Business & Management
Scholars Advocate for Private Sector Expansion to Boost Youth Employment
Published
2 years agoon

In light of recent findings from a comprehensive study on the effects of digitalization on youth employment, scholars, including Dr. Matovu Fred, the Principal Investigator, are calling for a significant expansion of the private sector to address the rising unemployment rates among educated youth. The research, which delves into how the youth in Uganda are adapting to technological advancements, highlights several key areas that require urgent policy intervention.
The study reveals that Ugandan youth are increasingly adapting to technological changes through self-education, peer-to-peer learning, and continuous formal education. Despite their proactive approach, only a few organizations are offering necessary training for technological adaptation, leaving many youths to navigate these changes on their own.

Importantly, the youth have shown a strong willingness to invest in acquiring digital skills to remain competitive in the job market. Many see the digital trend not as a threat but as an opportunity to secure more decent jobs, including remote work opportunities and the ability to undertake multiple jobs simultaneously.
Policy Recommendations
Based on these findings, the researchers have put forward several policy recommendations:
- Expansion of the Private Sector: There is a pressing need to expand the private sector to absorb the growing number of educated youth entering the job market. This expansion is critical to providing more employment opportunities and leveraging the skills of the young workforce.
- Improving Internet Connectivity: To support uninterrupted use of digital systems in workplaces, it is essential to improve the reliability of internet connectivity. This improvement will ensure that digitalization efforts are not hampered by technical issues, enabling smoother and more efficient work processes.
- Reducing Data Costs: Lowering subscription fees and the cost of data is crucial to expanding bandwidth availability, which is necessary for activities such as big data analytics. Affordable internet access will empower more youths to engage in digital learning and work.
- Enhancing Cybersecurity: The research underscores the need for central coordination of cybersecurity safeguards. Implementing early warning systems for hackers and related threats will protect company systems and bolster the digital economy’s integrity.
- Reliable Data Protection Systems: Ensuring that data protection systems are trustworthy is vital. Building trust in enterprise data among third-party users and government agencies, such as the Uganda Registration Services Bureau (URSB), Uganda Revenue Authority (URA), and Kampala Capital City Authority (KCCA), will encourage more businesses to digitize their operations.
Government and Private Sector Collaboration
The study’s authors emphasize that collaboration between the government and private sector is essential to implementing these recommendations effectively. By working together, they can create an environment that not only supports the digital adaptation of the youth but also drives economic growth and job creation.

In response to these findings, government officials and private sector leaders are urged to prioritize these policy recommendations. Expanding the private sector and improving digital infrastructure will play a critical role in harnessing the potential of Uganda’s youth, fostering innovation, and securing a brighter economic future for the nation.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, these strategic measures will ensure that Uganda’s youth are not left behind but are instead at the forefront of the country’s economic transformation.
The research was funded by the government of Uganda through Makerere University Research and Innovation Fund.
The research team
PI: Fred Matovu: Principal Investigator (PI), Makerere University
Susan Kavuma: Co-PI, Makerere University
Hassan Mbaziira: Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development
Richard Sebaggala: Uganda Christian University, Mukono
You may like
-


Over 9,200 to graduate at Makerere University’s 76th Graduation
-


76th Graduation Highlights
-


Mak Selected to Host Alliance for African Partnership Africa Office
-


Meet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-


Makerere University School of Public Health Graduates First Cohort of Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Short Course
-


Climate variability found to shape malaria trends in Yumbe District
Business & Management
Climate variability found to shape malaria trends in Yumbe District
Published
5 days agoon
February 20, 2026
A new study led by scientists from Makerere University School of Public Health has demonstrated that short-term climate variability plays a significant role in malaria transmission in Yumbe District, West Nile sub-region of Uganda. The study, Climate variability and malaria incidence trends in Yumbe District, West Nile Sub-region of Uganda (2017–2021), by Lesley Rose Ninsiima, Rogers Musiitwa, Zaitune Nanyunja, James Muleme, Chris Maasaba, Twahiri Anule, and David Musoke, was published in February 2026 in Malaria Journal through Springer Nature Link.
Today, malaria remains a major public health burden in Uganda, where environmental conditions support sustained transmission. Despite persistent outbreaks in northern Uganda, limited local evidence exists on how the changing climate patterns influence malaria trends. This study addressed that gap by examining five years of malaria surveillance data alongside district-level rainfall and temperature records.
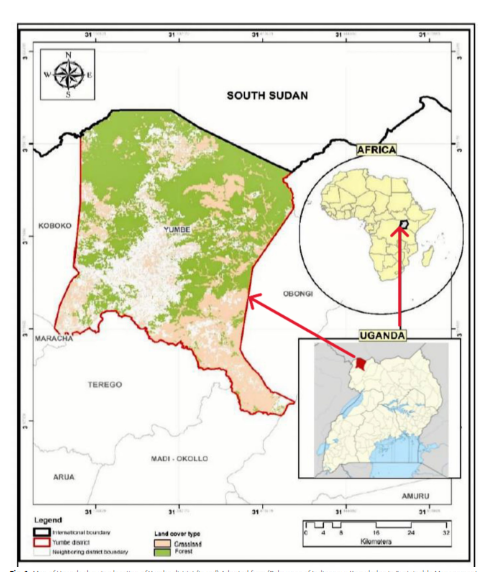
Using routine health facility reports from the District Health Information System (DHIS) and climate data from the Uganda National Meteorological Authority (UNMA), the researchers applied time-series analysis to assess seasonal patterns and delayed climate effects on malaria incidence. Between 2017 and 2021, Yumbe District recorded 2,066,711 malaria cases, with transmission showing clear seasonal peaks between May and July and September and November, aligning with rainy periods.
Their analysis showed that rainfall was the strongest climatic driver of malaria transmission. Increased rainfall was associated with higher malaria cases approximately one month later, reflecting the time needed for mosquito breeding and transmission cycles. In contrast, higher minimum temperatures were linked to reduced malaria incidence, while maximum temperature showed no significant effect. Together, rainfall and minimum temperature explained a substantial proportion of variation in malaria cases, highlighting malaria’s sensitivity to short-term climate fluctuations.
The study findings underscore the value of integrating climate information into malaria surveillance and early warning systems to anticipate transmission peaks and guide timely interventions. Strengthening collaboration between public health and meteorological sectors, the researchers argue, could improve preparedness and support climate-informed malaria control strategies in high-burden settings.
Further details: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12936-026-05824-0
Agriculture & Environment
Mak hosts First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling
Published
5 days agoon
February 20, 2026
African economies are increasingly exposed to climate-related shocks that threaten development gains, fiscal sustainability, and macroeconomic stability. From extreme weather events and biodiversity loss to the depletion of natural capital, climate risks are reshaping economic realities across the continent. Yet many macroeconomic frameworks used in public finance and planning continue to overlook climate and nature-related risks and the long-term benefits of resilience and adaptation investments.
To address this emerging reality, over 250 participants from Africa, Europe and beyond, convened at Makerere University – Kampala, on the 12th and 13th of February 2026, to participate in the First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling.
Following the theme, “Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomics: Rethinking Growth in Africa’s Natural Resource Base, the hybrid symposium organized by Makerere University through the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling (CEACM) within the School of Economics, under the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS), the Environment for Development Initiative (EfD), and the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development (MoFPED) in Uganda, brought onboard ministers, leading economists and planners, researchers, policy makers, the academia, development partners, climate change experts and the media.
The Symposium being the first of its kind on the continent, reflected Africa’s growing determination to work collectively in confronting shared development challenges, building on recent momentum such as the formation of Pan-African Finance Ministers Forum for Climate Action (PAFMCA).
Featuring speeches and presentations from notable speakers and partners, a keynote address on Natura Capital Accounting and Climate Change Nexus in Africa and their impact on Fiscal Policy, panel discussions, expert opinions, and exhibition kiosks (World Café), the symposium presented a platform to strengthen Africa’s analytical and institutional capacity to integrate climate and natural capital considerations into macroeconomic and fiscal policy.
Vice Chancellor underscores the role of universities
Welcoming the delegates to Makerere University, the Vice Chancellor-Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe emphasized that universities must lead innovation and collaborative research efforts to support collective climate change mitigation across the continent.
In the same vein, he advocated for strong collaboration between universities in Africa and government Ministries. “Makerere’s collaboration with the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, stands as a shining example of how academia and government can strengthen economic management,” he said.

Prof. Nawangwe revealed that the collaboration between Makerere University and the Ministry, has strengthened macroeconomic modelling, fiscal policy analysis, and technical capacity within government. In addition, the partnership led to the establishment of the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling, bridging academic scholarship with real-world policy application.
“We have jointly established the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling. The Centre (established in August 2025) is anchored within the School of Economics in the Department of Policy and Development Economics, under the Master of Science in Economic Policy and Investment Modelling, a program jointly facilitated by Makerere University, the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development and the Bank of Uganda,” he mentioned.
Climate and Economic transformation are inseparable
The Vice Chancellor highlighted the critical intersection between economic transformation and environmental sustainability, noting that economies in Africa, heavily dependent on natural resources, face unprecedented pressures from climate shocks, biodiversity loss, and environmental degradation. Convinced that economic growth cannot be pursued in isolation from climate and environmental realities, he stressed the importance of integrating natural capital accounting and climate considerations into national development strategies.
Prof. Nawangwe advocated for shared responsibility of universities, research institutions, and policymakers to develop innovative analytical tools, responsive policy frameworks, and strong institutional capacities that promote sustainable growth while safeguarding environmental assets for future generations.
The Vice Chancellor commended UN PAGE and the Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI) for funding the symposium, as well as, other stakeholders namely the European Union and the Coalition of Finance Ministers for Climate Action (CoFMCA), Ministry of Water and Environment (MoWE), National Planning Authority (NPA), Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS), the National Environment Management Authority (NEMA) for being reliable partners.
Integrating Climate into Fiscal Policy
During the opening ceremony, the Minister of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, Hon. Matia Kasaija underscored the urgency of embedding climate considerations into economic planning.
“As Ministers of Finance, we are often confronted with difficult trade-offs. Our task is to balance the needs of today with sustainability for future generations,” said Hon. Kasaija, in a speech read by Hon. Henry Musasizi, the Minister of State for Finance (General Duties).

The Minister guided that traditional macroeconomic models focusing only on growth, inflation, and fiscal balance are inadequate in an era of climate shocks. He affirmed that African economies are facing interconnected challenges which directly impact economic growth. He stressed that traditional macroeconomic frameworks must evolve to systematically incorporate environmental degradation and climate shocks, whose consequences can no longer be ignored in policy analysis.
“For countries such as Uganda, whose development prospects are closely linked to natural resources and the climate-sensitive sectors, these challenges are not abstract. They affect livelihoods, public finances and long-term economic resilience,” he mentioned.
The Minister emphasized that natural capital accounting and climate-sensitive macroeconomic modelling are vital for valuing natural assets, assessing environmental costs, and guiding sound investment decisions.
Protecting Africa’s Natural Capital
Hon. Beatrice Atim Anywar, Minister of State for Environment, emphasized the urgent need to protect Africa’s ecosystems. “Africa stands at a defining crossroads. Our economies remain anchored in natural capital—forests, water resources, biodiversity, land, and ecosystems—which sustain life, generate fiscal revenue, and underpin development,” she said.
She warned that climate-related shocks are already undermining growth and public investment. “Floods, droughts, land degradation, biodiversity loss, and water stress are no longer distant risks. They are present realities, already affecting productivity and macroeconomic stability,” she said.
She emphasized the need for improved economic models that account for environmental and climate risks: “Traditional macroeconomic frameworks have not adequately captured climate risks or the long-term economic benefits of resilience and adaptation. This limits our ability to make informed policy decisions as Africa pursues economic transformation, energy security, and fiscal stability,” she stated.
Hon. Anywar highlighted collaboration with GIZ, Makerere University, and government ministries, which led to the development of the MONCAP (Model for Natural Capital Policy Assessment). “This tool is being used to assess natural capital assets for climate change, energy transition, and their linkages to the macroeconomy. It supports budgeting by estimating the cost of depleted natural capital assets,” she said.
“Water security, forest conservation, ecosystem restoration, and climate adaptation are not costs. They are investments in Uganda’s long-term economic stability, productivity, and prosperity.”
Stakeholders urged to transform climate threats into opportunities
Adam Sparre Spliid, the Deputy Head of Mission, Danish Embassy said: “Integrating climate risk and natural capital into our macroeconomics frameworks is not only academic exercise, it is a massive de-risking strategy for private investment. By bridging the gap between government policy and planning, academia and research, and the private markets, we transform climate threats into tangible opportunities.”
Sustainability includes youth, jobs and human well-being
Dr. Steven Stone, Chair of the UN PAGE Management Board, emphasized that sustainability extends beyond the environment to encompass youth, jobs, economic growth, and human well-being. “While the environment is Africa’s foundational source of wealth, sustainable development requires balancing ecological stewardship with economic progress, including income and employment for the youth which are critical priorities for countries such as Uganda.”
Dr. Stone highlighted that UN PAGE, originating from the Rio+20 Conference, supports climate-sensitive economic policy in Africa, emphasizing that dialogue, scenario-building, cross-sector collaboration, and strong partnerships are key to advancing sustainable, inclusive, and climate-resilient development.
Africa’s Wealth Declining
In the keynote address titled, Natural Capital Accounting and Climate Change Nexus in Africa and their Impact on Fiscal Policy, Paul Jonathan Martin, Manager of Environmental Operations at the World Bank for Eastern and Southern Africa, and a specialist with over 30 years in climate and natural resources, warned that Africa’s overall wealth is under threat due to declining renewable natural capital.
“Produced capital has increased by 20%, human capital by a third, but renewable capital has declined by 30%,” Martin said. “When combined, Africa’s overall wealth trajectory has been weakening since 2010.”
He stressed that natural resources must be treated as economic assets requiring systematic accounting: “Africa’s rich natural resources are fundamental for sustainable development,” he said.
Citing examples from Ethiopia and Kenya, he highlighted successful integration of natural capital into public investment and budget decisions. “In Ethiopia, there are payments for ecosystems and investment prioritization tools. In Kenya, natural capital accounting integration into budgets has strengthened public investments. Climate change has deep, cascading effects across sectors, but Africa has major potential to lead climate solutions,” he said.

Martin also highlighted the economic benefits of climate adaptation: “From 2020–2050, the cumulative effect of adaptation on Uganda’s GDP is positive. Without action, under a dry/hot climate future, GDP could significantly deviate from projected growth paths.”
Drawing on insights from over 70 country climate and development reports produced by the World Bank, the keynote speaker highlighted the profound macroeconomic impacts of climate change across Africa. He stressed the importance of integrating climate and natural capital into macroeconomic planning. He noted that Africa’s forests, water systems, and biodiversity are vital for sustainable development but face growing threats from climate change, environmental degradation, and climate-related disasters that undermine productivity, public investment, and economic stability.
He observed that traditional macroeconomic models often fail to capture the value of natural assets and regulating ecosystem services, which are critical to both economic stability and resilience but are largely excluded from GDP calculations.
Africa-Led Solutions
Prof. Edward Bbaale, Principal, College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS), stressed the importance of developing African-led solutions. “We need to champion the Africa-led model. We need approaches that fit our unique context. Africa is not here to take in other frameworks blindly,” he said.
By supporting research, training, policy dialogue and modelling innovation, the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling (CEACM) positions Makerere University as a regional hub for advancing climate-sensitive macroeconomic policy across Africa.
He highlighted CEACM’s capacity-building programs: “Our goal is to ensure African Ministries of Finance have home-grown expertise to integrate climate and natural capital considerations into fiscal and macroeconomic policy. This is critical for long-term resilience and sustainable development,” he said.
The Principal explained that establishment of independent research centres enables Makerere University to go beyond traditional academic instruction and focus deeply on societal challenges, particularly those related to climate change, environmental degradation, and biodiversity loss.

He reported that the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling is structured to advance methodological innovation, develop new data systems, and strengthen climate-sensitive macroeconomic tools that are tailored to the African context.
MONCAP Model for Policy Assessment
Dr. Peter Babyenda, a member of faculty at CoBAMS, demonstrated MONCAP (Model for Natural Capital Policy Assessment), which integrates climate and natural capital variables into fiscal and macroeconomic planning.
“MONCAP allows policymakers to estimate the economic cost of depleting natural assets such as forests, wetlands, and water resources. It helps simulate policy options and determine how investments in natural capital yield long-term benefits,” Babyenda said. “We came up with this model to aid the Ministry of Water and Environment. This model is open—you can extend it,” he added.

He highlighted capacity-building initiatives, including short courses and the Master of Science in Macroeconomic and Investment Modelling, designed to train economists to incorporate natural capital and climate into policy planning.
International Perspectives
Sweetman Liam, Ireland’s Finance Minister, highlighted the economic value of ecosystems: “There is a deeper value of landscapes in flood prevention and biodiversity. Decision-making was informed, and people started understanding economic value,” he said.
Prof. Chukwuone Nnaemeka of the University of Nigeria emphasized collaboration with national statistical agencies: “We coordinate with the National Bureau of Statistics to develop natural capital accounting metrics. Increase the use of Natural Capital Accounting in decision-making,” he stated.
Technical and Parallel Sessions
The afternoon session featured three parallel sessions focusing on Natural Capital Accounting Methodologies and Best Practices, Climate-Sensitive Fiscal and Economic Modelling, and Natural Capital Accounting and Model Uptake and Use.
Drawing on diverse expertise, the panels highlighted innovative approaches and demonstrated that natural capital is not an environmental afterthought, but a central pillar of sustainable economic and policy planning.
The first day of the African Symposium drew to a close with interactive exhibitions at the World Café, where case studies and practical demonstrations highlighted innovative approaches to integrating climate and natural capital into economic planning. Participants actively engaged in discussions and networking, forging collaborations that promise to advance climate-sensitive fiscal and development strategies across Africa, setting a strong and optimistic tone for the days ahead.
Business & Management
First African Symposium underscores the role of the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling
Published
7 days agoon
February 18, 2026
During the First African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling held on 12th and 13th February 2026 at Makerere University-Kampala, notable speakers and experts urged government ministries and universities to initiate institutionalized approaches and frameworks to mitigate the natural capital account threats in Africa.
The discourse centred on the theme, Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomics: Rethinking Growth in Africa’s Natural Resource Base, which explored innovative approaches to integrate natural capital and climate risks into economic planning. The symposium highlighted that Africa’s economic transformation must be climate-informed and resilience-driven.
Committed to African-led capacity building, Makerere University is taking the lead in engaging other African universities to support fiscal policy in climate change modelling and analysis.
The participants and stakeholders across the globe lauded Makerere University, for partnering with the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development (MoFPED), and the Environment for Development Initiative (EfD), to establish the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling (CEACM).
Highlights about the CEACM
During the symposium, the Vice Chancellor of Makerere University-Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe, the Principal, College of Business and Management Sciences-Prof. Edward Bbaale, the Dean of the School of Economics-Associate Professor Ibrahim Mike Okumu, Dr. Peter Babyenda, Dr. Wilson Asiimwe and other members of faculty, articulated the mandate of the CEACM.

Situated at Makerere University, CEACM is anchored within the School of Economics in the Department of Policy and Development Economics, under the College of Business and Management Sciences. It is aligned with the Master of Science in Economic Policy and Investment Modelling, a program jointly facilitated by Makerere University, the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development and the Bank of Uganda.
Promotion of Africa-led Modelling
Addressing the participants, the University leadership and faculty, highlighted the Centre’s strong commitment to Africa-led modelling, as its key distinguishing feature.

According to Prof. Nawangwe, the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling-is a strategic initiative addressing Africa’s climate, environmental, and fiscal challenges.
Citing Africa’s unique economic realities such as heavy reliance on natural capital, widespread informality and heightened vulnerability to climate shocks, the Centre prioritizes the development of analytical frameworks that are rooted in local contexts rather than merely adapting externally developed models. This approach ensures that policy interventions, recommendations, and investment strategies are firmly grounded in the specific economic, environmental, and social dynamics of African countries.
University-Government collaboration to safeguard Africa
The Vice Chancellor stated that the Centre builds on a strong partnership between Makerere University and the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development (MoFPED), creating a direct bridge between academic training and real-world policy application. Through this structure, the Centre is preparing a new generation of economists equipped to embed climate considerations into macroeconomic analysis and public financial management.
“Our collaboration with the Ministry stands as an example of how academia and government can work together to strengthen economic management. This partnership has advanced macroeconomic modelling capacity, supported fiscal policy analysis, strengthened public investment management systems and enhanced training for economists and planners across government institutions,” he said.
Prof. Nawangwe observed that African economies remain deeply dependent on natural resources for livelihoods, public revenues and structural transformation, yet these resources are under increasing stress from climate shocks and ecological decline. In this context, he noted that economic transformation can no longer be pursued in isolation from environmental sustainability. The Centre was therefore established to strengthen analytical tools, policy frameworks and institutional capacities that integrate climate risks, natural capital accounting and long-term fiscal resilience into macroeconomic modelling.
He noted that the Centre strengthens Uganda’s contribution to continental and global climate finance and policy platforms, including the Coalition of Finance Ministers for Climate Action (CFMCA) and the Pan-African Coalition of Finance Ministers on Climate Action (PAFMCA). By supporting research, training, policy dialogue and modelling innovation, the Centre positions Makerere University as a regional hub for advancing climate-sensitive macroeconomic policy across Africa.
Capacity-Building Support for Climate and Nature-Resilient Economic Policies
Tackling the role of universities in Climate Fiscal Policy, Prof. Bbaale commended the strong collaboration between Makerere University and government through the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development, which provides a platform for academia-policy interface.

Additionally, the partnership of Makerere University, the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS), the Environment for Development Initiative (EfD), the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling (CEACM), with the Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development (MoFPED), positions the University, as an active technical partner to the Coalition of Finance Ministers for Climate Action (CFMCA).
Academic training, research and policy engagement
Firmly grounded in Makerere University’s three core pillars of academic training, research, and policy engagement, the Centre brings these pillars to life by equipping students and practitioners with robust analytical skills, producing rigorous and policy-relevant research, and translating evidence into actionable insights that directly inform decisions shaping economies and communities across Africa.
Prof. Bbaale noted that the establishment of independent research centres enables Makerere University to go beyond traditional academic instruction and focus deeply on societal challenges, particularly those related to climate change, environmental degradation, and biodiversity loss.
He reported that the Centre is structured to advance methodological innovation, develop new data systems, and strengthen climate-sensitive macroeconomic tools that are tailored to the African context.
Interventions on Climate issues in Africa
Prof. Bbaale outlined the following interventions being undertaken by Makerere University to address climate issues in Africa.
- Academic anchoring through the Master of Science in Macroeconomic and Investment Modelling at the School of Economics
- Establishment of the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling, which serves as a capacity building arm for PAFMCA
- Research that integrates Natural Capital Assets into National Policy and Fiscal planning
- Capacity building through short term courses at CEACM
- Publications featuring the MoFPED and Makerere University CEACM research efforts
Prof. Bbaale informed the audience that in collaboration with the respective government ministries and sectors, Makerere University is taking the lead in drafting fiscal policy briefs using existing Natural Capital Accounts (NCA) to inform Macro-Fiscal Policies.
CEACM Shaping Uganda’s Policy landscape
Building on to Prof. Bbaale’s presentation, Dr. Peter Babyenda- a member of faculty at the School of Economics, presented the Model for Natural Capital Policy Assessment (MONCAP). With support from GIZ Uganda, the EfD Centre at Makerere University, and the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling, developed the MONCAP model for the Ministry of Water and Environment (MoWE) in collaboration with MoFPED, Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS), National Planning Authority (NPA) among other stakeholders. The MONCAP model represents a holistic government approach to embedding environmental sustainability within national economic planning frameworks.
Dr. Babyenda explained that the model was developed in response to Uganda’s ambitious development trajectory, particularly the country’s 10-fold growth strategy under the National Development Plan. The model integrates natural capital accounting into macroeconomic analysis, thereby enabling policymakers to quantify environmental assets, assess climate risks and emissions, and evaluate how economic activities impact the country’s natural resource base.
Beyond tool development, Dr. Babyenda underscored the Centre’s commitment to capacity building through trainings, short courses, in addition to the Master of Science in Macroeconomic and Investment Modelling, which started this academic year (August 2025).

“To ensure capacity and produce more modellers, we are offering short courses on integrating climate and natural capital into macro models, as well as, the Master of Science in Macroeconomic and Investment Modelling. We call for continuous collaboration between policymakers, academia, and development partners so that we can develop more of these models,” he submitted.
Integrating data into macroeconomic models
Dr. Wilson Asiimwe, Senior Lecturer at the School of Economics, stressed the importance of integrating climate and natural capital data directly into macroeconomic models. He explained how forests, water, fisheries and land, which are vital for GDP and carbon sequestration, can be systematically incorporated into tools such as multiplier and CGE models using an Environmental Social Accounting Matrix.
“The first step is preparing the Social Accounting Matrix that captures all economic transactions in an economy—the demand and supply relationships among all economic agents. To integrate climate issues into CGE or multiplier models, you must map climate and natural capital data onto the existing Social Accounting Matrix of the country,” he said.
He elaborated that these models allow policymakers to simulate policy scenarios from forestry investments and infrastructure development to energy transitions, linking environmental outcomes to GDP, employment, revenue, and sectoral performance. By capturing emissions, resource use, and climate risks, Dr. Asiimwe emphasized that this approach provides actionable insights for sustainable growth, green investment, and climate-resilient planning in Uganda.
Symposium Outlook
By hosting the inaugural African Symposium on Natural Capital Accounting and Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling, the Centre of Excellence for Africa Climate-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling (CEACM-established in August 2025) reinforced its role as a continental hub for research, training, and policy dialogue. The symposium was supported by the Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI) and the Partnership for Action on Green Economy (UN PAGE), with thanks to the generous contribution of its funding partners -European Union, Germany, Finland, Norway, Korea, Sweden, Denmark, and Switzerland.
Trending
-

 Humanities & Social Sciences2 days ago
Humanities & Social Sciences2 days agoMeet Najjuka Whitney, The Girl Who Missed Law and Found Her Voice
-

 Health7 days ago
Health7 days agoUganda has until 2030 to end Open Defecation as Ntaro’s PhD Examines Kabale’s Progress
-

 Agriculture & Environment5 days ago
Agriculture & Environment5 days agoUganda Martyrs Namugongo Students Turn Organic Waste into Soap in an Innovative School Project on Sustainable Waste Management
-

 General7 days ago
General7 days agoMastercard Foundation Scholars embrace and honour their rich cultural diversity
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoCall for Applications: Short Course in Molecular Diagnostics March 2026
