakamale, such as “In this era of information and technology, we need to have the power of selection,” and “Focus on roots not fruits.”

Shaping her dream
Growing up, Nabbanja had always been fascinated by journalists, with the thrill of being on TV. “I used to hear that they earn 1 million, so that excited me.” However, it was her frequent trips to the dentist that truly sparked her interest in the field of dentistry. As she watched the dentists work their magic, Nabbanja was drawn to their ability to improve people’s dental health and change their lives for the better. “As a child I had so many dental issues, even at home. When I would visit the dentist, I would see a guy in a coat, doing some good work so I realized he doesn’t even work the night shift and it made me want to become a dentist,” she added.
Despite being tempted to pursue a career in law due to the time she spent at Ligomarc Advocates, Nabbanja held firm to her dream of attending medical school and becoming a dentist. She was determined to help her siblings, and others, achieve the confident smile they deserved.
However, her dream course, Dental Surgery, eluded her by just one point. Instead, she was given the opportunity to study Environmental Health Science, a subject that would soon become her passion.
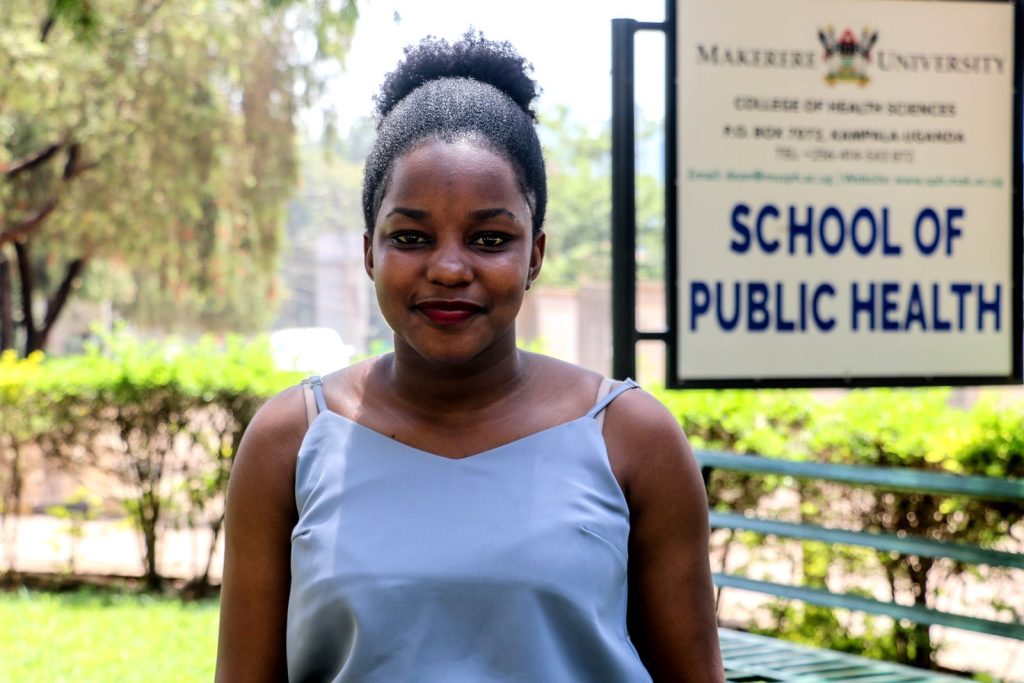
“I didn’t know much about MakSPH, actually my first few days were not that pleasant. I kept thinking about my friends who were doing my dream course even though they were on private not government sponsorship, but my mother didn’t have the money,” she says.
Ruth Mubeezi Neebye, an Assistant Lecturer in the Department of Disease Control and Environmental Health would later become Nabbanja’s mentor. According to Nabbanja, she has equally been inspired by Dr. Esther Buregyeya and Dr. David Musoke.
Throughout her time at MakSPH, Nabbanja has consistently stood out as a top performer, earning high grades and impressing her professors and peers alike. Despite her impressive academic record, she remains humble and grateful for the support she has received from her family, friends, and sponsors along the way.
Nabbanja, a sports personality
As a student at Makerere School of Public Health, Nabbanja was a standout in both academics and sports. She fell in love with swimming. As a member of the Makerere University swim team, Nabbanja excelled in competitions and brought home medals for the university. She found solace in the sport, using it as a way to relax after long days of lectures and studying. Swimming also provided her with the opportunity to travel and make new friends, as well as to work on her physical and mental health.
“Swimming gives you a lot of opportunities, so that inspired me as well. Very many people travel on University tickets, and since I love outdoor life and traveling, I looked at this as an opportunity. Swimming teaches you to read, and do other things like jogging before joining the pool. It is also an individual sport because when you don’t swim for a month, your time is cut,” says Nabbanja.

Journeying to First Class
For some students, University education is just a three-four-year period of attending lectures and socializing with peers. But for others, it’s a stepping stone to a brighter future. And that’s exactly what happened to Nabbanja, the best-graduating student from Makerere School of Public Health (MakSPH). She has not only excelled in academics but was also a talented swimmer who represented the University in various competitions.
Nabbanja’s success journey started with a clear plan and a strong determination to succeed. She believed that becoming a first-class student was not only about attending lectures but also about being self-aware and taking control of one’s own learning process. Nabbanja made a habit of reflecting on what was learned each day and relating it to real-life situations.
When asked about her experience at MakSPH, Nabbanja had nothing but praise for the staff and their professionalism. She says she never encountered any corrupt practices and appreciated the well-defined structure that made it easy to know where to go for assistance. Marks were received on time and she never felt lost or unsure of what to do next.
“The staff is also supportive, right from the reception, everyone is helpful—when inquiring about offices, or office protocol. We also get our marks on time, usually a week into the new semester. The service delivery is good and we are not tossed around.”
Nabbanja’s journey serves as a testament to the power of hard work, determination, and support from family and sponsors.
By Davidson Ndyabahika and Samantha Agasha
You may like
-


Emorimor Calls for Makerere to Upgrade Parenting Course
-


MakSPH, DJC Launch Short Course on Health Communication
-


Call for Abstracts: 2nd East African Symposium and Expo on Trauma, Injuries, and Emergency Care – 2025
-


CoNAS Participates in the 2025 National Science Week Exhibition
-


Scholarship Opportunity: Impact of Food Supplementation
-


Israeli Ambassador Lotem Talks Innovation on Farewell Visit
Health
Call for Abstracts: Digital Health Africa 2025
Published
2 days agoon
July 2, 2025By
Mak Editor
The Digital Health Africa 2025 Conference will provide practical insights in the potential applications of digital technologies, using maternal and child health, as important examples. Topics of interest will include patient registries, safety signals, vaccine use in pregnancy/breastfeeding, labelling of vaccines in pregnancy, emerging infections and antibiotic resistance, telemedicine, pharmacometric modelling, precision medicine, medicines regulation, ethical and legal aspects, and capability enhancement.
Applying an integrated multi-site face-to-face and remote format, this hybrid Conference will use digital tools to allow delegates and speakers from three different regions, South Africa, Uganda and Germany, as well as fully virtual participants to engage with one another. This will offer a nexus for collaboration and networking to promote partnerships among local and international stakeholders as well as capacity building for young scientists. Delegates will have the opportunity to engage with experts from industry, academia, healthcare providers, government and regulatory agencies as well as patient representatives to learn from one another and to gain valuable insights into the latest trends and best practices in digital health.
Abstracts should fit into one of these categories:
- Maternal and Child Health (MCH) & Digital Innovation
- Infectious Diseases & Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
- Digital Health Systems & Scaling
- Governance, Data Management & Interoperability
- Artificial Intelligence in Health & Research
- Pharmacometrics & Digital Tools
- Case Studies & Lessons Learned
- Cross-cutting & Strategic Perspectives
Submission deadline: 31st July 2025.
Accepted abstracts will be presented as interactive posters:
- a physical poster presentation at one of the conference sites
- an e-poster (digital version of your physical poster for sharing online)
- a 3-minute recorded presentation to accompany the poster.
Presenters with accepted posters will be offered complementary conference registration.
Submit your poster abstract here: https://forms.gle/aXYHeZSwX2EhEUas5
Health
Emorimor Calls for Makerere to Upgrade Parenting Course
Published
3 days agoon
June 30, 2025By
Zaam Ssali
The Iteso Cultural Leader, His Highness Emorimor Papa Paul Sande Emolot, has called on Makerere University to elevate the Science of Designing, Adaptation, and Implementation of Evidence-Based Parenting Interventions course into a fully-fledged programme. This, he argued, would strengthen the capacity of practitioners implementing parenting interventions across Uganda.
Speaking at a graduation ceremony held on 11th June 2025 at Makerere University where 35 practitioners completed the 12-week course, Emorimor Papa Emolot emphasized the transformative power of effective parenting. He urged aspiring parents and advocates of the Parenting for Respectability model to enroll in the course.
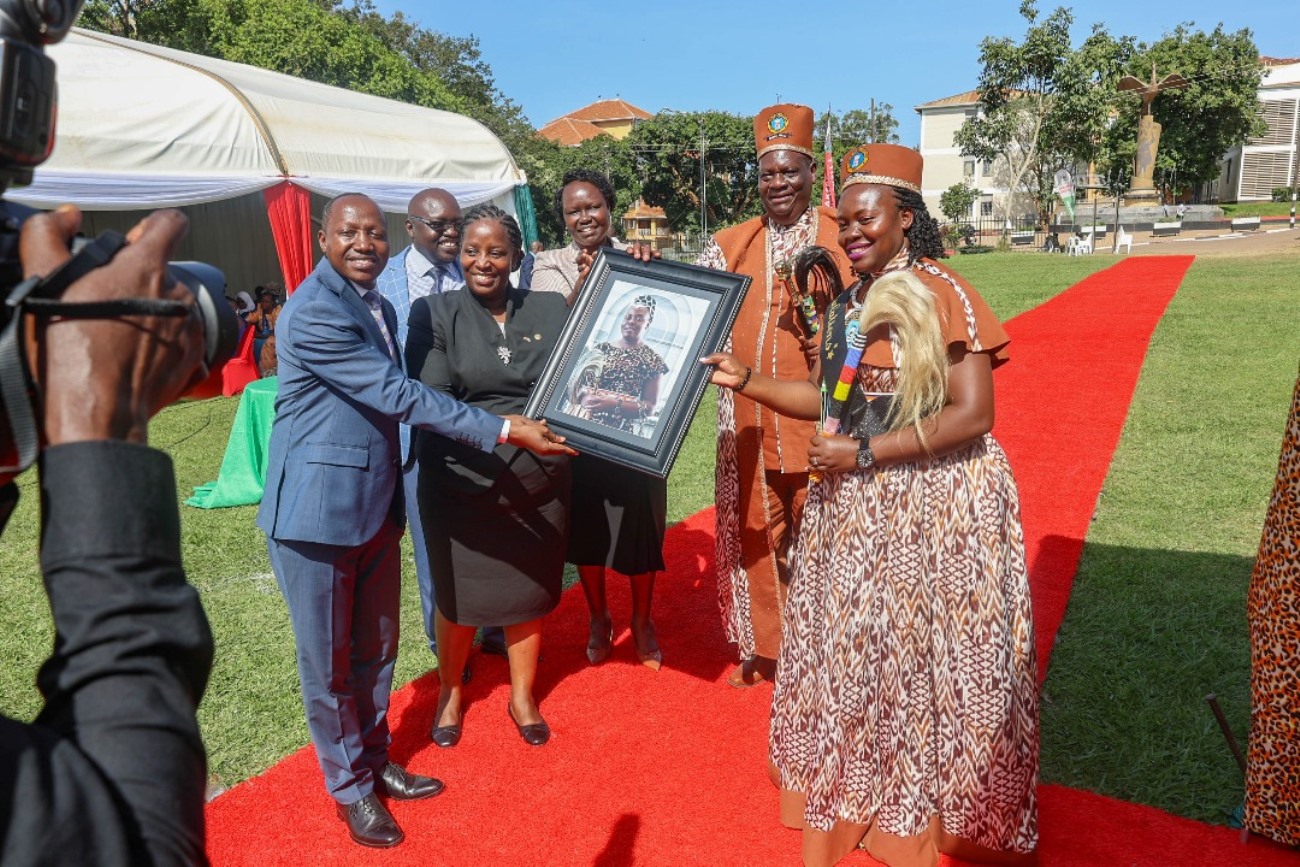

Citing the impact in his own sub-county and village, the cultural leader revealed that over 800 families had already benefited from the programme.
“We now see peace and love in homes where there was once conflict. Without good parenting, you risk raising animals instead of children,” he passionately stated.
He praised the course for equipping practitioners, policymakers, and researchers with the skills needed to design culturally sensitive, evidence-based parenting interventions tailored to Uganda’s context. Among the notable graduates was Her Royal Majesty Juliet Among Emolot Atomeileng Akaliat Toto, who reaffirmed her commitment to advancing family-strengthening initiatives using the skills and knowledge acquired.
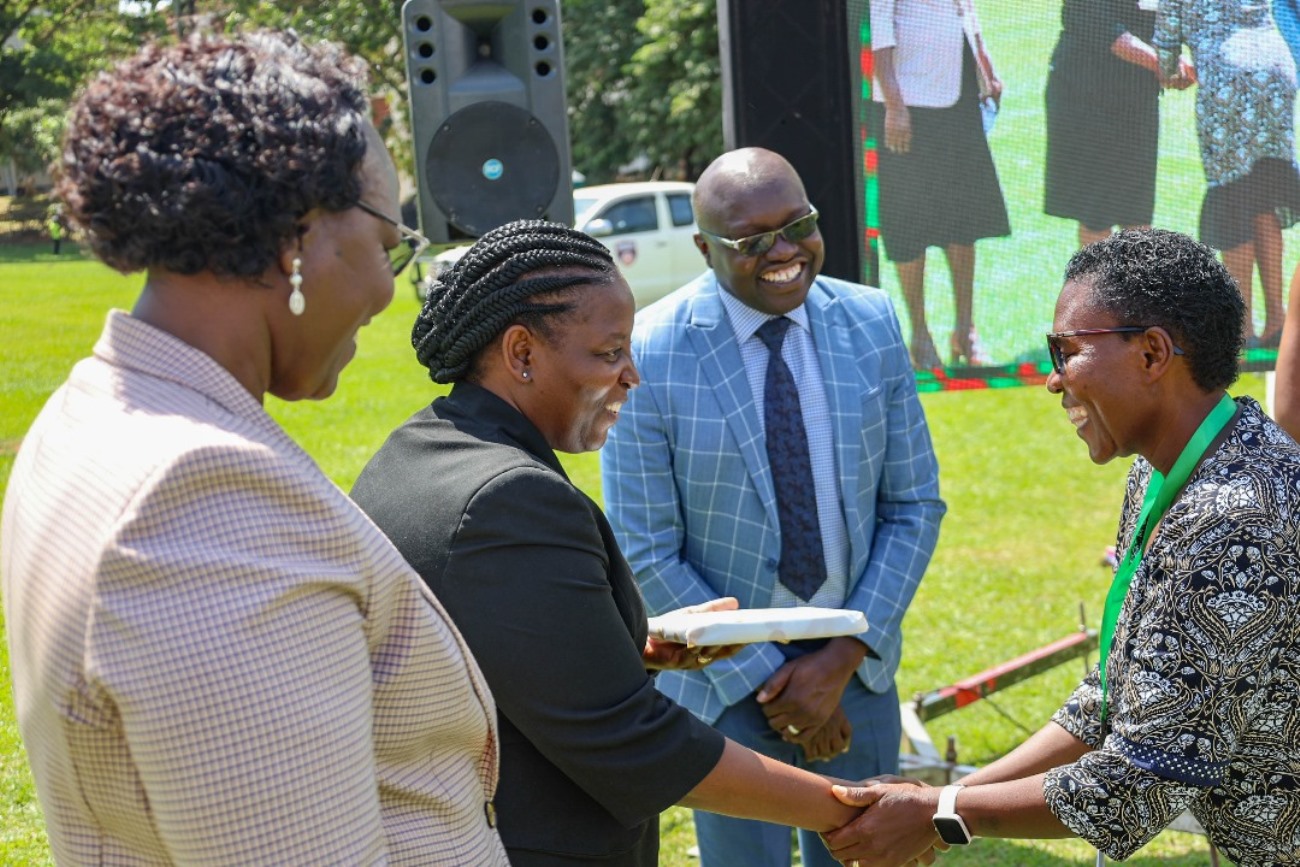

Dr. Godfrey Siu, Senior Lecturer and Course Leader at Makerere University, described the course as a timely intervention. During this remarks, Dr. Siu described the event as a significant milestone in advancing the field of evidence based parenting intervention and family strengthening in Uganda.
“This course is meant to empower you as practitioners, policy makers and all those involved in development and implementation of parenting work. It provides both theoretical knowledge and practical tools essential for developing high quality interventions”, Dr. Siu noted. He urged the pioneer group to carry forward the expertise as champions of designing, adaptation and implementation of evidence parenting interventions.
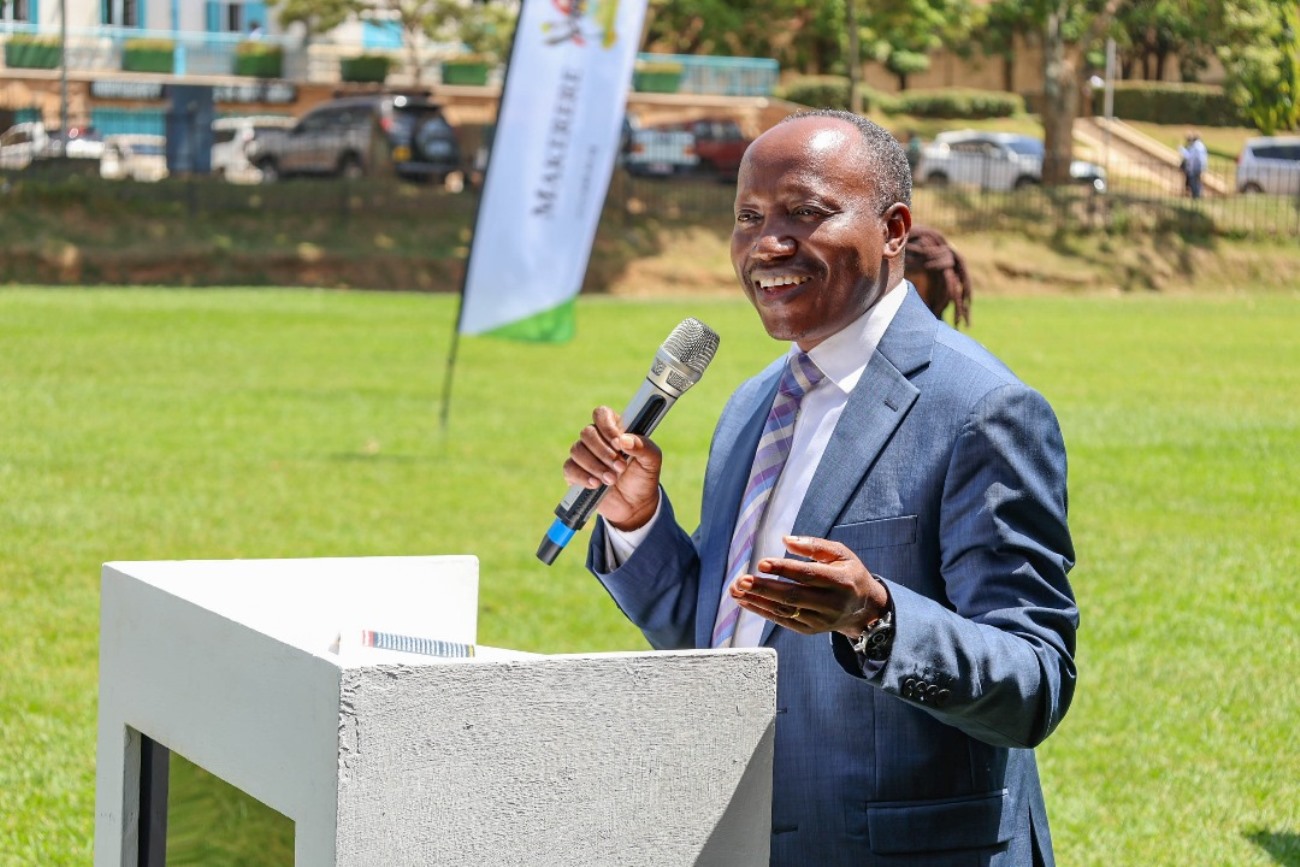

Representing the Permanent Secretary of the Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development, Dr. Aggrey David Kibenge, Juliana Naumo, Commissioner for Culture and Family Affairs, said the course supports the government’s agenda to address negative social outcomes affecting families.
“By grounding parenting in research, harmonizing policy with practice, and advocating for equity, we will ensure no family is left behind,” she said. “Cross-sectoral collaboration is key to unlocking transformative change.”
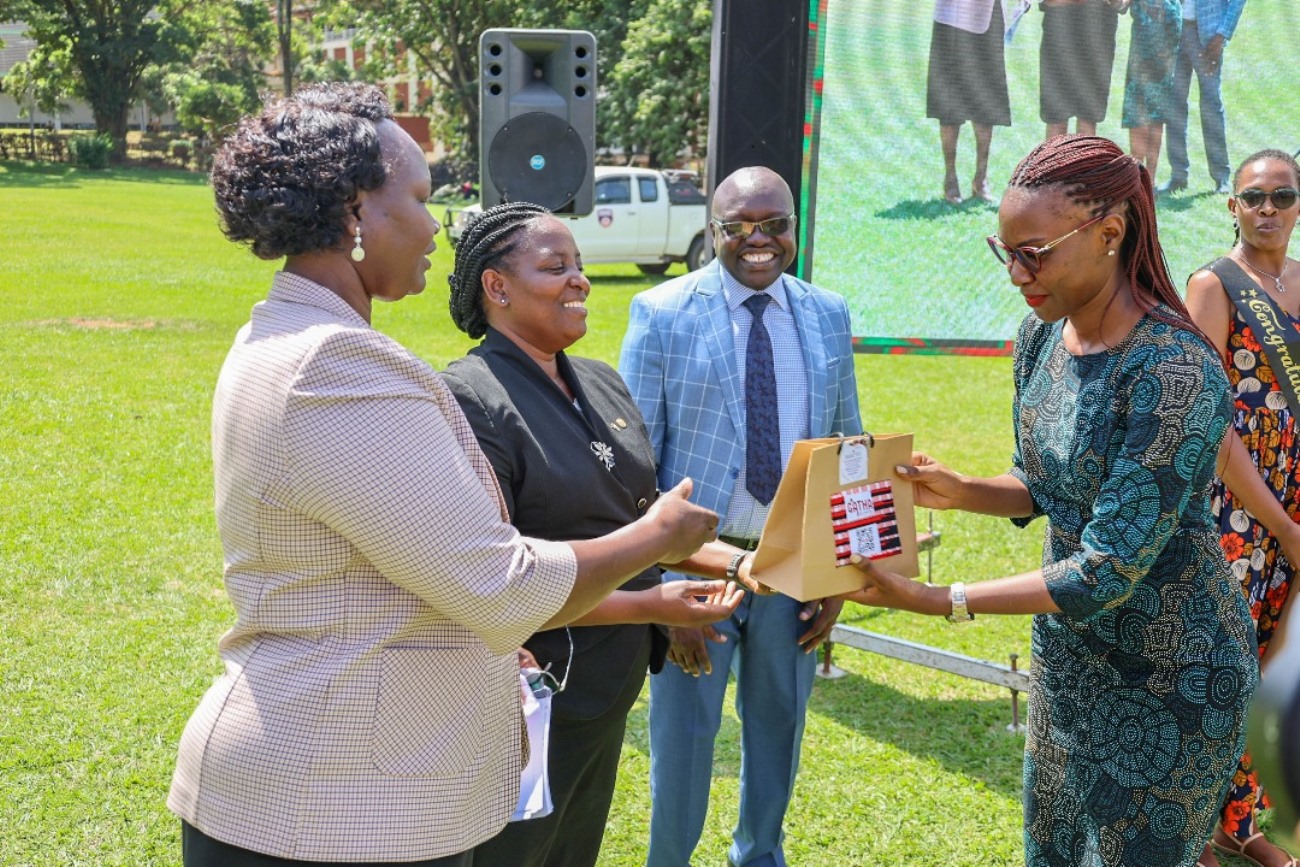

Ms. Naumo highlighted the government’s commitment—both technical and financial—to support outstanding student projects from the course. She stressed the importance of equipping professionals with the skills to bridge gaps between research and practice for consistent, high-quality parenting support across Uganda. While delivering the Vice chancellors speech by Dr. Helen Nambalirwa, Principal of the CHUSS, Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe commended the graduates as a beacon of hope.
“At a time when parenting faces challenges like digital distractions, changing societal norms, and a rising mental health crisis, Makerere reaffirms its support for interventions that drive the societal transformation we desire,” Nawangwe stated.
Prof. Richard Idro, Deputy Principal of the College of Health Sciences, acknowledged the growing parenting challenges in Uganda and the region, adding that the course was a major step towards standardizing parenting interventions nationwide.

He applauded the Child Health and Development Centre (CHDC) for leading this paramount and critical initiative.
Mr. Hosea Katende, Course Administrator at CHDC, emphasized the importance of integrating systematic methods, ethical principles, robust evidence, and collaboration to create lasting impact in parenting.

Dr. Aggrey Dhabangi, Lecturer at CHDC, representing Dr. Herbert Muyinda, Director of CHDC, acknowledged the contributions of partners such as the ELMA Foundation and Echidna Giving for their financial and capacity-building support. He also appreciated the Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development, among other stakeholders, for their technical guidance in the programme’s successful implementation.
Dr. Dhabangi extended gratitude to cultural institutions, especially the Kingdom of Teso, and acknowledged growing collaborations with other cultural institutions such as the Kingdom of Acholi, in the shared mission of building strong families as the foundation of Uganda’s future.

He extended his heartfelt gratitude to cultural institutions, especially the Kingdom of Teso, and others kingdoms such as the Kingdom of Acholi, in building Uganda’s future through creating strong families. Nuruh Mbalyowere, a Rehabilitation and Reintegration Officer with the Uganda Prisons Service, was honored for developing the best parenting intervention titled “Parenting Behind Prison Bars.” She expressed her intention to apply the knowledge gained both at home and in her workplace.
Health
MakSPH, DJC Launch Short Course on Health Communication
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 20, 2025
By Okeya John and Primrose Nabankema
The intensive one-month course, running for the first time from June 5 to July 24, 2025, is jointly offered by Makerere University School of Public Health (MakSPH)’s Department of Community Health and Behavioural Sciences (CHBS) and the Department of Journalism and Communication (DJC) at the School of Languages, Literature, and Communication (SLLC), co-designed in 2024 with support from the Rockefeller Foundation through Amref Health Africa.
It seeks to equip healthcare providers at the community level, public health and environmental health practitioners, communication specialists, health educators, community development officers, social scientists, and policy makers, among others, with strategic communication skills to improve public health messaging, strengthen community engagement, and support evidence-based interventions, ultimately empowering participants to effectively engage communities and improve population health outcomes across Uganda and the region.
Launching the course, the heads of the Department of Journalism and Communication and the Department of Community Health and Behavioural Sciences noted that participants who complete the short course will gain practical tools to influence behaviour change, build trust, and deliver timely, accurate, and relevant health information to the communities they serve. The first cohort attracted more than 60 applicants, with 36 reporting for the opening in-person session on June 5, 2025, at MakSPH in Mulago. Between now and July, participants will undergo a hands-on, multidisciplinary learning experience within the Certificate in Health Communication and Community Engagement program, which combines theory and practice.
Among the participants in the first cohort of the certificate course, designed as a pilot for the anticipated Master of Health Promotion and Communication to be jointly offered by the two departments at Makerere University, is Ms. Maureen Kisaakye, a medical laboratory technologist specialising in microbiology and antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and currently pursuing a Master’s in Immunology and Clinical Microbiology at Makerere. She is driven by a passion to help reverse the rising tide of AMR, a growing global health threat where drugs that once worked are no longer effective. Kisaakye is particularly concerned about common infections, like urinary tract infections, becoming increasingly resistant and harder to treat.
“I enrolled in this course because I’m an advocate against antimicrobial resistance, and it came at a time when I needed to deepen my knowledge on how to implement our projects more effectively and engage with communities. The experience has broadened my understanding of AMR and its impact on society, and strengthened my passion for community-driven health initiatives and advocacy,” Kisaakye said, explaining why she enrolled for the short course.

Kisaakye’s work in antimicrobial resistance extends beyond the lab. Having earned her degree in medical laboratory science from Mbarara University of Science and Technology, she founded Impala Tech Research in 2024 to drive impact and save lives. She has led grassroots AMR campaigns that integrate antimicrobial stewardship with water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) education in underserved urban communities, including the informal settlements in Kampala. She also has since designed peer-led initiatives that empower university students as AMR Champions, building a network of informed youth advocates. Kisaakye believes the health communication course will sharpen her ability to design and deliver impactful, community-centred interventions in response to the growing threat of drug resistance.
“The department collaborates with many partners within and beyond the University, including the School of Public Health, where we are working to develop the subfield of health communication and promotion. Our goal is to train specialists in this area and build a community of practice, something we have each been doing in our own spaces. There’s a lot of work ahead, and COVID-19 showed us just how urgently we need a generation trained to do this kind of work, and to do it very well,” said Dr. Aisha Nakiwala, Head of the Department of Journalism and Communication, during the opening of the short course on June 5.
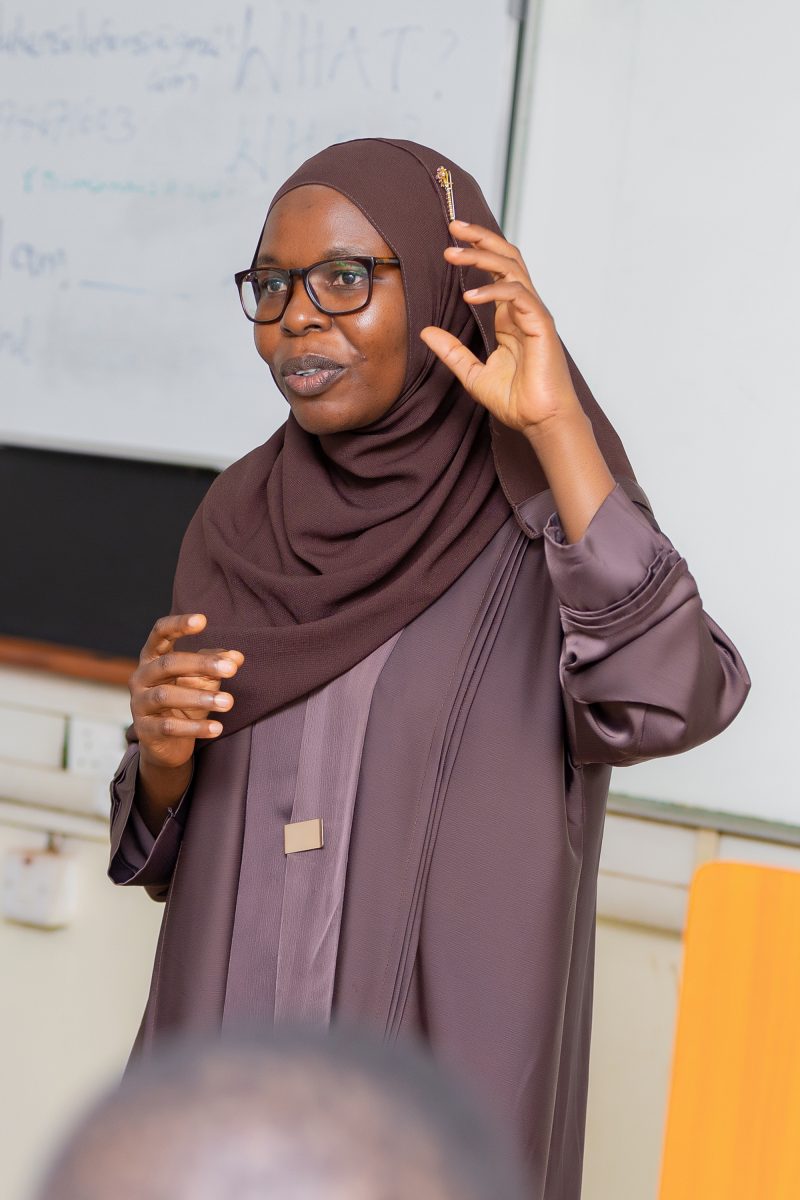

She assured participants they were in good hands and underscored the importance of the partnership between the Department of Journalism and Communication and the School of Public Health, describing it as a vital collaboration that brings together strategic communication and public health expertise. This dynamic, multidisciplinary approach, she noted, is essential to developing practical solutions that empower communities, strengthen health systems, and ultimately improve livelihoods.
The course offers a hands-on, multidisciplinary learning experience, with participants intended to explore key modules including Health Communication and Promotion, Risk Communication, Smart Advocacy, Community Mapping, Community Mobilisation and Empowerment, and Strategies for Community Engagement. The course combines theory with real-world application, and its assessment includes a field-based project and a final exam.
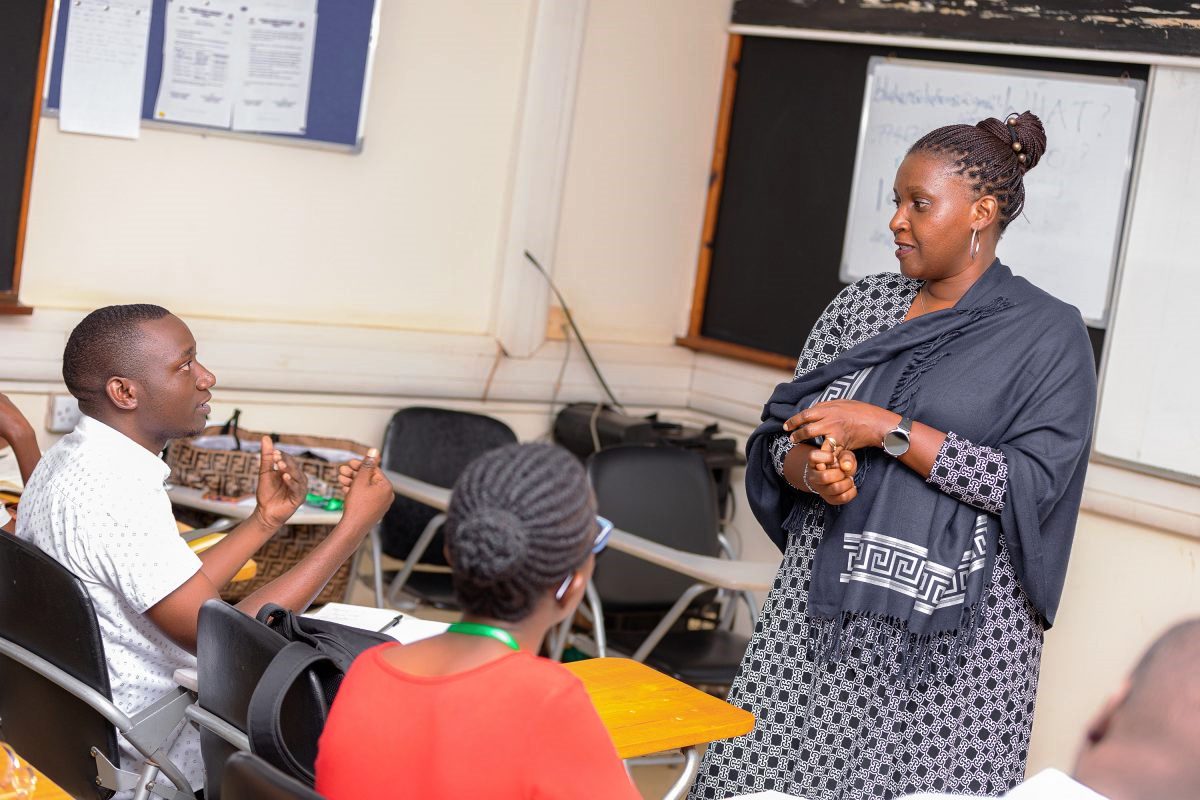
“You are our first cohort. We are seeing the fruits of our efforts in bringing this short course to life. It was born out of a joint initiative to develop a Master’s programme in Health Promotion and Communication,” said Dr. Christine Nalwadda, Head of the Department of Community Health and Behavioural Sciences. “We carried out extensive consultations with our different key stakeholders during the process and discovered a real need for such a course. It was the stakeholders who even named it; this course name didn’t come from us.”
For Kisaakye, by the end of the course in July, she hopes to have sharpened her skills in health promotion and strategic communication, particularly in crafting targeted messages that help individuals and communities effectively respond to threats such as antimicrobial resistance. She also aims to gain practical experience in designing, implementing, and evaluating community health initiatives that can strengthen her advocacy and drive lasting impact.

Trending
-

 General6 days ago
General6 days agoMature Age Scheme Exam Results for 2025/2026
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoFreshers’ Joining Instructions 2025/2026
-

 General2 days ago
General2 days agoUndergraduate Admission List Self Sponsorship Scheme 2025/2026
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks agoMastercard Foundation Board pays its inaugural visit to Makerere University
-

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoUVCF Makes Case for HEAC Programme
