Natural Sciences
Emergence of a Viral Disease Epidemic of Sweet potato in Eastern Africa is Imminent – Plant virologists warn
Published
3 years agoon
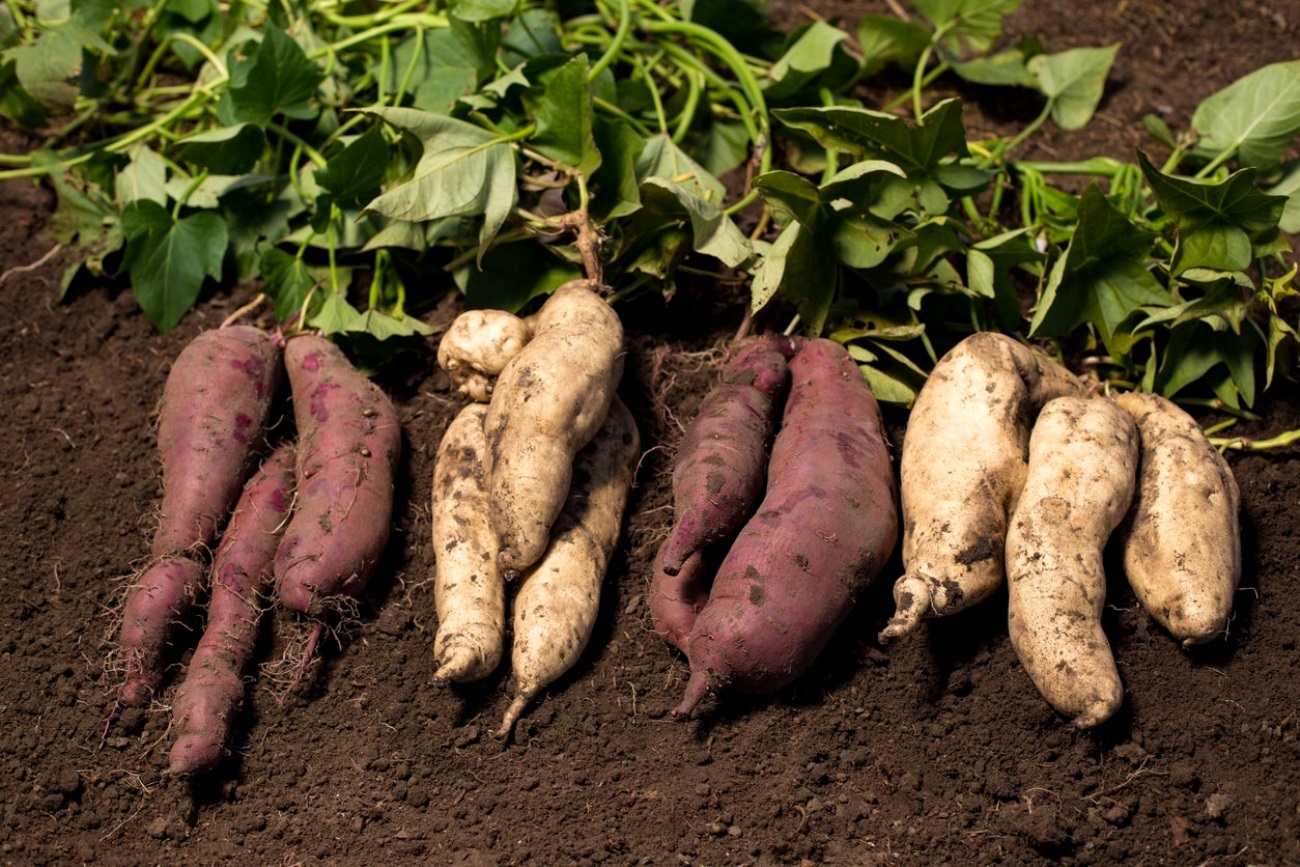

When COVID-19 emerged in 2019, it first remained temporarily localized as an epidemic in Huan China until it broke Chinese national and Asian continental borders attaining a global pandemic status. With COVID-19 and other epidemics and/or pandemics of humans and livestock, it is easier to explain the obvious impact on humans and/or livestock.

What about virus epidemics and pandemics that affect plants?
Virus epidemics and pandemics that affect plants cause significant disruptions in food production. In fact, the emergence and re-emergence of extremely dangerous plant viruses is the major pain to the 21st century agriculture and sustainable food production.
Viral diseases of plants lead to complex outcomes of food shortages, economic meltdown and loss of lives especially when the affected crop plants are central to the economics and livelihoods of the people. Think of what would happen if an epidemic caused significant effect or eliminated crops like maize, banana, cassava or sweetpotato from sub-Saharan Africa.

Most viruses affecting livestock and humans are spread and transmitted by means of physical contact between hosts. Furthermore, human and livestock hosts are mobile. On the other hand, plants do not move and must thus depend on other agents (vectors) for the spread of viruses between hosts. Consequently, over 98% of plant viruses are transmitted by vectors. These vectors may include arthropods (especially insects), nematodes, fungi, and parasitic plants. In plants, a virus disease epidemic becomes optimized by the ability of vectors facilitating fast spread of the virus in an agro-ecosystem.

New study predicts emergence of disease epidemic in sweetpotato
A new study led by Prof. Arthur Tugume at the Department of Plant Sciences, Microbiology and Biotechnology in the College of Natural Sciences at Makerere University predicts potential of emergence of a new disease epidemic in sweetpotato.
The study recognizes that by default, viruses are not constrained to perpetually occupy a single ecological niche. This is because viruses have inherent genetic and evolutionary abilities that enable their acquisition of better fitness to always expand their host and geographical ranges.
While viruses enjoy such fitness advantages in nature, the current study points out unique examples where some viruses in eastern Africa behave awkwardly. These viruses first hid under the guise of being less important and seemingly of no impact in cropping systems, and all of a sudden hell broke loose and the entire farming system was caught unaware.
The study titled; “Endemism and reemergence potential of the ipomovirus Sweetpotato mild mottle virus (family Potyviridae) in Eastern Africa: half a century of mystery” shows that a virus, named Sweetpotato mild mottle virus (SPMMV) was first detected in eastern Africa in the 1970’s. SPMMV is currently the third most prevalent virus of sweepotato in the region and is most destructive in mixed infections with other viruses. Very strangely, SPMMV is geographically restricted to eastern Africa (confirmed only in Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania). This sharply contradicts other known sweetpotato viruses that occur globally wherever sweetpotato is grown.
According to Dr. Deusdedith Mbanzibwa a co-author and Head of Disease Control Unit at Tanzanian Agricultural Research Institute, “it is a half-century-old mystery how SPMMV remains localized in East Africa while other viruses on sweetpotato show a global incidence.” Dr. Mbanzibwa adds, “it is important we generate basic information on this virus as soon as possible such that immediately an epidemic explodes we can counter-it based on the information we have as opposed to being caught unaware of the destructive effects of an epidemic.”

Why should we be concerned about outbreak of an epidemic on sweetpotato?
Plant disease epidemics cause a breakdown in food production and availability in communities that depend on the affected plants as food staples. If sweetpotato production breaks down, it directly translates into limited food supplies in local communities that depend on it for food.
According to Dr. Titus Alicai, a senior virologist and co-author based at the National Crops Resources Research Institute (NaCRRI), Namulonge Uganda, “between the 1980’s-1990’s, a devastating viral pandemic (cassava mosaic disease, CMD) destroyed cassava cropping systems in eastern Africa. As a result, dozens of lives were lost because many communities solely depended on cassava for food and income”. Although these viruses had been detected in the region as early as 1800’s, it was not until the 1980s that destructive effects of the disease became apparent.
Dr. Alicai adds that, “when cassava got destroyed by CMD, sweetpotato became an immediate alternative to millions of hungry people, but now sweetpotato is also burdened with diseases arising from viruses.” Despite heavy investments in disease control in cassava, the CMD pandemic is not completely controlled.
Why is eastern Africa important with respect to emergence of plant viruses?
According to this study, SPMMV is not the first unique virus to emerge or reemerge in eastern Africa. An earlier study by Prof. Tugume and colleagues published in 2010 in Molecular Ecology showed that East Africa is a hotspot for the evolutionary diversification of yet another virus in sweetpotato, named Sweetpotato feathery mottle virus (SPFMV).
Many studies show this region as the home of epidemics in rice caused by Rice yellow mottle virus (RYMV). Highly lethal strains of Cassava mosaic geminiviruses (CMGs) causing CMD initiated this epidemic from eastern Africa. Unique strains of Sweetpotato chlorotic stunt virus (SPCSV) are incident in eastern Africa. SPCSV is unique because it almost indiscriminately enhances the viral concentrations of other co-infecting viruses in sweetpotato. The list of damaging plant viruses or their strains that have emerged from eastern African region is long and cannot not be exhausted here.
Biologists studying diversity of plants and animals have also coded eastern Africa as a home of the “hottest hotspot of biodiversity” of endemic land plants and animals located in Eastern Arc Mountains of Kenya and Tanzania. The features of eastern African ecosystem that incite virus epidemics in plants are not fully known. However, it is suspected that the microclimatic changes as modulated by the Indian Ocean dipole could be one of the drivers of virus emergence and reemergence in the region.
Emergence of SPMMV in sweetpotato closely resemble that of viruses in cassava
The current study specifically compared SPMMV with two viruses infecting cassava: cassava brown streak virus, and Ugandan cassava brown streak virus, collectively called cassava brown streak ipomoviruses (CBSIs).
CBSIs first appeared in the 1930’s in coastal east Africa but went completely silent for about 70 years and then suddenly re-emerged in late 1990’s-mid 2000’s to what is today the single largest threat to cassava production in Africa. CBSIs cause a disease called “cassava brown streak disease” (CBSD). Between 1930’s-1990’s, the CBSIs were able to “amass ability” to cause untold suffering of cassava cropping from 2000’s to-date.
Similarly, since the 1970’s when SPMMV was first reported in the region, the virus has been “amassing an ability” to cause more disease in sweetpotato. This is implied directly by evidence of positive selection found in its genes. Positive selection refers to “survival for the fittest” in Charles Darwin’s terms to mean that, individual virus particles in the SPMMV population are becoming more and more highly efficient in causing disease. Today, half a century later, one can argue that it is about time that the SPMMV will incite a new disease.
Note that both SPMMV and CBSIs belong to the same taxonomic grouping of plant viruses in a genus called “Ipomovirus”, and family called “Potyviridae” which is the largest family of plant viruses with RNA genomes. Hence, similarities in the disease spread between SPMMV and CBSIs are not unexpected.
Expert guide to sweetpotato virology research for preparations against the epidemic
“If we can generate advance basic scientific information concerning how the SPMMV infects sweetpotato plants, how it is transmitted by vectors between plants, and circumstances fostering field spread of the virus, we will be better prepared to handle an epidemic that may arise from the virus,” Prof. Tugume states.
He adds: “we should be able to undertake these studies quickly because SPMMV is naturally incident on sweetpotatoes in Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania in levels causing less damage on its own at the moment, although this damage escalates when the virus occurs in multiple infections.”
The co-authors highlight serious research gaps for critical research investment in sweetpotato virology. Vector transmission is such an important aspect of virus disease epidemics of plants. Therefore, this study has proposed three possible explanations to account for the virus-vector and virus-host relationships of SPMMV. These are called hypothesis #1, #2, and #3, built in a fashion that allows experimentation to prove them right or wrong:
- Hypothesis #1: “SPMMV is opportunistically aphid-transmitted with potyvirus SPFMV as a helper virus.” This hypothesis postulates that SPMMV is transmitted by “chance” by a group of insects called aphids but this happens when SPMMV co-infects sweetpotatoes with another virus, SPFMV that is transmitted efficiently by aphids.
- Hypothesis #2: “Vector-mediated transmission of SPMMV is modulated by synergism with SPCSV.” Under this hypothesis, the concentrations of SPMMV in plant tissues increases when it co-infects with another virus, SPCSV, and this increases chances of SPMMV being picked by insects for transmission to other plants.
- Hypothesis #3: “SPMMV tropism and histo-localization changes upon co-infection with SPCSV.” How much viral concentration is found in different plant tissues can change depending on which tissues that are preferred by the virus. Certain plant viruses prefer to stay and multiply from certain tissues than others.
Dr. Alicai said, “If we can determine vector transmission dynamics including the actual vector(s) transmitting SPMMV, which plant tissues the virus prefers for its multiplication, and generate many complete sequences of SPMMV genomes, we will be better prepared for epidemics arising from the emergence of SPMMV”.
Sweetpotato is a vegetatively propagated plant in which the top-most 15-40cm part of the plant is used for initiating the new crop, a practice that is the main route of accelerated of virus spread in the cropping system. Also, insects especially aphids and whiteflies are the major vectors transmitting viruses in sweetpotato. The research gaps highlighted with respect to SPMMV require urgent attention for advance preparation in case an epidemic breaks loose on the sweetpotato cropping system.
This study has been published by the American Phytopathological Society (APS) in an open access journal, “Phytobiomes Journal”, and is freely accessible on https://apsjournals.apsnet.org/doi/10.1094/PBIOMES-05-22-0031-RVW
For more details, please contact;
Prof. Arthur Tugume
Lead Scientist
Department of Plant Sciences, Microbiology and Biotechnology
College of Natural Sciences (CoNAS)
Makerere University
Email: arthur.tugume@mak.ac.ug
Tel: +256772514841
Dr. Deusdedith Mbanzibwa
Tanzania Agricultural Research Institute (TARI),
Biosciences Centre, Dodoma, Tanzania
Email: d.mbanzibwa@yahoo.co.uk
Email: Tel: +255755881758
Dr. Titus Alicai
Root Crops Research Program
National Crops Resources Research Institute (NaCRRI)
National Agricultural Research Organization (NARO)
Email: talicai@hotmail.com
Tel: +256772970585
Hasifa Kabejja
Principal Communication Officer
College of Natural Sciences
Makerere University
Email: pr.cns@mak.ac.ug
Tel: +256774904211
You may like
-


Makerere University Launches Short Course to Strengthen Climate Change Reporting
-


Makerere University and World Bank Sign Partnership to Strengthen Environmental and Social Sustainability Capacity
-


Makerere University Explores Expanded Partnership with Stanbic Bank to Advance Innovation and Investment
-


Call for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-


Makerere University Researchers Awarded UCIF Grant to Tackle Maize Contamination with Innovative Plant-Based Fungicide
-


Makerere Graduation Underscores Investment in Africa’s Public Health Capacity
Natural Sciences
Makerere University Researchers Awarded UCIF Grant to Tackle Maize Contamination with Innovative Plant-Based Fungicide
Published
5 days agoon
March 4, 2026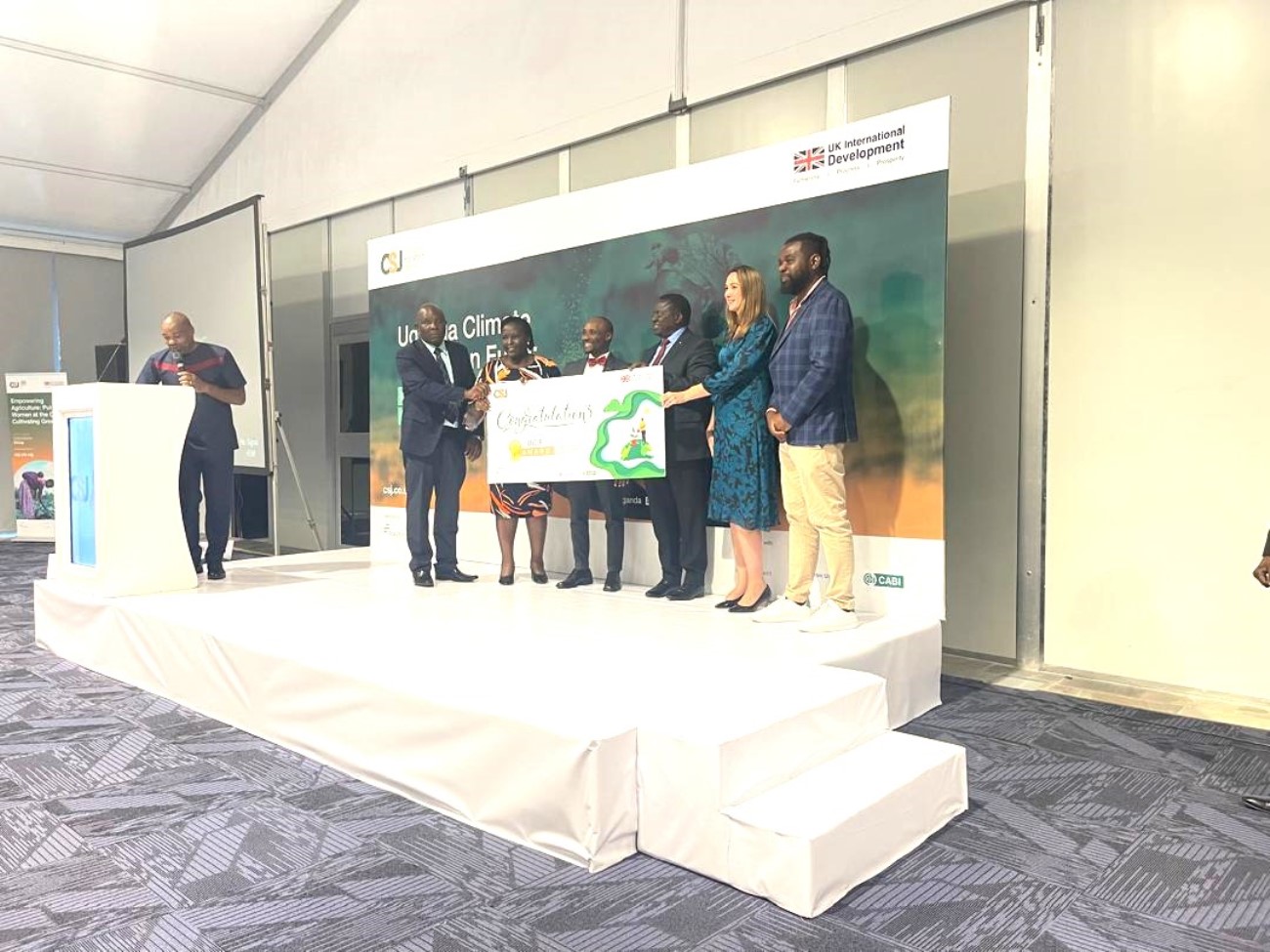
In a significant stride towards ensuring food safety and agricultural resilience, a team of researchers from Makerere University has been awarded the prestigious Uganda Climate Innovation Fund (UCIF) to support the development of a groundbreaking solution to maize contamination.
Maize, a staple food for millions of Ugandans, has long been threatened by Aspergillus fungi, which produce aflatoxins, highly toxic compounds that pose serious risks to human health, livestock, and the nation’s agricultural productivity. Recognizing the urgency of this challenge, the research team from the Department of Plant Sciences, Microbiology, and Biotechnology at the College of Natural Sciences (CoNAS), Makerere University, is pioneering the development of a plant-based organic fungicide aimed at significantly reducing Aspergillus growth and aflatoxin contamination in maize.
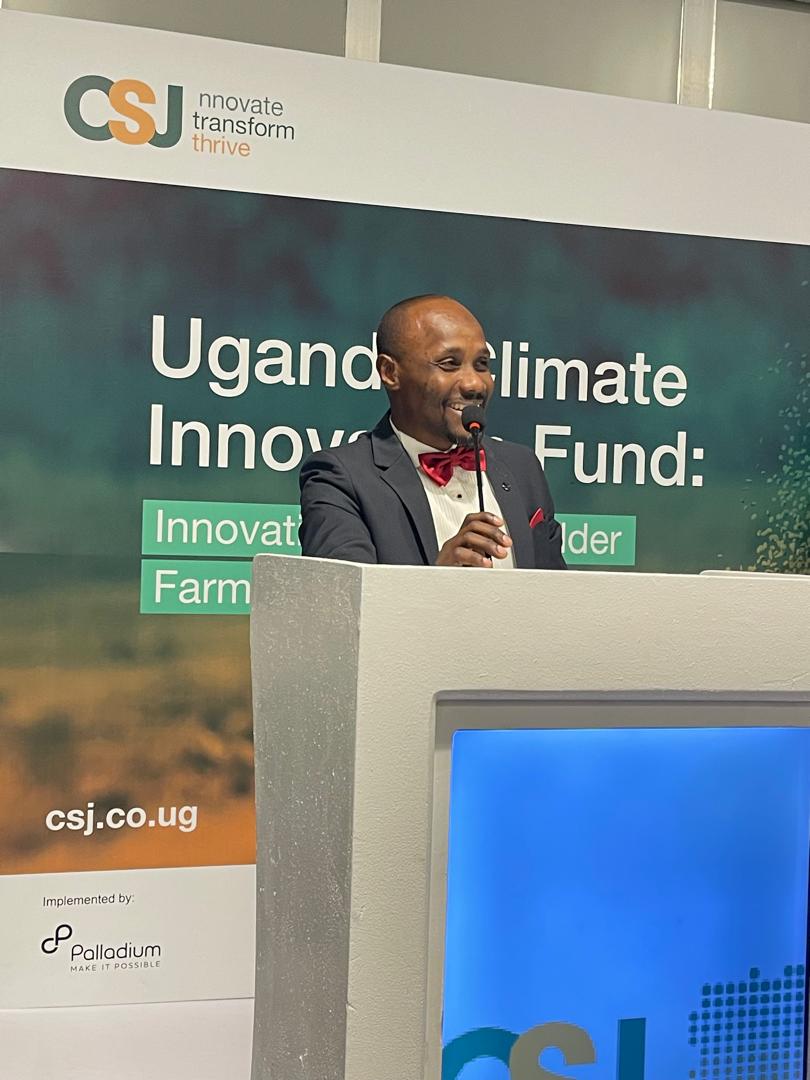

The initiative is spearheaded by Dr. Abubakar Sadik Mustafa (Principal Investigator), with major contributions from co-innovators Dr. Jamilu E. Ssenku, Dr. Patience Tugume, Mr. Frank Kalungi, and Mr. John Okello. The team officially received the UCIF award on 26 February 2026 at an event held at Kampala Serena Hotel.
“This recognition underscores the importance of locally-driven scientific innovation in safeguarding our food systems,” said Dr. Mustafa upon receiving the award. “Our goal is to deliver an environmentally friendly solution that not only protects maize but also contributes to public health and supports sustainable livelihoods for smallholder farmers.”

The UCIF grant, funded by the UK Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) under the Climate Smart Jobs initiative, is implemented by Palladium in collaboration with Stanbic Bank, Swissconnect, and CABI. The programme seeks to advance solutions that address the dual challenges of climate change and economic development by supporting innovations that foster sustainable agricultural practices, reduce environmental risks, and create climate-smart employment opportunities.
This breakthrough aligns closely with the global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those targeting good health and well-being (SDG 3), zero hunger (SDG 2), and climate action (SDG 13). By developing a natural, plant-based fungicide, the Makerere University team hopes to offer a scalable solution that mitigates food contamination risks while promoting environmentally sustainable farming practices across Uganda.
Natural Sciences
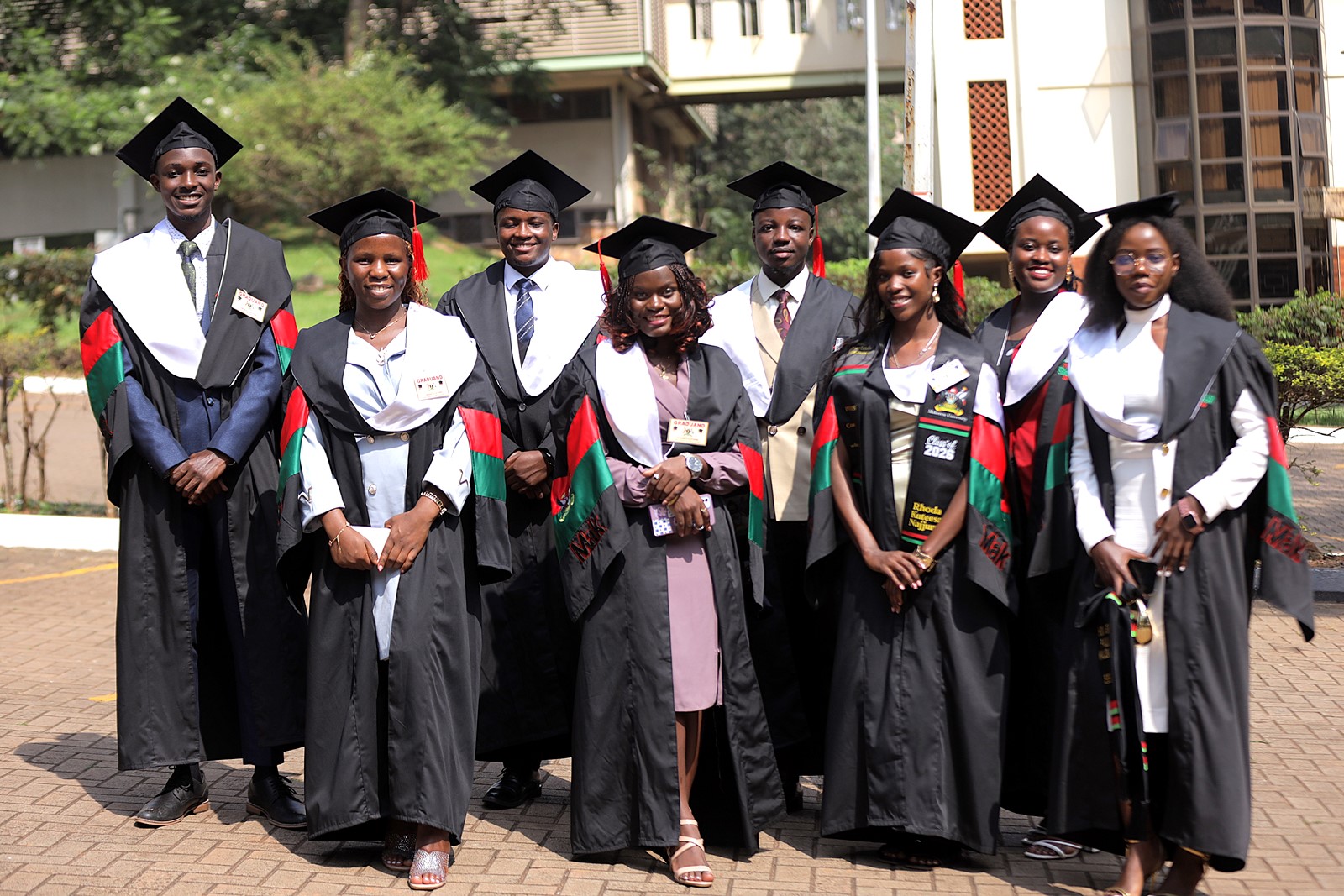
Mak 76th Graduation Ceremony: CoNAS Presents 16 PhDs & Best Performing Male Student in the Sciences
Published
2 weeks agoon
February 25, 2026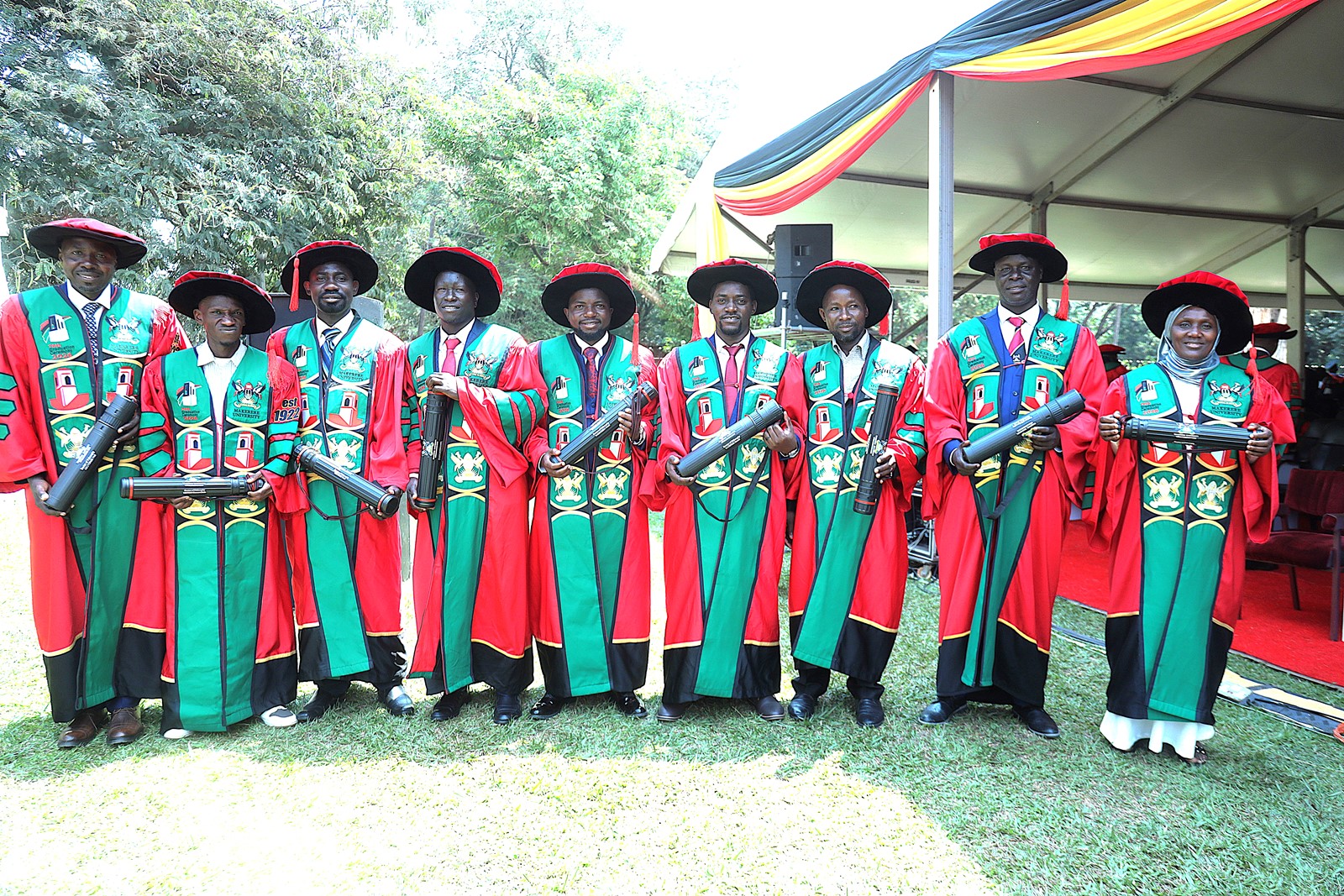
The College of Natural Sciences (CoNAS) presented 269 students for the award of degrees of Makerere University at the 76th graduation ceremony. Of these, 16 graduated with PhDs (4 female and 12 male), 83 with Masters (27 female and 56 male), and 170 with Bachelor’s degrees (45 female and 125 male). The College also presented the Best Performing male student in the sciences. Simon Mungudit graduated with a CGPA of 4.76 in the Bachelor of Science in Petroleum Geoscience and Production. The PhD graduates included; AfazalI Zabibu, a Lecturer at the College of Business and Management Sciences (CoBAMS); Akuyenze Paul, Kawuma Carol, Mutiso Duncan Chalo, Nabiyonga Lydia, and Osinde Cyprian (Plant Sciences, Microbiology and Biotechnology); Batte Hebert, Katende Ronald, and Namugera Frank (Mathematics), Chaciga Jimmy, Tusiime Swaleh, and Komaketch Ignatius (Physics), Kinyua Mbuci, Sekandi Peter, and Shehu Zaccheus (Chemistry), and Nakiyende Herbert (Zoology, Entomology, and Fisheries Sciences).

On the second day of the four-day graduation ceremony, which began on 24th February 2026, three colleges presented students for the award of degrees and diplomas of Makerere University. These included CoNAS, the College of Health Sciences (CHS), and the College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Resources and Biosecurity (COVAB).
Overall graduation Statistics
During the course of the 76th graduation ceremony, a total of 9,295 students will graduate with degrees and diplomas of Makerere University. Of these, 4,262 (46%) are female and 5,033 (54%) are male. A total of 213 students will graduate with PhDs, the highest number in the history of the University. 2,503 will graduate with Masters degrees; 6,343 with Bachelor’s degrees; 206 with postgraduate diplomas, and 30 with Diplomas.
Postgraduates constituted 31.4% of the total number of graduands.
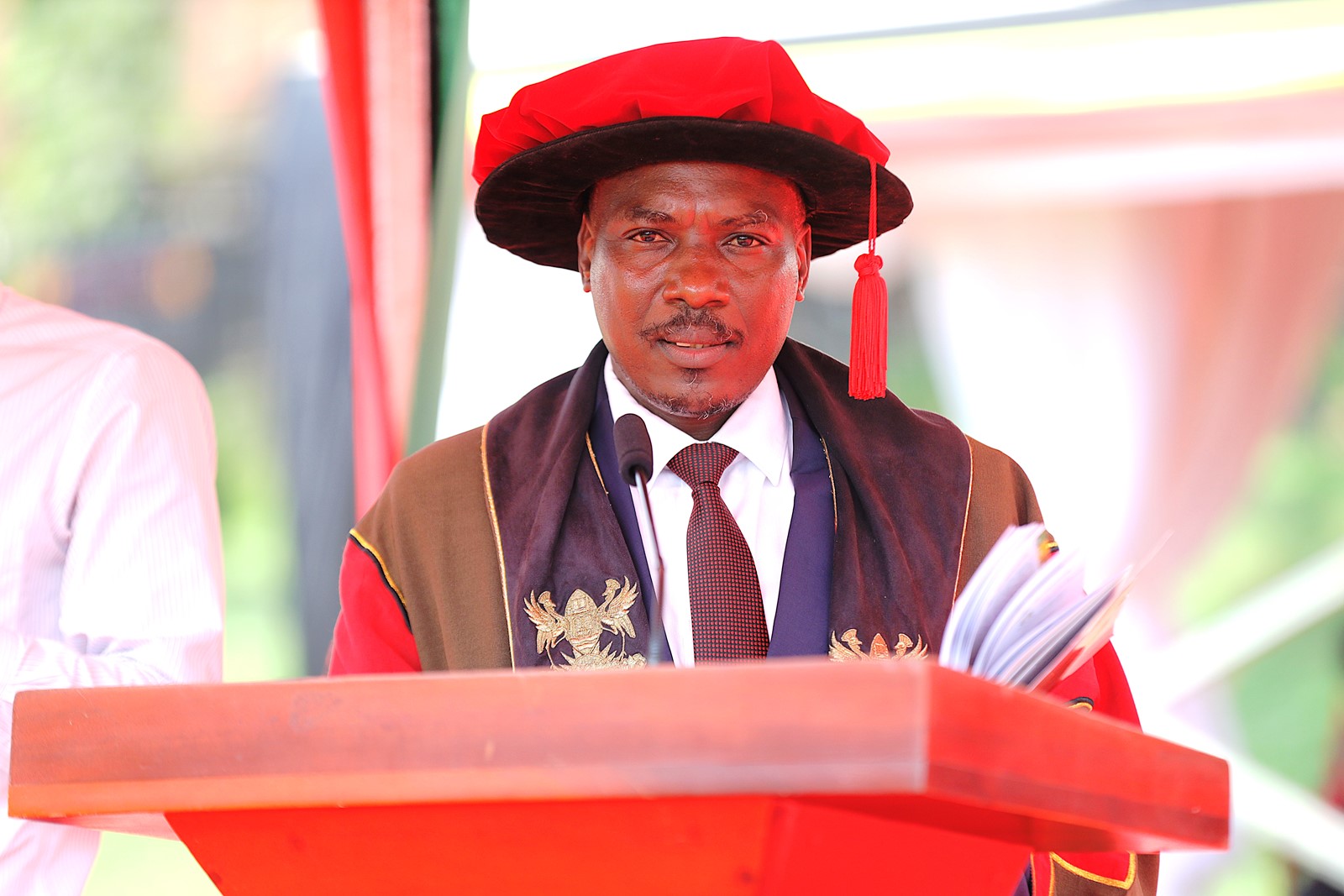

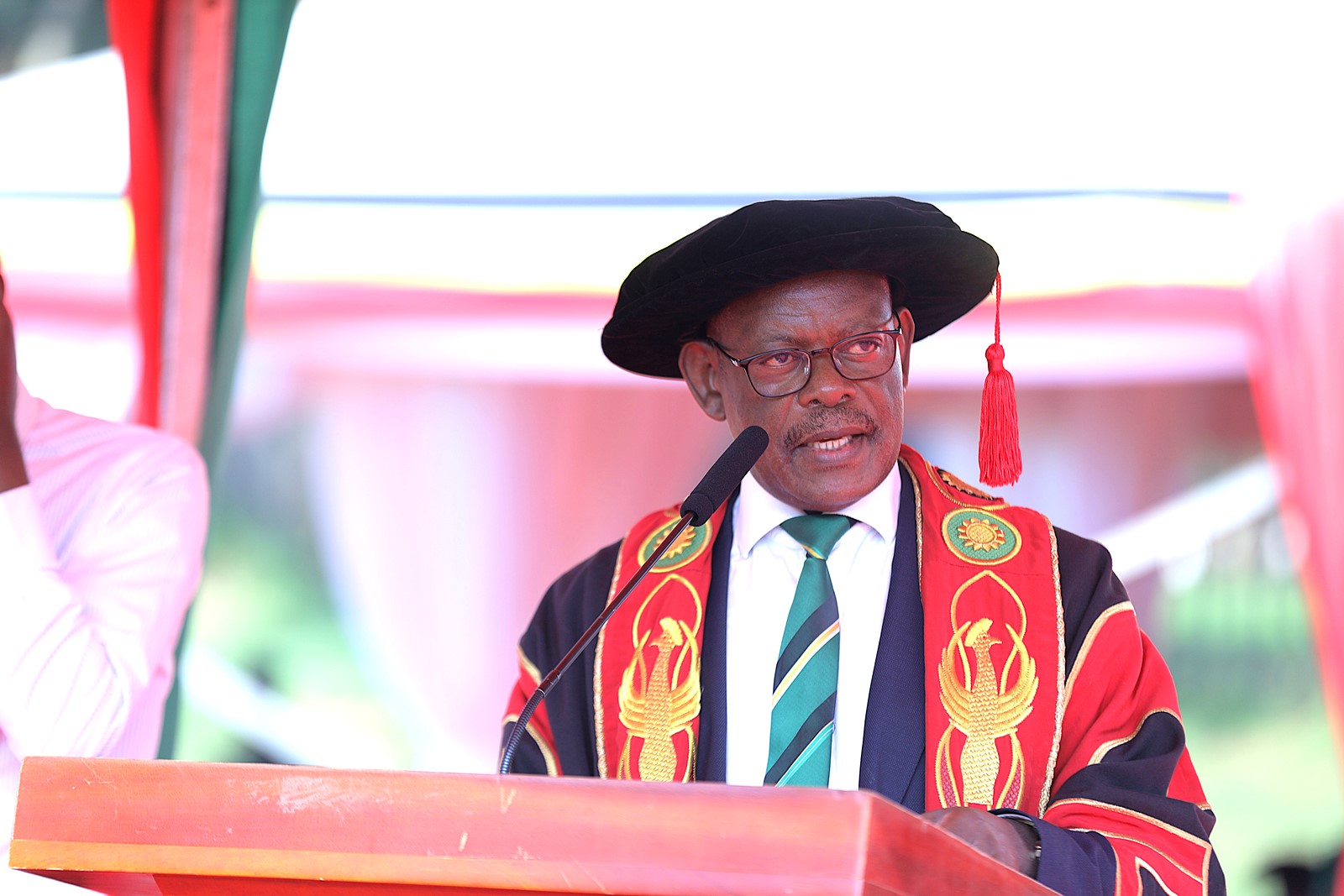
Vice Chancellor’s Remarks
In his remarks, Vice Chancellor Prof. Barnabas Nawangwe commended CoNAS for its transformative research initiatives that are positively impacting communities, highlighting the NutriFishPlus Project, INNOECOFOOD Project, and a project to conserve medicinal plants in Eastern Uganda. Funded by the International Development Research Centre (IDRC) and Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR) under the Cultivate Africa’s Future Fund Phase II, the NutriFishPlus seeks to scale up fish processing technologies and empower fishing communities in Uganda.
The EU-funded INNOECOFOOD Project is transforming food production in Uganda. Through eco-innovative, climate-smart systems, the project aims to improve nutrition, protect the environment, and create jobs- especially for youth and women. Central to this effort are solar- and wind-powered ECOHUBs. These innovative centres use AI and IoT technology to support sustainable fish farming, monitor water quality, reduce losses, and increase yields.
Meanwhile, researchers from the Department of Plant Sciences, Microbiology, and Biotechnology, under the leadership of Dr. Patience Tugume, are spearheading efforts to conserve medicinal plants in Namutumba District. To date, 174 plant species have been documented, with ongoing assessments of threats from unsustainable harvesting. These plants play a vital role in treating malaria, diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers.
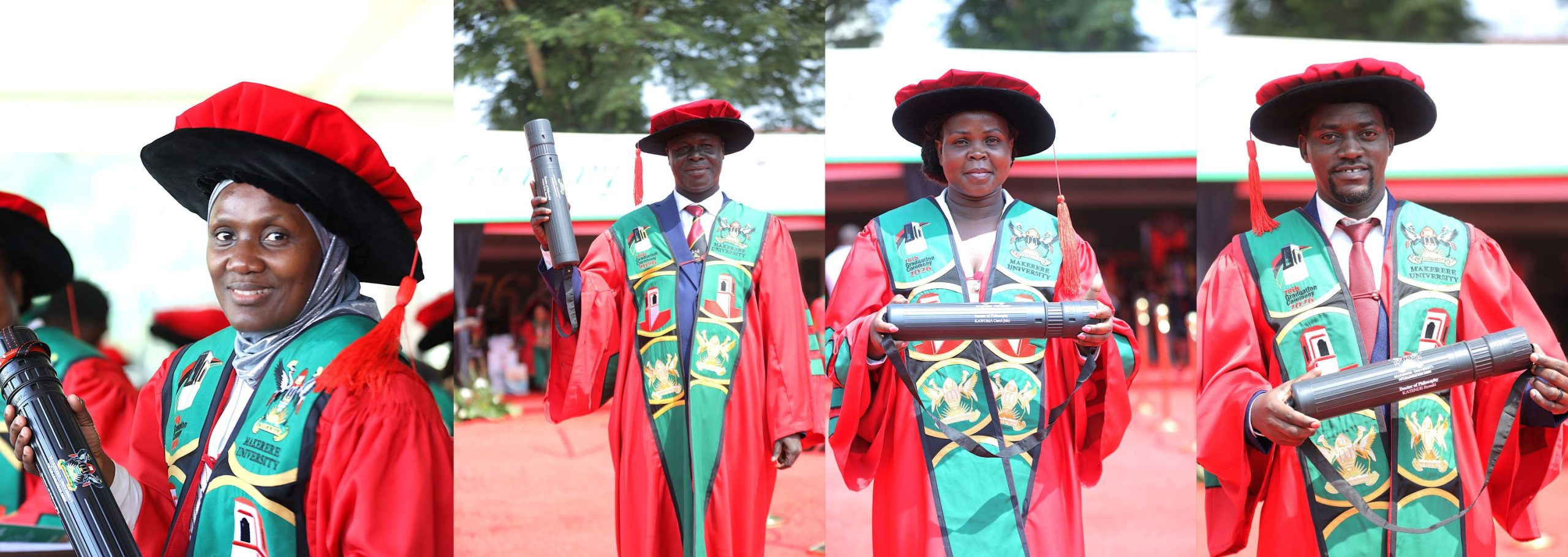

Efforts to Transform Makerere into a Research-led University
In his address, the Vice Chancellor reaffirmed the University Management’s commitment to transforming Makerere into a research-led institution. He expressed gratitude to the Government of Uganda for securing a USD 162 million loan from the Korea Exim Bank to support critical infrastructure development at the University. The funding will facilitate the construction of new facilities for the School of Medicine, School of Dentistry, School of Engineering, the Science and Technology Centre, and the completion of the School of Computing and Information Sciences- an unprecedented development in the University’s history.
The Vice Chancellor further highlighted the pivotal role of the Makerere University Technology and Innovations Centre (MUTIC) in advancing incubation and commercialization. “The Centre offers mentorship, business development training, intellectual property support, and industry linkages to help transform research outputs into viable enterprises.” To date, eleven spin-off companies have been established by students and staff, while the University’s Innovation Pod (UniPod) has incubated more than 100 projects in the past year. The short-term target is to establish 50 spin-off companies annually, with plans to double that number in the long term.
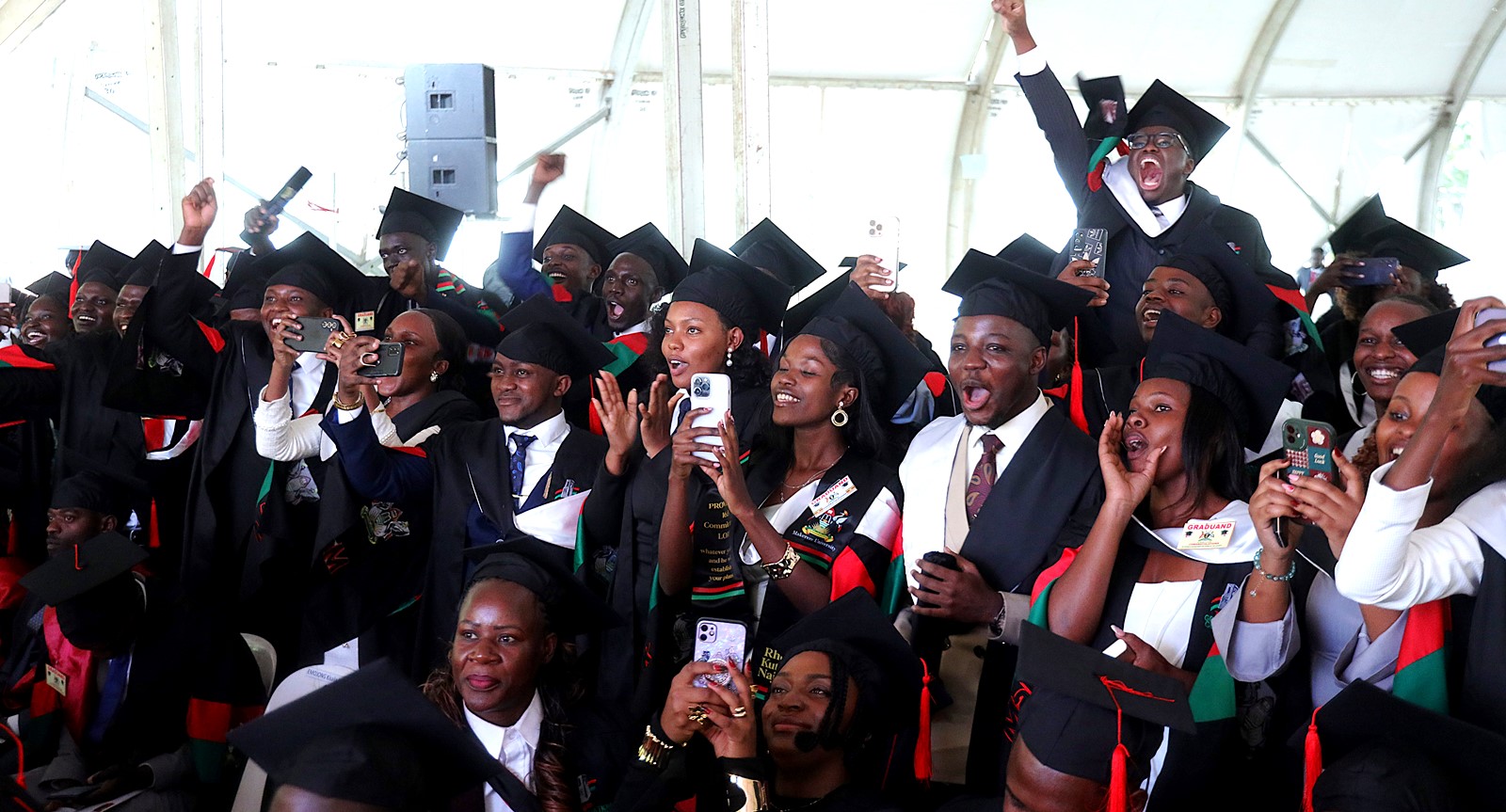

Prof. Nawangwe acknowledged the government’s contribution through the Makerere University Research and Innovations Fund (MakRIF). Through this initiative, the government has supported over 1,400 high-impact research and innovation projects, and facilitated the training of more than 200 PhD students.
In partnership with the Science, Technology and Innovation Secretariat in the Office of the President, the University has also introduced awards to recognize outstanding researchers and innovators. These include the Research Excellence and Innovation Commercialization Awards. “The Innovation Commercialization Award underscores the institution’s commitment to translating research into practical products, services, and technologies that address real-world challenges and support national development,” the Vice Chancellor noted.
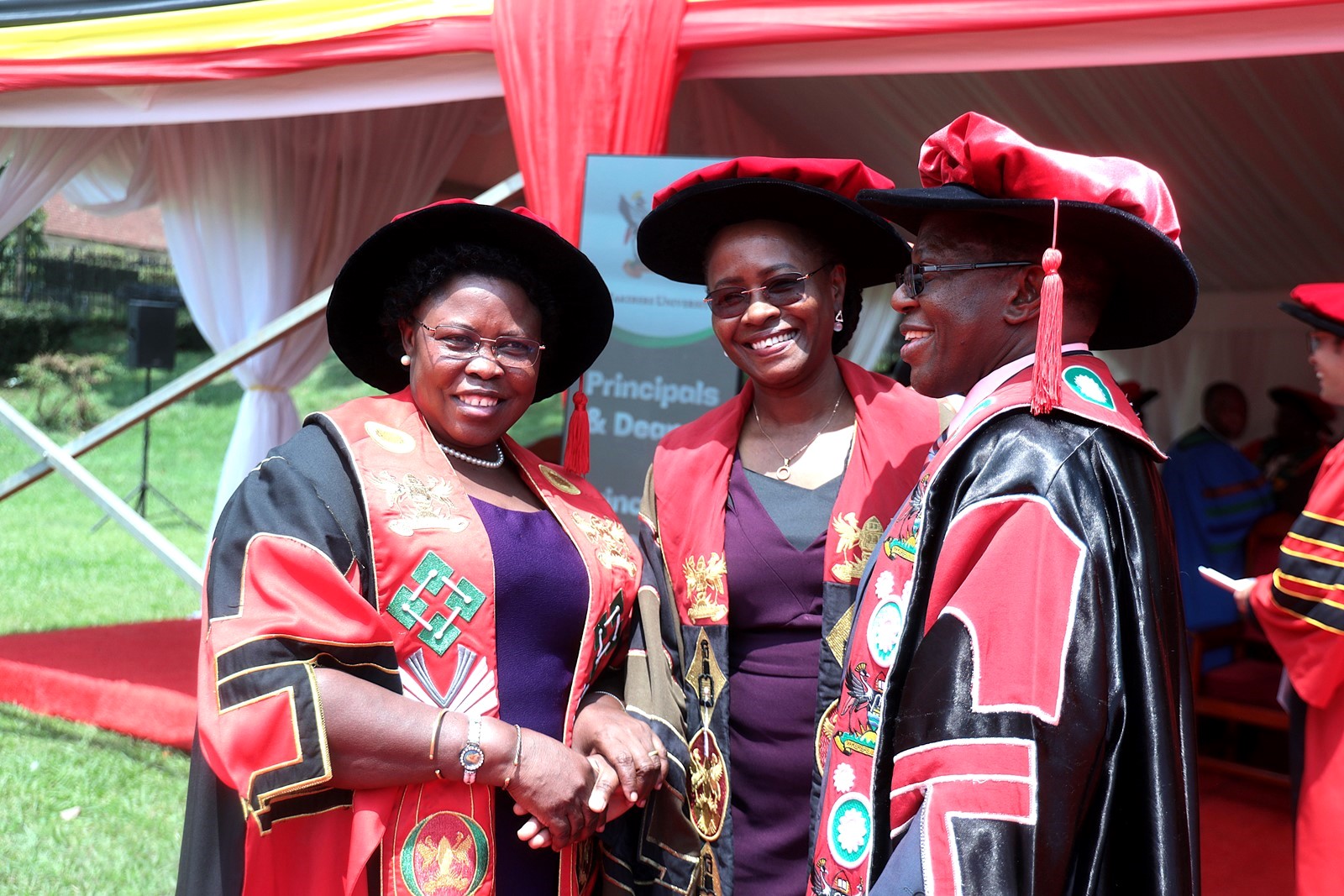

Vice Chancellor’s Message to the graduates and Appreciation to the Partners
The Vice Chancellor urged the graduates to uphold dignity, humility and diligence as they leave the gates of Makerere University, and begin the next chapter of their lives. “As you step out of the gates of Makerere, remain proud of your alma mater and serve as good ambassadors wherever you go. Use the knowledge acquired from one of the world’s leading universities to improve yourselves, your families, communities, country, and humanity at large.”
He equally appreciated the parents and guardians for supporting the students, and the development partners who have extended research funding to the university over the years. These include the Mastercard Foundation, the European Union, NORAD, Sida, IDRC, KOICA, DAAD, NIH, CDC, USAID, the Wellcome Trust, KfW, IUCEA, RUFORUM, ARUA, the PLUS Alliance, WUN, AAUN, AAP, the Madhvani Foundation, and the Government of Uganda through the Higher Education Students Financing Board. “We are equally grateful to the Embassy of China, the Chinese Chamber of Commerce, various Government Ministries, State House, private sector players, and many other partners whose generous support continues to advance our mission.”
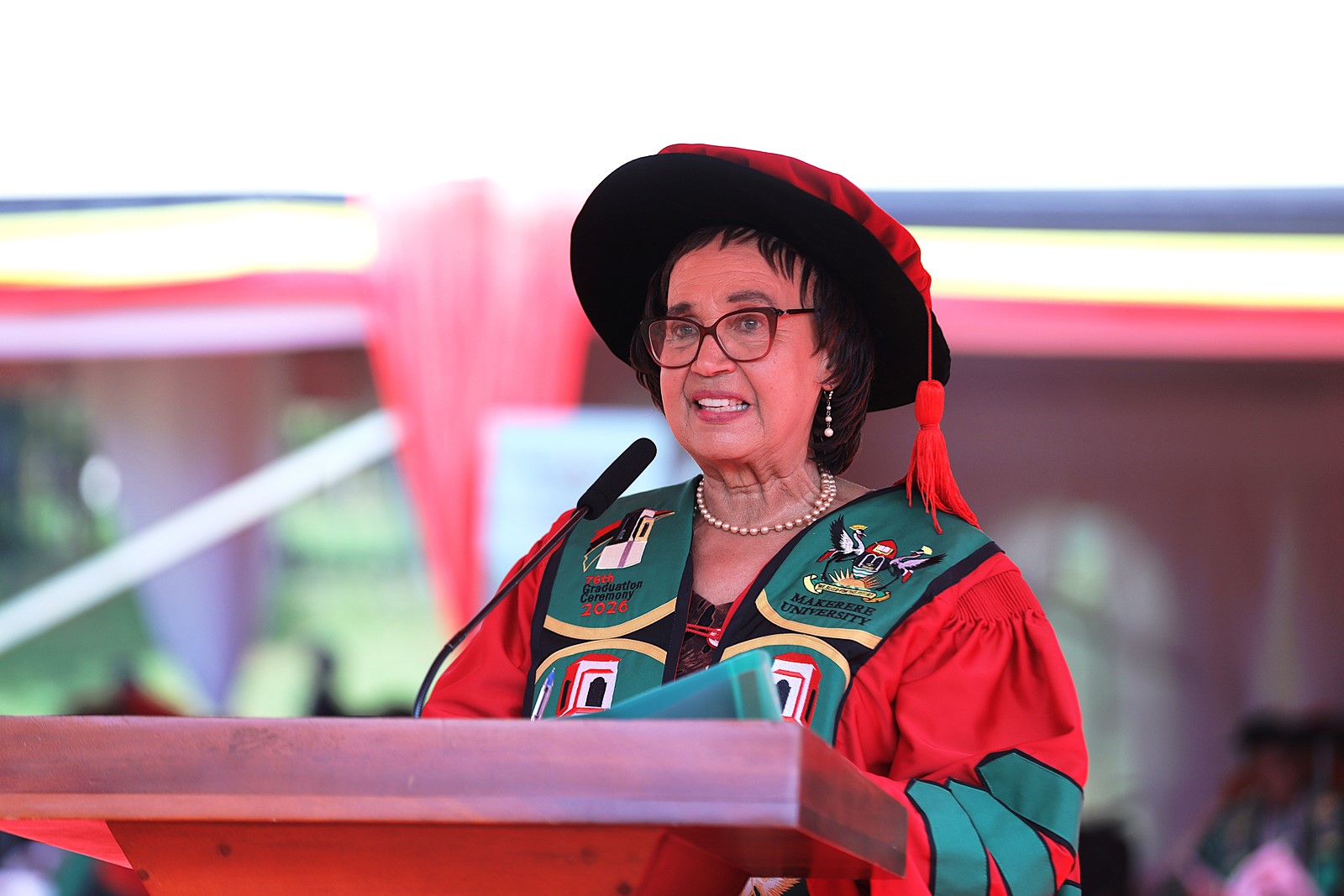

Remarks by the Chancellor
Makerere University Chancellor, Hon. Dr. Crispus Kiyonga congratulated the graduands on their achievement and commended the staff, parents, and partners for their invaluable support. He expressed gratitude to the Government for its steadfast commitment to advancing research through the annual UGX30 billion allocation to the Makerere University Research and Innovations Fund.
He underscored the University’s contribution to Uganda’s Fourth National Development Plan (NDP IV) through advancements in science, technology, and innovation, and encouraged graduates to embrace entrepreneurship amidst an increasingly competitive job market. He further called for enhanced research funding, stronger private sector collaboration, and deeper community engagement to accelerate national development.
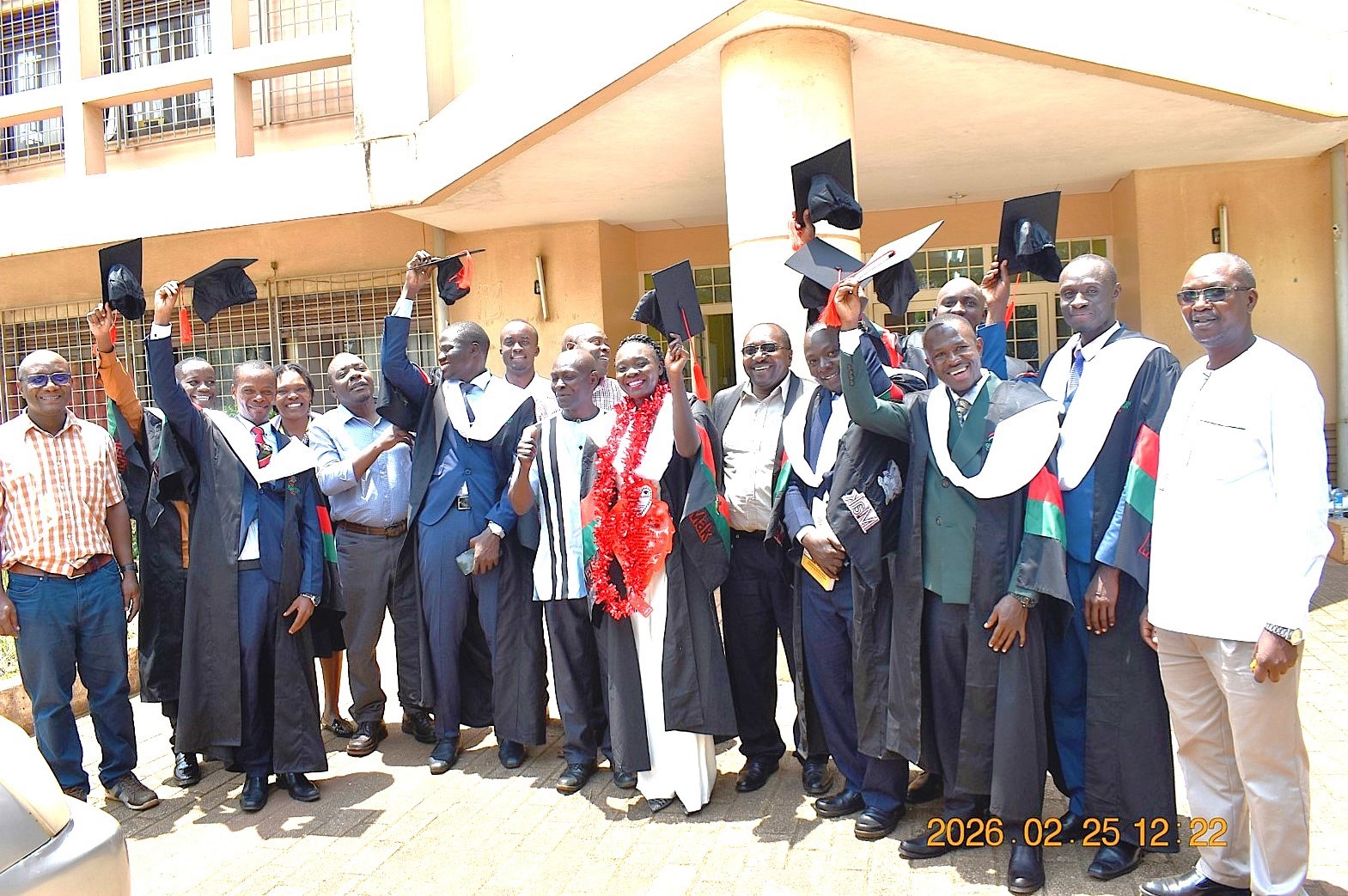

The Minister of Education and Sports
In her remarks, the Minister of Education and Sports, Hon. Janet Kataaha Museveni, represented by the Minister of State for Primary Education, Hon. Dr. Joyce Moriku Kaducu commended Makerere University for its pivotal role in driving national development. She highlighted the University’s contribution to knowledge generation and societal transformation. “The impressive number of PhD graduates this time round is testimony to the robust research output and academic excellence.” The Minister emphasized the importance of maintaining and enhancing academic standards, urging the University Administration to rigorously implement and uphold quality assurance measures that guarantee continued excellence of its programmes and global competitiveness of its graduates.
Implementing the Competence-based Education and Training
The Minister reiterated a key directive for all institutions of higher learning to prepare for the full implementation of Competence-Based Education and Training by July 2027. “This reform represents more than a policy shift. It signals a fundamental transformation in how graduates are prepared, with greater emphasis on practical skills, innovation, and problem-solving.” She urged the Vice Chancellor and his team to lead in curriculum reform, staff development, and infrastructure enhancement to ensure the successful rollout of competence-based education.
The Minister further urged the university management to ensure that all satellite campuses are fully accredited and that their programmes meet the same standards and relevance as those offered at the main campus.

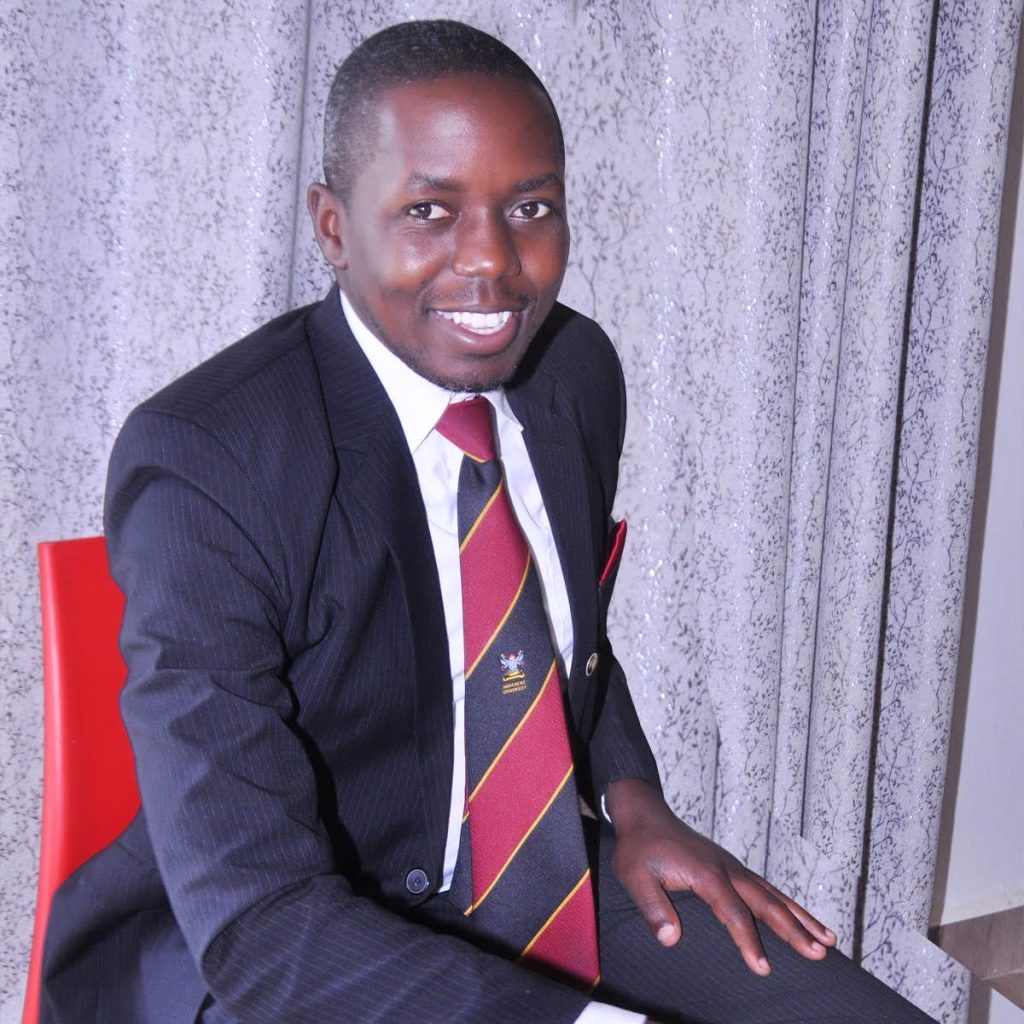
Commencement Lecture by Dr. Maggie Kigozi
At the ceremony, distinguished alumnus, and Chair of the Makerere University Endowment Fund, Dr. Maggie Kigozi delivered a compelling commencement lecture, reflecting on her journey since earning her first degree in 1976. She shared three guiding messages for the new alumni as they embark on their professional paths.
Dr. Kigozi emphasized that power comes with responsibility, urging graduates entering the health and life sciences to combine their expertise with ethical leadership and financial literacy to create sustainable, compassionate practices. She highlighted the global opportunities that a Makerere degree offers, explaining how her education empowered her to make meaningful contributions across Uganda, Kenya, and Zambia.
She also encouraged the graduates to view failure as a stepping stone to excellence, noting that mistakes are not setbacks, but lessons. She underscored the importance of balance, reminding graduates to manage their personal and professional responsibilities realistically.
Research Excellence Awards
During the graduation ceremony, Makerere University recognized the top researchers and innovators from the 10 Colleges. At CoNAS, Mr. Omara Timothy from the Department of Chemistry scooped the Overall Top Research and Early Career Researcher Awards, whereas Dr Godwin Anywar from the Department of Plant Sciences, Microbiology, and Biotechnology won the Mid-Career Researcher Award.

More about Simon Mungudit, the best performing male science student – https://cns.mak.ac.ug/simon-mungudit-maks-best-male-science-student-this-year-rising-star-in-petroleum-geoscience/
Natural Sciences
BOKU University Charts New Collaboration Strategies with Mak’s Department of Zoology, Entomology & Fisheries Sciences
Published
4 weeks agoon
February 12, 2026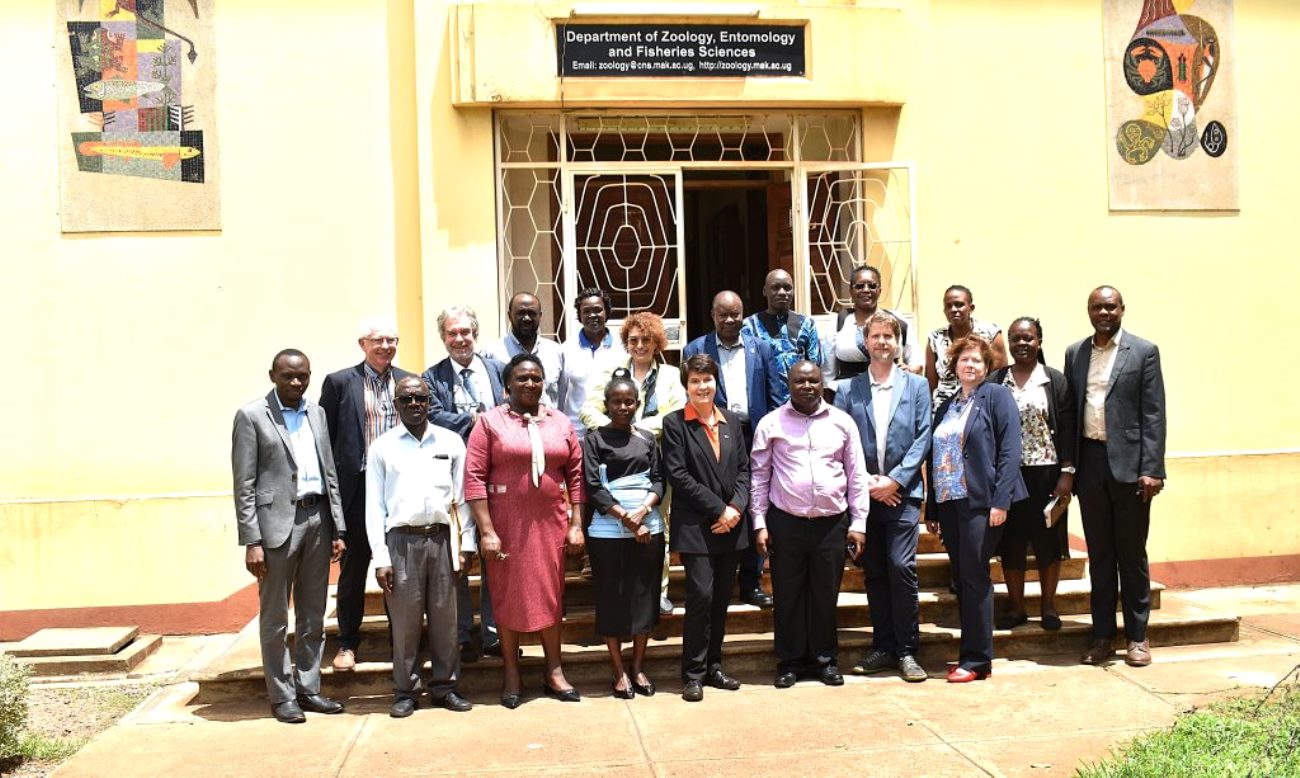
The Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences at Makerere University on 11th February 2026 hosted a high-level delegation from the University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna (BOKU), to discuss strategies for future collaboration in a partnership that has spanned five decades.
The meeting followed the BOKU team’s participation in the opening ceremony of the Promotion of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems towards Electricity Access in Uganda project, an initiative designed to expand access to decentralized renewable energy solutions. The project, implemented under CEDAT, is funded by the Austrian Partnership Programme in Higher Education and Research for Development (APPEAR), a programme of the Austrian Development Cooperation administered by OeAD.

Discussions at the Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences focused on deepening and broadening a historic collaboration that has shaped aquatic sciences, fisheries research, and environmental management in East Africa for half a century.
A Partnership Rooted in Limnology
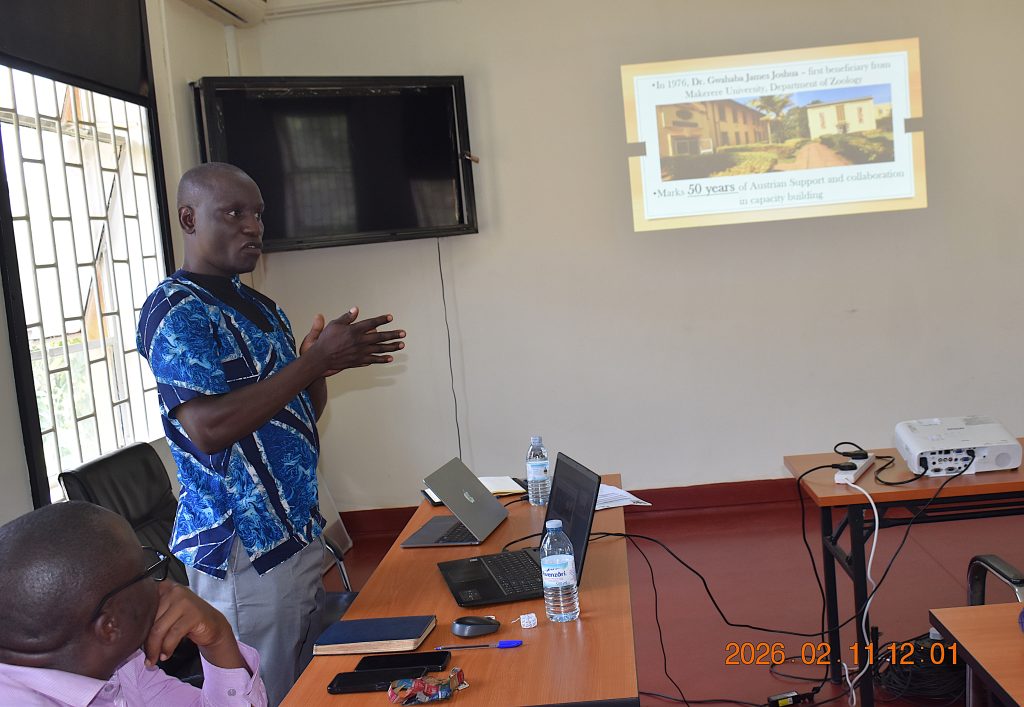
The collaboration between Makerere University and BOKU traces its origins to 1975 with the establishment of the International Post-Graduate Course in Limnology (IPGL) by the late Heinz Löffler (1927-2006). The eight-month UNESCO-supported course, hosted in Lunz, Mondsee and Vienna, was designed to train scientists from developing countries in limnology – the study of inland waters.

In 1976, Dr. Gwahaba James Joshua of Makerere’s Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences became the first beneficiary from the university. Two years later, Boniface Makanga attended the UNESCO course and went on to initiate a Marine Practical Course to the Indian Ocean in 1993. That programme has since grown into over 30 years of annual field activity in Mombasa, benefiting undergraduate and master’s students and strengthening hands-on marine science training at Makerere.
Over time, IPGL evolved into a vibrant International Joint Degree Master’s Programme in Limnology and Wetland Management. The programme has built capacity for 123 aquatic professionals – 56 female and 67 male, including 20 from Makerere University. Notably, 11 dedicated limnologists are currently based within the Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences, a testament to sustained capacity development.

Expanding into Fisheries, Aquaculture and Regional Networks
The Mak-BOKU collaboration progressively expanded beyond limnology into fisheries, aquaculture, and broader freshwater ecosystem management.
Among the key initiatives was STRECAFISH (2015-2018), which focused on strengthening regional capacity in fisheries and aquaculture research and training to improve food security and livelihoods in Eastern Africa. The programme adopted a modular approach, trained 28 MSc students, supported five full PhDs and 11 MSc research projects, and facilitated 14 staff exchanges.

This momentum continued under COTRA (Collaborative Training in Fisheries and Aquaculture in East, Central and Southern Africa) from 2017 to 2023. COTRA enhanced staff and student mobility, supporting 24 master’s students (six credit-seeking and 18 degree-seeking), 12 doctoral candidates (four credit-seeking and eight degree-seeking), and 10 faculty and administrative staff. The initiative emphasized fit-for-purpose PhD training in aquaculture and fisheries to address food security challenges in Sub-Saharan Africa under the ACP-EU Cooperation Programme in Higher Education (EDULINK II), in partnership with institutions such as Lilongwe University of Agriculture and Natural Resources.

Ongoing collaborations include the Erasmus+ KA1 Learning Mobility of Individuals programme (2021-2027), which connects BOKU and Makerere with Egerton University, Kyambogo University, Addis Ababa University, Bahir Dar University and others. Additional joint initiatives include:
FreshNet: A higher education and research network for sustainable management of freshwater ecosystems in Eastern Africa, involving BOKU, Egerton University, Addis Ababa University, Bahir Dar University, EIAR and IHE Delft.

SWAQ-Uganda (2021-2026): Sustainable water quality management supporting Uganda’s development ambitions, implemented with IIASA, BOKU and Uganda’s Ministry of Water and Environment.
BIOGOLD (2024–2027): A project on biosorption for sustainable small-scale gold mining in Uganda, involving Kyambogo University, Makerere University, Gulu University, the University for Continuing Education and the University of Pretoria.

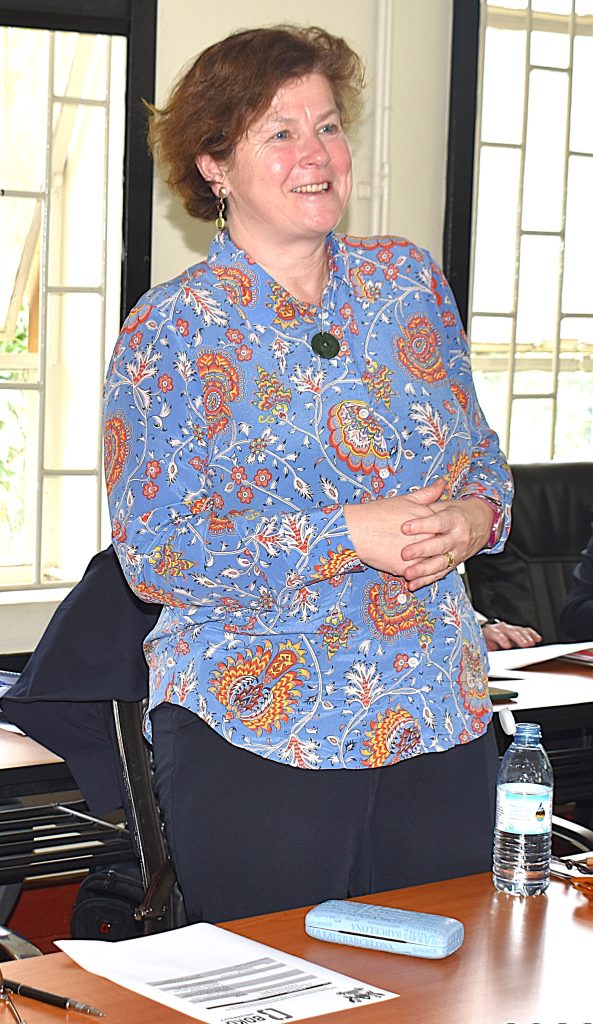
Collectively, these initiatives underscore a 50-year-old partnership that has built critical human resources at MSc and PhD levels in aquatic ecosystem management, conservation and utilization. The collaboration has also facilitated acquisition of essential research equipment, strengthened administrative capacity in project management, and nurtured a culture of knowledge sharing and innovation.

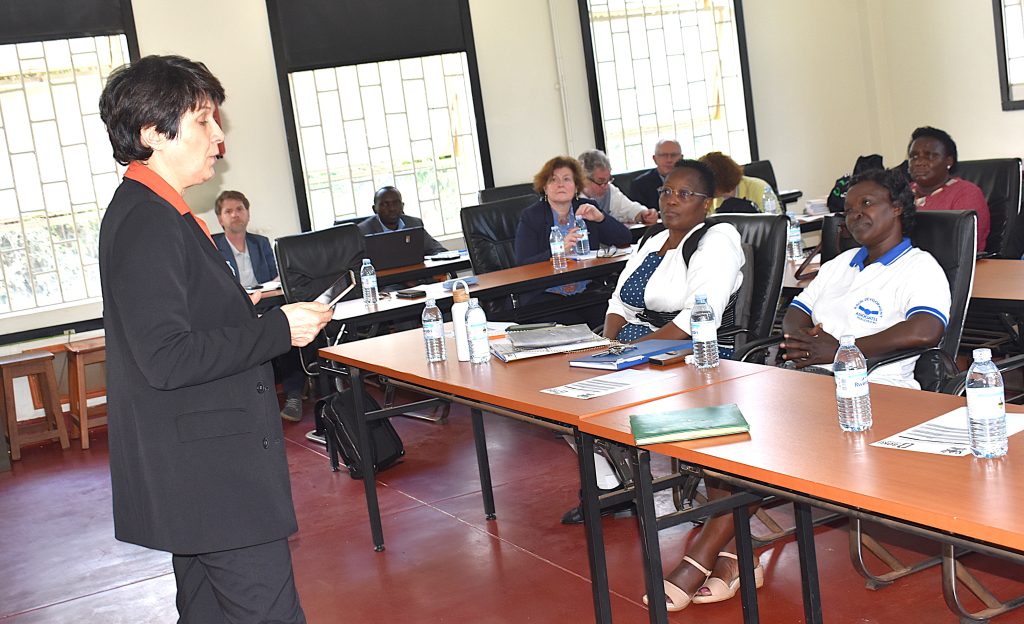
Meeting with the BOKU delegation
The BOKU delegation was led by the Rector, Prof. Eva Schulev-Steindl, a specialist in environmental law, and Vice Rector Assoc. Prof. Doris Damyanovic, an expert in landscape planning. They were accompanied by:
- Mag. Gerold Winkler, Coordinator of the Applied Limnology / Limnology and Wetland Master’s programme;
- Dr. Mathew Herrnegger, BOKU’s Africa Cooperation Country Coordinator and hydrology specialist; and
- Dr. Andreas Melcher, Africa-Uninet Coordinator from BOKU’s Institute for Development Research.
During the discussions with departmental staff, Dr. Akoll presented a detailed account of the partnership’s evolution and achievements, emphasizing its transformative impact on regional training and research capacity.

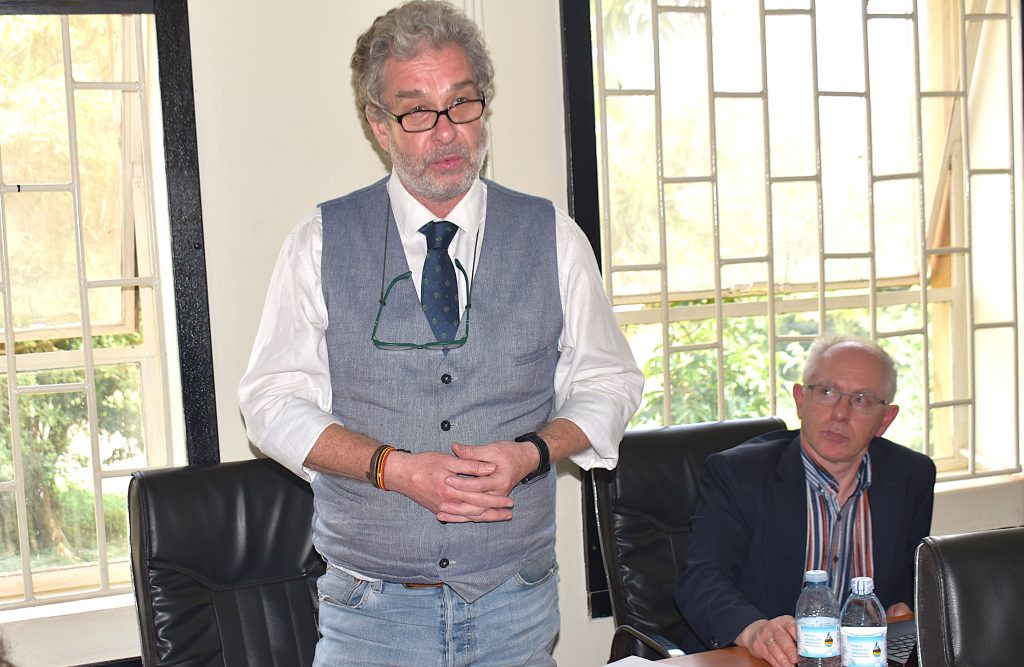
Charting the Next Chapter
As the partnership enters its sixth decade, both institutions are keen to expand into new frontiers. Key areas identified for future collaboration include:
- Enhanced staff and student exchanges;
- Joint research projects and co-publications;
- Introduction of short courses at the Makerere University Biological Field Station, Kibale beyond wildlife studies;
- Research on climate change and its effects on marine and freshwater resources;
- Advancement of basic biological research; and
- Strengthening fisheries research and innovation.

In his remarks, the Head of the Department of Zoology, Entomology and Fisheries Sciences, Dr. Godfrey Kawooya expressed gratitude for the enduring partnership, noting that it has significantly strengthened regional training capacity and supported the education of numerous Makerere staff and students. He added that the collaboration reinforces Makerere’s standing as one of the most collaborative universities globally and aligns closely with its research agenda.
Rector Schulev-Steindl reaffirmed BOKU’s commitment to advancing the longstanding relationship, describing it as a model of North-South academic cooperation built on mutual respect, shared knowledge and tangible impact.


Event pictorial: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1HkCCZf_TCPV0V7_ZR2PSVEw1zrEGhZeJ?usp=sharing
Trending
-

 General4 days ago
General4 days agoCall for Applications: Diploma Holders under Government Sponsorship 2026/2027
-

 General4 days ago
General4 days agoAdvert: Admissions for Diploma/Degree Holders under Private Sponsorship 2026/27
-

 General2 weeks ago
General2 weeks ago76th Graduation Highlights
-

 Agriculture & Environment2 weeks ago
Agriculture & Environment2 weeks agoCAES Presents Overall Best Performing Student in the Sciences & a Record 28 PhDs at the 76th Graduation Ceremony
-

 General4 days ago
General4 days agoExtension of Application Deadline for Diploma/Degree Holders 2026/2027
